
Marine protected areas (MPA) are
protected areas of
sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
s,
ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
s,
estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environmen ...
or in the US, the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
.
These marine areas can come in many forms ranging from wildlife refuges to research facilities. MPAs restrict human activity for a conservation purpose, typically to protect natural or cultural resources. Such
marine resources are protected by local, state, territorial, native, regional, national, or international authorities and differ substantially among and between nations. This variation includes different limitations on development, fishing practices, fishing seasons and catch limits, moorings and bans on removing or disrupting
marine life. In some situations (such as with the
Phoenix Islands Protected Area
The Phoenix Islands Protected Area (PIPA) is located in the Republic of Kiribati, an ocean nation in the central Pacific approximately midway between Australia and Hawaii. PIPA constitutes 11.34% of Kiribati's exclusive economic zone (EEZ), an ...
), MPAs also provide revenue for countries, potentially equal to the income that they would have if they were to grant companies permissions to fish. The value of MPA to mobile species is unknown.
There are a number of global examples of large marine conservation areas. The
Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, is situated in the central Pacific Ocean, around
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
, occupying an area of 1.5 million square kilometers. The area is rich in wild life, including the green turtle and the Hawaiian monkfish, alongside 7,000 other species, and 14 million seabirds. In 2017 the
Cook Islands
)
, image_map = Cook Islands on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, capital = Avarua
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Avarua
, official_languages =
, lan ...
passed the Marae Moana Act designating the whole of the country's marine
exclusive economic zone, which has an area of 1.9 million square kilometers as a zone with the purpose of protecting and conserving the "ecological, biodiversity and heritage values of the Cook Islands marine environment".
Other
large marine conservation areas include those around Antarctica, New Caledonia, Greenland, Alaska, Ascension island, and Brazil.
As areas of protected
marine biodiversity
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. M ...
expand, there has been an increase in ocean science funding, essential for preserving
marine resources.
In 2020, only around 7.5 to 8% of the global ocean area falls under a conservation designation. This area is equivalent to 27 million square kilometres, equivalent to the land areas of Russia and Canada combined, although some argue that the effective conservation zones (ones with the strictest regulations) occupy only 5% of the ocean area (about equivalent to the land area of Russia alone).
Marine conservation
Marine conservation, also known as ocean conservation, is the protection and preservation of ecosystems in oceans and seas through planned management in order to prevent the over-exploitation of these marine resources. Marine conservation is i ...
zones, as with their terrestrial equivalents, vary in terms of rules and regulations. Few zones rule out completely any sort of human activity within their area, as activities such as fishing, tourism, and transport of essential goods and services by ship, are part of the fabric of nation states.
Terminology

The
International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of nat ...
(IUCN) defines a
protected area as:
A clearly defined geographical space, recognised, dedicated and managed, through legal or other effective means, to achieve the long-term conservation of nature with associated ecosystem services
Ecosystem services are the many and varied benefits to humans provided by the natural environment and healthy ecosystems. Such ecosystems include, for example, agroecosystems, forest ecosystem, grassland ecosystems, and aquatic ecosystems. ...
and cultural values.
This definition is intended to make it more difficult to claim MPA status for regions where exploitation of marine resources occurs. If there is no defined long-term goal for conservation and ecological recovery and extraction of marine resources occurs, a region is not a marine protected area.
"Marine protected area (MPA)" is a term for protected areas that include
marine environment
Marine habitats are habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term ''marine'' comes from the Latin ''mare'', meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental ...
and
biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
.
Other definitions by the IUCN include (2010):
Any area of the intertidal or subtidal terrain, together with its overlying water and associated flora, fauna, historical and cultural features, which has been reserved by law or other effective means to protect part or all of the enclosed environment.
United States Executive Order 13158 in May 2000 established MPAs, defining them as:
Any area of the marine environment that has been reserved by federal, state, tribal, territorial, or local laws or regulations to provide lasting protection for part or all of the natural and cultural resources therein.
The
Convention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity (or biodiversity); the sustainable use of its ...
defined the broader term of ''marine and coastal protected area'' (MCPA):
Any defined area within or adjacent to the marine environment, together with its overlying water and associated flora, fauna, historical and cultural features, which has been reserved by legislation or other effective means, including custom, with the effect that its marine and/or coastal biodiversity enjoys a higher level of protection than its surroundings.
An apparently unique extension of the meaning is used by
NOAA to refer to protected areas on the Great Lakes of North America.
History
The form of marine protected areas trace the origins to the
World Congress on National Parks
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the worl ...
in 1962. In 1976, a process was delivered to the excessive rights to every
sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defined te ...
to establish marine protected areas at over 200 nautical miles.
Over the next two decades, a scientific body of evidence marked the utility in the designation of marine protected areas. In the aftermath of the
1992 Earth Summit
The United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), also known as the Rio Conference or the Earth Summit (Portuguese: ECO92), was a major United Nations conference held in Rio de Janeiro from June 3 to June 14, 1992.
Earth S ...
in
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a ...
, an international target was established with the encompassment of ten percent of the world's marine protected areas.
On 28 October 2016 in
Hobart,
Australia, the
agreed to establish the first
Antarctic and largest marine protected area in the world encompassing 1.55 million km
2 (600,000 sq mi) in the
Ross Sea
The Ross Sea is a deep bay of the Southern Ocean in Antarctica, between Victoria Land and Marie Byrd Land and within the Ross Embayment, and is the southernmost sea on Earth. It derives its name from the British explorer James Clark Ross who ...
