Machine Fault Diagnostics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fault detection, isolation, and recovery (FDIR) is a subfield of
 In model-based FDI techniques some model of the system is used to decide about the occurrence of fault. The system model may be
In model-based FDI techniques some model of the system is used to decide about the occurrence of fault. The system model may be
 Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are among the most mature and widely used mathematical classification algorithms in fault detection and diagnosis. ANNs are well-known for their efficient self-learning capabilities of the complex relations (which generally exist inherently in fault detection and diagnosis problems) and are easy to operate. Another advantage of ANNs is that they perform automatic feature extraction by allocating negligible weights to the irrelevant features, helping the system to avoid dealing with another feature extractor. However, ANNs tend to over-fit the training set, which will have consequences of having poor validation accuracy on the validation set. Hence, often, some regularization terms and prior knowledge are added to the ANN model to avoid over-fiting and achieve higher performance. Moreover, properly determining the size of the hidden layer needs an exhaustive parameter tuning, to avoid poor approximation and generalization capabilities.
In general, different SVMs and ANNs models (i.e. Back-Propagation Neural Networks and Multi-Layer Perceptron) have shown successful performances in the fault detection and diagnosis in industries such as
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are among the most mature and widely used mathematical classification algorithms in fault detection and diagnosis. ANNs are well-known for their efficient self-learning capabilities of the complex relations (which generally exist inherently in fault detection and diagnosis problems) and are easy to operate. Another advantage of ANNs is that they perform automatic feature extraction by allocating negligible weights to the irrelevant features, helping the system to avoid dealing with another feature extractor. However, ANNs tend to over-fit the training set, which will have consequences of having poor validation accuracy on the validation set. Hence, often, some regularization terms and prior knowledge are added to the ANN model to avoid over-fiting and achieve higher performance. Moreover, properly determining the size of the hidden layer needs an exhaustive parameter tuning, to avoid poor approximation and generalization capabilities.
In general, different SVMs and ANNs models (i.e. Back-Propagation Neural Networks and Multi-Layer Perceptron) have shown successful performances in the fault detection and diagnosis in industries such as
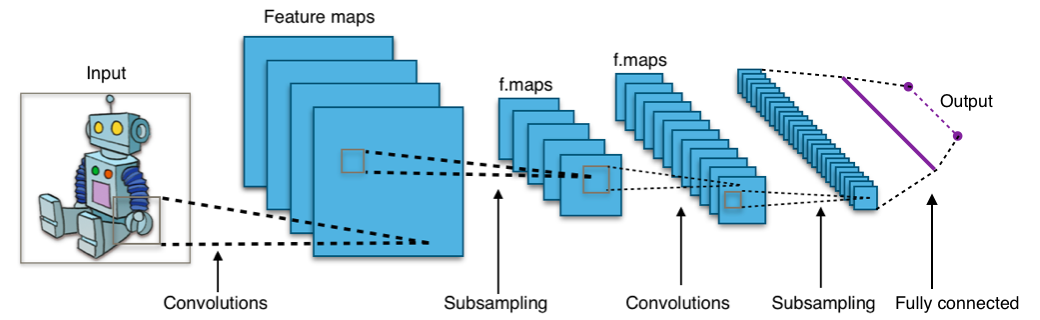 With the research advances in ANNs and the advent of deep learning algorithms using deep and complex layers, novel classification models have been developed to cope with fault detection and diagnosis.
Most of the shallow learning models extract a few feature values from signals, causing a
With the research advances in ANNs and the advent of deep learning algorithms using deep and complex layers, novel classification models have been developed to cope with fault detection and diagnosis.
Most of the shallow learning models extract a few feature values from signals, causing a
control engineering
Control engineering or control systems engineering is an engineering discipline that deals with control systems, applying control theory to design equipment and systems with desired behaviors in control environments. The discipline of controls o ...
which concerns itself with monitoring a system, identifying when a fault has occurred, and pinpointing the type of fault and its location. Two approaches can be distinguished: A direct pattern recognition of sensor readings that indicate a fault and an analysis of the discrepancy between the sensor readings and expected values, derived from some model. In the latter case, it is typical that a fault is said to be detected if the discrepancy or ''residual'' goes above a certain threshold. It is then the task of fault isolation to categorize the type of fault and its location in the machinery. Fault detection and isolation (FDI) techniques can be broadly classified into two categories. These include model-based FDI and signal processing based FDI.
