Macedonia national cricket team on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in
Online Etymology Dictionary a
 North Macedonia geographically roughly corresponds to the ancient kingdom of Paeonia, which was located immediately north of the ancient
North Macedonia geographically roughly corresponds to the ancient kingdom of Paeonia, which was located immediately north of the ancient
Book 7, Frg. 4:
/ref> Paeonia was inhabited by the Paeonians, a


 Several movements whose goals were the establishment of an autonomous Macedonia, which would encompass the entire region of Macedonia, began to arise in the late 19th century; the earliest of these was the Bulgarian Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Committees, later becoming Secret Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (SMARO). In 1905 it was renamed the Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (IMARO), and after
Several movements whose goals were the establishment of an autonomous Macedonia, which would encompass the entire region of Macedonia, began to arise in the late 19th century; the earliest of these was the Bulgarian Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Committees, later becoming Secret Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (SMARO). In 1905 it was renamed the Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (IMARO), and after
 Following the two Balkan Wars of 1912 and 1913 and the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire, most of its European-held territories were divided between Greece, Bulgaria and Serbia. Almost the territory that was to become North Macedonia was annexed by Serbia conforming to the treaty of peace concluded at Bucharest. However, Strumica region was passed to Bulgaria. Following the partition, an anti-Bulgarian campaign was carried out in the areas under Serbian and Greek control. As many as 641 Bulgarian schools and 761 churches were closed by the Serbs, while Exarchist clergy and teachers were expelled. The use of all
Following the two Balkan Wars of 1912 and 1913 and the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire, most of its European-held territories were divided between Greece, Bulgaria and Serbia. Almost the territory that was to become North Macedonia was annexed by Serbia conforming to the treaty of peace concluded at Bucharest. However, Strumica region was passed to Bulgaria. Following the partition, an anti-Bulgarian campaign was carried out in the areas under Serbian and Greek control. As many as 641 Bulgarian schools and 761 churches were closed by the Serbs, while Exarchist clergy and teachers were expelled. The use of all 
 In December 1944 the Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia (ASNOM) proclaimed the People's Republic of Macedonia as part of the ''People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia''. ASNOM remained an acting government until the end of the war. The Macedonian alphabet was codified by linguists of ASNOM, who based their alphabet on the phonetic alphabet of Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and the principles of Krste Petkov Misirkov. During the civil war in Greece (1946–1949), Macedonian communist insurgents supported the Greek communists. Many refugees fled to the Socialist Republic of Macedonia from there. The state dropped ''Socialist'' from its name in 1991 when it peacefully seceded from Yugoslavia.
The new republic became one of the six republics of the Yugoslav federation. Following the federation's renaming as the
In December 1944 the Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia (ASNOM) proclaimed the People's Republic of Macedonia as part of the ''People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia''. ASNOM remained an acting government until the end of the war. The Macedonian alphabet was codified by linguists of ASNOM, who based their alphabet on the phonetic alphabet of Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and the principles of Krste Petkov Misirkov. During the civil war in Greece (1946–1949), Macedonian communist insurgents supported the Greek communists. Many refugees fled to the Socialist Republic of Macedonia from there. The state dropped ''Socialist'' from its name in 1991 when it peacefully seceded from Yugoslavia.
The new republic became one of the six republics of the Yugoslav federation. Following the federation's renaming as the
 A
A
Statues of
 On 6 February 2019, the permanent representatives of NATO member states and Macedonian Foreign Affairs Minister Nikola Dimitrov, signed in
On 6 February 2019, the permanent representatives of NATO member states and Macedonian Foreign Affairs Minister Nikola Dimitrov, signed in
 North Macedonia has a total area of . It lies between latitudes 40° and 43° N, and mostly between longitudes 20° and 23° E (a small area lies east of 23°). North Macedonia has some of boundaries, shared with
North Macedonia has a total area of . It lies between latitudes 40° and 43° N, and mostly between longitudes 20° and 23° E (a small area lies east of 23°). North Macedonia has some of boundaries, shared with  The Aegean basin is the largest. It covers 87% of the territory of North Macedonia, which is .
The Aegean basin is the largest. It covers 87% of the territory of North Macedonia, which is .
 Four different seasons are found in the country with warm and dry summers and moderately cold and snowy winters. The range of temperatures recorded throughout the year ranges from in winter, to in summer. Low winter temperatures are influenced by winds from the north while heat seasons during summer arise due to the subtropical pressure of the Aegean Sea and climate influences from the Middle East, with the latter causing dry periods. There are three main climatic zones in the country: mildly continental climate, continental in the north, temperate Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean in the south and mountain climate, mountainous in the zones with high altitude. Along the valleys of the Vardar and Strumica rivers, in the regions of Gevgelija, Valandovo, Dojran, Strumica, and Radoviš, the climate is temperate Mediterranean. The warmest regions are Demir Kapija and Gevgelija, where the temperature in July and August frequently exceeds .
Average annual precipitation varies from in the western mountainous area to in the eastern area. There is a low level of precipitation in the Vardar valley with of water per year. The climate and irrigation diversity allow the cultivation of different plant types, including wheat, corn, potatoes, poppies, peanuts, and rice. There are thirty main and regular weather stations in the country.
Four different seasons are found in the country with warm and dry summers and moderately cold and snowy winters. The range of temperatures recorded throughout the year ranges from in winter, to in summer. Low winter temperatures are influenced by winds from the north while heat seasons during summer arise due to the subtropical pressure of the Aegean Sea and climate influences from the Middle East, with the latter causing dry periods. There are three main climatic zones in the country: mildly continental climate, continental in the north, temperate Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean in the south and mountain climate, mountainous in the zones with high altitude. Along the valleys of the Vardar and Strumica rivers, in the regions of Gevgelija, Valandovo, Dojran, Strumica, and Radoviš, the climate is temperate Mediterranean. The warmest regions are Demir Kapija and Gevgelija, where the temperature in July and August frequently exceeds .
Average annual precipitation varies from in the western mountainous area to in the eastern area. There is a low level of precipitation in the Vardar valley with of water per year. The climate and irrigation diversity allow the cultivation of different plant types, including wheat, corn, potatoes, poppies, peanuts, and rice. There are thirty main and regular weather stations in the country.
 North Macedonia is a parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy with an executive (government), executive government composed of a coalition of parties from the unicameralism, unicameral legislature (, ; ''Assembly'' in English) and an independent judiciary, judicial branch with a constitutional court. The Assembly of North Macedonia, Assembly is made up of 120 seats and the members are elected every four years. The role of the President of North Macedonia, president is mostly ceremonial, with the real power resting in the hands of the Prime Minister of North Macedonia, prime minister. The president is the commander-in-chief of the state armed forces and a president of the National security, State Security Council. The president is elected every five years and he or she can be elected twice at most.
Since 2019, local government functions are divided between 80 Municipalities of North Macedonia, municipalities (, ; Grammatical number, singular: , ). The capital, Skopje, is governed as a group of ten municipalities collectively referred to as the "City of Skopje". Municipalities in North Macedonia are units of local self-government. Neighbouring municipalities may establish co-operative arrangements.
The country's main political divergence is between the largely ethnically based political parties representing the country's ethnic Macedonian majority and Albanian minority. The issue of the power balance between the two communities led to a brief war in 2001, following which a power-sharing agreement was reached. In August 2004, parliament passed legislation redrawing local boundaries and giving greater local autonomy to ethnic Albanians in areas where they predominate.
After a troublesome pre-election campaign, North Macedonia saw a relatively calm and democratic change of government in the 2006 Macedonian parliamentary election, elections held on 5 July 2006. The elections were marked by a decisive victory of the centre-right party VMRO–DPMNE, VMRO-DPMNE led by Nikola Gruevski. Gruevski's decision to include the Democratic Party of Albanians in the new government, instead of the Democratic Union for Integration–Party for Democratic Prosperity coalition which won the majority of the Albanian votes, triggered protests throughout the parts of the country with a respective number of Albanian population. A dialogue was later established between the Democratic Union for Integration and the ruling VMRO-DMPNE party as an effort to talk about the disputes between the two parties and to support European and NATO aspirations of the country.
After the early parliamentary elections held in 2008, VMRO-DPMNE and Democratic Union for Integration formed a ruling coalition. In April 2009, presidential and local elections in the country were carried out peacefully, which was crucial for Macedonian aspirations to join the EU. The ruling conservative VMRO-DPMNE party won a victory in the local elections and the candidate supported by the party, Gjorgi Ivanov, was elected as the new president.
In June 2017, Zoran Zaev of the Social Democratic Party of Macedonia, Social Democratic Party, became the new prime minister six months after early elections. The new center-left government ended 11 years of conservative VMRO-DPMNE rule led by former prime minister Nikola Gruevski.
, the acting prime minister of North Macedonia was Oliver Spasovski and the current president of the Parliament is Talat Xhaferi. The election of Xhaferi was immediately met with protests led by VMRO-DPMNE, which was quickly handled by the police.
The early parliamentary elections took place on 15 July 2020. Zoran Zaev has served as the prime minister of the Republic of North Macedonia again since August 2020. Stevo Pendarovski was sworn in as North Macedonia's new president in May 2019. Prime minister Zoran Zaev announced his resignation after his party, the Social Democratic Union, suffered losses in local elections in October 2021. In January 2022, Dimitar Kovačevski was elected as prime minister. The new coalition cabinet composed of Kovačevski's Social Democrats and two ethnic Albanian parties.
Parliament, or Assembly ( mk, Собрание, ), is the country's legislative body. It makes, proposes and adopts laws. The Constitution of North Macedonia has been in use since shortly after the independence of the republic in 1991. It limits the power of the governments, both local and national. The military is also limited by the constitution. The constitution states that North Macedonia is a social free state, and that Skopje is the capital. The 120 members are elected for a mandate of four years through a general election. Each citizen aged 18 years or older can vote for one of the political parties. The current president of Parliament is since 2017 an ethnic Albanian, Talat Xhaferi.
Executive power in North Macedonia is exercised by the Government, whose prime minister is the most politically powerful person in the country. The members of the government are chosen by the prime minister and there are ministers for each branch of the society. There are ministers for economy, finance, information technology, society, internal affairs, foreign affairs and other areas. The members of the Government are elected for a mandate of four years. Judiciary power is exercised by courts, with the court system being headed by the Judicial Supreme court, Constitutional Court and the Republican Judicial Council. The assembly appoints the judges.
North Macedonia is a parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy with an executive (government), executive government composed of a coalition of parties from the unicameralism, unicameral legislature (, ; ''Assembly'' in English) and an independent judiciary, judicial branch with a constitutional court. The Assembly of North Macedonia, Assembly is made up of 120 seats and the members are elected every four years. The role of the President of North Macedonia, president is mostly ceremonial, with the real power resting in the hands of the Prime Minister of North Macedonia, prime minister. The president is the commander-in-chief of the state armed forces and a president of the National security, State Security Council. The president is elected every five years and he or she can be elected twice at most.
Since 2019, local government functions are divided between 80 Municipalities of North Macedonia, municipalities (, ; Grammatical number, singular: , ). The capital, Skopje, is governed as a group of ten municipalities collectively referred to as the "City of Skopje". Municipalities in North Macedonia are units of local self-government. Neighbouring municipalities may establish co-operative arrangements.
The country's main political divergence is between the largely ethnically based political parties representing the country's ethnic Macedonian majority and Albanian minority. The issue of the power balance between the two communities led to a brief war in 2001, following which a power-sharing agreement was reached. In August 2004, parliament passed legislation redrawing local boundaries and giving greater local autonomy to ethnic Albanians in areas where they predominate.
After a troublesome pre-election campaign, North Macedonia saw a relatively calm and democratic change of government in the 2006 Macedonian parliamentary election, elections held on 5 July 2006. The elections were marked by a decisive victory of the centre-right party VMRO–DPMNE, VMRO-DPMNE led by Nikola Gruevski. Gruevski's decision to include the Democratic Party of Albanians in the new government, instead of the Democratic Union for Integration–Party for Democratic Prosperity coalition which won the majority of the Albanian votes, triggered protests throughout the parts of the country with a respective number of Albanian population. A dialogue was later established between the Democratic Union for Integration and the ruling VMRO-DMPNE party as an effort to talk about the disputes between the two parties and to support European and NATO aspirations of the country.
After the early parliamentary elections held in 2008, VMRO-DPMNE and Democratic Union for Integration formed a ruling coalition. In April 2009, presidential and local elections in the country were carried out peacefully, which was crucial for Macedonian aspirations to join the EU. The ruling conservative VMRO-DPMNE party won a victory in the local elections and the candidate supported by the party, Gjorgi Ivanov, was elected as the new president.
In June 2017, Zoran Zaev of the Social Democratic Party of Macedonia, Social Democratic Party, became the new prime minister six months after early elections. The new center-left government ended 11 years of conservative VMRO-DPMNE rule led by former prime minister Nikola Gruevski.
, the acting prime minister of North Macedonia was Oliver Spasovski and the current president of the Parliament is Talat Xhaferi. The election of Xhaferi was immediately met with protests led by VMRO-DPMNE, which was quickly handled by the police.
The early parliamentary elections took place on 15 July 2020. Zoran Zaev has served as the prime minister of the Republic of North Macedonia again since August 2020. Stevo Pendarovski was sworn in as North Macedonia's new president in May 2019. Prime minister Zoran Zaev announced his resignation after his party, the Social Democratic Union, suffered losses in local elections in October 2021. In January 2022, Dimitar Kovačevski was elected as prime minister. The new coalition cabinet composed of Kovačevski's Social Democrats and two ethnic Albanian parties.
Parliament, or Assembly ( mk, Собрание, ), is the country's legislative body. It makes, proposes and adopts laws. The Constitution of North Macedonia has been in use since shortly after the independence of the republic in 1991. It limits the power of the governments, both local and national. The military is also limited by the constitution. The constitution states that North Macedonia is a social free state, and that Skopje is the capital. The 120 members are elected for a mandate of four years through a general election. Each citizen aged 18 years or older can vote for one of the political parties. The current president of Parliament is since 2017 an ethnic Albanian, Talat Xhaferi.
Executive power in North Macedonia is exercised by the Government, whose prime minister is the most politically powerful person in the country. The members of the government are chosen by the prime minister and there are ministers for each branch of the society. There are ministers for economy, finance, information technology, society, internal affairs, foreign affairs and other areas. The members of the Government are elected for a mandate of four years. Judiciary power is exercised by courts, with the court system being headed by the Judicial Supreme court, Constitutional Court and the Republican Judicial Council. The assembly appoints the judges.
 The Army of North Macedonia, military of North Macedonia comprises the army, Macedonian Air Force, air force, and Wolves (military), special forces. The government's national defence policy aims to guarantee the preservation of the independence and sovereignty of the state, the integrity of its land area and airspace and its constitutional order. Its main goals remain the development and maintenance of a credible capability to defend the nation's vital interests and development of the Armed Forces in a way that ensures their interoperability with the armed forces of NATO and the European Union member states and their capability to participate in the full range of NATO missions.
The Ministry of Defence develops the Republic's defence strategy and assesses possible threats and risks. It is also responsible for the defence system, including training, readiness, equipment, and development, and for drawing up and presenting the defence budget.
The Army of North Macedonia, military of North Macedonia comprises the army, Macedonian Air Force, air force, and Wolves (military), special forces. The government's national defence policy aims to guarantee the preservation of the independence and sovereignty of the state, the integrity of its land area and airspace and its constitutional order. Its main goals remain the development and maintenance of a credible capability to defend the nation's vital interests and development of the Armed Forces in a way that ensures their interoperability with the armed forces of NATO and the European Union member states and their capability to participate in the full range of NATO missions.
The Ministry of Defence develops the Republic's defence strategy and assesses possible threats and risks. It is also responsible for the defence system, including training, readiness, equipment, and development, and for drawing up and presenting the defence budget.
 The use of the name "Macedonia (terminology), Macedonia" was disputed between Greece and North Macedonia. The specific naming dispute was reignited after the breakup of Yugoslavia and the newly gained independence of the former Socialist Republic of Macedonia in 1991. Greece opposed the use of the name without a geographical qualifier so as to avoid confusion with its own region of
The use of the name "Macedonia (terminology), Macedonia" was disputed between Greece and North Macedonia. The specific naming dispute was reignited after the breakup of Yugoslavia and the newly gained independence of the former Socialist Republic of Macedonia in 1991. Greece opposed the use of the name without a geographical qualifier so as to avoid confusion with its own region of

 North Macedonia's statistical regions exist solely for legal and statistical purposes. The regions are:
* Eastern statistical region, Eastern
* Northeastern statistical region, Northeastern
* Pelagonia statistical region, Pelagonia
* Polog statistical region, Polog
* Skopje statistical region, Skopje
* Southeastern statistical region, Southeastern
* Southwestern statistical region, Southwestern
* Vardar statistical region, Vardar
In August 2004, the country was reorganised into 84 municipalities (; sing. ); 10 of the municipalities constitute the City of
North Macedonia's statistical regions exist solely for legal and statistical purposes. The regions are:
* Eastern statistical region, Eastern
* Northeastern statistical region, Northeastern
* Pelagonia statistical region, Pelagonia
* Polog statistical region, Polog
* Skopje statistical region, Skopje
* Southeastern statistical region, Southeastern
* Southwestern statistical region, Southwestern
* Vardar statistical region, Vardar
In August 2004, the country was reorganised into 84 municipalities (; sing. ); 10 of the municipalities constitute the City of
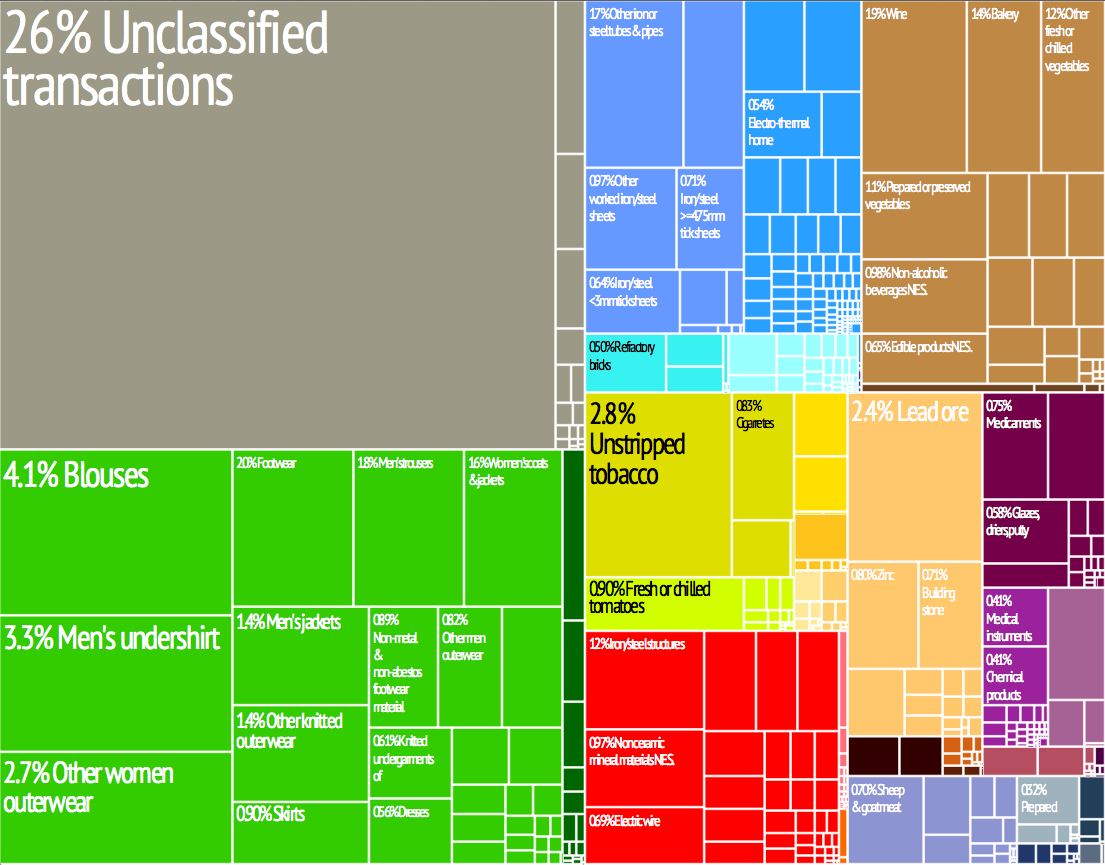 In terms of foreign trade, the largest sector contributing to the country's export in 2014 was "chemicals and related products" at 21.4%, followed by the "machinery and transport equipment" sector at 21.1%. North Macedonia's main import sectors in 2014 were "manufactured goods classified chiefly by material" with 34.2%, "machinery and transport equipment" with 18.7% and "mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials" with 14.4% of the total imports. Even 68.8% of the foreign trade in 2014 was done with the EU which makes the Union by far the largest trading partner of North Macedonia (23.3% with Germany, 7.9% with the UK, 7.3% with Greece, 6.2% with Italy, etc.). Almost 12% of the total external trade in 2014 was done with the Western Balkan countries.
