Mário Soares on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mário Alberto Nobre Lopes Soares, GColTE, GCC, GColL (; 7 December 1924 – 7 January 2017) was a
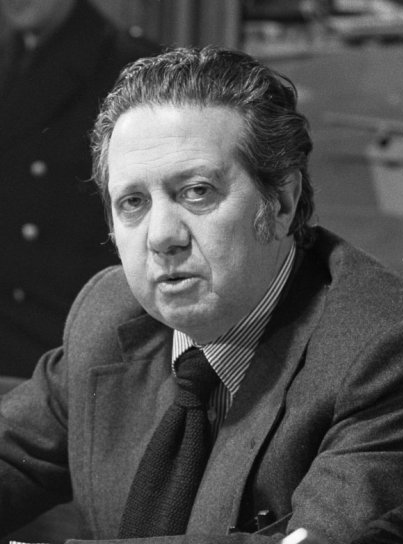 Within months of the revolution however (and in spite of the April 1975 Constituent Assembly election results which gave victory to the
Within months of the revolution however (and in spite of the April 1975 Constituent Assembly election results which gave victory to the
 In the 1986 presidential election, Soares was elected president of Portugal, beating
In the 1986 presidential election, Soares was elected president of Portugal, beating
he said
It was suggested (on the RTP1 TV programme ''Prós e Contras'' in March 2008) that one of the reasons for his weak support could be that the Portuguese were reluctant to elect any president for more than two terms (only allowed by the * In the TV programme '' Os Grandes Portugueses'' (English: The Greatest Portuguese), he was voted 12th, the highest-placed among living people chosen by the public.
* He was a member of the strongest
* In the TV programme '' Os Grandes Portugueses'' (English: The Greatest Portuguese), he was voted 12th, the highest-placed among living people chosen by the public.
* He was a member of the strongest
Nacionais com Ordens Portuguesas
recipients: * Grand Collar of the
Grand Collar of the  Grand Cross of the Order of Christ (GCC – 09/04/1981)
*
Grand Cross of the Order of Christ (GCC – 09/04/1981)
*  Grand Collar of the
Grand Collar of the  Grand Master of the Portuguese Orders (9 March 1986 – 9 March 1996):
Grand Master of the Portuguese Orders (9 March 1986 – 9 March 1996):
Nacionais com Ordens Estrangeiras
recipients: * Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Austrian Republic (
Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Austrian Republic ( Grand Cross of the National Order of Merit ( pt �
Grand Cross of the National Order of Merit ( pt �
B1
( Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Collar of the Order of the Southern Cross (Brazil, 1987/11/10)
*
Grand Collar of the Order of the Southern Cross (Brazil, 1987/11/10)
*  Grand Collar of the Order of the National Congress ( pt) (Brazil, 1987/04/13)
*
Grand Collar of the Order of the National Congress ( pt) (Brazil, 1987/04/13)
*  Grand Cross of the Ordef of Ipiranga ( pt) (State of
Grand Cross of the Ordef of Ipiranga ( pt) (State of  Collar of the Order of Merit of Bahia (State of
Collar of the Order of Merit of Bahia (State of  Order of the Balkan Mountains with Ribbon (
Order of the Balkan Mountains with Ribbon ( 1st Class of the Order of Amílcar Cabral (
1st Class of the Order of Amílcar Cabral ( Collar of the Grand Cross of the
Collar of the Grand Cross of the  Grand Collar of the
Grand Collar of the  Grand Cross of the Order of Merit ( Congo, 1989/09/12)
*
Grand Cross of the Order of Merit ( Congo, 1989/09/12)
*  1st Class of the
1st Class of the  Grand Collar of the
Grand Collar of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Knight of the
Knight of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Collar of the National Order of Merit (
Collar of the National Order of Merit ( Collar of the
Collar of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the National Order of Merit (
Grand Cross of the National Order of Merit ( Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross Special Class of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany (Germany, 1991/01/08)
*
Grand Cross Special Class of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany (Germany, 1991/01/08)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Collar of the
Collar of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Collar with Collar of the Order of the Falcon (Iceland, 1993/06/04)
*
Grand Collar with Collar of the Order of the Falcon (Iceland, 1993/06/04)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Merit of the Italian Republic (Italy, 1989/04/05)
*
Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Merit of the Italian Republic (Italy, 1989/04/05)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Knight of the
Knight of the  Honorary Companion of Honour of the National Order of Merit (
Honorary Companion of Honour of the National Order of Merit ( Collar of the Order pro merito Melitensi (
Collar of the Order pro merito Melitensi ( Knight Grand Cross of the
Knight Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the Order of St. Olav (
Grand Cross of the Order of St. Olav ( 1st Class of the Star of Palestine (
1st Class of the Star of Palestine ( Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Collar of the
Collar of the  Knight of the
Knight of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Honorary Knight Grand Cross (with Collar) of the
Honorary Knight Grand Cross (with Collar) of the  Honorary Knight Grand Cross of the
Honorary Knight Grand Cross of the  Grand Collar of the
Grand Collar of the 
 Great Star of the Order of the Yugoslav Star (Yugoslavia, 1990/04/24)
*
Great Star of the Order of the Yugoslav Star (Yugoslavia, 1990/04/24)
*  Grand Cordon of the
Grand Cordon of the
Comissão Nacional de Eleições
(2006)
Fundação Mário Soares
{{DEFAULTSORT:Soares, Mario 1924 births 2017 deaths Presidents of Portugal Prime Ministers of Portugal Portuguese democracy activists Portuguese anti-fascists People from Lisbon Former Roman Catholics Portuguese agnostics Golden Globes (Portugal) winners Portuguese Freemasons Portuguese Communist Party politicians Socialist Party (Portugal) politicians Socialist Party (Portugal) MEPs MEPs for Portugal 1999–2004 Foreign ministers of Portugal University of Lisbon alumni Rennes 2 University faculty 20th-century Portuguese lawyers Grand Collars of the Order of Liberty Grand Crosses of the Order of Christ (Portugal) Recipients of the Order of the Tower and Sword Grand Crosses of the Order of Polonia Restituta Grand Crosses of the Order of Merit of the Republic of Poland Grand Crosses Special Class of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany Recipients of the National Order of Merit (Brazil) Recipients of the Order pro Merito Melitensi International Simón Bolívar Prize recipients
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
politician, who served as prime minister of Portugal
The prime minister of Portugal ( pt, primeiro-ministro; ) is the head of government of Portugal. As head of government, the prime minister coordinates the actions of ministers, represents the Government of Portugal to the other bodies of state, ...
