MPGe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (MPGe or MPGge) is a measure of the average distance traveled per unit of energy consumed. MPGe is used by the
Miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (MPGe or MPGge) is a measure of the average distance traveled per unit of energy consumed. MPGe is used by the
 In May 2011, the
In May 2011, the
 Between 2008 and 2010 several major automakers began commercializing
Between 2008 and 2010 several major automakers began commercializing
/ref> is computed as: : :: This computation accounts for the well-to-wall losses resulting from the extraction of crude oil and refinement into gasoline (''Tp''), conversion to electricity (''Tg''), and the transmission grid (''Tt''); in summary, the total amount of useful electrical energy that can be extracted from gasoline is just % of its total theoretical stored energy. Substituting the numerical values into the first equation, : ::: ::: As noted above, when and are 1, as they would be for a pure-electric vehicle, . ;Examples In the example provided by the US DoE in its final rule, an electric car with an energy consumption of 265
eGallon Calculator: Compare the costs of driving with electricity
U.S. Department of Energy
Model Year 2014 Fuel Economy Guide
 Miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (MPGe or MPGge) is a measure of the average distance traveled per unit of energy consumed. MPGe is used by the
Miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (MPGe or MPGge) is a measure of the average distance traveled per unit of energy consumed. MPGe is used by the United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it ...
(EPA) to compare energy consumption of alternative fuel vehicle
An alternative fuel vehicle is a motor vehicle that runs on alternative fuel rather than traditional petroleum fuels (petrol or petrodiesel). The term also refers to any technology (e.g. electric car, hybrid electric vehicles, solar-powered ...
s, plug-in electric vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any road vehicle that can utilize an external source of electricity (such as a wall socket that connects to the power grid) to store electrical power within its onboard rechargeable battery packs, which then ...
s and other advanced technology vehicles with the energy consumption of conventional internal combustion
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combust ...
vehicles rated in miles per U.S.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
gallon
The gallon is a unit of volume in imperial units and United States customary units. Three different versions are in current use:
*the imperial gallon (imp gal), defined as , which is or was used in the United Kingdom, Ireland, Canada, Austr ...
.
The unit of energy consumed is deemed to be 33.7 kWh kilowatt-hours without regard to the efficiency of conversion of heat energy into electrical energy, also measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). The equivalence of this unit to energy in a gallon of gasoline is true if and only if the heat engine, generating equipment, and power delivery to the car battery are 100% efficient. Actual heat engines differ vastly from this assumption.
MPGe does not necessarily represent an equivalency in the operating costs between alternative fuel vehicles and the MPG rating of internal combustion engine vehicles due to the wide variation in costs for the fuel sources regionally since the EPA assumes prices that represents the national averages. Miles per gallon equivalent cost for alternate fuel can be calculated with a simple conversion to the conventional mpg (miles per gallon, miles/gal). See conversion to MPG by cost below.
The MPGe metric was introduced in November 2010 by EPA in the Monroney sticker
The Monroney sticker or window sticker is a label required in the United States to be displayed in all new automobiles and includes the listing of certain official information about the car. The window sticker was named after Almer Stillwell ...
of the Nissan Leaf
The , stylized as LEAF, is a compact five-door hatchback battery electric vehicle (BEV) manufactured by Nissan. It was introduced in Japan and the United States in December 2010, and its second generation was introduced in October 2017. The Lea ...
electric car and the Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid manufactured by General Motors, also marketed in rebadged variants as the Holden Volt in Australia and New Zealand and the Buick Velite 5 in China, and with a different fascia as the Vauxhall Ampera in th ...
plug-in hybrid. The ratings are based on EPA's formula, in which of electricity is equivalent to one (U.S.) gallon of gasoline, and the energy consumption of each vehicle during EPA's five standard drive cycle tests simulating varying driving conditions. All new cars and light-duty trucks sold in the U.S. are required to have this label showing the EPA's estimate of fuel economy of the vehicle.
In a joint ruling issued in May 2011 the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA ) is an agency of the U.S. federal government, part of the Department of Transportation. It describes its mission as "Save lives, prevent injuries, reduce vehicle-related crashes" rel ...
(NHTSA) and EPA established the new requirements for a fuel economy and environment label
The Monroney sticker or window sticker is a label required in the United States to be displayed in all new automobiles and includes the listing of certain official information about the car. The window sticker was named after Almer Stillwell "M ...
that is mandatory for all new passenger cars and trucks starting with model year
The model year (sometimes abbreviated "MY") is a method of describing the version of a product which has been produced over multiple years. The model year may or may not be the same as the calendar year in which the product was manufactured.
...
2013. This ruling uses miles per gallon gasoline equivalent for all fuel and advanced technology vehicles available in the U.S. market including plug-in hybrids, electric vehicles, flexible-fuel vehicle
A flexible-fuel vehicle (FFV) or dual-fuel vehicle (colloquially called a flex-fuel vehicle) is an alternative fuel vehicle with an internal combustion engine designed to run on more than one fuel, usually gasoline blended with either ethanol fu ...
s, hydrogen fuel cell vehicle, natural gas vehicle
A natural gas vehicle (NGV) is an alternative fuel vehicle that uses compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG). Natural gas vehicles should not be confused with autogas vehicles powered by liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), ma ...
s, diesel-powered vehicles, and gasoline-powered vehicles. In addition to being displayed on new vehicles, fuel economy ratings are used by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) to publish the annual Fuel Economy Guide; the U.S. Department of Transportation
The United States Department of Transportation (USDOT or DOT) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. It is headed by the secretary of transportation, who reports directly to the President of the United States and ...