. Other large MPAs are in the
Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
,
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
, and
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
s, in certain
exclusive economic zones of Australia and overseas territories of
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, with major ( or larger) new or expanded MPAs by these nations since 2012—such as
Natural Park of the Coral Sea
The Natural Park of the Coral Sea (french: Le Parc Naturel de la Mer de Corail), founded in 2014, is a marine park located in New Caledonia, a special collectivity of France. As of 2017 it is the fourth largest protected area in the world, en ...
,
Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument
The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument is a group of unorganized, mostly unincorporated United States Pacific Island territories managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service of the United States Department of the Int ...
, Coral Sea Commonwealth Marine Reserve and
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Marine Protected Area. When counted with MPAs of all sizes from many other countries, as of August 2016 there are more than 13,650 MPAs, encompassing 2.07% of the world's oceans, with half of that area – encompassing 1.03% of the world's oceans – receiving complete "
no-take" designation.
Classifications

Several types of compliant MPA can be distinguished:
*A totally marine area with no significant terrestrial parts.
*An area containing both marine and terrestrial components, which can vary between two extremes; those that are predominantly maritime with little land (for example, an
atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can gr ...
would have a tiny island with a significant maritime population surrounding it), or that is mostly terrestrial.
*Marine ecosystems that contain land and
intertidal
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of habitats with various species ...
components only. For example, a
mangrove forest would contain no open sea or ocean marine environment, but its river-like marine ecosystem nevertheless complies with the definition.
IUCN offered seven
categories of protected area, based on management objectives and four broad governance types.
Related
protected area categories include the following;
*
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
(WHS) – an area exhibiting extensive natural or cultural history. Maritime areas are poorly represented, however, with only 46 out of over 800 sites.
*
Man and the Biosphere
Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB) is an intergovernmental scientific program, launched in 1971 by UNESCO, that aims to establish a scientific basis for the improvement of relationships between people and their environments.
MAB's work engag ...
–
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
program that promotes "a balanced relationship between humans and the
biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also ...
". Under article 4, biosphere reserves must "encompass a mosaic of ecological systems", and thus combine terrestrial, coastal, or marine ecosystems. In structure they are similar to Multiple-use MPAs, with a core area ringed by different degrees of protection.
*
Ramsar site – must meet
certain criteria for the definition of "Wetland" to become part of a global system. These sites do not necessarily receive protection, but are indexed by importance for later recommendation to an agency that could designate it a protected area.
While "area" refers to a single contiguous location, terms such as "''network''", "''system''", and "''region''" that group MPAs are not always consistently employed."''System''" is more often used to refer to an individual MPA, whereas "''region''" is defined by the
World Conservation Monitoring Centre
The UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC) is a collaboration centre of UN Environment Programme, based in Cambridge in the United Kingdom. UNEP-WCMC has been part of UN Environment Programme since 2000, and has ...
as:
A collection of individual MPAs operating cooperatively, at various spatial scales and with a range of protection levels that are designed to meet objectives that a single reserve cannot achieve.
At the 2004
Convention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity (or biodiversity); the sustainable use of its ...
, the agency agreed to use "''network''" on a global level, while adopting ''system'' for national and regional levels. The ''network'' is a mechanism to establish regional and local systems, but carries no authority or mandate, leaving all activity within the "''system''".

''No take zones'' (NTZs), are areas designated in a number of the world's MPAs, where all forms of exploitation are prohibited and severely limits human activities. These no take zones can cover an entire MPA, or specific portions. For example, the
Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, the world's largest MPA (and largest protected area of any type, land or sea), is a 100% no take zone.
Related terms include; ''specially protected area'' (SPA), ''
Special Area of Conservation
A Special Area of Conservation (SAC) is defined in the European Union's Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), also known as the ''Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora''. They are to protect the 220 habitats and a ...
'' (SAC), the United Kingdom's ''marine conservation zones'' (MCZs), or ''area of special conservation'' (ASC) etc. which each provide specific restrictions.
Stressors
Stressors that affect oceans include the impact of
extractive industries
Extractivism is the process of extracting natural resources from the Earth to sell on the world market. It exists in an economy that depends primarily on the extraction or removal of natural resources that are considered valuable for exportation w ...
,
marine pollution, and changes to the ocean's chemistry (
ocean acidification
Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxid ...
) resulting from elevated
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
levels, due to our
greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
(see also
effects of climate change on oceans).
MPAs have been cited as the ocean's single greatest hope for increasing the resilience of the marine environment to such stressors.
[Laffoley, D. d'A., (ed.) 2008. Towards Networks of Marine Protected Areas. The MPA Plan of Action for IUCN's World Commission on Protected Areas. IUCN WCPA, Gland, Switzerland. 28 pp.] Well-designed and managed MPAs developed with input and support from interested stakeholders can conserve biodiversity and protect and restore
fisheries.
Economics
MPAs can help sustain local economies by supporting fisheries and tourism. For example,
Apo Island in the
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
made protected one quarter of their reef, allowing fish to recover, jumpstarting their economy. This was shown in the film, ''Resources at Risk: Philippine Coral Reef''.
A 2016 report by the
Center for Development and Strategy
The Center for Development and Strategy (CDS) is an environmental and economic American think tank and online publisher based in Buffalo, New York, in the United States. The center develops policy studies, risk briefs, and OpEds on political, econ ...
found that programs like the
United States National Marine Sanctuary system can develop considerable economic benefits for communities through
Public–private partnership
A public–private partnership (PPP, 3P, or P3) is a long-term arrangement between a government and private sector institutions.Hodge, G. A and Greve, C. (2007), Public–Private Partnerships: An International Performance Review, Public Adminis ...
s.