from 1976 to 1978 and from 1983 to 1985, and subsequently as the 17th president of Portugal
The president of Portugal, officially the president of the Portuguese Republic ( pt, Presidente da República Portuguesa, ), is the head of state and highest office of Portugal.
The powers, functions and duties of prior presidential offices, an ...
from 1986 to 1996. He was the first secretary-general of the Socialist Party
Socialist Party is the name of many different political parties around the world. All of these parties claim to uphold some form of socialism, though they may have very different interpretations of what "socialism" means. Statistically, most of th ...
, from its foundation in 1973 to 1986. A major political figure in Portugal, he is considered the father of Portuguese democracy.
Family
Soares was the son of João Lopes Soares ( Leiria, Arrabal, 17 November 1879 –Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
, Campo Grande, 31 July 1970), founder of the Colégio Moderno in Lisbon, government minister
A minister is a politician who heads a ministry, making and implementing decisions on policies in conjunction with the other ministers. In some jurisdictions the head of government is also a minister and is designated the ‘prime minister’, � ...
and then anti-fascist republican activist who had been a priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particu ...
before impregnating and marrying Elisa Nobre Baptista ( Santarém, Pernes, 8 September 1887 – Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
, Campo Grande, 28 February 1955), Mário Soares's mother, at the 7th Conservatory of the Civil Register of Lisbon on 5 September 1934. His father also had another son by an unknown mother named Tertuliano Lopes Soares. His mother had previously been married and had two children, J. Nobre Baptista and Cândido Nobre Baptista. Mário Soares was raised as a Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, but came to identify himself as a republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
, secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin ''saeculum'', "worldly" or "of a generation"), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. Anything that does not have an explicit reference to religion, either negativ ...
and socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the e ...
.
Early life
Soares was born in the Coração de Jesus neighbourhood ofLisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
, and graduated in history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
and philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
from the University of Lisbon
The University of Lisbon (ULisboa; pt, Universidade de Lisboa, ) is a public research university in Lisbon, and the largest university in Portugal. It was founded in 2013, from the merger of two previous public universities located in Lisbon, th ...
. He became a university lecturer in 1957, but his activities in opposition to the dictatorship of António de Oliveira Salazar
António de Oliveira Salazar (, , ; 28 April 1889 – 27 July 1970) was a Portuguese dictator who served as President of the Council of Ministers from 1932 to 1968. Having come to power under the ("National Dictatorship"), he reframed the re ...
led to repeated arrests. He was active in resistance groups such as the Movement for Anti-Fascist National Unity and the Movement for Democratic Unity.
Soares began his studies at Colégio Moderno, owned by his father. There, for a short period he was taught geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and ...
by Álvaro Cunhal
Álvaro Barreirinhas Cunhal (; 10 November 1913 – 13 June 2005) was a Portuguese communist revolutionary and politician. He was one of the major opponents of the dictatorial regime of the '' Estado Novo''. He served as secretary-general of the P ...
, who would later become the towering figure of Portuguese Communism and one of Soares' greatest political rivals.
While a student at university, Soares joined the Portuguese Communist Party
The Portuguese Communist Party ( pt, Partido Comunista Português, , PCP) is a communist, Marxist–Leninist political party in Portugal based upon democratic centralism. The party also considers itself patriotic and internationalist,Portugue ...
, being responsible for the youth section. In this capacity, he organised demonstrations in Lisbon to celebrate the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. He was first arrested by PIDE
The International and State Defense Police ( pt, Polícia Internacional e de Defesa do Estado; PIDE) was a Portuguese security agency that existed during the '' Estado Novo'' regime of António de Oliveira Salazar. Formally, the main roles of th ...
, the Portuguese political police, in 1946, when he was a member of the Central Committee of the Movement of Democratic Unity The Movement of Democratic Unity ( pt, Movimento de Unidade Democrática or MUD) was a quasi-legal platform of Portuguese democratic organizations that opposed the authoritarian regime of António de Oliveira Salazar and was founded in October 1945 ...
( pt, Movimento de Unidade Democrática), at the time chaired by . Soares was arrested twice in 1949. On those latter occasions, he was the secretary of General Norton de Matos Norton may refer to:
Places
Norton, meaning 'north settlement' in Old English, is a common place name. Places named Norton include: Canada
* Rural Municipality of Norton No. 69, Saskatchewan
* Norton Parish, New Brunswick
**Norton, New Brunswick, ...
, a candidate for the Presidency. However, he became estranged from de Matos when the latter discovered Soares's Communist sympathies.
