Magdeburg-class cruiser on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The class of light cruisers was a group of four ships built for the
 The four vessels each had a crew of 18 officers and 336 enlisted men. They carried a number of smaller boats, including one picket boat, one barge, one cutter, two
The four vessels each had a crew of 18 officers and 336 enlisted men. They carried a number of smaller boats, including one picket boat, one barge, one cutter, two
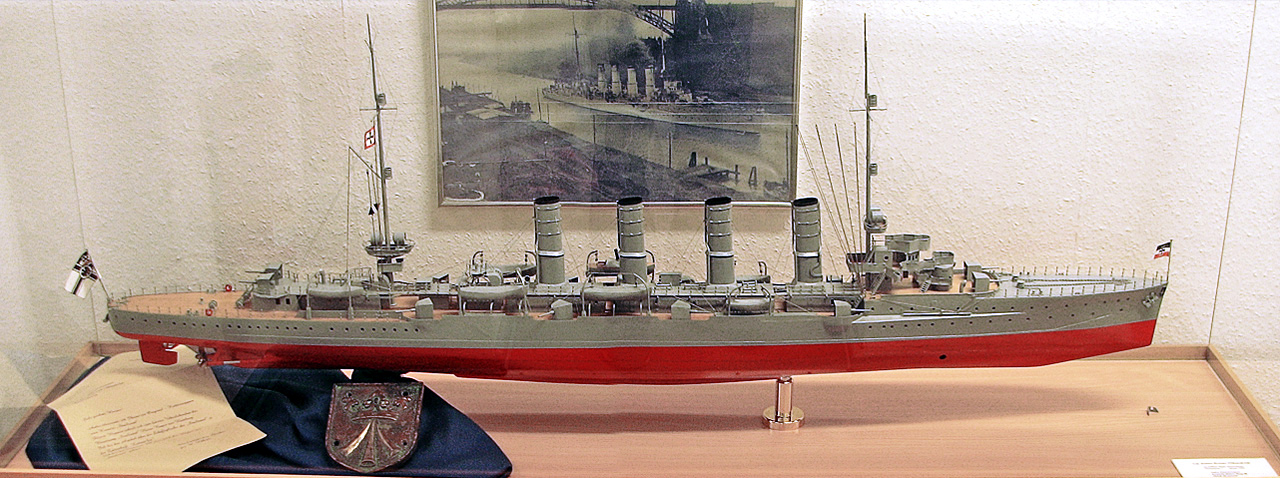 The four -class ships were armed with a main battery of twelve SK L/45 guns in single pedestal mounts. Two were placed side by side forward on the
The four -class ships were armed with a main battery of twelve SK L/45 guns in single pedestal mounts. Two were placed side by side forward on the
 Following her commissioning, and the
Following her commissioning, and the
 spent the first year of her service overseas, after which she was assigned to the reconnaissance forces of the High Seas Fleet. She saw significant action at the Battle of Heligoland Bight in August 1914 and participated in the
spent the first year of her service overseas, after which she was assigned to the reconnaissance forces of the High Seas Fleet. She saw significant action at the Battle of Heligoland Bight in August 1914 and participated in the
Imperial German Navy
The Imperial German Navy or the Imperial Navy () was the navy of the German Empire, which existed between 1871 and 1919. It grew out of the small Prussian Navy (from 1867 the North German Federal Navy), which was mainly for coast defence. Wilhel ...
. The class comprised , the lead ship, , , and . All four ships were laid down in 1910 and were completed by the end of 1912. They were armed with a main battery of twelve 10.5 cm guns, though over the course of their careers, , , and were rearmed with more powerful 15 cm guns. They displaced at full load and were rated at a top speed of , though all four vessels exceeded that figure on trials.
was used as a torpedo test ship before the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in August 1914, after which she was assigned to the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
. She conducted a series of raids on Russian positions culminating in a sweep into the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
that resulted in her grounding off the Estonian coast. Russian cruisers seized the stranded ship and captured code books; they gave one copy to the British Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
, which used it to great advantage. was assigned to the with the battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of attr ...
in 1912 and remained in the Mediterranean until the outbreak of war. After evading British warships, the two vessels reached Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, where they were transferred to the Ottoman Navy. She operated primarily in the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
against the Russian Navy, but in January 1918 she ventured into the Mediterranean and was mined and sunk after the Battle of Imbros
The Battle of Imbros was a naval action that took place during the First World War. The battle occurred on 20 January 1918 when an Ottoman squadron engaged a flotilla of the British Royal Navy off the island of Imbros in the Aegean Sea. A lack ...