(DOT) to administer the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) program; and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to collect gas guzzler taxes.
Fuel economy estimates for window stickers and CAFE standard compliance are different. The EPA MPGe rating shown in the Monroney label is based on the consumption of the on-board energy content stored in the fuel tank or in the vehicle's battery, or any other energy source, and only represents the tank-to-wheel
Life cycle assessment or LCA (also known as life cycle analysis) is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case o ...
energy consumption. CAFE estimates are based on a well-to-wheel
Life cycle assessment or LCA (also known as life cycle analysis) is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case of ...
basis and in the case of liquid fuels and electric drive vehicles also account for the energy consumed upstream to produce the fuel or electricity and deliver it to the vehicle. Fuel economy for CAFE purposes include an incentive adjustment for alternative fuel vehicles and plug-in electric vehicles which results in higher MPGe than those estimated for window stickers.
Background
1988: Alternative Motor Fuels Act
The Alternative Motor Fuels Act (AMFA) enacted in 1988 provides Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) incentives for manufacturingalternative fuel vehicle
An alternative fuel vehicle is a motor vehicle that runs on alternative fuel rather than traditional petroleum fuels (petrol or petrodiesel). The term also refers to any technology (e.g. electric car, hybrid electric vehicles, solar-powered ...
s (AFVs) that are powered by ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
, methanol, or natural gas fuels, either exclusively or in conjunction with gasoline or diesel fuel. These dual-fuel vehicles also are known as flexible-fuel vehicle
A flexible-fuel vehicle (FFV) or dual-fuel vehicle (colloquially called a flex-fuel vehicle) is an alternative fuel vehicle with an internal combustion engine designed to run on more than one fuel, usually gasoline blended with either ethanol fu ...
s (FFVs). To provide incentives for the widespread use of these fuels and to promote the production of AFVs and FFVs, AMFA grants AFV/FFV manufacturers CAFE credits, which allows them to raise their overall fleet fuel economy levels to comply with the CAFE standards.
Beginning in 1993, manufacturers of qualified AFVs can improve their CAFE estimation by computing the weighted average of the fuel economy when operating on conventional fuel (gasoline and diesel) and when operating on alternative fuel(s). AMFA provides the following energy content-based equivalency factors:
* 1 gal (alcohol) = 0.15 gal (gasoline)
* 100 ft3 (natural gas) = 0.823 gal-equivalent (natural gas)
** 1 gal-equivalent (natural gas) = 0.15 gal (gasoline)
A dedicated AFV which operates solely on alcohol would divide the alcohol fuel economy by the energy-equivalency factor of 0.15. As an example, a dedicated AFV that achieves 15 mpg fuel economy while operating on alcohol would have a CAFE calculated as follows:
For FFVs, an assumption is made that the vehicles would operate 50% of the time on the alternative fuel and 50% of the time on conventional fuel, resulting in a fuel economy that is based on a harmonic average of alternative fuel and conventional fuel. For example, for an alternative dual-fuel model that achieves 15 miles per gallon operating on an alcohol fuel and 25 mpg on the conventional fuel, the resulting CAFE would be:
Calculation of fuel economy for natural gas vehicles is similar. For the purposes of this calculation, the fuel economy is equal to the weighted average of the fuel economy while operating on natural gas and while operating on either gasoline or diesel fuel. AMFA specifies the energy content of 100 cubic feet of natural gas to be equal to 0.823 gallons-equivalent of natural gas, and the gallon equivalency of natural gas is considered to have a fuel content, similar to that for alcohol fuels, equal to 0.15 gallons of fuel. For example, under this conversion and gallon equivalency, a dedicated natural gas vehicle that achieves 25 miles per 100 cubic feet of natural gas would have a CAFE value as follows:
The Energy Policy Act of 1992
The Energy Policy Act of 1992, effective October 24, 1992, (102nd Congress H.R.776.ENR, abbreviated as EPACT92) is a United States government act. It was passed by Congress and set goals, created mandates, and amended utility laws to increase c ...
expanded the definition of alternative fuel to include liquefied petroleum gas, hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
, liquid fuels derived from coal and biological materials, electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
and any other fuel that the Secretary of Transportation determines to be substantially non-petroleum based and has environmental and energy security benefits. Beginning in 1993, manufacturers of these other alternative fuel automobiles that meet the qualifying requirements can also benefit for special treatment in the calculation of their CAFE.
1994: Gasoline gallon equivalent
In 1994 the U.S.National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical s ...
(NIST) introduced gasoline gallon equivalent
Gasoline gallon equivalent (GGE) or gasoline-equivalent gallon (GEG) is the amount of an alternative fuel it takes to equal the energy content of one liquid gallon of gasoline. GGE allows consumers to compare the energy content of competing fu ...