They can be self-financed through a surrounding "conservation finance area" in which a limited number licenses are granted to benefit from the spillover of the marine protected area.
Management
Typical MPAs restrict
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
,
oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
and
gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
mining and/or
tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
. Other restrictions may limit the use of
ultrasonic
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies fr ...
devices like
sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on o ...
(which may confuse the guidance system of
cetaceans), development, construction and the like. Some fishing restrictions include "no-take" zones, which means that no fishing is allowed. Less than 1% of US MPAs are no-take.
Ship transit can also be restricted or banned, either as a preventive measure or to avoid direct disturbance to individual species. The degree to which environmental regulations affect shipping varies according to whether MPAs are located in
territorial waters
The term territorial waters is sometimes used informally to refer to any area of water over which a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potent ...
,
exclusive economic zones, or the
high seas
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed region ...
. The
law of the sea regulates these limits.
Most MPAs have been located in territorial waters, where the appropriate government can enforce them. However, MPAs have been established in exclusive economic zones and in
international waters
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed region ...
. For example, Italy, France and Monaco in 1999 jointly established a cetacean sanctuary in the
Ligurian Sea
The Ligurian Sea ( it, Mar Ligure; french: Mer Ligurienne; lij, Mâ Ligure) is an arm of the Mediterranean Sea. It lies between the Italian Riviera (Liguria) and the island of Corsica. The sea is thought to have been named after the ancient ...
named the
Pelagos Sanctuary for Mediterranean Marine Mammals
Originally called the International Ligurian Sea Cetacean Sanctuary (Ligurian Sea Sanctuary), what is now known as the Pelagos Sanctuary for Mediterranean Marine Mammals is a Marine Protected Area aimed at the protection of marine mammals (cetacean ...
. This sanctuary includes both national and international waters. Both the
CBD and
IUCN recommended a variety of management systems for use in a protected area system. They advocated that MPAs be seen as one of many "nodes" in a network of protected areas. The following are the most common management systems:

Seasonal and temporary management—Activities, most critically fishing, are restricted seasonally or temporarily, e.g., to protect spawning/nursing grounds or to let a rapidly reducing species recover.
Multiple-use MPAs—These are the most common and arguably the most effective. These areas employ two or more protections. The most important sections get the highest protection, such as a no take zone and are surrounded with areas of lesser protections.
Community involvement and related approaches—Community-managed MPAs empower local communities to operate partially or completely independent of the governmental jurisdictions they occupy. Empowering communities to manage resources can lower conflict levels and enlist the support of diverse groups that rely on the resource such as subsistence and commercial fishers, scientists, recreation, tourism businesses, youths and others. Mistrust between fishermen and regulating authorities is of central importance there, and needs to be addressed. Recent evidence from regions like Scandinavia, Spain, Portugal or Canada reveals success stories based on the tested cooperation between marine scientists and fishermen in jointly managing coastal marine reserves.
Marine Protected Area Networks
Marine Protected Area Networks or MPA networks have been defined as "A group of MPAs that interact with one another ecologically and/or socially form a network".
These networks are intended to connect individuals and MPAs and promote education and cooperation among various administrations and user groups. "MPA networks are, from the perspective of resource users, intended to address both environmental and socio-economic needs, complementary ecological and social goals and designs need greater research and policy support".
Filipino communities connect with one another to share information about MPAs, creating a larger network through the social communities' support. Emerging or established MPA networks can be found in
Australia, Belize, the
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
,
Gulf of Aden and Mexico.
Future approaches
To be truly representative of the ocean and its range of marine resources,
marine conservation
Marine conservation, also known as ocean conservation, is the protection and preservation of ecosystems in oceans and seas through planned management in order to prevent the over-exploitation of these marine resources. Marine conservation is i ...
parks should encompass the great variety of ocean geological and geographical terrains, as these, in turn, influence the biosphere around them. As time progresses it would be strategically advantageous to develop parks that include oceanic features such as
ocean ridges,
ocean trenches,
island arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle alon ...
systems, ocean
seamounts,
ocean plateaus, and abyssal plains, which occupy half the earth's surface. Another factor that will influence the development of marine conservation areas is ownership. Who owns the world's oceans? Approximately 64% of the world's oceans are "
international waters
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed region ...
" and subject to regulations such as the Law of the sea, Law of the Sea and the governance of UN bodies such as the International Seabed Authority. The remaining 36% of the ocean is under the governance of individual countries within their Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs). Some individual national EEZ's Exclusive economic zone#Rankings by area, cover very large areas, such as France and USA (>11 million km
2), and Australia, Russia, UK, and Indonesia (>6 million km
2). Some states have very small land areas but extremely large EEZ's such as Kiribati, the Federated States of Micronesia, Marshall Islands, and Cook Islands who have individual EEZ areas of between 1.9 and 3.5 million km
2. The national EEZ's are the ones where governance is easier, and agreements to create marine parks are within national jurisdictions, such as is the case with Marae Moana and the Cook islands.
One alternative to imposing MPAs on an indigenous population is through the use of Indigenous Protected Areas, such as those in Australia.
International efforts
The 17th
International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of nat ...
(IUCN) General Assembly in San Jose, California, San Jose, California, the 19th IUCN assembly and the fourth World Parks Congress all proposed to centralise the establishment of protected areas. The Earth Summit 2002, World Summit on Sustainable Development in 2002 called for The Evian agreement, signed by G8, G8 Nations in 2003, agreed to these terms. The Durban Action Plan, developed in 2003, called for regional action and targets to establish a network of protected areas by 2010 within the jurisdiction of regional Environmental science, environmental protocols.It recommended establishing protected areas for 20 to 30% of the world's oceans by the goal date of 2012. The
Convention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity (or biodiversity); the sustainable use of its ...
considered these recommendations and recommended requiring countries to set up marine parks controlled by a central organization before merging them. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change agreed to the terms laid out by the convention, and in 2004, its member nations committed to the following targets;
*By 2006 complete an area system gap analysis at national and regional levels.
