Marine pollution on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Marine pollution occurs when substances used or spread by humans, such as industrial,
 There are many ways to categorize and examine the inputs of pollution into marine ecosystems. There are three main types of inputs of pollution into the ocean: direct discharge of waste into the oceans, runoff into the waters due to rain, and pollutants released from the atmosphere.
One common path of entry by contaminants to the sea are rivers. The evaporation of water from oceans exceeds precipitation. The balance is restored by rain over the continents entering rivers and then being returned to the sea. The
There are many ways to categorize and examine the inputs of pollution into marine ecosystems. There are three main types of inputs of pollution into the ocean: direct discharge of waste into the oceans, runoff into the waters due to rain, and pollutants released from the atmosphere.
One common path of entry by contaminants to the sea are rivers. The evaporation of water from oceans exceeds precipitation. The balance is restored by rain over the continents entering rivers and then being returned to the sea. The
 Pollutants enter rivers and the sea directly from urban sewerage and
Pollutants enter rivers and the sea directly from urban sewerage and
 Ships can pollute waterways and oceans in many ways. Oil spills can have devastating effects. In addition to being toxic to marine life, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), found in
Ships can pollute waterways and oceans in many ways. Oil spills can have devastating effects. In addition to being toxic to marine life, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), found in
Deep Sea Invasion: The Impact of Invasive Species
PBS: NOVA. Retrieved 26 November 2009 Ballast water taken up at sea and released in port is a major source of unwanted exotic marine life. The invasive freshwater zebra mussels, native to the Black, Caspian, and Azov seas, were probably transported to the Great Lakes via ballast water from a transoceanic vessel. Meinesz believes that one of the worst cases of a single invasive species causing harm to an ecosystem can be attributed to a seemingly harmless
 Another pathway of pollution occurs through the atmosphere. The ocean has long been affected by the passage of chemicals from the atmosphere (e.g. nutrient source; pH influence). Wind-blown dust and debris, including
Another pathway of pollution occurs through the atmosphere. The ocean has long been affected by the passage of chemicals from the atmosphere (e.g. nutrient source; pH influence). Wind-blown dust and debris, including




Parla un boss: Così lo Stato pagava la 'ndrangheta per smaltire i rifiuti tossici
''L'Espresso'' * Since the end of World War II, various nations, including the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, the United States, and Germany, have disposed of chemical weapons in the
 Much
Much
A/RES/71/313
The title of Target 14.1 is: "By 2025, prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds, in particular from land-based activities, including
 Although marine pollution has a long history, significant international laws to counter it were not enacted until the twentieth century. Marine pollution was a concern during several United Nations Conventions on the Law of the Sea beginning in the 1950s. Most scientists believed that the oceans were so vast that they had unlimited ability to dilute, and thus render pollution harmless.
In the late 1950s and early 1960s, there were several controversies about dumping radioactive waste off the coasts of the United States by companies licensed by the Atomic Energy Commission, into the Irish Sea from the British reprocessing facility at Windscale, and into the Mediterranean Sea by the French Commissariat à l'Energie Atomique. After the Mediterranean Sea controversy, for example,
Although marine pollution has a long history, significant international laws to counter it were not enacted until the twentieth century. Marine pollution was a concern during several United Nations Conventions on the Law of the Sea beginning in the 1950s. Most scientists believed that the oceans were so vast that they had unlimited ability to dilute, and thus render pollution harmless.
In the late 1950s and early 1960s, there were several controversies about dumping radioactive waste off the coasts of the United States by companies licensed by the Atomic Energy Commission, into the Irish Sea from the British reprocessing facility at Windscale, and into the Mediterranean Sea by the French Commissariat à l'Energie Atomique. After the Mediterranean Sea controversy, for example,

agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
and residential
A residential area is a land used in which housing predominates, as opposed to industrial and commercial areas.
Housing may vary significantly between, and through, residential areas. These include single-family housing, multi-family resi ...
waste
Waste (or wastes) are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor economic value. A waste pr ...
, particles, noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference aris ...
, excess carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
or invasive organisms enter the ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wor ...
and cause harmful effects there. The majority of this waste (80%) comes from land-based activity, although marine transportation significantly contributes as well. Since most inputs come from land, either via the river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of ...
s, sewage or the atmosphere, it means that continental shelves
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
are more vulnerable to pollution. Air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different type ...
is also a contributing factor by carrying off iron, carbonic acid, nitrogen, silicon, sulfur, pesticides or dust particles into the ocean. The pollution often comes from nonpoint source Nonpoint source, or non-point source, or NPS, is a source that does not come from a single point.
