Medgrid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Medgrid project, created at the end of 2010 in Paris, is a large industrial project planned in

 The
The 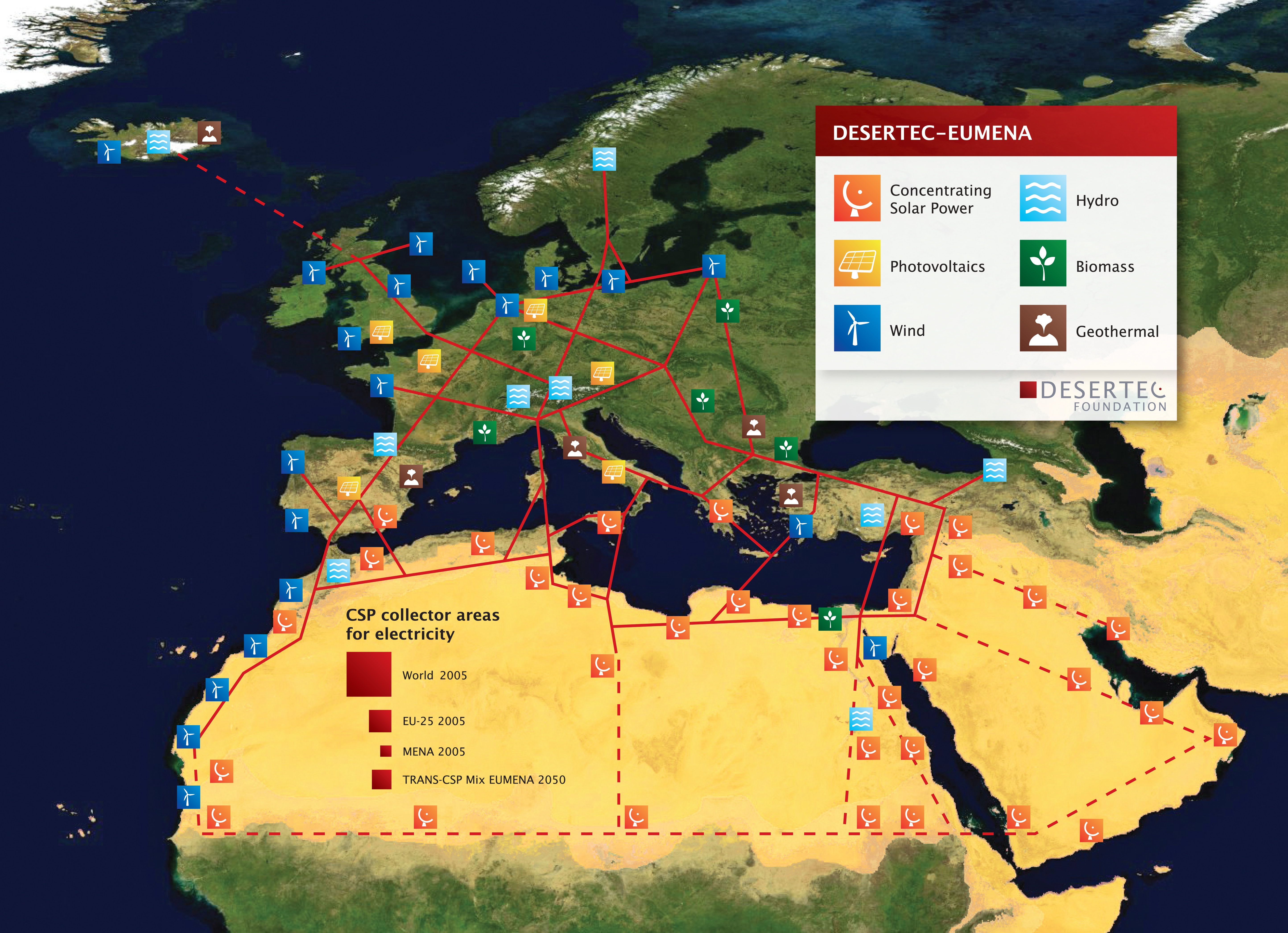
 Complementing a similar Saharan desert based renewable energy project - DESERTEC, the industrial project Transgreen was launched in
Complementing a similar Saharan desert based renewable energy project - DESERTEC, the industrial project Transgreen was launched in
Friends of the supergrid
an
Renewables Grid Initiative
signed a joint declaration to support the effective and complete integration, in a single electricity market, of renewable energy from both large-scale and decentralised sources, which shall not be played out against each other in Europe and in its neighbouring regions. The medgrid together with Desertec would serve as the backbone of the ' European Supergrid' and the benefits of investing in
/ref> CEO of Medgrid.
Medgrids official website
{{Economy of Morocco Proposed solar power stations Renewable energy in the European Union Proposed electric power infrastructure in Africa Proposed electric power infrastructure in Europe
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, which aims to promote and develop a Euro-Mediterranean electricity network that would provide North Africa & Europe with inexpensive renewable electricity
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
, mostly from solar. The goal is to install 20 gigawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wat ...
s (GW) of generating capacity, with 5 GW being devoted for exports to Europe.
The Medgrid project was envisioned by a consortium of twenty plus utilities, grid operators, equipment makers, financing institutions and investors, mostly European.
On 24 Nov 2011, a MoU was signed between Medgrid and Desertec Industry Initiative (Dii) to study, design and promote an interconnected electrical grid with the 400 billion euro ($536 billion) renewable energy ' Desertec' project in North Africa. The medgrid together with Desertec would serve as the backbone of the ' European Supergrid' and the benefits of investing in HVDC
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system (also called a power superhighway or an electrical superhighway) uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating curre ...
technology are being assessed to reach the final goal – the 'SuperSmart Grid (SSG)'.
History