*By 2008 address the less represented marine ecosystems, accounting for those beyond national jurisdiction in accordance.
*By 2009 designate the protected areas identified through the gap analysis.
*By 2012 complete the establishment of a comprehensive and ecologically representative network.

"The establishment by 2010 of terrestrial and by 2012 for marine areas of comprehensive, effectively managed, and ecologically representative national and regional systems of protected areas that collectively, inter alia through a global network, contribute to achieving the three objectives of the Convention and the 2010 target to significantly reduce the current late of biodiversity loss at the global, regional, national, and sub-national levels and contribute to poverty reduction and the pursuit of sustainable development."
Global goals
The UN later endorsed another decision, Decision VII/15, in 2006:
The 10% conservation goal is also found in Sustainable Development Goal 14 (which is part of the
Convention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity (or biodiversity); the sustainable use of its ...
) and which sets this 10% goal to a later date (2020). In 2017, the UN held the United Nations Ocean Conference aiming to find ways and urge for the implementation of Sustainable Development Goal 14. In that 2017 conference, it was clear that just between 3.6 and 5.7% of the world's oceans were protected, meaning another 6.4 to 4.3% of the world's oceans needed to be protected within 3 years.
The 10% protection goal is described as a "baby step" as 30% is the real amount of ocean protection scientists agree on that should be implemented.
Global treaties
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
The Antarctic Treaty System
On 7 April 1982, the Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CAMLR Convention) came into force after discussions began in 1975 between parties of the then-current Antarctic Treaty to limit large-scale exploitation of krill by commercial fisheries. The Convention bound contracting nations to abide by previously agreed upon Antarctic territorial claims and peaceful use of the region while protecting ecosystem integrity south of the Antarctic Convergence and 60th parallel south, 60 S latitude. In so doing, it also established a commission of the original signatories and acceding parties called the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) to advance these aims through protection, scientific study, and rational use, such as harvesting, of those marine resources. Though separate, the Antarctic Treaty and CCAMLR, make up part the broader system of international agreements called the Antarctic Treaty System. Since 1982, the CCAMLR meets annually to implement binding conservations measures like the creation of 'protected areas' at the suggestion of the convention's scientific committee.
In 2009, the CCAMLR created the first 'high-seas' MPA entirely within international waters over the southern shelf of the South Orkney Islands. This area encompasses and all fishing activity including transhipment, and dumping or discharge of waste is prohibited with the exception of scientific research endeavors. On 28 October 2016, the CCAMLR, composed of 24 member countries and the European Union at the time, agreed to establish the world's largest marine park encompassing 1.55 million km
2 (600,000 sq mi) in the Ross Sea after several years of failed negotiations. Establishment of the Ross Sea MPA required unanimity of the commission members and enforcement will begin in December 2017. However, due to a sunset provision inserted into the proposal, the new marine park will only be in force for 35 years.
National Targets
Many countries have established national targets, accompanied by action plans and implementations. The UN Council identified the need for countries to collaborate with each other to establish effective regional conservation plans. Some national targets are listed in the table below
The prevalent practice of area-based targets was criticized in 2019 by a group of environmental scientists because politicians tended to protect parts of the oceans where little fishing happened to meet the goals. The lack of fishing in these areas made them easy to protect, but it also had little positive impact.
Regional and national efforts
The marine protected area network is still in its infancy. As of October 2010, approximately 6,800 MPAs had been established, covering 1.17% of global ocean area. Protected areas covered 2.86% of exclusive economic zones (EEZs).
MPAs covered 6.3% of territorial seas. Many prohibit the use of harmful fishing techniques yet only 0.01% of the ocean's area is designated as a "no take zone". This coverage is far below the projected goal of 20%-30% Those targets have been questioned mainly due to the cost of managing protected areas and the conflict that protections have generated with human demand for marine goods and services.
Africa
South Africa
Greater Caribbean
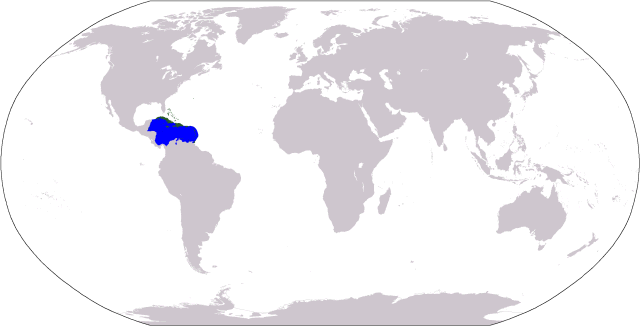
The Caribbean, Greater Caribbean subdivision encompasses an area of about of ocean and 38 nations. The area includes island countries like the Bahamas and Cuba, and the majority of Central America. The Convention for Protection and Development of the Marine Environment of the Wider Caribbean Region (better known as the Curitiba#UN Convention on Biodiversity, Cartagena Convention) was established in 1983. Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety, Protocols involving protected areas were ratified in 1990. As of 2008, the region hosted about 500 MPAs. Coral reefs are the best represented.
Two networks are under development, the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System (a long Coral reef, barrier reef that borders the coast of much of Central America), and the "Islands in the Stream" program (covering the Gulf of Mexico).