* Point source, contrasts with nonpoint source
* Nonpoint source pollution, water pollution
* Nonpoint source water pollution regulations, water pollu ...
s such as agricultural runoff
Runoff, run-off or RUNOFF may refer to:
* RUNOFF, the first computer text-formatting program
* Runoff or run-off, another name for bleed, printing that lies beyond the edges to which a printed sheet is trimmed
* Runoff or run-off, a stock marke ...
, wind-blown debris, and dust. These nonpoint sources are largely due to runoff that enters the ocean through rivers, but wind-blown debris and dust can also play a role, as these pollutants can settle into waterways and oceans. Pathways of pollution include direct discharge, land runoff, ship pollution, atmospheric pollution and, potentially, deep sea mining.
The types of marine pollution can be grouped as pollution from marine debris
Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created waste that has deliberately or accidentally been released in a sea or ocean. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing ...
, plastic pollution
Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic objects and particles (e.g. plastic bottles, bags and microbeads) in the Earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat. Plastics that act as pollutants are cate ...
, including microplastics, ocean acidification
Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxid ...
, nutrient pollution, toxins and underwater noise. Plastic pollution in the ocean is a type of marine pollution by plastics
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptabi ...
, ranging in size from large original material such as bottles and bags, down to microplastics formed from the fragmentation of plastic material. Marine debris is mainly discarded human rubbish which floats on, or is suspended in the ocean. Plastic pollution is harmful to marine life
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. ...
.
Another concern is the runoff of nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excre ...
s (nitrogen and phosphorus) from intensive agriculture
Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming (as opposed to extensive farming), conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of crop plants and of animals, with higher levels of input and output per unit of ag ...
, and the disposal of untreated or partially treated sewage to rivers and subsequently oceans. These nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
and phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ea ...
nutrients (which are also contained in fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s) stimulate phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
...
and macroalgal growth, which can lead to harmful algal blooms (eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phyt ...
) which can be harmful to humans as well as marine creatures. Excessive algal growth can also smother sensitive coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of Colony (biology), colonies of coral polyp (zoology), polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, wh ...
s and lead to loss of biodiversity and coral health. A second major concern is that the degradation of algal blooms can lead to consumption of oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
in coastal waters, a situation that may worsen with climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
as warming reduces vertical mixing of the water column.
Many potentially toxic chemicals adhere to tiny particles which are then taken up by plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a cruc ...
and benthic animals, most of which are either deposit feeders or filter feeder
Filter feeders are a sub-group of suspension feeding animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water, typically by passing the water over a specialized filtering structure. Some animals that use this method of feedin ...
s. In this way, the toxins are concentrated upward within ocean food chains. When pesticides are incorporated into the marine ecosystem, they quickly become absorbed into marine food webs. Once in the food webs, these pesticides can cause mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
s, as well as diseases, which can be harmful to humans as well as the entire food web. Toxic metals can also be introduced into marine food webs. These can cause a change to tissue matter, biochemistry, behavior, reproduction, and suppress growth in marine life. Also, many animal feeds
Animal feed is food given to domestic animals, especially livestock, in the course of animal husbandry. There are two basic types: fodder and forage. Used alone, the word ''feed'' more often refers to fodder. Animal feed is an important input to ...
have a high fish meal
Fish meal is a commercial product made from whole wild-caught fish, bycatch and fish by-products to feed farm animals, e.g., pigs, poultry, and farmed fish.R. D. Miles and F. A. Chapman.FA122: The Benefits of Fish Meal in Aquaculture DietsFisher ...
or fish hydrolysate content. In this way, marine toxins can be transferred to land animals, and appear later in meat and dairy products.
Pathways of pollution
 There are many ways to categorize and examine the inputs of pollution into marine ecosystems. There are three main types of inputs of pollution into the ocean: direct discharge of waste into the oceans, runoff into the waters due to rain, and pollutants released from the atmosphere.
One common path of entry by contaminants to the sea are rivers. The evaporation of water from oceans exceeds precipitation. The balance is restored by rain over the continents entering rivers and then being returned to the sea. The
There are many ways to categorize and examine the inputs of pollution into marine ecosystems. There are three main types of inputs of pollution into the ocean: direct discharge of waste into the oceans, runoff into the waters due to rain, and pollutants released from the atmosphere.
One common path of entry by contaminants to the sea are rivers. The evaporation of water from oceans exceeds precipitation. The balance is restored by rain over the continents entering rivers and then being returned to the sea. The Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between Ne ...
in New York State
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. sta ...
and the Raritan River
Raritan River is a major river of New Jersey. Its watershed drains much of the mountainous area of the central part of the state, emptying into the Raritan Bay on the Atlantic Ocean.
History
Geologists assert that the lower Raritan provided t ...
in New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delawa ...
, which empty at the northern and southern ends of Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey b ...