(GGE) as a metric for fuel economy for natural gas vehicle
A natural gas vehicle (NGV) is an alternative fuel vehicle that uses compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG). Natural gas vehicles should not be confused with autogas vehicles powered by liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), ma ...
s. NIST defined a gasoline gallon equivalent (GGE) as 5.660 pounds of natural gas, and gasoline liter equivalent (GLE) as 0.678 kilograms of natural gas.
2000: Petroleum-equivalent fuel economy
During the late 1990s and early 2000s several electric cars were produced in limited quantities as a result of theCalifornia Air Resources Board
The California Air Resources Board (CARB or ARB) is the "clean air agency" of the government of California. Established in 1967 when then-governor Ronald Reagan signed the Mulford-Carrell Act, combining the Bureau of Air Sanitation and the Moto ...
(CARB) mandate for more fuel-efficient zero-emissions vehicle
A zero-emission vehicle, or ZEV, is a vehicle that does not emit exhaust gas or other pollutants from the onboard source of power. The California definition also adds that this includes under any and all possible operational modes and conditions ...
s. Popular models available in California included the General Motors EV1
The General Motors EV1 was an electric car produced and leased by General Motors from 1996 to 1999. It was the first mass-produced and purpose-designed electric vehicle of the modern era from a major automaker and the first GM car designed to b ...
and the Toyota RAV4 EV
The Toyota RAV4 EV is an all-electric version of the popular RAV4 SUV produced by Toyota until 2014. Two generations of the EV model were sold in California, and to fleets elsewhere in the US, with a gap of almost ten years between them.
The fi ...
. The U.S. DoE and EPA rating for on board energy efficiency for these electric vehicles was expressed as kilowatt hour/mile ( KWh/mi), the most commonly known metric in science and engineering for measuring energy consumption, and used as the billing unit for energy delivered to consumers by electric utilities
An electric utility is a company in the electric power industry (often a public utility) that engages in electricity generation and distribution of electricity for sale generally in a regulated market. The electrical utility industry is a major p ...
.
In order to address the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) regulations mandated by the U.S. Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washin ...
in 1975, the U.S. Department of Energy established in July 2000 a methodology for calculating the petroleum-equivalent fuel economy of electric vehicles on a well-to-wheel
Life cycle assessment or LCA (also known as life cycle analysis) is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case of ...
basis. The methodology considers the upstream efficiency of the processes involved in the two fuel cycles. The energy content of gasoline is reduced from 33,705 Wh/gal to 83% of that, or about 27,975 Wh/gal well-to-tank, to account for the energy used in refinement and distribution. Similarly, the energy value for electricity produced from fossil fuel is reduced to 30.3%, due to energy lost in generation and transmission, according to the national average. This is normalized to the previous gasoline value, resulting in a well-to-vehicle gasoline-equivalent energy content of electricity of only 12,307 Wh/gal.
The formula also includes a "fuel content factor" of 1/0.15 (about 6.667) to benefit electric vehicles, raising the value from 12,307 to 82,049 Wh/gal. This reward factor is intended provide an incentive for vehicle manufactures to produce and sell electric vehicles, as a higher equivalent fuel economy for EVs improves the carmaker overall fleet fuel economy levels in complying with the CAFE standards, and Congress anticipated that such an incentive would help accelerate the commercialization of electric vehicles. The incentive factor chosen by DoE for EVs is the same 1/0.15 factor already applied in the regulatory treatment of other types of alternative fuel vehicle
An alternative fuel vehicle is a motor vehicle that runs on alternative fuel rather than traditional petroleum fuels (petrol or petrodiesel). The term also refers to any technology (e.g. electric car, hybrid electric vehicles, solar-powered ...
s. When all factors are considered in DoE's formula, the energy efficiency or equivalent fuel economy of electric vehicles increases, being calculated in miles per the petroleum-equivalency factor of 82,049 Wh/gal rather than miles per the usual gasoline gallon equivalent of 33,705 Wh/gallon, for the purposes of CAFE credits to manufacturers.
2007: X Prize
The Automotive X Prize competition was intended to encourage development of automobiles that would be capable of operating 100 miles on a gallon of gasoline (mpg). Comparison of electric vehicles to vehicles that carried their own engine was debated, since the notion of a miles per gallon equivalent as a metric for electric vehicles made the competition trivial for electric vehicles and a corresponding miles per gallon as a metric for the others extremely difficult for the others. Miastrada Company made the case that this defeated the purpose of the competition, to no avail. In April 2007, as part of Draft Competition Guidelines released at the New York Auto Show, MPGe was announced as the main merit metric for theProgressive Insurance Automotive X Prize
The Progressive Insurance Automotive X PRIZE (PIAXP or AXP) was a set of competitions, programs and events, from the X Prize Foundation, to "inspire a new generation of super-efficient vehicles that help break America's addiction to oil and ste ...
, a competition developed by the X Prize Foundation for super-efficient vehicles that can achieve at least 100 MPGe. In February 2009, '' Consumer Reports'' announced that, as part of a partnership with the X Prize Foundation, they planned to report MPGe as one of several measures that will help consumers understand and compare vehicle efficiency for alternative fuel vehicle
An alternative fuel vehicle is a motor vehicle that runs on alternative fuel rather than traditional petroleum fuels (petrol or petrodiesel). The term also refers to any technology (e.g. electric car, hybrid electric vehicles, solar-powered ...
s.
