
The Louvre Palace (french: link=no, Palais du Louvre, ), often referred to simply as the Louvre, is an iconic French palace located on the
Right Bank of the
Seine
)
, mouth_location = Le Havre/ Honfleur
, mouth_coordinates =
, mouth_elevation =
, progression =
, river_system = Seine basin
, basin_size =
, tributaries_left = Yonne, Loing, Eure, Risle
, tributa ...
in
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
, occupying a vast expanse of land between the
Tuileries Gardens and the church of
Saint-Germain l'Auxerrois. Originally a military facility, it has served numerous government-related functions in the past, including intermittently as a royal residence between the 14th and 18th centuries. It is now mostly used by the
Louvre Museum, which first opened there in 1793.
Whereas the area had been inhabited for thousands of years,
[ the Louvre's history starts around 1190 with its first construction as a ]castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
defending the western front of the Wall of Philip II Augustus
The Wall of Philip Augustus is the oldest city wall of Paris (France) whose plan is accurately known. Partially integrated into buildings, more traces of it remain than of the later fortifications.
History
The wall was built during the struggle ...
. The Louvre's oldest section still standing above ground, its Lescot Wing, dates from the late 1540s, when Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
started the replacement of the medieval castle with a new design inspired by classical antiquity and Italian Renaissance architecture
Renaissance architecture is the European architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 16th centuries in different regions, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman thought ...
. Most parts of the current building were constructed in the 17th and 19th centuries.Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, f ...
, created to the west of the Louvre by Catherine de' Medici
Catherine de' Medici ( it, Caterina de' Medici, ; french: Catherine de Médicis, ; 13 April 1519 – 5 January 1589) was an Florentine noblewoman born into the Medici family. She was Queen of France from 1547 to 1559 by marriage to King ...
in 1564 and finally demolished in 1883. The Tuileries was the main seat of French executive power during the last third of that period, from the return of Louis XVI
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was ...
and his court from Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, ...
in October 1789 until the palace was set on fire during the Paris Commune
The Paris Commune (french: Commune de Paris, ) was a revolutionary government that seized power in Paris, the capital of France, from 18 March to 28 May 1871.
During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard had defende ...
of 1871. The Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
and Pavillon de Marsan, which used to respectively mark the southern and northern ends of the Tuileries, are now considered part of the Louvre Palace. The Carrousel Garden
The Tuileries Garden (french: Jardin des Tuileries, ) is a public garden located between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. Created by Catherine de' Medici as the garden of the Tuileries Palace ...
, first created in the late 19th century in what used to be the great courtyard of the Tuileries (or Cour du Carrousel
The Tuileries Garden (french: Jardin des Tuileries, ) is a public garden located between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. Created by Catherine de' Medici as the garden of the Tuileries Palace ...
), is now considered part of the Tuileries Garden. A less high-profile but historically significant dependency of the Louvre was to its immediate east, the Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon
The Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon, a former Parisian town house of the House of Bourbon, royal family of Bourbon, was located on the Rive Droite, right bank of the Seine on the rue d'Autriche, between the :en:Louvre Palace, Louvre to the west and the ...
, appropriated by the monarchy following the betrayal of the Constable of Bourbon in 1523 and mostly demolished in October 1660 to give way to the Louvre's expansion. The last remains of the Petit-Bourbon were cleared in the 1760s.
General description
This sections provides a summary description of the present-day complex and its main constituent parts.
Location and layout

 The Louvre Palace is situated on the right bank of the
The Louvre Palace is situated on the right bank of the Seine
)
, mouth_location = Le Havre/ Honfleur
, mouth_coordinates =
, mouth_elevation =
, progression =
, river_system = Seine basin
, basin_size =
, tributaries_left = Yonne, Loing, Eure, Risle
, tributa ...
, between the Quai François Mitterrand to its south, the to its west (thus named since 1957; formerly and , converted into an underpass in 1987–1989), the Rue de Rivoli to its north, and the Place du Louvre to its east. The complex occupies about 40 hectares
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100- metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is ...
with buildings distributed around two main open spaces: the eastern Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
(square courtyard), which is closed by four wings that form the square of its name, and the central Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
, which is open on its western side, beyond the thoroughfare known as Place du Carrousel, towards the Carrousel Garden
The Tuileries Garden (french: Jardin des Tuileries, ) is a public garden located between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. Created by Catherine de' Medici as the garden of the Tuileries Palace ...
and the rest of the Tuileries Garden.
The Louvre is slightly askew of the Historic Axis ('' Axe historique''), a roughly eight-kilometre (five-mile) architectural line bisecting the city. The axis begins with the Louvre courtyard, at a point now symbolically marked by a lead copy of Bernini's equestrian statue of Louis XIV, and runs west along the Champs-Élysées to La Défense
La Défense () is a major business district in France, located west of the city limits of Paris. It is part of the Paris metropolitan area in the Île-de-France region, located in the department of Hauts-de-Seine in the communes of Courbev ...
and slightly beyond.
Since 1988, the Louvre Pyramid
The Louvre Pyramid (Pyramide du Louvre) is a large glass and metal structure designed by the Chinese-American architect I. M. Pei. The pyramid is in the main courtyard (Cour Napoléon) of the Louvre Palace in Paris, surrounded by three smalle ...
in the middle of the Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
has marked the center of the Louvre complex. At the same time, the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the '' Venus de Milo''. A central ...
Museum has adopted a toponymy developed by the Carbone Smolan Agency
Carbone Smolan Agency is an independent branding agency founded in 1976 in New York City.
History
In 1976 Ken Carbone opened the New York office of the Canadian graphic design firm Gottschalk+Ash International. In 1977 he met and became busine ...
to refer to the three clusters of buildings that surround that central focus point:
* To the east, the "Sully Wing" is the square-shaped set of buildings that surrounds the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
, named after Maximilien de Béthune, Duke of Sully
Maximilien de Béthune, 1st Duke of Sully, Marquis of Rosny and Nogent, Count of Muret and Villebon, Viscount of Meaux (13 December 156022 December 1641) was a nobleman, soldier, statesman, and counselor of King Henry IV of France. Historians emp ...
. It includes the 16th-century Lescot Wing and the footprint of the Medieval Louvre whose remains are displayed underground;
* To the south, the "Denon Wing" is the array of buildings between the Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
and the Seine
)
, mouth_location = Le Havre/ Honfleur
, mouth_coordinates =
, mouth_elevation =
, progression =
, river_system = Seine basin
, basin_size =
, tributaries_left = Yonne, Loing, Eure, Risle
, tributa ...
, named after the Louvre's first director Vivant Denon. the Louvre's southwestern wing is the Aile de Flore. The long Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
runs on the first floor for much of the length of this building, on the Seine-facing side.
* To the north, the "Richelieu Wing" is the almost-symmetrical array of buildings between the Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
and the rue de Rivoli, named after Cardinal Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis, Duke of Richelieu (; 9 September 1585 – 4 December 1642), known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a French clergyman and statesman. He was also known as ''l'Éminence rouge'', or "the Red Eminence", a term derived from the ...
. Its western extension alongside rue de Rivoli is the , itself continued by the Aile de Marsan
The Pavillon de Marsan or Marsan Pavilion was built in the 1660s as the northern end of the Tuileries Palace in Paris, and reconstructed in the 1870s after the Tuileries burned down at the end of the Paris Commune. Following the completion of th ...
.
The Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the '' Venus de Milo''. A central ...
Museum occupies most of the palace's space, but not all of it. The main other users are at the building's two western tips: in the southwestern Aile de Flore, the École du Louvre and Center for Research and Restoration of Museums of France (C2RMF); and in the northwestern Aile de Marsan
The Pavillon de Marsan or Marsan Pavilion was built in the 1660s as the northern end of the Tuileries Palace in Paris, and reconstructed in the 1870s after the Tuileries burned down at the end of the Paris Commune. Following the completion of th ...
, the Musée des Arts Décoratifs. In total, some 51,615 square meters (555,000 square feet) in the palace complex are devoted to public exhibition floor space.
Many sections of the Louvre are referred to as " wings" () and " pavilions" () – typically, the pavilions are the blocks at either the end or the center of a wing. In the Louvre's context, the word "wing" does not denote a peripheral location: the Lescot Wing, in particular, was built as the Louvre's main corps de logis. Given the Louvre wings' length and the fact that they typically abutted parts of the city with streets and private buildings, several of them have passageways on the ground floor which in the Louvre's specific context are called .
Toponymy
The origin of the name Louvre is unclear. French historian Henri Sauval
Henri Sauval (5 March 1623 (baptised) – 21 March 1676) was a French historian.
Biography
Sauval was the son of an advocate in the Parlement, he was born in Paris, and baptized on 5 March 1623. He devoted most of his life to researches among th ...
, probably writing in the 1660s, stated that he had seen "in an old Latin-Saxon glossary, Leouar is translated castle" and thus took Leouar to be the origin of Louvre. According to Keith Briggs, Sauval's theory is often repeated, even in recent books, but this glossary has never been seen again, and Sauval's idea is viewed as obsolete. Briggs suggests that H. J. Wolf's proposal in 1969 that Louvre derives instead from Latin ''Rubras'', meaning "red soil", is more plausible. David Hanser suggests instead that the word may come from French , a "place where dogs were trained to chase wolves".[
] Beyond the name of the palace itself, the toponymy of the Louvre can be treacherous. Partly because of the building's long history and links to changing politics, different names have applied at different times to the same structures or rooms. For example, what used to be known in the 17th and 18th centuries the or is now generally referred to as
Beyond the name of the palace itself, the toponymy of the Louvre can be treacherous. Partly because of the building's long history and links to changing politics, different names have applied at different times to the same structures or rooms. For example, what used to be known in the 17th and 18th centuries the or is now generally referred to as Pavillon de l'Horloge
The Pavillon de l’Horloge ("Clock Pavilion"), also known as the Pavillon Sully, is a prominent architectural structure located in the center of the western wing of the Cour Carrée of the Palais du Louvre in Paris. Since the late 19th century ...
, or (especially when considered from the west), or also after the architect Jacques Lemercier
Jacques Lemercier (c. 1585 in Pontoise – 13 January 1654 in Paris) was a French architect and engineer, one of the influential trio that included Louis Le Vau and François Mansart who formed the classicizing French Baroque manner, drawing ...
who first designed it in 1624. In some cases, the same name has designated different parts of the building at different times. For example, in the 19th century, the referred to what was later called the (still later, ), on the south side of the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
facing the Seine, before becoming the name for the main pavilion of the Richelieu Wing On the rue de Rivoli, its exact symmetrical point from the Louvre Pyramid. The main room on the first floor of the Lescot Wing has been the , , , , in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was fragmented into apartments during the 18th century, then recreated in the early 19th and called successively , or (the latter also being the name of two other ceremonial rooms, created in the 1850s and 1860s respectively); then as part of the museum, , after 1871 in honor of donor Louis La Caze, , and since 2021 . The room immediately below, now known as , has also been called , , , , (from 1692 to 1793), and in the past, among other names.