North Macedonia has one of the highest shares of people struggling financially, with 72% of its citizens stating that they could manage on their household's income only "with difficulty" or "with great difficulty", though North Macedonia, along with Croatia, was the only country in the Western Balkans to not report an increase in this statistic. Corruption and a relatively ineffective legal system also act as significant restraints on successful economic development. North Macedonia still has one of the lowest List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, per capita GDPs in Europe. Furthermore, the country's grey market is estimated at close to 20% of GDP. PPS GDP per capita stood at 36% of the EU average in 2017. With a GDP per capita of US$9,157 at purchasing power parity and a List of countries by Human Development Index, Human Development Index of 0.701, North Macedonia is less developed and has a considerably smaller economy than most of the former Yugoslav states.
In terms of foreign trade, the largest sector contributing to the country's export in 2014 was "chemicals and related products" at 21.4%, followed by the "machinery and transport equipment" sector at 21.1%. North Macedonia's main import sectors in 2014 were "manufactured goods classified chiefly by material" with 34.2%, "machinery and transport equipment" with 18.7% and "mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials" with 14.4% of the total imports. Even 68.8% of the foreign trade in 2014 was done with the EU which makes the Union by far the largest trading partner of North Macedonia (23.3% with Germany, 7.9% with the UK, 7.3% with Greece, 6.2% with Italy, etc.). Almost 12% of the total external trade in 2014 was done with the Western Balkan countries.
North Macedonia has one of the highest shares of people struggling financially, with 72% of its citizens stating that they could manage on their household's income only "with difficulty" or "with great difficulty", though North Macedonia, along with Croatia, was the only country in the Western Balkans to not report an increase in this statistic. Corruption and a relatively ineffective legal system also act as significant restraints on successful economic development. North Macedonia still has one of the lowest List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, per capita GDPs in Europe. Furthermore, the country's grey market is estimated at close to 20% of GDP. PPS GDP per capita stood at 36% of the EU average in 2017. With a GDP per capita of US$9,157 at purchasing power parity and a List of countries by Human Development Index, Human Development Index of 0.701, North Macedonia is less developed and has a considerably smaller economy than most of the former Yugoslav states.
 Tourism plays a significant role in the economy of North Macedonia accounting for 6.7% of its GDP in 2016. The annual income from tourism was estimated at 38.5 billion denars (€616 million) in that year. Following its independence, the most serious negative impact on tourism performance occurred due to the armed conflicts taking place in 2001. The number of foreign visitors has been on the rise since, with a 14.6% increase in 2011. In 2019, North Macedonia received 1,184,963 tourist arrivals out of which 757,593 foreign. Most numerous are tourists from Turkey, neighboring Serbia, Greece and Bulgaria, Poland and other countries of Western Europe. The biggest bulk of tourists, approximately 60% of the million tourists that visited the country in 2017, was situated in Skopje and the southwestern region of the country.
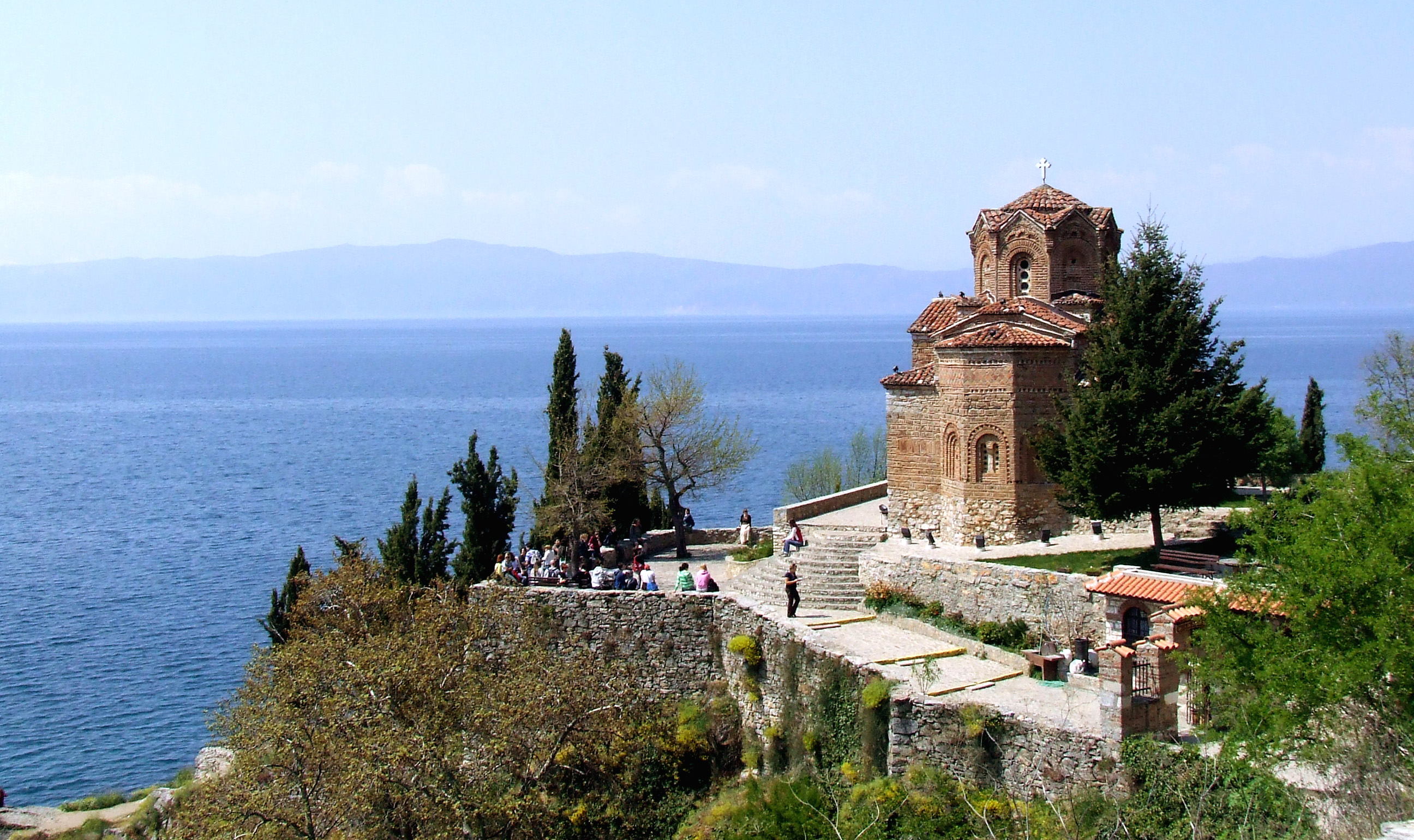
The most significant tourism branches are lake tourism as there are three lakes in Ohrid, Prespa and Dojran and over 50 small glacial lakes of variable sizes, mountainous tourism as there are 16 mountains higher than 2,000 metres. Other forms of tourism also include rural and ecotourism, city tourism and cultural tourism, represented through gastronomy, traditional music, cultural celebrations and cultural heritage sites.
Tourism plays a significant role in the economy of North Macedonia accounting for 6.7% of its GDP in 2016. The annual income from tourism was estimated at 38.5 billion denars (€616 million) in that year. Following its independence, the most serious negative impact on tourism performance occurred due to the armed conflicts taking place in 2001. The number of foreign visitors has been on the rise since, with a 14.6% increase in 2011. In 2019, North Macedonia received 1,184,963 tourist arrivals out of which 757,593 foreign. Most numerous are tourists from Turkey, neighboring Serbia, Greece and Bulgaria, Poland and other countries of Western Europe. The biggest bulk of tourists, approximately 60% of the million tourists that visited the country in 2017, was situated in Skopje and the southwestern region of the country.
The most significant tourism branches are lake tourism as there are three lakes in Ohrid, Prespa and Dojran and over 50 small glacial lakes of variable sizes, mountainous tourism as there are 16 mountains higher than 2,000 metres. Other forms of tourism also include rural and ecotourism, city tourism and cultural tourism, represented through gastronomy, traditional music, cultural celebrations and cultural heritage sites.
 North Macedonia (along with Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kosovo) belongs to the less-developed southern region of the former Yugoslavia. It suffered severe economic difficulties after independence, when the Yugoslav internal market collapsed and subsidies from Belgrade ended. In addition, it faced many of the same problems faced by other former socialist Eastern Europe, East European countries during the transition to a market economy. Its main land and rail exports route, through Serbia, remains unreliable with high transit costs, thereby affecting the export of its formerly highly profitable, early vegetables market to Germany.
North Macedonia's IT market increased 63.8% year on year in 2007, which was the fastest growing in the Adriatic region.
North Macedonia is in its position a continental country in the middle of the Balkan peninsula, and the main transport links in the country are those that connect the different parts of the peninsula (transbalkan links). Particularly important is the connection between north–south and Vardar valley, which connects Greece with the rest of Europe.
The total length of the railway network in North Macedonia is . Operated by Makedonski Železnici, the most important railway line is the line on the border with Serbia–Kumanovo–Skopje–Veles–Gevgelija–border with Greece. Since 2001, the railway line Beljakovci has been built—the border with Bulgaria, which will get a direct connection Skopje-Sofia. The most important railway hub in the country is Skopje, while the other two are Veles and Kumanovo.
North Macedonia Post is the state-owned company for the provision of postal traffic. It was founded in 1992 as PTT Macedonia. In 1993 it was admitted to the Universal Postal Union, World Postal Union in 1997, PTT Macedonia was divided into Macedonian Telekom and Macedonian Post (later renamed North Macedonia Post).
As far as water transport is concerned, only lake traffic through Ohrid and Prespan Lake has been developed, mostly for tourist purposes.
There are 17 airports officially in North Macedonia, of which 11 are with solid substrates. Among them are two airports of international character, since they are listed on the airport's IATA airport code International Airport Skopje and Ohrid St. Paul the Apostle Airport.
North Macedonia (along with Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kosovo) belongs to the less-developed southern region of the former Yugoslavia. It suffered severe economic difficulties after independence, when the Yugoslav internal market collapsed and subsidies from Belgrade ended. In addition, it faced many of the same problems faced by other former socialist Eastern Europe, East European countries during the transition to a market economy. Its main land and rail exports route, through Serbia, remains unreliable with high transit costs, thereby affecting the export of its formerly highly profitable, early vegetables market to Germany.
North Macedonia's IT market increased 63.8% year on year in 2007, which was the fastest growing in the Adriatic region.
North Macedonia is in its position a continental country in the middle of the Balkan peninsula, and the main transport links in the country are those that connect the different parts of the peninsula (transbalkan links). Particularly important is the connection between north–south and Vardar valley, which connects Greece with the rest of Europe.
The total length of the railway network in North Macedonia is . Operated by Makedonski Železnici, the most important railway line is the line on the border with Serbia–Kumanovo–Skopje–Veles–Gevgelija–border with Greece. Since 2001, the railway line Beljakovci has been built—the border with Bulgaria, which will get a direct connection Skopje-Sofia. The most important railway hub in the country is Skopje, while the other two are Veles and Kumanovo.
North Macedonia Post is the state-owned company for the provision of postal traffic. It was founded in 1992 as PTT Macedonia. In 1993 it was admitted to the Universal Postal Union, World Postal Union in 1997, PTT Macedonia was divided into Macedonian Telekom and Macedonian Post (later renamed North Macedonia Post).
As far as water transport is concerned, only lake traffic through Ohrid and Prespan Lake has been developed, mostly for tourist purposes.
There are 17 airports officially in North Macedonia, of which 11 are with solid substrates. Among them are two airports of international character, since they are listed on the airport's IATA airport code International Airport Skopje and Ohrid St. Paul the Apostle Airport.
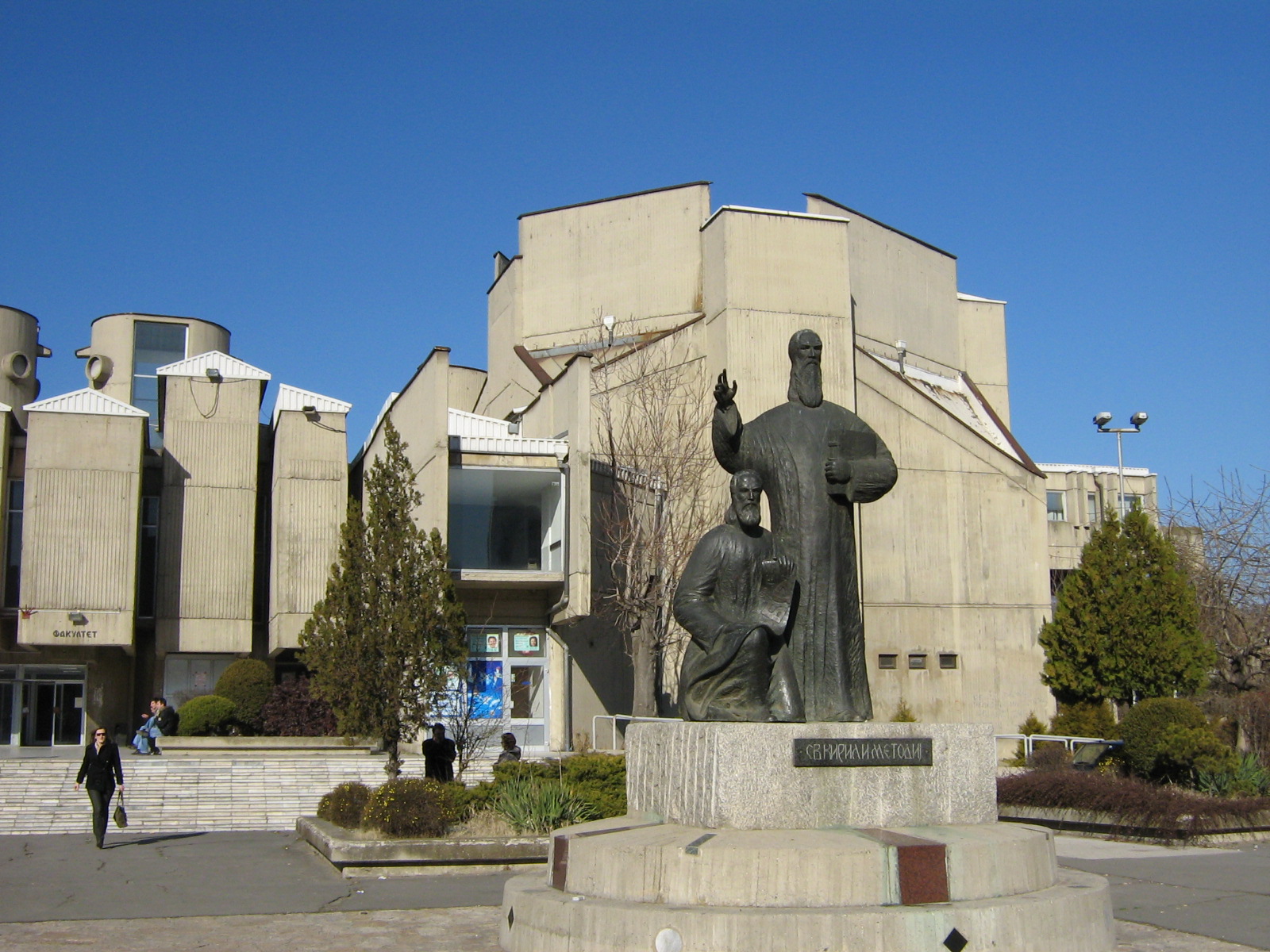 The higher levels of education can be obtained at one of the five state universities: Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje, St. Clement of Ohrid University of Bitola, Goce Delčev University of Štip, State University of Tetova and University of Information Science and Technology "St. Paul The Apostle" in Ohrid. There are a number of private university institutions, such as the European University, Slavic University in Sveti Nikole, the South East European University and others. North Macedonia was ranked 59th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021 and 2019.
The United States Agency for International Development has underwritten a project called ''Macedonia Connects'', which has made North Macedonia the first all-broadband wireless country in the world. The Ministry of Education and Sciences reports that 461 schools (primary and secondary) are now connected to the Internet. In addition, an Internet service provider (On.net), has created a MESH Network to provide WIFI services in the 11 largest cities/towns in the country. The national library of North Macedonia, National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid", is in Skopje.