Model-based FDI
 In model-based FDI techniques some model of the system is used to decide about the occurrence of fault. The system model may be
In model-based FDI techniques some model of the system is used to decide about the occurrence of fault. The system model may be mathematical
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
or knowledge based. Some of the model-based FDI techniques include observer-based approach, parity-space approach, and parameter identification based methods. There is another trend of model-based FDI schemes, which is called set-membership methods. These methods guarantee the detection of fault under certain conditions. The main difference is that instead of finding the most likely model, these techniques omit the models, which are not compatible with data.
The example shown in the figure on the right illustrates a model-based FDI technique for an aircraft elevator reactive controller through the use of a truth table and a state chart. The truth table defines how the controller reacts to detected faults, and the state chart defines how the controller switches between the different modes of operation (passive, active, standby, off, and isolated) of each actuator. For example, if a fault is detected in hydraulic system 1, then the truth table sends an event to the state chart that the left inner actuator should be turned off. One of the benefits of this model-based FDI technique is that this reactive controller can also be connected to a continuous-time model of the actuator hydraulics, allowing the study of switching transients.
Signal processing based FDI
In signal processing based FDI, some mathematical or statistical operations are performed on the measurements, or some neural network is trained using measurements to extract the information about the fault. A good example of signal processing based FDI is time domain reflectometry where a signal is sent down a cable or electrical line and the reflected signal is compared mathematically to original signal to identify faults. Spread Spectrum Time Domain Reflectometry, for instance, involves sending down a spread spectrum signal down a wire line to detect wire faults. Several clustering methods have also been proposed to identify the novel fault and segment a given signal into normal and faulty segments.Machine fault diagnosis
Machine fault diagnosis is a field ofmechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, an ...
concerned with finding faults arising in machines. A particularly well developed part of it applies specifically to rotating machinery, one of the most common types encountered. To identify the most probable faults leading to failure, many methods are used for data collection, including vibration
Vibration is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. The word comes from Latin ''vibrationem'' ("shaking, brandishing"). The oscillations may be periodic, such as the motion of a pendulum—or random, su ...
monitoring, thermal imaging
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared i ...
, oil particle analysis, etc. Then these data are processed utilizing methods like spectral analysis, wavelet analysis, wavelet transform, short term Fourier transform, Gabor Expansion, Wigner-Ville distribution (WVD), cepstrum, bispectrum, correlation method, high resolution spectral analysis, waveform analysis (in the time domain, because spectral analysis usually concerns only frequency distribution and not phase information) and others. The results of this analysis are used in a root cause failure analysis in order to determine the original cause of the fault. For example, if a bearing fault is diagnosed, then it is likely that the bearing was not itself damaged at installation, but rather as the consequence of another installation error (e.g., misalignment) which then led to bearing damage. Diagnosing the bearing's damaged state is not enough for precision maintenance purposes. The root cause needs to be identified and remedied. If this is not done, the replacement bearing will soon wear out for the same reason and the machine will suffer more damage, remaining dangerous. Of course, the cause may also be visible as a result of the spectral analysis undertaken at the data-collection stage, but this may not always be the case.
The most common technique for detecting faults is the time-frequency analysis technique. For a rotating machine, the rotational speed of the machine (often known as the RPM
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
), is not a constant, especially not during the start-up and shutdown stages of the machine. Even if the machine is running in the steady state, the rotational speed will vary around a steady-state mean value, and this variation depends on load and other factors. Since sound and vibration signals obtained from a rotating machine are strongly related to its rotational speed, it can be said that they are time-variant signals in nature. These time-variant features carry the machine fault signatures. Consequently, how these features are extracted and interpreted is important to research and industrial applications.
The most common method used in signal analysis is the FFT
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in the ...
, or Fourier transform. The Fourier transform and its inverse counterpart offer two perspectives to study a signal: via the time domain or via the frequency domain. The FFT
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in the ...