Sully Wing
The Sully Wing forms a square of approximately side length. The protruding sections at the corners and center of each side are known as . Clockwise from the northwest corner, they are named as follows: (after a now-disappeared street), (after the nearby ), (also ), (also ), (also ), , , and , the latter also known as . The section between the Pavillon du Roi and the Pavillon Sully, known as the Lescot Wing () as it was designed by architect Pierre Lescot, is the oldest standing part of the entire Louvre Palace. The section between the Pavillon Sully and the Pavillon de Beauvais, which was modeled after the Lescot Wing by architect Jacques Lemercier
Jacques Lemercier (c. 1585 in Pontoise – 13 January 1654 in Paris) was a French architect and engineer, one of the influential trio that included Louis Le Vau and François Mansart who formed the classicizing French Baroque manner, drawing ...
, is similarly known as the Lemercier Wing (). The eastern wing is the , named after its iconic eastern façade, the Louvre Colonnade
The Louvre Colonnade is the easternmost façade of the Palais du Louvre in Paris.
It has been celebrated as the foremost masterpiece of French Architectural Classicism since its construction, mostly between 1667 and 1674. The design, dominated b ...
initially designed by Charles Perrault
Charles Perrault ( , also , ; 12 January 1628 – 16 May 1703) was an iconic French author and member of the Académie Française. He laid the foundations for a new literary genre, the fairy tale, with his works derived from earlier folk tale ...
.
Denon and Flore Wings
 On the southern side of the
On the southern side of the Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
, the Denon Wing's three main pavilions are named respectively, from east to west, after Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
-era officials Pierre Daru
Pierre Antoine Noël Bruno, Comte de Daru (12 January 1767 – 5 September 1829) was a French soldier, statesman, historian, and poet.
Early career
Born in Montpellier, he was educated at the Oratorian-maintained military school of Tou ...
, Vivant Denon and Nicolas François Mollien. Between these and the wing facing the seine are three courtyards, from east to west the (covered as a glass atrium since 1934), (ground floor covered since 2012), and . On the side of the Seine
)
, mouth_location = Le Havre/ Honfleur
, mouth_coordinates =
, mouth_elevation =
, progression =
, river_system = Seine basin
, basin_size =
, tributaries_left = Yonne, Loing, Eure, Risle
, tributa ...
, this wing starts with the north–south bordering a side garden known as the , and continues westwards along the Quai François Mitterrand with the Salon Carré, Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
, and Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
. In the middle of the Grande Galerie are the , a composition of three monumental arches flanked by two narrow pavilions named respectively after the Duke of Lesdiguières and Henri de La Trémoille ( and ). Further west are the , a protruding structure on the northern side, the , a passageway to the quay, the on the north side, now the main entrance to the École du Louvre, and finally the Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
.
Richelieu and Marsan Wings
Similarly, on the northern side of the Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
are, from east to west, the pavilions named after Jean-Baptiste Colbert
Jean-Baptiste Colbert (; 29 August 1619 – 6 September 1683) was a French statesman who served as First Minister of State from 1661 until his death in 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV. His lasting impact on the organization of the country ...
, Cardinal Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis, Duke of Richelieu (; 9 September 1585 – 4 December 1642), known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a French clergyman and statesman. He was also known as ''l'Éminence rouge'', or "the Red Eminence", a term derived from the ...
, and Anne Robert Jacques Turgot. Between these and the rue de Rivoli are three courtyards, from east to west the (formerly ), (formerly or ), and (formerly or ). On the side facing the rue de Rivoli, the main salient feature is the , which connects to the through the ground-floor (formerly ) between the and . Further west are the and the , built in the early 19th century and named after the nearby , then the and the Pavillon de Marsan, both rebuilt by Hector Lefuel in the 1870s.
Pyramid and underground spaces
The Louvre Pyramid
The Louvre Pyramid (Pyramide du Louvre) is a large glass and metal structure designed by the Chinese-American architect I. M. Pei. The pyramid is in the main courtyard (Cour Napoléon) of the Louvre Palace in Paris, surrounded by three smalle ...
, built in the 1980s on a design by I. M. Pei, is now the centerpiece of the entire Louvre complex. It leads to the underground which in turn serves a vast complex of underground spaces, including the Carrousel du Louvre
The Carrousel du Louvre is an underground shopping mall in Paris, France, managed by Unibail-Rodamco. The name refers to two nearby sites, the Louvre museum and the Place du Carrousel. The mall contains a famous skylight, ''La Pyramide Inversée'' ...
commercial mall around an inverted pyramid further west.
Architectural style
The present-day Louvre Palace is a vast complex of wings and pavilions which, although superficially homogeneous in scale and architecture, is the result of many phases of building, modification, destruction and reconstruction. Its apparent stylistic consistency is largely due to conscious efforts of architects over several centuries to echo each other's work and preserve a strong sense of historical continuity, mirroring that of the French monarchy and state; American essayist Adam Gopnik has written that "The continuity the Louvre represents is the continuity of the French state." For example, from the 1620s to the 1650s Jacques Lemercier
Jacques Lemercier (c. 1585 in Pontoise – 13 January 1654 in Paris) was a French architect and engineer, one of the influential trio that included Louis Le Vau and François Mansart who formed the classicizing French Baroque manner, drawing ...
thoroughly replicated the Lescot Wing's patterns for his design of the northern half of the western wing of the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
. In the 1660s Louis Le Vau echoed Lemercier's Pavillon de l'Horloge
The Pavillon de l’Horloge ("Clock Pavilion"), also known as the Pavillon Sully, is a prominent architectural structure located in the center of the western wing of the Cour Carrée of the Palais du Louvre in Paris. Since the late 19th century ...
for his redesign of the central pavillon of the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, f ...
further west (burnt in 1871 and demolished in 1883), and mostly continued Lescot's and Lemercier's pattern for the completion of the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
. A separate design a few years later, that associated with Claude Perrault
Claude Perrault (25 September 1613 – 9 October 1688) was a French physician and an amateur architect, best known for his participation in the design of the east façade of the Louvre in Paris.[Louvre Colonnade
The Louvre Colonnade is the easternmost façade of the Palais du Louvre in Paris.
It has been celebrated as the foremost masterpiece of French Architectural Classicism since its construction, mostly between 1667 and 1674. The design, dominated b ...]
, included window shapes on the ground level based on Lescot's for the Pavillon du Roi a century earlier, ensuring visual continuity even though the dramatic colonnade on the upper level was different from anything that had been done at the Louvre so far. In the 1810s, Percier and Fontaine copied the giant order of the western section of the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
, built in the early 17th century and attributed to Jacques II Androuet du Cerceau, for their design of the northern wing to connect the Tuileries with the Louvre along the rue de Rivoli. In the 1850s during Napoleon III's Louvre expansion, architects Louis Visconti
Louis Tullius Joachim Visconti (Rome February 11, 1791 – December 29, 1853) was an Italian-born French architect and designer.
Life
Son of the Italian archaeologist and art historian Ennio Quirino Visconti, Visconti designed many Pa ...
then Hector Lefuel built the Denon and Richelieu pavilions as echoes of Lemercier's Pavillon de l'Horloge. In the 1860s and 1870s, Lefuel used designs inspired by the Lescot Wing even as he replaced the prior giant-order patterns created by Androuet du Cerceau and replicated by Percier and Fontaine. Finally, in the 1980s, I. M. Pei made explicit reference to André Le Nôtre
André Le Nôtre (; 12 March 1613 – 15 September 1700), originally rendered as André Le Nostre, was a French landscape architect and the principal gardener of King Louis XIV of France. He was the landscape architect who designed the gard ...
, the designer of the Tuileries Garden, for his design of the Louvre Pyramid
The Louvre Pyramid (Pyramide du Louvre) is a large glass and metal structure designed by the Chinese-American architect I. M. Pei. The pyramid is in the main courtyard (Cour Napoléon) of the Louvre Palace in Paris, surrounded by three smalle ...
.
Building history
This section focuses on matters of design, construction and decoration, leaving aside the fitting or remodeling of exhibition spaces within the museum, which are described in the article Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the '' Venus de Milo''. A central ...
. No fewer than twenty building campaigns have been identified in the history of the Louvre Palace. The architect of the largest such campaign, Hector Lefuel, crisply summarized the identity of the complex by noting: "" (translatable as "The Louvre is a building that has gone through a lot"). In the early 1920s Henri Verne, who would soon become the Louvre's Director, noted that "it has become, through the very slow pace of its development, the most representative monument of our national life."
Late 12th and 13th centuries
 In 1190 King Philip II of France, who was about to leave for the
In 1190 King Philip II of France, who was about to leave for the Third Crusade
The Third Crusade (1189–1192) was an attempt by three European monarchs of Western Christianity ( Philip II of France, Richard I of England and Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor) to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by ...
, ordered the construction of a defensive wall all around Paris. To protect the city, he opted to build the Louvre as a fortress just outside the wall's junction with the Seine
)
, mouth_location = Le Havre/ Honfleur
, mouth_coordinates =
, mouth_elevation =
, progression =
, river_system = Seine basin
, basin_size =
, tributaries_left = Yonne, Loing, Eure, Risle
, tributa ...
on its right bank, on the road to the Duchy of Normandy that was still controlled by his English rivals.Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
, and some of its remains, excavated between late 1983 and late 1985, are conserved underground.[
The original Louvre was nearly square in plan, at seventy-eight by seventy-two meters, and enclosed by a 2.6-metre thick crenellated and machicolated curtain wall. The entire structure was surrounded by a water-filled ]moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
. On the outside of the walls were ten round defensive towers: one at each corner and at the center of the northern and western sides, and two pairs respectively flanking the narrow gates on the southern and eastern sides.
In the courtyard, slightly offset to the northeast, was the cylindrical keep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in c ...
or donjon, known as the (Great Tower of the Louvre), thirty meters high and fifteen meters wide with 4-meter-thick external walls. The keep was encircled by a deep, dry ditch with stone counterscarps to help prevent the scaling of its walls with ladders. Accommodations in the fortress were supplied by the vaulted chambers of the keep as well as two wings built against the insides of the curtain walls of the western and southern sides. The circular plans of the towers and the keep avoided the dead angles created by square or rectangular designs which allowed attackers to approach out of firing range. Cylindrical keeps were typical of French castles at the time, but few were as large as the Louvre's .
Louis IX
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the House of Capet, Direct Capetians. He was Coronation of the French monarch, c ...
added constructions in the 1230s, included the medieval Louvre's main ceremonial room or in which several historical events took place, and the castle's first chapel. The partly preserved basement part of that program was rediscovered during heating installations at the Louvre in 1882–1883, and has since then been known successively as the and, after renovation in the 1980s, as the .
14th century
In the late 1350s, the growth of the city and the insecurity brought by the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagen ...
led Etienne Marcel, provost of the merchants (i.e. municipal leader) of Paris, to initiate the construction of a new protective wall beyond that of Philip II. King Charles V continued the project in the 1360s, and it was later known as the Wall of Charles V. From its westernmost point at the Tour du Bois, the new wall extended east along the north bank of the Seine to the old wall, enclosing the Louvre and greatly reducing its military value.[Ballon 1991, p. 15.] Remains of that wall have been uncovered and reconstructed in the present-day Louvre's Carrousel du Louvre
The Carrousel du Louvre is an underground shopping mall in Paris, France, managed by Unibail-Rodamco. The name refers to two nearby sites, the Louvre museum and the Place du Carrousel. The mall contains a famous skylight, ''La Pyramide Inversée'' ...