The higher levels of education can be obtained at one of the five state universities: Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje, St. Clement of Ohrid University of Bitola, Goce Delčev University of Štip, State University of Tetova and University of Information Science and Technology "St. Paul The Apostle" in Ohrid. There are a number of private university institutions, such as the European University, Slavic University in Sveti Nikole, the South East European University and others. North Macedonia was ranked 59th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021 and 2019.
The United States Agency for International Development has underwritten a project called ''Macedonia Connects'', which has made North Macedonia the first all-broadband wireless country in the world. The Ministry of Education and Sciences reports that 461 schools (primary and secondary) are now connected to the Internet. In addition, an Internet service provider (On.net), has created a MESH Network to provide WIFI services in the 11 largest cities/towns in the country. The national library of North Macedonia, National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid", is in Skopje.
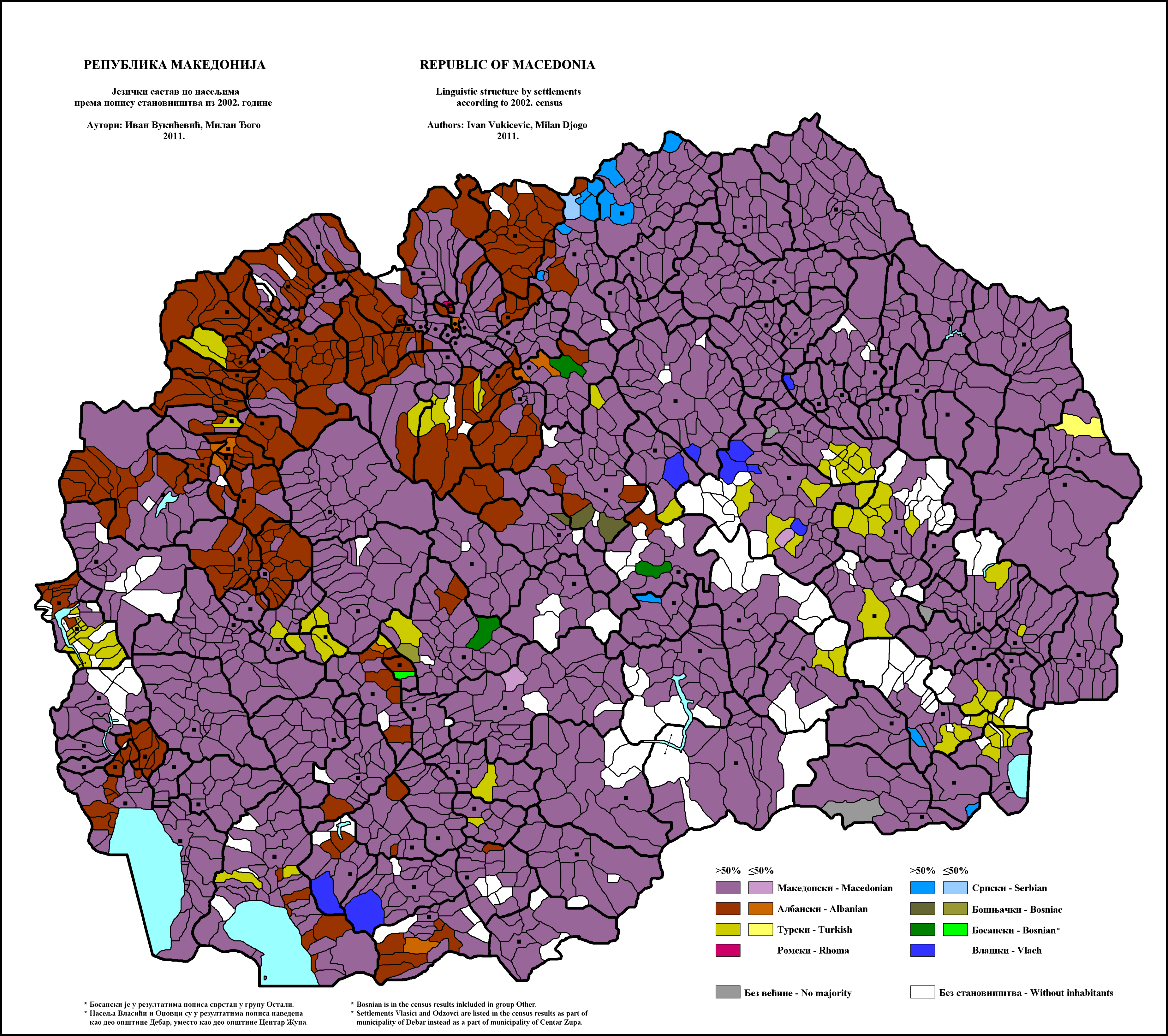 The national and official language in all aspects of the whole territory of North Macedonia and in its international relations is the
The national and official language in all aspects of the whole territory of North Macedonia and in its international relations is the
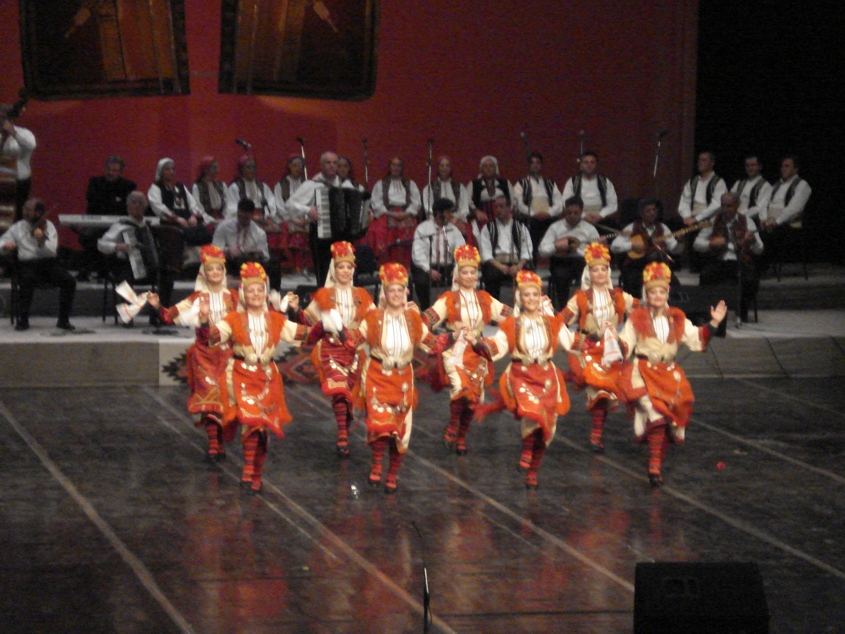 North Macedonia has a rich cultural heritage in art, architecture, poetry and music. It has many ancient, protected religious sites. Poetry, cinema, and music festivals are held annually. Music of North Macedonia, Macedonian music styles developed under the strong influence of Byzantine music, Byzantine church music. North Macedonia has a significant number of preserved Byzantine art, Byzantine fresco paintings, mainly from the period between the 11th and 16th centuries. There are several thousands of square metres of fresco painting preserved, the major part of which is in very good condition and represent masterworks of the Macedonian school of ecclesiastical painting.
The most important cultural events in the country are the
North Macedonia has a rich cultural heritage in art, architecture, poetry and music. It has many ancient, protected religious sites. Poetry, cinema, and music festivals are held annually. Music of North Macedonia, Macedonian music styles developed under the strong influence of Byzantine music, Byzantine church music. North Macedonia has a significant number of preserved Byzantine art, Byzantine fresco paintings, mainly from the period between the 11th and 16th centuries. There are several thousands of square metres of fresco painting preserved, the major part of which is in very good condition and represent masterworks of the Macedonian school of ecclesiastical painting.
The most important cultural events in the country are the
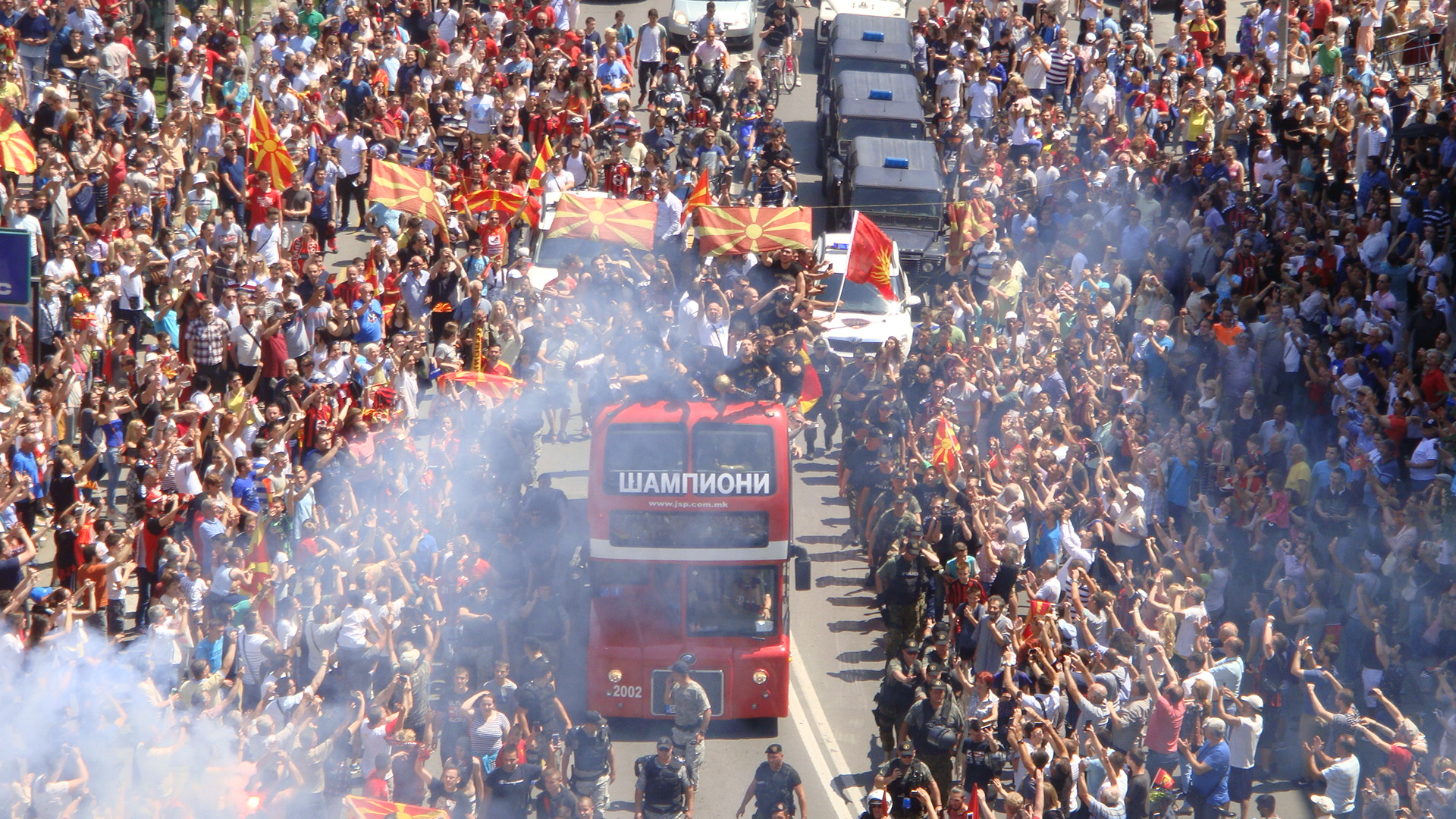
 Association football, Football, handball, and basketball are the most popular sports in North Macedonia. The North Macedonia national football team is controlled by the Football Federation of Macedonia. Their home stadium is the Toše Proeski Arena. In November 2003, to celebrate UEFA's jubilee, Darko Pančev was selected as the UEFA Jubilee Awards, Golden Player of Macedonia as their most outstanding player of the past 50 years. He was the winner of the European Golden Shoe, European Golden Boot award in 1991 and he is best known for scoring the winning penalty in the 1991 European Cup Final, bringing Red Star Belgrade the most prestigious trophy in European football for the first time in its 50-year existence. In 2020, the national team qualified for UEFA Euro 2020 (held in 2021), their first major tournament in the country's history.
Handball is the other important team sport in the country. Macedonian clubs have enjoyed success in European competitions. RK Vardar won 2016–17 EHF Champions League, 2016–17 and 2018–19 EHF Champions League, while Kometal Gjorče Petrov Skopje won the 2002 EHF Champions League, EHF Women's Champions League. The European Women's Handball Championship took place in 2008 in North Macedonia in Skopje and Ohrid; the North Macedonia women's national handball team, women's national team finished seventh place. The country's North Macedonia men's national handball team, men's national team has appeared in the European and World championships multiple times, with a best finish of fifth at the former (2012 European Men's Handball Championship, 2012) and ninth at the latter (2015 World Men's Handball Championship, 2015).
The North Macedonia men's national basketball team, North Macedonia national basketball team represents North Macedonia in international basketball. The team is run by the Basketball Federation of North Macedonia, the governing body of basketball in North Macedonia which was created in 1992 and joined FIBA in 1993. North Macedonia has participated in three EuroBaskets since then with its best finish at 4th place in EuroBasket 2011, 2011. It plays its home games at the Boris Trajkovski Sports Center in Skopje. Pero Antić became the List of foreign NBA players, first Macedonian basketball player to play in the National Basketball Association. He also won three EuroLeague trophies.
In the summer months the Ohrid Swimming Marathon is an annual event on
Association football, Football, handball, and basketball are the most popular sports in North Macedonia. The North Macedonia national football team is controlled by the Football Federation of Macedonia. Their home stadium is the Toše Proeski Arena. In November 2003, to celebrate UEFA's jubilee, Darko Pančev was selected as the UEFA Jubilee Awards, Golden Player of Macedonia as their most outstanding player of the past 50 years. He was the winner of the European Golden Shoe, European Golden Boot award in 1991 and he is best known for scoring the winning penalty in the 1991 European Cup Final, bringing Red Star Belgrade the most prestigious trophy in European football for the first time in its 50-year existence. In 2020, the national team qualified for UEFA Euro 2020 (held in 2021), their first major tournament in the country's history.
Handball is the other important team sport in the country. Macedonian clubs have enjoyed success in European competitions. RK Vardar won 2016–17 EHF Champions League, 2016–17 and 2018–19 EHF Champions League, while Kometal Gjorče Petrov Skopje won the 2002 EHF Champions League, EHF Women's Champions League. The European Women's Handball Championship took place in 2008 in North Macedonia in Skopje and Ohrid; the North Macedonia women's national handball team, women's national team finished seventh place. The country's North Macedonia men's national handball team, men's national team has appeared in the European and World championships multiple times, with a best finish of fifth at the former (2012 European Men's Handball Championship, 2012) and ninth at the latter (2015 World Men's Handball Championship, 2015).
The North Macedonia men's national basketball team, North Macedonia national basketball team represents North Macedonia in international basketball. The team is run by the Basketball Federation of North Macedonia, the governing body of basketball in North Macedonia which was created in 1992 and joined FIBA in 1993. North Macedonia has participated in three EuroBaskets since then with its best finish at 4th place in EuroBasket 2011, 2011. It plays its home games at the Boris Trajkovski Sports Center in Skopje. Pero Antić became the List of foreign NBA players, first Macedonian basketball player to play in the National Basketball Association. He also won three EuroLeague trophies.
In the summer months the Ohrid Swimming Marathon is an annual event on
 The history of film making in the country dates back over 110 years. The first film to be produced on the territory of the present-day country was made in 1895 by Manakis brothers, Janaki and Milton Manaki in Bitola. Throughout the past century, the medium of film has depicted the history, culture and everyday life of the Macedonian people. Over the years many Macedonian films have been presented at film festivals around the world and several of these films have won prestigious awards. The first Macedonian feature film was ''Frosina'', released in 1952 and directed by Vojislav Nanović.
The first feature film in colour was ''Miss Stone'', a movie about a Protestant missionary in Ottoman Macedonia. It was released in 1958. The highest grossing feature film in North Macedonia was ''Bal-Can-Can'', having been seen by over 500,000 people in its first year alone. In 1994, Milcho Manchevski's film ''Before the Rain (1994 film), Before the Rain'' was nominated for an Academy Award in the category of Academy Award for Best International Feature Film, Best International Feature Film. Manchevski continues to be the most prominent modern filmmaker in the country having subsequently written and directed ''Dust (2001 film), Dust'' and ''Shadows (2007 film), Shadows''. In 2020, the documentary ''Honeyland (2019 film), Honeyland'' (2019) directed by Tamara Kotevska and Ljubomir Stefanov, received nominations in the categories for Academy Award for Best International Feature Film, Best International Feature Film and Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature, Best Documentary Feature at the 92nd Academy Awards, making it the first non-fictional film to receive a nomination in both categories.
The history of film making in the country dates back over 110 years. The first film to be produced on the territory of the present-day country was made in 1895 by Manakis brothers, Janaki and Milton Manaki in Bitola. Throughout the past century, the medium of film has depicted the history, culture and everyday life of the Macedonian people. Over the years many Macedonian films have been presented at film festivals around the world and several of these films have won prestigious awards. The first Macedonian feature film was ''Frosina'', released in 1952 and directed by Vojislav Nanović.
The first feature film in colour was ''Miss Stone'', a movie about a Protestant missionary in Ottoman Macedonia. It was released in 1958. The highest grossing feature film in North Macedonia was ''Bal-Can-Can'', having been seen by over 500,000 people in its first year alone. In 1994, Milcho Manchevski's film ''Before the Rain (1994 film), Before the Rain'' was nominated for an Academy Award in the category of Academy Award for Best International Feature Film, Best International Feature Film. Manchevski continues to be the most prominent modern filmmaker in the country having subsequently written and directed ''Dust (2001 film), Dust'' and ''Shadows (2007 film), Shadows''. In 2020, the documentary ''Honeyland (2019 film), Honeyland'' (2019) directed by Tamara Kotevska and Ljubomir Stefanov, received nominations in the categories for Academy Award for Best International Feature Film, Best International Feature Film and Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature, Best Documentary Feature at the 92nd Academy Awards, making it the first non-fictional film to receive a nomination in both categories.
North Macedonia
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
North Macedonia
from RFE/RL
North Macedonia
from BBC News * *
Key Development Forecasts for North Macedonia
from International Futures {{Authority control North Macedonia, Balkan countries Landlocked countries Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of the United Nations Member states of NATO Republics Southeastern European countries Southern European countries States and territories established in 1991 1991 establishments in the Republic of Macedonia Countries in Europe Albanian-speaking countries and territories Country name changes Countries of Europe with multiple official languages
Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (a ...
. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
. It is a landlocked country
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
bordering Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
to the northwest, Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
to the north, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
to the east, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
to the south, and Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
to the west. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia
Macedonia () is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid 19th century. T ...
. Skopje
Skopje ( , , ; mk, Скопје ; sq, Shkup) is the capital and List of cities in North Macedonia by population, largest city of North Macedonia. It is the country's political, cultural, economic, and academic centre.
The territory of Sk ...
, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's 1.83 million people. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
, Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
, Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
, Bosniaks, Aromanians
The Aromanians ( rup, Armãnji, Rrãmãnji) are an ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgaria, northern and ...
and a few other minorities.
The region's history begins with the kingdom of Paeonia, a mixed Thraco- Illyrian polity. In the late sixth century BC, the area was subjugated by the Persian Achaemenid Empire, then incorporated into the Kingdom of Macedonia
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
in the fourth century BC. The Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
conquered the region in the second century BC and made it part of the larger province of Macedonia. The area remained part of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, but was often raided and settled by Slavic tribes
This is a list of Slavic peoples and Slavic tribes reported in Late Antiquity and in the Middle Ages, that is, before the year AD 1500.
Ancestors
*Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers)
** Proto-Balto-Slavs (common ancestors of B ...
beginning in the sixth century of the Christian era. Following centuries of contention between the Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
, Byzantine, and Serbian Empire
The Serbian Empire ( sr, / , ) was a medieval Serbian state that emerged from the Kingdom of Serbia. It was established in 1346 by Dušan the Mighty, who significantly expanded the state.
Under Dušan's rule, Serbia was the major power in the ...
s, it was part of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
from the mid-14th until the early 20th century, when, following the Balkan Wars of 1912 and 1913, the modern territory of North Macedonia came under Serbian rule.
During the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the territory was ruled by Bulgaria, but after the end of the war it returned to Serbian rule as part of the newly formed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
. During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, it was again ruled by Bulgaria; and in 1945 it was established as a constituent state
Administrative division, administrative unit,Article 3(1). country subdivision, administrative region, subnational entity, constituent state, as well as many similar terms, are generic names for geographical areas into which a particular, ind ...
of communist Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yugo ...
, which it remained until its peaceful secession in 1991. The country became a member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
in April 1993, but as a result of a dispute with Greece over the name "Macedonia", it was admitted under the provisional description "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (abbreviated as "FYR Macedonia" or "FYROM"). In June 2018, Macedonia and Greece resolved the dispute with an agreement that the country should rename itself "Republic of North Macedonia". This renaming came into effect in February 2019.
A unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigrou ...
parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
al republic, North Macedonia is a member of the UN, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
, the Council of Europe, the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
, OSCE
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
, CEFTA, BSEC
The Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation (BSEC) is a regional international organization focusing on multilateral political and economic initiatives aimed at fostering cooperation, peace, stability and prosperity in the Black Sea ...
and the WTO
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
. Since 2005, it has also been a candidate for joining the European Union. North Macedonia is an upper-middle-income country according to the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
's definitions and has undergone considerable economic reform since its independence in developing an open economy
An open economy is a type of economy where not only domestic factors but also entities in other countries engage in trade of products (goods and services). Trade can take the form of managerial exchange, technology transfers, and all kinds of goo ...
. It is a developing country, ranked 82nd on the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
; and provides social security
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifical ...
, a universal health care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized ar ...
system, and free primary and secondary education to its citizens.
Names and etymology
The state's name derives from theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word (''Makedonía''),MacedoniaOnline Etymology Dictionary a
kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
(later, region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
) named after the ancient Macedonians
The Macedonians ( el, Μακεδόνες, ''Makedónes'') were an ancient tribe that lived on the alluvial plain around the rivers Haliacmon and lower Axios in the northeastern part of mainland Greece. Essentially an ancient Greek people ...
. Their name, (''Makedónes''), ultimately derives from the ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
adjective μακεδνός (''makednós''), meaning 'tall' or 'taper', which shares the same root as the adjective (''makrós'', 'long, tall, high') in ancient Greek. The name is believed to have originally meant either 'highlanders' or 'the tall ones', possibly descriptive of the people
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of prope ...
. According to linguist Robert S. P. Beekes
Robert Stephen Paul Beekes (; 2 September 1937 – 21 September 2017) was a Dutch linguist who was emeritus professor of Comparative Indo-European Linguistics at Leiden University and an author of many monographs on the Proto-Indo-European langu ...
, both terms are of pre-Greek substrate origin and cannot be explained in terms of Indo-European morphology. However, according to linguist Filip De Decker, Beekes's arguments are insufficient.
In the early 19th century, the name of Macedonia was almost unknown in the modern-day area. It was revived only in middle of the century, with the rise of nationalism in the Ottoman Empire
The rise of the Western notion of nationalism in the Ottoman Empire eventually caused the breakdown of the Ottoman ''millet'' concept. An understanding of the concept of nationhood prevalent in the Ottoman Empire, which was different from the c ...
. In the early 20th century the region was already a national cause, contested among Bulgarian, Greek and Serbian nationalists. During the interwar period the use of the name ''Macedonia'' was prohibited in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, due to the implemented policy of Serbianisation
Serbianisation American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), or Serbianization, also known as Serbification, and Serbisation American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), or ...
of the local Slavic-speakers. The name ''Macedonia'' was adopted officially for the first time at the end of the Second World War by the new Socialist Republic of Macedonia, which became one of the six constituent countries of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. After the fall of Communism
The Revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, was a revolutionary wave that resulted in the end of most communist states in the world. Sometimes this revolutionary wave is also called the Fall of Nations or the Autumn of Nat ...
, with the beginning of the breakup of Yugoslavia, this federal entity declared independence and changed its official name to the Republic of Macedonia in 1991. Prior to June 2018, the use of the name ''Macedonia'' was disputed between Greece and the then-Republic of Macedonia.
The Prespa agreement
The Prespa agreement,; In mk, Договорот од Преспа, translit=Dogovorot od Prespa or Преспански договор, ''Prespanski dogovor'' also known as the Treaty of Prespa, the Prespes deal or the Prespa accord, is an agre ...
of June 2018 saw the country change its name to the ''Republic of North Macedonia'' eight months later. A non-binding national referendum on the matter passed with 90% approval but did not reach the required 50% turnout amidst a boycott, leaving the final decision with parliament to ratify the result. Parliament approved of the name change on 19 October, reaching the required two-thirds majority needed to enact constitutional changes. The vote to amend the constitution and change the name of the country passed on 11 January 2019 in favour of the amendment. The amendment entered into force on 12 February, following the ratification of the Prespa agreement and the Protocol on the Accession of North Macedonia to NATO by the Greek Parliament
The Hellenic Parliament ( el, Ελληνικό Κοινοβούλιο, Elliniko Kinovoulio; formally titled el, Βουλή των Ελλήνων, Voulí ton Ellínon, Boule of the Hellenes, label=none), also known as the Parliament of the He ...
. Despite the renaming, the country is unofficially referred to as 'Macedonia' by most of its citizens and most of the local media outlets.
History
Early history
 North Macedonia geographically roughly corresponds to the ancient kingdom of Paeonia, which was located immediately north of the ancient
North Macedonia geographically roughly corresponds to the ancient kingdom of Paeonia, which was located immediately north of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
.Strabo, ''Geography''Book 7, Frg. 4:
/ref> Paeonia was inhabited by the Paeonians, a
Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied ...
people
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of prope ...
, whilst the northwest was inhabited by the Dardani
The Dardani (; grc, Δαρδάνιοι, Δάρδανοι; la, Dardani) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their ...
and the southwest by tribes known historically as the Enchelae, Pelagones, and Lyncestae; the latter two are generally regarded as Molossian
The Molossians () were a group of ancient Greek tribes which inhabited the region of Epirus in classical antiquity. Together with the Chaonians and the Thesprotians, they formed the main tribal groupings of the northwestern Greek group. On thei ...
tribes of the northwestern Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
group, whilst the former two are considered Illyrian.The Cambridge Ancient History Volume 3, Part 3: The Expansion of the Greek World, Eighth to Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman and N. G. L. Hammond, 1982, , p. 284. The headwaters of the Axios river
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around ...
are mentioned by Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
as the home of the Paeonians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
allies of Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in present-day Turkey, south-west of Ç ...
.
In the late 6th century BC, the Achaemenid Persia
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
ns under Darius the Great conquered the Paeonians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
, incorporating what is today North Macedonia within their vast territories. Following the loss in the Second Persian invasion of Greece in 479 BC, the Persians eventually withdrew from their European territories, including from what is today North Macedonia.

Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
absorbedWarfare in the ancient world: from the Bronze Age to the fall of Rome. By Stefan G. Chrissanthos, p. 75 the regions of Upper Macedonia (Lynkestis and Pelagonia) and the southern part of Paeonia (Deuriopus Deuriopus or Derriopos ( Strabo: Δευρίοπος ''Deuriopos''; Stephanus of Byzantium: Δουρίοπος ''Douriopos'') was a subdivision of Paionia, in what is today North Macedonia. Its exact limits are unclear, but it is known that it conta ...
) into the kingdom of Macedon in 356 BC. Philip's son Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
conquered the remainder of the region and incorporated it in his empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
, reaching as far north as Scupi
Scupi (''Σκούποι'' in ancient greek) is an archaeological site located between Zajčev Rid (''Зајчев Рид'' 'Rabbit Hill') and the Vardar River, several kilometers from the center of Skopje in North Macedonia. A Roman military camp w ...
, but the city and the surrounding area remained part of Dardania.Macedonia yesterday and today Author Giorgio Nurigiani, Publisher Teleurope, 1967 p. 77. After the death of Alexander, Celtic armies began to bear down on the southern regions, threatening the kingdom of Macedon. In 310 BC, they attacked the area, but were defeated.
The Romans established the province of Macedonia in 146 BC. By the time of Diocletian, the province had been subdivided between ''Macedonia Prima'' ("first Macedonia") on the south, encompassing most of the kingdom of Macedon, and ''Macedonia Salutaris'' (meaning "wholesome Macedonia", known also as ''Macedonia Secunda'', "second Macedonia") on the north, encompassing partially Dardania and the whole of Paeonia; most of the country's modern boundaries fell within the latter, with the city of Stobi
Stobi or Stoboi ( grc, Στόβοι, Stóboi; la, Stobi; mk, Стоби, Stobi), was an ancient town of Paeonia, later conquered by Macedon, and finally turned into the capital of the Roman province of Macedonia Salutaris. It is located near ...
as its capital.A Companion to Ancient Macedonia, By Joseph Roisman and Ian Worthington, p. 549 Roman expansion brought the Scupi area under Roman rule in the time of Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
(81–96 AD), and it fell within the Province of Moesia. Whilst Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
remained the dominant language in the eastern part of the Roman empire, especially south of the Jireček Line
The Jireček Line is a conceptual boundary through the ancient Balkans that divides the influence of the Latin (in the north) and Greek (in the south) languages in the Roman Empire from antiquity until the 4th century. The border has been repeate ...
, Latin spread to some extent in Macedonia.A. F. Christidis (2007). ''A History of Ancient Greek: From the Beginnings to Late Antiquity'', Cambridge University Press, p. 351: "Despite Roman domination, there was no retreat on the part of Greek tradition in the eastern part of the empire, and only in Macedonia did Latin spread in some extent".
Medieval period

Slavic tribes
This is a list of Slavic peoples and Slavic tribes reported in Late Antiquity and in the Middle Ages, that is, before the year AD 1500.
Ancestors
*Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers)
** Proto-Balto-Slavs (common ancestors of B ...
settled in the Balkan region including North Macedonia by the late 6th century AD. They were led by Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars () were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai ( el, Βαρχονίτες, Varchonítes), or Pseudo-Avars ...
. The Slavs settled on places of earlier settlements and probably merged later with the local populations to form mixed ''Byzantine-Slavic communities''. Historical records document that in a Bulgar
Bulgar may refer to:
*Bulgars, extinct people of Central Asia
*Bulgar language, the extinct language of the Bulgars
* Oghur languages
Bulgar may also refer to:
*Bolghar, the capital city of Volga Bulgaria
*Bulgur, a wheat product
* Bulgar, an Ash ...
ruler called Kuber
Kuber, (also Kouber or Kuver), was a Bulgar leader who, according to the ''Miracles of Saint Demetrius'', liberated a mixed Bulgar and Byzantine Christian population in the 670s, whose ancestors had been transferred from the Eastern Roman Empi ...
led a group of largely Christians called ''Sermesianoi'' who were his subjects, and they settled in the region of Pelagonia. They may have consisted of Bulgars, Byzantines, Slavs and even Germanic tribes. There is no more information of Kuber's life. Presian's reign apparently coincides with the extension of Bulgarian control over the Slavic tribes in and around Macedonia. The Slavic tribes that settled in the region of Macedonia converted to Christianity around the 9th century during the reign of Tsar Boris I of Bulgaria. The Ohrid Literary School
The Ohrid Literary School or Ohrid- ''Devol'' Literary school was one of the two major cultural centres of the First Bulgarian Empire, along with the Preslav Literary School ( Pliska Literary School). The school was established in Ohrid (in what i ...
became one of the two major cultural centres of the First Bulgarian Empire, along with the Preslav Literary School
The Preslav Literary School ( bg, Преславска книжовна школа), also known as the Pliska Literary School or Pliska-Preslav Literary school was the first literary school in the medieval Bulgarian Empire. It was established by ...
. Established in Ohrid in 886 by Saint Clement of Ohrid
Saint Clement of Ohrid ( Bulgarian, Serbian and Macedonian: Свети Климент Охридски, ; el, Ἅγιος Κλήμης τῆς Ἀχρίδας; sk, svätý Kliment Ochridský; – 916) was one of the first medieval Bulgarian ...
on the order of Boris I, the Ohrid Literary School was involved in the spreading of the Cyrillic script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking co ...
.
After Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria
Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria refers to a conflict beginning in 967/968 and ending in 971, carried out in the eastern Balkans, and involving the Kievan Rus', Bulgaria, and the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantines encouraged the Rus' ruler Sviatosl ...
, the Byzantines took control of East Bulgaria. Samuil
Samuel (also Samuil; bg, Самуил, ; mk, Самоил/Самуил, ; Old Church Slavonic: Самоилъ; died October 6, 1014) was the Tsar (''Emperor'') of the First Bulgarian Empire from 997 to 6 October 1014. From 977 to 997, he was ...
, one of the Cometopuli brothers, was proclaimed Tsar of Bulgaria
The monarchs of Bulgaria ruled the country during three periods of Bulgaria's history as an independent country: from the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 to the Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria in 1018; from the Uprising of As ...
. He moved the capital to Skopje and then to Ohrid, which had been the cultural and military centre of southwestern Bulgaria since Boris I's rule. Samuil reestablished Bulgarian power, but after several decades of conflicts, in 1014, the Byzantine Emperor Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar S ...
defeated his armies, and within four years the Byzantines restored control over the Balkans (modern-day North Macedonia was included into a new province, called Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
) for the first time since the 7th century. The rank of the autocephalous Bulgarian Patriarchate
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgarsk ...
was lowered due to its subjugation to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
and it was transformed into the Archbishopric of Ohrid
The Archbishopric of Ohrid, also known as the Bulgarian Archbishopric of Ohrid
*T. Kamusella in The Politics of Language and Nationalism in Modern Central Europe, Springer, 2008, p. 276
*Aisling Lyon, Decentralisation and the Management of Ethni ...
. By the late 12th century, Byzantine decline saw the region contested by various political entities, including a brief Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
occupation in the 1080s.
In the early 13th century, a revived Bulgarian Empire gained control of the region. Plagued by political difficulties, the empire did not last, and the region came once again under Byzantine control in the early 14th century. In the 14th century, it became part of the Serbian Empire
The Serbian Empire ( sr, / , ) was a medieval Serbian state that emerged from the Kingdom of Serbia. It was established in 1346 by Dušan the Mighty, who significantly expanded the state.
Under Dušan's rule, Serbia was the major power in the ...
. Skopje became the capital of Tsar Stefan Dušan
Stefan Uroš IV Dušan ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Урош IV Душан, ), known as Dušan the Mighty ( sr, / ; circa 1308 – 20 December 1355), was the King of Serbia from 8 September 1331 and Tsar (or Emperor) and autocrat of the Serbs, Gre ...
's empire. Following Dušan's death, a weak successor appeared, and power struggles between nobles divided the Balkans once again. These events coincided with the entry of the Ottoman Turks into Europe.
Ottoman period
The Kingdom of Prilep was one of the short-lived states that emerged from the collapse of the Serbian Empire in the 14th century, which was seized by the Ottomans at the end of the same century. Gradually, all of the central Balkans were conquered by theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
and remained under its domination for five centuries as part of the province or Eyalet of Rumelia. The name '' Rumelia'' ( Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Turkish, referring to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Turks from the Byzantine Empire. Over the centuries Rumelia Eyalet was reduced in size through administrative reforms, until by the 19th century it consisted of a region of central Albania and western North Macedonia with its capital at Manastir or present-day Bitola. Rumelia Eyalet was abolished in 1867 and that territory of Macedonia subsequently became part of vilayets of Manastir, Kosova
The Republic of Kosova ( sq, Republika e Kosovës) or First Republic of Kosovo was a self-declared proto-state in Southeastern Europe established in 1991. During its peak, it tried to establish its own parallel political institutions in oppo ...
and Selanik
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area, and the capi ...
until the end of Ottoman rule in 1912. With the beginning of the Bulgarian National Revival
The Bulgarian National Revival ( bg, Българско национално възраждане, ''Balgarsko natsionalno vazrazhdane'' or simply: Възраждане, ''Vazrazhdane'', and tr, Bulgar ulus canlanması) sometimes called the Bu ...
in the 19th century, many of the reformers were from this region, including the Miladinov brothers
The Miladinov brothers ( bg, Братя Миладинови, ''Bratya Miladinovi'', mk, Браќа Миладиновци, ''Brakja Miladinovci''), Dimitar Miladinov (1810–1862) and Konstantin Miladinov (1830–1862), were Bulgarian poets ...
, Rajko Žinzifov, Joakim Krčovski, Kiril Pejčinoviḱ and others. The bishoprics of Skopje, Debar
Debar ( mk, Дебaр ; Albanian: ''Dibër''/''Dibra'' or ''Dibra e Madhe;'' ) is a city in the western part of North Macedonia, near the border with Albania, off the road from Struga to Gostivar. It is the seat of Debar Municipality. Debar has ...