Soares married Maria de Jesus Barroso Soares, an actress
An actor or actress is a person who portrays a Character (arts), character in a performance. The actor performs "in the flesh" in the traditional medium of the theatre or in modern media such as film, radio, and television. The analogous Greek ...
, on 22 February 1949, while in the Aljube prison, at the Third Conservatory of the Civil Register of Lisbon. They had a son, João Soares, who later became Mayor of Lisbon, and a daughter, Isabel Barroso Soares (born in 1951), who now manages the Colégio Moderno.
Soares's multiple arrests for political activism made it impossible for him to continue with his career as a lecturer of history and philosophy. Therefore, he decided to study law and become an attorney.
Political activity during the ''Estado Novo''
In 1958, Soares was very active in the presidential election supporting GeneralHumberto Delgado
Humberto da Silva Delgado, ComC, GCA, GOA, ComA, OA, ComSE, GCL, OIP, CBE (Portuguese pronunciation: �ˈbɛɾtu dɛɫˈɡadu 15 May 1906 – 13 February 1965) was a General of the Portuguese Air Force, diplomat and politician.
Early life ...
. Later, he would become Delgado's family lawyer, when Humberto Delgado was murdered in 1965, in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, by agents of the dictatorship's secret police (PIDE). As a lawyer, he defended some of Portuguese political prisoners and participated in numerous trials conducted in the Plenary Court and in the Special Military Court. Represented, particularly, Álvaro Cunhal
Álvaro Barreirinhas Cunhal (; 10 November 1913 – 13 June 2005) was a Portuguese communist revolutionary and politician. He was one of the major opponents of the dictatorial regime of the '' Estado Novo''. He served as secretary-general of the P ...
when he was accused of several political crimes, and along with Adelino da Palma Carlos
Adelino da Palma Carlos, GCC, GCIH, GOL (; Faro, 3 May 1905 – Lisbon, 25 October 1992), was a Portuguese lawyer, scholar, politician and a freemason, one of at least five sons of Manuel Carlos and wife Auta Vaz Velho da Palma. He was a ...
he also defended the dynastic cause of Maria Pia of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha Braganza
Maria may refer to:
People
* Mary, mother of Jesus
* Maria (given name), a popular given name in many languages
Place names Extraterrestrial
*170 Maria, a Main belt S-type asteroid discovered in 1877
*Lunar maria (plural of ''mare''), large, da ...
.
In April 1964, in Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaki ...
, Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, Soares together with Francisco Ramos da Costa
Francisco is the Spanish and Portuguese form of the masculine given name ''Franciscus''.
Nicknames
In Spanish, people with the name Francisco are sometimes nicknamed "Paco (name), Paco". Francis of Assisi, San Francisco de Asís was known as '' ...
and Manuel Tito de Morais
Manuel Alfredo Tito de Morais (28 June 1910 in Lisbon – 14 December 1999), was a Portuguese politician.
Background
He was the eldest child and son of Tito Augusto de Morais (Peso da Régua, 11 February 1880 - 1963), a Navy Officer of the ...
created the ''Acção Socialista Portuguesa'' ( Portuguese Socialist Action). At this point he was already quite distant from his former Communist friends (having quit the Communist Party in 1951); his views were now clearly inclined towards economic liberalism
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberalism ...
.
In March 1968, Soares was arrested again by PIDE, and a military tribunal sentenced him to banishment in the colony of São Tomé and Principe
SAO or Sao may refer to:
Places
* Sao civilisation, in Middle Africa from 6th century BC to 16th century AD
* Sao, a town in Boussé Department, Burkina Faso
* Saco Transportation Center (station code SAO), a train station in Saco, Maine, U.S. ...
in the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is in the ...
. His wife and two children, Isabel and João, accompanied him. However, they returned to Lisbon eight months later for in the meantime dictator Salazar had been replaced by Marcello Caetano
Marcelo José das Neves Alves Caetano (; 17 August 1906 – 26 October 1980) was a Portuguese politician and scholar. He was the second and last leader of the Estado Novo after succeeding António Salazar. He served as prime minister from 196 ...
. The new dictator wanted to present a more democratic face to the world, so many political prisoners, Soares among them, were released and allowed exile in France.
In the October 1969 general election, which was rigged, the democratic opposition (whose political rights were severely restricted) entered with two different lists. Soares participated actively in the campaign supporting the ''Coligação Eleitoral de Unidade Democrática'' or CEUD ( Electoral Coalition for Democratic Unity). CEUD was clearly anti-fascist, but they also reaffirmed their opposition to Communism.
In 1970, Soares was exiled to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, but eventually settled in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
where he taught at the Universities of Vincennes, Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
and Rennes
Rennes (; br, Roazhon ; Gallo: ''Resnn''; ) is a city in the east of Brittany in northwestern France at the confluence of the Ille and the Vilaine. Rennes is the prefecture of the region of Brittany, as well as the Ille-et-Vilaine department ...
. In 1973, the 'Portuguese Socialist Action' became the Socialist Party
Socialist Party is the name of many different political parties around the world. All of these parties claim to uphold some form of socialism, though they may have very different interpretations of what "socialism" means. Statistically, most of th ...
, and Soares was elected Secretary-General. The Socialist party was created under the umbrella of Willy Brandt
Willy Brandt (; born Herbert Ernst Karl Frahm; 18 December 1913 – 8 October 1992) was a German politician and statesman who was leader of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) from 1964 to 1987 and served as the chancellor of West Ge ...
's SPD in Bad Münstereifel
Bad Münstereifel () is a historical spa town in the district of Euskirchen, Germany, with about 17,000 inhabitants, situated in the far southwest of the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The little town is one of only a few historical tow ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, on 19 April 1973.