.
Shortly after becoming king in 1364 Charles V abandoned the Palais de la Cité, which he associated with the insurgency led by Etienne Marcel, and made the Louvre into a royal residence for the first time, with the transformation designed by his architect . This was a political statement as well as a utility project – one scholar wrote that Charles V "made the Louvre his political manifesto in stone" and referred to it as "a remarkably discursive monument-a form of architectural rhetoric that proclaimed the revitalization of France after years of internal strife and external menace."
15th century
In the late 14th and early 15th centuries, the preferred royal residence in Paris was the Hôtel Saint-Pol
The Hôtel Saint-Pol was a royal residence begun in 1360 by Charles V of France on the ruins of a building constructed by Louis IX. It was used by Charles V and Charles VI. Located on the Right Bank, to the northwest of the Quartier de l'Arsenal ...
in what became the Marais, until the Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War resulted in the monarchy leaving Paris altogether; in the 1420s and 1430s Charles VII resided largely at or near Bourges
Bourges () is a commune in central France on the river Yèvre. It is the capital of the department of Cher, and also was the capital city of the former province of Berry.
History
The name of the commune derives either from the Bituriges, ...
, whereas his rival English claimant Henry VI's representative, the Duke of Bedford, generally resided in his base of Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the region of Normandy and the department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of medieval Europe, the population ...
, and while in Paris in his Hôtel des Tournelles. Even after Charles VII's ceremonial entry into Paris in 1437 and after the effective end of the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagen ...
in 1453, French monarchs preferred residing in the Châteaux of the Loire Valley
The châteaux of the Loire Valley (french: châteaux de la Loire) are part of the architectural heritage of the historic towns of Amboise, Angers, Blois, Chinon, Montsoreau, Orléans, Saumur, and Tours along the river Loire in France. They illu ...
, the Palace of Fontainebleau
Palace of Fontainebleau (; ) or Château de Fontainebleau, located southeast of the center of Paris, in the commune of Fontainebleau, is one of the largest French royal châteaux. The medieval castle and subsequent palace served as a residence ...
or, when in Paris, at the Château de Vincennes
The Château de Vincennes () is a former fortress and royal residence next to the town of Vincennes, on the eastern edge of Paris, alongside the Bois de Vincennes. It was largely built between 1361 and 1369, and was a preferred residence, afte ...
or the Hôtel des Tournelles. Meanwhile, the Louvre Castle was left in a state of increasing disrepair, even as it remained used as an arsenal and prison.
File:Fouilles exécutées dans la cour du Louvre - Mise à jour des fondations de l'ancienne tour de Philippe Auguste.jpg, First excavation of the medieval Louvre by Adolphe Berty
Adolphe Berty (also known as Boulet; 13 May 1818, Paris – 18 August 1867, Paris) was a historiographer, archaeologist, historian of architecture, and French architect.
Berty was the founder of Parisian topography; he was also responsible for i ...
in 1866
File:Louvre medieval foundations flickr.jpg, Remains of the Louvre's basement level, restored and opened to the public in the 1980s
File:Salle Saint-Louis (Louvre).jpg, The following its remodeling in the 1980s
File:Louvre - Les Très Riches Heures.jpg, The Louvre pictured in the '' Très Riches Heures du Duc de Berry'', 1410s
File:Tour de Nesle and Louvre castle on the Crucifixion of the Parlement of Paris.jpg, The Louvre pictured in the ', mid-15th century
File:Pieta de Saint-Germain-des-Près - Old Louvre castle.jpg, The Louvre seen from the south, pictured in the ''Pietà of Saint-Germain-des-Prés'', late 15th century
16th century
In 1528, after returning from his captivity in Spain following his defeat at Pavia, Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
ordered the demolition of the Louvre's old keep. In 1546 he formally commissioned the architect Pierre Lescot and sculptor Jean Goujon
Jean Goujon (c. 1510 – c. 1565)Thirion, Jacques (1996). "Goujon, Jean" in ''The Dictionary of Art'', edited by Jane Turner; vol. 13, pp. 225–227. London: Macmillan. Reprinted 1998 with minor corrections: . was a French Renaissance sculpt ...
to modernize the Louvre into a Renaissance style palace, but the project appears to have actually started in 1545 since Lescot ordered stone deliveries in December of that year.[ The death of Francis I in 1547 interrupted the work, but it restarted under Francis's successor Henry II who on 10 July 1549 ordered changes in the building's design.][
Lescot tore down the western wing of the old Louvre Castle and rebuilt it as what has become known as the Lescot Wing, ending on the southern side with the Pavillon du Roi. In the latter, he designed in 1556 the ceiling for Henry II's bedroom, still largely preserved after relocation in 1829 to the Louvre's Colonnade Wing, for which he departed from the French tradition of beamed ceilings. On the ground floor, Lescot installed monumental stone caryatids based on classical precedents in the , now known as the . On the northern end of the new wing, Lescot created a monumental staircase in the 1550s, long known as the (now , with sculpted ceilings attributed to ]Jean Goujon
Jean Goujon (c. 1510 – c. 1565)Thirion, Jacques (1996). "Goujon, Jean" in ''The Dictionary of Art'', edited by Jane Turner; vol. 13, pp. 225–227. London: Macmillan. Reprinted 1998 with minor corrections: . was a French Renaissance sculpt ...
.
During the early 1560s, Lescot demolished the southern wing of the old Louvre and started to replace it with a duplication of the Lescot Wing. His plan may have been to create a square complex of a similar size as the old Louvre, not dissimilar to the Château d'Écouen
The Château d'Écouen is an historic château in the commune of Écouen, some 20 km north of Paris, France, and a notable example of French Renaissance architecture. Since 1975, it has housed the collections of the Musée national de la Renaissa ...
that had been recently completed on Jean Bullant's design, with an identical third wing to the north and a lower, entrance wing on the eastern side. A contested hypothesis attributes to Lescot the first intent to extend the Louvre's courtyard to its current size by doubling the lengths of the wings, even though no implementation was made of such plans until the 1620s.
Lescot also credited with the design of the Petite Galerie, which ran from the southwest corner of the Louvre to the Seine. All work stopped in the late 1560s, however, as the Wars of Religion
A religious war or a war of religion, sometimes also known as a holy war ( la, sanctum bellum), is a war which is primarily caused or justified by differences in religion. In the modern period, there are frequent debates over the extent to wh ...
gathered momentum.
In the meantime, beginning in 1564, Catherine de' Medici
Catherine de' Medici ( it, Caterina de' Medici, ; french: Catherine de Médicis, ; 13 April 1519 – 5 January 1589) was an Florentine noblewoman born into the Medici family. She was Queen of France from 1547 to 1559 by marriage to King ...
directed the building of a new residence to the west, outside the wall of Charles V. It became known as the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, f ...
because it was built on the site of old tile factories (). Architect Philibert de l'Orme started the project, and was replaced after his death in 1570 by Jean Bullant. A letter of March 1565 indicates that Catherine de' Medici
Catherine de' Medici ( it, Caterina de' Medici, ; french: Catherine de Médicis, ; 13 April 1519 – 5 January 1589) was an Florentine noblewoman born into the Medici family. She was Queen of France from 1547 to 1559 by marriage to King ...
already considered a building to connect the Tuileries with the older Louvre building.
File:Bastiments v1 (Gregg 1972 p20) - Louvre west wing court facade.jpg, Court facade of the Lescot Wing, engraved by Jacques Androuet du Cerceau
Jacques I Androuet du Cerceau, also given as Du Cerceau, DuCerceau, or Ducerceau (1510–1584) was a well-known French designer of architecture, ornament, furniture, metalwork and other decorative designs during the 16th century, and the founder ...
, 1576
File:Bastiments v1 (Gregg 1972 p21) - Louvre Pavillon du Roi river facade.jpg, Pavillon du Roi, south facade, du Cerceau, 1576
File:Manuscrit Français 9152 - Palais du Louvre.jpg, The Louvre in an engraving, 1580s
File:Plan of the Louvre with the modifications by Lescot - Berty 1868 after p168 – Gallica 2013 (adjusted).jpg, Ground-floor plan of the Renaissance Louvre with the Lescot Wing at the top and the south wing on the left
File:West facade of the Lescot wing by H Legrand - Berty 1885 v2 after p56 - Gallica 2013 (adjusted).jpg, West facade of the Lescot Wing c. 1560, elevation drawing by architect Henri Legrand (1868) based on historical documents
File:Israël Silvestre 049-10 Veüe et Perspective de la partie du Louure ou sont les apartemens du Roy et de la Reyne du coste du Jardin.jpg, South facade with the Pavillon du Roi on the left and the southeast tower of the old Louvre on the right (engraved by Israël Silvestre, c. 1650)
File:Israël Silvestre 049-09 Veüe et Perspectiue de la Galerie du Louure, dans laquelle sont les Portraus des Roys des Reynes et des plus Illustres du Royaume.jpg, View of the Petite Galerie with the south wing on the right (engraved by Silvestre before 1654)
Henry IV, France's new king from 1589 (the first from the House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spani ...
) and master of Paris from 1594, is associated with the further articulation of what became known as the ("Grand Design") of uniting the Louvre and the Tuileries in a single building, together with the extension of the eastern courtyard to the current dimensions of the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
. From early 1595 he directed the construction of the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
, designed by his competing architects Louis Métezeau
Louis Métezeau (1559 – 18 August 1615) was a French architect.Babelon 1996, p. 345.
Life and career
He was born in Dreux, Eure-et-Loir, and died in Paris. He was the son of Thibault Métezeau, the brother of Clément II Métezeau and the ...
and Jacques II Androuet du Cerceau, who are respectively credited with the eastern and western sections of the building by a long tradition of scholarship. This major addition, about 460 meters long, was built along the bank of the Seine. On the ground floor at the eastern end of the new wing, Métezeau created a lavishly decorated room that was known as the or , later called and now .Marie de' Medici
Marie de' Medici (french: link=no, Marie de Médicis, it, link=no, Maria de' Medici; 26 April 1575 – 3 July 1642) was Queen of France and Navarre as the second wife of King Henry IV of France of the House of Bourbon, and Regent of the Kingdom ...
by Frans Pourbus the Younger
Frans Pourbus the Younger (1569–1622) was a Flemish painter, son of Frans Pourbus the Elder and grandson of Pieter Pourbus. He was born in Antwerp and died in Paris. He is also referred to as "Frans II".
Pourbus worked for many of the highl ...
, still in the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the '' Venus de Milo''. A central ...
, is a rare remnant of this series.
17th century
 In 1624,
In 1624, Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crow ...
initiated the construction on a new building echoing the Pavillon du Roi on the northern end of the Lescot Wing, now known as the Pavillon de l'Horloge
The Pavillon de l’Horloge ("Clock Pavilion"), also known as the Pavillon Sully, is a prominent architectural structure located in the center of the western wing of the Cour Carrée of the Palais du Louvre in Paris. Since the late 19th century ...