, are a source of mercury contamination of zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
(copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have ...
s) in the open ocean. The highest concentration in the filter-feeding copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have ...
s is not at the mouths of these rivers but south, nearer Atlantic City
Atlantic City, often known by its initials A.C., is a coastal resort city in Atlantic County, New Jersey, United States. The city is known for its casinos, boardwalk, and beaches. In 2020, the city had a population of 38,497.
, because water flows close to the coast. It takes a few days before toxins are taken up by the plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a cruc ...
.
Pollution is often classed as point source or nonpoint source pollution. Point source pollution occurs when there is a single, identifiable, localized source of the pollution. An example is directly discharging sewage and industrial waste into the ocean. Pollution such as this occurs particularly in developing nations. Nonpoint source pollution occurs when the pollution is from ill-defined and diffuse sources. These can be difficult to regulate. Agricultural runoff
Runoff, run-off or RUNOFF may refer to:
* RUNOFF, the first computer text-formatting program
* Runoff or run-off, another name for bleed, printing that lies beyond the edges to which a printed sheet is trimmed
* Runoff or run-off, a stock marke ...
and wind blown debris are prime examples.
Direct discharge
 Pollutants enter rivers and the sea directly from urban sewerage and
Pollutants enter rivers and the sea directly from urban sewerage and industrial waste
Industrial waste is the waste produced by industrial activity which includes any material that is rendered useless during a manufacturing process such as that of factories, mills, and mining operations. Types of industrial waste include dirt an ...
discharges, sometimes in the form of hazardous and toxic wastes, or in the form of plastics.
In a study published by ''Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
'', Jambeck ''et al.'' (2015) estimated that the 10 largest emitters of oceanic plastic pollution worldwide are, from the most to the least, China, Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Egypt, Malaysia, Nigeria, and Bangladesh.
Inland mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the econom ...
for copper, gold, etc., is another source of marine pollution. Most of the pollution is simply soil, which ends up in rivers flowing to the sea. However, some minerals discharged in the course of the mining can cause problems, such as copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
, a common industrial pollutant, which can interfere with the life history and development of coral polyps. Mining has a poor environmental track record. For example, according to the United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it ...
, mining has contaminated portions of the headwaters of over 40% of watersheds in the western continental US. Much of this pollution finishes up in the sea.
Land runoff
Surface runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow) is the flow of water occurring on the ground surface when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other sources, can no longer sufficiently rapidly infiltrate in the soil. This can occur when t ...
from farming, as well as urban runoff
Urban runoff is surface runoff of rainwater, landscape irrigation, and car washing created by urbanization. Impervious surfaces (roads, parking lots and sidewalks) are constructed during land development. During rain , storms and other precip ...
and runoff from the construction of roads, buildings, ports, channels, and harbours, can carry soil and particles laden with carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and minerals. This nutrient-rich water can cause fleshy algae and phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
...
to thrive in coastal areas; known as algal blooms, which have the potential to create hypoxic conditions by using all available oxygen. In the coast of southwest Florida, harmful algal blooms have existed for over 100 years. These algal blooms have been a cause of species of fish, turtles, dolphins, and shrimp to die and cause harmful effects on humans who swim in the water.
Polluted runoff from roads and highways can be a significant source of water pollution in coastal areas. About 75% of the toxic chemicals that flow into Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ) is a sound of the Pacific Northwest, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean, and part of the Salish Sea. It is located along the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected m ...
are carried by stormwater
Stormwater, also spelled storm water, is water that originates from precipitation ( storm), including heavy rain and meltwater from hail and snow. Stormwater can soak into the soil ( infiltrate) and become groundwater, be stored on depressed l ...
that runs off paved roads and driveways, rooftops, yards and other developed land. In California, there are many rainstorms that runoff into the ocean. These rainstorms occur from October to March, and these runoff waters contain petroleum, heavy metals, pollutants from emissions, etc.
In China, there is a large coastal population that pollutes the ocean through land runoff. This includes sewage discharge and pollution from urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly th ...
and land use. In 2001, more than 66,795 mi2 of the Chinese coastal ocean waters were rated less than Class I of the Sea Water Quality Standard of China. Much of this pollution came from Ag, Cu, Cd, Pb, As, DDT, PCBs, etc., which occurred from contamination through land runoff.
Ship pollution
 Ships can pollute waterways and oceans in many ways. Oil spills can have devastating effects. In addition to being toxic to marine life, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), found in
Ships can pollute waterways and oceans in many ways. Oil spills can have devastating effects. In addition to being toxic to marine life, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), found in crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
, are very difficult to clean up, and last for years in the sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
and marine environment.
Oil spills are probably the most emotive of marine pollution events. However, while a tanker wreck may result in extensive newspaper headlines, much of the oil in the world's seas comes from other smaller sources, such as tankers discharging ballast water from oil tanks used on return ships, leaking pipelines or engine oil disposed of down sewers.