.
and served with the High Seas Fleet in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
against the British. They saw action at the Battle of Heligoland Bight in August 1914 and served in the reconnaissance screen for the battlecruisers of the I Scouting Group on several bombardments of the British coast in 1914–1915. was also present at the Battle of Dogger Bank, but was not heavily engaged. saw action during Operation Albion
Operation Albion was a World War I German air, land and naval operation against the Russian forces in October 1917 to occupy the West Estonian Archipelago. The land campaign opened with German landings at the Tagalaht bay on the island of S ...
against the Russians in the Baltic. Both ships were surrendered to the Allies after the end of the war; was ceded to Italy and renamed ; she served with the Italian Navy until 1943, when she was scuttled after the Italian surrender. She was raised by the Germans and sunk by Allied bombers twice in 1943–1944, and finally scrapped in 1946–1947. was given to France and renamed . She served only until 1925, when she was placed in reserve. She was ultimately broken up in 1935.
Design
The design for the ships of the class was prepared in 1908–1909. The design incorporated a number of innovations, including a new longitudinal frame system in the hull, the development of which delayed construction by three to four years. Thehull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
form was also redesigned to improve efficiency, and a new clipper
A clipper was a type of mid-19th-century merchant sailing vessel, designed for speed. Clippers were generally narrow for their length, small by later 19th century standards, could carry limited bulk freight, and had a large total sail area. "C ...
bow was used instead of the old cruiser ram
Ram, ram, or RAM may refer to:
Animals
* A male sheep
* Ram cichlid, a freshwater tropical fish
People
* Ram (given name)
* Ram (surname)
* Ram (director) (Ramsubramaniam), an Indian Tamil film director
* RAM (musician) (born 1974), Dutch
* Ra ...
bow. They were the first German light cruisers to incorporate an armor belt
Belt armor is a layer of heavy metal armor plated onto or within the outer hulls of warships, typically on battleships, battlecruisers and cruisers, and aircraft carriers.
The belt armor is designed to prevent projectiles from penetrating to t ...
at the waterline
The waterline is the line where the hull of a ship meets the surface of the water. Specifically, it is also the name of a special marking, also known as an international load line, Plimsoll line and water line (positioned amidships), that indi ...
; this increased the strength of the hull and became standard practice in warship construction for decades. The quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on bo ...
was cut down to provide a location to drop mines. All of these features became standard for subsequent German cruiser designs.
General characteristics and machinery
The ships of the class werelong at the waterline
A vessel's length at the waterline (abbreviated to L.W.L)Note: originally Load Waterline Length is the length of a ship or boat at the level where it sits in the water (the ''waterline''). The LWL will be shorter than the length of the boat over ...
and long overall
__NOTOC__
Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, and ...
. They had a beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
of and a draft of forward and aft. They displaced normally and up to at full load. The hulls were built with longitudinal steel frames and contained fourteen watertight compartment
A compartment is a portion of the space within a ship defined vertically between decks and horizontally between bulkheads. It is analogous to a room within a building, and may provide watertight subdivision of the ship's hull important in retain ...
s in , , and . s hull was divided into sixteen watertight compartments. All four vessels had a double bottom
A double hull is a ship Hull (watercraft), hull design and construction method where the bottom and sides of the ship have two complete layers of watertight hull surface: one outer layer forming the normal hull of the ship, and a second inner hull ...
that extended for forty-five percent of the length of the hull.