, and of a wing further north that would start the quadrupling of the Louvre's courtyard. Architect Jacques Lemercier
Jacques Lemercier (c. 1585 in Pontoise – 13 January 1654 in Paris) was a French architect and engineer, one of the influential trio that included Louis Le Vau and François Mansart who formed the classicizing French Baroque manner, drawing ...
won the design competition against Jean Androuet du Cerceau, Clément II Métezeau, and the son of Salomon de Brosse. The works were stopped in 1628 at a time of hardship for the kingdom and state finances, and only progressed very slowly if at all until 1639. In 1639 Lemercier started a new building campaign during which the Pavillon de l'Horloge was completed. Its second staircase, mirroring Lescot's to the north, was still unfinished when the Fronde again interrupted the works in the 1640s, and its decoration has never been completed since then. At that time, much of the construction (though not the decoration) of the new wing had been completed, but the northern pavilion, or , designed by Lemercier similarly as Lescot's Pavillon du Roi, had barely been started.
File:Tour du bois, porte Neuve, le Louvre et la Seine.jpg, The unfinished Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
and the (end tower of the Wall of Charles V) in the early 1600s
File:Le chateau du Louvre sur un plan de 1615.jpg, The Pavillon du Roi and Lescot Wing with the rest of the medieval castle still standing, Merian map of Paris (1615)
File:Israël Silvestre, Vues de Paris 129 Veuë du Louvre, et de la Porte de Nesle, du costé du Fauxbourg St. Germain.jpg, View of the Louvre from the Left Bank, with the Pavillon du Roi and Pavillon de l'Horloge
The Pavillon de l’Horloge ("Clock Pavilion"), also known as the Pavillon Sully, is a prominent architectural structure located in the center of the western wing of the Cour Carrée of the Palais du Louvre in Paris. Since the late 19th century ...
(left) and the medieval Louvre's towers still standing (right), by Israël Silvestre
File:Zeeman 1656 Louvre south facade – Gallica btv1b103031628 2013 (adjusted).jpg, Similar view in 1656, by Reinier Nooms
File:Reinier Nooms, View of the Louvre and the Tuileries, from Views of Paris and Neighborhoods, plate 1.jpg, The (now Pont Royal), Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
and western section of the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
with the still standing in the mid-17th century, by Reinier Nooms
File:Israël Silvestre 049-11 Veue du Louure et de la grande Galerie du costé des Offices.jpg, West facade of the Louvre with Jacques Lemercier
Jacques Lemercier (c. 1585 in Pontoise – 13 January 1654 in Paris) was a French architect and engineer, one of the influential trio that included Louis Le Vau and François Mansart who formed the classicizing French Baroque manner, drawing ...
's northward extension and the ground-floor walls of in the foreground; engraving c.1644 by Israël Silvestre
File:Israël Silvestre 049-08 Veue et Perspectiue du dedans du Louure, faict du Regne de Louis XIII.jpg, Lemercier's wing pictured at a later date with the Pavillon de Beauvais completed and the start of the north wing heading east, engraving by Israël Silvestre
File:Israël Silvestre 051-08 Veuë du Louure par dedans le Bastiment neuf.jpg, Demolition of the north wing of the old Louvre Castle with the northeast tower still intact, engraving by Israël Silvestre
File:Israël Silvestre, La façade occidentale du Louvre et les nouveaux batîments de Levau (Cabinet des dessins du Louvre) – Hautecoeur 1927 planche 20.jpg , The Louvre's western façade facing the Tuileries, after Le Vau's 1660s reconstruction of the , by Israël Silvestre
File:L'Architecture française (Marot) – Façade sur le quai de l'extrémité de la Galerie d'Apollon – Mauban 1944 Fig 16.jpg, View of the Salon Carré and the southern end of the Petite Galerie from the south, engraving c.1670 by Jean Marot
Jean Marot (Mathieu, near Caen, 1463 – c. 1526) was a French poet of the late 15th and early 16 century and the father of the French Renaissance poet Clément Marot. He is often grouped with the "Grands Rhétoriqueurs". Jean Marot seems to h ...
On the southern side, Lemercier commissioned Nicolas Poussin
Nicolas Poussin (, , ; June 1594 – 19 November 1665) was the leading painter of the classical French Baroque style, although he spent most of his working life in Rome. Most of his works were on religious and mythological subjects painted for ...
to decorate the ceiling of the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
. Poussin arrived from Rome in early 1641, but returned to Italy in November 1642 leaving the work unfinished. During Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
's minority and the Fronde, from 1643 to 1652 the Louvre was left empty as the royal family stayed at the Palais-Royal
The Palais-Royal () is a former royal palace located in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. The screened entrance court faces the Place du Palais-Royal, opposite the Louvre. Originally called the Palais-Cardinal, it was built for Cardinal R ...
or outside of Paris;Anne of Austria
Anne of Austria (french: Anne d'Autriche, italic=no, es, Ana María Mauricia, italic=no; 22 September 1601 – 20 January 1666) was an infanta of Spain who became Queen of France as the wife of King Louis XIII from their marriage in 1615 unt ...
, like Marie de' Medici
Marie de' Medici (french: link=no, Marie de Médicis, it, link=no, Maria de' Medici; 26 April 1575 – 3 July 1642) was Queen of France and Navarre as the second wife of King Henry IV of France of the House of Bourbon, and Regent of the Kingdom ...
as queen mother
A queen mother is a former queen, often a queen dowager, who is the mother of the reigning monarch. The term has been used in English since the early 1560s. It arises in hereditary monarchies in Europe and is also used to describe a number of ...
before her, inhabited the ground-floor apartment in the Cour Carrée's southern wing. She extended it to the ground floor of the Petite Galerie, which had previously been the venue for the King's Council That "summer apartment" was fitted by architect Louis Le Vau, who had succeeded Lemercier upon the latter's death in 1654. The ceilings, decorated in 1655–1658 by Giovanni Francesco Romanelli
Giovanni Francesco Romanelli (Viterbo, 1610Baldinucci claims the date is May 14, 1617.– Viterbo, 1662) was a major Italian painter of the Baroque period, celebrated for his use of bright, vivid colors and also for his clarity of detail. Many ...
who had been recommended by Cardinal Mazarin, are still extant in the suite of rooms now known as the .
In 1659, Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
instigated a new phase of construction under Le Vau and painter Charles Le Brun.Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon
The Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon, a former Parisian town house of the House of Bourbon, royal family of Bourbon, was located on the Rive Droite, right bank of the Seine on the rue d'Autriche, between the :en:Louvre Palace, Louvre to the west and the ...
was demolished to make way for the completion of the Cour Carrée. On the courtyard's southern side the was completed in 1663, with a design by Le Vau that echoed that of the Pavillon de l'Horloge.Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
was also decorated with wood panelling, even though that work was left unfinished. The Salon Carré, however, was still undecorated when the court left for Versailles in the late 1670s. Meanwhile, landscape architect André Le Nôtre
André Le Nôtre (; 12 March 1613 – 15 September 1700), originally rendered as André Le Nostre, was a French landscape architect and the principal gardener of King Louis XIV of France. He was the landscape architect who designed the gard ...
redesigned the Tuileries, first created in 1564 in the Italian style, as a French formal garden
The French formal garden, also called the (), is a style of garden based on symmetry and the principle of imposing order on nature. Its epitome is generally considered to be the Gardens of Versailles designed during the 17th century by the ...
.[Edwards 1893, p. 198.]
The other major project of the 1660s was to create the Louvre's façade towards the city and thus complete the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
on its eastern side. It involved a convoluted process, with the king's minister Jean-Baptiste Colbert
Jean-Baptiste Colbert (; 29 August 1619 – 6 September 1683) was a French statesman who served as First Minister of State from 1661 until his death in 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV. His lasting impact on the organization of the country ...
first sidelining Le Vau and then summoning Gian Lorenzo Bernini
Gian Lorenzo (or Gianlorenzo) Bernini (, , ; Italian Giovanni Lorenzo; 7 December 159828 November 1680) was an Italian sculptor and architect. While a major figure in the world of architecture, he was more prominently the leading sculptor of his ...
from Italy. Bernini stayed in Paris from May 1665 to 1666 but none of his four striking designs gained approval, even though some building works started on their basis. Eventually a committee comprising Le Vau, Charles Le Brun and Claude Perrault
Claude Perrault (25 September 1613 – 9 October 1688) was a French physician and an amateur architect, best known for his participation in the design of the east façade of the Louvre in Paris.[Corinthian order
The Corinthian order ( Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order ...]
colonnade with paired columns. Works started in 1667 and the exterior structures were largely completed by 1674, but would not be fully decorated and roofed until the early 19th century under Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
. To harmonize the Louvre's exterior, the decision was made in 1668 to create a new façade in front of Le Vau's for the southern wing, designed by the same architectural committee, albeit not on the northern side whose earlier design by Le Vau was just being completed.
The works at the louvre, however, stopped in the late 1670s as the king redirected all construction budgets at the Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, u ...
, despite his minister Colbert's insistence on completing the Louvre. Louis XIV had already left the Louvre from the beginning of 1666, immediately after the death of his mother Anne of Austria
Anne of Austria (french: Anne d'Autriche, italic=no, es, Ana María Mauricia, italic=no; 22 September 1601 – 20 January 1666) was an infanta of Spain who became Queen of France as the wife of King Louis XIII from their marriage in 1615 unt ...
in her ground-floor apartment, and would never reside there again, preferring Versailles, Vincennes, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, or if he had to be in Paris, the Tuileries. From the 1680s a new era started for the Louvre, with comparatively little external construction and fragmentation of its interior spaces across a variety of different uses.
File:Louvre - Élévation de la façade du côté de la rue St Honoré - Architecture françoise Tome4 Livre6 Pl16.jpg, Le Vau's design for the North façade, 1660s, engraved by Jacques-François Blondel in 1756
File:Louvre - Ancienne façade du côté de la rivière exécutée sur le dessein de Le Veau - Architecture françoise Tome4 Livre6 Pl13.jpg, Le Vau's design for the South façade, c.1660, engraved by Jacques-François Blondel in 1756
File:South facade of the Louvre by Le Vau about 1665, detail from a painting by Van der Meulen.jpg, From 1660 to 1663, Louis Le Vau extended the south wing by duplicating Lescot's austere terminal pavilion and wing but providing an original central pavilion with a colossal order
In classical architecture, a giant order, also known as colossal order, is an order whose columns or pilasters span two (or more) storeys. At the same time, smaller orders may feature in arcades or window and door framings within the storeys th ...
of engaged Corinthian columns
The Corinthian order ( Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric ord ...
rising from the ground (detail from an engraving by Jan van Huchtenburg
J(oh)an and Jacob van Huchtenburg (also known as Hughtenburg or Hugtenburg(h)) were two Dutch Golden Age painters in the second half of the seventeenth century. Both brothers were natives of Haarlem, moved to Paris, but died in Amsterdam. The main ...
after Adam Frans van der Meulen)
File:Raguenet – View of the old Louvre in 1763 (detail from A View of Paris from the Pont Neuf) – Getty Museum.jpg, Detail from a 1763 painting by Raguenet showing the south wing with its new facade. The new rows of rooms added behind the new facade in front of Le Vau's older facade remained unroofed, and the topmost stories and steep-pitched roofs of the old pavilions had not yet been removed.
