Madison is the
county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US st ...
of
Dane County
Dane County is a county in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2020 census, the population was 561,504, making it the second-most populous county in Wisconsin. The county seat is Madison, which is also the state capital.
Dane County is the ...
and the
capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses t ...
of the
U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of
Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
. As of the
2020 census the population was 269,840, making it the second-largest city in Wisconsin by population, after
Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee ...
, and the
80th-largest in the U.S. The city forms the core of the
Madison Metropolitan Area which includes Dane County and neighboring
Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to th ...
,
Green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combi ...
, and
Columbia counties for a population of 680,796. Madison is named for American
Founding Father
The following list of national founding figures is a record, by country, of people who were credited with establishing a state. National founders are typically those who played an influential role in setting up the systems of governance, (i.e. ...
and President
James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for h ...
. The city is located on the traditional land of the
Ho-Chunk, and the Madison area is known as ''Dejope'', meaning "four lakes", or ''Taychopera'', meaning "land of the four lakes", in the
Ho-Chunk language
The Ho-Chunk language (''Hoocąk, Hocąk''), also known as Winnebago, is the traditional language of the Ho-Chunk (or Winnebago) nation of Native Americans in the United States. The language is part of the Siouan language family, and is closely ...
.
Located on an
isthmus
An isthmus (; ; ) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthmus ...
and lands surrounding four lakes—
Lake Mendota
Lake Mendota is a freshwater eutrophic lake that is the northernmost and largest of the four lakes in Madison, Wisconsin. The lake borders Madison on the north, east, and south, Middleton on the west, Shorewood Hills on the southwest, Maple Bl ...
,
Lake Monona
Lake Monona is a freshwater drainage lake in Dane County, Wisconsin, surrounded on three sides by the city of Madison, Wisconsin, and on the south east side by the city of Monona, Wisconsin. It is the second-largest of a chain of four lakes along ...
,
Lake Kegonsa
Lake Kegonsa State Park is a state park of Wisconsin, United States, on the northeast shore of Lake Kegonsa. It is located in Dane County southeast of Madison, Wisconsin. The park consists of forest, prairie, and wetlands. Known for its camp ...
and
Lake Waubesa
Lake Waubesa is one of the four major lakes in Dane County, Wisconsin that surround the city of Madison. The lake has a surface area of and a max depth of .
In 2013, the Wisconsin state record Yellow bass was caught in Lake Waubesa. It was ...
—the city is home to the
University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
, the
Wisconsin State Capitol
The Wisconsin State Capitol, located in Madison, Wisconsin, houses both chambers of the Wisconsin legislature along with the Wisconsin Supreme Court and the Office of the Governor. Completed in 1917, the building is the fifth to serve as the Wi ...
, the
Overture Center for the Arts, and the
Henry Vilas Zoo
Henry Vilas Zoo is a public zoo in Madison, Wisconsin, United States, that is accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA). Owned by Dane County, the zoo charges no admission or parking fees. It receives over 750,000 visitors annua ...
. Madison is home to an extensive network of parks and bike trails; it has the most parks and playgrounds per capita of any of
the 100 largest U.S. cities and is one of five communities to have received a "
Platinum Bicycle Friendly Community" rating from the
League of American Bicyclists
The League of American Bicyclists (LAB), officially the League of American Wheelmen, is a membership organization that promotes cycling for fun, fitness and transportation through advocacy and education.
A Section 501(c)(3) nonprofit organizat ...
.
Madison is also home to
nine
9 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
9 or nine may also refer to:
Dates
* AD 9, the ninth year of the AD era
* 9 BC, the ninth year before the AD era
* 9, numerical symbol for the month of September
Places
* Nine, Portugal, a parish in the ...
National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
s, including several buildings designed by architect
Frank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright (June 8, 1867 – April 9, 1959) was an American architect, designer, writer, and educator. He designed more than 1,000 structures over a creative period of 70 years. Wright played a key role in the architectural movements o ...
, such as his 1937
Jacobs I House, which is a
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
.
Residents of Madison are known as
Madisonians. Madison has long been a center for
progressive political activity, protests, and demonstrations, and contemporary Madison is considered the most
politically liberal
Liberalism is a political and moral philosophy based on the rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostility to autocracy, cultural distaste for c ...
city in Wisconsin.
The presence of the University of Wisconsin–Madison (the largest employer in the state) as well as other educational institutions has
a significant impact on the
economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
,
culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
, and
demographics
Demography () is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as ed ...
of Madison.
As of 2021, Madison is the
fastest-growing city in Wisconsin. Madison's economy features a large and growing technology sector, and the Madison area is home to the headquarters of
Epic Systems
Epic Systems Corporation, or Epic, is an American privately held healthcare software company. According to the company, hospitals that use its software held medical records of 78% of patients in the United States and over 3% of patients worldwi ...
,
American Family Insurance
American Family Insurance, also abbreviated as AmFam, is an American private mutual company that focuses on property, casualty, and auto insurance, and also offers commercial insurance, life, health, and homeowners coverage as well as investm ...
,
Exact Sciences
The exact sciences, sometimes called the exact mathematical sciences, are those sciences "which admit of absolute precision in their results"; especially the mathematical sciences. Examples of the exact sciences are mathematics, optics, astron ...
,
Promega
Promega Corporation is a Madison, Wisconsin-based manufacturer of enzymes and other products for biotechnology and molecular biology with a portfolio covering the fields of genomics, protein analysis and expression, cellular analysis, drug disc ...
,
American Girl,
Sub-Zero,
Lands' End
Lands' End is an American clothing and home decor retailer founded in 1963 and based in Dodgeville, Wisconsin, that specializes in casual clothing, luggage, and home furnishings. The majority of the company's business is conducted through mail ...
,
Spectrum Brands
Spectrum Brands Holdings, Inc. is an American diversified company. Headquartered in Middleton, Wisconsin, it was established in 2005 as the successor company to Rayovac Corporation. It is one of the Fortune 500 companies, and among the largest of ...
, a regional office for
Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
, and the University Research Park, as well as many
biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used ...
and health systems startups. Madison is a popular
visitor destination, with tourism generating over $1 billion for Dane County's economy in 2018. A booming population combined with a lack in the quantity of housing due to restrictive
zoning density regulations have contributed to rising housing costs in many Madison neighborhoods, with a 23% increase in median rent between 2014 and 2019.
History
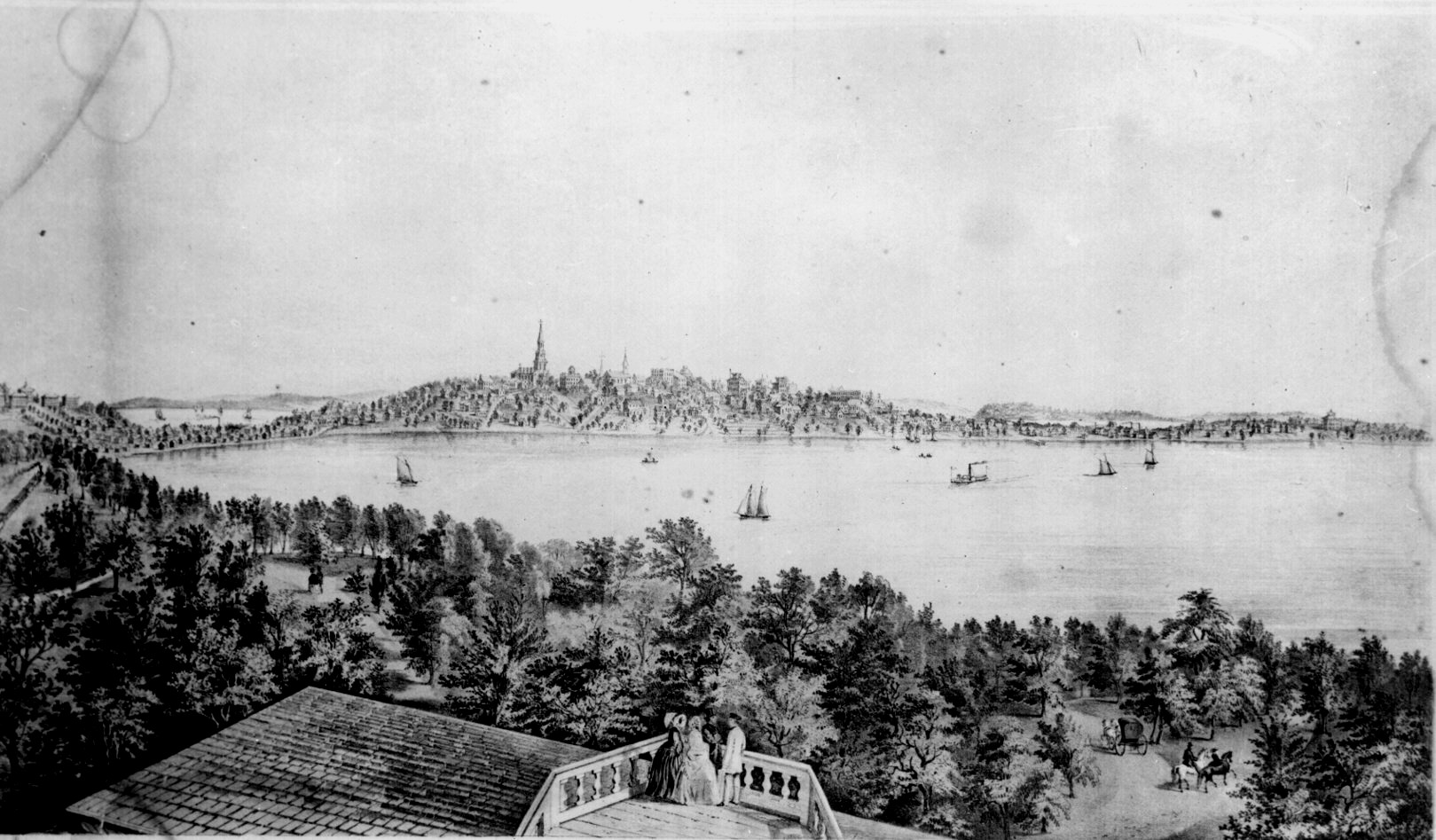

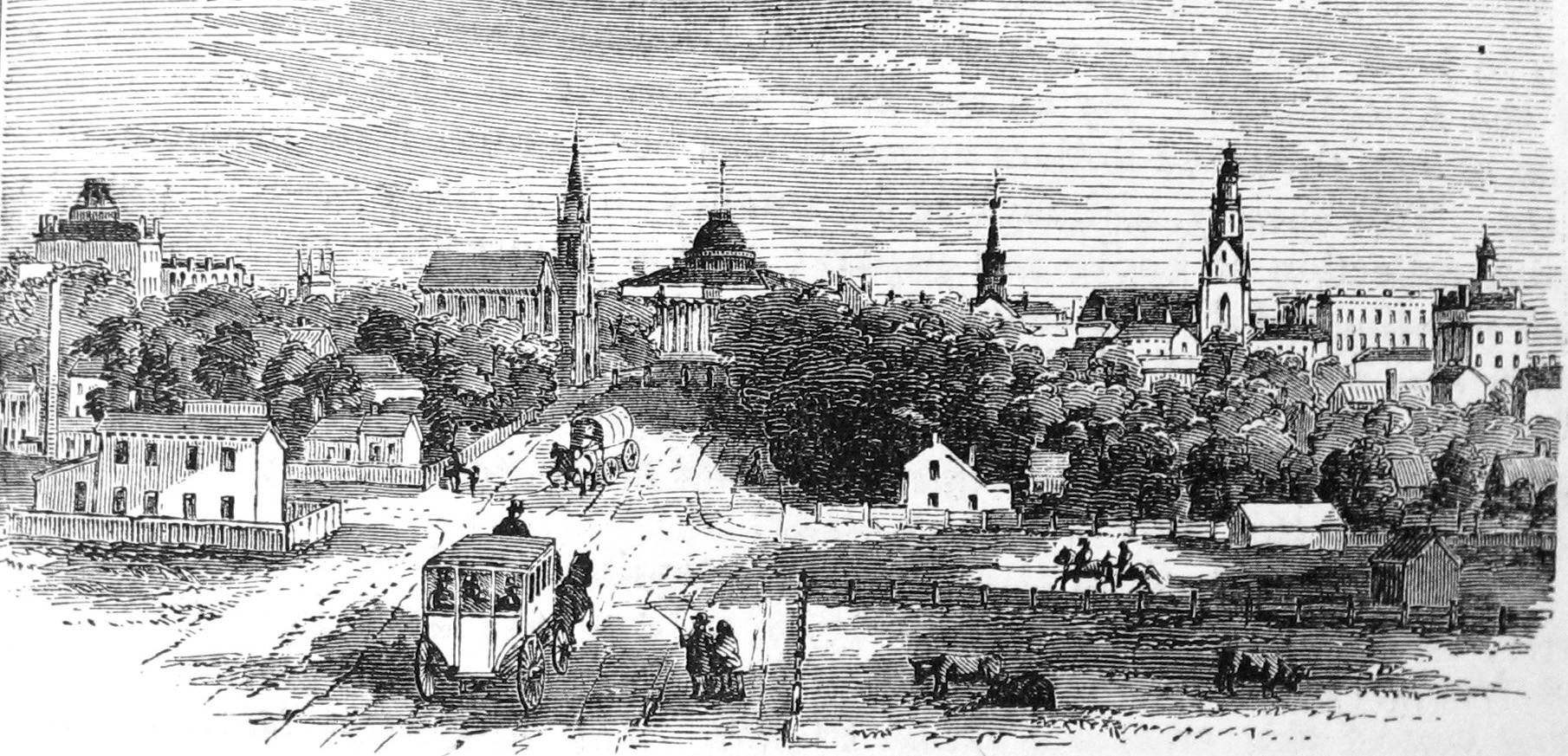
Native Americans
Before Europeans, humans inhabited the area in and around Madison for about 12,000 years. In 1800, the Madison area was
Ho-Chunk (Winnebago) Country. The Native Americans called this place Taychopera (Ta-ko-per-ah), meaning "land of the four lakes" (Mendota, Monona, Waubesa, and Kegonsa).