Discharge of cargo residues from bulk carrier
A bulk carrier or bulker is a merchant ship specially designed to transport unpackaged bulk cargo — such as grains, coal, ore, steel coils, and cement — in its cargo holds. Since the first specialized bulk carrier was built in 1852, eco ...
s can pollute ports, waterways, and oceans. In many instances vessels intentionally discharge illegal wastes despite foreign and domestic regulation prohibiting such actions. An absence of national standards provides an incentive for some cruise liners to dump waste in places where the penalties are inadequate. It has been estimated that container ship
A container ship (also called boxship or spelled containership) is a cargo ship that carries all of its load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. Container ships are a common means of commercial intermoda ...
s lose over 10,000 containers
A container is any receptacle or enclosure for holding a product used in storage, packaging, and transportation, including shipping.
Things kept inside of a container are protected on several sides by being inside of its structure. The ter ...
at sea each year (usually during storms). Ships also create noise pollution
Noise pollution, also known as environmental noise or sound pollution, is the propagation of noise with ranging impacts on the activity of human or animal life, most of them are harmful to a degree. The source of outdoor noise worldwide is mai ...
that disturbs natural wildlife, and water from ballast tanks can spread harmful algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
and other invasive species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species adv ...
.Meinesz, A. (2003Deep Sea Invasion: The Impact of Invasive Species
PBS: NOVA. Retrieved 26 November 2009 Ballast water taken up at sea and released in port is a major source of unwanted exotic marine life. The invasive freshwater zebra mussels, native to the Black, Caspian, and Azov seas, were probably transported to the Great Lakes via ballast water from a transoceanic vessel. Meinesz believes that one of the worst cases of a single invasive species causing harm to an ecosystem can be attributed to a seemingly harmless
jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbre ...
. ''Mnemiopsis leidyi
''Mnemiopsis leidyi'', the warty comb jelly or sea walnut, is a species of tentaculate ctenophore (comb jelly). It is native to western Atlantic coastal waters, but has become established as an invasive species in European and western Asian re ...
'', a species of comb jellyfish that spread so it now inhabits estuaries in many parts of the world, was first introduced in 1982, and thought to have been transported to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
in a ship's ballast water. The population of the jellyfish grew exponentially and, by 1988, it was wreaking havoc upon the local fishing industry
The fishing industry includes any industry or activity concerned with taking, culturing, processing, preserving, storing, transporting, marketing or selling fish or fish products. It is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization as including ...
. "The anchovy catch fell from 204,000 tons in 1984 to 200 tons in 1993; sprat from 24,600 tons in 1984 to 12,000 tons in 1993; horse mackerel from 4,000 tons in 1984 to zero in 1993." Now that the jellyfish have exhausted the zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
, including fish larvae, their numbers have fallen dramatically, yet they continue to maintain a stranglehold on the ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
.
Invasive species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species adv ...
can take over once occupied areas, facilitate the spread of new diseases, introduce new genetic material, alter underwater seascapes, and jeopardize the ability of native species
In biogeography, a native species is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only local natural evolution (though often popularised as "with no human intervention") during history. The term is e ...
to obtain food. Invasive species are responsible for about $138 billion annually in lost revenue and management costs in the US alone.
Atmospheric pollution
 Another pathway of pollution occurs through the atmosphere. The ocean has long been affected by the passage of chemicals from the atmosphere (e.g. nutrient source; pH influence). Wind-blown dust and debris, including
Another pathway of pollution occurs through the atmosphere. The ocean has long been affected by the passage of chemicals from the atmosphere (e.g. nutrient source; pH influence). Wind-blown dust and debris, including plastic bag
A plastic bag, poly bag, or pouch is a type of container made of thin, flexible, plastic film, nonwoven fabric, or plastic textile. Plastic bags are used for containing and transporting goods such as foods, produce, powders, ice, magazine ...
s, are blown seaward from landfill
A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. Landfill is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of the wast ...
s and other areas. Dust from the Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
moving around the southern periphery of the subtropical ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as subtropical ridges, or highs. It is a high-press ...
moves into the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean ...
and Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
during the warm season as the ridge builds and moves northward through the subtropical Atlantic. Dust can also be attributed to a global transport from the Gobi
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast ...
and Taklamakan
The Taklimakan or Taklamakan Desert (; zh, s=塔克拉玛干沙漠, p=Tǎkèlāmǎgān Shāmò, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Такәламаган Шамә; ug, تەكلىماكان قۇملۇقى, Täklimakan qumluqi; also spelled Taklimakan and Te ...
deserts across Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
, and the Northern Pacific to the Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost ...
.