2010–2011: Miles per gallon equivalent
As required by the 2007 Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA), with the introduction of advanced-technology vehicles in the U.S. new information should be incorporated in theMonroney label
The Monroney sticker or window sticker is a label required in the United States to be displayed in all new automobiles and includes the listing of certain official information about the car. The window sticker was named after Almer Stillwell "M ...
of new cars and light-duty trucks sold in the country, such as ratings on fuel economy, greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
, and other air pollutant
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different type ...
s. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon pro ...
and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA ) is an agency of the U.S. federal government, part of the Department of Transportation. It describes its mission as "Save lives, prevent injuries, reduce vehicle-related crashes" rel ...
(NHTSA) have conducted a series of studies to determine the best way to redesign this label to provide consumers with simple energy and environmental comparisons across all vehicles types, including battery electric vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, ...
s (BEV), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV), and conventional internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal c ...
vehicles powered by gasoline and diesel, in order to help consumers choose more efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles. These changes were proposed to be introduced in new vehicles beginning with model year 2012.
The EPA rating for on board energy efficiency for electric vehicles before 2010 was expressed as kilowatt hour per 100 miles (kWh/100 mi). For example, the window sticker
The Monroney sticker or window sticker is a label required in the United States to be displayed in all new automobiles and includes the listing of certain official information about the car. The window sticker was named after Almer Stillwell "M ...
of the 2009 Mini E
The Mini E was a demonstration electric car developed by BMW as a conversion of its Mini Cooper car. The Mini E was developed for field trials and deployed in several countries, including the United States, Germany, UK, France, Japan and Chin ...
showed an energy consumption of 33 kWh/100mi for city driving and 36 kWh/100mi on the highway, technically equivalent to city and highway. Similarly, the 2009 Tesla Roadster was rated in city and on the highway.
As part of the research and redesign process, EPA conducted focus group
A focus group is a group interview involving a small number of demographically similar people or participants who have other common traits/experiences. Their reactions to specific researcher/evaluator-posed questions are studied. Focus groups are ...
s where participants were presented with several options to express the consumption of electricity for plug-in electric vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any road vehicle that can utilize an external source of electricity (such as a wall socket that connects to the power grid) to store electrical power within its onboard rechargeable battery packs, which then ...
s. The research showed that participants did not understand the concept of a kilowatt hour as a measure of electric energy use despite the use of this unit in their monthly electric bills. Instead, participants favored a miles per gallon equivalent, MPGe, as the metric to compare with the familiar miles per gallon used for gasoline vehicles. The research also concluded that the kWh per 100 miles metric was more confusing to focus group participants compared to a miles per kWh. Based on these results, EPA decided to use the following fuel economy and fuel consumption metrics on the redesigned labels: MPG (city and highway, and combined); MPGe (city and highway, and combined); Gallons per 100 miles; kWh per 100 miles.
The proposed design and final content for two options of the new sticker label that would be introduced in 2013 model year
The model year (sometimes abbreviated "MY") is a method of describing the version of a product which has been produced over multiple years. The model year may or may not be the same as the calendar year in which the product was manufactured.
...
cars and trucks were consulted for 60 days with the public in 2010, and both include miles per gallon equivalent and kWh per 100 miles as the fuel economy metrics for plug-in cars, but in one option MPGe and annual electricity cost are the two most prominent metrics. In November 2010, EPA introduced MPGe as comparison metric on its new sticker for fuel economy for the Nissan Leaf
The , stylized as LEAF, is a compact five-door hatchback battery electric vehicle (BEV) manufactured by Nissan. It was introduced in Japan and the United States in December 2010, and its second generation was introduced in October 2017. The Lea ...
and the Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid manufactured by General Motors, also marketed in rebadged variants as the Holden Volt in Australia and New Zealand and the Buick Velite 5 in China, and with a different fascia as the Vauxhall Ampera in th ...
.
 In May 2011, the
In May 2011, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA ) is an agency of the U.S. federal government, part of the Department of Transportation. It describes its mission as "Save lives, prevent injuries, reduce vehicle-related crashes" rel ...
(NHTSA) and EPA issued a joint final rule establishing new requirements for a fuel economy and environment label
The Monroney sticker or window sticker is a label required in the United States to be displayed in all new automobiles and includes the listing of certain official information about the car. The window sticker was named after Almer Stillwell "M ...
that is mandatory for all new passenger cars and trucks starting with model year
The model year (sometimes abbreviated "MY") is a method of describing the version of a product which has been produced over multiple years. The model year may or may not be the same as the calendar year in which the product was manufactured.
...