Effigy mounds
An effigy mound is a raised pile of earth built in the shape of a stylized animal, symbol, religious figure, human, or other figure. The Effigy Moundbuilder culture is primarily associated with the years 550-1200 CE during the Late Woodland Peri ...
, which had been constructed for ceremonial and burial purposes over 1,000 years earlier, dotted the rich prairies around the lakes.
Founding
Madison's European origins begin in 1829, when former federal judge
James Duane Doty
James Duane Doty (November 5, 1799 – June 13, 1865) was a land speculator and politician in the United States who played an important role in the development of Wisconsin and Utah Territory.
Early life and legal career
A descendant of ''Mayflo ...
purchased over a thousand acres (4 km
2) of swamp and forest land on the isthmus between Lakes Mendota and Monona, with the intention of building a city in the Four Lakes region. He purchased 1,261 acres for $1,500. When the
Wisconsin Territory
The Territory of Wisconsin was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 3, 1836, until May 29, 1848, when an eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Wisconsin. Belmont was ...
was created in 1836 the territorial legislature convened in
Belmont, Wisconsin
Belmont is a village in Lafayette County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 986 at the 2010 census.
History
Founded in 1835 by land speculator John Atchison, Belmont was the original capital of the Wisconsin Territory, and the origi ...
. One of the legislature's tasks was to select a permanent location for the territory's capital. Doty lobbied aggressively for Madison as the new capital, offering
buffalo robes to the freezing legislators and choice lots in Madison at discount prices to undecided voters. He had James Slaughter
plat
In the United States, a plat ( or ) (plan) is a cadastral map, drawn to scale, showing the divisions of a piece of land. United States General Land Office surveyors drafted township plats of Public Lands Surveys to show the distance and bea ...
two cities in the area, Madison and "The City of Four Lakes", near present-day
Middleton.
Doty named his city Madison for
James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for h ...
, the fourth President of the U.S. who had died on June 28, 1836, and he named the streets for the other
38 signers of the
U.S. Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the nation ...
. Although the city existed only on paper, the territorial legislature voted on November 28, 1836 in favor of Madison as its capital, largely because of its location halfway between the new and growing cities around
Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee ...
in the east and the long established strategic post of
Prairie du Chien
Prairie du Chien () is a city in and the county seat of Crawford County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 5,506 at the 2020 census. Its ZIP Code is 53821.
Often referred to as Wisconsin's second oldest city, Prairie du Chien was esta ...
in the west, and between the highly populated
lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
mining regions in the southwest and Wisconsin's oldest city,
Green Bay, in the northeast.
Expansion

The cornerstone for the Wisconsin capitol was laid in 1837, and the legislature first met there in 1838. On October 9, 1839,
Kintzing Prichett registered the
plat
In the United States, a plat ( or ) (plan) is a cadastral map, drawn to scale, showing the divisions of a piece of land. United States General Land Office surveyors drafted township plats of Public Lands Surveys to show the distance and bea ...
of Madison at the registrar's office of the then-territorial
Dane County
Dane County is a county in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2020 census, the population was 561,504, making it the second-most populous county in Wisconsin. The county seat is Madison, which is also the state capital.
Dane County is the ...
.
Madison was incorporated as a village in 1846, with a population of 626. When Wisconsin became a state in 1848, Madison remained the capital, and the following year it became the site of the University of Wisconsin (now
University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
). The
Milwaukee & Mississippi Railroad (a predecessor of the
Milwaukee Road) connected to Madison in 1854. Madison incorporated as a city in 1856, with a population of 6,863, leaving the unincorporated remainder as a separate
Town of Madison. The original capitol was replaced in 1863 and the second capitol burned in 1904. The current capitol was built between 1906 and 1917.
During the
Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, Madison served as a center of the
Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union of the collective states. It proved essential to th ...
in Wisconsin. The intersection of Milwaukee, East Washington, Winnebago, and North Streets is known as Union Corners, because a tavern there was the last stop for Union soldiers before heading to fight the Confederates.
Camp Randall
Camp Randall was a United States Army base in Madison, Wisconsin, the largest staging point for Wisconsin troops entering the American Civil War. At this camp fresh volunteers received quick training before heading off to join the Union Army. Also ...
, on the west side of Madison, was built and used as a training camp, a military hospital, and a prison camp for captured
Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between 1 ...
soldiers. After the war ended, the Camp Randall site was absorbed into the University of Wisconsin and
Camp Randall Stadium
Camp Randall Stadium is an outdoor stadium in Madison, Wisconsin, located on the campus of the University of Wisconsin. It has been the home of the Wisconsin Badgers football team in rudimentary form since 1895, and as a fully functioning stadiu ...
was built there in 1917. In 2004 the last vestige of active military training on the site was removed when the stadium renovation replaced a firing range used for
ROTC training.
1960s and 1970s

In the 1960s and 1970s, the Madison
counterculture
A counterculture is a culture whose values and norms of behavior differ substantially from those of mainstream society, sometimes diametrically opposed to mainstream cultural mores.Eric Donald Hirsch. ''The Dictionary of Cultural Literacy''. Hou ...
was centered in the neighborhood of Mifflin and Bassett streets, referred to as "Miffland". The area contained many three-story apartments where students and counterculture youth lived, painted murals, and operated the co-operative grocery store, the Mifflin Street Co-op. Residents of the neighborhood often came into conflict with authorities, particularly during the administration of Republican mayor
Bill Dyke. Dyke was viewed by students as a direct antagonist in efforts to protest the
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
because of his efforts to suppress local protests. The annual
Mifflin Street Block Party
The Mifflin Street Block Party is an annual block party celebration held on Mifflin Street in Madison, Wisconsin. The party is held on the last Saturday of April and attended predominantly by students attending the University of Wisconsin–Madis ...
became a focal point for protest, although by the late 1970s it had become a mainstream community party.
During the late 1960s and early 1970s, thousands of students and other citizens took part in
anti-Vietnam War marches and demonstrations, with more violent incidents drawing national attention to the city and UW campus. These include:
* the 1967 student protest of
Dow Chemical Company, with 74 injured;
* the 1969 strike to secure greater representation and rights for African-American students and faculty, which resulted in the involvement of the Wisconsin
Army National Guard;
* the 1970 fire that caused damage to the Army
ROTC headquarters housed in the
University of Wisconsin Armory and Gymnasium
The University of Wisconsin Armory and Gymnasium, also called "the Red Gym", is a building on the campus of University of Wisconsin–Madison. It was originally used as a combination gymnasium and armory beginning in 1894. Designed in the Romanesqu ...
, also known as the Red Gym; and
* the 1970 late-summer predawn
ANFO
ANFO ( ) (or AN/FO, for ammonium nitrate/fuel oil) is a widely used bulk industrial explosive. It consists of 94% porous prilled ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) (AN), which acts as the oxidizing agent and absorbent for the fuel, and 6% number 2 fue ...
bombing of the Army Mathematics Research Center in Sterling Hall, killing a postdoctoral researcher, Robert Fassnacht. ''(See
Sterling Hall bombing)''
These protests were the subject of the 1979 documentary
''The War at Home''.
David Maraniss
David Maraniss ( ; born 1949) is an American journalist and author, currently serving as an associate editor for ''The Washington Post''.
Career
''The Washington Post'' assigned Maraniss the job of biographer for their coverage of 2008 president ...
's 2004 book, ''
They Marched into Sunlight'', incorporated the 1967 Dow protests into a larger
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
narrative. Tom Bates wrote the book ''Rads'' on the subject (). Bates wrote that Dyke's attempt to suppress the annual
Mifflin Street Block Party
The Mifflin Street Block Party is an annual block party celebration held on Mifflin Street in Madison, Wisconsin. The party is held on the last Saturday of April and attended predominantly by students attending the University of Wisconsin–Madis ...
"would take three days, require hundreds of officers on overtime pay, and engulf the student community from the nearby Southeast Dorms to
Langdon Street's fraternity row.
Tear gas
Tear gas, also known as a lachrymator agent or lachrymator (), sometimes colloquially known as "mace" after the early commercial aerosol, is a chemical weapon that stimulates the nerves of the lacrimal gland in the eye to produce tears. In ...
hung like heavy fog across the Isthmus." In the fracas, student activist
Paul Soglin
Paul R. Soglin (born April 22, 1945) is an American politician and former three-time Mayor of Madison, Wisconsin, having served a total of 22 years in that office between 1973 and 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, he was a candidate for Gov ...
, then a city
alderman
An alderman is a member of a municipal assembly or council in many jurisdictions founded upon English law. The term may be titular, denoting a high-ranking member of a borough or county council, a council member chosen by the elected members t ...
, was arrested twice and taken to
jail. Soglin was later elected mayor of Madison, serving several times.

21st century
In early 2011, Madison was the site for
large protests against a bill proposed by Governor
Scott Walker that abolished almost all
collective bargaining
Collective bargaining is a process of negotiation between employers and a group of employees aimed at agreements to regulate working salaries, working conditions, benefits, and other aspects of workers' compensation and rights for workers. The ...
for public worker unions. The protests at the capitol ranged in size from 10,000 to over 100,000 people and lasted for several months.
Geography

Madison is located in the center of Dane County in south-central Wisconsin, west of
Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee ...
and northwest of
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
. The city completely surrounds the smaller
town of Madison, the city of
Monona, and the
villages
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to ...
of
Maple Bluff and
Shorewood Hills. Madison shares borders with its largest suburb,
Sun Prairie, and three other suburbs,
Middleton,
McFarland McFarland may refer to:
People
*McFarland (surname)
Places in the United States
*McFarland, California, a city
*McFarland, Kansas, a city
*McFarland, Missouri, a ghost town
*McFarland, Wisconsin, a village
Other uses
* USS ''McFarland'' (DD-237) ...
, and
Fitchburg. Other suburbs include the city of
Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
and the villages of
Cottage Grove,
DeForest, and
Waunakee as well as
Mount Horeb
Mount Horeb (Hebrew: ''Har Ḥōrēḇ''; Greek in the Septuagint: ; Latin in the Vulgate: ') is the mountain at which the Ten Commandments were given to Moses by Yahweh, according to the Book of Deuteronomy in the Hebrew Bible. It is describe ...
,
Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
,
Stoughton, and
Cross Plains.
According to the
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of t ...
, the city has a total area of , of which is land and is water.
The city is sometimes described as ''The City of Four Lakes'', comprising the four successive lakes of the
Yahara River
The Yahara River is a tributary of the Rock River in southern Wisconsin. It is about longU.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed May 13, 2011 (including the distance across inte ...
:
Lake Mendota
Lake Mendota is a freshwater eutrophic lake that is the northernmost and largest of the four lakes in Madison, Wisconsin. The lake borders Madison on the north, east, and south, Middleton on the west, Shorewood Hills on the southwest, Maple Bl ...
("Fourth Lake"),
Lake Monona
Lake Monona is a freshwater drainage lake in Dane County, Wisconsin, surrounded on three sides by the city of Madison, Wisconsin, and on the south east side by the city of Monona, Wisconsin. It is the second-largest of a chain of four lakes along ...
("Third Lake"),
Lake Waubesa
Lake Waubesa is one of the four major lakes in Dane County, Wisconsin that surround the city of Madison. The lake has a surface area of and a max depth of .
In 2013, the Wisconsin state record Yellow bass was caught in Lake Waubesa. It was ...
("Second Lake") and
Lake Kegonsa
Lake Kegonsa State Park is a state park of Wisconsin, United States, on the northeast shore of Lake Kegonsa. It is located in Dane County southeast of Madison, Wisconsin. The park consists of forest, prairie, and wetlands. Known for its camp ...
("First Lake"), although Waubesa and Kegonsa are not actually in Madison, but just south of it. A fifth smaller lake,
Lake Wingra
Lake Wingra is a small lake located inside the city limits of the U.S. city of Madison, Wisconsin. The smallest of the five major lakes drained by the Yahara River in Dane County, Lake Wingra is bordered by the University of Wisconsin–Madison Ar ...
, is within the city as well; it is connected to the Yahara River chain by Wingra Creek. The Yahara flows into the
Rock River, which flows into the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
. Downtown Madison is located on an
isthmus
An isthmus (; ; ) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthmus ...
between Lakes Mendota and Monona. The city's trademark of "Lake, City, Lake" reflects this geography. The city's lowest elevation is Lake Monona, at . The highest elevation is located along S. Pleasant View Rd. on the far west side of the city, atop a portion of a terminal moraine of the Green Bay Lobe of the Wisconsin Glaciation, at .