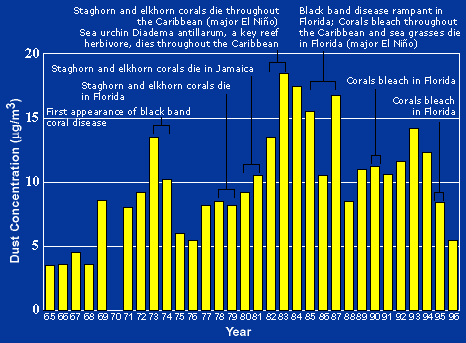
Since 1970, dust outbreaks have worsened due to periods of drought in Africa. There is a large variability in dust transport to the Caribbean and Florida from year to year; however, the flux is greater during positive phases of the North Atlantic Oscillation. The USGS links dust events to a decline in the health of coral reefs across the Caribbean and Florida, primarily since the 1970s.
Climate change is raising ocean temperatures and raising levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. These rising levels of carbon dioxide are acidifying the oceans. This, in turn, is altering aquatic ecosystems and modifying fish distributions, with impacts on the sustainability of fisheries and the livelihoods of the communities that depend on them. Healthy ocean ecosystems are also important for the mitigation of climate change.
Deep sea mining
Some of the potential toxic metals include copper, zinc, cadmium, lead as well as rare earth elements such aslanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between l ...
and yttrium. Following the release of toxins there is an increase of noise, light, sediment le dan plumes and elements that have the potential to impact the ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
s.
Deep sea minerals (DSM) can be extremely beneficial, it can cause wealth, raising living standards as well as economic opportunities for both current and future generations. In addition, if the wealth is poorly managed it can have the potential to cause great economic and social damage . The instability of price and production levels of minerals can cause an external economic shock leading to a significant backlash on the domestic economy.
Types of pollution

Marine debris pollution

Plastic pollution
Ocean acidification

Nutrient pollution
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phyt ...
is an increase in chemical nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excre ...
s, typically compounds containing nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
or phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ea ...
, in an ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
. It can result in an increase in the ecosystem's primary productivity (excessive plant growth and decay), and further effects including lack of oxygen and severe reductions in water quality, fish, and other animal populations. Nutrient pollution, a form of water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, so that it negatively affects its uses. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. ...
, refers to contamination by excessive inputs of nutrients. It is a primary cause of eutrophication of surface waters, in which excess nutrients, usually nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insolu ...
s or phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
s, stimulate algae growth. Such blooms are naturally occurring but may be increasing as a result of anthropogenic inputs or alternatively may be something that is now more closely monitored and so more frequently reported.
The biggest culprit are rivers that empty into the ocean, and with it the many chemicals used as fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s in agriculture as well as waste from livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
and human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s. An excess of oxygen-depleting chemicals in the water can lead to hypoxia and the creation of a dead zone.Gerlach, S. A. (1975) ''Marine Pollution'', Springer, Berlin
Estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environme ...
tend to be naturally eutrophic because land-derived nutrients are concentrated where runoff
Runoff, run-off or RUNOFF may refer to:
* RUNOFF, the first computer text-formatting program
* Runoff or run-off, another name for bleed, printing that lies beyond the edges to which a printed sheet is trimmed
* Runoff or run-off, a stock marke ...
enters the marine environment in a confined channel. The World Resources Institute has identified 375 hypoxic coastal zones around the world, concentrated in coastal areas in Western Europe, the Eastern and Southern coasts of the US, and East Asia, particularly in Japan. In the ocean, there are frequent red tide algae blooms that kill fish and marine mammals and cause respiratory problems in humans and some domestic animals when the blooms reach close to shore.
In addition to land runoff, atmospheric anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Counterintuitively, anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human i ...
fixed nitrogen can enter the open ocean. A study in 2008 found that this could account for around one third of the ocean's external (non-recycled) nitrogen supply and up to three per cent of the annual new marine biological production. It has been suggested that accumulating reactive nitrogen in the environment may have consequences as serious as putting carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
One proposed solution to eutrophication in estuaries is to restore shellfish populations, such as oysters. Oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not ...
reefs remove nitrogen from the water column and filter out suspended solids, subsequently reducing the likelihood or extent of harmful algal blooms or anoxic conditions. Filter feeding activity is considered beneficial to water quality by controlling phytoplankton density and sequestering nutrients, which can be removed from the system through shellfish harvest, buried in the sediments, or lost through denitrification
Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process where nitrate (NO3−) is reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products. Facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denit ...
. Foundational work toward the idea of improving marine water quality through shellfish cultivation to was conducted by Odd Lindahl et al., using mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other edible clams, which ...
s in Sweden.
Toxicants
Apart from plastics, there are particular problems with other toxic pollutants that either do not break down or only very slowly in the marine environment. Examples of persistent toxicants are PCBs, DDT, TBT,pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and ...
s, furan
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
Furan is a colorless, flammable, highl ...
s, dioxins, phenols, and radioactive waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapon ...
. Heavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals are generally defined as ...
are metallic chemical elements that have a relatively high density and are toxic or poisonous at low concentrations. Examples are mercury, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
and cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Li ...
. Some toxicants can accumulate in the tissues of many species of aquatic life in a process called bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance at a rate faster than that at which the substance is lost or eliminated ...
. They are also known to accumulate in benthic environments, such as estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environme ...
and bay mud
Bay mud consists of thick deposits of soft, unconsolidated silty clay, which is saturated with water; these soil layers are situated at the bottom of certain estuaries, which are normally in temperate regions that have experienced cyclical glac ...
s: a geological record of human activities of the last century.
;Specific examples:
* Chinese and Russian industrial pollution such as phenols and heavy metals in the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China (Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long ...
have devastated fish stocks and damaged its estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
soil.
* Acute and chronic pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, th ...
events have been shown to impact southern California kelp forests, though the intensity of the impact seems to depend on both the nature of the contaminants and duration of exposure.
* Due to their high position in the food chain and the subsequent accumulation
Accumulation may refer to:
Finance
* Accumulation function, a mathematical function defined in terms of the ratio future value to present value
* Capital accumulation, the gathering of objects of value
Science and engineering
* Accumulate (highe ...
of heavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals are generally defined as ...
from their diet, mercury levels can be high in larger species such as bluefin and albacore. As a result, in March 2004 the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
FDA issued guidelines recommending that pregnant women, nursing mothers and children limit their intake of tuna and other types of predatory fish.
* Some shellfish and crabs can survive polluted environments, accumulating heavy metals or toxins in their tissues. For example, mitten crabs have a remarkable ability to survive in highly modified aquatic habitat
Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life, organisms in the sea. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies s ...
s, including polluted waters. The farming and harvesting of such species needs careful management if they are to be used as a food.
* Surface runoff of pesticides can alter the gender of fish species genetically, transforming male into female fish.
* Heavy metals enter the environment through oil spills – such as the Prestige oil spill
The ''Prestige'' oil spill occurred off the coast of Galicia, Spain in November 2002, caused by the sinking of the 26-year-old, structurally deficient oil tanker , carrying 77,000 tonnes of heavy fuel oil. During a storm, it burst a tank on ...
on the Galician coast and Gulf of Mexico which unleashed an estimated 3.19 million barrels of oil – or from other natural or anthropogenic sources.
* In 2005, the 'Ndrangheta
The 'Ndrangheta (, , ) is a prominent Italian Mafia-type organized crime syndicate and secret society, criminal society based in the peninsular and mountainous region of Calabria and dating back to the late 18th century. It is considered one of ...
, an Italian mafia syndicate, was accused of sinking at least 30 ships loaded with toxic waste, much of it radioactive. This has led to widespread investigations into radioactive waste disposal Radioactive waste disposal may refer to:
*High-level radioactive waste management
* Low-level waste disposal
* Ocean disposal of radioactive waste
** Ocean floor disposal
* Deep borehole disposal
*Deep geological repository
A deep geological repo ...
rackets.Bocca, Riccardo (5 August 2005Parla un boss: Così lo Stato pagava la 'ndrangheta per smaltire i rifiuti tossici
''L'Espresso'' * Since the end of World War II, various nations, including the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, the United States, and Germany, have disposed of chemical weapons in the
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
, raising concerns of environmental contamination.
* The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in 2011 caused radioactive toxins from the damaged power plant to leak into the air and ocean. There are still many isotopes in the ocean, which directly affects the benthic food web and also affects the whole food chain. The concentration of 137Cs in the bottom sediment that was contaminated by water with high concentrations in April–May 2011 remains quite high and is showing signs of very slow decrease with time.
Underwater noise
Marine life can be susceptible to noise or the sound pollution from sources such as passing ships, oil exploration seismic surveys, and naval low-frequency activesonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on o ...
. Sound travels more rapidly and over larger distances in the sea than in the atmosphere. Marine animals, such as cetacean
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel th ...
s, often have weak eyesight, and live in a world largely defined by acoustic information. This applies also to many deeper sea fish, who live in a world of darkness. Between 1950 and 1975, ambient noise at one location in the Pacific Ocean increased by about ten decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a ...
s (that is a tenfold increase in intensity).
Noise also makes species communicate louder, which is called the Lombard vocal response. Whale songs are longer when submarine-detectors are on. If creatures don't "speak" loud enough, their voice can be masked by anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Counterintuitively, anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human i ...
sounds. These unheard voices might be warnings, finding of prey, or preparations of net-bubbling. When one species begins speaking louder, it will mask other species voices, causing the whole ecosystem to eventually speak louder.
According to the oceanographer Sylvia Earle
Sylvia Alice Earle (née Reade; born August 30, 1935) is an American marine biologist, oceanographer, explorer, author, and lecturer. She has been a National Geographic explorer-in-residence since 1998. Earle was the first female chief scien ...