Carnation Revolution
On 25 April 1974, elements of thePortuguese Army
The Portuguese Army ( pt, Exército Português) is the land component of the Armed Forces of Portugal and is also its largest branch. It is charged with the defence of Portugal, in co-operation with other branches of the Armed Forces. With its ...
seized power in Lisbon, overthrowing Salazar's successor, Marcello Caetano
Marcelo José das Neves Alves Caetano (; 17 August 1906 – 26 October 1980) was a Portuguese politician and scholar. He was the second and last leader of the Estado Novo after succeeding António Salazar. He served as prime minister from 196 ...
. Soares and other political exiles returned home to celebrate what was termed the "Carnation Revolution
The Carnation Revolution ( pt, Revolução dos Cravos), also known as the 25 April ( pt, 25 de Abril, links=no), was a military coup by left-leaning military officers that overthrew the authoritarian Estado Novo regime on 25 April 1974 in Lisbo ...
".
In the provisional government which was formed after the revolution, led by the Movement of the Armed Forces (MFA), Soares became minister for overseas negotiations, charged with organising the independence of Portugal's overseas colonies. Among other encounters, he met with Samora Machel
Samora Moisés Machel (29 September 1933 – 19 October 1986) was a Mozambican military commander and political leader. A socialist in the tradition of Marxism–Leninism, he served as the first President of Mozambique from the country's ...
, the leader of Frelimo
FRELIMO (; from the Portuguese , ) is a democratic socialist political party in Mozambique. It is the dominant party in Mozambique and has won a majority of the seats in the Assembly of the Republic in every election since the country's firs ...
, to negotiate the independence of Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
.
 Within months of the revolution however (and in spite of the April 1975 Constituent Assembly election results which gave victory to the
Within months of the revolution however (and in spite of the April 1975 Constituent Assembly election results which gave victory to the Socialist Party
Socialist Party is the name of many different political parties around the world. All of these parties claim to uphold some form of socialism, though they may have very different interpretations of what "socialism" means. Statistically, most of th ...
and clearly favored the pro-democracy political parties), it became apparent that the Portuguese Communist Party
The Portuguese Communist Party ( pt, Partido Comunista Português, , PCP) is a communist, Marxist–Leninist political party in Portugal based upon democratic centralism. The party also considers itself patriotic and internationalist,Portugue ...
, allied with a radical group of officers in the MFA, was attempting to extend its control over the government. The prime minister, Vasco dos Santos Gonçalves, was accused of being an agent of the Communists and a bitter confrontation developed between the Socialists and Communists over control of the newspaper '' República''.
President Francisco da Costa Gomes
Francisco da Costa Gomes, ComTE, GOA (; 30 June 1914 – 31 July 2001) was a Portuguese military officer and politician, the 15th president of Portugal (the second after the Carnation Revolution).
Life
He was one of the eleven children of A ...
dismissed Vasco Gonçalves in September 1975 and a failed far-left
Far-left politics, also known as the radical left or the extreme left, are politics further to the left on the left–right political spectrum than the standard political left. The term does not have a single definition. Some scholars consider ...
coup in late November ended the far-left influence in Portuguese government and politics. After the approval of the 1976 Constitution, a democratic government was finally established when national elections were held on 25 April 1976.
Prime minister
The 1976 legislative election gave the Socialists a plurality of seats in the newly created Assembly of the Republic and Soares becameprime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
. Deep hostility between the Socialists and the Communists made a left-wing majority government impossible, and Soares formed a weak minority government. Vast fiscal and currency account deficits generated by previous governments forced Soares to adopt a strict austerity policy, which made him deeply unpopular. Soares had to resign from office after only two years, in 1978.
The wave of left-wing sentiment which followed the 1974 revolution had now dissipated, and a succession of conservative governments held office until 1983, with Soares' Socialist Party
Socialist Party is the name of many different political parties around the world. All of these parties claim to uphold some form of socialism, though they may have very different interpretations of what "socialism" means. Statistically, most of th ...
unsuccessful in the 1979 special elections and 1980 elections. Soares again became prime minister following the 1983 elections
The following elections occurred in the year 1983.
Africa
* 1983 Cameroonian parliamentary election
* 1983 Equatorial Guinean legislative election
* 1983 Kenyan general election
* 1983 Malagasy parliamentary election
* 1983 Malawian general elec ...
, holding office until late 1985. His main achievement in office was negotiating Portugal's entry into the European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
. Portugal at the time was very wary of integrating itself into the EEC
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
, and Soares almost single-handedly turned public opinion around.
Presidency
 In the 1986 presidential election, Soares was elected president of Portugal, beating
In the 1986 presidential election, Soares was elected president of Portugal, beating Diogo Freitas do Amaral
Diogo Pinto de Freitas do Amaral (; 21 July 1941 – 3 October 2019), known as Freitas do Amaral, was a Portuguese politician and law professor. He was Minister of Foreign Affairs from 10 January 1980 to 12 January 1981 and from 12 March 2005 t ...
by little more than 2%. He was reelected in 1991, this time with almost 70% of the vote. For most of Soares' two terms of office, Portugal was governed by the centre-right Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
Fo ...
, led by Aníbal Cavaco Silva
Aníbal António Cavaco Silva, GCC, GColL, GColIH (; born 15 July 1939) is a Portuguese economist who served as the 19th president of Portugal, in office from 9 March 2006 to 9 March 2016. He had been previously prime minister of Portugal fro ...
.