Neighborhoods
Local identity varies throughout Madison, with over 120 officially recognized neighborhood associations, such as the east side Williamson-Marquette Neighborhood. Historically, the north, east, and south sides were
blue collar
A blue-collar worker is a working class person who performs manual labor. Blue-collar work may involve skilled or unskilled labor. The type of work may involving manufacturing, warehousing, mining, excavation, electricity generation and power ...
while the west side was
white collar, and to a certain extent this remains true. Students dominate on the
University of Wisconsin
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, ...
campus and to the east into downtown, while to its south and in
Shorewood Hills on its west, faculty have been a major presence since those neighborhoods were originally developed. The turning point in Madison's development was the university's 1954 decision to develop its experimental farm on the western edge of town; since then, the city has grown substantially along suburban lines.
Major commercial areas
Hilldale
The Hilldale area comprises the Hill Farms neighborhood, Sunset Village Neighborhood, and part of the suburb of
Shorewood Hills. The area has long winding streets, and according to a planning document issued by the neighborhood association, a "suburban-like feel". The area is also a commercial district, and contains
Hilldale Shopping Center
Hilldale Shopping Center, or simply Hilldale, is a partially enclosed shopping mall/lifestyle center development on the west side of Madison, Wisconsin, United States. Originally opened in October 1962, Hilldale has four anchor stores - Macy's, Ta ...
, an outdoor shopping center containing restaurants, a movie theater, and national retail chains.
Capitol Square
The Capitol Square Area is Madison's
central business district. It is home to high rise apartments, restaurants, and shopping outlets. It contains several museums and is home to the
Wisconsin State Capitol
The Wisconsin State Capitol, located in Madison, Wisconsin, houses both chambers of the Wisconsin legislature along with the Wisconsin Supreme Court and the Office of the Governor. Completed in 1917, the building is the fifth to serve as the Wi ...
building and the
Monona Terrace
Monona Terrace (officially the Monona Terrace Community and Convention Center) is a convention center on the shores of Lake Monona in Madison, Wisconsin.
Controversy
Originally designed by Wisconsin native Frank Lloyd Wright, it was first propo ...
. The capitol square holds a number of public events for the city of Madison including the
Dane County Farmers' Market,
Concerts on the Square, Taste of Madison and
Art Fair on the Square
Art Fair on the Square is an annual event held on the Capitol Square in Madison, Wisconsin, United States. The Juried (competition), juried event brings together around 500 artists from across America on the second weekend of July. Most art forms ...
. The area's nightlife is served by several bars and live music venues.
State Street
State Street, which links the University of Wisconsin campus with the Capitol Square, is lined with restaurants, espresso cafes, and shops. Only pedestrians, buses, emergency vehicles, delivery vehicles, and bikes are allowed on State Street. State Street is home to much of the nightlife of the University of Wisconsin–Madison, as it is the location of a number of bars and performance venues ranging from comedy clubs to multiple large theaters, including the Overture Center, which features local ballets and Broadway touring casts. State street is also home to
Freakfest
The State Street Halloween Party, renamed Freakfest in 2006, is an annual city-sponsored Halloween festival in Madison, Wisconsin. It is considered the largest Halloween festival in the Midwest.
Freakfest is a gathering place for tens of thousan ...
, the annual Halloween party in Madison. A newer event on State Street is the Madison Night Market that occurs four nights during the year.
Park Street
The Park Street Area is located in the south of Madison, and contains multiple official neighborhoods, including the Burr Oaks Neighborhood Association and Greenbush. It has been described as the "racially and economically diverse area of Madison". Park Street is home to ethnic restaurants and specialty grocery stores, as well as retail. Residential areas to the sides of Park Street tend to have smaller houses or condos, and a higher density of houses.
Monroe Street
The Dudgeon-Monroe neighborhood neighbors downtown Madison. It is located around Monroe Street, a commercial area which has local shops, coffee houses, dining and galleries. It is home to a neighborhood jazz fest and Wingra Park, where people can rent paddle boats and canoes at the boathouse on
Lake Wingra
Lake Wingra is a small lake located inside the city limits of the U.S. city of Madison, Wisconsin. The smallest of the five major lakes drained by the Yahara River in Dane County, Lake Wingra is bordered by the University of Wisconsin–Madison Ar ...
.
Willy Street
The Marquette neighborhood sits on the near east side of Madison. Willy (Williamson) Street contains locally owned shops, restaurants, and entertainment establishments, as well as art galleries, and the
Willy Street Co-op. The houses in the Marquette neighborhood fall into two separate historic districts, Third Lake Ridge Historic District and Marquette Bungalow Historic District. The area is also the location of festivals like the Waterfront Festival (June),
La Fete de Marquette (July), Orton Park Festival (August), and Willy Street Fair (September). The Willy Street neighborhood is a hub for Madison's bohemian culture. Houses lining the street are often painted colorfully, and the area has several murals.
Climate
Madison, along with the rest of the state, has a
humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(
Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
: ''Dfa''), characterized by variable weather patterns and a large seasonal temperature variance: winter temperatures can be well below freezing, with moderate to occasionally heavy snowfall and temperatures reaching on 17 mornings annually; high temperatures in summer average in the lower 80s °F (27–28 °C), reaching on an average 12 afternoons per year,
with lower humidity levels than winter but higher than spring. Summer accounts for a greater proportion of annual rainfall, but winter still sees significant precipitation.
Demographics
2020 census
As of the
census of 2020,
the population was 269,840. The
population density
Population density (in agriculture: Stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical ...
was . There were 126,070 housing units at an average density of . Ethnically, the population was 8.7%
Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to viceroyalties forme ...
or
Latino
Latino or Latinos most often refers to:
* Latino (demonym), a term used in the United States for people with cultural ties to Latin America
* Hispanic and Latino Americans in the United States
* The people or cultures of Latin America;
** Latin A ...
of any race. When grouping both Hispanic and non-Hispanic people together by race, the city was 71.0%
White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
, 9.5%
Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
, 7.4%
Black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ...
or
African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 0.5%
Native American, 0.1%
Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of O ...
, 3.8% from
other races
Other often refers to:
* Other (philosophy), a concept in psychology and philosophy
Other or The Other may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''The Other'' (1913 film), a German silent film directed by Max Mack
* ''The Other'' (1930 film), a ...
, and 7.8% from two or more races.
The 2020 census population of the city included 548 people incarcerated in adult correctional facilities and 9,909 people in university student housing.
According to the
American Community Survey estimates for 2016-2020, the median income for a household in the city was $67,565, and the median income for a family was $96,502. Male full-time workers had a median income of $56,618 versus $48,760 for female workers. The
per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
for the city was $39,595. About 6.0% of families and 16.4% of the population were below the
poverty line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for t ...
, including 11.3% of those under age 18 and 6.4% of those age 65 or over.
Of the population age 25 and over, 95.9% were high school graduates or higher and 58.5% had a bachelor's degree or higher.
2010 census
As of the
census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses in ...
of 2010, there were 233,209 people, 102,516 households, and 47,824 families residing in the city. The
population density
Population density (in agriculture: Stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical ...
was . There were 108,843 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the city was 78.9 percent white, 7.3 percent black, 0.4 percent American Indian, 7.4 percent Asian, 2.9 percent other races, and 3.1 from two or more races.
Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to viceroyalties forme ...
or
Latino
Latino or Latinos most often refers to:
* Latino (demonym), a term used in the United States for people with cultural ties to Latin America
* Hispanic and Latino Americans in the United States
* The people or cultures of Latin America;
** Latin A ...
of any race were 6.8 percent of the population.
There were 102,516 households, of which 22.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 35.1% were married couples living together, 8.4% had a female householder with no husband present, 3.2% had a male householder with no wife present, and 53.3% were non-families. 36.2% of all households were made up of individuals, and 7.5% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.17 and the average family size was 2.87.
The median age in the city was 30.9 years. 17.5 percent of residents were under the age of 18; 19.6% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 31.4% were from 25 to 44; 21.9% were from 45 to 64; and 9.6% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the city was 49.2% male and 50.8% female.
Combined Statistical Area
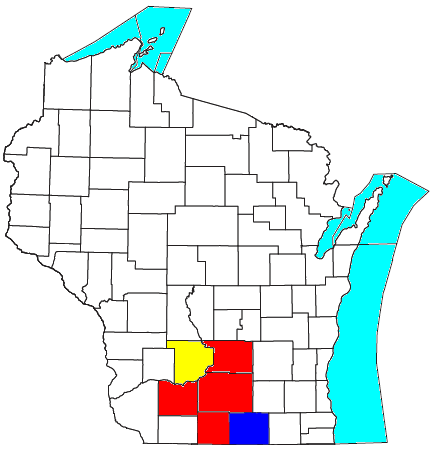
Madison is the larger principal city of the
Madison-Janesville-Beloit, WI CSA
The Madison, Wisconsin, metropolitan area, also known as Greater Madison, is the metropolitan area surrounding the city of Madison, Wisconsin. Madison is the state capital of Wisconsin and is Wisconsin's second largest city (after Milwaukee), and t ...
, a
Combined Statistical Area
Combined statistical area (CSA) is a United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) term for a combination of adjacent metropolitan (MSA) and micropolitan statistical areas (µSA) across the 50 US states and the territory of Puerto Ric ...
that includes the Madison metropolitan area (Columbia, Dane, Green and Iowa counties), the Janesville-Beloit metropolitan area (
Rock County), and the
Baraboo
Baraboo is a city in the Midwest and the county seat of Sauk County, Wisconsin, United States. The largest city in the county, Baraboo is the principal city of the Baraboo Micropolitan Statistical Area. Its 2020 population was 12,556. It is situ ...
micropolitan area (
Sauk County
Sauk County is a county in Wisconsin. It is named after a large village of the Sauk people. As of the 2020 census, the population was 65,763. Its county seat and largest city is Baraboo. The county was created in 1840 from Wisconsin Territory a ...
). As of the 2020 census, the Madison MSA had a population of 680,796 and the Madison CSA had a population of 910,246.
Religion
Madison is the
episcopal see for the
Roman Catholic Diocese of Madison
The Diocese of Madison ( la, Diœcesis Madisonensis) is a Roman Catholic diocese in the U.S. State of Wisconsin. It comprises Columbia, Dane, Grant, Green, Green Lake, Iowa, Jefferson, Lafayette, Marquette, Rock, and Sauk counties. The are ...
.
Saint Raphael's Cathedral, damaged by arson in 2005 and demolished in 2008, was the mother church of the diocese. The steeple and spire survived and have been preserved with the intention they could be incorporated in the structure of a replacement building.
InterVarsity Christian Fellowship
InterVarsity Christian Fellowship/USA is an inter-denominational, evangelical Christian campus ministry founded in 1941, working with students and faculty on U.S. college and university campuses. InterVarsity is a charter member of the Internat ...
/USA has its headquarters in Madison.
The
Wisconsin Evangelical Lutheran Synod
The Wisconsin Evangelical Lutheran Synod (WELS), also referred to simply as the Wisconsin Synod, is an American Confessional Lutheran denomination of Christianity. Characterized as theologically conservative, it was founded in 1850 in Milwauke ...
has three churches in Madison: Eastside Lutheran Church, Our Redeemer Lutheran Church, and Wisconsin Lutheran Chapel.
The
Evangelical Lutheran Synod
The Evangelical Lutheran Synod (ELS) is a US-based Protestant Christian denomination based in Mankato, Minnesota. It describes itself as a conservative, Confessional Lutheran body. The ELS has 130 congregations and has missions in Peru, Chile ...
has three churches in Madison: Grace Lutheran Church, Holy Cross Lutheran Church, and Our Saviour's Lutheran Church.
Bethel Lutheran Church of the Evangelical Church in America, in downtown Madison, is one of the largest Lutheran congregations in the country.
Most American Christian movements are represented in the city, including mainline denominations, evangelical, charismatic and fully independent churches, including an
LDS
LDS may refer to:
Organizations
* LDS Hospital, Salt Lake City, Utah, US Religion
* Latter Day Saint movement (LDS movement), a collection of independent church groups
**The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, the largest group within t ...
stake. The city also has multiple
Sikh Gurdwaras,
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
temples, three
mosques and several
synagogues
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of wors ...
, a community center serving the
Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the essential worth of all religions and the unity of all people. Established by Baháʼu'lláh in the 19th century, it initially developed in Iran and parts of the ...
, a
Quaker Meeting House
A Friends meeting house is a meeting house of the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), where meeting for worship is usually held.
Typically, Friends meeting houses are simple and resemble local residential buildings. Steeples, spires, and ...
, and a
Unity Church
Unity, known informally as Unity Church, is an organization founded by Charles and Myrtle Fillmore in 1889. It grew out of Transcendentalism and became part of the New Thought movement. Unity is known for its '' Daily Word'' devotional publi ...
congregation.
The nation's third largest congregation of
Unitarian Universalists
Unitarian Universalism (UU) is a liberal religion characterized by a "free and responsible search for truth and meaning". Unitarian Universalists assert no creed, but instead are unified by their shared search for spiritual growth, guided by ...