2013. The ruling includes new labels for alternative fuel
Alternative fuel, known as non-conventional and advanced fuels, are any materials or substances that can be used as fuels, other than conventional fuels like; ''fossil fuels'' (petroleum (oil), coal, and natural gas), as well as nuclear materi ...
and alternative propulsion vehicles available in the US market, such as plug-in hybrids, electric vehicles, flexible-fuel vehicle
A flexible-fuel vehicle (FFV) or dual-fuel vehicle (colloquially called a flex-fuel vehicle) is an alternative fuel vehicle with an internal combustion engine designed to run on more than one fuel, usually gasoline blended with either ethanol fu ...
s, hydrogen fuel cell vehicle, and natural gas vehicle
A natural gas vehicle (NGV) is an alternative fuel vehicle that uses compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG). Natural gas vehicles should not be confused with autogas vehicles powered by liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), ma ...
s.''EPA-420-F-11-017'' The common fuel economy metric adopted to allow the comparison of alternative fuel and advanced technology vehicles with conventional internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal c ...
vehicles is miles per gallon of gasoline equivalent
Miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (MPGe or MPGge) is a measure of the average distance traveled per unit of energy consumed. MPGe is used by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to compare energy consumption of alternative ...
(MPGe). A gallon of gasoline equivalent means the number of kilowatt hours of electricity, cubic feet of compressed natural gas
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is a fuel gas mainly composed of methane (CH4), compressed to less than 1% of the volume it occupies at standard atmospheric pressure. It is stored and distributed in hard containers at a pressure of , usually in cy ...
(CNG), or kilograms of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
that is equal to the energy in a gallon of gasoline.
The new labels also show for the first time an estimate of how much fuel or electricity it takes to drive , introducing to U.S. consumers with fuel consumption per distance traveled, a metric commonly used in other countries. EPA explained that the objective is to avoid the traditional miles per gallon metric that can be potentially misleading when consumers compare fuel economy improvements, and known as the "MPG illusion."
As mentioned above, confusion and misinterpretation is common in the public between the two types of " fuel efficiency". Fuel economy measures how far a vehicle will go per amount of fuel (units of MPGe). Fuel consumption is the reciprocal of fuel economy, and measures the fuel used to drive a fixed distance (units of gal/100 miles or kWh/100 miles). The unit of Gal/100 miles is accurately described as fuel consumption in some EPA brochures, but this unit appears in the fuel economy section of the Monroney label (which doesn't use the term fuel consumption).
Description
The miles per gallon gasoline equivalent is based on the energy content of gasoline. The energy obtainable from burning one US gallon of gasoline is 115,000 BTU, , or . To convert the mile per gallon rating into other units of distance per unit energy used, the mile per gallon value can be multiplied by one of the following factors to obtain other units: :Conversion to MPGe
MPGe is determined by converting the vehicle consumption per unit distance, as determined through computer modeling or completion of an actual driving cycle, from its native units into a gasoline energy equivalent. Examples of native units include W·h for electric vehicles, kg- for hydrogen vehicles, gallons forbiodiesel
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat ( tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oil ...
or liquefied natural gas
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the vol ...
vehicles, cubic feet for compressed natural gas
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is a fuel gas mainly composed of methane (CH4), compressed to less than 1% of the volume it occupies at standard atmospheric pressure. It is stored and distributed in hard containers at a pressure of , usually in cy ...
vehicles, and pounds for propane or Liquefied petroleum gas vehicles. Special cases for specific alternative fuels are discussed below, but a general formula for MPGe is:
For EPA, this considers the tank-to-wheel for liquids and wall-to-wheel energy consumption for electricity, i.e. it measures the energy for which the owner usually pays. For EVs the energy cost includes the conversions from AC to charge the battery. The EPA MPGe ratings displayed in window stickers do not account for the energy consumption upstream, which includes the energy or fuel required to generate the electricity or to extract and produce the liquid fuel; the energy losses due to power transmission; or the energy consumed for the transportation of the fuel from the well to the station.
Basic values for the energy content of various fuels are given by the defaults used in the Department of Energy GREET (Greenhouse gases, Regulated Emissions, and Energy used in Transportation) model, as follows:
Note: 1 kWh is equivalent to 3,412 BTU
The energy content of a particular fuel can vary somewhat given its specific chemistry and production method. For example, in the new efficiency ratings that have been developed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it ...
(EPA) for battery electric vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, ...
s (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) – see below – the energy content of a gallon of gasoline is assumed to be 114,989.12 BTU or 33.7 kWh.