, Bitola, Ohrid
Ohrid ( mk, Охрид ) is a city in North Macedonia and is the seat of the Ohrid Municipality. It is the largest city on Lake Ohrid and the List of cities in North Macedonia, eighth-largest city in the country, with the municipality recording ...
, Veles, and Strumica voted to join the Bulgarian Exarchate after it was established in 1870.
Modern period
Macedonian autonomism

 Several movements whose goals were the establishment of an autonomous Macedonia, which would encompass the entire region of Macedonia, began to arise in the late 19th century; the earliest of these was the Bulgarian Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Committees, later becoming Secret Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (SMARO). In 1905 it was renamed the Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (IMARO), and after
Several movements whose goals were the establishment of an autonomous Macedonia, which would encompass the entire region of Macedonia, began to arise in the late 19th century; the earliest of these was the Bulgarian Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Committees, later becoming Secret Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (SMARO). In 1905 it was renamed the Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization (IMARO), and after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
the organisation separated into the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization
The Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO; bg, Вътрешна Македонска Революционна Организация (ВМРО), translit=Vatrešna Makedonska Revoljucionna Organizacija (VMRO); mk, Внатр� ...
(IMRO) and the Internal Thracian Revolutionary Organisation
The Internal Thracian Revolutionary Organisation ( Bulgarian: Вътрешна тракийска революционна организация, ''Vatreshna trakiyska revolutsionna organizatsiya'', ITRO) was a Bulgarian revolutionary organisatio ...
(ITRO).
In the early years of the organisation, membership eligibility was exclusive to Bulgarians, but later it was extended to all inhabitants of European Turkey regardless of ethnicity or religion. The majority of its members were Macedonian Bulgarians
Macedonians or Macedonian Bulgarians ( bg, македонци or македонски българи), sometimes also referred to as Macedono-Bulgarians, Macedo-Bulgarians, or Bulgaro-Macedonians are a regional, ethnographic group of et ...
. In 1903, IMRO organised the Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising
The Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising, or simply the Ilinden Uprising of August–October 1903 ( bg, Илинденско-Преображенско въстание, Ilindensko-Preobrazhensko vastanie; mk, Илинденско востание, ...
against the Ottomans, which after some initial successes, including the forming of the Kruševo Republic, was crushed with much loss of life. The uprising and the forming of the Kruševo Republic are considered the cornerstone and precursors to the eventual establishment of the Macedonian state. The leaders of the Ilinden uprising are celebrated as national heroes in North Macedonia. The names of IMRO revolutionaries like Gotse Delchev
Georgi Nikolov Delchev ( Bulgarian/ Macedonian: Георги/Ѓорѓи Николов Делчев; 4 February 1872 – 4 May 1903), known as Gotse Delchev or Goce Delčev (''Гоце Делчев'', originally spelled in older Bulgar ...
, Pitu Guli
Pitu Guli (; 1865–1903) was an Aromanian revolutionary in Ottoman Macedonia, a local leader of what is commonly referred to as the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO).Brown, K. (2003) ''The Past in Question: Modern Mace ...
, Dame Gruev
Damyan Yovanov Gruev (,The first names can also be transliterated as ''Damjan Jovanov'', after Bulgarian Дамян Йованов Груев and Macedonian Дамјан Јованов Груев. The last name is also sometimes rendered as ''G ...
and Yane Sandanski were included into the lyrics of the national anthem of the state of North Macedonia "Denes nad Makedonija
"" ( mk, Денес над Македонија, ; ) is the national anthem of North Macedonia; both the music and lyrics date from the early 1940s. Todor Skalovski composed the music, while the lyrics were written by Vlado Maleski. It was adopte ...
" ("Today over Macedonia"). The major national holiday of North Macedonia, the Republic Day
Republic Day is the name of a holiday in several countries to commemorate the day when they became republics.
List
January 1 January in Slovak Republic
The day of creation of Slovak republic. A national holiday since 1993. Officially cal ...
, is celebrated on 2 August, Ilinden (St. Elijah day), the day of the Ilinden uprising.
Kingdom of Serbia
Macedonian dialects
The dialects of Macedonian comprise the Slavic dialects spoken in the Republic of North Macedonia as well as some varieties spoken in the wider geographic region of Macedonia. They are part of the dialect continuum of South Slavic languages that ...
and standard Bulgarian were proscribed. IMRO, together with local Albanians, organised the Ohrid–Debar uprising against the Serbian rule. Within a few days the rebels captured the towns of Gostivar, Struga and Ohrid, expelling the Serbian troops. According to the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace report, a Serbian army of 100,000 regulars suppressed the uprising. Many were killed and tens of thousands refugees fled to Bulgaria and Albania.

World War I
During theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, most of today's North Macedonia was part of the Bulgarian occupied zone of Serbia after the country was invaded by the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
in the fall of 1915. The region was known as the “Military Inspection Area of Macedonia” and was administered by a Bulgarian military commander. A policy of Bulgarization of the region and its population was immediately initiated, during the period the IMRO arose from a clandestine organization to serve as gendarmerie, taking control of the whole police structure, enforcing the Bulgarization of the region. According to Robert Gerwarth
Robert Gerwarth (born 12 February 1976) is a German historian and author who specialises in European history, with an emphasis on German history. Since finishing a British Academy Postdoctoral Fellowship at the University of Oxford, he has held ...
, the Bulgarian denationalization policy, including its paramilitary aspect, was almost identical in its intent and execution to the Serbian policy that preceded it.
Bulgarian language was to be exclusively used, Serbian Cyrillic
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet ( sr, / , ) is a variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language, updated in 1818 by Serbian linguist Vuk Karadžić. It is one of the two alphabets used to write standard modern Serbian, t ...
was forbidden, Serbian priests were arrested and deported, Serbian-sounding names had to be changed to Bulgarian ones, schoolteachers were brought from Bulgaria while Serbian books were taken from schools and libraries and publicly destroyed. Adult males were sent to labour camps or forced to join the Bulgarian Army, representatives of the Serbian intelligentsia were deported or executed. According to Paul Mojzes
Paul Mojzes (born 10 November 1936) is an academic who is professor emeritus of Religious Studies at Rosemont College.
Education and career
Mojzes was born in Osijek and grew up in Novi Sad, Yugoslavia. Upon graduation from the gymnasium in No ...
the aim of the Bulgarian government was to create pure Bulgarian territories by denationalizing the non-Bulgarian Slavic population of Macedonia.
Kingdom of Yugoslavia
After the capitulation of Bulgaria and the end of the First World War, the area returned under Belgrade control as part of the newly formedKingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
"Kraljevina Jugoslavija! Novi naziv naše države. No, mi smo itak med seboj vedno dejali Jugoslavija, četudi je bilo na vseh uradnih listih Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev. In tudi drugi narodi, kakor Nemci in Francozi, so pisali že prej v svojih listih mnogo o Jugoslaviji. 3. oktobra, ko je kralj Aleksander podpisal "Zakon o nazivu in razdelitvi kraljevine na upravna območja", pa je bil naslov kraljevine Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev za vedno izbrisan." (Naš rod ("Our Generation", a monthly Slovenian language periodical), Ljubljana 1929/30, št. 1, str. 22, letnik I.) and saw a reintroduction of anti-Bulgarian measures. Bulgarian teachers and clergy were expelled, Bulgarian language signs and books removed, and all Bulgarian organisations dissolved. Also after the Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine
The Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine (french: Traité de Neuilly-sur-Seine) required Bulgaria to cede various territories, after Bulgaria had been one of the Central Powers defeated in World War I. The treaty was signed on 27 November 1919 at Neuilly ...
, the Strumica region was annexed to Serbian Macedonia in 1919.
The Serbian government pursued a policy of forced Serbianisation
Serbianisation American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), or Serbianization, also known as Serbification, and Serbisation American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), or ...
in the region, which included systematic suppression of Bulgarian activists, altering family surnames, internal colonisation, exploiting workers, and intense propaganda. To aid the implementation of this policy, some 50,000 Serbian army and gendarmerie were stationed in present-day North Macedonia. By 1940 about 280 Serbian colonies (comprising 4,200 families) were established as part of the government's internal colonisation program (initial plans envisaged 50,000 families settling in present-day North Macedonia).
In 1929, the Kingdom was officially renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
, and divided into provinces called ''banovinas''. South Serbia, including all of present-day North Macedonia, became the Vardar Banovina
The Vardar Banovina, or Vardar Banate ( mk, Вардарска бановина, Vardarska banovina; sr, Вардарска бановина, translit=Vardarska Banovina; al, Banovina e Vardarit, italics=no), was a province ( banate) of the Kin ...
of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.
The Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization
The Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO; bg, Вътрешна Македонска Революционна Организация (ВМРО), translit=Vatrešna Makedonska Revoljucionna Organizacija (VMRO); mk, Внатр� ...
(IMRO) promoted the concept of an Independent Macedonia in the interwar period. Its leaders—including Todor Alexandrov
Todor Aleksandrov Poporushov, best known as Todor Alexandrov ( Bulgarian/ Macedonian: Тодор Александров), also spelt as Alexandroff (4 March 1881 – 31 August 1924), was a Bulgarian revolutionary, army officer, politician and t ...
, Aleksandar Protogerov
Alexandar Protogerov ( Bulgarian: Александър Протогеров) (28 February 1867, Ohrid – 7 July 1928, Sofia) was a Bulgarian general, politician and revolutionary, as well as a member of the revolutionary movement in Macedonia, ...
, and Ivan Mihailov
Ivan Mihailov Gavrilov ( bg, Иван Михайлов Гаврилов; mk, Ванчо Михајлов Гаврилов;He is credited in English-language sources as ''Mihailov'', while the Bulgarian and Macedonian transliteration schemes ...
—promoted independence of the Macedonian territory split between Serbia and Greece for the whole population, regardless of religion and ethnicity. The Bulgarian government of Alexander Malinov in 1918 offered to give Pirin Macedonia
Pirin Macedonia or Bulgarian Macedonia ( bg, Пиринска Македония; Българска Македония) (''Pirinska Makedoniya or Bulgarska Makedoniya'') is the third-biggest part of the geographical region Macedonia located on t ...
for that purpose after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, but the Great Powers did not adopt this idea because Serbia and Greece opposed it. In 1924, the Communist International
The Communist International (Comintern), also known as the Third International, was a Soviet-controlled international organization founded in 1919 that advocated world communism. The Comintern resolved at its Second Congress to "struggle by ...
(Comintern) suggested that all Balkan communist parties adopt a platform of a "United Macedonia
United Macedonia ( mk, Обединета Македонија, ''Obedineta Makedonija''), or Greater Macedonia (, ''Golema Makedonija''), is an irredentist concept among ethnic Macedonian nationalists that aims to unify the transnational regio ...
" but the suggestion was rejected by the Bulgarian and Greek communists.
IMRO followed by starting an insurgent war in Vardar Macedonia, together with Macedonian Youth Secret Revolutionary Organization
The Macedonian Youth Secret Revolutionary Organization or MYSRO ( bg, Македонска младежка тайна революционна организация, mk, Македонска младинска тајна револуционер ...
, which also conducted guerrilla attacks against the Serbian administrative and army officials there. In 1923 in Stip, a paramilitary organisation called Association against Bulgarian Bandits
The Association against Bulgarian Bandits ( sr, Удружење против бугарских бандита / Udruženje protiv bugarskih bandita) was a paramilitary organization based in Štip, then in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Sloven ...
was formed by Serbian chetniks, IMRO renegades and Macedonian Federative Organization
The Macedonian Federative Organization (MFO) ( Bulgarian and Macedonian: Македонска федеративна организация/организација (MFO/МФО) ) was established in Sofia in 1921 by former Internal Macedonian Revo ...
(MFO) members to oppose IMRO and MMTRO. On 9 October 1934 IMRO member Vlado Chernozemski
Vlado Chernozemski ( Bulgarian: Владо Черноземски; born Velichko Dimitrov Kerin, bg, Величко Димитров Керин; 19 October 1897 – 9 October 1934), was a Bulgarian revolutionary. Also known as "Vlado the Chauff ...
assassinated Alexander I of Yugoslavia
Alexander I ( sr-Cyrl, Александар I Карађорђевић, Aleksandar I Karađorđević, ) ( – 9 October 1934), also known as Alexander the Unifier, was the prince regent of the Kingdom of Serbia from 1914 and later the King of Yu ...
.
The Macedonist ideas increased in Yugoslav Vardar Macedonia and among the left diaspora in Bulgaria during the interwar period. They were supported by the Comintern. In 1934, the Comintern issued a special resolution {{refimprove, date=August 2011
In business or commercial law, an extraordinary resolution or special resolutionSome jurisdictions use both terms, but meaning slightly different things. For example, in the United Kingdom, an extraordinary resolutio ...
in which for the first time directions were provided for recognising the existence of a separate Macedonian nation and Macedonian language.
World War II
During World War II, Yugoslavia was occupied by theAxis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
from 1941 to 1945. The Vardar Banovina was divided between Bulgaria and Italian-occupied Albania. Bulgarian Action Committees were established to prepare the region for the new Bulgarian administration and army. The committees were mostly formed by former members of IMRO and Macedonian Youth Secret Revolutionary Organization
The Macedonian Youth Secret Revolutionary Organization or MYSRO ( bg, Македонска младежка тайна революционна организация, mk, Македонска младинска тајна револуционер ...
(MYSRO, but some IMRO (United) former members also participated.
As leader of the Vardar Macedonian communists, Metodi Shatorov
Metodi Tasev Shatorov - Sharlo ( bg, Методи Шаторов - Шарло; mk, Методиja Шаторов - Шарло) (January 10, 1897, Prilep, Manastir Vilayet, Ottoman Empire – September 12, 1944 near Velingrad, Bulgaria) was a Bul ...
("Sharlo") switched from the Yugoslav Communist Party
The League of Communists of Yugoslavia, mk, Сојуз на комунистите на Југославија, Sojuz na komunistite na Jugoslavija known until 1952 as the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, sl, Komunistična partija Jugoslavije mk ...
to the Bulgarian Communist Party
The Bulgarian Communist Party (BCP; bg, Българска Комунистическа Партия (БКП), Balgarska komunisticheska partiya (BKP)) was the founding and ruling party of the People's Republic of Bulgaria from 1946 until 198 ...
and refused to start military action against the Bulgarian Army
The Bulgarian Land Forces ( bg, Сухопътни войски на България, Sukhopŭtni voĭski na Bŭlgariya, lit=Ground Forces of Bulgaria) are the ground warfare branch of the Bulgarian Armed Forces. The Land Forces were establishe ...
.
The Bulgarian authorities, under German pressure, were responsible for the round-up and deportation of over 7,000 Jews in Skopje and Bitola. Harsh rule by the occupying forces encouraged many Vardar Macedonians to support the Communist Partisan resistance movement of Josip Broz Tito after 1943,This policy changed after 1943 with the arrival of Tito's envoy Montenegrin Serb Svetozar Vukmanović
Svetozar Vukmanović - Tempo ( sh-Cyrl, Светозар Вукмановић - Темпо; 3 August 1912 – 6 December 2000) was a leading Montenegrin communist and member of the Central Committee of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia. D ...
-Tempo. He began in earnest to organise armed resistance to the Bulgarian rule and sharply criticised Sharlo's pro-Bulgarian policy. At a meeting of the partisan brigades, as well as a group of battalions in the Resen region on 21 December 1943, Tempo makes the following comments about Shatorov and the leadership of the MCP: "They thought that the Macedonian people were Bulgarians and that they were oppressed by the hegemony of Great Serbia and had to be transferred to Bulgaria. Their basic slogan is: 'All non-Macedonians out of Macedonia'. The capital ''J'' erbo-Croatian spelling of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavian, etc.was deleted from all documents. In fact they did not want Yugoslavia, no matter where it stood politically. When the war started, the initial decision of this leadership was to be separate from Yugoslavia and from Tito. They declared that Macedonia would be free as soon as the Bulgarians came...." and the National Liberation War
Wars of national liberation or national liberation revolutions are conflicts fought by nations to gain independence. The term is used in conjunction with wars against foreign powers (or at least those perceived as foreign) to establish separat ...
ensued."НОБ на Македонија" Јован Поповски. Скопје, 1962"Историја на Македонскиот Народ" Александар Стојановски, Иван Катарџиев, Данчо Зографски. Скопје, 1988
In Vardar Macedonia, after the Bulgarian coup d'état of 1944
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
, the Bulgarian troops, surrounded by German forces, fought their way back to the old borders of Bulgaria. Under the leadership of the new Bulgarian pro-Soviet government, four armies, 455,000 strong in total, were mobilised and reorganised. Most of them re-entered occupied Yugoslavia in early October 1944 and moved from Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
to Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the Nišava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, while ...
, Skopje and Pristina
Pristina, ; sr, / (, ) is the capital and largest city of Kosovo. The city's municipal boundaries in Pristina District form the largest urban center in Kosovo. After Tirana, Pristina has the second largest population of ethnic Albanians an ...
with the strategic task of blocking the German forces withdrawing from Greece. The Bulgarian army would reach the Alps in Austria, participating in the expulsion of the Germans to the west, through Yugoslavia and Hungary.
Compelled by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
with a view towards the creation of a large South Slav Federation, in 1946 the new Communist government, led by Georgi Dimitrov, agreed to give Bulgarian Macedonia to a United Macedonia
United Macedonia ( mk, Обединета Македонија, ''Obedineta Makedonija''), or Greater Macedonia (, ''Golema Makedonija''), is an irredentist concept among ethnic Macedonian nationalists that aims to unify the transnational regio ...
. With the Bled agreement, in 1947 Bulgaria formally confirmed the envisioned unification of the Macedonian region, but postponed this act until after the formation of the future Federation. It was the first time it accepted the existence of a separate Macedonian ethnicity and language. After the Tito–Stalin split
The Tito–Stalin split or the Yugoslav–Soviet split was the culmination of a conflict between the political leaderships of Yugoslavia and the Soviet Union, under Josip Broz Tito and Joseph Stalin, respectively, in the years following World W ...
the region of Pirin Macedonia remained part of Bulgaria and later the Bulgarian Communist Party revised its view of the existence of a separate Macedonian nation and language.
Socialist Yugoslavia
 In December 1944 the Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia (ASNOM) proclaimed the People's Republic of Macedonia as part of the ''People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia''. ASNOM remained an acting government until the end of the war. The Macedonian alphabet was codified by linguists of ASNOM, who based their alphabet on the phonetic alphabet of Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and the principles of Krste Petkov Misirkov. During the civil war in Greece (1946–1949), Macedonian communist insurgents supported the Greek communists. Many refugees fled to the Socialist Republic of Macedonia from there. The state dropped ''Socialist'' from its name in 1991 when it peacefully seceded from Yugoslavia.