, the
First Unitarian Society of Madison
The First Unitarian Society of Madison (FUS) is a Unitarian Universalist congregation in Shorewood Hills, Wisconsin. Its meeting house was designed by Frank Lloyd Wright and built by Marshall Erdman in 1949–1951, and has been designated a U.S ...
, makes its home in the historic Unitarian Meeting House, designed by one of its members,
Frank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright (June 8, 1867 – April 9, 1959) was an American architect, designer, writer, and educator. He designed more than 1,000 structures over a creative period of 70 years. Wright played a key role in the architectural movements o ...
.
Madison is home to the
Freedom from Religion Foundation
The Freedom From Religion Foundation (FFRF) is an American nonprofit organization, which advocates for atheists, agnostics, and nontheists. Formed in 1976, FFRF promotes the separation of church and state, and challenges the legitimacy of many ...
, a non-profit organization that promotes the
separation of church and state
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the state. Conceptually, the term refers to the creation of a secular sta ...
.
Crime
There were 53 homicides reported by Madison Police from 2000 to 2009.
The highest total was 10 in 2008. Police reported 28 murders from 2010 to 2015, with the highest year being 7 murders in 2011.
Economy
Madison's economy is marked by the sectors of tech business and state employment.
As of late 2018, the two largest employers in the Madison Metropolitan Area were the
University of Wisconsin-Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, th ...
, and
Epic Systems
Epic Systems Corporation, or Epic, is an American privately held healthcare software company. According to the company, hospitals that use its software held medical records of 78% of patients in the United States and over 3% of patients worldwi ...
. The Wisconsin state government and the University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics remain the two major state employers. Madison's economy today is evolving from a government-based economy to a consumer services and high-tech base, particularly in the health, biotech, and advertising sectors. Beginning in the early 1990s, the city experienced a steady economic boom and has been less affected by recession than other areas of the state. Underpinning the boom is the development of high-tech companies, many fostered by UW–Madison working with local businesses and entrepreneurs to transfer the results of academic research into real-world applications, especially bio-tech applications.
Many businesses are attracted to Madison's skill base, taking advantage of the area's high level of education. 48.2% of Madison's population over the age of 25 holds at least a bachelor's degree. ''
Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. ''Forbes'' also r ...
'' magazine reported in 2004 that Madison had the highest percentage of individuals holding Ph.D.s in the United States. Madison was also named in a number of ''Forbes'' 'Ten Best Cities' lists several times in the early 21st century.
State enterprises
As Madison is the State Capital of
Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, it is home to many Wisconsin state agencies and bureaus. Madison also contains the
University of Wisconsin-Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, th ...
, a research institution that employs 22,365 faculty and staff.
The University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics is an important regional teaching hospital and regional trauma center, with strengths in transplant medicine, oncology, digestive disorders, and endocrinology. Other Madison hospitals include
St. Mary's Hospital,
Meriter Hospital, and the
VA Medical Center
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the component of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) led by the Under Secretary of Veterans Affairs for Health that implements the healthcare program of the VA through a nationa ...
.
Business
The Madison metropolitan area is home to companies such as
Spectrum Brands
Spectrum Brands Holdings, Inc. is an American diversified company. Headquartered in Middleton, Wisconsin, it was established in 2005 as the successor company to Rayovac Corporation. It is one of the Fortune 500 companies, and among the largest of ...
(formerly
Rayovac),
Trek,
Alliant Energy
Alliant Energy is a public utility holding company headquartered in Madison, Wisconsin, providing power in Iowa and Wisconsin.
History
Interstate Power and Light Company (IPL) expanded greatly in the late 1920s to include operations in Iowa, ...
, the
Credit Union National Association
The Credit Union National Association, commonly known as CUNA (pronounced "Cue-Nuh"), is a national trade association for both state- and federally chartered credit unions located in the United States. CUNA provides member credit unions with tr ...
(CUNA),
MGE Energy,
EatStreet, and
Sub-Zero & Wolf Appliance. Insurance companies based in Madison include
American Family Insurance
American Family Insurance, also abbreviated as AmFam, is an American private mutual company that focuses on property, casualty, and auto insurance, and also offers commercial insurance, life, health, and homeowners coverage as well as investm ...
,
CUNA Mutual Group
TruStage Financial Group, Inc., formerly known as CUNA Mutual Group, is a mutual insurance company that provides financial services to cooperatives, credit unions, their members, and other customers worldwide. TruStage Financial Group sells comm ...
, and
National Guardian Life. Technology companies in Madison include
Broadjam,
Zendesk
Zendesk is an American company headquartered in San Francisco, California. It provides software-as-a-service products related to customer support, sales, and other customer communications. The company was founded in Copenhagen, Denmark, in 2007. ...
,
Full Compass Systems,
Raven Software
Raven Software Corporation is an American video game developer based in Wisconsin and founded in 1990. In 1997, Raven made an exclusive publishing deal with Activision and was subsequently acquired by them. After the acquisition, many of the stu ...
, and
TDS Telecom
TDS Telecom is an American telecommunications company with headquarters in Madison, Wisconsin. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of Telephone and Data Systems Inc, and is the seventh-largest local exchange carrier in the U.S. TDS Telecom offers t ...
.
Some economic growth in Madison is driven by biotech and health information technology. Biotech firms include
Panvera (now part of Invitrogen),
Exact Sciences
The exact sciences, sometimes called the exact mathematical sciences, are those sciences "which admit of absolute precision in their results"; especially the mathematical sciences. Examples of the exact sciences are mathematics, optics, astron ...
,
Promega
Promega Corporation is a Madison, Wisconsin-based manufacturer of enzymes and other products for biotechnology and molecular biology with a portfolio covering the fields of genomics, protein analysis and expression, cellular analysis, drug disc ...
, and
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals among others. The
contract research organization Covance
Labcorp Drug Development is a contract research organization (CRO) headquartered in Burlington, North Carolina, providing nonclinical, preclinical, clinical and commercialization services to pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Formerl ...
is a major employer in the city.
Madison's community
hackerspaces/makerspaces are Sector67, which serves inventors and entrepreneurs, and The Bodgery, which serves hobbyists, artists, and tinkerers. Start up incubators and connectors include StartingBlock,
gener8tor and University Research Park.
Epic Systems
Epic Systems Corporation, or Epic, is an American privately held healthcare software company. According to the company, hospitals that use its software held medical records of 78% of patients in the United States and over 3% of patients worldwi ...
was based in Madison from 1979 to 2005, when it moved to a larger campus in the nearby Madison suburb of
Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
. Other firms include Nordic, Forward Health, and Forte Research Systems.
Oscar Mayer
Oscar Mayer is an American meat and cold cut producer known for its hot dogs, bologna, bacon, ham, and Lunchables products. The company is a subsidiary of the Kraft Heinz Company and based in Chicago, Illinois.
History Early years
German im ...
was a Madison fixture for decades, and was a family business for many years before being sold to
Kraft Foods
The second incarnation of Kraft Foods is an American food manufacturing and processing conglomerate, split from Kraft Foods Inc. in 2012 and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. It became part of Kraft Heinz in 2015.
A merger with Heinz, arran ...
. ''
The Onion
''The Onion'' is an American digital media company and newspaper organization that publishes satire, satirical articles on international, national, and local news. The company is based in Chicago but originated as a weekly print publication on ...
'' satirical newspaper, as well as the pizza chains
Rocky Rococo and the
Glass Nickel Pizza Company, originated in Madison.
Arts and culture
Food
The city is home to several
James Beard Award
The James Beard Foundation Awards are annual awards presented by the James Beard Foundation to recognize chefs, restaurateurs, authors and journalists in the United States. They are scheduled around James Beard's May 5 birthday. The media award ...
winners, gastropubs, and farm-to-table restaurants.
Madison is home to unique foods such as the large spring-rolls sold from the food carts on the Capital Square and State Street, particularly in warmer months. Other foods that are unique to the area are
cheese curds
Cheese curds are moist pieces of curdled milk, eaten either alone or as a snack, or used in prepared dishes. They are consumed throughout the northern United States and Canada. Notably, cheese curds are popular in Quebec, as part of the dish ...
, served either fried with dipping sauce, such as
ranch dressing
Ranch dressing is an American salad dressing usually made from buttermilk, salt, garlic, onion, mustard, herbs (commonly chives, parsley and dill), and spices (commonly pepper, paprika and ground mustard seed) mixed into a sauce based on ma ...
, or "squeaky" (not cooked, so called because of the squeaking sound they often make against the teeth when chewed), usually served without dipping sauce. Another popular food is
hot and spicy cheese bread, made by some Madison bakeries and available at farmer's markets around the city.
On Saturday mornings in the summer, the
Dane County Farmers' Market is held around the Capitol Square, the largest producer-only farmers' market in the country. A smaller version of this market is held on Martin Luther King Boulevard on Wednesdays during the summer. In late fall, this market moves indoors, first as the Holiday Market at the
Monona Terrace
Monona Terrace (officially the Monona Terrace Community and Convention Center) is a convention center on the shores of Lake Monona in Madison, Wisconsin.
Controversy
Originally designed by Wisconsin native Frank Lloyd Wright, it was first propo ...
. Later it becomes the Late Winter Market at the Madison Senior Center. This market attracts numerous vendors who sell fresh produce, meat, cheese, and other products.
Some restaurants in Madison follow the general Wisconsin supper club practice of restaurants serving "Friday fish fry, Saturday prime rib special, Sunday chicken dinner special."
The Great Taste of the Midwest craft beer festival, established in 1987 and the second-longest-running such event in North America, is held the second Saturday in August. The highly coveted tickets sell out within an hour of going on sale in May.
Architecture

Madison's architectural landmarks reflect a wide range of styles, from the densest cluster of
Native American effigy mounds
An effigy mound is a raised pile of earth built in the shape of a stylized animal, symbol, religious figure, human, or other figure. The Effigy Moundbuilder culture is primarily associated with the years 550-1200 CE during the Late Woodland Peri ...
in the United States to the
Beaux-Arts Wisconsin State Capitol
The Wisconsin State Capitol, located in Madison, Wisconsin, houses both chambers of the Wisconsin legislature along with the Wisconsin Supreme Court and the Office of the Governor. Completed in 1917, the building is the fifth to serve as the Wi ...
, the
Renaissance Revival
Renaissance Revival architecture (sometimes referred to as "Neo-Renaissance") is a group of 19th century architectural revival styles which were neither Greek Revival nor Gothic Revival but which instead drew inspiration from a wide range o ...
University of Wisconsin Memorial Union and the
Overture Center for the Arts, designed by
postmodern architect César Pelli. Madison is home to
eight buildings designed by influential Wisconsin-born
modern architect Frank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright (June 8, 1867 – April 9, 1959) was an American architect, designer, writer, and educator. He designed more than 1,000 structures over a creative period of 70 years. Wright played a key role in the architectural movements o ...
, more than any other city outside of the
Chicago metropolitan area
The Chicago metropolitan area, also colloquially referred to as Chicagoland, is a metropolitan area in the Midwestern United States. Encompassing 10,286 sq mi (28,120 km2), the metropolitan area includes the city of Chicago, its suburbs and h ...
. Wright, who spent much of his childhood in Madison and studied briefly at the
University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
, was based at
Taliesin
Taliesin ( , ; 6th century AD) was an early Brittonic poet of Sub-Roman Britain whose work has possibly survived in a Middle Welsh manuscript, the '' Book of Taliesin''. Taliesin was a renowned bard who is believed to have sung at the courts ...
in nearby
Spring Green for most of his career. His designs in Madison include
Monona Terrace
Monona Terrace (officially the Monona Terrace Community and Convention Center) is a convention center on the shores of Lake Monona in Madison, Wisconsin.
Controversy
Originally designed by Wisconsin native Frank Lloyd Wright, it was first propo ...
, the city's
lakefront convention center, as well as Wright's first
Usonia
Usonia () is a word that was used by American architect Frank Lloyd Wright to refer to the United States in general (in preference to ''America''), and more specifically to his vision for the landscape of the country, including the planning of ...
n house, the
Herbert and Katherine Jacobs First House
Herbert and Katherine Jacobs First House, commonly referred to as Jacobs I, is a single family home located at 441 Toepfer Avenue in Madison, Wisconsin, United States. Designed by noted American architect Frank Lloyd Wright, it was constructed i ...
,
which is a
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
.
The height of Madison's skyline is limited by a state law that restricts building heights in the downtown area. All buildings within one mile (1.6 km) of the
Wisconsin State Capitol
The Wisconsin State Capitol, located in Madison, Wisconsin, houses both chambers of the Wisconsin legislature along with the Wisconsin Supreme Court and the Office of the Governor. Completed in 1917, the building is the fifth to serve as the Wi ...
have to be less than above sea level to preserve the view of the building in most areas of the city. The
Wisconsin State Capitol
The Wisconsin State Capitol, located in Madison, Wisconsin, houses both chambers of the Wisconsin legislature along with the Wisconsin Supreme Court and the Office of the Governor. Completed in 1917, the building is the fifth to serve as the Wi ...
dome was modeled after the dome of the
U.S. Capitol
The United States Capitol, often called The Capitol or the Capitol Building, is the seat of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, which is formally known as the United States Congress. It is located on Capitol Hill at ...