 The four vessels each had a crew of 18 officers and 336 enlisted men. They carried a number of smaller boats, including one picket boat, one barge, one cutter, two
The four vessels each had a crew of 18 officers and 336 enlisted men. They carried a number of smaller boats, including one picket boat, one barge, one cutter, two yawl
A yawl is a type of boat. The term has several meanings. It can apply to the rig (or sailplan), to the hull type or to the use which the vessel is put.
As a rig, a yawl is a two masted, fore and aft rigged sailing vessel with the mizzen mast p ...
s, and two dinghies. The German Navy regarded the ships as good sea boats, with slight weather helm and gentle motion in a swell. The cruisers were maneuverable, but were slow going into a turn. Steering was controlled by a single large rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally aircraft, air or watercraft, water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to ...
. They lost speed only slightly in a head sea, but lost up to sixty percent in hard turns. They had a transverse metacentric height of .
Their propulsion systems consisted of steam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbin ...
s of various types. Each ship had turbines built by different manufacturers to evaluate each design and configuration. had three engines produced by , which drove three screw propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
s. was equipped with two pairs of AG Vulcan turbines, which powered four 3-bladed screws in diameter. had a pair of Marine-type turbines with two wide propellers. initially had three Bergmann turbines with three screws, though by the end of the war the center shaft was removed. All four propulsion systems were rated at , but reached significantly higher speeds in service.
The ships' turbines were powered by sixteen coal-fired Marine-type water-tube boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-gene ...
s, although they were later altered to use fuel oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil, marine fuel oil (MFO), bun ...
that was sprayed on the coal to increase its burn rate. These were divided into five boiler rooms on the centerline. These gave the ships a top speed of , though on speed trials all four ships exceeded this by at least half a knot. The ships carried of coal, and an additional of oil that gave them a range of approximately at . At , the range fell considerably to . , , and each had four turbo generators with a combined output of at 220 Volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defi ...
s; only had two generators.
Armament and armor
 The four -class ships were armed with a main battery of twelve SK L/45 guns in single pedestal mounts. Two were placed side by side forward on the
The four -class ships were armed with a main battery of twelve SK L/45 guns in single pedestal mounts. Two were placed side by side forward on the forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is the phrase " be ...
, eight were located amidships, four on either side, and two were side by side aft. The guns had a maximum elevation of 30 degrees, which allowed them to engage targets out to . They were supplied with 1,800 rounds of ammunition, for 150 shells per gun. They were also equipped with a pair of torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
s with five torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, su ...
es submerged in the hull on the broadside
Broadside or broadsides may refer to:
Naval
* Broadside (naval), terminology for the side of a ship, the battery of cannon on one side of a warship, or their near simultaneous fire on naval warfare
Printing and literature
* Broadside (comic ...
. The ships could also carry 120 mines.
Over the course of their careers, the ships all had their armament upgraded, with the exception of . In 1916, two of s 10.5 cm guns were replaced with SK L/45 guns, which had a range of . The following year, the remaining ten 10.5 cm guns were replaced with six 15 cm guns. In 1915, was rearmed with seven 15 cm guns, two SK L/45 guns, and two deck-mounted 50 cm torpedo tubes. was modified similarly, though her submerged torpedo tubes were removed during the refit.
The ships were protected by a waterline armor belt that was thick amidships and thick on the bow. The stern was unarmored. The deck was covered with up to 60 mm thick armor plate forward, thick amidships
This glossary of nautical terms is an alphabetical listing of terms and expressions connected with ships, shipping, seamanship and navigation on water (mostly though not necessarily on the sea). Some remain current, while many date from the 17th t ...
, and thick aft. Sloped armor 40 mm thick connected the deck and belt armor. The conning tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armored, from which an officer in charge can conn the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and gro ...
had thick sides and a 20 mm thick roof. A rangefinder
A rangefinder (also rangefinding telemeter, depending on the context) is a device used to measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, such as photography an ...
was added with thick steel plating. The main battery guns had thick gun shield
A U.S. Marine manning an M240 machine gun equipped with a gun shield
A gun shield is a flat (or sometimes curved) piece of armor designed to be mounted on a crew-served weapon such as a machine gun, automatic grenade launcher, or artillery piece ...
s.