The new republic became one of the six republics of the Yugoslav federation. Following the federation's renaming as the
In December 1944 the Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Macedonia (ASNOM) proclaimed the People's Republic of Macedonia as part of the ''People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia''. ASNOM remained an acting government until the end of the war. The Macedonian alphabet was codified by linguists of ASNOM, who based their alphabet on the phonetic alphabet of Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and the principles of Krste Petkov Misirkov. During the civil war in Greece (1946–1949), Macedonian communist insurgents supported the Greek communists. Many refugees fled to the Socialist Republic of Macedonia from there. The state dropped ''Socialist'' from its name in 1991 when it peacefully seceded from Yugoslavia.
The new republic became one of the six republics of the Yugoslav federation. Following the federation's renaming as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yu ...
in 1963, the People's Republic of Macedonia was likewise renamed the Socialist Republic of Macedonia.
Declaration of independence
North Macedonia officially celebrates 8 September 1991 as Independence day ( mk, Ден на независноста, ''Den na nezavisnosta''), with regard to the referendum endorsing independence from Yugoslavia. Nohlen, D & Stöver, P (2010) ''Elections in Europe: A data handbook'', p. 1278 The anniversary of the start of theIlinden Uprising Ilinden ( Bulgarian/Macedonian Cyrillic: Илинден) or Ilindan (Serbian Cyrillic: Илиндан), meaning "Saint Elijah
Elijah ( ; he, אֵלִיָּהוּ, ʾĒlīyyāhū, meaning "My God is Yahweh/YHWH"; Greek form: Elias, ''Elías'' ...
( St. Elijah's Day) on 2 August is also widely celebrated on an official level as the Day of the Republic.
Robert Badinter
Robert Badinter (; born 30 March 1928) is a French lawyer, politician and author who enacted the abolition of the death penalty in France in 1981, while serving as Minister of Justice under François Mitterrand. He has also served in high-lev ...
, as the head of the Arbitration Commission of the Peace Conference on Yugoslavia The Arbitration Commission of the Conference on Yugoslavia (commonly known as Badinter Arbitration Committee) was an arbitration body set up by the Council of Ministers of the European Economic Community (EEC) on 27 August 1991 to provide the confer ...
, recommended EC recognition in January 1992. On 15 January 1992, Bulgaria was the first country to recognize the independence of the republic.
Macedonia remained at peace through the Yugoslav Wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and insurgencies that took place in the SFR Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001. The conflicts both led up to and resulted from ...
of the early 1990s. A few very minor changes to its border with Yugoslavia were agreed upon to resolve problems with the demarcation line between the two countries. It was seriously destabilised by the Kosovo War
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that started 28 February 1998 and lasted until 11 June 1999. It was fought by the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (i.e. Serbia and Montenegro), which controlled Kosovo before the wa ...
in 1999, when an estimated 360,000 ethnic Albanian refugees from Kosovo took refuge in the country. They departed shortly after the war, and Albanian nationalists on both sides of the border took up arms soon after in pursuit of autonomy or independence for the Albanian-populated areas of Macedonia.
21st century
2001 insurgency
conflict
Conflict may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Films
* ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton
* ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne
* ''Conflict'' (1937 film) ...
took place between the government and ethnic Albanian insurgents, mostly in the north and west of the country, between February and August 2001. The war ended with the intervention of a NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
ceasefire monitoring force. Under the terms of the Ohrid Agreement
The Ohrid Framework Agreement ( mk, Охридски рамковен договор, Ohridski ramkoven dogovor) was the peace deal signed by the government of the Republic of Macedonia (now North Macedonia) and representatives of the Albanian ...
, the government agreed to devolve greater political power and cultural recognition to the Albanian minority. The Albanian side agreed to abandon separatist demands and to recognise all Macedonian institutions fully. In addition, according to this accord, the NLA were to disarm and hand over their weapons to a NATO force. However the Macedonian security forces had two more armed confrontations with Albanian militant groups, in 2007 and 2015 respectively.
Inter-ethnic tensions flared in Macedonia in 2012, with incidents of violence between ethnic Albanians and Macedonians. In April 2017, a mob of Macedonian nationalists stormed the Macedonian Parliament in response to the election of Talat Xhaferi, an ethnic Albanian and former National Liberation Army commander during the 2001 conflict, as the Speaker of the Assembly.
Antiquisation
Upon its coming to power in 2006, but especially since the country's non-invitation to NATO in 2008, the VMRO-DPMNE government pursued a policy of "Antiquisation
Antiquization ( mk, антиквизација), otherwise known as ancient Macedonism ( mk, links=no, антички македонизам), is a term used mainly to critically describe the identity policies conducted by the nationalist VMRO- ...
" ("Antikvizatzija") as a way of putting pressure on Greece as well as for the purposes of domestic identity-building."Ghosts of the past endanger Macedonia's future". Boris Georgievski, ''Balkan Insight'', 27 October 200Statues of
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
and Philip II of Macedon, Philip of Macedon have been built in several cities across the country. Additionally, many pieces of public infrastructure, such as airports, highways, and stadiums were renamed after Alexander and Philip. These actions were seen as deliberate provocations in neighbouring Greece, exacerbating the dispute and further stalling the country's EU and NATO applications. The policy has also attracted criticism domestically, as well as from EU diplomats, and, following the Prespa agreement, it has been partly reversed after 2016 by the new SDSM
The Social Democratic Union of Macedonia ( mk, Социјалдемократски сојуз на Македонија – СДСМ, ''Socijaldemokratski Sojuz na Makedonija'' – SDSM, sq, Lidhja socialdemokrate e Maqedonisë – LSDM) is a ...
government of North Macedonia. Moreover, per Prespa agreement both countries have acknowledged that their respective understanding of the terms "Macedonia" and "Macedonian" refers to a different historical context and cultural heritage.
EU and NATO path
In August 2017, what was then the Republic of Macedonia signed a friendship agreement with Bulgaria, aiming to end the "anti-Bulgarian ideology" in the country and to solve the historical issues between the two. Under thePrespa agreement
The Prespa agreement,; In mk, Договорот од Преспа, translit=Dogovorot od Prespa or Преспански договор, ''Prespanski dogovor'' also known as the Treaty of Prespa, the Prespes deal or the Prespa accord, is an agre ...
, signed with Greece on 17 June 2018, the country agreed to change its name to the Republic of North Macedonia and stop public use of the Vergina Sun
The Vergina Sun ( el, Ήλιος της Βεργίνας, Ilios tis Vergínas, Sun of Vergina), also known as the Star of Vergina, Vergina Star or Argead Star, is a rayed solar symbol first appearing in ancient Greek art of the period between th ...
. It retained the demonym "Macedonian", but clarified this as distinct from the Hellenistic Macedonian identity in northern Greece. The agreement included removal of irredentist material from textbooks and maps in both countries, and official UN recognition of the Slavic Macedonian language
Macedonian (; , , ) is an Eastern South Slavic language. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken as a first language by around two million ...
. It replaced the bilateral Interim Accord of 1995.
The withdrawal of the Greek veto, along with the signing the friendship agreement with Bulgaria, resulted in the European Union on 27 June approving the start of accession talks, which were expected to take place in 2019, under the condition that the Prespa deal was implemented. On 5 July, the Prespa agreement was ratified by the Macedonian parliament with 69 MPs voting in favour of it. On 12 July, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
invited Macedonia to start accession talks in a bid to become the alliance's 30th member. On 30 July, the parliament of Macedonia approved plans to hold a non-binding referendum on changing the country's name, which took place on 30 September. Ninety-one percent of voters voted in favour with a 37% turnout, but the referendum was not carried because of a constitutional requirement for a 50% turnout.
 On 6 February 2019, the permanent representatives of NATO member states and Macedonian Foreign Affairs Minister Nikola Dimitrov, signed in
On 6 February 2019, the permanent representatives of NATO member states and Macedonian Foreign Affairs Minister Nikola Dimitrov, signed in Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
the accession protocol of North Macedonia into NATO. The protocol was then ratified on 8 February by the Greek parliament, thus completing all the preconditions for putting into force the Prespa agreement. Subsequently, on 12 February the Macedonian government announced the formal activation of the constitutional amendments which effectively renamed the country as North Macedonia and informed accordingly the United Nations and its member states.
In March 2020, after the ratification process by all NATO members was completed, North Macedonia acceded to NATO, becoming the 30th member state. The same month, the leaders of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
formally gave approval to North Macedonia to begin talks to join the EU. On 17 November 2020, Bulgaria refused to approve the European Union's negotiation framework for North Macedonia, effectively blocking the official start of accession talks with this country. The explanation from the Bulgarian side was: no implementation of the friendship treaty from 2017, state-supported hate speech, minority claims, and an "ongoing nation-building process" based on historical negationism of the Bulgarian identity, culture and legacy in the broader region of Macedonia
Macedonia () is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid 19th century. T ...
. The veto received condemnation by intellectuals from both states and criticism from international observers.
Protests broke out in July 2022, organized by the opposition parties, over the ''French proposal'' for the accession of North Macedonia to the EU. The accession talks for the accession of North Macedonia to the EU officially began in the same month, after the French proposal was passed by the Assembly of North Macedonia.
Geography
Location
 North Macedonia has a total area of . It lies between latitudes 40° and 43° N, and mostly between longitudes 20° and 23° E (a small area lies east of 23°). North Macedonia has some of boundaries, shared with
North Macedonia has a total area of . It lies between latitudes 40° and 43° N, and mostly between longitudes 20° and 23° E (a small area lies east of 23°). North Macedonia has some of boundaries, shared with Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
() to the North, Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
() to the northwest, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
() to the east, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
() to the south, and Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
() to the west. It is a transit way for shipment of goods from Greece, through the Balkans, towards Eastern, Western and Central Europe and through Bulgaria to the east. It is part of the larger region of Macedonia, which also includes Greek Macedonia
Macedonia (; el, Μακεδονία, Makedonía ) is a geographic and former administrative region of Greece, in the southern Balkans. Macedonia is the largest and Greek geographic region, with a population of 2.36 million in 2020. It is ...
and the Blagoevgrad Province in southwestern Bulgaria.
North Macedonia is a landlocked country
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
that is geographically clearly defined by a central valley formed by the Vardar river and framed along its borders by mountain ranges. The terrain is mostly rugged, located between the Šar Mountains
The Šar Mountains (Serbian and mk, Шар Планина, Šar Planina, colloquially also ) or Sharr Mountains ( sq, Malet e Sharrit), form a mountain range in the Balkans that extends from Kosovo and the northwest of North Macedonia to north ...
and Osogovo
Osogovo ( Bulgarian/Macedonian: ), or Osogovska Planina or Osogovski Planini (Осоговска Планина or Осоговски Планини), is a mountain range and ski resort between the south-western part of Bulgaria (Kyustendil Provi ...
, which frame the valley of the Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
river. Three large lakes—Lake Ohrid
Lake Ohrid ( mk, Охридско Езеро , al, Liqeni i Ohrit , also referred as ''Liqeni i Pogradecit'';) is a lake which straddles the mountainous border between the southwestern part of North Macedonia and eastern Albania. It is one of E ...
, Lake Prespa
The Lake Prespa is located on the tripoint of North Macedonia, Albania, and Greece. It is a system of two lakes separated by an isthmus: the Great Prespa Lake, divided between the three countries, and the Little Prespa Lake, mostly within Gree ...
and Dojran Lake
Doiran Lake (, ''Dojransko Ezero''; , ''Límni Dhoïráni''), also spelled Dojran Lake is a lake with an area of shared between North Macedonia () and Greece ().
To the west is the city of Nov Dojran (Нов Дојран), to the east the vill ...
—lie on the southern borders, bisected by the frontiers with Albania and Greece. Ohrid is considered to be one of the oldest lakes and biotopes in the world. The region is seismically active and has been the site of destructive earthquakes in the past, most recently in 1963 when Skopje was heavily damaged by a major earthquake, killing over 1,000.
North Macedonia also has scenic mountains. They belong to two different mountain ranges: the first is the Šar Mountains that continues to the West Vardar/Pelagonia group of mountains ( Baba Mountain, Nidže, Kožuf and Jakupica), also known as the Dinaric range. The second range is the Osogovo
Osogovo ( Bulgarian/Macedonian: ), or Osogovska Planina or Osogovski Planini (Осоговска Планина or Осоговски Планини), is a mountain range and ski resort between the south-western part of Bulgaria (Kyustendil Provi ...
–Belasica
Belasica (Macedonian and Bulgarian: , also translit. ''Belasitsa'' or ''Belasitza'', Ottoman Turkish: بلش Turkish: ''Beleş''), Belles ( el, Μπέλλες, ''Bélles'') or Kerkini (, ''Kerkíni'';), is a mountain range in the region of M ...
mountain chain, also known as the Rhodope Mountains, Rhodope range. The mountains belonging to the Šar Mountains and the West Vardar/Pelagonia range are younger and higher than the older mountains of the Osogovo-Belasica mountain group. Mount Korab of the Šar Mountains on the Albanian border, at , is the tallest mountain in North Macedonia. In North Macedonia there are 1,100 large sources of water. The rivers flow into three different basins: the Aegean, the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and the Black Sea.
 The Aegean basin is the largest. It covers 87% of the territory of North Macedonia, which is .
The Aegean basin is the largest. It covers 87% of the territory of North Macedonia, which is . Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . Th ...
, the largest river in this basin, drains 80% of the territory or . Its valley plays an important part in the economy and the communication system of the country. The Vardar Valley project is considered to be crucial for the strategic development of the country. The river Black Drin forms the Adriatic basin, which covers an area of about , i.e., 13% of the territory. It receives water from Lakes Prespa and Ohrid. The Black Sea basin is the smallest with only . It covers the northern side of Mount Skopska Crna Gora. This is the source of the river Binachka Morava, which joins the Great Morava, Morava, and later, the Danube, which flows into the Black Sea. North Macedonia has around fifty ponds and three natural lakes, Lake Ohrid
Lake Ohrid ( mk, Охридско Езеро , al, Liqeni i Ohrit , also referred as ''Liqeni i Pogradecit'';) is a lake which straddles the mountainous border between the southwestern part of North Macedonia and eastern Albania. It is one of E ...
, Lake Prespa
The Lake Prespa is located on the tripoint of North Macedonia, Albania, and Greece. It is a system of two lakes separated by an isthmus: the Great Prespa Lake, divided between the three countries, and the Little Prespa Lake, mostly within Gree ...
and Lake Dojran. In North Macedonia there are nine spa towns and resorts: Banište, Banja Bansko, Istibanja, Katlanovo, Kežovica, Kosovrasti, Banja Kočani, Kumanovski Banji and Negorci.
Climate
Biodiversity
The flora of North Macedonia is represented by around 210 family (biology), families, 920 genus (biology), genera, and around 3,700 plant species. The most abundant group are the flowering plants with around 3,200 species, followed by mosses (350 species) and ferns (42). Phytogeography, Phytogeographically, North Macedonia belongs to the Illyrian province of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) and the Digital Map of European Ecological Regions by the European Environment Agency, the territory of the Republic can be subdivided into four terrestrial ecoregions: the Pindus Mountains mixed forests, Balkan mixed forests, Rodope montane mixed forests, and Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests. North Macedonia had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 7.42/10, ranking it 40th globally out of 172 countries. The native forest fauna is abundant and includes bears, wild boars, wolves, foxes, squirrels, chamois and deer. The Eurasian lynx, lynx is found, very rarely, in the mountains of western Macedonia, while deer can be found in the region of Demir Kapija. Forest birds include the blackcap, the grouse, the black grouse, the Eastern imperial eagle, imperial eagle and the forest owl. The country has four national parks:Politics
 North Macedonia is a parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy with an executive (government), executive government composed of a coalition of parties from the unicameralism, unicameral legislature (, ; ''Assembly'' in English) and an independent judiciary, judicial branch with a constitutional court. The Assembly of North Macedonia, Assembly is made up of 120 seats and the members are elected every four years. The role of the President of North Macedonia, president is mostly ceremonial, with the real power resting in the hands of the Prime Minister of North Macedonia, prime minister. The president is the commander-in-chief of the state armed forces and a president of the National security, State Security Council. The president is elected every five years and he or she can be elected twice at most.
Since 2019, local government functions are divided between 80 Municipalities of North Macedonia, municipalities (, ; Grammatical number, singular: , ). The capital, Skopje, is governed as a group of ten municipalities collectively referred to as the "City of Skopje". Municipalities in North Macedonia are units of local self-government. Neighbouring municipalities may establish co-operative arrangements.
The country's main political divergence is between the largely ethnically based political parties representing the country's ethnic Macedonian majority and Albanian minority. The issue of the power balance between the two communities led to a brief war in 2001, following which a power-sharing agreement was reached. In August 2004, parliament passed legislation redrawing local boundaries and giving greater local autonomy to ethnic Albanians in areas where they predominate.
After a troublesome pre-election campaign, North Macedonia saw a relatively calm and democratic change of government in the 2006 Macedonian parliamentary election, elections held on 5 July 2006. The elections were marked by a decisive victory of the centre-right party VMRO–DPMNE, VMRO-DPMNE led by Nikola Gruevski. Gruevski's decision to include the Democratic Party of Albanians in the new government, instead of the Democratic Union for Integration–Party for Democratic Prosperity coalition which won the majority of the Albanian votes, triggered protests throughout the parts of the country with a respective number of Albanian population. A dialogue was later established between the Democratic Union for Integration and the ruling VMRO-DMPNE party as an effort to talk about the disputes between the two parties and to support European and NATO aspirations of the country.
After the early parliamentary elections held in 2008, VMRO-DPMNE and Democratic Union for Integration formed a ruling coalition. In April 2009, presidential and local elections in the country were carried out peacefully, which was crucial for Macedonian aspirations to join the EU. The ruling conservative VMRO-DPMNE party won a victory in the local elections and the candidate supported by the party, Gjorgi Ivanov, was elected as the new president.
In June 2017, Zoran Zaev of the Social Democratic Party of Macedonia, Social Democratic Party, became the new prime minister six months after early elections. The new center-left government ended 11 years of conservative VMRO-DPMNE rule led by former prime minister Nikola Gruevski.
, the acting prime minister of North Macedonia was Oliver Spasovski and the current president of the Parliament is Talat Xhaferi. The election of Xhaferi was immediately met with protests led by VMRO-DPMNE, which was quickly handled by the police.
The early parliamentary elections took place on 15 July 2020. Zoran Zaev has served as the prime minister of the Republic of North Macedonia again since August 2020. Stevo Pendarovski was sworn in as North Macedonia's new president in May 2019. Prime minister Zoran Zaev announced his resignation after his party, the Social Democratic Union, suffered losses in local elections in October 2021. In January 2022, Dimitar Kovačevski was elected as prime minister. The new coalition cabinet composed of Kovačevski's Social Democrats and two ethnic Albanian parties.