Conversion to MPG by cost
The miles per gallon equivalent cost of an alternative fuel vehicle can be calculated by a simple formula to directly compare the MPG operating costs (rather than the energy consumption of MPGe) with traditional vehicles since the cost of resources varies substantially from region to region. For reference, the complete equation is: Also for those that prefer kWh/100 mi an equivalent is simply: This equation reduces down to a simple formula that works with only the capacity of the fuel source and its possible range to compare vehicles. With your local rates for gasoline and your fuel source you can easily compare your alternative fuel vehicle operating cost directly with a gasoline engine model with the following: The formula includes the inherent efficiency of the vehicle as the range capability of a specific fuel source capacity directly represents the EPA testing, it then becomes universal regardless of weight, vehicle size, co-efficient of drag, rolling resistance as these directly influence the range possible and are accounted for. Driving style and weather conditions can be accounted for by using the achieved range instead of the advertised range for the calculation. The formula works by deriving how much alternative fuel can be purchased for the cost of a single gallon of gasoline, and creates a ratio of how this quantity compares to the storage capacity of the vehicle, then multiplies this ratio to the vehicles possible range. The result is number of miles the vehicle travels on alternative fuel for the same cost of a single gallon of gasoline. The end computation results in MPG unit and is directly comparable to a standard internal combustion engine vehicle’s fuel costs for its rated MPG.Examples
The formula with the correct units for a BEV or PHEV in all electric mode is like this. Using EPA 2018 Fuel Economy Guides assumptions for national average pricing of $2.56/gal regular gasoline and $0.13/kWh we can calculate a vehicle that is rated at 84 MPGe or 40 kW/100 Mi efficiency and has a 16.5 kW EV battery of which 13.5 kWh is usable for electric driving with an advertised range of 33 miles per charge. Note: Using the battery size instead of the usable charge will provide a conservative value. Using actual charge and actual range driven will provide actual economy. Calculate how many kWh per gallon Now the same vehicle where gasoline with worth $3.20/gal and electricity is $0.085/kWh. Calculate how many kWh per gallonElectric and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles
 Between 2008 and 2010 several major automakers began commercializing
Between 2008 and 2010 several major automakers began commercializing battery electric vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, ...
s (BEVs), which are powered exclusively on electricity, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), which use electricity together with a liquid fuel stored in an on-board fuel tank, usually gasoline, but it might be also powered by diesel
Diesel may refer to:
* Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression
* Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines
* Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engin ...
, ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
, or flex-fuel
A flexible-fuel vehicle (FFV) or dual-fuel vehicle (colloquially called a flex-fuel vehicle) is an alternative fuel vehicle with an internal combustion engine designed to run on more than one fuel, usually gasoline blended with either ethanol or ...
engines.
For battery electric vehicles, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon pro ...
's formula to calculate the well-to-wheel MPGe is based on energy standards established by the U.S. Department of Energy in 2000: The well-to-wheel conversion is used in calculation of corporate-average fuel economy (CAFE) but for window sticker (Monroney) fuel economy. For Monroney fuel economy the equation is
:
where
: is expressed as miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (as shown in the Monroney label
The Monroney sticker or window sticker is a label required in the United States to be displayed in all new automobiles and includes the listing of certain official information about the car. The window sticker was named after Almer Stillwell "M ...
)
: energy content per gallon of gasoline = 115,000 Btu
The British thermal unit (BTU or Btu) is a unit of heat; it is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. It is also part of the United States customary units. The modern SI u ...
/gallon, as set by U.S. DoE and reported by the Alternative Fuel Data Center.
: wall-to-wheel electrical energy consumed per mile ( Wh/mi) as measured through EPA's five standard drive cycle tests for electric cars and SAE test procedures
: energy unit conversion factor (rounded) = 3.412 Btu/Wh
The formula employed by the EPA for calculating their rated MPGe does not account for any fuel or energy consumed upstream such as the generation and transmission of electrical power, or well-to-wheel
Life cycle assessment or LCA (also known as life cycle analysis) is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case of ...
life cycle, as EPA's comparison with internal combustion
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combust ...
vehicles is made on a tank-to-wheel
Life cycle assessment or LCA (also known as life cycle analysis) is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case o ...
versus battery-to wheel basis.
The California Air Resources Board
The California Air Resources Board (CARB or ARB) is the "clean air agency" of the government of California. Established in 1967 when then-governor Ronald Reagan signed the Mulford-Carrell Act, combining the Bureau of Air Sanitation and the Moto ...
uses a different dynamometer
A dynamometer or "dyno" for short, is a device for simultaneously measuring the torque and rotational speed ( RPM) of an engine, motor or other rotating prime mover so that its instantaneous power may be calculated, and usually displayed by ...
testing than EPA, and considers reformulated gasoline sold in that state. For CARB estimates the formula becomes:
:
The new SAE J1711 standard for measuring the exhaust emissions and fuel economy of hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of hybrid vehicle that combines a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) system with an electric propulsion system (hybrid vehicle drivetrain). The presence of the electric powertrain is intended ...
s and plug-in hybrids was approved in July 2010. The recommended procedures for PHEVs were revised at Argonne National Laboratory, and EPA's new regulation to define PHEV fuel economy reporting protocol is expected to be based on SAE J1711. In November 2010 EPA decided to rate electric mode and gasoline only mode separately, and these are the two figures prominently displayed in the window sticker of the 2011 Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid manufactured by General Motors, also marketed in rebadged variants as the Holden Volt in Australia and New Zealand and the Buick Velite 5 in China, and with a different fascia as the Vauxhall Ampera in th ...
. In electric mode the Volt's rating is estimated with the same formula as an electric car. The overall or composite fuel economy rating combining electricity and gasoline powered are displayed in the Monroney label in a much smaller type, and as part of the comparison of the Volt's fuel economy among all vehicles and within compact car
Compact car is a vehicle size class — predominantly used in North America — that sits between subcompact cars and mid-size cars. "Small family car" is a British term and a part of the C-segment in the European car classification. However, ...
s. EPA has considered several methodologies for rating the overall fuel economy of PHEVs, but as of February 2011 EPA has not announced the final methodology that will be applied for the purposes of estimating the new manufacture's 2012–2016 Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) credits for plug-in hybrids.