Construction
was ordered under the contract name " " and was laid down at theAG Weser
Aktien-Gesellschaft „Weser" (abbreviated A.G. „Weser”) was one of the major German shipbuilding companies, located at the Weser River in Bremen. Founded in 1872 it was finally closed in 1983. All together, A.G. „Weser" built about 1,400 ...
shipyard in Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consis ...
in 1910 and launched on 13 May 1911, after which fitting-out
Fitting out, or outfitting, is the process in shipbuilding that follows the float-out/launching of a vessel and precedes sea trials. It is the period when all the remaining construction of the ship is completed and readied for delivery to her o ...
work commenced. She was commissioned into the High Seas Fleet on 20 August 1912. was ordered under the contract name " " and was laid down at the AG Vulcan shipyard in Stettin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin language, Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital city, capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the Po ...
in 1910. At her launching ceremony on 16 May 1911, she was christened by the mayor of Breslau, the ship's namesake. After her launching, fitting-out work commenced and lasted until mid-1912. She was commissioned into the High Seas Fleet on 10 May 1912.
was ordered under the contract name " " and was laid down at the shipyard in Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven (, ''Wilhelm's Harbour''; Northern Low Saxon: ''Willemshaven'') is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea, and has a population of 76,089. Wilhelmsha ...
in 1910 and launched on 24 August 1911, after which fitting-out work commenced. She was commissioned into the High Seas Fleet on 9 October 1912. was ordered under the contract name " " and was laid down at the AG Weser shipyard in 1910 and launched on 4 November 1911, after which fitting-out work commenced. She was commissioned into the High Seas Fleet on 10 December 1912.
Service history
''Magdeburg''
was used as a torpedo test ship after her commissioning until the outbreak ofWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in August 1914, when she was brought to active service and deployed to the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
. In the Baltic, fired the first shots of the war against the Russians on 2 August, when she shelled the port of Libau. She participated in a series of bombardments of Russian positions until late August. On the 26th, she participated in a sweep of the entrance to the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
; while steaming off the Estonian coast, she ran aground off the island of Odensholm
Osmussaar ( sv, Odensholm, german: Odinsholm) is an Estonian island situated in the mouth of the Gulf of Finland in the Baltic Sea, 7.5 km off the Estonian mainland. Administratively the island is part of Lääne-Nigula Parish in Lääne ...
and could not be freed. A pair of Russian cruisers appeared and seized the ship. Fifteen crew members were killed in the brief engagement. They recovered three intact German code books, one of which they passed to the British. The ability to decrypt German wireless signals provided the British with the ability to ambush German units on several occasions during the war, including the Battle of Jutland
The Battle of Jutland (german: Skagerrakschlacht, the Battle of the Skagerrak) was a naval battle fought between Britain's Royal Navy Grand Fleet, under Admiral John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, Sir John Jellicoe, and the Imperial German Navy ...
. The Russians partially scrapped while she remained grounded before completely destroying the wreck.
''Breslau''
 Following her commissioning, and the
Following her commissioning, and the battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of attr ...
were assigned to the in response to the Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defe ...
. After evading British warships in the Mediterranean to reach Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, and were transferred to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in August 1914, to entice the Ottomans to join the Central Powers in World War I. The ships were renamed and , respectively, and saw extensive service with the Ottoman fleet, primarily in the Black Sea against the Russian Black Sea Fleet
Chernomorskiy flot
, image = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet
, dates = May 13, ...
. The two ships, along with several other Ottoman vessels, raided Russian ports in October 1914, prompting a Russian declaration of war.
was active in laying minefield
A land mine is an explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically detonated automati ...
s off the Russian coast, bombarding Russian ports and installations and, because of a shortage of Ottoman merchant ships, transporting troops and supplies to the Black Sea ports supplying Ottoman troops fighting in the Caucasus Campaign
The Caucasus campaign comprised armed conflicts between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, later including Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, the Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus, the German Empire, the Central Caspian Dicta ...