Parliament, or Assembly ( mk, Собрание, ), is the country's legislative body. It makes, proposes and adopts laws. The Constitution of North Macedonia has been in use since shortly after the independence of the republic in 1991. It limits the power of the governments, both local and national. The military is also limited by the constitution. The constitution states that North Macedonia is a social free state, and that Skopje is the capital. The 120 members are elected for a mandate of four years through a general election. Each citizen aged 18 years or older can vote for one of the political parties. The current president of Parliament is since 2017 an ethnic Albanian, Talat Xhaferi.
Executive power in North Macedonia is exercised by the Government, whose prime minister is the most politically powerful person in the country. The members of the government are chosen by the prime minister and there are ministers for each branch of the society. There are ministers for economy, finance, information technology, society, internal affairs, foreign affairs and other areas. The members of the Government are elected for a mandate of four years. Judiciary power is exercised by courts, with the court system being headed by the Judicial Supreme court, Constitutional Court and the Republican Judicial Council. The assembly appoints the judges.
North Macedonia is a parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy with an executive (government), executive government composed of a coalition of parties from the unicameralism, unicameral legislature (, ; ''Assembly'' in English) and an independent judiciary, judicial branch with a constitutional court. The Assembly of North Macedonia, Assembly is made up of 120 seats and the members are elected every four years. The role of the President of North Macedonia, president is mostly ceremonial, with the real power resting in the hands of the Prime Minister of North Macedonia, prime minister. The president is the commander-in-chief of the state armed forces and a president of the National security, State Security Council. The president is elected every five years and he or she can be elected twice at most.
Since 2019, local government functions are divided between 80 Municipalities of North Macedonia, municipalities (, ; Grammatical number, singular: , ). The capital, Skopje, is governed as a group of ten municipalities collectively referred to as the "City of Skopje". Municipalities in North Macedonia are units of local self-government. Neighbouring municipalities may establish co-operative arrangements.
The country's main political divergence is between the largely ethnically based political parties representing the country's ethnic Macedonian majority and Albanian minority. The issue of the power balance between the two communities led to a brief war in 2001, following which a power-sharing agreement was reached. In August 2004, parliament passed legislation redrawing local boundaries and giving greater local autonomy to ethnic Albanians in areas where they predominate.
After a troublesome pre-election campaign, North Macedonia saw a relatively calm and democratic change of government in the 2006 Macedonian parliamentary election, elections held on 5 July 2006. The elections were marked by a decisive victory of the centre-right party VMRO–DPMNE, VMRO-DPMNE led by Nikola Gruevski. Gruevski's decision to include the Democratic Party of Albanians in the new government, instead of the Democratic Union for Integration–Party for Democratic Prosperity coalition which won the majority of the Albanian votes, triggered protests throughout the parts of the country with a respective number of Albanian population. A dialogue was later established between the Democratic Union for Integration and the ruling VMRO-DMPNE party as an effort to talk about the disputes between the two parties and to support European and NATO aspirations of the country.
After the early parliamentary elections held in 2008, VMRO-DPMNE and Democratic Union for Integration formed a ruling coalition. In April 2009, presidential and local elections in the country were carried out peacefully, which was crucial for Macedonian aspirations to join the EU. The ruling conservative VMRO-DPMNE party won a victory in the local elections and the candidate supported by the party, Gjorgi Ivanov, was elected as the new president.
In June 2017, Zoran Zaev of the Social Democratic Party of Macedonia, Social Democratic Party, became the new prime minister six months after early elections. The new center-left government ended 11 years of conservative VMRO-DPMNE rule led by former prime minister Nikola Gruevski.
, the acting prime minister of North Macedonia was Oliver Spasovski and the current president of the Parliament is Talat Xhaferi. The election of Xhaferi was immediately met with protests led by VMRO-DPMNE, which was quickly handled by the police.
The early parliamentary elections took place on 15 July 2020. Zoran Zaev has served as the prime minister of the Republic of North Macedonia again since August 2020. Stevo Pendarovski was sworn in as North Macedonia's new president in May 2019. Prime minister Zoran Zaev announced his resignation after his party, the Social Democratic Union, suffered losses in local elections in October 2021. In January 2022, Dimitar Kovačevski was elected as prime minister. The new coalition cabinet composed of Kovačevski's Social Democrats and two ethnic Albanian parties.
Parliament, or Assembly ( mk, Собрание, ), is the country's legislative body. It makes, proposes and adopts laws. The Constitution of North Macedonia has been in use since shortly after the independence of the republic in 1991. It limits the power of the governments, both local and national. The military is also limited by the constitution. The constitution states that North Macedonia is a social free state, and that Skopje is the capital. The 120 members are elected for a mandate of four years through a general election. Each citizen aged 18 years or older can vote for one of the political parties. The current president of Parliament is since 2017 an ethnic Albanian, Talat Xhaferi.
Executive power in North Macedonia is exercised by the Government, whose prime minister is the most politically powerful person in the country. The members of the government are chosen by the prime minister and there are ministers for each branch of the society. There are ministers for economy, finance, information technology, society, internal affairs, foreign affairs and other areas. The members of the Government are elected for a mandate of four years. Judiciary power is exercised by courts, with the court system being headed by the Judicial Supreme court, Constitutional Court and the Republican Judicial Council. The assembly appoints the judges.
Foreign relations
North Macedonia became a member state of the UN on 8 April 1993, eighteen months after its independence from Yugoslavia. It was referred to within the UN as "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia", until the resolution of the Macedonia naming dispute, long-running dispute with Greece about the country's name. The major interest of the country is a full integration in the European and the wikt:transatlantic, Trans-Atlantic integration processes. North Macedonia is a member of the following international and regional organisations: IMF (since 1992), WHO (since 1993), EBRD (since 1993), Central European Initiative (since 1993), Council of Europe (since 1995), OSCE (since 1995), Southeast European Cooperative Initiative, SECI (since 1996), Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, La Francophonie (since 2001), WTO (since 2003), CEFTA (since 2006),NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
(since 2020).
In 2005, the country was officially recognised as a European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
candidate state.
At the NATO 2008 Bucharest summit, Macedonia failed to gain an invitation to join the organisation because Greece vetoed the move after the dispute over the name issue. The U.S. had previously expressed support for an invitation, but the summit then decided to extend an invitation only on condition of a resolution of the naming conflict with Greece.
In March 2009, the European Parliament expressed support for North Macedonia's EU candidacy and asked the EU Commission to grant the country a date for the start of accession talks by the end of 2009. The parliament also recommended a speedy lifting of the visa regime for Macedonian citizens. Prior to the Prespa agreement, the country failed to receive a start date for accession talks as a result of the naming dispute. However, after the Prespa agreement, North Macedonia became a member state of NATO on 27 March 2020. The EU's stance was similar to NATO's in that resolution of the naming dispute was a precondition for the start of accession talks.
In October 2012, the EU Enlargement Commissioner Štefan Füle proposed a start of accession negotiations with the country for the fourth time, while the previous efforts were blocked each time by Greece. At the same time Füle visited Bulgaria in a bid to clarify the state's position with respect to Macedonia. He established that Bulgaria had almost joined Greece in vetoing the accession talks. The Bulgarian position was that Sofia cannot grant an EU certificate to Skopje, which is systematically employing an ideology of hate towards Bulgaria.
Military
 The Army of North Macedonia, military of North Macedonia comprises the army, Macedonian Air Force, air force, and Wolves (military), special forces. The government's national defence policy aims to guarantee the preservation of the independence and sovereignty of the state, the integrity of its land area and airspace and its constitutional order. Its main goals remain the development and maintenance of a credible capability to defend the nation's vital interests and development of the Armed Forces in a way that ensures their interoperability with the armed forces of NATO and the European Union member states and their capability to participate in the full range of NATO missions.
The Ministry of Defence develops the Republic's defence strategy and assesses possible threats and risks. It is also responsible for the defence system, including training, readiness, equipment, and development, and for drawing up and presenting the defence budget.
The Army of North Macedonia, military of North Macedonia comprises the army, Macedonian Air Force, air force, and Wolves (military), special forces. The government's national defence policy aims to guarantee the preservation of the independence and sovereignty of the state, the integrity of its land area and airspace and its constitutional order. Its main goals remain the development and maintenance of a credible capability to defend the nation's vital interests and development of the Armed Forces in a way that ensures their interoperability with the armed forces of NATO and the European Union member states and their capability to participate in the full range of NATO missions.
The Ministry of Defence develops the Republic's defence strategy and assesses possible threats and risks. It is also responsible for the defence system, including training, readiness, equipment, and development, and for drawing up and presenting the defence budget.
Naming dispute
Greek Macedonia
Macedonia (; el, Μακεδονία, Makedonía ) is a geographic and former administrative region of Greece, in the southern Balkans. Macedonia is the largest and Greek geographic region, with a population of 2.36 million in 2020. It is ...
to the south. As some ethnic Greeks identify themselves as Macedonians, unrelated to the Slavic people who are associated with North Macedonia, Greece further objected to the use of the term ''Macedonian'' for the neighbouring country's largest ethnic group; it accused the country of appropriating symbols and figures that are historically considered parts of Culture of Greece, Greece's culture (such as Vergina Sun
The Vergina Sun ( el, Ήλιος της Βεργίνας, Ilios tis Vergínas, Sun of Vergina), also known as the Star of Vergina, Vergina Star or Argead Star, is a rayed solar symbol first appearing in ancient Greek art of the period between th ...
and Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
), and of promoting the irredentist concept of a United Macedonia
United Macedonia ( mk, Обединета Македонија, ''Obedineta Makedonija''), or Greater Macedonia (, ''Golema Makedonija''), is an irredentist concept among ethnic Macedonian nationalists that aims to unify the transnational regio ...
, which would include territories of Greece, Bulgaria, Albania, and Serbia.
The UN adopted the provisional reference ''the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia'' ( mk, Поранешна Југословенска Република Македонија) when the country was admitted to the organisation in 1993. The lower-cased "former" was chosen intentionally to display the provisionality of the name although most UN member countries soon abandoned the provisional reference and recognised the country as the ''Republic of Macedonia'' instead. Most international organisations adopted the same convention along with over 100 UN members and four of the five permanent United Nations Security Council, UN Security Council members. In the period between 1991 and 2019, the country's name was an ongoing issue in bilateral and international relations. The UN set up a negotiating process with a mediator, Matthew Nimetz, and the two parties to try to mediate the dispute. Following the ratification of the Prespa agreement, most major international organisations welcomed the settlement of the long-standing dispute, and adopted the country's new name.
Human rights
North Macedonia is a signatory to the European Convention on Human Rights and the UN Geneva Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees and United Nations Convention Against Torture, Convention against Torture, and the Constitution guarantees basic human rights to all Macedonian citizens. According to human rights organisations, in 2003 there were suspected extrajudicial executions, threats against, and intimidation of, human rights activists and opposition journalists, and allegations of torture by the police.Subdivisions
 North Macedonia's statistical regions exist solely for legal and statistical purposes. The regions are:
* Eastern statistical region, Eastern
* Northeastern statistical region, Northeastern
* Pelagonia statistical region, Pelagonia
* Polog statistical region, Polog
* Skopje statistical region, Skopje
* Southeastern statistical region, Southeastern
* Southwestern statistical region, Southwestern
* Vardar statistical region, Vardar
In August 2004, the country was reorganised into 84 municipalities (; sing. ); 10 of the municipalities constitute the City of
North Macedonia's statistical regions exist solely for legal and statistical purposes. The regions are:
* Eastern statistical region, Eastern
* Northeastern statistical region, Northeastern
* Pelagonia statistical region, Pelagonia
* Polog statistical region, Polog
* Skopje statistical region, Skopje
* Southeastern statistical region, Southeastern
* Southwestern statistical region, Southwestern
* Vardar statistical region, Vardar
In August 2004, the country was reorganised into 84 municipalities (; sing. ); 10 of the municipalities constitute the City of Skopje
Skopje ( , , ; mk, Скопје ; sq, Shkup) is the capital and List of cities in North Macedonia by population, largest city of North Macedonia. It is the country's political, cultural, economic, and academic centre.
The territory of Sk ...
, a distinct unit of local self-government and the country's capital.
Most of the current municipalities were unaltered or merely amalgamated from the previous 123 municipalities established in September 1996; others were consolidated and their borders changed. Prior to this, local government was organised into 34 administrative districts, communes, or counties (also opštini).
Economy
Ranked as the fourth "best reformatory state" out of 178 countries ranked by theWorld Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
in 2009, North Macedonia has undergone considerable economic reform since independence. The country has developed an open economy
An open economy is a type of economy where not only domestic factors but also entities in other countries engage in trade of products (goods and services). Trade can take the form of managerial exchange, technology transfers, and all kinds of goo ...
with trade accounting for more than 90% of GDP in recent years. Since 1996, North Macedonia has witnessed steady, though slow, economic growth with GDP growing by 3.1% in 2005. This figure was projected to rise to an average of 5.2% in the 2006–2010 period. The government has proven successful in its efforts to combat inflation, with an inflation rate of only 3% in 2006 and 2% in 2007, and has implemented policies focused on attracting foreign direct investment, foreign investment and promoting the development of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
The current government introduced a flat tax system with the intention of making the country more attractive to foreign investment. The flat tax rate was 12% in 2007 and was further lowered to 10% in 2008.
North Macedonia's unemployment, unemployment rate was 37.2% and its poverty threshold, poverty rate was 22%. Due to a number of employment measures as well as the successful process of attracting multinational corporations, and according to the State Statistical Office of North Macedonia, the country's unemployment rate in the first quarter of 2015 decreased to 27.3%. Government's policies and efforts in regards to foreign direct investments have resulted with the establishment of local subsidiaries of several world leading manufacturing companies, especially from the automotive industry, such as: Johnson Controls, Johnson Controls Inc., Van Hool, Van Hool NV, Johnson Matthey, Johnson Matthey plc, Lear Corporation, Lear Corp., Visteon, Visteon Corp., Kostal-Gruppe, Kostal GmbH, Gentherm Incorporated, Gentherm Inc., Dräxlmaier Group, Kromberg & Schubert, Marquardt Group, Marquardt GmbH, Amphenol, Amphenol Corp., Tekno Hose SpA, KEMET Corporation, KEMET Corp., Key Safety Systems Inc., ODW-Elektrik GmbH, etc.
In terms of GDP structure, the manufacturing sector, including mining and construction constituted the largest part of GDP at 21.4%, up from 21.1% in 2012. The trade, transportation and accommodation sector represents 18.2% of GDP in 2013, up from 16.7% in 2012, while agriculture represents 9.6%, up from 9.1% in the previous year.
 In terms of foreign trade, the largest sector contributing to the country's export in 2014 was "chemicals and related products" at 21.4%, followed by the "machinery and transport equipment" sector at 21.1%. North Macedonia's main import sectors in 2014 were "manufactured goods classified chiefly by material" with 34.2%, "machinery and transport equipment" with 18.7% and "mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials" with 14.4% of the total imports. Even 68.8% of the foreign trade in 2014 was done with the EU which makes the Union by far the largest trading partner of North Macedonia (23.3% with Germany, 7.9% with the UK, 7.3% with Greece, 6.2% with Italy, etc.). Almost 12% of the total external trade in 2014 was done with the Western Balkan countries.
North Macedonia has one of the highest shares of people struggling financially, with 72% of its citizens stating that they could manage on their household's income only "with difficulty" or "with great difficulty", though North Macedonia, along with Croatia, was the only country in the Western Balkans to not report an increase in this statistic. Corruption and a relatively ineffective legal system also act as significant restraints on successful economic development. North Macedonia still has one of the lowest List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, per capita GDPs in Europe. Furthermore, the country's grey market is estimated at close to 20% of GDP. PPS GDP per capita stood at 36% of the EU average in 2017. With a GDP per capita of US$9,157 at purchasing power parity and a List of countries by Human Development Index, Human Development Index of 0.701, North Macedonia is less developed and has a considerably smaller economy than most of the former Yugoslav states.
In terms of foreign trade, the largest sector contributing to the country's export in 2014 was "chemicals and related products" at 21.4%, followed by the "machinery and transport equipment" sector at 21.1%. North Macedonia's main import sectors in 2014 were "manufactured goods classified chiefly by material" with 34.2%, "machinery and transport equipment" with 18.7% and "mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials" with 14.4% of the total imports. Even 68.8% of the foreign trade in 2014 was done with the EU which makes the Union by far the largest trading partner of North Macedonia (23.3% with Germany, 7.9% with the UK, 7.3% with Greece, 6.2% with Italy, etc.). Almost 12% of the total external trade in 2014 was done with the Western Balkan countries.
North Macedonia has one of the highest shares of people struggling financially, with 72% of its citizens stating that they could manage on their household's income only "with difficulty" or "with great difficulty", though North Macedonia, along with Croatia, was the only country in the Western Balkans to not report an increase in this statistic. Corruption and a relatively ineffective legal system also act as significant restraints on successful economic development. North Macedonia still has one of the lowest List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, per capita GDPs in Europe. Furthermore, the country's grey market is estimated at close to 20% of GDP. PPS GDP per capita stood at 36% of the EU average in 2017. With a GDP per capita of US$9,157 at purchasing power parity and a List of countries by Human Development Index, Human Development Index of 0.701, North Macedonia is less developed and has a considerably smaller economy than most of the former Yugoslav states.
Trade
The outbreak of the Yugoslav wars and the imposition of sanctions on Serbia and Montenegro caused great damage to the country's economy, with Serbia constituting 60% of its markets before the disintegration of Yugoslavia. When Greece imposed a trade embargo on the Republic in 1994–95, the economy was also affected. Some relief was afforded by the end of the Bosnian War in November 1995 and the lifting of the Greek embargo, but theKosovo War
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that started 28 February 1998 and lasted until 11 June 1999. It was fought by the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (i.e. Serbia and Montenegro), which controlled Kosovo before the wa ...
of 1999 and the 2001 Albanian crisis caused further destabilisation.
Since the end of the Greek embargo, Greece has become the country's most important business partner. (See Greek investments in North Macedonia.) Many Greek companies have bought former state companies in North Macedonia, such as the oil refinery Okta, the baking company Zhito Luks, a marble mine in Prilep, textile facilities in Bitola, etc., and employ 20,000 people. The moving of business to North Macedonia in the oil sector has been caused by the rise of Greece in the oil markets.
Other key partners are Germany, Italy, the United States, Slovenia, Austria and Turkey.