File:3888ParigiLouvre.JPG, East wing of the Louvre (constructed 1667–1674), one of the most influential classical facades ever built in Europe, as it appeared in 2009
18th century
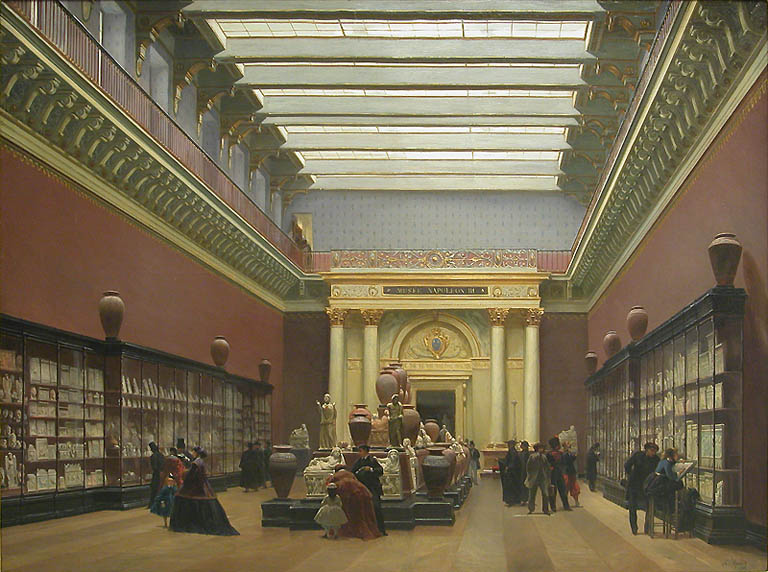
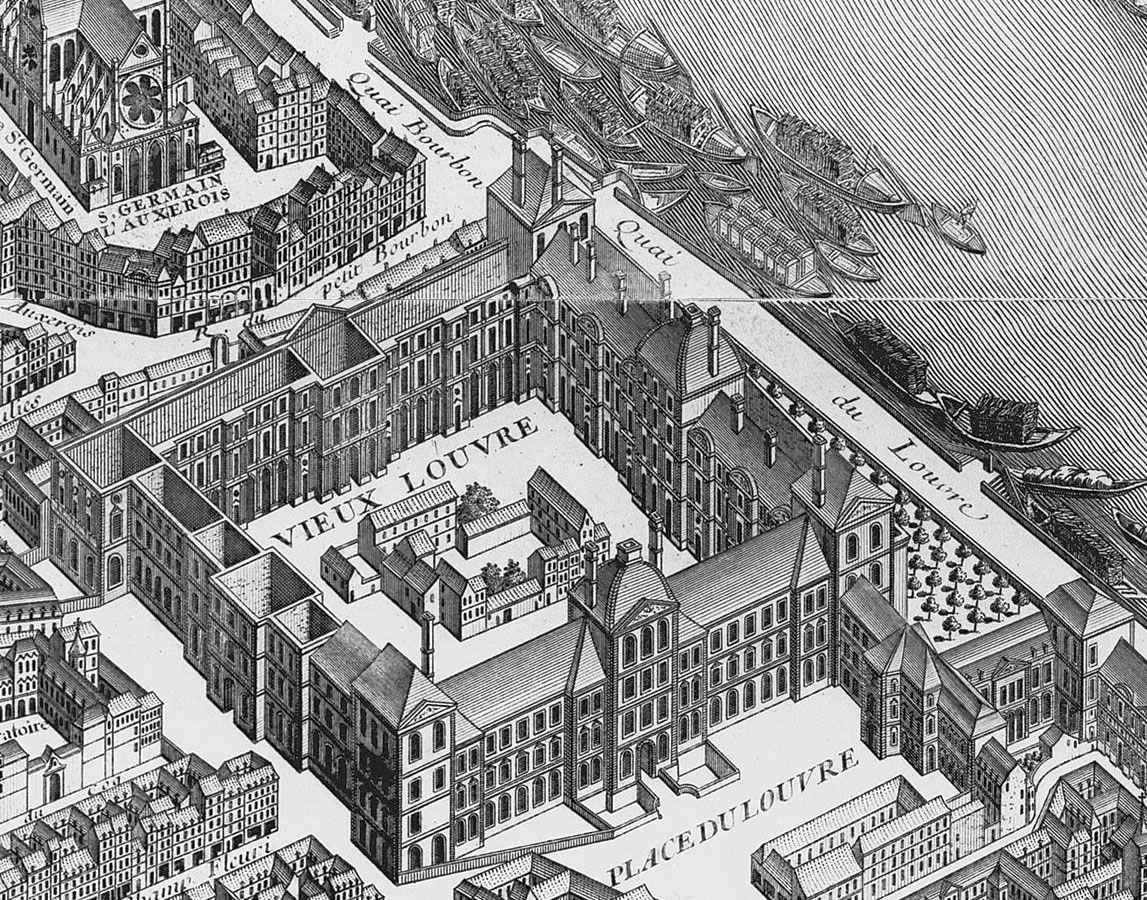 After the definitive departure of the royal court for Versailles in 1682, the Louvre became occupied by multiple individuals and organizations, either by royal favor or simply
After the definitive departure of the royal court for Versailles in 1682, the Louvre became occupied by multiple individuals and organizations, either by royal favor or simply squatting
Squatting is the action of occupying an abandoned or unoccupied area of land or a building, usually residential, that the squatter does not own, rent or otherwise have lawful permission to use. The United Nations estimated in 2003 that there ...
. Its tenants included the infant Mariana Victoria of Spain
Mariana Victoria of Spain ( pt, Mariana Vitória; 31 March 1718 – 15 January 1781) was an '' Infanta of Spain'' by birth and was later the Queen of Portugal as wife of King Joseph I. She acted as regent of Portugal in 1776–1777, during the l ...
during her stay in Paris in the early 1720s, artists, craftsmen, the Academies, and various royal officers. For example, in 1743 courtier and author Michel de Bonneval Michel de Bonneval, real name Louis-Charles-Michel de Bonneval, (Le Mans 18th century - 1766) was a French opera libretto, librettist.
A general controller of silverware and an intendant of the Menus-Plaisirs du Roi, Bonneval regulated as such the ...
was granted the right to refurbish much of the wing between the and the into his own house on his own expense, including 28 rooms on the ground floor and two mezzanine levels, and an own entrance on the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
. After Bonneval's death in 1766 his family was able to keep the house for a few more years. Some new houses were even erected in the middle of the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
, but were eventually torn down on the initiative of the Marquis de Marigny
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman wi ...
in early 1756. A follow-up 1758 decision led to the clearance of buildings on most of what is now the Place du Louvre in front of the Colonnade, except for the remaining parts of the Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon
The Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon, a former Parisian town house of the House of Bourbon, royal family of Bourbon, was located on the Rive Droite, right bank of the Seine on the rue d'Autriche, between the :en:Louvre Palace, Louvre to the west and the ...
which were preserved for a few more years.
Marigny had ambitious plans for the completion of the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
, but their execution was cut short in the late 1750s by the adverse developments of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754 ...
. Jacques-Germain Soufflot
Jacques-Germain Soufflot (, 22 July 1713 – 29 August 1780) was a French architect in the international circle that introduced neoclassicism. His most famous work is the Panthéon in Paris, built from 1755 onwards, originally as a church d ...
in 1759 led the demolition of the upper structures of Le Vau's dome above the Pavillon des Arts, whose chimneys were in poor condition, and designed the northern and eastern passageways () of the Cour Carrée in the late 1750s. The southern was designed by in 1779 and completed in 1780. Three arched were also opened in 1760 under the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
, through the and immediately to its west.
The 1790s were a time of turmoil for the Louvre as for the rest of France. On 5 October 1789, the king and court were forced to return from Versailles and settled in the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, f ...
; many courtiers moved into the Louvre. Many of these in turn emigrated during the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
, and more artists swiftly moved into their vacated Louvre apartments.
File:Louvre - Plan du premier étage - Architecture françoise Tome4 Livre6 Pl6.jpg, Plan of the Louvre's first floor in 1756, by Jacques-François Blondel, showing uninhabitable and generally unroofed areas shaded (marked "A")
File:Pierre-Antoine Demachy - Clearing the Area in front of the Louvre Colonnade - Paris Museum Collections.jpg, Demolition of the remaining buildings of the Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon
The Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon, a former Parisian town house of the House of Bourbon, royal family of Bourbon, was located on the Rive Droite, right bank of the Seine on the rue d'Autriche, between the :en:Louvre Palace, Louvre to the west and the ...
in front of the Louvre, c.1760, by Pierre-Antoine Demachy, Musée Carnavalet
File:Pierre-Antoine Demachy - Dégagement de la colonnade du Louvre - P88 - Musée Carnavalet.jpg, Another view of the demolitions in front of the Colonnade, by Pierre-Antoine Demachy, 1764
19th century
In December 1804, Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
appointed Pierre Fontaine as architect of the Tuileries and the Louvre. Fontaine had forged a strong professional bond with his slightly younger colleague Charles Percier
Charles Percier (; 22 August 1764 – 5 September 1838) was a neoclassical French architect, interior decorator and designer, who worked in a close partnership with Pierre François Léonard Fontaine, originally his friend from student days. For ...
.attic
An attic (sometimes referred to as a ''loft'') is a space found directly below the pitched roof of a house or other building; an attic may also be called a ''sky parlor'' or a garret. Because attics fill the space between the ceiling of the ...
modeled on the architecture of the Colonnade wing, thus removing the existing second-floor ornamentation and sculptures, of which some were by Jean Goujon
Jean Goujon (c. 1510 – c. 1565)Thirion, Jacques (1996). "Goujon, Jean" in ''The Dictionary of Art'', edited by Jane Turner; vol. 13, pp. 225–227. London: Macmillan. Reprinted 1998 with minor corrections: . was a French Renaissance sculpt ...
and his workshop. The Cour Carrée and Colonnade wing were completed in 1808–1809, and Percier and Fontaine created the monumental staircase on the latter's southern and northern ends between 1807 and 1811. Percier and Fontaine also created the monumental decoration of most of the ground-floor rooms around the Cour Carrée, most of which still retain it, including their renovation of Jean Goujon's . On the first floor, they recreated the former of the Lescot Wing, which had been partitioned in the 18th century, and gave it double height by creating a visitors' gallery in what had formerly been the Lescot Wing's attic.