, and was erected on the high point of the isthmus. Capitol Square is located in Madison's urban core.
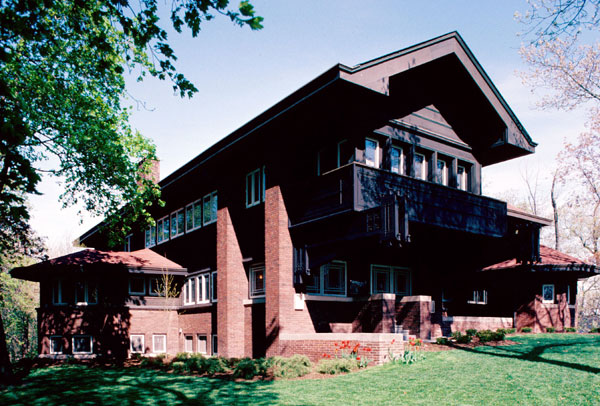
The
Harold C. Bradley House in the University Heights neighborhood was designed collaboratively by
Louis H. Sullivan and
George Grant Elmslie
George Grant Elmslie (February 20, 1869 – April 23, 1952) was a Scottish-born American Prairie School architect whose work is mostly found in the Midwestern United States. He worked with Louis Sullivan and later with William Gray Purcell as ...
in 1908–1910, and now serves as the
Sigma Phi Society
The Sigma Phi Society () was founded on the Fourth of March in the year 1827, on the campus of Union College as a part of the Union Triad in Schenectady, New York. It is the second Greek fraternal organization founded in the United States. chapter house.

The
Overture Center for the Arts, opened 2004, and the adjacent
Madison Museum of Contemporary Art
The Madison Museum of Contemporary Art (MMoCA), formerly known as the Madison Art Center, is an independent, non-profit art museum located in downtown Madison, Wisconsin.
MMoCA is dedicated to exhibiting, collecting, and preserving modern and co ...
, opened 2006, on State Street near the capitol were designed by architect
César Pelli. Within the Overture Center are Overture Hall, Capitol Theater, and The Playhouse. Its
modernist
Modernism is both a philosophy, philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western world, Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new fo ...
style, with simple expanses of glass framed by stone, was designed to complement nearby historic building facades.
The architectural firm
Claude and Starck Claude and Starck was an architectural firm in Madison, Wisconsin, at the turn of the twentieth century. The firm was a partnership of Louis W. Claude (1868-1951) and Edward F. Starck (1868-1947). Established in 1896, the firm dissolved in 1928. Th ...
designed over 175 Madison buildings, and many are still standing, including
Breese Stevens Field
Breese Stevens Municipal Athletic Field is a multi-purpose stadium in Madison, Wisconsin. Located eight blocks northeast of the Wisconsin State Capitol on the Madison Isthmus, it is the oldest extant masonry grandstand in Wisconsin.
The field ...
, Doty School (now condominiums), and many private residences.
Architecture on the University of Wisconsin campus includes many buildings designed or supervised by the firm
J. T. W. Jennings
John T. W. Jennings (Brooklyn, New York (state), 1856 to ?) was the Milwaukee Railroad's architect from 1885 to 1893, and was part-time supervising architect for the University of Wisconsin from 1899 to 1906. He contributed to many prominent campu ...
, such as the Dairy Barn and Agricultural Hall, or by architect
Arthur Peabody
Arthur Peabody (November 16, 1858 – September 6, 1942) was the campus architect for the University of Wisconsin from 1905 to 1915 and the state architect of Wisconsin from 1915 to 1938.
Peabody was born in Eau Claire, Wisconsin. He graduated fr ...
, such as the Memorial Union and Carillon Tower. Several campus buildings erected in the 1960s followed the
brutalist architectural style. In 2005, the university embarked on a major redevelopment at the east end of its campus. The plan called for the
razing of nearly a dozen 1950s to 1970s vintage buildings; the construction of new dormitories, administration, and classroom buildings; as well as the development of a new pedestrian mall extending to Lake Mendota. The campus now includes 12- to 14-story buildings.
Points of interest

*
Alliant Energy Center
Alliant Energy Center (formerly Dane County Coliseum) is a multi-building complex located in unincorporated Madison, Wisconsin. It comprises of greenspace and includes the Exhibition Hall, the 10,000-seat Veterans Memorial Coliseum, the Willo ...
/ Veteran's Memorial Coliseum and Exhibition Hall
*
Camp Randall Stadium
Camp Randall Stadium is an outdoor stadium in Madison, Wisconsin, located on the campus of the University of Wisconsin. It has been the home of the Wisconsin Badgers football team in rudimentary form since 1895, and as a fully functioning stadiu ...
*
Chazen Museum of Art
The Chazen Museum of Art is an art museum located at the University of Wisconsin–Madison in Madison, Wisconsin. The Chazen Museum of Art is accredited by the American Alliance of Museums.
History
Until 2005, the Museum was known regularly as th ...
*
Madison Museum of Contemporary Art
The Madison Museum of Contemporary Art (MMoCA), formerly known as the Madison Art Center, is an independent, non-profit art museum located in downtown Madison, Wisconsin.
MMoCA is dedicated to exhibiting, collecting, and preserving modern and co ...
*
Madison Children's Museum
*
Henry Vilas Zoo
Henry Vilas Zoo is a public zoo in Madison, Wisconsin, United States, that is accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA). Owned by Dane County, the zoo charges no admission or parking fees. It receives over 750,000 visitors annua ...
* The
Kohl Center
The Kohl Center is an arena and athletic center at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, United States. The building, which opened in 1998, is the home of the university's men's basketball and ice hockey teams, and the women's basketball team. ...
* Mifflin Street, home to the annual
Mifflin Street Block Party
The Mifflin Street Block Party is an annual block party celebration held on Mifflin Street in Madison, Wisconsin. The party is held on the last Saturday of April and attended predominantly by students attending the University of Wisconsin–Madis ...
*
Monona Terrace
Monona Terrace (officially the Monona Terrace Community and Convention Center) is a convention center on the shores of Lake Monona in Madison, Wisconsin.
Controversy
Originally designed by Wisconsin native Frank Lloyd Wright, it was first propo ...
Community and Convention Center designed by
Frank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright (June 8, 1867 – April 9, 1959) was an American architect, designer, writer, and educator. He designed more than 1,000 structures over a creative period of 70 years. Wright played a key role in the architectural movements o ...
*
Memorial Union
*
Olbrich Botanical Gardens
*
Overture Center
Overture Center for the Arts is a performing arts center and art gallery in Madison, Wisconsin, United States. The center opened on September 19, 2004, replacing the former Civic Center. In addition to several theaters, the center also houses the ...
for the Arts
* The
Gates of Heaven Synagogue
Shaarei Shamayim (Gates of Heaven) has been the name of two Jewish congregations in Madison, Wisconsin. The first, dating to the 19th century but no longer in existence, built what is now the eighth- oldest synagogue building still standing in the ...
in
James Madison Park is the
eighth-oldest-surviving synagogue building in the U.S.
*
State Street
* Williamson ("Willy") Street
*
Smart Studios
Smart Studios was a recording studio located in Madison, Wisconsin. It was set up in 1983 by Butch Vig and Steve Marker to produce local bands. The studio produced bands such as Killdozer, The Smashing Pumpkins, L7, Tad, and Nirvana. After in ...
,
Butch Vig
Bryan David "Butch" Vig (born August 2, 1955) is an American musician, songwriter, and record producer, best known as the drummer and co-producer of the alternative rock band Garbage and the producer of the diamond-selling Nirvana album ''Neve ...
and
Steve Marker's longtime studio where many notable alternative rock records of the 1990s and 2000s were recorded and/or produced
*
Unitarian Meeting House, another notable and tourable Frank Lloyd Wright structure, is adjacent to Madison city limits in suburban
Shorewood Hills
*
University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
*
University of Wisconsin–Madison Arboretum
The University of Wisconsin–Madison Arboretum is a teaching and research facility of the University of Wisconsin–Madison and the site of historic research in ecological restoration. In addition to its in Madison, Wisconsin (located about fou ...
*
University of Wisconsin Field House
*
UW–Madison Geology Museum
*
Wisconsin Historical Society
The Wisconsin Historical Society (officially the State Historical Society of Wisconsin) is simultaneously a state agency and a private membership organization whose purpose is to maintain, promote and spread knowledge relating to the history of N ...
/
Wisconsin Historical Museum
*
Wisconsin Veterans Museum
The Wisconsin Veterans Museum, located on Capitol Square in Madison, Wisconsin, United States, is dedicated to telling the stories of the veterans of the state of Wisconsin.
The museum is composed of two galleries that chronicle the history of Wis ...
*
Wisconsin State Capitol
The Wisconsin State Capitol, located in Madison, Wisconsin, houses both chambers of the Wisconsin legislature along with the Wisconsin Supreme Court and the Office of the Governor. Completed in 1917, the building is the fifth to serve as the Wi ...
*
Lakeshore Nature Preserve Lake Shore or Lakeshore may refer to:
* the shore of a lake
Places
* Lakeshore, Ontario, Canada
**Lakeshore (provincial electoral district)
* Lakeshore, California (disambiguation), the name of several places in the U.S.
* Lakeshore, Florida, U. ...
, a campus-associated preserve which features notable long peninsula called Picnic Point
Nightlife
Much of the city's nightlife is centralized to the downtown area which includes a variety of bars, restaurants, and performance venues.
State Street and the surrounding area are popular with tourists and University of Wisconsin-Madison students. Venues in the Capital Square neighborhood are popular with local young professionals and provide many
happy hour specials. Another center of nightlife is the Williamson (Willy) Street Neighborhood. Madison is also home to a number of
nightclub
A nightclub (music club, discothèque, disco club, or simply club) is an entertainment venue during nighttime comprising a dance floor, lightshow, and a stage for live music or a disc jockey (DJ) who plays recorded music.
Nightclubs gener ...
s,
gay bar
A gay bar is a drinking establishment that caters to an exclusively or predominantly lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) clientele; the term '' gay'' is used as a broadly inclusive concept for LGBT communities.
Gay bars once serv ...
s and live music venues. The
Mifflin Street Block Party
The Mifflin Street Block Party is an annual block party celebration held on Mifflin Street in Madison, Wisconsin. The party is held on the last Saturday of April and attended predominantly by students attending the University of Wisconsin–Madis ...
and the
Freakfest Halloween Party also attract thousands of partygoers.
Music
Madison's music scene covers a spectrum of musical culture.
Several venues offer live music nightly, spreading from the historic Barrymore Theatre and High Noon Saloon on the east side to small coffee houses and wine bars. The biggest headliners sometimes perform at the Orpheum Theatre, the
Overture Center
Overture Center for the Arts is a performing arts center and art gallery in Madison, Wisconsin, United States. The center opened on September 19, 2004, replacing the former Civic Center. In addition to several theaters, the center also houses the ...
,
Breese Stevens Field
Breese Stevens Municipal Athletic Field is a multi-purpose stadium in Madison, Wisconsin. Located eight blocks northeast of the Wisconsin State Capitol on the Madison Isthmus, it is the oldest extant masonry grandstand in Wisconsin.
The field ...
, the
Alliant Energy Center
Alliant Energy Center (formerly Dane County Coliseum) is a multi-building complex located in unincorporated Madison, Wisconsin. It comprises of greenspace and includes the Exhibition Hall, the 10,000-seat Veterans Memorial Coliseum, the Willo ...
, or the UW Theatre on campus. Other major rock and pop venues include the Majestic Theatre, the Sylvee, and The Bartell. During the summer, the Memorial Union Terrace on the University of Wisconsin campus, offers live music five nights a week. The Union is located on the shores of Lake Mendota.
Concerts on the Square is a weekly Madison tradition during the summer. On Wednesday evenings, the
Wisconsin Chamber Orchestra performs free concerts on the capitol's lawn, and people come to listen to the music while picnicking on the grass.
The
Madison Scouts Drum and Bugle Corps
The Madison Scouts Drum and Bugle Corps is a World Class competitive junior drum and bugle corps based in Madison, Wisconsin. The Madison Scouts were one of the thirteen founding member corps of Drum Corps International (DCI), and are a two-time ...
has provided youth aged 16–22 opportunities to perform across North America every summer since 1938. The
University of Wisconsin Marching Band is a local marching band.
Madison has a lively independent rock scene, and local independent record labels include Crustacean Records, Science of Sound, Kind Turkey Records, and Art Paul Schlosser Inc. A Dr. Demento and weekly live karaoke favorite is The Gomers, who have a Madison Mayoral Proclamation named after them. They have performed with fellow
Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
residents Les Paul and Steve Miller (musician), Steve Miller.
Madison is also home to other nationally known artists such as Paul Kowert of Punch Brothers, Mama Digdown's Brass Band, Clyde Stubblefield of Funky Drummer and James Brown fame, and musicians Roscoe Mitchell, Richard Davis (double bassist), Richard Davis, Ben Sidran, Sexy Ester and the Pretty Mama Sisters, Reptile Palace Orchestra, Ted Park, DJ Pain 1, Killdozer (band), Killdozer, Zola Jesus, VO5 (band), VO5, Caustic (band), Caustic, PHOX, Masked Intruder, and Lou & Peter Berryman, among others. The band Garbage (band), Garbage formed in Madison in 1994, and has sold 17 million albums.