Asia
Southeast Asia is a global epicenter for marine diversity. 12% of its coral reefs are in MPAs. The Philippines have some the world's best coral reefs and protect them to attract international tourism. Most of the Philippines' MPAs are established to secure protection for its coral reef and sea grass habitats. Indonesia has MPAs designed for tourism and relies on tourism as a main source of income.
China
China has developed its unique MPA management system, which divides MPAs into two main categories: Marine Natural Reserves (MNRs) and Special Marine Protected Areas (SMPAs).
As of 2016, China has designated 267 MPAs, including 160 MNRs and 107 SMPAs, covering nearly 4% of the sea area.
MNRs are the no-take areas under comprehensive protection that prohibit any kind of resource exploitation.
Unlike such traditional MPAs, SMPAs have been established in China since 2002.
SMPAs allow the use of marine resources in a supervised and sustainable way, aiming at reducing local development conflicts caused by MNRs (such as the survival of coastal fishermen) and greater matching of national economic development strategies.
Depending on local ecological considerations, SMPAs will subdivide into different functional zones. Areas with rare and endangered species or damaged and fragile environments are strict no-take areas and ecological restoration areas, while other areas will be considered sustainable resource use zone for current use and reserved zone for future use.
Despite all the efforts, as China constructs MPA based on administrative hierarchy (national, provincial, municipal, and county), there exist problems of fragmentized division and inconsistent enforcement of MPAs.
Philippines
The
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
host one of the most highly biodiverse regions, with 464 reef-building coral species. Due to overfishing, destructive fishing techniques, and rapid coastal development, these are in rapid decline. The country has established some 600 MPAs. However, the majority are poorly enforced and are highly ineffective. However, some have positively impacted reef health, increased fish biomass, decreased coral bleaching and increased yields in adjacent fisheries. One notable example is the MPA surrounding Apo Island.
Latin America
Latin America has designated one large MPA system. As of 2008, 0.5% of its marine environment was protected, mostly through the use of small, multiple-use MPAs.
Mexico designed a Marine Strategy that goes from the years 2018-2021.
Pacific Ocean
Governments in the "South Pacific network" (ranging from Belize to Chile) adopted the List of international environmental agreements#Marine environment – global conventions, Lima convention and action plan in 1981. An MPA-specific protocol was ratified in 1989. The permanent commission on the exploitation and conservation on the marine resources of the South Pacific promotes the exchange of studies and information among participants.

The region is currently running one comprehensive cross-national program, the Tropical Eastern Pacific Marine Corridor Network, signed in April 2004. The network covers about .
The Marae Moana Conservation Park in
Cook Islands
)
, image_map = Cook Islands on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, capital = Avarua
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Avarua
, official_languages =
, lan ...
has many stakeholders within its governance structure, including a variety of Government Ministries, NGOs, traditional landowners, and society representatives.
The Marae Moana conservation area is managed through a spatial zoning principle, whereby specific designations are given to specific zones, though these designations may change over time. For example, some areas may allow fishing, whilst fishing may be prohibited in other areas.
The "North Pacific network" covers the western coasts of Mexico, Canada, and the U.S. The "Antigua Convention" and an action plan for the north Pacific region were adapted in 2002. Participant nations manage their own national systems.
In 2010–2011, the State of California completed hearings and actions via the state Department of Fish and Game to establish new MPAs.
Indian Ocean
In exchange for some of its Government debt, national debt being written off, the Seychelles designates two new marine protected areas in the Indian Ocean, covering about . It is the result of a financial deal, brokered in 2016 by The Nature Conservancy.
In 2021
Australia announced the creation of 2 national marine parks in size of 740,000 square kilometers. With those parks 45% of the Australian marine territory will be protected.
Ten countries in the Western Indian Ocean have launched the "Great Blue Wall" initiative, which seeks to create a network of linked MPAs throughout the region. These are generally expected to be under IUCN protected area categories, IUCN category IV protection, which allows for local fishing but prohibits industrial exploitation.
Mediterranean Sea
The Natura 2000 ecological network, ecological MPA network in the European Union included MPAs in the North Atlantic, the Mediterranean Sea and the Baltic Sea. The member states had to define NATURA 2000 areas at sea in their Exclusive Economic Zone.
Two assessments, conducted thirty years apart, of three Mediterranean MPAs, demonstrate that proper protection allows commercially valuable and slow-growing red coral (''Corallium rubrum'') to produce large colonies in shallow water of less than . Shallow-water colonies outside these decades-old MPAs are typically very small. The MPAs are Banyuls, Carry-le-Rouet and Scandola, off the island of Corsica.
* The Mediterranean Science Commission proposed the creation of eight large, international, MPAs ("CIESM Marine Peace Parks") with the dual benefits of protecting unique oceanographic features and mitigating trans-frontier conflicts
* WWF together with other partners proposed the creation of MedPan (Mediterranean Network of Marine Protected Areas Managers) which aims to protect 10% of the surface of the Mediterranean by 2020.
A 2018 study published in Science (journal), Science found that trawling is more intense inside official EU marine sanctuaries and that endangered fish species such as sharks and rays are more common outside them.
United States
As of June 2020, 26% of U.S. waters (including the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
) wwere in an MPA. Only 3% of US waters are no-take MPAs. Almost all of the no-take zones are located in two large MPAs in the remote Pacific Ocean,
Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument and
Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument
The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument is a group of unorganized, mostly unincorporated United States Pacific Island territories managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service of the United States Department of the Int ...
.
[ ]
United Kingdom and British Overseas Territories
Near half of England's seas are MPAs. Those MPAs only ban in specific places some of the most damaging activities.