In 1989, he was the first foreign head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
to visit Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
in the course of the Velvet Revolution
The Velvet Revolution ( cs, Sametová revoluce) or Gentle Revolution ( sk, Nežná revolúcia) was a non-violent transition of power in what was then Czechoslovakia, occurring from 17 November to 28 November 1989. Popular demonstrations agains ...
, invited by Václav Havel
Václav Havel (; 5 October 193618 December 2011) was a Czech statesman, author, poet, playwright, and former dissident. Havel served as the last president of Czechoslovakia from 1989 until the dissolution of Czechoslovakia in 1992 and then as ...
, who was elected president of Czechoslovakia two days later.
He devised the so-called ''Presidência Aberta'' (Open Presidency), a series of tours around the country, each addressing a particular issue, such as the environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
or a particular region of Portugal. Although generally well received by the public, some claimed that he was criticizing the government and exceeding his constitutional role. Others stated that the tours were in the style of medieval courts. Yet the name stuck for today's presidential initiatives of the same type.
Post-Presidency
*Soares retired in 1996, but in 1998 he headed the Independent World Commission on the Oceans. *In 1999 he headed the Socialist ticket in elections to theEuropean Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adopts ...
, where he served until the 2004 elections. He ran for President of the Parliament, but lost to Nicole Fontaine
Nicole Fontaine (16 January 1942 – 17 May 2018) was a French politician who served as Member of the European Parliament for the Île-de-France from 1984 until 2002 and from 2004 until 2009. She was a member of the Union for a Popular Movement, ...
.
*In 2000 he was awarded the North-South Prize
''North-South'' ( hy, Հյուսիս-Հարավ) or ''Four Buddies and the Bride'' is an Armenian comedy directed by Davit Babakhanyan and Vazgen Muradyan, starring Diana Malenko, Sona Shahgeldyan and David Tovmasyan. The film was produced by L ...
.
*Soares was a member of the Club de Madrid
Club de Madrid is an independent non-profit organization created to promote democracy and change in the international community. Composed of 121 regular members from 72 countries, including 7 Nobel Peace Prize laureates and 20 first female heads ...
, an independent organization of more than 80 former democratic statesmen from around the world. The group works to strengthen democratic governance and leadership.
*In March 2005, he launched a petition urging the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
to start membership talks with Cape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
.
*On 30 August 2005, he announced his candidacy to run for president in the election that occurred on 22 January 2006, when he was 81 years old. However, he lost the election to Aníbal Cavaco Silva
Aníbal António Cavaco Silva, GCC, GColL, GColIH (; born 15 July 1939) is a Portuguese economist who served as the 19th president of Portugal, in office from 9 March 2006 to 9 March 2016. He had been previously prime minister of Portugal fro ...
and was even behind Manuel Alegre, receiving 14% of the vote. "The results went against my expectations. I accept this defeat with a feeling of mission accomplished,he said
It was suggested (on the RTP1 TV programme ''Prós e Contras'' in March 2008) that one of the reasons for his weak support could be that the Portuguese were reluctant to elect any president for more than two terms (only allowed by the
Portuguese Constitution of 1976
The present Constitution of Portugal was adopted in 1976 after the Carnation Revolution. It was preceded by a number of constitutions including the first one created in 1822 (following the Liberal Revolution of 1820), 1826 (drawn up by King D ...
if non-consecutive).
 * In the TV programme '' Os Grandes Portugueses'' (English: The Greatest Portuguese), he was voted 12th, the highest-placed among living people chosen by the public.
* He was a member of the strongest
* In the TV programme '' Os Grandes Portugueses'' (English: The Greatest Portuguese), he was voted 12th, the highest-placed among living people chosen by the public.
* He was a member of the strongest Masonic lodge
A Masonic lodge, often termed a private lodge or constituent lodge, is the basic organisational unit of Freemasonry. It is also commonly used as a term for a building in which such a unit meets. Every new lodge must be warranted or chartered ...
in Portugal.
* He was president of the then ( pt, Fundação Mário Soares, links=no (FMS)).
* He sat on the board of directors of the ( pt, Fundação Oriente, links=no).
* He was a Member of the Portuguese Council of State
The Council of State ( pt, Conselho de Estado, ) is a body established by the Portuguese Constitution to advise the President of the Republic in the exercise of many of his or her discretionary powers.
History
Although there are notices about th ...
, as a former elected president of Portugal.
*After the Finnish general elections on 17 April 2011, Soares opined that "Finland has changed into an extremely conservative country, where solidarity is unknown." Soares evoked the memory of Kalevi Sorsa
Taisto Kalevi Sorsa (21 December 1930 – 16 January 2004) was a Finnish politician who served as Prime Minister of Finland three times: 1972–1975, 1977–1979 and 1982–1987. At the time of his death he still held the record for most day ...
, contrasting his generosity with "those dwarfs, who now want to rule Finland, their ethical values and hostility to Portugal". According to Soares the Finns live in an illusion, believing that "speculative markets and credit criminals can destroy nations with nine hundred years' independent history".