-based spectrum of a time signal shows us the existence of its frequency contents. By studying these and their magnitude or phase relations, we can obtain various types of information, such as harmonics
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the '' fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', ...
, sidebands, beat frequency
In acoustics, a beat is an interference pattern between two sounds of slightly different frequencies, ''perceived'' as a periodic variation in volume whose rate is the difference of the two frequencies.
With tuning instruments that can produce ...
, bearing fault frequency and so on. However, the FFT
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in the ...
is only suitable for signals whose frequency contents do not change over time; however, as mentioned above, the frequency contents of the sound and vibration signals obtained from a rotating machine are very much time-dependent. For this reason, FFT
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in the ...
-based spectra are unable to detect how the frequency contents develop over time. To be more specific, if the RPM
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
of a machine is increasing or decreasing during its startup or shutdown period, its bandwidth in the FFT spectrum will become much wider than it would be simply for the steady state. Hence, in such a case, the harmonics are not so distinguishable in the spectrum.
The time frequency approach for machine fault diagnosis can be divided into two broad categories: linear methods and the quadratic methods. The difference is that linear transforms can be inverted to construct the time signal, thus, they are more suitable for signal processing, such as noise reduction and time-varying filtering. Although the quadratic method describes the energy distribution of a signal in the joint time frequency domain, which is useful for analysis, classification, and detection of signal features, phase information is lost in the quadratic time-frequency representation; also, the time histories cannot be reconstructed with this method.
The short-term Fourier transform ( STFT) and the Gabor transform The Gabor transform, named after Dennis Gabor, is a special case of the short-time Fourier transform. It is used to determine the sinusoidal frequency and phase content of local sections of a signal as it changes over time. The function to be tran ...
are two algorithms commonly used as linear time-frequency methods. If we consider linear time-frequency analysis to be the evolution of the conventional FFT
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in the ...
, then quadratic time frequency analysis would be the power spectrum counterpart. Quadratic algorithms include the Gabor spectrogram, Cohen's class and the adaptive spectrogram. The main advantage of time frequency analysis is discovering the patterns of frequency changes, which usually represent the nature of the signal. As long as this pattern is identified the machine fault associated with this pattern can be identified. Another important use of time frequency analysis is the ability to filter out a particular frequency component using a time-varying filter.
Robust fault diagnosis
In practice, model uncertainties and measurement noise can complicate fault detection and isolation. As a result, using fault diagnostics to meet industrial needs in a cost-effective way, and to reduce maintenance costs without requiring more investments than the cost of what is to be avoided in the first place, requires an effective scheme of applying them. This is the subject ofmaintenance, repair and operations
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure, and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installa ...
; the different strategies include:
*Condition-based maintenance
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure, and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installa ...
* Planned preventive maintenance
*Preventive maintenance
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure, and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installa ...
*Corrective maintenance
Corrective maintenance is a maintenance task performed to identify, isolate, and rectify a fault so that the failed equipment, machine, or system can be restored to an operational condition within the tolerances or limits established for in-servi ...
(does not use diagnostics)
*Integrated vehicle health management Integrated vehicle health management (IVHM) or integrated system health management (ISHM) is the unified capability of systems to assess the current or future state of the member system health and integrate that picture of system health within a fra ...
Fault detection and diagnosis using artificial intelligence
Machine learning techniques for fault detection and diagnosis
In fault detection and diagnosis, mathematical classification models which in fact belong tosupervised learning
Supervised learning (SL) is a machine learning paradigm for problems where the available data consists of labelled examples, meaning that each data point contains features (covariates) and an associated label. The goal of supervised learning alg ...
methods, are trained on the training set
In machine learning, a common task is the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data. Such algorithms function by making data-driven predictions or decisions, through building a mathematical model from ...
of a labeled dataset A data set (or dataset) is a collection of data. In the case of tabular data, a data set corresponds to one or more database tables, where every column of a table represents a particular variable, and each row corresponds to a given record of the ...
to accurately identify the redundancies, faults and anomalous samples. During the past decades, there are different classification and preprocessing models that have been developed and proposed in this research area. ''K''-nearest-neighbors algorithm (''k''NN) is one of the oldest techniques which has been used to solve fault detection and diagnosis problems. Despite the simple logic that this instance-based algorithm has, there are some problems with large dimensionality
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coordin ...
and processing time when it is used on large dataset A data set (or dataset) is a collection of data. In the case of tabular data, a data set corresponds to one or more database tables, where every column of a table represents a particular variable, and each row corresponds to a given record of the ...
s. Since ''k''NN is not able to automatically extract the features to overcome the curse of dimensionality
The curse of dimensionality refers to various phenomena that arise when analyzing and organizing data in high-dimensional spaces that do not occur in low-dimensional settings such as the three-dimensional physical space of everyday experience. T ...
