Magnetic activity on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A stellar magnetic field is a
A stellar magnetic field is a
 The magnetic field of a star can be measured by means of the
The magnetic field of a star can be measured by means of the
 A
A
 A stellar magnetic field is a
A stellar magnetic field is a magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
generated by the motion of conductive plasma inside a star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
. This motion is created through convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the c ...
, which is a form of energy transport involving the physical movement of material. A localized magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
exerts a force on the plasma, effectively increasing the pressure without a comparable gain in density. As a result, the magnetized region rises relative to the remainder of the plasma, until it reaches the star's photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated.
The term itself is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos, photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it ...
. This creates starspot
Starspots are stellar phenomena, so-named by analogy with sunspots.
Spots as small as sunspots have not been detected on other stars, as they would cause undetectably small fluctuations in brightness. The commonly observed starspots are in gene ...
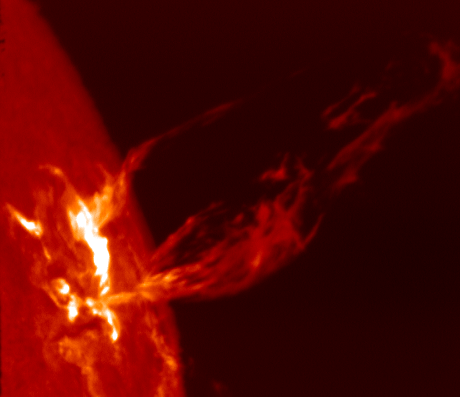
s on the surface, and the related phenomenon of coronal loop
In solar physics, a coronal loop is a well-defined arch-like structure in the Sun's atmosphere made up of relatively dense plasma confined and isolated from the surrounding medium by magnetic flux tubes. Coronal loops begin and end at two f ...
s.
Measurement
Zeeman effect
The Zeeman effect (; ) is the effect of splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of a static magnetic field. It is named after the Dutch physicist Pieter Zeeman, who discovered it in 1896 and received a Nobel pr ...
. Normally the atoms in a star's atmosphere will absorb certain frequencies of energy in the electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging fro ...
, producing characteristic dark absorption line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to ident ...
s in the spectrum. When the atoms are within a magnetic field, however, these lines become split into multiple, closely spaced lines. The energy also becomes polarized with an orientation that depends on orientation of the magnetic field. Thus the strength and direction of the star's magnetic field can be determined by examination of the Zeeman effect lines.
A stellar spectropolarimeter is used to measure the magnetic field of a star. This instrument consists of a spectrograph
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify mate ...
combined with a polarimeter
A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure the angle of rotation caused by passing polarized light through an optically active substance.Bernard Lyot Telescope
The Bernard Lyot Telescope (''Téléscope Bernard Lyot'', or TBL) is a 2 m Cassegrain telescope operating in the visible domain, since 1980. It is located at 2877 m elevation on the Pic du Midi in the French Pyrenees. Since 2007, the Bernard L ...
at the Pic du Midi de Bigorre
The Pic du Midi de Bigorre or simply the Pic du Midi (elevation ) is a mountain in the French Pyrenees. It is the site of the Pic du Midi Observatory.
Pic du Midi Observatory
The Pic du Midi Observatory (french: Observatoire du Pic du Midi ...
in the French Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
mountains.
Various measurements—including magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, ...
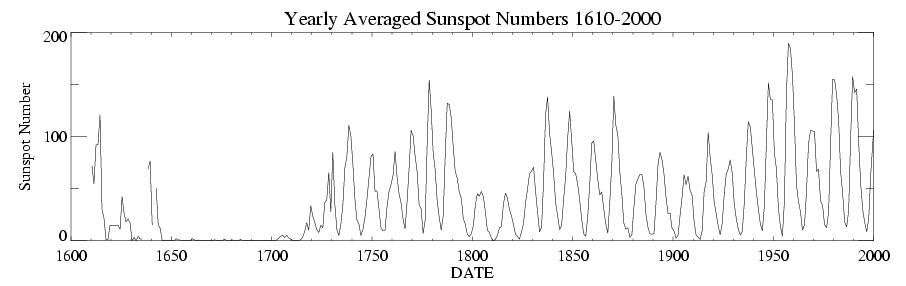
measurements over the last 150 years; 14C in tree rings; and 10Be in ice cores—have established substantial magnetic variability of the Sun on decadal, centennial and millennial time scales.