Further west, Percier and Fontaine created the monumental entrance for the Louvre Museum (called since 1804). This opened from what was at the time called the , abutting the Lescot Wing to the west, into the , the monumental room at the northern end of the . The entrance door was dominated by a colossal bronze head of the emperor by Lorenzo Bartolini, installed in 1805. Visitors could either visit the classical antiquities collection () in Anne of Austria's rooms or in the redecorated ground floor of the Cour Carrée's southern wing to the left, or they could turn right and access Percier and Fontaine's new monumental staircase, leading to both the Salon Carré and the (formerly ) on the first floor (replaced in the 1850s by the Escalier Daru). The two architects also remade the interior design of the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
, in which they created nine sections separated by groups of monumental columns, and a system of roof lighting with lateral skylight
A skylight (sometimes called a rooflight) is a light-permitting structure or window, usually made of transparent or translucent glass, that forms all or part of the roof space of a building for daylighting and ventilation purposes.
History
Open ...
s.
On the eastern front of the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, f ...
, Percier and Fontaine had the existing buildings cleared away to create a vast open space, the Cour du Carrousel
The Tuileries Garden (french: Jardin des Tuileries, ) is a public garden located between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. Created by Catherine de' Medici as the garden of the Tuileries Palace ...
, which they had closed with an iron fence in 1801. Somewhat ironically, the clearance effort was facilitated by the Plot of the rue Saint-Nicaise, a failed bomb attack on Napoleon on 24 December 1800, which damaged many of the neighborhood's building that were later demolished without compensation. In the middle of the Cour du Carrousel, the Arc de Triomphe du Carrousel was erected in 1806–1808 to commemorate Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
's military victories. On 10 April 1810, Percier and Fontaine's plan for the completion of the of uniting the Louvre and the Tuileries was approved, following a design competition among forty-seven participants. Works started immediately afterwards to build an entirely new wing starting from the Pavillon de Marsan, with the intent to expand it all the way to the Pavillon de Beauvais on the northwestern corner of the Cour Carrée. By the end of Napoleon's rule the works had progressed up to the . The architectural design of the southern façade of that wing replicated that attributed to Jacques II Androuet du Cerceau for the western section of the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
.
File:Percier Fontaine Louvre Tuileries 1831.jpg, One version of Percier and Fontaine's plan for uniting the Louvre and Tuileries
File:Louvre et Tuileries Percier et Fontaine 1.jpg, Percier and Fontaine's perspective of the completed Louvre viewed from the west
File:Louvre et Tuileries Percier et Fontaine 2.jpg, Percier and Fontaine's perspective of the completed Louvre viewed from the east
Percier and Fontaine were retained by Louis XVIII
Louis XVIII (Louis Stanislas Xavier; 17 November 1755 – 16 September 1824), known as the Desired (), was King of France from 1814 to 1824, except for a brief interruption during the Hundred Days in 1815. He spent twenty-three years in ...
at the beginning of the Bourbon Restoration Bourbon Restoration may refer to:
France under the House of Bourbon:
* Bourbon Restoration in France (1814, after the French revolution and Napoleonic era, until 1830; interrupted by the Hundred Days in 1815)
Spain under the Spanish Bourbons:
* Ab ...
, and kept working on the decoration projects they had started under Napoleon. The was opened to the public on 25 August 1819. But there were no further budget allocations for the completion of the Louvre Palace during the reigns of Louis XVIII, Charles X and Louis-Philippe I
Louis Philippe (6 October 1773 – 26 August 1850) was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, and the penultimate monarch of France.
As Louis Philippe, Duke of Chartres, he distinguished himself commanding troops during the Revolutionary Wa ...
, while the kings resided in the Tuileries. By 1825, Percier and Fontaine's northern wing had only been built up to the , and made no progress in the following 25 years. Further attempts at budget appropriations to complete the Louvre, led by Adolphe Thiers
Marie Joseph Louis Adolphe Thiers ( , ; 15 April 17973 September 1877) was a French statesman and historian. He was the second elected President of France and first President of the French Third Republic.
Thiers was a key figure in the July Rev ...
in 1833 and again in 1840, were rejected by the .
From the early days of the Second Republic, a greater level of ambition for the Louvre was again signaled. On 24 March 1848, the provisional government published an order that renamed the louvre as the ("People's Palace") and heralded the project to complete it and dedicate it to the exhibition of art and industry as well as the National Library. In a February 1849 speech at the National Assembly, Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
described the project as making the Louvre into a focal point for world culture, which he referred to a "Mecca of intelligence".
During the Republic's brief existence, the palace was extensively restored by Louvre architect Félix Duban, especially the exterior façades of the Petite Galerie and Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
, on which Duban designed the ornate portal now known as . Meanwhile, Duban restored or completed several of the Louvre's main interior spaces, especially the , Galerie d'Apollon and Salon Carré, which Prince-President Louis Napoleon inaugurated on 5 June 1851 Expropriation arrangements were made for the completion of the Louvre and the rue de Rivoli, and the remaining buildings that cluttered the space that is now the Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
were cleared away.. No new buildings had been started, however, by the time of the December 1851 coup d'état.
On this basis, Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A neph ...
was able to finally unite the Louvre with the Tuileries in a single, coherent building complex.Louis Visconti
Louis Tullius Joachim Visconti (Rome February 11, 1791 – December 29, 1853) was an Italian-born French architect and designer.
Life
Son of the Italian archaeologist and art historian Ennio Quirino Visconti, Visconti designed many Pa ...
, a disciple of Percier, who died suddenly in December 1853 and was succeeded in early 1854 by Hector Lefuel. Lefuel developed Visconti's plan into a higher and more ornate building concept, and executed it at record speed so that the "" was inaugurated by the emperor on 14 August 1857. The new buildings were arranged around the space then called , later and, since the 20th century, Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
. Before his death, Visconti also had time to rearrange the Louvre's gardens outside the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
, namely the to the south, the to the east and the to the north, and also designed the Orangerie and Jeu de Paume on the western end of the Tuileries Garden. In the 1860s, Lefuel also demolished the Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
and nearly half of the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
, and reconstructed them on a modified design that included the passageway known as the (later , now Porte des Lions), a new for state functions, and the monumental replacing those created in 1760 near the .
At the end of the Paris Commune
The Paris Commune (french: Commune de Paris, ) was a revolutionary government that seized power in Paris, the capital of France, from 18 March to 28 May 1871.
During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard had defende ...
on 23 May 1871, the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, f ...
was burned down, as also was the Louvre Imperial Library in what is now the Richelieu Wing. The rest of palace, including the museum, was saved by the efforts of troopers, firemen and museum curators.
In the 1870s, the ever-resourceful Lefuel led the repairs to the Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
between 1874 and 1879, reconstructed the wing that had hosted the Louvre Library between 1873 and 1875, and the Pavillon de Marsan between 1874 and 1879.Antonin Mercié
Marius Jean Antonin Mercié (October 30, 1845 in Toulouse – December 12, 1916 in Paris), was a French sculptor, medallist and painter.
Biography
Mercié entered the École des Beaux-Arts, Paris, and studied under Alexandre Falguière and Fr ...
was installed in the place of Antoine-Louis Barye's equestrian statue of Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A neph ...
, which had been toppled in September 1870.
Meanwhile, the fate of the Tuileries' ruins kept being debated. Both Lefuel and influential architect Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
Eugène Emmanuel Viollet-le-Duc (; 27 January 181417 September 1879) was a French architect and author who restored many prominent medieval landmarks in France, including those which had been damaged or abandoned during the French Revolution. H ...
advocated their preservation and the building reconstruction, but after the latter died in 1879 and Lefuel in 1880, the Third Republic opted to erase that memory of the former monarchy. The final decision was made in 1882 and executed in 1883, thus forever changing the Louvre's layout. Later projects to rebuild the Tuileries have resurfaced intermittently but never went very far.
File:The Medusa shown at the Louvre, in color.jpg, The held in 1831 in the eponymous Salon Carré, painted by and showing Géricault's '' The Raft of the Medusa'' in the middle
File:Petite Galerie, Louvre Museum, Paris February 2016.jpg, The eastern façade of the Petite Galerie following its extensive exterior restoration by Félix Duban
File:Demolition of houses for the Place du Carrousel in 1852 – Christ 1949 Fig134.jpg, Demolition of the last buildings on the Place du Carrousel in 1852, with the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, f ...
and the Pavillon de Marsan in the background
File:État actuel de la place du Carrousel.jpg, The North (Richelieu) Wing under construction, with the Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
and the Tuileries in the background
File:Pavillon Richelieu, the Louvre, 1850s.jpg, The brand-new photographed in the late 1850s
File:Tuileries Palace in 1871 after the burning during the fights of the Commune de Paris.jpg, The Tuileries Palace was set afire by the Communards during the suppression of the Paris Commune
The Paris Commune (french: Commune de Paris, ) was a revolutionary government that seized power in Paris, the capital of France, from 18 March to 28 May 1871.
During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard had defende ...
in May 1871
File:Tuileries Palace; Pavillon de Flore WDL1252.png, The Tuileries (left) and Pavillon de Flore (right) damaged after the 1871 fire, showing the greater damage to the former than to the latter
 A tall was planned in 1884 and erected in 1888 in front of the two gardens on what is now the ''Cour Napoléon''. That initiative carried heavy political symbolism, since Gambetta was widely viewed as the founder of the Third Republic, and his outsized celebration in the middle of Napoleon III's landmark thus affirmed the final victory of
A tall was planned in 1884 and erected in 1888 in front of the two gardens on what is now the ''Cour Napoléon''. That initiative carried heavy political symbolism, since Gambetta was widely viewed as the founder of the Third Republic, and his outsized celebration in the middle of Napoleon III's landmark thus affirmed the final victory of republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology centered on citizenship in a state organized as a republic. Historically, it emphasises the idea of self-rule and ranges from the rule of a representative minority or oligarchy to popular sovereignty. ...
over monarchism
Monarchism is the advocacy of the system of monarchy or monarchical rule. A monarchist is an individual who supports this form of government independently of any specific monarch, whereas one who supports a particular monarch is a royalist. ...
nearly a century after the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
. Most of the monument's sculptures were in bronze and in 1941 were melted for military use by German occupying forces. What remained of the Gambetta Monument was dismantled in 1954.
20th century
Some long unfinished parts of Lefuel's expansion were only completed in the early 20th century, such as the Decorative Arts Museum in the Marsan Wing, by Gaston Redon
Gaston Redon (28 October 1853 – 20 November 1921) was a French architect, teacher, and graphic artist.
Biography
Redon was born in Bordeaux, Aquitaine to a prosperous family, the younger brother of Odilon Redon. Gaston attended the Écol ...
, and the arch between the and , designed by and built in 1910–1914.
 Aside from the interior refurbishment of the
Aside from the interior refurbishment of the Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
in the 1960s, there was little change to the Louvre's architecture during most of the 20th century. The most notable was the initiative taken in 1964 by minister André Malraux to excavate and reveal the basement level of the Louvre Colonnade
The Louvre Colonnade is the easternmost façade of the Palais du Louvre in Paris.
It has been celebrated as the foremost masterpiece of French Architectural Classicism since its construction, mostly between 1667 and 1674. The design, dominated b ...