Examples
In November 2010 the EPA began including "MPGe" in its new sticker for fuel economy and environmental comparisons. The EPA rated theNissan Leaf
The , stylized as LEAF, is a compact five-door hatchback battery electric vehicle (BEV) manufactured by Nissan. It was introduced in Japan and the United States in December 2010, and its second generation was introduced in October 2017. The Lea ...
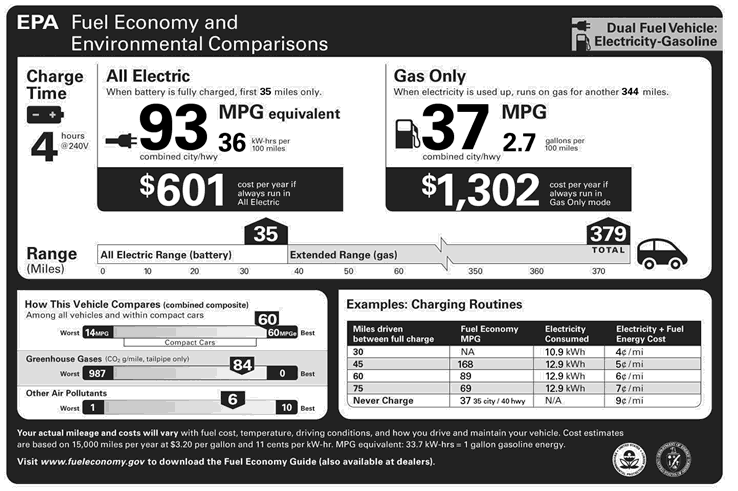
electric car with a combined fuel economy of 99 MPGe, and rated the Chevrolet Volt plug-in hybrid with a combined fuel economy of 93 MPGe in all-electric mode
Charge-depleting or EV mode refers to a mode of vehicle operation that is dependent on the
energy from the battery pack. Battery electric vehicles operate solely in this mode. Most plug-in hybrids operate in charge-depleting mode at startup, and ...
, 37 MPG when operating with gasoline only, and an overall fuel economy rating of 60 mpg-US (3.9 L/100 km) combining power from electricity and gasoline. For both vehicles EPA calculated the MPGe rating under its five-cycle tests using the formula displayed earlier with a conversion factor of 33.7 kWh of electricity being the energy equivalent of a gallon of gasoline.
= All-electric cars
== Plug-in hybrids
=Fuel cell vehicles
The following table compares EPA's fuel economy expressed in miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (MPGe) for the two models ofhydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
fuel cell vehicle
A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is an electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell, sometimes in combination with a small battery or supercapacitor, to power its onboard electric motor. Fuel cells in vehicles generate e ...
s rated by the EPA , and available in California. ''One kg of hydrogen is roughly equivalent to one U.S. gallon of gasoline.''
Conversion using GGE
The same method can be applied to any other alternative fuel vehicle when that vehicle's energy consumption is known. Generally the energy consumption of the vehicle is expressed in units other than W·h/mile, or Btu/mile so additional arithmetic is required to convert to agasoline gallon equivalent
Gasoline gallon equivalent (GGE) or gasoline-equivalent gallon (GEG) is the amount of an alternative fuel it takes to equal the energy content of one liquid gallon of gasoline. GGE allows consumers to compare the energy content of competing fu ...
(GGE), using 33.7 kWh / gallon = 114989.17 btu / gallon.
Hydrogen example with GGE
The 2008Honda FCX Clarity
The Honda Clarity is a nameplate used by Honda on alternative fuel vehicles. It was initially used only on hydrogen fuel-cell electric vehicles such as the 2008 Honda FCX Clarity, but in 2017 the nameplate was expanded to include the battery-elec ...
is advertised to have a vehicle consumption of 72 mi/kg-. Hydrogen at atmospheric pressure has an energy density of 120 MJ/kg (113,738 BTU/kg), by converting this energy density to a GGE, it is found that 1.011 kg of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
is needed to meet the equivalent energy of one gallon of gasoline. This conversion factor can now be used to calculate the MPGe for this vehicle.
: ,
:
Life cycle assessment
Pump/Well-to-wheel
EPA's miles per gallon equivalent metric shown in the window sticker does not measure a vehicle's full cycleenergy efficiency
Energy efficiency may refer to:
* Energy efficiency (physics), the ratio between the useful output and input of an energy conversion process
** Electrical efficiency, useful power output per electrical power consumed
** Mechanical efficiency, a ra ...
or well-to-wheel
Life cycle assessment or LCA (also known as life cycle analysis) is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case of ...
life cycle. Rather, the EPA presents MPGe in the same manner as MPG for conventional internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal c ...
vehicles as displayed in the Monroney sticker
The Monroney sticker or window sticker is a label required in the United States to be displayed in all new automobiles and includes the listing of certain official information about the car. The window sticker was named after Almer Stillwell ...