Tourism
 Tourism plays a significant role in the economy of North Macedonia accounting for 6.7% of its GDP in 2016. The annual income from tourism was estimated at 38.5 billion denars (€616 million) in that year. Following its independence, the most serious negative impact on tourism performance occurred due to the armed conflicts taking place in 2001. The number of foreign visitors has been on the rise since, with a 14.6% increase in 2011. In 2019, North Macedonia received 1,184,963 tourist arrivals out of which 757,593 foreign. Most numerous are tourists from Turkey, neighboring Serbia, Greece and Bulgaria, Poland and other countries of Western Europe. The biggest bulk of tourists, approximately 60% of the million tourists that visited the country in 2017, was situated in Skopje and the southwestern region of the country.
The most significant tourism branches are lake tourism as there are three lakes in Ohrid, Prespa and Dojran and over 50 small glacial lakes of variable sizes, mountainous tourism as there are 16 mountains higher than 2,000 metres. Other forms of tourism also include rural and ecotourism, city tourism and cultural tourism, represented through gastronomy, traditional music, cultural celebrations and cultural heritage sites.
Tourism plays a significant role in the economy of North Macedonia accounting for 6.7% of its GDP in 2016. The annual income from tourism was estimated at 38.5 billion denars (€616 million) in that year. Following its independence, the most serious negative impact on tourism performance occurred due to the armed conflicts taking place in 2001. The number of foreign visitors has been on the rise since, with a 14.6% increase in 2011. In 2019, North Macedonia received 1,184,963 tourist arrivals out of which 757,593 foreign. Most numerous are tourists from Turkey, neighboring Serbia, Greece and Bulgaria, Poland and other countries of Western Europe. The biggest bulk of tourists, approximately 60% of the million tourists that visited the country in 2017, was situated in Skopje and the southwestern region of the country.
The most significant tourism branches are lake tourism as there are three lakes in Ohrid, Prespa and Dojran and over 50 small glacial lakes of variable sizes, mountainous tourism as there are 16 mountains higher than 2,000 metres. Other forms of tourism also include rural and ecotourism, city tourism and cultural tourism, represented through gastronomy, traditional music, cultural celebrations and cultural heritage sites.
Infrastructure
Transport
Education
 The higher levels of education can be obtained at one of the five state universities: Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje, St. Clement of Ohrid University of Bitola, Goce Delčev University of Štip, State University of Tetova and University of Information Science and Technology "St. Paul The Apostle" in Ohrid. There are a number of private university institutions, such as the European University, Slavic University in Sveti Nikole, the South East European University and others. North Macedonia was ranked 59th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021 and 2019.
The United States Agency for International Development has underwritten a project called ''Macedonia Connects'', which has made North Macedonia the first all-broadband wireless country in the world. The Ministry of Education and Sciences reports that 461 schools (primary and secondary) are now connected to the Internet. In addition, an Internet service provider (On.net), has created a MESH Network to provide WIFI services in the 11 largest cities/towns in the country. The national library of North Macedonia, National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid", is in Skopje.
The higher levels of education can be obtained at one of the five state universities: Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje, St. Clement of Ohrid University of Bitola, Goce Delčev University of Štip, State University of Tetova and University of Information Science and Technology "St. Paul The Apostle" in Ohrid. There are a number of private university institutions, such as the European University, Slavic University in Sveti Nikole, the South East European University and others. North Macedonia was ranked 59th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021 and 2019.
The United States Agency for International Development has underwritten a project called ''Macedonia Connects'', which has made North Macedonia the first all-broadband wireless country in the world. The Ministry of Education and Sciences reports that 461 schools (primary and secondary) are now connected to the Internet. In addition, an Internet service provider (On.net), has created a MESH Network to provide WIFI services in the 11 largest cities/towns in the country. The national library of North Macedonia, National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid", is in Skopje.
Demographics
Census data from 2002 shows a population of 2,022,547 inhabitants. An official estimate from 2009, without significant change, gives a figure of 2,050,671. The results from the last 2021 North Macedonia census, 2021 census show a population of 1,836,713. According to the 2002 census data, the largest ethnic group in the country are the ethnic Macedonians. The second-largest group are the Albanians, who dominated much of the northwestern part of the country. Following them,Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
are the third-biggest ethnic group of the country where official census data put them close to 80,000 and unofficial estimates suggest numbers between 170,000 and 200,000. Some unofficial estimates indicate that there are possibly up to 260,000 Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
.
Religion
Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox Christianity is the majority faith of North Macedonia, making up 65% of the population, the vast majority of whom belong to the Macedonian Orthodox Church. Various other Christian denominations account for 0.4% of the population. Muslims constitute 33.3% of the population. North Macedonia has the fifth-highest proportion of Muslims in Europe, after those of Kosovo (96%), Turkey (90%), Albania (59%), and Bosnia and Herzegovina (51%). Most Muslims are Albanians, Turks, or Romani; few are Macedonian Muslims. The remaining 1.4% was determined to be "unaffiliated" by a 2010 Pew Research estimation. There were 1,842 churches and 580 mosques in the country at the end of 2011. The Orthodox and Islamic religious communities have secondary religion schools in Skopje. There is an Orthodox Seminary, theological college in the capital. The Macedonian Orthodox Church has jurisdiction over 10 provinces (seven in the country and three abroad), has 10 bishops and about 350 priests. A total of 30,000 people are baptised in all the provinces every year. The Macedonian Orthodox Church, which declared autocephaly in 1967, remained unrecognised by the other Orthodox Churches until 2022 when it restored relations with the Serbian Orthodox Church and the Ecumenical Patriarchate, which has been followed by recognition from other churches. The reaction of the Macedonian Orthodox Church was to cut off all relations with the new Ohrid Archbishopric and to prevent bishops of the Serbian Orthodox Church from entering North Macedonia. Bishop Jovan was jailed for 18 months for "defaming the Macedonian Orthodox church and harming the religious feelings of local citizens" by distributing Serbian Orthodox church calendars and pamphlets. The Macedonian Greek Catholic Church, Macedonian Byzantine Catholic Church has approximately 11,000 adherents in North Macedonia. The Church was established in 1918, and is made up mostly of converts to Catholicism and their descendants. The Church is of the Byzantine Rite and is in communion with the Roman and Eastern Catholic Churches. Its liturgical worship is performed in Macedonian. There is a small Protestant community. The most famous Protestant in the country is the late president Boris Trajkovski. He was from the Methodism, Methodist community, which is the largest and oldest Protestant church in the Republic, dating back to the late 19th century. Since the 1980s the Protestant community has grown, partly through new confidence and partly with outside missionary help. The History of the Jews in North Macedonia, country's Jewish community, which numbered some 7,200 people on the eve of World War II, was almost entirely destroyed during the war: only 2% survived the Holocaust. After their liberation and the end of the War, most opted to emigrate to Israel. Today, the country's Jewish community numbers approximately 200 persons, almost all of whom live in Skopje. Most Macedonian Jews are Sephardi Jews, Sephardic—the descendants of 15th-century refugees who had been expelled from Alhambra Decree, Castile, Aragon and Persecution of Jews and Muslims by Manuel I of Portugal, Portugal.Languages
 The national and official language in all aspects of the whole territory of North Macedonia and in its international relations is the
The national and official language in all aspects of the whole territory of North Macedonia and in its international relations is the Macedonian language
Macedonian (; , , ) is an Eastern South Slavic language. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken as a first language by around two million ...
. Albanian language, Albanian is co-official at a state level (excluding defence, central police and monetary policy) and in local self-government units where speakers are 20% or more. Macedonian belongs to the Eastern branch of the South Slavic languages, South Slavic language group, while Albanian occupies an independent branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family of languages. In municipalities where at least 20% of the population is part of another ethnic minority, those individual languages are used for official purposes in local government, alongside Macedonian and Albanian or just Macedonian.
Macedonian is closely related to and Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible with standard Bulgarian language, Bulgarian. It also has some similarities with standard Serbian language, Serbian and the intermediate Torlakian dialect, Torlakian/Shopi#Dialects, Shop dialects spoken mostly in southeastern Serbia and western Bulgaria (and by speakers in the northeast of Macedonia). The standard language was Codification (linguistics), codified in the period following World War II and has accumulated a thriving literary tradition.
Besides Macedonian and Albanian, minority languages with substantial numbers of speakers are Turkish (including Balkan Gagauz Turkish language, Balkan Gagauz), Romani language, Romani, Serbian language, Serbian/Bosnian language, Bosnian and Aromanian language, Aromanian (including Megleno-Romanian language, Megleno-Romanian). Macedonian Sign Language is the primary language of those of the deaf community who did not pick up an oral language in childhood.
According to the last census, 1,344,815 citizens of North Macedonia declared that they spoke Macedonian, 507,989 declared Albanian, 71,757 Turkish, 38,528 Romani, 24,773 Serbian, 8,560 Bosnian, 6,884 Aromanian and 19,241 spoke other languages.
Cities
Culture
 North Macedonia has a rich cultural heritage in art, architecture, poetry and music. It has many ancient, protected religious sites. Poetry, cinema, and music festivals are held annually. Music of North Macedonia, Macedonian music styles developed under the strong influence of Byzantine music, Byzantine church music. North Macedonia has a significant number of preserved Byzantine art, Byzantine fresco paintings, mainly from the period between the 11th and 16th centuries. There are several thousands of square metres of fresco painting preserved, the major part of which is in very good condition and represent masterworks of the Macedonian school of ecclesiastical painting.
The most important cultural events in the country are the
North Macedonia has a rich cultural heritage in art, architecture, poetry and music. It has many ancient, protected religious sites. Poetry, cinema, and music festivals are held annually. Music of North Macedonia, Macedonian music styles developed under the strong influence of Byzantine music, Byzantine church music. North Macedonia has a significant number of preserved Byzantine art, Byzantine fresco paintings, mainly from the period between the 11th and 16th centuries. There are several thousands of square metres of fresco painting preserved, the major part of which is in very good condition and represent masterworks of the Macedonian school of ecclesiastical painting.
The most important cultural events in the country are the Ohrid
Ohrid ( mk, Охрид ) is a city in North Macedonia and is the seat of the Ohrid Municipality. It is the largest city on Lake Ohrid and the List of cities in North Macedonia, eighth-largest city in the country, with the municipality recording ...
Summer festival of classical music and drama, the Struga Poetry Evenings which gather poets from more than 50 countries in the world, International Camera Festival in Bitola, Open Youth Theatre and Skopje Jazz Festival in Skopje etc.
The National Opera opened in 1947, then named "Macedonian Opera", with a performance of ''Cavalleria rusticana'' under the direction of Branko Pomorisac. Every year, the May Opera Evenings are held in Skopje for around 20 nights. The first May Opera performance was that of Kiril Makedonski's ''Tsar Samuil'' in May 1972.
Cuisine
The country's cuisine is representative of that of the Balkans—reflecting Mediterranean cuisine, Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisine, Middle Eastern (Ottoman cuisine, Ottoman) influences, and to a lesser extent Italian cuisine, Italian, German cuisine, German and Eastern European (especially Hungarian cuisine, Hungarian) ones. The relatively warm climate in North Macedonia provides excellent growth conditions for a variety of vegetables, herbs and fruits. Thus, Macedonian cuisine is particularly diverse. Macedonian cuisine is also noted for the diversity and quality of its dairy products, wines, and local alcoholic beverages, such as rakija. Tavče gravče and mastika are considered the national dish and drink of North Macedonia, respectively. Some other important dishes include Šopska salad, an appetiser and side dish that accompanies the main meal, ajvar, stuffed peppers, pastrmajlija and others.Sport

 Association football, Football, handball, and basketball are the most popular sports in North Macedonia. The North Macedonia national football team is controlled by the Football Federation of Macedonia. Their home stadium is the Toše Proeski Arena. In November 2003, to celebrate UEFA's jubilee, Darko Pančev was selected as the UEFA Jubilee Awards, Golden Player of Macedonia as their most outstanding player of the past 50 years. He was the winner of the European Golden Shoe, European Golden Boot award in 1991 and he is best known for scoring the winning penalty in the 1991 European Cup Final, bringing Red Star Belgrade the most prestigious trophy in European football for the first time in its 50-year existence. In 2020, the national team qualified for UEFA Euro 2020 (held in 2021), their first major tournament in the country's history.
Handball is the other important team sport in the country. Macedonian clubs have enjoyed success in European competitions. RK Vardar won 2016–17 EHF Champions League, 2016–17 and 2018–19 EHF Champions League, while Kometal Gjorče Petrov Skopje won the 2002 EHF Champions League, EHF Women's Champions League. The European Women's Handball Championship took place in 2008 in North Macedonia in Skopje and Ohrid; the North Macedonia women's national handball team, women's national team finished seventh place. The country's North Macedonia men's national handball team, men's national team has appeared in the European and World championships multiple times, with a best finish of fifth at the former (2012 European Men's Handball Championship, 2012) and ninth at the latter (2015 World Men's Handball Championship, 2015).
The North Macedonia men's national basketball team, North Macedonia national basketball team represents North Macedonia in international basketball. The team is run by the Basketball Federation of North Macedonia, the governing body of basketball in North Macedonia which was created in 1992 and joined FIBA in 1993. North Macedonia has participated in three EuroBaskets since then with its best finish at 4th place in EuroBasket 2011, 2011. It plays its home games at the Boris Trajkovski Sports Center in Skopje. Pero Antić became the List of foreign NBA players, first Macedonian basketball player to play in the National Basketball Association. He also won three EuroLeague trophies.
In the summer months the Ohrid Swimming Marathon is an annual event on
Association football, Football, handball, and basketball are the most popular sports in North Macedonia. The North Macedonia national football team is controlled by the Football Federation of Macedonia. Their home stadium is the Toše Proeski Arena. In November 2003, to celebrate UEFA's jubilee, Darko Pančev was selected as the UEFA Jubilee Awards, Golden Player of Macedonia as their most outstanding player of the past 50 years. He was the winner of the European Golden Shoe, European Golden Boot award in 1991 and he is best known for scoring the winning penalty in the 1991 European Cup Final, bringing Red Star Belgrade the most prestigious trophy in European football for the first time in its 50-year existence. In 2020, the national team qualified for UEFA Euro 2020 (held in 2021), their first major tournament in the country's history.
Handball is the other important team sport in the country. Macedonian clubs have enjoyed success in European competitions. RK Vardar won 2016–17 EHF Champions League, 2016–17 and 2018–19 EHF Champions League, while Kometal Gjorče Petrov Skopje won the 2002 EHF Champions League, EHF Women's Champions League. The European Women's Handball Championship took place in 2008 in North Macedonia in Skopje and Ohrid; the North Macedonia women's national handball team, women's national team finished seventh place. The country's North Macedonia men's national handball team, men's national team has appeared in the European and World championships multiple times, with a best finish of fifth at the former (2012 European Men's Handball Championship, 2012) and ninth at the latter (2015 World Men's Handball Championship, 2015).
The North Macedonia men's national basketball team, North Macedonia national basketball team represents North Macedonia in international basketball. The team is run by the Basketball Federation of North Macedonia, the governing body of basketball in North Macedonia which was created in 1992 and joined FIBA in 1993. North Macedonia has participated in three EuroBaskets since then with its best finish at 4th place in EuroBasket 2011, 2011. It plays its home games at the Boris Trajkovski Sports Center in Skopje. Pero Antić became the List of foreign NBA players, first Macedonian basketball player to play in the National Basketball Association. He also won three EuroLeague trophies.
In the summer months the Ohrid Swimming Marathon is an annual event on Lake Ohrid
Lake Ohrid ( mk, Охридско Езеро , al, Liqeni i Ohrit , also referred as ''Liqeni i Pogradecit'';) is a lake which straddles the mountainous border between the southwestern part of North Macedonia and eastern Albania. It is one of E ...
and during the winter months there is skiing in North Macedonia's winter sports centres. North Macedonia also takes part in the Olympic Games. Participation in the Games is organised by the Olympic Committee of North Macedonia. Magomed Ibragimov (wrestler, born 1974), Magomed Ibragimov competed for Macedonia in the Wrestling at the 2000 Summer Olympics – Men's freestyle 85 kg, freestyle 85 kg competition at the 2000 Summer Olympics and won the bronze medal, which was the first medal for independent country. Wrestlers Shaban Trstena and Shaban Sejdiu born in North Macedonia, as well as boxers Redžep Redžepovski and Ace Rusevski, won Olympic medals as part of Yugoslav Olympic team.
Cinema
Media
The oldest newspaper in the country is ''Nova Makedonija'' from 1944. Other well known newspaper and magazines are: ''Utrinski vesnik'', ''Dnevnik (Skopje), Dnevnik'', ''Vest'', ''Fokus'', ''Večer (Skopje), Večer'', ''Tea Moderna (magazine), Tea Moderna'', ''Makedonsko Sonce'', and ''Koha''. Public channel is Macedonian Radio Television founded in 1993 by the Assembly of North Macedonia. TEKO TV (1989) from Štip is the first private television channel in the country. Other popular private channels are: Sitel (TV channel), Sitel, Kanal 5 (Macedonia), Kanal 5, Telma (TV channel), Telma, Alfa TV (TV channel Macedonia), Alfa TV, and Alsat-M.Public holidays
The main public holidays in North Macedonia are: Besides these, there are several major religious & minorities holidays. (See: ''Public holidays in North Macedonia'')Symbols
* Sun: The official flag of the Republic of North Macedonia, adopted in 1995, is a yellow sun with eight broadening rays extending to the edges of the red field. * Coat of arms: After independence in 1991, North Macedonia retained the Coat of arms of North Macedonia, coat of arms adopted in 1946 by the People's Assembly of the People's Republic of Macedonia on its second extraordinary session held on 27 July 1946, later on altered by article 8 of the Constitution of the Socialist Federal Republic of Macedonia. The coat-of-arms is composed by a double bent garland of ears of wheat, tobacco and poppy, tied by a ribbon with the embroidery of a traditional folk costume. In the center of such a circular room there are mountains, rivers, lakes and the sun. All this is said to represent "the richness of our country, our struggle, and our freedom".International rankings
See also
* Outline of North MacedoniaNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * *Further reading
North Macedonia
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
External links
* *North Macedonia
from RFE/RL
North Macedonia
from BBC News * *
Key Development Forecasts for North Macedonia
from International Futures {{Authority control North Macedonia, Balkan countries Landlocked countries Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of the United Nations Member states of NATO Republics Southeastern European countries Southern European countries States and territories established in 1991 1991 establishments in the Republic of Macedonia Countries in Europe Albanian-speaking countries and territories Country name changes Countries of Europe with multiple official languages