In the summer Madison hosts many Festival, music festivals, including the Waterfront Festival, the Willy St. Fair, Atwood Summerfest, the Isthmus Jazz Festival, the Orton Park Festival, 94.1 WJJO's Band Camp, Greekfest, the WORT Block Party and the Sugar Maple Traditional Music Festival, and the Madison World Music Festival sponsored by the Wisconsin Union Theater (held at the Memorial Union Terrace and at the Willy St. Fair in September). Past festivals include the Madison Pop Festival and Forward Music Festival (2009–2010.) One of the latest additions is the La Fete de Marquette, Fête de Marquette, taking place around Bastille Day at various east side locations. This new festival celebrates French music, with a focus on Cajun influences. Madison also hosts an annual electronic music festival, Reverence, and the Folk Ball, a world music and Folk dance festival held annually in January. Madison is home to the LGBT, LBGTQA festival, Fruit Fest, celebrating queer culture and LGBT allies. Madison also plays host to the National Women's Music Festival.
UW-Madison also hosts the annual music and arts festival, Revelry, on campus at the Memorial Union each spring. The festival is put on by students for students as an end of the year celebration on campus.
Art
Art museums include the University of Wisconsin–Madison, UW–Madison's
Chazen Museum of Art
The Chazen Museum of Art is an art museum located at the University of Wisconsin–Madison in Madison, Wisconsin. The Chazen Museum of Art is accredited by the American Alliance of Museums.
History
Until 2005, the Museum was known regularly as th ...
(formerly the Elvehjem Museum), and the
Madison Museum of Contemporary Art
The Madison Museum of Contemporary Art (MMoCA), formerly known as the Madison Art Center, is an independent, non-profit art museum located in downtown Madison, Wisconsin.
MMoCA is dedicated to exhibiting, collecting, and preserving modern and co ...
, which annually organizes the Art Fair on the Square. Madison also has independent art studios, galleries, and arts organizations, with events such as Art Fair on the Square (Madison), Art Fair Off the Square. Other museums include
Wisconsin Historical Museum (run by the
Wisconsin Historical Society
The Wisconsin Historical Society (officially the State Historical Society of Wisconsin) is simultaneously a state agency and a private membership organization whose purpose is to maintain, promote and spread knowledge relating to the history of N ...
), the
Wisconsin Veterans Museum
The Wisconsin Veterans Museum, located on Capitol Square in Madison, Wisconsin, United States, is dedicated to telling the stories of the veterans of the state of Wisconsin.
The museum is composed of two galleries that chronicle the history of Wis ...
, and the
Madison Children's Museum.
Performing arts
The Madison Opera, the Madison Symphony Orchestra, Forward Theater Company, the
Wisconsin Chamber Orchestra, and the Madison Ballet are some of the professional resident companies of the
Overture Center
Overture Center for the Arts is a performing arts center and art gallery in Madison, Wisconsin, United States. The center opened on September 19, 2004, replacing the former Civic Center. In addition to several theaters, the center also houses the ...
for the Arts. The city is also home to a number of smaller performing arts organizations, including a group of theater companies that present in the Bartell Theatre, a former movie palace renovated into live theater spaces, and Opera for the Young, an opera company that performs for elementary school students across the Midwest. Music Theatre of Madison is a professional musical theater company that performs new and lesser-known musicals in a variety of venues. The Wisconsin Union Theater (a 1,300-seat theater) is home to seasonal attractions and is the main stage for Four Seasons Theatre, a community theater company specializing in musical theater, and other groups. The Young Shakespeare Players, a theater group for young people, performs uncut Shakespeare and George Bernard Shaw, George B. Shaw plays.
Community-based theater groups include Children's Theatre of Madison, Strollers Theatre, Madison Theatre Guild, the Mercury Players, and Broom Street Theater (which is no longer on Broom Street).
Madison has one comedy club, the Comedy Club on State (which has hosted the Madison's Funniest Comic competition every year since 2010), owned by the Paras family. Madison has other options for more alternative humor, featuring several improv groups, such as Atlas Improv Company, Monkey Business Institute, and open mic nights.
Madison is home to a large entertainment industry archive at the Wisconsin Center for Film and Theater Research, part of the
Wisconsin Historical Society
The Wisconsin Historical Society (officially the State Historical Society of Wisconsin) is simultaneously a state agency and a private membership organization whose purpose is to maintain, promote and spread knowledge relating to the history of N ...
.
Other cultural events
The Madison metro area has a higher percentage of gay couples than any other city in the area outside of Chicago and Minneapolis.
Madison was host to Rhythm and Booms, a large fireworks celebration coordinated to music. It began with a fly-over by General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon, F-16s from the local Wisconsin Air National Guard. This celebration was the largest fireworks display in the Midwest in length, number of shells fired, and the size of its annual budget. Effective 2015, the event location was changed to downtown and renamed Shake The Lake.
There are several cooperative organizations in the Madison area, ranging from grocery stores (such as the Willy Street Cooperative) to housing co-ops (such as Madison Community Cooperative and Nottingham Housing Cooperative) to worker cooperatives (including an engineering firm, a wholesale organic bakery and a cab company).
Every April, the Wisconsin Film Festival is held in Madison. This five-day event features films from a variety of genres shown in theaters across the city. The University of Wisconsin–Madison Arts Institute sponsors the Film Festival.
Madison is known for its unique official bird. In 2009, the Madison Common Council voted to name the plastic pink flamingo as the official city bird.
Sports

Madison is known for having its athletics fan base centered on the University of Wisconsin-Madison. In 2003, ''Sports Illustrated'' identified the city as one of the "best college sports towns" in the nation. In 2019, Sports Illustrated named Madison the greatest college football town in the nation.
The University of Wisconsin–Madison, UW–Madison teams play their home-field sporting events in venues in and around Madison. The Wisconsin Badgers football team plays at
Camp Randall Stadium
Camp Randall Stadium is an outdoor stadium in Madison, Wisconsin, located on the campus of the University of Wisconsin. It has been the home of the Wisconsin Badgers football team in rudimentary form since 1895, and as a fully functioning stadiu ...
where crowds of as many as 83,000 have attended games. The Wisconsin Badgers men's basketball and Wisconsin Badgers men's ice hockey teams play at the
Kohl Center
The Kohl Center is an arena and athletic center at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, United States. The building, which opened in 1998, is the home of the university's men's basketball and ice hockey teams, and the women's basketball team. ...
. Construction on the $76 million arena was completed in 1997. The Wisconsin Badgers women's ice hockey team plays at the LaBahn Arena. Some events are played at the county-owned
Alliant Energy Center
Alliant Energy Center (formerly Dane County Coliseum) is a multi-building complex located in unincorporated Madison, Wisconsin. It comprises of greenspace and includes the Exhibition Hall, the 10,000-seat Veterans Memorial Coliseum, the Willo ...
(formerly Dane County Memorial Coliseum) and the University-owned Wisconsin Field House.
In 2014, the Madison Capitols made their return to the Madison area following 19 years of dormancy. The Capitols play their home games at Bob Suter's Capitol Ice Arena following three years at
Alliant Energy Center
Alliant Energy Center (formerly Dane County Coliseum) is a multi-building complex located in unincorporated Madison, Wisconsin. It comprises of greenspace and includes the Exhibition Hall, the 10,000-seat Veterans Memorial Coliseum, the Willo ...
.
On May 17, 2018, it was announced that Forward Madison FC would become Madison's first professional soccer team, which plays at the historic
Breese Stevens Field
Breese Stevens Municipal Athletic Field is a multi-purpose stadium in Madison, Wisconsin. Located eight blocks northeast of the Wisconsin State Capitol on the Madison Isthmus, it is the oldest extant masonry grandstand in Wisconsin.
The field ...
.
Madison is home to the Madison Mallards, a college wood-bat summer baseball league team in the Northwoods League. They play in Warner Park on the city's north side from June to August.
Prominent sports teams
Former teams
The Madison Muskies, a Class A, Midwest League affiliate of the Oakland A's, left town in 1993 after 11 seasons. The Madison Hatters, another Class A, Midwest League team, played in Madison for only the 1994 season. The Madison Black Wolf, an independent Northern League (baseball, 1993–2010), Northern League franchise lasted five seasons (1996–2000), before decamping for Lincoln, Nebraska.
Parks and recreation

Parks
Madison has of park space, which is 13.5% of the city's total area. The city has 12.7 parks per 10,000 residents – more than any other city. Parks in the city include
James Madison Park, which has views of Lake Mendota; Frank W. Hoyt Park, which is listed on the National Register of Historic Places; Garner Park, where the Madison Opera holds an "Opera in the Park" event; and Warner Park, which is home to the stadium for the Madison Mallards baseball team.
Recreation
During the winter months, sports enthusiasts enjoy iceboat, ice-boating, ice skating, ice hockey, ice fishing, cross-country skiing, and snowkiting. During the rest of the year, outdoor recreation includes sailing on the local lakes, bicycling, and hiking.
Madison is known for its extensive biking infrastructure, with numerous bike paths and bike lanes throughout the city. Several of these bike paths connect to state trails, such as the Capital City State Trail, Military Ridge State Trail, and Badger State Trail. In addition to these bike paths, most city streets have designated bike lanes or are designated as bicycle boulevards, which give high priority to bicyclists. In 2015 Madison was awarded platinum level Bicycle Friendly Community designation from the League of American Bicyclists, one of only five cities in the US to receive this (highest) level.
Amateur sports
Madison has an active amateur sports scene, with ultimate (sport), ultimate, endurance sports, and soccer being common pastimes.
Madison has several active ultimate (sport), ultimate disc leagues organized through the nonprofit Madison Ultimate Frisbee Association. In 2013, the Madison Radicals, a professional ultimate frisbee team, debuted in the city.
Madison is home to several endurance sports racing events, such as the Crazylegs Classic, the CrossFit Games, Paddle and Portage, the Mad City Marathon, and Ironman triathlon, Ironman Wisconsin, which attracts over 45,000 spectators.
The Wisconsin Rugby Club, the 1998 and 2013 USA Rugby Division II National Champions, and the Wisconsin Women's Rugby Football Club are the state's only Division I women's rugby team. All Madison rugby teams play within the Wisconsin Rugby Football Union—the Midwest Rugby Union and USA Rugby.
The Madison Curling Club was founded in 1921. Team Spatola of the Madison Curling Club won the 2014 Women's US National Championship. Team members are: Nina Spatola, Becca Hamilton, Tara Peterson, Sophie Brorson.
Madison's Gaelic sports club hosts a hurling team organized as Hurling Club of Madison, The Hurling Club of Madison and a Gaelic football club with men's and women's teams.
The roller derby league, Madison Roller Derby, was formed in Madison in 2004 and is a member of the Women's Flat Track Derby Association. Madison is also home to Wisconsin United Roller Derby, a member league of the Men's Roller Derby Association.
The adult women's ice hockey teams (Thunder, Lightning, Freeze, UW–B and C teams) play in the Women's Central Hockey League.
The Blackhawk Ski Club, formed in 1947, provides ski jumping, cross country skiing and alpine skiing. The club's programs have produced several Olympic ski jumpers, two Olympic ski jumping coaches and one Olympic ski jumping director. The club had the first Nordic ski facility with lighted night jumping.
As of 2017, the CrossFit Games have been held at the
Alliant Energy Center
Alliant Energy Center (formerly Dane County Coliseum) is a multi-building complex located in unincorporated Madison, Wisconsin. It comprises of greenspace and includes the Exhibition Hall, the 10,000-seat Veterans Memorial Coliseum, the Willo ...
. After seven years at the Dignity Health Sports Park, StubHub Center in Carson, California, the Games moved to Madison for an initial three-year contract. CrossFit chose the multi-building entertainment venue, which encompasses , after posting a national request for proposals.
Government
City voters have supported the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party in national elections in the last half-century, and a liberal and progressive majority is generally elected to the city council. Detractors often refer to Madison as "77 square miles surrounded by reality", a phrase coined by former Wisconsin Republican governor Lee S. Dreyfus, while campaigning in 1978.
In 2013, there was a motion in the city council to turn Dreyfus' humor into the official city "punchline," but it was voted down by the city council.
The city's voters are generally much more liberal than voters in the rest of Wisconsin. For example, 76% of Madison voters voted against a 2006 state Wisconsin Referendum 1, constitutional amendment to ban gay marriage, even though the ban passed statewide with 59% of the vote.
In 1992, a local third party, Progressive Dane, was founded. City policies supported in the Progressive Dane platform have included an inclusionary zoning ordinance, later abandoned by the mayor and a majority of the city council, and a city minimum wage. The party holds several seats on the Madison City Council and Dane County Board of Supervisors, and is aligned variously with the Democratic and Green parties.
Madison has a mayor-council system of government. Madison's Madison Common Council, city council, known as the Madison Common Council, Common Council, consists of 20 members, one from each district. The mayor Mayoral elections in Madison, Wisconsin, is elected in a citywide vote.