, so often some data preprocessing Data preprocessing can refer to manipulation or dropping of data before it is used in order to ensure or enhance performance, and is an important step in the data mining process. The phrase "garbage in, garbage out" is particularly applicable to ...
techniques like Principal component analysis(PCA), Linear discriminant analysis(LDA) or Canonical correlation analysis
In statistics, canonical-correlation analysis (CCA), also called canonical variates analysis, is a way of inferring information from cross-covariance matrices. If we have two vectors ''X'' = (''X''1, ..., ''X'n'') and ''Y' ...
(CCA) accompany it to reach a better performance. In many industrial cases, the effectiveness of ''k''NN has been compared with other methods, specially with more complex classification models such as Support Vector Machines (SVMs), which is widely used in this field. Thanks to their appropriate nonlinear mapping using kernel methods
In machine learning, kernel machines are a class of algorithms for pattern analysis, whose best known member is the support-vector machine (SVM). The general task of pattern analysis is to find and study general types of relations (for example ...
, SVMs have an impressive performance in generalization, even with small training data. However, general SVMs do not have automatic feature extraction themselves and just like ''k''NN, are often coupled with a data pre-processing Data preprocessing can refer to manipulation or dropping of data before it is used in order to ensure or enhance performance, and is an important step in the data mining process. The phrase "garbage in, garbage out" is particularly applicable to ...
technique. Another drawback of SVMs is that their performance is highly sensitive to the initial parameters, particularly to the kernel method
In machine learning, kernel machines are a class of algorithms for pattern analysis, whose best known member is the support-vector machine (SVM). The general task of pattern analysis is to find and study general types of relations (for example ...
s, so in each signal dataset A data set (or dataset) is a collection of data. In the case of tabular data, a data set corresponds to one or more database tables, where every column of a table represents a particular variable, and each row corresponds to a given record of the ...
, a parameter tuning process is required to be conducted first. Therefore, the low speed of the training phase is a limitation of SVMs when it comes to its usage in fault detection and diagnosis cases.
 Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are among the most mature and widely used mathematical classification algorithms in fault detection and diagnosis. ANNs are well-known for their efficient self-learning capabilities of the complex relations (which generally exist inherently in fault detection and diagnosis problems) and are easy to operate. Another advantage of ANNs is that they perform automatic feature extraction by allocating negligible weights to the irrelevant features, helping the system to avoid dealing with another feature extractor. However, ANNs tend to over-fit the training set, which will have consequences of having poor validation accuracy on the validation set. Hence, often, some regularization terms and prior knowledge are added to the ANN model to avoid over-fiting and achieve higher performance. Moreover, properly determining the size of the hidden layer needs an exhaustive parameter tuning, to avoid poor approximation and generalization capabilities.
In general, different SVMs and ANNs models (i.e. Back-Propagation Neural Networks and Multi-Layer Perceptron) have shown successful performances in the fault detection and diagnosis in industries such as
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are among the most mature and widely used mathematical classification algorithms in fault detection and diagnosis. ANNs are well-known for their efficient self-learning capabilities of the complex relations (which generally exist inherently in fault detection and diagnosis problems) and are easy to operate. Another advantage of ANNs is that they perform automatic feature extraction by allocating negligible weights to the irrelevant features, helping the system to avoid dealing with another feature extractor. However, ANNs tend to over-fit the training set, which will have consequences of having poor validation accuracy on the validation set. Hence, often, some regularization terms and prior knowledge are added to the ANN model to avoid over-fiting and achieve higher performance. Moreover, properly determining the size of the hidden layer needs an exhaustive parameter tuning, to avoid poor approximation and generalization capabilities.