Field generation
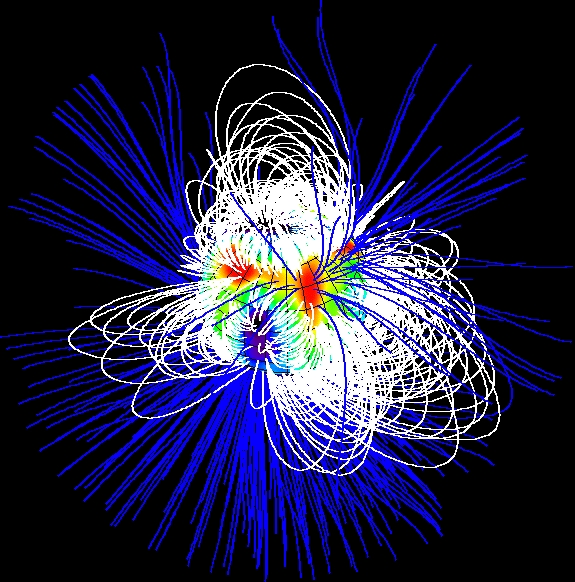
Stellar magnetic fields, according to solar dynamo theory, are caused within the convective zone of the star. The convective circulation of the conducting plasma functions like adynamo
"Dynamo Electric Machine" (end view, partly section, )
A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos were the first electrical generators capable of delivering power for industry, and the foundati ...
. This activity destroys the star's primordial magnetic field, then generates a dipolar magnetic field. As the star undergoes differential rotation—rotating at different rates for various latitudes—the magnetism is wound into a toroidal field of "flux ropes" that become wrapped around the star. The fields can become highly concentrated, producing activity when they emerge on the surface.
The magnetic field of a rotating body of conductive gas or liquid develops self-amplifying electric current
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume. The movi ...
s, and thus a self-generated magnetic field, due to a combination of differential rotation (different angular velocity of different parts of body), Coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
s and induction. The distribution of currents can be quite complicated, with numerous open and closed loops, and thus the magnetic field of these currents in their immediate vicinity is also quite twisted. At large distances, however, the magnetic fields of currents flowing in opposite directions cancel out and only a net dipole field survives, slowly diminishing with distance. Because the major currents flow in the direction of conductive mass motion (equatorial currents), the major component of the generated magnetic field is the dipole field of the equatorial current loop, thus producing magnetic poles near the geographic poles of a rotating body.
The magnetic fields of all celestial bodies are often aligned with the direction of rotation, with notable exceptions such as certain pulsar
A pulsar (from ''pulsating radio source'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Ea ...
s.
Periodic field reversal
Another feature of this dynamo model is that the currents are AC rather than DC. Their direction, and thus the direction of the magnetic field they generate, alternates more or less periodically, changing amplitude and reversing direction, although still more or less aligned with the axis of rotation. TheSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
's major component of magnetic field reverses direction every 11 years (so the period is about 22 years), resulting in a diminished magnitude of magnetic field near reversal time. During this dormancy, the sunspot
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. S ...
s activity is at maximum (because of the lack of magnetic braking on plasma) and, as a result, massive ejection of high energy plasma into the solar corona
A corona ( coronas or coronae) is the outermost layer of a star's atmosphere. It consists of plasma.
The Sun's corona lies above the chromosphere and extends millions of kilometres into outer space. It is most easily seen during a total solar ...
and interplanetary space takes place. Collisions of neighboring sunspots with oppositely directed magnetic fields result in the generation of strong electric fields near rapidly disappearing magnetic field regions. This electric field accelerates electrons and protons to high energies (kiloelectronvolts) which results in jets of extremely hot plasma leaving the Sun's surface and heating coronal plasma to high temperatures (millions of kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and ...
).
If the gas or liquid is very viscous (resulting in turbulent
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between ...
differential motion), the reversal of the magnetic field may not be very periodic. This is the case with the Earth's magnetic field, which is generated by turbulent currents in a viscous outer core.
Surface activity
Starspot
Starspots are stellar phenomena, so-named by analogy with sunspots.
Spots as small as sunspots have not been detected on other stars, as they would cause undetectably small fluctuations in brightness. The commonly observed starspots are in gene ...
s are regions of intense magnetic activity on the surface of a star. (On the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
they are termed sunspot
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. S ...
s.) These form a visible component of magnetic flux tubes that are formed within a star's convection zone
A convection zone, convective zone or convective region of a star is a layer which is unstable due to convection. Energy is primarily or partially transported by convection in such a region. In a radiation zone, energy is transported by radiatio ...