In 2020, Greenpeace revealed that in 2019 the UK legally allowed industrial boats to fish in the Marine protected area. This point is related to the concern of overfishing, while fishing is an object to the ongoing Trade negotiation between the UK and the EU, trade negotiations between the EU and the UK. Result of those negotiations might replace Common Fisheries Policy in the UK.
United Kingdom
There are a number of marine protected areas around the coastline of the United Kingdom, known as Marine Conservation Zones in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland, and Marine Protected Areas in Scotland, Marine Protected Areas in Scotland. They are to be found in inshore and offshore waters. In June 2020, a review led by Richard Benyon Member of parliament, MP, stated that nearly 50 areas around the UK coastline should become Highly Protected Marine Areas (HPMAs). This would see the banning of dredging, sewage dumping, drilling, offshore wind-turbine construction and catch-and-release sea fishing.
British Overseas Territories
The United Kingdom is also creating marine protected reserves around several British Overseas Territories.
The UK is responsible for 6.8 million square kilometres of ocean around the world, larger than all but four other countries. In 2016 the UK government established the Blue Belt Programme to enhance the
protection and management of the marine environment.
The Chagos Marine Protected Area in the Indian Ocean was established in 2010 as a "no-take-zone". With a total surface area of , it was the world's largest contiguous marine reserve. In March 2015, the UK announced the creation of a marine reserve around the Pitcairn Islands in the Southern Pacific Ocean to protect its special biodiversity. The area of surpassed the Chagos Marine Protected Area as the world's largest contiguous marine reserve,
until the August 2016 expansion of the
Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument in the United States to .
In January 2016, the UK government announced the intention to create a marine protected area around Ascension Island. The protected area will be , half of which will be closed to fishing.
On 13 November 2020 it was announced that the of the waters surrounding the Tristan da Cunha and neighboring islands will become a Marine Protection Zone. The move will make the zone the largest no-take zone in the Atlantic and the fourth largest on the planet.
Notable marine protected areas

* The Bowie Seamount, Bowie Seamount Marine Protected Area off the British Columbia Coast, coast of British Columbia, Canada.
* The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park in Queensland, Australia, Queensland, Australia.
* The Ligurian Sea Cetacean Sanctuary in the seas of Italy, Monaco and France.
* The Dry Tortugas National Park in the Florida Keys, USA.
* The
Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument in
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
.
* The
Phoenix Islands Protected Area
The Phoenix Islands Protected Area (PIPA) is located in the Republic of Kiribati, an ocean nation in the central Pacific approximately midway between Australia and Hawaii. PIPA constitutes 11.34% of Kiribati's exclusive economic zone (EEZ), an ...
, Kiribati.
* The Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary in California, USA.
* The Chagos Marine Protected Area in the Indian Ocean.
*The Wadden Sea bordering the North Sea in the Netherlands, Germany, and Denmark.
Marine protected areas as percentage of territorial waters
The following shows a list of countries and their marine protected areas as percentage of their territorial waters (click "show" to expand).
Assessment

Managers and scientists use geographic information systems and remote sensing to map and analyze MPAs. NOAA Coastal Services Center compiled an "Inventory of GIS-Based Decision-Support Tools for MPAs". The report focuses on GIS tools with the highest utility for MPA processes.
Remote sensing uses advances in aerial photography image capture, pop-up archival satellite tags, Earth observation satellite#Environmental monitoring, satellite satellite imagery, imagery, acoustic data, and radar imagery. Mathematical models that seek to reflect the complexity of the natural setting may assist in planning harvesting strategies and sustaining fishing grounds. Other techniques such as on-site monitoring sensors, crowdsensing via local people, research and sampling endeavors, autonomous ships and underwater robots (Unmanned underwater vehicle, UAV) could also be used and developed.
Such data can then be used for assessing marine protection-quality and -extents. In 2021, 43 expert scientists published the first scientific framework version that – via integration, scientific review, review, clarifications and standardization#Environmental protection, standardization – enables coherent evaluation of levels of protection of marine protected areas and serve as a guide for improving, planning and monitoring these such as in efforts towards the 30%-protection-goal of the "Global Deal For Nature" and the UN's Sustainable Development Goal 14.
Coral reefs
Coral reef systems have been in decline worldwide. Causes include overfishing, pollution and
ocean acidification
Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxid ...
. As of 2013 30% of the world's reefs were severely damaged. Approximately 60% will be lost by 2030 without enhanced protection. Marine reserves with "no take zones" are the most effective form of protection. Only about 0.01% of the world's coral reefs are inside effective MPAs.
Fish
MPAs can be an effective tool to maintain fish populations; see refuge (ecology). The general concept is to create overpopulation within the MPA. The fish expand into the surrounding areas to reduce crowding, increasing the population of unprotected areas. This helps support local fisheries in the surrounding area, while maintaining a healthy population within the MPA. Such MPAs are most commonly used for coral reef ecosystems.
One example is at Goat Island Bay in New Zealand, established in 1977. Research gathered at Goat Bay documented the spillover effect. "Spillover and larval export—the drifting of millions of eggs and larvae beyond the reserve—have become central concepts of marine conservation". This positively impacted commercial fishermen in surrounding areas.
Another unexpected result of MPAs is their impact on predatory marine species, which in some conditions can increase in population. When this occurs, prey populations decrease. One study showed that in 21 out of 39 cases, "trophic cascades", caused a decrease in herbivores, which led to an increase in the quantity of plant life. (This occurred in the Malindi Kisite and Watamu Marian National Parks in Kenya; the Leigh Marine Reserve in New Zealand; and Brackett's Landing Conservation Area in the US.
