Mark 21 nuclear bomb on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The Mark 21 nuclear bomb was a
The Mark 21 nuclear bomb was a
Nuclear Weapon Archive: List of All U.S. Nuclear Weapons
/ref>

 The Mark 21 nuclear bomb was a
The Mark 21 nuclear bomb was a United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
thermonuclear gravity bomb
An unguided bomb, also known as a free-fall bomb, gravity bomb, dumb bomb, or iron bomb, is a conventional or nuclear aircraft-delivered bomb that does not contain a guidance system and hence simply follows a ballistic trajectory. This describe ...
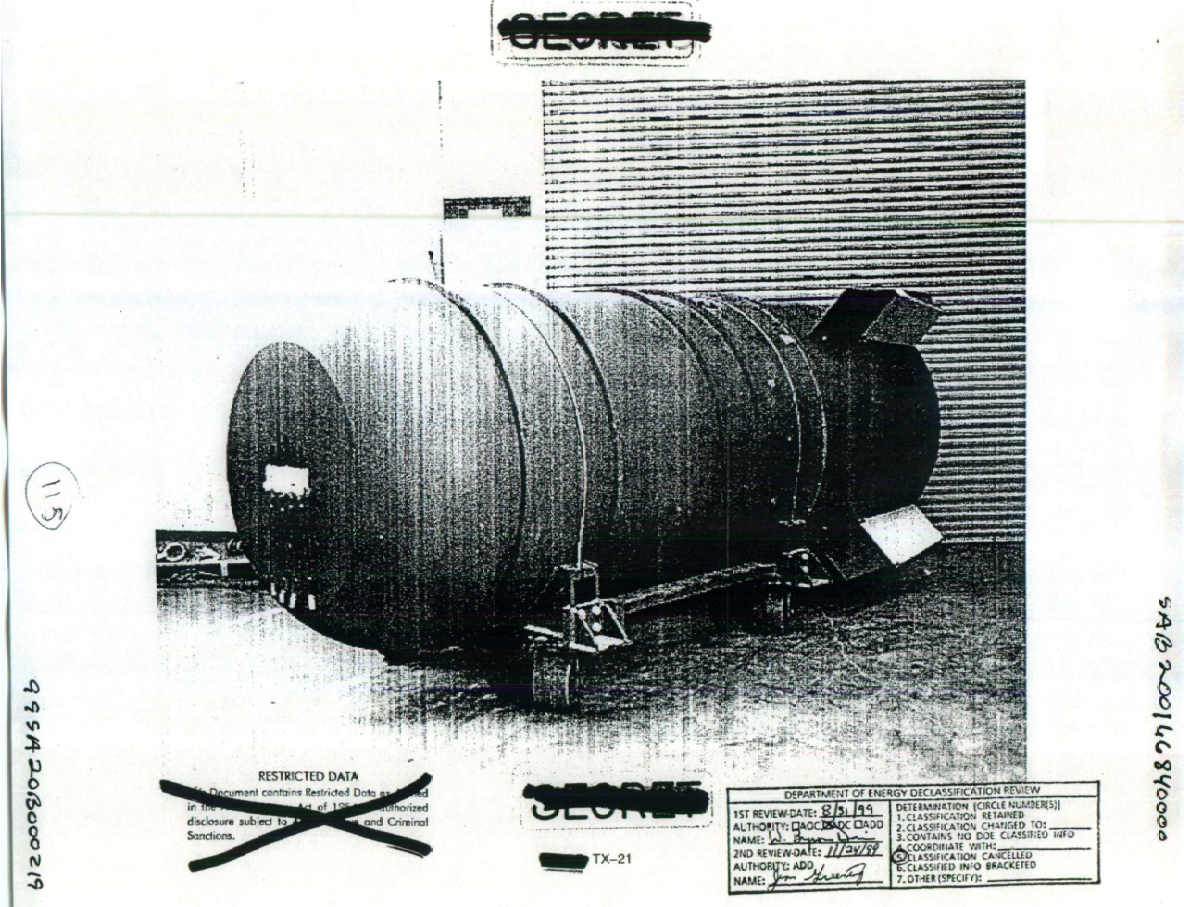
first produced in 1955. It was based on the TX 21 "Shrimp" prototype that had been detonated during the Castle Bravo
Castle Bravo was the first in a series of high-yield thermonuclear weapon design tests conducted by the United States at Bikini Atoll, Marshall Islands, as part of '' Operation Castle''. Detonated on March 1, 1954, the device was the most powerful ...