, "Undersea noise pollution is like the death of a thousand cuts. Each sound in itself may not be a matter of critical concern, but taken all together, the noise from shipping, seismic surveys, and military activity is creating a totally different environment than existed even 50 years ago. That high level of noise is bound to have a hard, sweeping impact on life in the sea."
Noise from ships and human activity can damage Cnidarians and Ctenophora, which are very important organisms in the marine ecosystem. They promote high diversity and they are used as models for ecology and biology because of their simple structures. When there is underwater noise, the vibrations in the water damage the cilia hairs in the Coelenterates. In a study, the organisms were exposed to sound waves for different numbers of times and the results showed that damaged hair cells were extruded or missing or presented bent, flaccid or missed kinocilia and stereocilia. Ships can be certified to meet certain noise criteria.
Other
There are a variety of secondary effects stemming not from the original pollutant, but a derivative condition. An example issilt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel ...
-bearing surface runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow) is the flow of water occurring on the ground surface when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other sources, can no longer sufficiently rapidly infiltrate in the soil. This can occur when t ...
, which can inhibit the penetration of sunlight through the water column, hampering photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in ...
in aquatic plants.
Mitigation
 Much
Much anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Counterintuitively, anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human i ...
pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, th ...
ends up in the ocean. The 2011 edition of the United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on ...
Year Book identifies as the main emerging environmental issues the loss to the oceans of massive amounts of phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ea ...
, "a valuable fertilizer needed to feed a growing global population", and the impact billions of pieces of plastic waste are having globally on the health of marine environments.
Bjorn Jennssen (2003) notes in his article, "Anthropogenic pollution may reduce biodiversity and productivity of marine ecosystems, resulting in reduction and depletion of human marine food resources". There are two ways the overall level of this pollution can be mitigated: either the human population is reduced, or a way is found to reduce the ecological footprint
The ecological footprint is a method promoted by the Global Footprint Network to measure human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people or an economy. It tracks this demand through an ecological accounti ...
left behind by the average human. If the second way is not adopted, then the first way may be imposed as the world ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
s falter.
The second way is for humans, individually, to pollute less. That requires social and political will, together with a shift in awareness so more people respect the environment and are less disposed to abuse it. At an operational level, regulations, and international government participation is needed. It is often very difficult to regulate marine pollution because pollution spreads over international barriers, thus making regulations hard to create as well as enforce.
Without appropriate awareness of marine pollution, the necessary global will to effectively address the issues may prove inadequate. Balanced information on the sources and harmful effects of marine pollution need to become part of general public awareness, and ongoing research is required to fully establish, and keep current, the scope of the issues. As expressed in Daoji and Dag's research, one of the reasons why environmental concern is lacking among the Chinese is because the public awareness is low and therefore should be targeted.
The amount of awareness on marine pollution is vital to the support of keeping the prevention of trash from entering waterways and ending up in our oceans. The EPA reports that in 2014 Americans generated about 258 million tons of waste, and only a third was recycled or composted. In 2015, there was over 8 million tons of plastic that made it into the ocean. The Ocean Conservancy reported that China, Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam dump more plastic in the sea than all other countries combined. Through more sustainable packing this could lead to; eliminating toxic constituents, using fewer materials, making more readily available recyclable plastic. However, awareness can only take these initiatives so far. The most abundant plastic is PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) and is the most resistant to biodegradables. Researchers have been making great strides in combating this problem. In one way has been by adding a special polymer called a tetrablock copolymer. The tetrablock copolymer acts as a laminate between the PE and iPP which enables for an easier breakdown but still be tough. Through more awareness, individuals will become more cognizant of their carbon footprints. Also, from research and technology, more strides can be made to aid in the plastic pollution problem.Jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbre ...
have been considered a potential mitigating organism for pollution.
Global goals
In 2017, the United Nations adopted a resolution establishingSustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
, including reduced marine pollution as a measured goal under Goal 14. The international community has agreed that reducing pollution in the oceans is a priority, which is tracked as part of Sustainable Development Goal 14 which actively seeks to undo these human impacts on the oceans.United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable DevelopmentA/RES/71/313
The title of Target 14.1 is: "By 2025, prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds, in particular from land-based activities, including
marine debris
Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created waste that has deliberately or accidentally been released in a sea or ocean. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing ...
and nutrient pollution."
History
 Although marine pollution has a long history, significant international laws to counter it were not enacted until the twentieth century. Marine pollution was a concern during several United Nations Conventions on the Law of the Sea beginning in the 1950s. Most scientists believed that the oceans were so vast that they had unlimited ability to dilute, and thus render pollution harmless.