. Due to the differential rotation of the star, the tube becomes curled up and stretched, inhibiting convection and producing zones of lower than normal temperature. Coronal loop
In solar physics, a coronal loop is a well-defined arch-like structure in the Sun's atmosphere made up of relatively dense plasma confined and isolated from the surrounding medium by magnetic flux tubes. Coronal loops begin and end at two f ...
s often form above starspots, forming from magnetic field lines that stretch out into the stellar corona
A corona ( coronas or coronae) is the outermost layer of a star's atmosphere. It consists of plasma.
The Sun's corona lies above the chromosphere and extends millions of kilometres into outer space. It is most easily seen during a total sola ...
. These in turn serve to heat the corona to temperatures over a million kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and ...
s.
The magnetic fields linked to starspots and coronal loops are linked to flare
A flare, also sometimes called a fusée, fusee, or bengala in some Latin-speaking countries, is a type of pyrotechnic that produces a bright light or intense heat without an explosion. Flares are used for distress signaling, illumination, ...
activity, and the associated coronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant release of plasma and accompanying magnetic field from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accept ...
. The plasma is heated to tens of millions of kelvins, and the particles are accelerated away from the star's surface at extreme velocities.
Surface activity appears to be related to the age and rotation rate of main-sequence stars. Young stars with a rapid rate of rotation exhibit strong activity. By contrast middle-aged, Sun-like stars with a slow rate of rotation show low levels of activity that varies in cycles. Some older stars display almost no activity, which may mean they have entered a lull that is comparable to the Sun's Maunder minimum. Measurements of the time variation in stellar activity can be useful for determining the differential rotation rates of a star.

Magnetosphere
A star with a magnetic field will generate amagnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior d ...
that extends outward into the surrounding space. Field lines from this field originate at one magnetic pole on the star then end at the other pole, forming a closed loop. The magnetosphere contains charged particles that are trapped from the stellar wind
A stellar wind is a flow of gas ejected from the upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spherically symmetric.
...
, which then move along these field lines. As the star rotates, the magnetosphere rotates with it, dragging along the charged particles.
As stars emit matter with a stellar wind from the photosphere, the magnetosphere creates a torque on the ejected matter. This results in a transfer of angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed syst ...
from the star to the surrounding space, causing a slowing of the stellar rotation
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface.
The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bulge ...
rate. Rapidly rotating stars have a higher mass loss rate, resulting in a faster loss of momentum. As the rotation rate slows, so too does the angular deceleration. By this means, a star will gradually approach, but never quite reach, the state of zero rotation.
Magnetic stars
 A
A T Tauri star
T Tauri stars (TTS) are a class of variable stars that are less than about ten million years old. This class is named after the prototype, T Tauri, a young star in the Taurus star-forming region. They are found near molecular clouds and ide ...
is a type of pre–main sequence star that is being heated through gravitational contraction and has not yet begun to burn hydrogen at its core. They are variable stars that are magnetically active. The magnetic field of these stars is thought to interact with its strong stellar wind, transferring angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed syst ...
to the surrounding protoplanetary disk
A protoplanetary disk is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may also be considered an accretion disk for the star itself, be ...
. This allows the star to brake its rotation rate as it collapses.
Small, M-class stars (with 0.1–0.6 solar mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass ...
es) that exhibit rapid, irregular variability are known as flare star
A flare star is a variable star that can undergo unpredictable dramatic increases in brightness for a few minutes. It is believed that the flares on flare stars are analogous to solar flares in that they are due to the magnetic energy stored in th ...
s. These fluctuations are hypothesized to be caused by flares, although the activity is much stronger relative to the size of the star. The flares on this class of stars can extend up to 20% of the circumference, and radiate much of their energy in the blue and ultraviolet portion of the spectrum.
Straddling the boundary between stars that undergo nuclear fusion in their cores and non-hydrogen fusing brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs (also called failed stars) are substellar objects that are not massive enough to sustain nuclear fusion of ordinary hydrogen ( 1H) into helium in their cores, unlike a main-sequence star. Instead, they have a mass between the most ...
s are the ultracool dwarfs. These objects can emit radio waves due to their strong magnetic fields. Approximately 5–10% of these objects have had their magnetic fields measured. The coolest of these, 2MASS J10475385+2124234 with a temperature of 800-900 K, retains a magnetic field stronger than 1.7 kG, making it some 3000 times stronger than the Earth's magnetic field. Radio observations also suggest that their magnetic fields periodically change their orientation, similar to the Sun during the solar cycle
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surf ...
.