Success criteria
Both
CBD and
IUCN have criteria for setting up and maintaining MPA networks, which emphasize four factors:
[
The ]International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of nat ...
defines a ''protected area'' as:
"A clearly defined geographical space, recognized, dedicated, and managed, through legal or effective means, to achieve the long-term conservation of nature with associated ecosystem service and cultural value."
*Adequacy—ensuring that the sites have the size, shape, and distribution to ensure the success of selected species.
*Representability—protection for all of the local environment's biological processes
*Resilience—the resistance of the system to natural disaster, such as a tsunami or flood.
*Connectivity—maintaining population links across nearby MPAs.
Misconceptions
Misconceptions about MPAs include the belief that all MPAs are no-take or no-fishing areas. Less than 1 percent of US waters are no-take areas. MPA activities can include consumption fishing, diving and other activities.
Another misconception is that most MPAs are federally managed. Instead, MPAs are managed under hundreds of laws and jurisdictions. They can exist in state, commonwealth, territory and tribal waters.
Another misconception is that a federal mandate dedicates a set percentage of ocean to MPAs. Instead the mandate requires an evaluation of current MPAs and creates a public resource on current MPAs.
Criticism
Land use right
Some existing and proposed MPAs have been criticized by indigenous populations and their supporters, as impinging on land usage rights. For example, the proposed Chagos Protected Area in the Chagos Islands is contested by Chagossians deported from their homeland in 1965 by the United Kingdom, British as part of the creation of the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT). According to WikiLeaks CableGate documents,
> the UK proposed that the BIOT become a "marine reserve" with the aim of preventing the former inhabitants from returning to their lands and to protect the joint UK/US military base on Diego Garcia Island.
Climate change
Oceans are the primary carbon sink and have been greatly affected by global warming, especially in recent years. The ability of existing MPA designs to cope with changes in marine biodiversity due to ocean acidification, sea level rise, sea surface temperature increase, oxygen reduction, and other marine environmental issues remains questionable.
Despite differences in species adaptations, warming has affected the habitats of some marine species, such as corals, to move from lower to higher latitudes.
If MPA assumes a relatively stable ecological environment within the area as before, it may become ineffective when the range of species distribution changes or becomes extensive.
Hence, there's need to incorporate the climate change adaptation to the framework.
Other critiques
Other critiques include: their cost (higher than that of passive management), conflicts with human development goals, inadequate scope to address factors such as climate change and invasive species.
In Scotland, environmental groups have criticised the government for failing to enforce fishing rules around MPAs.
See also
*Eco hotel#Additional initiatives, Eco hotels as funding vehicles for marine protection initiatives
*Hope Spots: marine areas rich in biodiversity
*Important marine mammal area
*Law of the sea
*Marine park
*Marine spatial planning
*Special Protection Area
*Specially Protected Areas of Mediterranean Importance
*
United States National Marine Sanctuary
References
Sources
*
*
*
External links
*
Marine Protected Areasby Project Regeneration
Marine Protection Atlas- an online tool from the Marine Conservation Institute that provides information on the world's protected areas and global MPA campaigns. Information comes from a variety of sources, including the World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA), and many regional and national databases.
*Marine protected areas - viewable vi
Protected Planet an online interactive search engine hosted by the United Nations Environment Programme's World Conservation Monitoring Center (UNEP-WCMC).
{{DEFAULTSORT:Marine Protected Area
Marine reserves,
Marine conservation
Protected areas
Oceanography
Fisheries science
Fisheries law
Marine protected areas,
 Marine protected areas (MPA) are protected areas of
Marine protected areas (MPA) are protected areas of  The
The  Several types of compliant MPA can be distinguished:
*A totally marine area with no significant terrestrial parts.
*An area containing both marine and terrestrial components, which can vary between two extremes; those that are predominantly maritime with little land (for example, an
Several types of compliant MPA can be distinguished:
*A totally marine area with no significant terrestrial parts.
*An area containing both marine and terrestrial components, which can vary between two extremes; those that are predominantly maritime with little land (for example, an  ''No take zones'' (NTZs), are areas designated in a number of the world's MPAs, where all forms of exploitation are prohibited and severely limits human activities. These no take zones can cover an entire MPA, or specific portions. For example, the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, the world's largest MPA (and largest protected area of any type, land or sea), is a 100% no take zone.
Related terms include; ''specially protected area'' (SPA), ''
''No take zones'' (NTZs), are areas designated in a number of the world's MPAs, where all forms of exploitation are prohibited and severely limits human activities. These no take zones can cover an entire MPA, or specific portions. For example, the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, the world's largest MPA (and largest protected area of any type, land or sea), is a 100% no take zone.
Related terms include; ''specially protected area'' (SPA), '' Seasonal and temporary management—Activities, most critically fishing, are restricted seasonally or temporarily, e.g., to protect spawning/nursing grounds or to let a rapidly reducing species recover.
Multiple-use MPAs—These are the most common and arguably the most effective. These areas employ two or more protections. The most important sections get the highest protection, such as a no take zone and are surrounded with areas of lesser protections.
Community involvement and related approaches—Community-managed MPAs empower local communities to operate partially or completely independent of the governmental jurisdictions they occupy. Empowering communities to manage resources can lower conflict levels and enlist the support of diverse groups that rely on the resource such as subsistence and commercial fishers, scientists, recreation, tourism businesses, youths and others. Mistrust between fishermen and regulating authorities is of central importance there, and needs to be addressed. Recent evidence from regions like Scandinavia, Spain, Portugal or Canada reveals success stories based on the tested cooperation between marine scientists and fishermen in jointly managing coastal marine reserves.