Madison is the heart of in the United States House of Representatives, represented by Mark Pocan (D). Melissa Agard (D) and Kelda Roys (D) represent Madison in the Wisconsin State Senate, and Jimmy P. Anderson (D), Samba Baldeh (D), Francesca Hong (D), Shelia Stubbs, Sheila Stubbs (D), and Lisa Subeck (D) represent Madison in the Wisconsin State Assembly.
Ron Johnson (Wisconsin politician), Ron Johnson (R) and Tammy Baldwin (D) represent Madison, and all of Wisconsin, in the United States Senate. Baldwin is a Madison resident; she represented the 2nd from 1999 to 2013 before handing it to Pocan.
Election results
Education
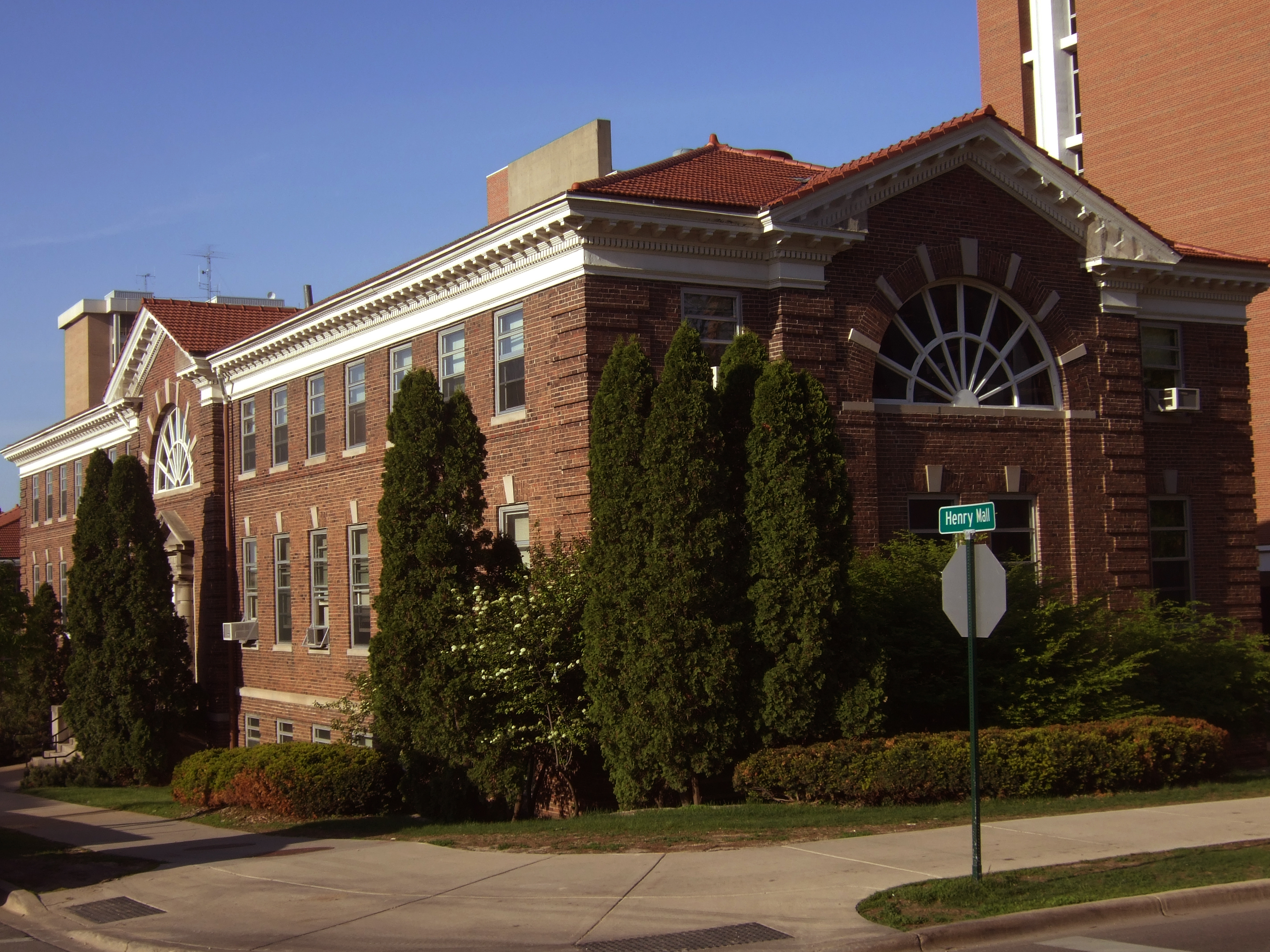

The Madison Metropolitan School District serves the city while a variety of other districts serve the surrounding area. With an enrollment of approximately 25,000 students in 46 schools, it is the second largest school district in Wisconsin behind the Milwaukee School District. The five public high schools are Vel Phillips Memorial High School, Vel Phillips Memorial, Madison West, Madison East High School, Madison East, La Follette High School, La Follette, and Malcolm Shabazz City High School, an alternative school.
Among private church-related high schools are Abundant Life Christian School, Edgewood High School (Wisconsin), Edgewood High School, near the Edgewood College campus, and St. Ambrose Academy, a Catholic school offering grades 6 through 12. Madison Country Day School is a private high school with no religious affiliation.
The city is home to the
University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
, Edgewood College and Madison Area Technical College, giving the city a post-secondary student population of nearly 55,000. The University of Wisconsin accounts for the vast majority of students, with an enrollment of roughly 44,000, of whom 31,750 are undergraduates.
Additional degree programs are available through satellite campuses of Cardinal Stritch University, Concordia University-Wisconsin, Globe University, Lakeland College (Wisconsin), Lakeland College, the University of Phoenix, and Upper Iowa University. Madison also has a non-credit learning community with multiple programs and many private businesses also offering classes.
Media
Print
Madison is home to an extensive and varied number of print publications, reflecting the city's role as the state capital and its diverse political, cultural and academic population. The ''Wisconsin State Journal'' (weekday circulation: ~95,000; Sundays: ~155,000) is published in the mornings, while its sister publication, ''The Capital Times'' (Thursday supplement to the Journal) is published online daily, with two printed editions a week. Though jointly operated under the name Capital Newspapers, the ''Journal'' is owned by the national chain Lee Enterprises, and the ''Times'' is independently owned. ''Wisconsin State Journal'' is the descendant of the ''Wisconsin Express'', a paper founded in the Wisconsin Territory in 1839. ''The Capital Times'' was founded in 1917 by William T. Evjue, a business manager for the ''State Journal'' who disagreed with that paper's editorial criticisms of Wisconsin Republican Senator Robert M. La Follette, Sr. for his opposition to U.S. entry into World War I.
The free weekly alternative newspaper ''Isthmus (newspaper), Isthmus'' (weekly circulation: ~65,000) was founded in Madison in 1976. ''
The Onion
''The Onion'' is an American digital media company and newspaper organization that publishes satire, satirical articles on international, national, and local news. The company is based in Chicago but originated as a weekly print publication on ...
'', a satirical weekly, was founded in Madison in 1988 and published from there until it moved to New York in 2001. Two student newspapers are published during the academic year, ''The Daily Cardinal'' (Mon–Fri circulation: ~10,000) and ''The Badger Herald'' (Mon–Fri circulation: ~16,000). Other specialty print publications focus on local music, politics and sports, including ''The Capital City Hues'',
[Madison Public Library]
News and Media
[Jordan S. Gaines.]
". ''The Capital Times'', July 20, 2015. ''The Madison Times'',
''Madison Magazine'', ''The Simpson Street Free Press'', ''Umoja Magazine'',
and fantasy-sports web site RotoWire, RotoWire.com. Local community blogs include Ann Althouse, Althouse and dane101.
Madison is associated with Robert M. La Follette, Sr., "Fighting Bob" La Follette and the Progressive Party (United States, 1924), Progressive movement. La Follette's magazine, ''The Progressive'', founded in 1909, is still published in Madison. It is a Far-left politics, far left-wing periodical that may be best known for the attempt of the U.S. government in 1979 to suppress one of its articles before publication. The magazine eventually prevailed in the landmark First Amendment case, ''United States v. The Progressive, Inc.'' During the 1970s, there were two radical weeklies published in Madison, known as ''TakeOver'' and ''Free for All'', as well as a Madison edition of the ''Bugle (newspaper), Bugle-American'' underground newspaper.
Radio
Madison has three large media companies that own the majority of the commercial radio stations within the market. These companies consist of iHeartMedia, Entercom Communications, and Mid-West Family Broadcasting as well as other smaller broadcasters. Madison is home to Mid-West Family Broadcasting, which is an independently owned broadcasting company that originated and is headquartered in Madison. Mid-West Family owns radio stations throughout the state and the Midwestern United States, Midwest.
Madison hosts two volunteer-operated and community-oriented radio stations, WORT and WSUM. WORT Community Radio (89.9 FM), founded in 1975, is one of the oldest volunteer-powered radio stations in the United States. A listener-sponsored community radio station, WORT offers locally produced diverse music and talk programming. WSUM (91.7 FM) is a free-form student radio station programmed and operated almost entirely by students.
Madison's Wisconsin Public Radio station, WHA (AM), WHA, was one of the first radio stations in the nation to begin broadcasting. Public radio programs that originate at the WPR studios include ''Michael Feldman's Whad'Ya Know?'', ''Zorba Pastor On Your Health'', ''To the Best of Our Knowledge'',''Calling All Pets'', and the longest running radio program in America, ''Chapter a Day''.
WXJ-87 is the NOAA Weather Radio, NOAA Weather Radio All Hazards station on Madison's west side, with broadcasts originating from the National Weather Service in Sullivan, Wisconsin.
TV
Madison has six commercial stations, two public television stations and two religious stations. The commercial stations consist of WISC-TV "News 3 Now" (CBS), WMTV "NBC 15" (NBC), WKOW-TV "27 News" (American Broadcasting Company, ABC), WMSN-TV "FOX 47" (Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox), WIFS (TV), WIFS "Wisconsin's 57" (Ion Television, Ion) and WZCK-LD. Religious stations consist of WMWD-LD (Daystar (TV network), Daystar) and W23BW-D (Three Angels Broadcasting Network, 3ABN). Madison has two public television stations: WHA-TV, which is owned by the University of Wisconsin–Extension and airs throughout the state with the exception of
Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee ...
, and Madison City Channel, which is owned and operated by the City of Madison covering city governmental affairs.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Madison is served by the Dane County Regional Airport, which serves nearly 2.2 million passengers annually. Most major general aviation operations take place at Morey Field in Middleton, WI, Middleton from Madison's city center. Madison Metro operates bus routes throughout the city and to some neighboring suburbs. Madison has four taxicab companies (Union, Badger, Madison, and Green), and several companies provide specialized transit for individuals with disabilities. Several carsharing services are also available in Madison, including Community Car, a locally owned company, and U-Haul subsidiary Uhaul Car Share.
Starting from the last decades of the 20th century, Madison has been among the leading cities for bicycling as a form of transportation, with about 3% of working residents pedaling on their journey to work. The share of Madison workers who bicycled to work increased to 5.3% by 2014. The 2016 survey by
American Community Survey indicated that 65.7% of working Madison residents commuted by driving alone, 6.7% carpooled, 8.6% used public transportation, and 8.5% walked. About 6% used all other forms of transportation, including bicycles, motorcycles, and taxis. About 4.5% worked at home. According to Walk Score, Madison has an overall 48 out of 100 in walkability, making it a "largely car dependent city", and a 65 out of 100 for bicycling. However, the State-Langdon and Downtown areas scored significantly higher, 94 and 93 for walkability, and 87 and 89 for biking, respectively.
In 2015, 11.2% of Madison households were without a car, which was unchanged in 2016. The national average was 8.7% in 2016. Madison averaged 1.5 cars per household in 2016, compared to a national average of 1.8 per household.
Railways
Passenger train service between Madison and
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
on the ''Sioux (train), Sioux'' and the ''Varsity (train), Varsity'' was provided by the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (Milwaukee Road) until 1971. The Chicago and North Western Railway also provided service to the east side of Madison, ending in 1965. A high-speed rail route from Chicago through
Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee ...
and Madison to Minneapolis–Saint Paul, Minnesota, was proposed as part of the Chicago Hub Network, Midwest Regional Rail Initiative. Funding for the railway connecting Madison to Milwaukee was approved in January 2010, but then Governor-elect
Scott Walker's opposition to the project led the Federal Railroad Administration to retract the $810 million in funding and reallocate it to projects in other states. Plans to establish Amtrak service within the city of Madison were revived in 2021, pending federal legislative action, Madison is again slated to receive a rail link to Chicago via Milwaukee, likely with an expansion of the Hiawatha Service. Longer-term plans include a connection to the Twin Cities, potentially via Eau Claire; however, this has not been officially established at this time. The city is served by the Columbus station, Columbus Amtrak station to the northeast with once daily trains to Chicago Union Station, Chicago, Portland Union Station, Portland, OR and King Street Station, Seattle, WA and stops in between via the Empire Builder route. While located outside of the city proper, the station is listed on Amtrak timetables as Madison's official stop in addition to thruway bus services within the city.
Railroad freight services are provided to Madison by the Wisconsin and Southern Railroad (WSOR) and the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP) under its legal trading alias, the Soo Line Railroad.
Buses
In addition to public transportation, regional buses connect Madison to
Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee ...