test in March 1954. While most of the Operation Castle
Operation Castle was a United States series of high-yield (high-energy) nuclear tests by Joint Task Force 7 (JTF-7) at Bikini Atoll beginning in March 1954. It followed ''Operation Upshot–Knothole'' and preceded ''Operation Teapot''.
Condu ...
tests were intended to evaluate weapons intended for immediate stockpile, or which were already available for use as part of the Emergency Capability Program, Castle Bravo was intended to test a design which would drastically reduce the size and costs of the first generation of air-droppable atomic weapons (the Mk 14, Mk 17 & Mk 24).
Design
At long, in diameter, a span over the fins, and weighing , the Mk 21 was half the length and less than half the weight of the Mk 17/24 weapons it replaced. The Mk 21 Y1 had a yield of 18 to 19 megatons. The "clean" Mk 21 Y2 (later designated Mk 26) was tested at 4.5 megatons. All 275 Mk 21 weapons stockpiled were the Y1 version. Quantity production of the Mk 21 started in December 1955 and ran until July 1956. Starting in June 1957 all Mk 21 bombs were converted to the more advanced Mk 36, which was removed from service in 1962./ref>
Delivery system
The Mark 21 could only be delivered by bomber; it was carried by theB-36
The Convair B-36 "Peacemaker" is a strategic bomber that was built by Convair and operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) from 1949 to 1959. The B-36 is the largest mass-produced Reciprocating engine, piston-engined aircraft ever built. It ...
and B-47
The Boeing B-47 Stratojet (Boeing company designation Model 450) is a retired American long- range, six-engined, turbojet-powered strategic bomber designed to fly at high subsonic speed and at high altitude to avoid enemy interceptor aircr ...
. Weapon was carried in a sling apparatus. Aircraft speed at release was limited to , so as to not exceed an opening shock of 6,000 gees on the parachute harness. The bomb was equipped with a two-stage deployment system, including a main ribbon canopy which provided up to 108 seconds of retardation.
To carry the Mk 21, the B-47 required the installation of special fin recesses in the bomb bay doors.
Tests
The Mk 21 (Mk 21 Y1, the version in the stockpile) was never tested. The Mk 21C (Mk 21 Y2) was proof tested as theOperation Redwing
Operation Redwing was a United States series of 17 nuclear test detonations from May to July 1956. They were conducted at Bikini and Enewetak atolls by Joint Task Force 7 (JTF7).Blumenson, Martin and Hugh D. Hexamer (1956). ''A History of ...
Navajo shot, with a yield of 4.5 megatons.
Specifications
* Length: * Diameter: * Weight: * Fuzing:airburst
An air burst or airburst is the detonation of an explosive device such as an anti-personnel artillery shell or a nuclear weapon in the air instead of on contact with the ground or target. The principal military advantage of an air burst over ...
—Contact burst was also available.
* Yield: 18 to 19 megatons
* Thermonuclear weapon
Users
*United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
See also
*List of nuclear weapons
This is a list of nuclear weapons listed according to country of origin, and then by type within the states.
United States
US nuclear weapons of all types – bombs, warheads, shells, and others – are numbered in the same sequence starting wi ...
References
*Hansen, Chuck. ''U.S. Nuclear Weapons," Arlington, Texas, Areofax, Inc., 1988. . *O'Keefe, Bernard J. "Nuclear Hostages," Boston, Houghton Mifflin Company, 1983, . *Goetz, Peter. "A Technical History of America's Nuclear Arms Volume 1," 2020, {{United States nuclear devices Cold War aerial bombs of the United States Nuclear bombs of the United States Military equipment introduced in the 1950s