, thus removing the and giving the Place du Louvre its current shape.Louvre Pyramid
The Louvre Pyramid (Pyramide du Louvre) is a large glass and metal structure designed by the Chinese-American architect I. M. Pei. The pyramid is in the main courtyard (Cour Napoléon) of the Louvre Palace in Paris, surrounded by three smalle ...
and its underground lobby, the , opened to the public on 29 March 1989. A second phase of the Grand Louvre project, completed in 1993, created underground space below the Place du Carrousel to accommodate car parks, multi-purpose exhibition halls and a shopping mall named Carrousel du Louvre
The Carrousel du Louvre is an underground shopping mall in Paris, France, managed by Unibail-Rodamco. The name refers to two nearby sites, the Louvre museum and the Place du Carrousel. The mall contains a famous skylight, ''La Pyramide Inversée'' ...
. Daylight is provided at the intersection of its axes by the Louvre Inverted Pyramid (), "a humorous reference to its bigger, right-side-up sister upstairs." The Louvre's new spaces in the reconstructed Richelieu Wing were near-simultaneously inaugurated in November 1993. The third phase of the Grand Louvre, mostly executed by the late 1990s, involved the refurbishment of the museum's galleries in the Sully and Denon Wings where much exhibition space had been freed during the project second phase. The renovation of the Carrousel Garden
The Tuileries Garden (french: Jardin des Tuileries, ) is a public garden located between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. Created by Catherine de' Medici as the garden of the Tuileries Palace ...
was also completed in 2001
21st century
The renovation of the Carrousel Garden was also completed in 2001
Uses
Whereas the name "Louvre Palace" refers to its intermittent role as a monarchical residence, this is neither its original nor its present function. The Louvre has always been associated with French state power and representation, under many modalities that have varied within the vast building and across its long history. Percier and Fontaine thus captured something of the long-term identity of the Louvre when they described it in 1833 as "viewed as the shrine of rench
The Rench is a right-hand tributary of the Rhine in the Ortenau ( Central Baden, Germany). It rises on the southern edge of the Northern Black Forest at Kniebis near Bad Griesbach im Schwarzwald. The source farthest from the mouth is that of the ...
monarchy, now much less devoted to the usual residence of the sovereign than to the great state functions, pomp, festivities, solennities and public ceremonies." Except at the very beginning of its existence, as a fortress, and at the very end (nearly exclusively) as a museum building, the Louvre Palace has continuously hosted a variety of different activities.
Military facility
The Louvre started as a military facility and retained military uses during most of its history. The initial rationale in 1190 for building a reinforced fortress on the western end of the new fortifications of Paris was the lingering threat of English-held Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
. After the construction of the Wall of Charles V, the Louvre was still part of the defensive arrangements for the city, as the wall continued along the Seine between it and the farther west, but it was no longer on the frontline. In the next centuries, there was no rationale for specific defenses of the Louvre against foreign invasion, but the palace long retained defensive features such as moats to guard against the political troubles that regularly engulfed Paris. The Louvre hosted a significant arsenal
An arsenal is a place where arms and ammunition are made, maintained and repaired, stored, or issued, in any combination, whether privately or publicly owned. Arsenal and armoury (British English) or armory (American English) are mostl ...
in the 15th and most of the 16th centuries, until its transfer in 1572 to the facility that is now the Bibliothèque de l'Arsenal.
From 1697 on, the French state's collection of plans-reliefs was stored in the Grande Galerie, of which it occupied all the space by 1754 with about 120 items placed on wooden tables. The plans-reliefs were used to study and prepare defensive and offensive siege operations of the fortified cities and strongholds they represented. In 1777, as plans started being made to create a museum in the Grande Galerie, the plans-reliefs were removed to the Hôtel des Invalides, where most of them are still displayed in the Musée des Plans-Reliefs
The Musée des Plans-Reliefs is a museum of military models located within the Hôtel des Invalides in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France.
The construction of models dates to 1668 when François-Michel le Tellier, Marquis de Louvois and ...
. Meanwhile, a collection of models of ships and navy yards, initially started by naval engineer Henri-Louis Duhamel du Monceau, was displayed between 1752 and 1793 in a next to the Académie des Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French scientific research. It was at ...
's rooms on the first floor of the Lescot Wing. That collection later formed the core of the maritime museum created in 1827, which remained at the Louvre until 1943 and is now the Musée national de la Marine.
During Napoleon III's Louvre expansion, the new building program included barracks for the Imperial Guard
An imperial guard or palace guard is a special group of troops (or a member thereof) of an empire, typically closely associated directly with the Emperor or Empress. Usually these troops embody a more elite status than other imperial forces, i ...
in the new North (Richelieu) Wing, and for the Cent-gardes Squadron in the South (Denon) Wing.
Feudal apex
The round keep of Philip II's Louvre Castle became the symbolic location from which all the king's fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form ...
s depended. The traditional formula for these, that they "depended on the king for his great keep of the Louvre" () remained in use until the 18th century, long after the keep itself had been demolished in the 1520s.
Archive
Philip II also created a permanent repository for the royal archive at the Louvre, following the loss of the French kings' previously itinerant records at the Battle of Fréteval
The Battle of Fréteval, which took place on 3 July 1194, was a medieval battle, part of the ongoing fighting between Richard the Lionheart and Philip II of France that lasted from 1193 to Richard's death in April 1199. During the battle, the Angl ...
(1194). That archive, known as the Trésor des Chartes, was relocated under Louis IX
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the House of Capet, Direct Capetians. He was Coronation of the French monarch, c ...
to the Palais de la Cité in 1231.
A number of state archives were again lodged in the Louvre's vacant spaces in the 18th century, e.g. the minutes of the in the attic of the Lescot Wing, and the archives of the Conseil du Roi in several ground-floor rooms in the late 1720s. The kingdom's diplomatic archives were kept in the Pavillon de l'Horloge
The Pavillon de l’Horloge ("Clock Pavilion"), also known as the Pavillon Sully, is a prominent architectural structure located in the center of the western wing of the Cour Carrée of the Palais du Louvre in Paris. Since the late 19th century ...
until their transfer to Versailles in 1763, after which the archives of the Maison du Roi and of the soon took their place. In 1770, the archives of the Chambre des Comptes were placed in the Louvre's attic, followed by the archives of the Marshals of France in 1778 and those of the Order of Saint Michael
, status = Abolished by decree of Louis XVI on 20 June 1790Reestablished by Louis XVIII on 16 November 1816Abolished in 1830 after the July RevolutionRecognised as a dynastic order of chivalry by the ICOC
, founder = Louis XI of France
...
in 1780. In 1825, after the Conseil d'État had been relocated to the Lemercier Wing, its archives were moved to the entresol below the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
, near the .
Prison
The Louvre became a high-profile prison in the immediate aftermath of the Battle of Bouvines
The Battle of Bouvines was fought on 27 July 1214 near the town of Bouvines in the County of Flanders. It was the concluding battle of the Anglo-French War of 1213–1214. Although estimates on the number of troops vary considerably among mod ...
in July 1214, as Ferdinand, Count of Flanders was taken into captivity by Philip II. Ferdinand stayed there for 12 years. Other celebrity inmates included Enguerrand IV de Coucy
Enguerrand IV, Lord of Coucy (c. 1236 – 1311) was the son of Enguerrand III, Lord of Coucy and Marie de Montmirail. He succeeded his older brother Raoul II, Lord of Coucy, serving as the Sire de Coucy from his brother's death in 1250 until ...
in the 1250s, Guy of Flanders in 1304, Bishop in 1308–1313, Louis de Dampierre in 1310, Enguerrand de Marigny in 1314, John of Montfort
John of Montfort ( xbm, Yann Moñforzh, french: Jean de Montfort) (1295 – 26 September 1345,Etienne de Jouy. Œuvres complètes d'Etienne Jouy'. J. Didot Ainé. p. 373. Château d'Hennebont), sometimes known as John IV of Brittany, and 6th ...
in 1341–1345, Charles II of Navarre in 1356, and Jean III de Grailly from 1372 to his death there in 1375. The Louvre was reserved for high-ranking prisoners, while other state captives were held in the Grand Châtelet. Its use as a prison declined after the completion of the Bastille in the 1370s, but was not ended: for example, Antoine de Chabannes
Antoine is a French given name (from the Latin ''Antonius'' meaning 'highly praise-worthy') that is a variant of Danton, Titouan, D'Anton and Antonin.
The name is used in France, Switzerland, Belgium, Canada, West Greenland, Haiti, French Guiana ...
was held at the Louvre in 1462–1463, John II, Duke of Alençon in 1474–1476, and Leonora Dori
Leonora Dori Galigaï (19 May 1568 – 8 July 1617) was a French courtier of Italian origin, an influential favourite of the French regent Marie de' Medici, mother of King Louis XIII of France. Galigaï was married to Concino Concini, the later m ...
in 1617 upon the assassination of her husband Concino Concini at the Louvre's entrance following Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crow ...
's orders.
Treasury
Under Philip II and his immediate successors, the royal treasure was kept in the Paris precinct of the Knights Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross
, colors_label = Attire
, march =
, mascot = Two knights riding a single horse
, equipment ...
, located at the present-day Square du Temple. King Philip IV created a second treasury at the Louvre, whose first documented evidence dates from 1296. Following the suppression of the Templars' Order by the same Philip IV in the early 14th century, the Louvre became the sole location of the king's treasury in Paris, which remained there in various forms until the late 17th century. In the 16th century, following the reorganization into the in 1523, it was kept in one of the remaining medieval towers of the Louvre Castle, with a dedicated guard.
Place of worship
By contrast to the Palais de la Cité with its soaring Sainte-Chapelle, the religious function was never particularly prominent at the Louvre. The royal household used the nearby Saint-Germain l'Auxerrois as their parish church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in community activities, ...
.[ A chapel of modest size was built by ]Louis IX
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the House of Capet, Direct Capetians. He was Coronation of the French monarch, c ...
in the 1230s in the western wing, whose footprint remains in the southern portion of the Lescot Wing's lower main room. In the 1580s, King Henry III projected to build a large chapel and then a convent in the space between the Louvre and the Seine, but only managed to demolish some of the existing structures on that spot.Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
resided at the Louvre, a new chapel was established on the first floor of the Pavillon de l'Horloge
The Pavillon de l’Horloge ("Clock Pavilion"), also known as the Pavillon Sully, is a prominent architectural structure located in the center of the western wing of the Cour Carrée of the Palais du Louvre in Paris. Since the late 19th century ...
and consecrated on 18 February 1659 as Our Lady of Peace and of Saint Louis, the reference to peace being made in the context of negotiation with Spain that resulted later that year in the Treaty of the Pyrenees
The Treaty of the Pyrenees (french: Traité des Pyrénées; es, Tratado de los Pirineos; ca, Tractat dels Pirineus) was signed on 7 November 1659 on Pheasant Island, and ended the Franco-Spanish War that had begun in 1635.
Negotiations were ...
. This room was of double height, including what is now the pavilion's second floor (or attic). In 1915, the Louvre's architect considered restoring that volume to its original height of more than 12 meters, but did not complete that plan.Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
and Marie Louise of Austria
Marie Louise (12 December 1791 – 17 December 1847) was an Austrian archduchess who reigned as Duchess of Parma from 11 April 1814 until her death. She was Napoleon's second wife and as such Empress of the French and Queen of Italy from their ...