In the late 1950s and early 1960s, there were several controversies about dumping radioactive waste off the coasts of the United States by companies licensed by the Atomic Energy Commission, into the Irish Sea from the British reprocessing facility at Windscale, and into the Mediterranean Sea by the French Commissariat à l'Energie Atomique. After the Mediterranean Sea controversy, for example,
Although marine pollution has a long history, significant international laws to counter it were not enacted until the twentieth century. Marine pollution was a concern during several United Nations Conventions on the Law of the Sea beginning in the 1950s. Most scientists believed that the oceans were so vast that they had unlimited ability to dilute, and thus render pollution harmless.
In the late 1950s and early 1960s, there were several controversies about dumping radioactive waste off the coasts of the United States by companies licensed by the Atomic Energy Commission, into the Irish Sea from the British reprocessing facility at Windscale, and into the Mediterranean Sea by the French Commissariat à l'Energie Atomique. After the Mediterranean Sea controversy, for example, Jacques Cousteau
Jacques-Yves Cousteau, (, also , ; 11 June 191025 June 1997) was a French naval officer, oceanographer, filmmaker and author. He co-invented the first successful Aqua-Lung, open-circuit SCUBA ( self-contained underwater breathing apparatus). T ...
became a worldwide figure in the campaign to stop marine pollution. Marine pollution made further international headlines after the 1967 crash of the oil tanker Torrey Canyon
SS ''Torrey Canyon'' was an LR2 Suezmax class oil tanker with a cargo capacity of of crude oil. She ran aground off the western coast of Cornwall, United Kingdom, on 18 March 1967, causing an environmental disaster. At that time she was the ...
, and after the 1969 Santa Barbara oil spill off the coast of California.
Marine pollution was a major area of discussion during the 1972 United Nations Conference on the Human Environment, held in Stockholm. That year also saw the signing of the Convention on the Prevention of Marine Pollution by Dumping of Wastes and Other Matter, sometimes called the London Convention. The London Convention did not ban marine pollution, but it established black and gray lists for substances to be banned (black) or regulated by national authorities (gray). Cyanide and high-level radioactive waste, for example, were put on the black list. The London Convention applied only to waste dumped from ships, and thus did nothing to regulate waste discharged as liquids from pipelines.
Society and culture

Laws and policies
There are different ways for the ocean to get polluted, therefore there have been multiple laws, policies, and treaties put into place throughout history. In order to protect the ocean from marine pollution, policies have been developed internationally. * In 1948, Harry Truman signed a law formerly known as theFederal Water Pollution Control Act
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to:
Politics
General
*Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies
*Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or ...
that allowed the federal government to control marine pollution in United States of America.
* In 1972, the Marine Protection, Research, and Sanctuaries Act of 1972
Marine Protection, Research and Sanctuaries Act of 1972 (MPRSA) or Ocean Dumping Act is one of several key environmental laws passed by the US Congress in 1972. The Act has two essential aims: to regulate intentional ocean disposal of materials, ...
(MPRSA) was passed by the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is Bicameralism, bicameral, composed of a lower body, the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, and an upper body, ...
, and regulates ocean dumping of waste in US waters.
* The 1954 Convention for the Prevention of Pollution of the Sea by Oil and the 1973 International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution by Ships were weakly enforced due to a lack of respect for the laws from flag states.
* In 1973 and 1978, MARPOL 73/78 was a treaty written to control vessel pollution, especially regarding oil. In 1983, the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships enforced the MARPOL 73/78 treaty internationally.
* The 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea ( UNCLOS) was established to protect the marine environment by governing states to control their pollution to the ocean. It put restrictions on the amount of toxins and pollutants that come from all ships internationally.
* In 2006, the Marine Debris Research, Prevention and Reduction Ac. It was established by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) to help identify, determine the source of, reduce and prevent marine debris
Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created waste that has deliberately or accidentally been released in a sea or ocean. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing ...
.
* In December 2017, the UN Environmental Agency (UNEA) established the Ad Hoc Open-Ended Expert Group on Marine Litter and Microplastics with the purpose of examining marine plastic pollution
Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic objects and particles (e.g. plastic bottles, bags and microbeads) in the Earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat. Plastics that act as pollutants are cate ...
s and to evaluate ways to handle the issue.
See also
* Aquatic toxicology *Environmental impact of pesticides
The environmental effects of pesticides describe the broad series of consequences of using pesticides. The unintended consequences of pesticides is one of the main drivers of the negative impact of modern industrial agriculture on the environme ...
* Mercury pollution in the ocean
* National Cleanup Day
* Oil pollution toxicity to marine fish
* Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants
Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants is an international environmental treaty, signed on 22 May 2001 in Stockholm and effective from 17 May 2004, that aims to eliminate or restrict the production and use of persistent organi ...
* Sea snot
* World Oceans Day
References
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Marine PollutionPollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, th ...
Sanitation