Death and state funeral
Soares died on 7 January 2017 at the age of 92. He had been admitted to the hospital on 13 December, and although his condition at first showed slight signs of improvement, he lapsed into a coma on 26 December from which he never recovered. ThePortuguese Government
, border = Central
, image =
, caption =
, date =
, state = Portuguese Republic
, address = Official Residence of the Prime Minister Estrela, Lisbon
, appointed = President ...
offered a state funeral and declared three days of national mourning. It was the first state funeral in Portugal after that of President Óscar Carmona
António Óscar de Fragoso Carmona (; 24 November 1869 – 18 April 1951) was a Portuguese Army officer and politician who served as prime minister of Portugal from 1926 to 1928 and as the 11th president of Portugal from 1926 until his death i ...
in 1951. After lying in state at Jerónimos Monastery
The Jerónimos Monastery or Hieronymites Monastery ( pt, Mosteiro dos Jerónimos, ) is a former monastery of the Order of Saint Jerome near the Tagus river in the parish of Belém, in the Lisbon Municipality, Portugal. It became the necropolis o ...
during 9 January, his remains were transported to Prazeres Cemetery
Prazeres Cemetery ( pt, Cemitério dos Prazeres) is one of the largest cemeteries in Lisbon, Portugal; it is located in the '' freguesia'' (civil parish) of Estrela, in western Lisbon (formerly, within the parish of Prazeres). It is considered ...
the next day, and now lie at the family vault next to those of his wife.
Honours and awards
National honours
N.B. according to "Ordens honoríficas portuguesas �Nacionais com Ordens Portuguesas
recipients: *
 Grand Collar of the
Grand Collar of the Order of the Tower and Sword
The Ancient and Most Noble Military Order of the Tower and of the Sword, of the Valour, Loyalty and Merit ( pt, Antiga e Muito Nobre Ordem Militar da Torre e Espada, do Valor, Lealdade e Mérito), before 1910 Royal Military Order of the Tower an ...
(GColTE – 9 March 1991)
* Order of Liberty
The Order of Liberty, or the Order of Freedom ( pt, Ordem da Liberdade), is a Portuguese honorific civil order that distinguishes relevant services to the cause of democracy and freedom, in the defense of the values of civilization and human di ...
(GColL – 9 March 1996)
* Foreign honours
N.B. according to "Ordens honoríficas portuguesas �Nacionais com Ordens Estrangeiras
recipients: *
 Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Austrian Republic (
Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Austrian Republic (Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, 1987/03/10)
*  Grand Cross of the National Order of Merit ( pt �
Grand Cross of the National Order of Merit ( pt �B1
(
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, 1988/03/30)
* Order of the Southern Cross
Emperor Pedro I of Brazil founded the National Order of the Southern Cross ( pt, Ordem Nacional do Cruzeiro do Sul) as a Brazilian order of chivalry on 1 December 1822. The order aimed to commemorate the independence of Brazil (7 September 1822) ...
(Brazil, 1987/03/10)
*  Grand Collar of the Order of the National Congress ( pt) (Brazil, 1987/04/13)
*
Grand Collar of the Order of the National Congress ( pt) (Brazil, 1987/04/13)
*  Grand Cross of the Ordef of Ipiranga ( pt) (State of
Grand Cross of the Ordef of Ipiranga ( pt) (State of São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for 'Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaWC a ...
, 1987/04/13)
*  Collar of the Order of Merit of Bahia (State of
Collar of the Order of Merit of Bahia (State of Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 Federative units of Brazil, states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo (sta ...
, 1988/03/30)
* Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
, 1994/10/26)
*  1st Class of the Order of Amílcar Cabral (
1st Class of the Order of Amílcar Cabral (Cape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
, 2001/01/05)
* Order of Merit
The Order of Merit (french: link=no, Ordre du Mérite) is an order of merit for the Commonwealth realms, recognising distinguished service in the armed forces, science, art, literature, or for the promotion of culture. Established in 1902 by K ...
(Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
, 1992/07/22)
*  Grand Collar of the
Grand Collar of the Order of Boyaca
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
(Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
, 1988/05/27)
*  1st Class of the
1st Class of the Order of Diplomatic Service Merit
The Order of Diplomatic Service Merit (Hangul: 수교훈장) is one of South Korea's orders of merit. It is awarded by the President of South Korea for "outstanding meritorious services in the interest of enhancing national prestige and promoting ...
(South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, 1987/04/23)
* Order of Makarios III
The Order of Makarios III ( el, Τάγμα Μακάριου Γ') is the highest order of merit awarded by Cyprus. Established in 1991, the order is named after the first President of Cyprus, Archbishop Makarios III.
Grades
The Order of Makarios ...
(Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
, 1990/05/29)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of the Dannebrog
The Order of the Dannebrog ( da, Dannebrogordenen) is a Danish order of chivalry instituted in 1671 by Christian V. Until 1808, membership in the order was limited to fifty members of noble or royal rank, who formed a single class known a ...
(Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
, 1988/03/30)
* Order of the Elephant
The Order of the Elephant ( da, Elefantordenen) is a Danish order of chivalry and is Denmark's highest-ranked honour. It has origins in the 15th century, but has officially existed since 1693, and since the establishment of constitutional ...
(Denmark, 1992/05/06)
* Order of Merit of Duarte, Sánchez and Mella
The Order of Merit of Duarte, Sánchez and Mella (''Orden al Mérito de Duarte, Sánchez y Mella'') is the principal order of the Dominican Republic. It was established on 24 February 1931 as the ''Juan Pablo Duarte Order of Merit'' (''Orden al M ...
(Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares wit ...
, 1987/03/10)
*  Collar of the National Order of Merit (
Collar of the National Order of Merit (Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ''Eku ...
, 1989/09/12)
*  Collar of the
Collar of the Order of the Nile
The Order of the Nile (''Kiladat El Nil'') was established in 1915 and was one of the Kingdom of Egypt's principal orders until the monarchy was abolished in 1953. It was then reconstituted as the Republic of Egypt's highest state honor.
Sultana ...
(Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, 1992/04/04)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of the White Rose of Finland
The Order of the White Rose of Finland ( fi, Suomen Valkoisen Ruusun ritarikunta; sv, Finlands Vita Ros’ orden) is one of three official orders in Finland, along with the Order of the Cross of Liberty, and the Order of the Lion of Finland. ...
with Collar (Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
,1990)
* France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, 1988/05/26)
* Legion of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour (french: Ordre national de la Légion d'honneur), formerly the Royal Order of the Legion of Honour ('), is the highest French order of merit, both military and civil. Established in 1802 by Napoleon, ...
(France, 1990/05/07)
* Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany
The Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany (german: Verdienstorden der Bundesrepublik Deutschland, or , BVO) is the only federal decoration of Germany. It is awarded for special achievements in political, economic, cultural, intellect ...
(Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, 1987/03/10)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of the Redeemer
The Order of the Redeemer ( el, Τάγμα του Σωτήρος, translit=Tágma tou Sotíros), also known as the Order of the Saviour, is an order of merit of Greece. The Order of the Redeemer is the oldest and highest decoration awarded by the ...
(Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, 1987/11/20)
* Order of Pope Pius IX
The Order of Pope Pius IX ( it, Ordine di Pio IX), also referred as the Pian Order ( it, Ordine Piano), is a papal order of knighthood originally founded by Pope Pius IV in 1560. Currently, it is the highest honor conferred by the Holy See (being ...
(Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of Rome ...
, 1991/01/08)
* Order of Merit of the Republic of Hungary
The Hungarian Order of Merit ( hu, Magyar Érdemrend) is the fourth highest State Order of Hungary. Founded in 1991, the order is a revival of an original order founded in 1946 and abolished in 1949. Its origins, however, can be traced to the O ...
(Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
, 1993/01/25)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of the Falcon
The Order of the Falcon ( is, Hin íslenska fálkaorða) is the only order of chivalry in Iceland, founded by King Christian X of Denmark and Iceland on 3 July 1921. The award is awarded for merit for Iceland and humanity and has five degrees. N ...
(Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
, 1983/11/21)
*  Grand Collar with Collar of the Order of the Falcon (Iceland, 1993/06/04)
*
Grand Collar with Collar of the Order of the Falcon (Iceland, 1993/06/04)
* Order of Merit of the Italian Republic
The Order of Merit of the Italian Republic ( it, Ordine al Merito della Repubblica Italiana) is the senior Italian order of merit. It was established in 1951 by the second President of the Italian Republic, Luigi Einaudi.
The highest-ranking ...
(Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, 1984/04/26)
* National Order of the Ivory Coast
The National Order of the Ivory Coast (sometimes simply mentioned as National Order) is the highest state order of knighthood of the Ivory Coast.
History
The Order was founded on 10 April 1961 to celebrate the independence of the Ivory Coast wh ...
(Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
, 1990/06/01)
*  Knight of the
Knight of the Order of the Gold Lion of the House of Nassau
The Order of the Gold Lion of the House of Nassau (french: Ordre du Lion d'Or de la Maison de Nassau, nl, Huisorde van de Gouden Leeuw van Nassau) is a chivalric order shared by the two branches of the House of Nassau (the Ottonian and Walramian ...
(Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
, 1988/05/26)
* Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, 1994/10/09)
* Sovereign Military Order of Malta
The Sovereign Military Order of Malta (SMOM), officially the Sovereign Military Hospitaller Order of Saint John of Jerusalem, of Rhodes and of Malta ( it, Sovrano Militare Ordine Ospedaliero di San Giovanni di Gerusalemme, di Rodi e di Malta; ...
, 1989/05/09)
* Special Class of the Order of Sovereignty (Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
, 1992/02/06)
*  Knight Grand Cross of the
Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Netherlands Lion
The Order of the Netherlands Lion, also known as the Order of the Lion of the Netherlands ( nl, De Orde van de Nederlandse Leeuw, french: L'Ordre du Lion Néerlandais) is a Dutch order of chivalry founded by King William I of the Netherlands on ...
(Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, 1991/09/26)
* Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
, 1987/03/10)
* Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
, 1993/11/18)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Republic of Poland
The Order of Merit of the Republic of Poland ( pl, Order Zasługi Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej) is a Polish order of merit created in 1974, awarded to persons who have rendered great service to Poland. It is granted to foreigners or Poles resident ab ...
(Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
, 1993/05/21)
* Order of Polonia Restituta
The Order of Polonia Restituta ( pl, Order Odrodzenia Polski, en, Order of Restored Poland) is a Polish state decoration, state Order (decoration), order established 4 February 1921. It is conferred on both military and civilians as well as on al ...
(Poland, 1994/10/26)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of Merit
The Order of Merit (french: link=no, Ordre du Mérite) is an order of merit for the Commonwealth realms, recognising distinguished service in the armed forces, science, art, literature, or for the promotion of culture. Established in 1902 by K ...
(Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
, 1996/02/28)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of Good Hope
The Order of Good Hope or Order of the Cape of Good Hope is a dormant order of merit of the Republic of South Africa.
History
The Order of Good Hope was founded in 1973, by the republican government of South Africa, to grant those who had disti ...
(South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
, 1995)
* Order of Isabella the Catholic
The Order of Isabella the Catholic ( es, Orden de Isabel la Católica) is a Spanish civil order and honor granted to persons and institutions in recognition of extraordinary services to the homeland or the promotion of international relations a ...
(Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, 1977/11/21)
* Order of Charles III
The Royal and Distinguished Spanish Order of Charles III, originally Royal and Much Distinguished Order of Charles III ( es, Real y Distinguida Orden Española de Carlos III, originally es, Real y Muy Distinguida Orden de Carlos III) was establ ...
