Magneto ignition on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 An ignition magneto, or high-tension magneto, is a
An ignition magneto, or high-tension magneto, is a



 An ignition magneto, or high-tension magneto, is a
An ignition magneto, or high-tension magneto, is a magneto
A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce periodic pulses of alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, a magneto does not contain a commutator to produce direct current. It is categorized as a form of alternator, ...
that provides current for the ignition system
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines, oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, rocket engines, etc. The widest application for spark i ...
of a spark-ignition engine
A spark-ignition engine (SI engine) is an internal combustion engine, generally a petrol engine, where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from a spark plug. This is in contrast to compression-ignition engines, ty ...
, such as a petrol engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as ' ...
. It produces pulses of high voltage
High voltage electricity refers to electrical potential large enough to cause injury or damage. In certain industries, ''high voltage'' refers to voltage above a certain threshold. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant sp ...
for the spark plug
A spark plug (sometimes, in British English, a sparking plug, and, colloquially, a plug) is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/ai ...
s. The older term ''tension'' means ''voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to ...
''.
The use of ignition magnetos is now confined mainly to engines where there is no other available electrical supply, for example in lawnmower
A lawn mower (also known as a mower, grass cutter or lawnmower) is a device utilizing one or more revolving blades (or a reel) to cut a grass surface to an even height. The height of the cut grass may be fixed by the design of the mower, but g ...
s and chainsaw
A chainsaw (or chain saw) is a portable gasoline-, electric-, or battery-powered saw that cuts with a set of teeth attached to a rotating chain driven along a guide bar. It is used in activities such as tree felling, limbing, bucking, pru ...
s. It is also widely used in aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes airplane, fixed-wing and helicopter, rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as aerostat, lighter- ...
piston engines even though an electrical supply is usually available. In this case, the magneto's self-powered operation is considered to offer increased reliability; in theory, the magneto should continue operation as long as the engine is turning.
History
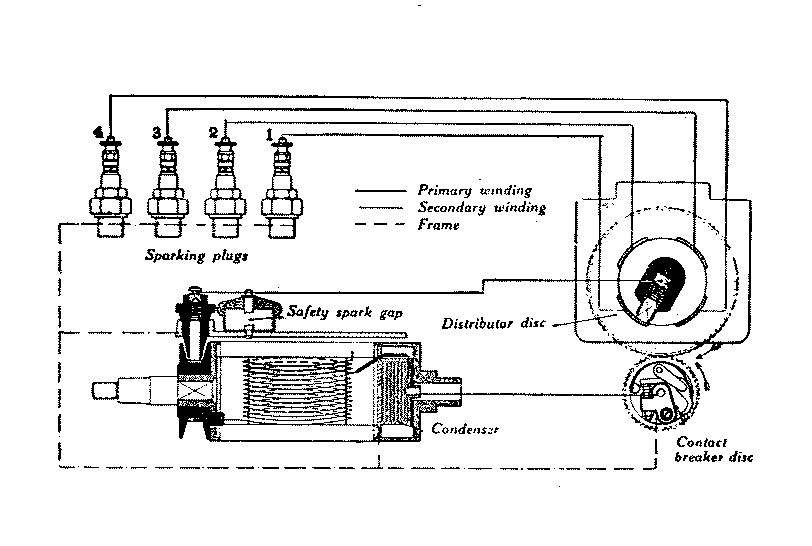
Firing the gap of aspark plug
A spark plug (sometimes, in British English, a sparking plug, and, colloquially, a plug) is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/ai ...
, particularly in the combustion chamber of a high-compression engine, requires a greater voltage (or ''higher tension'') than can be achieved by a simple magneto. The ''high-tension magneto'' combines an alternating current magneto generator and a transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
. A high current at low voltage is generated by the magneto, then transformed to a high voltage (even though this is now a far smaller current) by the transformer.
The first person to develop the idea of a high-tension magneto was André Boudeville, but his design omitted a condenser (capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of ...
); Frederick Richard Simms in partnership with Robert Bosch
Robert Bosch (23 September 1861 – 12 March 1942) was a German industrialist, engineer and inventor, founder of Robert Bosch GmbH.
Biography
Bosch was born in Albeck, a village to the northeast of Ulm in southern Germany as the eleventh of ...
were the first to develop a practical high-tension magneto.
Magneto ignition was introduced on the 1899 Daimler Phönix. This was followed by Benz, Mors, Turcat-Mery, and Nesseldorf, and soon was used on most cars up until about 1918 in both low voltage (voltage for secondary coils to fire the spark plugs) and high voltage magnetos (to fire the spark plug directly, similar to coil ignitions, introduced by Bosch in 1903).
Operation
In the type known as a ''shuttle magneto'', the engine rotates a coil of wire between the poles of amagnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nicke ...
. In the ''inductor magneto'', the magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nicke ...
is rotated and the coil remains stationary.
As the magnet moves with respect to the coil, the magnetic flux linkage of the coil changes. This induces an EMF in the coil, which in turn causes a current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
to flow. One or more times per revolution, just as the magnet pole moves away from the coil and the magnetic flux begins to decrease, a cam
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the bin ...
opens the contact breaker
A contact breaker (or "points") is a type of electrical switch, found in the ignition systems of spark-ignition internal combustion engines. The switch is automatically operated by a cam driven by the engine. The timing of operation of the switch ...
(called “the points” in reference to the two points of a circuit breaker) and interrupts the current. This causes the electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. non-quantum) field produced by (stationary or moving) electric charges. It is the field described by classical electrodynamics (a classical field theory) and is the classical ...
in the primary coil to collapse rapidly. As the field collapses rapidly there is a large voltage induced (as described by Faraday's Law) across the primary coil.