In general, different SVMs and ANNs models (i.e. Back-Propagation Neural Networks and Multi-Layer Perceptron) have shown successful performances in the fault detection and diagnosis in industries such as gearbox
Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion power of a machine. The term ''transmission'' properly refers to the whole drivetrain, including clutch, gearbox, prop shaft (for rear-wheel drive vehicles), differe ...
, machinery parts (i.e. mechanical bearing
A bearing is a machine element that constrains relative motion to only the desired motion, and reduces friction between moving parts. The design of the bearing may, for example, provide for free linear movement of the moving part or for free ro ...
s), compressors, wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ho ...
and gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directio ...
s and steel plates.
Deep learning techniques for fault detection and diagnosis
 With the research advances in ANNs and the advent of deep learning algorithms using deep and complex layers, novel classification models have been developed to cope with fault detection and diagnosis.
Most of the shallow learning models extract a few feature values from signals, causing a
With the research advances in ANNs and the advent of deep learning algorithms using deep and complex layers, novel classification models have been developed to cope with fault detection and diagnosis.
Most of the shallow learning models extract a few feature values from signals, causing a dimensionality
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coordin ...
reduction from the original signal
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing' ...
. By using Convolutional neural network
In deep learning, a convolutional neural network (CNN, or ConvNet) is a class of artificial neural network (ANN), most commonly applied to analyze visual imagery. CNNs are also known as Shift Invariant or Space Invariant Artificial Neural Netwo ...
s, the continuous wavelet transform
Continuity or continuous may refer to:
Mathematics
* Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include
** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics
** Continuous g ...
scalogram can be directly classified to normal and faulty classes. Such a technique avoids omitting any important fault message and results in a better performance of fault detection and diagnosis.
In addition, by transforming signals to image constructions, 2D Convolutional neural network
In deep learning, a convolutional neural network (CNN, or ConvNet) is a class of artificial neural network (ANN), most commonly applied to analyze visual imagery. CNNs are also known as Shift Invariant or Space Invariant Artificial Neural Netwo ...
s can be implemented to identify faulty signals from vibration image features.
Deep belief network
In machine learning, a deep belief network (DBN) is a generative graphical model, or alternatively a class of deep neural network, composed of multiple layers of latent variables ("hidden units"), with connections between the layers but not bet ...
s, Restricted Boltzmann machine
A restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) is a generative stochastic artificial neural network that can learn a probability distribution over its set of inputs.
RBMs were initially invented under the name Harmonium by Paul Smolensky in 1986,
and rose ...
s and Autoencoder
An autoencoder is a type of artificial neural network used to learn efficient codings of unlabeled data ( unsupervised learning). The encoding is validated and refined by attempting to regenerate the input from the encoding. The autoencoder lea ...
s are other deep neural networks
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks with representation learning. Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised.
...
architectures which have been successfully used in this field of research. In comparison to traditional machine learning, due to their deep architecture, deep learning models are able to learn more complex structures from dataset A data set (or dataset) is a collection of data. In the case of tabular data, a data set corresponds to one or more database tables, where every column of a table represents a particular variable, and each row corresponds to a given record of the ...
s, however, they need larger samples and longer processing time to achieve higher accuracy.
Fault recovery
Fault Recovery in FDIR is the action taken after a failure has been detected and isolated to return the system to a stable state. Some examples of fault recoveries are: * Switch-off of a faulty equipment * Switch-over from a faulty equipment to a redundant equipment * Change of state of the complete system into a Safe Mode with limited functionalitiesSee also
* Control reconfiguration *Control theory
Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a ...
* Failure mode and effects analysis
Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA; often written with "failure modes" in plural) is the process of reviewing as many components, assemblies, and subsystems as possible to identify potential failure modes in a system and their causes and effe ...
* Fault-tolerant system
Fault tolerance is the property that enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of one or more faults within some of its components. If its operating quality decreases at all, the decrease is proportional to the ...
* Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance techniques are designed to help determine the condition of in-service equipment in order to estimate when maintenance should be performed. This approach promises cost savings over routine or time-based preventive maintena ...
* Spread-spectrum time-domain reflectometry
* System identification
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Fault Detection And Isolation Control theory Systems engineering