(Spain, 1987/03/10)
* Order of Charles III
The Royal and Distinguished Spanish Order of Charles III, originally Royal and Much Distinguished Order of Charles III ( es, Real y Distinguida Orden Española de Carlos III, originally es, Real y Muy Distinguida Orden de Carlos III) was establ ...
(Spain, 1988/03/30)
* Order of the Seraphim
The Royal Order of the Seraphim ( sv, Kungliga Serafimerorden; ''Seraphim'' being a category of angels) is a Swedish order of chivalry created by King Frederick I on 23 February 1748, together with the Order of the Sword and the Order of the P ...
(Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
, 1987/01/28)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of the Seventh of November
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
(Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, 1993/02/16)
* Order of the Bath
The Most Honourable Order of the Bath is a British order of chivalry founded by George I of Great Britain, George I on 18 May 1725. The name derives from the elaborate medieval ceremony for appointing a knight, which involved Bathing#Medieval ...
(United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, 1994/05/19)
*Order of St Michael and St George
The Most Distinguished Order of Saint Michael and Saint George is a British order of chivalry founded on 28 April 1818 by George IV, George IV, Prince of Wales, while he was acting as prince regent for his father, George III, King George III.
...
(United Kingdom, 1996)
*  Grand Collar of the
Grand Collar of the Order of the Liberator
The Order of the Liberator was the highest distinction of Venezuela and was appointed for services to the country, outstanding merit and benefits made to the community. For Venezuelans the order ranks first in the order of precedence from other or ...
(Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, 1987/11/10)
* 
Order of the Yugoslav Star
The Order of the Yugoslav Star sr, Орден југословенске звезде, ''Orden jugoslovenske zvezde'' sl, Red jugoslovanske zvezde mk, Орден на југословенската ѕвезда, ''Orden na jugoslovenskata zvezda'' ...
with Sash (Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
, 1988/03/30)
*  Great Star of the Order of the Yugoslav Star (Yugoslavia, 1990/04/24)
*
Great Star of the Order of the Yugoslav Star (Yugoslavia, 1990/04/24)
*  Grand Cordon of the
Grand Cordon of the National Order of the Leopard
The National Order of the Leopard (french: Ordre national du Léopard) was the highest honorific decoration of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from 1966 until 2002 when it was discontinued and replaced by the Order of the National Heroes Kabi ...
(Zaire
Zaire (, ), officially the Republic of Zaire (french: République du Zaïre, link=no, ), was a Congolese state from 1971 to 1997 in Central Africa that was previously and is now again known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Zaire was, ...
, 1989/12/04)
Foreign awards
In 1998, Soares won theInternational Simón Bolívar Prize
The International Simón Bolívar Prize serves to recognise activities of outstanding merit that, in accordance with the ideals of Latin American independence hero Simón Bolívar, "contribute to the freedom, independence and dignity of peoples a ...
of UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
.
In 2000, Soares received the North-South Prize
''North-South'' ( hy, Հյուսիս-Հարավ) or ''Four Buddies and the Bride'' is an Armenian comedy directed by Davit Babakhanyan and Vazgen Muradyan, starring Diana Malenko, Sona Shahgeldyan and David Tovmasyan. The film was produced by L ...
of the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
.
He was an honorary member of the Club of Rome
The Club of Rome is a nonprofit, informal organization of intellectuals and business leaders whose goal is a critical discussion of pressing global issues. The Club of Rome was founded in 1968 at Accademia dei Lincei in Rome, Italy. It consists ...
and member of High Council of Francophonie.
He was appointed Doctor of Laws ''(honoris causa)'' by the University of Leicester
, mottoeng = So that they may have life
, established =
, type = public research university
, endowment = £20.0 million
, budget = £326 million
, chancellor = David Willetts
, vice_chancellor = Nishan Canagarajah
, head_labe ...
in 1994.
Soares was named the "patron" for the College of Europe
The College of Europe (french: Collège d'Europe) is a post-graduate institute of European studies with its main campus in Bruges, Belgium and a second campus in Warsaw, Poland. The College of Europe in Bruges was founded in 1949 by leading ...
's academic year 2020-2021.
Electoral results
1986 Portuguese presidential election
Mário Soares won the election with 3,010,756 votes (51.18%) after the second round of voting.1991 Portuguese presidential election
Mário Soares won the election with 3,459,521 votes (70.35%).2006 Portuguese presidential election
Mário Soares finished third with 785,355 votes (14.31%).(2006)
Notes
References
Further reading
* Wilsford, David, ed. ''Political Leaders of Contemporary Western Europe: A Biographical Dictionary'' (Greenwood, 1995) pp. 413–21.External links
Fundação Mário Soares
{{DEFAULTSORT:Soares, Mario 1924 births 2017 deaths Presidents of Portugal Prime Ministers of Portugal Portuguese democracy activists Portuguese anti-fascists People from Lisbon Former Roman Catholics Portuguese agnostics Golden Globes (Portugal) winners Portuguese Freemasons Portuguese Communist Party politicians Socialist Party (Portugal) politicians Socialist Party (Portugal) MEPs MEPs for Portugal 1999–2004 Foreign ministers of Portugal University of Lisbon alumni Rennes 2 University faculty 20th-century Portuguese lawyers Grand Collars of the Order of Liberty Grand Crosses of the Order of Christ (Portugal) Recipients of the Order of the Tower and Sword Grand Crosses of the Order of Polonia Restituta Grand Crosses of the Order of Merit of the Republic of Poland Grand Crosses Special Class of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany Recipients of the National Order of Merit (Brazil) Recipients of the Order pro Merito Melitensi International Simón Bolívar Prize recipients