Planetary nebula
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelate ...
e are created when a red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around o ...
star ejects its outer envelope, forming an expanding shell of gas. However it remains a mystery why these shells are not always spherically symmetrical. 80% of planetary nebulae do not have a spherical shape; instead forming bipolar or elliptical nebulae. One hypothesis for the formation of a non-spherical shape is the effect of the star's magnetic field. Instead of expanding evenly in all directions, the ejected plasma tends to leave by way of the magnetic poles. Observations of the central stars in at least four planetary nebulae have confirmed that they do indeed possess powerful magnetic fields.
After some massive stars have ceased thermonuclear fusion
Thermonuclear fusion is the process of atomic nuclei combining or “fusing” using high temperatures to drive them close enough together for this to become possible. There are two forms of thermonuclear fusion: ''uncontrolled'', in which the re ...
, a portion of their mass collapses into a compact body of neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Since protons and ...
s called a neutron star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. w ...
. These bodies retain a significant magnetic field from the original star, but the collapse in size causes the strength of this field to increase dramatically. The rapid rotation of these collapsed neutron stars results in a pulsar
A pulsar (from ''pulsating radio source'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Ea ...
, which emits a narrow beam of energy that can periodically point toward an observer.
Compact and fast-rotating astronomical objects (white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
s, neutron star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. w ...
s and black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can def ...
s) have extremely strong magnetic fields. The magnetic field of a newly born fast-spinning neutron star is so strong (up to 108 teslas) that it electromagnetically radiates enough energy to quickly (in a matter of few million years) damp down the star rotation by 100 to 1000 times. Matter falling on a neutron star also has to follow the magnetic field lines, resulting in two hot spots on the surface where it can reach and collide with the star's surface. These spots are literally a few feet (about a metre) across but tremendously bright. Their periodic eclipsing during star rotation is hypothesized to be the source of pulsating radiation (see pulsar
A pulsar (from ''pulsating radio source'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Ea ...
s).
An extreme form of a magnetized neutron star is the magnetar
A magnetar is a type of neutron star with an extremely powerful magnetic field (∼109 to 1011 T, ∼1013 to 1015 G). The magnetic-field decay powers the emission of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, particularly X-rays and gamma rays.War ...
. These are formed as the result of a core-collapse supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when ...
. The existence of such stars was confirmed in 1998 with the measurement of the star SGR 1806-20. The magnetic field of this star has increased the surface temperature to 18 million K and it releases enormous amounts of energy in gamma ray burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are immensely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most energetic and luminous electromagnetic events since the Big Bang. Bursts can last from ten millise ...
s.
Jets of relativistic plasma Relativistic plasmas in physics are plasmas for which relativistic corrections to a particle's mass and velocity are important. Such corrections typically become important when a significant number of electrons reach speeds greater than 0.86 c (Lo ...
are often observed along the direction of the magnetic poles of active black holes in the centers of very young galaxies.
Star-Planet Interaction Controversy
In 2008, a team of astronomers first described how as the exoplanet orbiting HD 189733 A reaches a certain place in its orbit, it causes increased stellar flaring. In 2010, a different team found that every time they observe theexoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
at a certain position in its orbit, they also detected X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
flares. Theoretical research since 2000 suggested that an exoplanet very near to the star that it orbits may cause increased flaring due to the interaction of their magnetic fields
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
, or because of tidal force
The tidal force is a gravitational effect that stretches a body along the line towards the center of mass of another body due to a gradient (difference in strength) in gravitational field from the other body; it is responsible for diverse phenomen ...
s. In 2019, astronomers combined data from Arecibo Observatory
The Arecibo Observatory, also known as the National Astronomy and Ionosphere Center (NAIC) and formerly known as the Arecibo Ionosphere Observatory, is an observatory in Barrio Esperanza, Arecibo, Puerto Rico owned by the US National Science ...
, MOST, and the Automated Photoelectric Telescope, in addition to historical observations of the star at radio, optical, ultraviolet, and X-ray wavelengths to examine these claims. Their analysis found that the previous claims were exaggerated and the host star failed to display many of the brightness and spectral characteristics associated with stellar flaring and solar active regions
An active region is a temporary region in the Sun's atmosphere characterized by a strong and complex magnetic field. They are often associated with sunspots and are commonly the source of violent eruptions such as coronal mass ejections and sola ...
, including sunspots. They also found that the claims did not stand up to statistical analysis, given that many stellar flares are seen regardless of the position of the exoplanet, therefore debunking the earlier claims. The magnetic fields of the host star and exoplanet do not interact, and this system is no longer believed to have a "star-planet interaction."
See also
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Stellar Magnetic FieldMagnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
Magnetism in astronomy