Background
As per the statement made by Dr Gerhard Knies, German physicist and founder of the Trans-Mediterranean Renewable Energy Cooperation (TREC) network of researchers - "The world’s deserts collect more energy from the sun in six hours than mankind consumes in an entire year". It illustrates the idea behind the ambitious project - Medgrid which will exploit solar energy from desert areas. The
The Sahara desert
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
was chosen as an ideal location for solar farms as they enjoy strong direct sunlight for much of the year (3,000 to 4,000 hours of sunlight per year). In addition, the deserts are sparsely populated, making it possible to set up large solar farms. Lastly, sand deserts can provide silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ta ...
, a raw material that is essential in the production of solar panels.

Inception of Medgrid consortium (July 2010 - present)
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
in July 2010 as a French initiative within the framework of the Union for the Mediterranean
The Union for the Mediterranean (UfM; french: Union pour la Méditerranée, ar, الإتحاد من أجل المتوسط ''Al-Ittiḥād min ajl al-Mutawasseṭ'') is an intergovernmental organization of 43 member states from Europe and the M ...
(UfM). A consortium of twenty-plus, mostly European, utilities, grid operators, equipment makers, financing institutions and investors envisioned the company named Medgrid in December 2010. The aim was to promote and develop a Euro-Mediterranean electricity network that would provide North Africa & Europe with inexpensive renewable electricity
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
, mostly from solar. The goal is to install 20 GW of generating capacity, with 5 GW being devoted for exports to Europe. France and Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
will launch the first experiment to transport solar power from the south to the north of the Mediterranean.
Since the Euro-Mediterranean projects, Medgrid and Desertec are both attempting to generate solar energy from deserts and complement each other, a MoU was signed on 24 Nov 2011 between Medgrid and Desertec Industry Initiative (Dii) to study, design and promote an interconnected electrical grid with the 400 billion euro ($536 billion) renewable energy " Desertec" project in North Africa. The plan is to build five interconnections at a cost of around 5 billion euros ($6.7 billion), including between Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. The activities of Dii and Medgrid are covered by the Mediterranean Solar Plan (MSP), a political initiative within the framework of the Union for the Mediterranean
The Union for the Mediterranean (UfM; french: Union pour la Méditerranée, ar, الإتحاد من أجل المتوسط ''Al-Ittiḥād min ajl al-Mutawasseṭ'') is an intergovernmental organization of 43 member states from Europe and the M ...
(UfM).
In March 2012 Dii, MedgridFriends of the supergrid
an
Renewables Grid Initiative
signed a joint declaration to support the effective and complete integration, in a single electricity market, of renewable energy from both large-scale and decentralised sources, which shall not be played out against each other in Europe and in its neighbouring regions. The medgrid together with Desertec would serve as the backbone of the ' European Supergrid' and the benefits of investing in
HVDC
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system (also called a power superhighway or an electrical superhighway) uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating curre ...
technology are being assessed to reach the final goal – the 'SuperSmart Grid (SSG)'. by Tamás Kugyela
Consortium
The consortium of twenty plus utilities, grid operators, equipment makers, financing institutions and investors include, * Abengoa SA (Spain) * Alstom SA (France) * Areva SA (France) * Atos Worldgrid (France) * cdc infrastructure (France) * EDF SA (France) * GDF Suez SA (France) * NEMO (Italy) * Nexans (France) * L'Office National de l'Électricité (ONE) (Morocco) * Pan Med Trading and Investment (Jordan) * Prysmian (Italy) * Red Electrica Corp. SA (Spain) * REN (Portugal) * RTE (France) *Siemens AG
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''E ...
(Germany)
* Soitec
Soitec is an international company, based in France, that manufactures high performance substrates used in the manufacture of semiconductors.
Soitec's semiconductor materials are used to manufacture chips which equip smartphones, tablets, ...
(France)
* Taqa Arabia (Egypt)
* Terna SA (Italy)
* Tunur (United Kingdom)
* Walid Elias Establishment (Syria)
The consortium is led by André Merlin,Medgrid Team/ref> CEO of Medgrid.
See also
* Supersmart Grid * Desertec *European super grid
The European super grid is a possible future super grid that would ultimately interconnect the various European countries and the regions around Europe's borders – including North Africa, Kazakhstan, and Turkey – with a high-voltage ...
References
External links
Medgrids official website
{{Economy of Morocco Proposed solar power stations Renewable energy in the European Union Proposed electric power infrastructure in Africa Proposed electric power infrastructure in Europe