, and in both cases the rating only considers the pump-to-wheel or wall-to-wheel energy consumption, i.e. it measures the energy for which the owner usually pays. For EVs the energy cost includes the conversions from AC from the wall used to charge the battery The EPA ratings displayed in window stickers do not account for the energy consumption upstream, which includes the energy or fuel required to generate the electricity or to extract and produce the liquid fuel; the energy losses due to power transmission; or the energy consumed for the transportation of the fuel from the well to the station.
Petroleum-equivalency factor (PEF) – a CAFE metric
In 2000 theUnited States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United Stat ...
(DOE) established the methodology for calculating the petroleum-equivalent fuel economy of electric vehicles based on the well-to-wheel
Life cycle assessment or LCA (also known as life cycle analysis) is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case of ...
(WTW) gasoline-equivalent energy content of electricity (). The methodology considers the upstream efficiency of the processes involved in the two fuel cycles, and considers the national average electricity generation and transmission efficiencies because a battery electric vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, ...
burns its fuel (mainly fossil fuels) off-board at the power generation plant. This methodology is used by carmakers to estimate credits into their overall Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) for manufacturing electric drive vehicles.
The petroleum equivalent fuel economy of electric vehicles is determined by the following equations:
:
::where:
::: = Petroleum-equivalent fuel economy
::: = Gasoline-equivalent energy content of electricity factor
::: = "Fuel content" factor or incentive factor. DoE selected a value of to retain consistency with existing regulatory and statutory procedures, and to provide a similar treatment to manufacturers of all types of alternative fuel vehicle
An alternative fuel vehicle is a motor vehicle that runs on alternative fuel rather than traditional petroleum fuels (petrol or petrodiesel). The term also refers to any technology (e.g. electric car, hybrid electric vehicles, solar-powered ...
s
::: = Petroleum-fueled accessory factor; this is equal to 1 if the electric drive vehicle does not have petroleum-powered accessories installed, and 0.90 if it does.
::: = Driving pattern factor; this is equal to 1, as DoE considered that electric vehicles eligible for inclusion in CAFE will offer capabilities, perhaps excepting driving range, similar to those of conventional vehicles.
The gasoline-equivalent energy content of electricity factor, abbreviated as , is defined as:
:
::where:
::: = U.S. average fossil-fuel electricity generation efficiency = 0.328
::: = U.S. average electricity transmission efficiency = 0.924
::: = Petroleum refining and distribution efficiency = 0.830
::: = Watt hours of energy per gallon of gasoline conversion factor = alternative URL/ref> is computed as: : :: This computation accounts for the well-to-wall losses resulting from the extraction of crude oil and refinement into gasoline (''Tp''), conversion to electricity (''Tg''), and the transmission grid (''Tt''); in summary, the total amount of useful electrical energy that can be extracted from gasoline is just % of its total theoretical stored energy. Substituting the numerical values into the first equation, : ::: ::: As noted above, when and are 1, as they would be for a pure-electric vehicle, . ;Examples In the example provided by the US DoE in its final rule, an electric car with an energy consumption of 265
Watt hour
A kilowatt-hour ( unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bi ...
per mile in urban driving, and 220 Watt hour per mile in highway driving, results in a petroleum-equivalent fuel economy of 335.24 miles per gallon, based on a driving schedule factor of 55 percent urban, and 45 percent highway, and using a petroleum equivalency factor of 82,049 Watt hours per gallon.
::
In 2009, the Monroney sticker for the Mini E
The Mini E was a demonstration electric car developed by BMW as a conversion of its Mini Cooper car. The Mini E was developed for field trials and deployed in several countries, including the United States, Germany, UK, France, Japan and Chin ...
rated the wall-to-wheel energy consumption at for the city and highway driving cycles, respectively. The petroleum-equivalent fuel economy is MPGPE, assuming a 55%/45% urban/highway split.
For comparison, the 2017 Chevrolet Bolt EV has a rated (wall-to-wheel) consumption of listed on the Monroney sticker for the urban/highway driving cycles, respectively. The petroleum-equivalent fuel economy for the Bolt, using the DoE rule to consider well-to-wall energy losses, is MPGPE, computed using the same 55%/45% urban/highway split.
See also
* Alternative propulsion * Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) * Energy conversion efficiency * Energy density *Fuel efficiency in transportation
The energy efficiency in transport is the useful travelled distance, of passengers, goods or any type of load; divided by the total energy put into the transport propulsion means. The energy input might be rendered in several different types depe ...
* Gasoline gallon equivalent
Gasoline gallon equivalent (GGE) or gasoline-equivalent gallon (GEG) is the amount of an alternative fuel it takes to equal the energy content of one liquid gallon of gasoline. GGE allows consumers to compare the energy content of competing fu ...
(GGE)
* List of unusual units of measurement
An unusual unit of measurement is a unit of measurement that does not form part of a coherent system of measurement, especially because its exact quantity may not be well known or because it may be an inconvenient multiple or fraction of a base ...
Notes
References
External links
eGallon Calculator: Compare the costs of driving with electricity
U.S. Department of Energy
Model Year 2014 Fuel Economy Guide
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon pro ...
and U.S. Department of Energy, April 2014.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Miles per gallon gasoline equivalent
Car costs
Energy conservation
Energy economics
Equivalent units
Green vehicles
Transport economics
Energy in transport