As the points begin to open, point spacing is initially such that the voltage across the primary coil would arc across the points. A capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of ...
is placed across the points which absorbs the energy stored in the leakage inductance
Leakage inductance derives from the electrical property of an imperfectly-coupled transformer whereby each winding behaves as a self-inductance in series with the winding's respective ohmic resistance constant. These four winding constants also ...
of the primary coil, and slows the rise time of the primary winding voltage to allow the points to open fully. The capacitor's function is similar to that of a snubber as found in a flyback converter
The flyback converter is used in both AC/DC, and DC/DC conversion with galvanic isolation between the input and any outputs. The flyback converter is a buck-boost converter with the inductor split to form a transformer, so that the voltage ra ...
.
A second coil, with many more turns than the primary, is wound on the same iron core to form an electrical transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
. The ratio of turns in the secondary winding to the number of turns in the primary winding, is called the ''turns ratio''. Voltage across the primary coil results in a proportional voltage being induced across the secondary winding of the coil. The turns ratio between the primary and secondary coil is selected so that the voltage across the secondary reaches a very high value, enough to arc across the gap of the spark plug. As the voltage of the primary winding rises to several hundred volts, the voltage on the secondary winding rises to several tens of thousands of volts, since the secondary winding typically has 100 times as many turns as the primary winding.
The capacitor and the coil together form a resonant circuit which allows the energy to oscillate from the capacitor to the coil and back again. Due to the inevitable losses in the system, this oscillation decays fairly rapidly. This dissipates the energy that was stored in the condenser in time for the next closure of the points, leaving the condenser discharged and ready to repeat the cycle.
On more advanced magnetos the cam ring can be rotated by an external linkage to alter the ignition timing.
In a modern installation, the magneto only has a single low tension winding which is connected to an external ignition coil
An ignition coil (also called a spark coil) is an induction coil in an automobile's ignition system that transforms the battery's voltage to the thousands of volts needed to create an electric spark in the spark plugs to ignite the fuel. So ...
which not only has a low tension winding, but also a secondary winding of many thousands of turns to deliver the high voltage required for the spark plug(s). Such a system is known as an "energy transfer" ignition system. Initially this was done because it was easier to provide good insulation for the secondary winding of an external coil than it was in a coil buried in the construction of the magneto (early magnetos had the coil assembly externally to the rotating parts to make them easier to insulate—at the expense of efficiency). In more modern times, insulation materials have improved to the point where constructing self-contained magnetos is relatively easy, but energy transfer systems are still used where the ultimate in reliability is required such as in aviation engines.
Aviation
Because it requires nobattery
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
or other source of electrical energy, the magneto is a compact and reliable self-contained ignition system, which is why it remains in use in many general aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services ...
applications.
Since the beginning of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
in 1914, magneto-equipped aircraft engines have typically been ''dual-plugged'', whereby each cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an ...
has two spark plug
A spark plug (sometimes, in British English, a sparking plug, and, colloquially, a plug) is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/ai ...
s, with each plug having a separate magneto system. Dual plugs provide both redundancy should a magneto fail, and better engine performance (through enhanced combustion). Twin sparks provide two flame fronts within the cylinder, these two flame fronts decreasing the time needed for the fuel charge to burn. As the size of the combustion chamber determines the time to burn the fuel charge, dual ignition was especially important for the large-bore aircraft engine
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years ma ...
s around World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
where it was necessary to combust the entire fuel mixture in a shorter time than a single plug could provide, in order to build peak cylinder pressure at the rpm desired.
Impulse coupling
Because the magneto has low voltage output at low speed, starting an engine is more difficult. Therefore, some magnetos have an impulse coupling, a springlike mechanical linkage between the engine and magneto drive shaft which "winds up" and "lets go" at the proper moment for spinning the magneto shaft. The impulse coupling uses a spring, a hub cam with flyweights, and a shell. The hub of the magneto rotates while the drive shaft is held stationary, and the spring tension builds up. When the magneto is supposed to fire, the flyweights are released by the action of the body contacting the trigger ramp. This allows the spring to unwind giving the rotating magnet a rapid rotation and letting the magneto spin at such a speed to produce a spark.Automobile
Some aviation engines as well as some early luxury cars have had dual-plugged systems with one set of plugs fired by a magneto, and the other set wired to a coil,dynamo
"Dynamo Electric Machine" (end view, partly section, )
A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos were the first electrical generators capable of delivering power for industry, and the foundati ...
, and battery circuit. This was often done to ease engine starting, as larger engines may be too difficult to crank at sufficient speed to operate a magneto, even with an impulse coupling. As the reliability of battery ignition systems improved, the magneto fell out of favour for general automotive use, but may still be found in sport or racing engines.
See also
*Ignition system
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines, oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, rocket engines, etc. The widest application for spark i ...
* Faraday's law of induction
Faraday's law of induction (briefly, Faraday's law) is a basic law of electromagnetism predicting how a magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit to produce an electromotive force (emf)—a phenomenon known as electromagnetic in ...
* Induction coil
An induction coil or "spark coil" ( archaically known as an inductorium or Ruhmkorff coil after Heinrich Rühmkorff) is a type of electrical transformer used to produce high-voltage pulses from a low-voltage direct current (DC) supply. p.98 ...
* Transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ignition MagnetoMagneto
A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce periodic pulses of alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, a magneto does not contain a commutator to produce direct current. It is categorized as a form of alternator, ...
Electrical generators