. She was lightly damaged several times by Russian ships, but the most serious damage was inflicted by a mine in 1915, which kept her out of service for half of a year. The ship was mined and sunk in January 1918 during the Battle of Imbros
The Battle of Imbros was a naval action that took place during the First World War. The battle occurred on 20 January 1918 when an Ottoman squadron engaged a flotilla of the British Royal Navy off the island of Imbros in the Aegean Sea. A lack ...
in which was also mined and badly damaged. The majority of her crew were killed in the sinking.
''Strassburg''
 spent the first year of her service overseas, after which she was assigned to the reconnaissance forces of the High Seas Fleet. She saw significant action at the Battle of Heligoland Bight in August 1914 and participated in the
spent the first year of her service overseas, after which she was assigned to the reconnaissance forces of the High Seas Fleet. She saw significant action at the Battle of Heligoland Bight in August 1914 and participated in the raid on Scarborough, Hartlepool and Whitby
The Raid on Scarborough, Hartlepool and Whitby on 16 December 1914 was an attack by the Imperial German Navy on the British ports of Scarborough, Hartlepool, West Hartlepool and Whitby. The bombardments caused hundreds of civilian casualties an ...
in December 1914. By 1916, the ship was transferred to the Baltic to operate against the Russian Navy. She saw action during Operation Albion
Operation Albion was a World War I German air, land and naval operation against the Russian forces in October 1917 to occupy the West Estonian Archipelago. The land campaign opened with German landings at the Tagalaht bay on the island of S ...
in the Gulf of Riga
The Gulf of Riga, Bay of Riga, or Gulf of Livonia ( lv, Rīgas līcis, et, Liivi laht) is a bay of the Baltic Sea between Latvia and Estonia.
The island of Saaremaa (Estonia) partially separates it from the rest of the Baltic Sea. The main con ...
in October 1917, including screening for the battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1880s to describe a type of ...
s and during the Battle of Moon Sound. She returned to the North Sea for the planned final operation against the British Grand Fleet in the last weeks of the war, and was involved in the mutinies that forced the cancellation of the operation.
The ship served briefly in the new in 1919 before being transferred to Italy as a war prize
A prize of war is a piece of enemy property or land seized by a belligerent party during or after a war or battle, typically at sea. This term was used nearly exclusively in terms of captured ships during the 18th and 19th centuries. Basis in inte ...
. She was formally transferred in July 1920 and renamed for service in the Italian Navy
"Fatherland and Honour"
, patron =
, colors =
, colors_label =
, march = ( is the return of soldiers to their barrack, or sailors to their ship after a ...
. In 1936–1937, she was rebuilt for colonial duties and additional anti-aircraft guns were installed. She saw no significant action during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
until the Armistice that ended Italy's participation in the war. She was scuttled by the Italian Navy, captured and raised by the Germans, and sunk by Allied bombers in October 1943. The Germans raised the ship again, which was sunk a second time by bombers in September 1944. was finally broken up for scrap in 1946–1947.
''Stralsund''
was assigned to the reconnaissance forces of the High Seas Fleet for the majority of her career. She saw significant action in the early years of World War I, including several operations off the British coast and the Battles of Heligoland Bight andDogger Bank
Dogger Bank (Dutch: ''Doggersbank'', German: ''Doggerbank'', Danish: ''Doggerbanke'') is a large sandbank in a shallow area of the North Sea about off the east coast of England.
During the last ice age the bank was part of a large landmass c ...
, in August 1914 and November 1915, respectively. She was not damaged in either action. The ship was in dockyard hands during the Battle of Jutland, and so she missed the engagement. After the end of the war, she served briefly in the before being surrendered to the Allies. She was ceded to the French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in t ...
, where she served as until 1925. She was formally stricken in 1933 and broken up for scrap two years later.
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Magdeburg Cruiser classes World War I cruisers of Germany Ship classes of the French Navy