,
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
, Minneapolis–Saint Paul, and many other communities. Badger Bus, which connects Madison and Milwaukee, runs several trips daily. Greyhound Lines, a nationwide bus company, serves Madison on its Chicago, Milwaukee, and Minneapolis–Saint Paul route. Van Galder Bus Company, a subsidiary of Coach USA, provides transportation through Rockford, Illinois, Rockford to Chicago—stopping at Union Station (Chicago), Union Station, O'Hare International Airport, O'Hare Airport, and Chicago Midway International Airport, Midway Airport. Jefferson Lines provides transportation to Minneapolis–Saint Paul via La Crosse, Wisconsin, La Crosse. Megabus (North America), Megabus provides limited-stop service to Chicago and Minneapolis–Saint Paul. Lamers Bus Lines has once-daily trips from Madison to Wausau, Wisconsin, Wausau, Dubuque, Iowa, Dubuque, and
Green Bay.
Highways
Interstate 39 (I-39), Interstate 90 in Wisconsin, I-90 and Interstate 94, I-94 run along the far east side of the city, connecting to Janesville, Wisconsin, Janesville to the south, Milwaukee, Wisconsin, Milwaukee to the east, and to Portage, Wisconsin, Portage, La Crosse, Wisconsin, La Crosse, Eau Claire, Wisconsin, Eau Claire, and Wausau, Wisconsin, Wausau heading north and northwest.
U.S. Route 151, U.S. Highway 151 (US 151) runs through downtown and serves as the main thoroughfare through the northeast (as Washington Avenue) and south-central parts (as Park Street) of the city, connecting Madison with Dubuque, Iowa to the southwest and Fond du Lac, Wisconsin, Fond du Lac and Manitowoc, Wisconsin, Manitowoc to the northeast.
U.S. Route 12 in Wisconsin, US 12, frequently referred to by locals as the Beltline, is a six- to eight-lane freeway serving the south and west sides of Madison and is the main link from the western suburb of
Middleton to Cambridge, Wisconsin, Cambridge. Southeast of the area, US 12 connects to Lake Geneva, Wisconsin, Lake Geneva, and going northwest, it heads to Wisconsin Dells.
U.S. Route 18 in Wisconsin, US 18 is also a component highway of the Beltine, continuing south along US 151 and east towards Waukesha, Wisconsin, Waukesha and Milwaukee.
Public safety
Madison Police Department
The Madison Police Department is the law enforcement agency in the city led by Police Chief Shon Barnes. The department has six districts: Central, East, North, South, West and Midtown District
Special units in the police department include:
* K9 Unit
* Crime Scene Unit
* Forensic Unit
* Narcotics and Gangs Task Force
* Parking Enforcement
* Traffic Enforcement Safety Team
* S.W.A.T Team
* Special Events Team
* C.O.P.S (Safety Education)
* Mounted Patrol
* Crime Stoppers
* Amigos en Azul
The Madison Police Department was criticized for absolving Officer Steve Heimsness of any wrongdoing in the November 2012 shooting death of an unarmed man, Paul Heenan. The department's actions resulted in community protests, including demands that the shooting be examined and reviewed by an independent investigative body. WisconsinWatch.org called into question the MPD's facts and findings, stating that the use of deadly force by Heimsness was unwarranted. There were calls for an examination of the Madison Police Department's rules of engagement and due process for officers who use lethal force in the line of duty.
Community criticism of the department's practices resurfaced after MPD officer Matt Kenny Shooting of Tony Robinson, shot Tony Robinson, an unarmed man. The shooting was particularly controversial given the context of the ongoing Black Lives Matter movement. Due to new Wisconsin state legislation that addresses the mechanisms under which officer-on-civilian violence is handled by state prosecutors, proceedings were handed over to a special unit of the Wisconsin Department of Justice in Madison. On March 27, 2015, the state concluded its investigation and gave its findings to Ismael Ozanne, the district attorney of Dane County. On May 12, 2015, Ozanne determined that the shooting was justified self-defense.
Madison Fire Department
The Madison Fire Department (MFD) provides fire protection and emergency medical services to the city. The MFD operates out of 14 fire stations, with a fleet of 12 engines, 5 ladders, 2 rescue squads, 2 hazmat units, a lake rescue team, and 9 ambulances. The MFD also provides mutual aid to surrounding communities.
Notable people
Nicknames
Over the years, Madison has acquired nicknames and slogans that include:
* Mad City
* Madtown
* The Berkeley, California, Berkeley of the Midwest
* 77 square miles surrounded by reality
* Four Lakes City
*People's Republic of Madison
Sister cities
Madison is Sister city, twinned with:
* Arcatao, El Salvador (1986)
* Bahir Dar, Ethiopia (2019)
* Camagüey, Cuba (1994)
* Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany (1988)
* Kanifing (Gambia), Kanifing, Gambia (2016)
* Mantua, Italy (2001)
* Obihiro, Hokkaido, Obihiro, Japan (2003)
* Tepatitlán, Tepatitlán de Morelos, Mexico (2012)
* Vilnius, Lithuania (1988)
See also
* List of tallest buildings in Madison
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
* Bates, Tom, ''Rads: The 1970 Bombing of the Army Math Research Center at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and Its Aftermath'' (1993)
* Durrie, Daniel S.
A History of Madison, the Capital of Wisconsin; Including the Four Lake Country'. Madison: Atwood & Culver, 1874.
*
Madison, Dane County and Surrounding Towns'. Madison: Wm. J. Park & Co., 1877.
* David Maraniss, Maraniss, David, ''They Marched Into Sunlight: War and Peace Vietnam and America October 1967'' (2003) (about the Dow Chemical protest, and a battle in Vietnam that took place the previous day)
* Mollenhoff, David V. ''Madison, a history of the formative years'' (Univ of Wisconsin Press, 2003).
* Nolen, John.
Madison: a Model City'. Boston: 1911.
* Reuben Gold Thwaites, Thwaites, Reuben Gold.
The Story of Madison'. J. N. Purcell, 1900.
External links
*
Greater Madison Convention & Visitors Bureau* Th
State of Wisconsin Collectionpresented by th
UW Digital Collections Centerincludes digital resources on Madison, including:
*
Historical County Plat Maps from South Central Wisconsin and Early Madison City Directories** Sanborn fire insurance maps
18851892189819021908
{{Authority control
Madison, Wisconsin,
Cities in Wisconsin
Cities in Dane County, Wisconsin
Isthmuses of the United States
Populated places established in 1836
County seats in Wisconsin
Madison, Wisconsin, metropolitan statistical area
1836 establishments in Wisconsin Territory

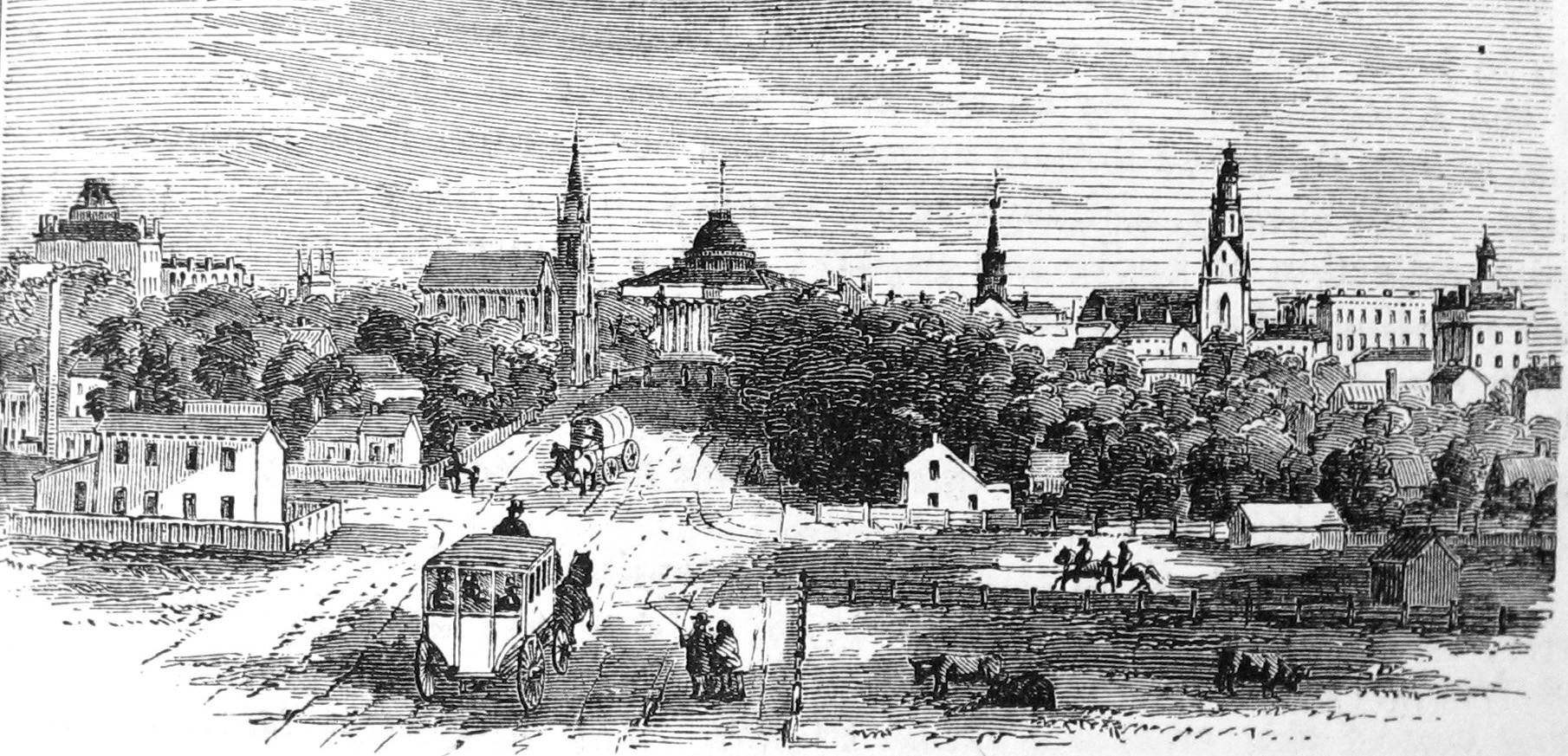
 The cornerstone for the Wisconsin capitol was laid in 1837, and the legislature first met there in 1838. On October 9, 1839, Kintzing Prichett registered the
The cornerstone for the Wisconsin capitol was laid in 1837, and the legislature first met there in 1838. On October 9, 1839, Kintzing Prichett registered the  In the 1960s and 1970s, the Madison
In the 1960s and 1970s, the Madison 
 Madison is located in the center of Dane County in south-central Wisconsin, west of
Madison is located in the center of Dane County in south-central Wisconsin, west of  Madison is the larger principal city of the
Madison is the larger principal city of the  Madison's architectural landmarks reflect a wide range of styles, from the densest cluster of Native American
Madison's architectural landmarks reflect a wide range of styles, from the densest cluster of Native American  The Overture Center for the Arts, opened 2004, and the adjacent
The Overture Center for the Arts, opened 2004, and the adjacent  *
*  Madison is known for having its athletics fan base centered on the University of Wisconsin-Madison. In 2003, ''Sports Illustrated'' identified the city as one of the "best college sports towns" in the nation. In 2019, Sports Illustrated named Madison the greatest college football town in the nation.
The University of Wisconsin–Madison, UW–Madison teams play their home-field sporting events in venues in and around Madison. The Wisconsin Badgers football team plays at
Madison is known for having its athletics fan base centered on the University of Wisconsin-Madison. In 2003, ''Sports Illustrated'' identified the city as one of the "best college sports towns" in the nation. In 2019, Sports Illustrated named Madison the greatest college football town in the nation.
The University of Wisconsin–Madison, UW–Madison teams play their home-field sporting events in venues in and around Madison. The Wisconsin Badgers football team plays at  The Madison Metropolitan School District serves the city while a variety of other districts serve the surrounding area. With an enrollment of approximately 25,000 students in 46 schools, it is the second largest school district in Wisconsin behind the Milwaukee School District. The five public high schools are Vel Phillips Memorial High School, Vel Phillips Memorial, Madison West, Madison East High School, Madison East, La Follette High School, La Follette, and Malcolm Shabazz City High School, an alternative school.
Among private church-related high schools are Abundant Life Christian School, Edgewood High School (Wisconsin), Edgewood High School, near the Edgewood College campus, and St. Ambrose Academy, a Catholic school offering grades 6 through 12. Madison Country Day School is a private high school with no religious affiliation.
The city is home to the
The Madison Metropolitan School District serves the city while a variety of other districts serve the surrounding area. With an enrollment of approximately 25,000 students in 46 schools, it is the second largest school district in Wisconsin behind the Milwaukee School District. The five public high schools are Vel Phillips Memorial High School, Vel Phillips Memorial, Madison West, Madison East High School, Madison East, La Follette High School, La Follette, and Malcolm Shabazz City High School, an alternative school.
Among private church-related high schools are Abundant Life Christian School, Edgewood High School (Wisconsin), Edgewood High School, near the Edgewood College campus, and St. Ambrose Academy, a Catholic school offering grades 6 through 12. Madison Country Day School is a private high school with no religious affiliation.
The city is home to the