Seasonal and temporary management—Activities, most critically fishing, are restricted seasonally or temporarily, e.g., to protect spawning/nursing grounds or to let a rapidly reducing species recover.
Multiple-use MPAs—These are the most common and arguably the most effective. These areas employ two or more protections. The most important sections get the highest protection, such as a no take zone and are surrounded with areas of lesser protections.
Community involvement and related approaches—Community-managed MPAs empower local communities to operate partially or completely independent of the governmental jurisdictions they occupy. Empowering communities to manage resources can lower conflict levels and enlist the support of diverse groups that rely on the resource such as subsistence and commercial fishers, scientists, recreation, tourism businesses, youths and others. Mistrust between fishermen and regulating authorities is of central importance there, and needs to be addressed. Recent evidence from regions like Scandinavia, Spain, Portugal or Canada reveals success stories based on the tested cooperation between marine scientists and fishermen in jointly managing coastal marine reserves.
 The Caribbean, Greater Caribbean subdivision encompasses an area of about of ocean and 38 nations. The area includes island countries like the Bahamas and Cuba, and the majority of Central America. The Convention for Protection and Development of the Marine Environment of the Wider Caribbean Region (better known as the Curitiba#UN Convention on Biodiversity, Cartagena Convention) was established in 1983. Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety, Protocols involving protected areas were ratified in 1990. As of 2008, the region hosted about 500 MPAs. Coral reefs are the best represented.
Two networks are under development, the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System (a long Coral reef, barrier reef that borders the coast of much of Central America), and the "Islands in the Stream" program (covering the Gulf of Mexico).
The Caribbean, Greater Caribbean subdivision encompasses an area of about of ocean and 38 nations. The area includes island countries like the Bahamas and Cuba, and the majority of Central America. The Convention for Protection and Development of the Marine Environment of the Wider Caribbean Region (better known as the Curitiba#UN Convention on Biodiversity, Cartagena Convention) was established in 1983. Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety, Protocols involving protected areas were ratified in 1990. As of 2008, the region hosted about 500 MPAs. Coral reefs are the best represented.
Two networks are under development, the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System (a long Coral reef, barrier reef that borders the coast of much of Central America), and the "Islands in the Stream" program (covering the Gulf of Mexico).
 The region is currently running one comprehensive cross-national program, the Tropical Eastern Pacific Marine Corridor Network, signed in April 2004. The network covers about .
The Marae Moana Conservation Park in
The region is currently running one comprehensive cross-national program, the Tropical Eastern Pacific Marine Corridor Network, signed in April 2004. The network covers about .
The Marae Moana Conservation Park in  * The Bowie Seamount, Bowie Seamount Marine Protected Area off the British Columbia Coast, coast of British Columbia, Canada.
* The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park in Queensland, Australia, Queensland, Australia.
* The Ligurian Sea Cetacean Sanctuary in the seas of Italy, Monaco and France.
* The Dry Tortugas National Park in the Florida Keys, USA.
* The Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument in
* The Bowie Seamount, Bowie Seamount Marine Protected Area off the British Columbia Coast, coast of British Columbia, Canada.
* The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park in Queensland, Australia, Queensland, Australia.
* The Ligurian Sea Cetacean Sanctuary in the seas of Italy, Monaco and France.
* The Dry Tortugas National Park in the Florida Keys, USA.
* The Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument in  Managers and scientists use geographic information systems and remote sensing to map and analyze MPAs. NOAA Coastal Services Center compiled an "Inventory of GIS-Based Decision-Support Tools for MPAs". The report focuses on GIS tools with the highest utility for MPA processes. Remote sensing uses advances in aerial photography image capture, pop-up archival satellite tags, Earth observation satellite#Environmental monitoring, satellite satellite imagery, imagery, acoustic data, and radar imagery. Mathematical models that seek to reflect the complexity of the natural setting may assist in planning harvesting strategies and sustaining fishing grounds. Other techniques such as on-site monitoring sensors, crowdsensing via local people, research and sampling endeavors, autonomous ships and underwater robots (Unmanned underwater vehicle, UAV) could also be used and developed.
Such data can then be used for assessing marine protection-quality and -extents. In 2021, 43 expert scientists published the first scientific framework version that – via integration, scientific review, review, clarifications and standardization#Environmental protection, standardization – enables coherent evaluation of levels of protection of marine protected areas and serve as a guide for improving, planning and monitoring these such as in efforts towards the 30%-protection-goal of the "Global Deal For Nature" and the UN's Sustainable Development Goal 14.
Managers and scientists use geographic information systems and remote sensing to map and analyze MPAs. NOAA Coastal Services Center compiled an "Inventory of GIS-Based Decision-Support Tools for MPAs". The report focuses on GIS tools with the highest utility for MPA processes. Remote sensing uses advances in aerial photography image capture, pop-up archival satellite tags, Earth observation satellite#Environmental monitoring, satellite satellite imagery, imagery, acoustic data, and radar imagery. Mathematical models that seek to reflect the complexity of the natural setting may assist in planning harvesting strategies and sustaining fishing grounds. Other techniques such as on-site monitoring sensors, crowdsensing via local people, research and sampling endeavors, autonomous ships and underwater robots (Unmanned underwater vehicle, UAV) could also be used and developed.
Such data can then be used for assessing marine protection-quality and -extents. In 2021, 43 expert scientists published the first scientific framework version that – via integration, scientific review, review, clarifications and standardization#Environmental protection, standardization – enables coherent evaluation of levels of protection of marine protected areas and serve as a guide for improving, planning and monitoring these such as in efforts towards the 30%-protection-goal of the "Global Deal For Nature" and the UN's Sustainable Development Goal 14.