. Meanwhile, in planning the Louvre's expansion and reunion with the Tuileries, Napoleon insisted that a major church should be part of the complex. In 1810 Percier and Fontaine made plans to build it on the northern side of the present-day Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
. Its entrance would have been through a new protruding structure now known as the , facing the symmetrical entrance of the Louvre museum on the southern side in the . The church was to be dedicated to Saint Napoleon, a hitherto obscure figure promoted by Napoleon as patron saint of his incipient dynasty (Napoleon also instituted a national holiday on his birthday on 15 August and called it the ). It was intended to "equal in greatness and magnificence that of the Château de Versailles" (i.e. the Palace Chapel). Percier and Fontaine initiated work on the Rotonde de Beauvais, which was completed during Napoleon III's Louvre expansion, but the construction of the main church building was never started.
Home of national representation
In 1303, the Louvre was the venue of the second-ever meeting of France's Estates General, in the wake of the first meeting held the previous year at Notre-Dame de Paris
Notre-Dame de Paris (; meaning "Our Lady of Paris"), referred to simply as Notre-Dame, is a Middle Ages#Art and architecture, medieval Catholic cathedral on the Île de la Cité (an island in the Seine River), in the 4th arrondissement of Paris ...
. The meeting was held in the on the ground floor of the castle's western wing.Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon
The Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon, a former Parisian town house of the House of Bourbon, royal family of Bourbon, was located on the Rive Droite, right bank of the Seine on the rue d'Autriche, between the :en:Louvre Palace, Louvre to the west and the ...
, in effect a contiguous dependency of the Louvre at that time.
During the Bourbon Restoration Bourbon Restoration may refer to:
France under the House of Bourbon:
* Bourbon Restoration in France (1814, after the French revolution and Napoleonic era, until 1830; interrupted by the Hundred Days in 1815)
Spain under the Spanish Bourbons:
* Ab ...
, the same first-floor room that had been used for the 1593 meeting, recreated by Percier and Fontaine as the , was used for the yearly ceremonial opening of the legislative session, which was attended by the king in person – even though ordinary sessions were held in other buildings, namely the Palais Bourbon
The Palais Bourbon () is the meeting place of the National Assembly, the lower legislative chamber of the French Parliament. It is located in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, on the '' Rive Gauche'' of the Seine, across from the Place de la Con ...
for the Lower Chamber and the Luxembourg Palace for the Chamber of Peers. During the July Monarchy
The July Monarchy (french: Monarchie de Juillet), officially the Kingdom of France (french: Royaume de France), was a liberal constitutional monarchy in France under , starting on 26 July 1830, with the July Revolution of 1830, and ending 23 ...
, the yearly opening session was located at the Palais Bourbon, but it was brought back to the Louvre under the Second Empire. From 1857 onwards, the new in the South (Denon) Wing of Napoleon III's Louvre expansion was used for that purpose. In the 1860s Napoleon III and Lefuel planned a new venue to replace the in the newly purpose-built , but it was not yet ready for use at the time of the Empire's fall in September 1870.
That role of the Louvre disappeared following the end of the French monarchy in 1870. As a legacy of the temporary relocation of both assemblies in the Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, u ...
in the 1870s, their joint sessions have been held there ever since, in a room that was purpose-built for that use () and completed in 1875 in the Versailles palace's South Wing.
Royal residence
For centuries, the seat of executive power in Paris had been established at the Palais de la Cité, at or near the spot where Julian had been proclaimed Roman Emperor back in 360 CE. The political turmoil that followed the death of Philip IV, however, led to the emergence of rival centers of power in and around Paris, of which the Louvre was one. In 1316 Clementia of Hungary
Clementia of Hungary (french: Clémence; 1293–13 October 1328) was Queen of France and Navarre as the second wife of King Louis X.
Life
Clementia was the daughter of Charles Martel of Anjou, the titular King of Hungary, and Clemence of Austria ...
, the widow of recently deceased king Louis X Louis X may refer to:
* Louis X of France, "the Quarreller" (1289–1316).
* Louis X, Duke of Bavaria (1495–1545)
* Louis I, Grand Duke of Hesse
Louis I, Grand Duke of Hesse (14 June 1753 in Prenzlau – 6 April 1830 in Darmstadt) was '' ...
, spent much of her pregnancy at the Château de Vincennes
The Château de Vincennes () is a former fortress and royal residence next to the town of Vincennes, on the eastern edge of Paris, alongside the Bois de Vincennes. It was largely built between 1361 and 1369, and was a preferred residence, afte ...
but resided at the Louvre when she gave birth to baby king John I John I may refer to:
People
* John I (bishop of Jerusalem)
* John Chrysostom (349 – c. 407), Patriarch of Constantinople
* John of Antioch (died 441)
* Pope John I, Pope from 523 to 526
* John I (exarch) (died 615), Exarch of Ravenna
* John I ...
on 15 November 1316, who died five days later. John was thus both the only king of France born at the Louvre, and almost certainly the only one who died there ( Henry IV is now generally believed to have died before his carriage arrived at the Louvre following his fatal stabbing in the rue de la Ferronnerie on 14 May 1610). Philip VI occasionally resided at the Louvre, as documented by some of his letters in mid-1328. King John II is also likely to have resided at the Louvre in 1347, since his daughter Joan of Valois was betrothed there to Henry of Brabant on 21 June 1347, and his short-lived daughter Marguerite was born at the Louvre on 20 September 1347.Hôtel Saint-Pol
The Hôtel Saint-Pol was a royal residence begun in 1360 by Charles V of France on the ruins of a building constructed by Louis IX. It was used by Charles V and Charles VI. Located on the Right Bank, to the northwest of the Quartier de l'Arsenal ...
, which became his main place of residence in Paris. Upon becoming king in 1364, he started transforming the Louvre into a permanent and more majestic royal residence, even though he stayed there less often than at the Hôtel Saint-Pol. After Charles V's death, his successor Charles VI also mainly stayed at the Hôtel Saint-Pol, but as he was incapacitated by mental illness, his wife Isabeau of Bavaria resided in the Louvre and ruled from there.
Later 15th-century kings did not reside in the Louvre, nor did either Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
or Henry II even as they partly converted the Louvre as a Renaissance palace. The royal family only came back to reside in the newly rebuilt complex following Catherine de' Medici
Catherine de' Medici ( it, Caterina de' Medici, ; french: Catherine de Médicis, ; 13 April 1519 – 5 January 1589) was an Florentine noblewoman born into the Medici family. She was Queen of France from 1547 to 1559 by marriage to King ...
's abandonment of the Hôtel des Tournelles after her husband Henry II's traumatic death there in July 1559. From then, the king and court would stay mainly in the Louvre between 1559 and 1588 when Henry III escaped Paris, then between 1594 and 1610 under Henry IV. Beyond his minority, Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crow ...
did not much reside in the Louvre and preferred the suburban residences of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (where Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
was born on 5 September 1638, and where Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crow ...
himself died on 14 May 1643) and Fontainebleau
Fontainebleau (; ) is a commune in the metropolitan area of Paris, France. It is located south-southeast of the centre of Paris. Fontainebleau is a sub-prefecture of the Seine-et-Marne department, and it is the seat of the ''arrondissemen ...
(where Louis XIII had been born on 27 September 1601).Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
stayed away from the Louvre during the Fronde between 1643 and 1652, and departed from there following the death of his mother in 1666. Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reache ...
only briefly resided in the Louvre's in 1719, as the Tuileries were undergoing refurbishment.
Both Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
in the 1660s and Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
in the 1810s made plans to establish their main residence in the Colonnade Wing, but none of these respective projects came to fruition. Napoleon's attempt led to Percier and Fontaine's creation of the two monumental staircase on both ends of the wing, but was abandoned in February 1812.
Library
 Charles V was renowned for his interest in books (thus his moniker "" which translates as "learned" as well as "wise"), and in 1368 established a library of about 900 volumes on three levels inside the northwestern tower of the Louvre, then renamed from to . The next year he appointed , one of his officials, as the librarian. This action has been widely viewed as foundational, transitioning from the kings' prior practice of keeping books as individual objects to organizing a collection with proper cataloguing; as such, Charles V's library is generally considered a precursor to the
Charles V was renowned for his interest in books (thus his moniker "" which translates as "learned" as well as "wise"), and in 1368 established a library of about 900 volumes on three levels inside the northwestern tower of the Louvre, then renamed from to . The next year he appointed , one of his officials, as the librarian. This action has been widely viewed as foundational, transitioning from the kings' prior practice of keeping books as individual objects to organizing a collection with proper cataloguing; as such, Charles V's library is generally considered a precursor to the French National Library
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, even though it was dismantled in the 15th century.[
In 1767, a project to relocate the Royal Library from its site on ]rue de Richelieu
The Rue de Richelieu is a long street of Paris, starting in the south of the 1st arrondissement at the Comédie-Française and ending in the north of the 2nd arrondissement. For the first half of the 19th century, before Georges-Eugène Haussman ...
into the Louvre was presented by Jacques-Germain Soufflot
Jacques-Germain Soufflot (, 22 July 1713 – 29 August 1780) was a French architect in the international circle that introduced neoclassicism. His most famous work is the Panthéon in Paris, built from 1755 onwards, originally as a church d ...
, endorsed by Superintendent de Marigny and approved by Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reache ...
, but remained stillborn for lack of funds. A similar project was endorsed by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
from February 1805, for which Percier and Fontaine planned a new Library wing as the centerpiece of their program to fill the space between Louvre and Tuileries, but it was not implemented either.
A separate and smaller was formed from book collections seized during the Revolution and grew during the 19th century's successive regimes. Initially located in the Tuileries in 1800, it was moved to the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
's entresol
A mezzanine (; or in Italian, a ''mezzanino'') is an intermediate floor in a building which is partly open to the double-height ceilinged floor below, or which does not extend over the whole floorspace of the building, a loft with non-sloped w ...
in 1805. In 1860 it was moved to a new space created by Lefuel on the second floor of the new North (Richelieu) Wing of Napoleon III's Louvre expansion, whose main pavilion on the rue de Rivoli was accordingly named . The new library was served by an elegant staircase, now , and was decorated by and Alexandre-Dominique Denuelle. It was destroyed by arson in May 1871 at the same time as the Tuileries, and only a few of its precious holdings could be saved.[ and executed in early 2016 after much delay. Several smaller libraries remain in the Louvre: a in the BCMN's former spaces, open to the public; a specialized scholarly library on art of the eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East, located on the and thus known as the ; and two other specialized libraries, respectively on painting in the and decorative arts in the .
]
Ceremonial venue
On the occasion of Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV's visit to Paris in 1377–1378, the main banquet was held at the Palais de la Cité but the French king used the Louvre's on the next day to give a major speech on his political position in the conflict now known as the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagen ...
.[ The medieval Louvre's western wing was were the ceremonial spaces were located, and that geography did not change with the 16th century's reconstruction as Lescot Wing. Following the latter, most major functions were held either on the lower main room now known as , or in the upper main room then known under various names (see above) and now as the .
A number of betrothals and weddings were concluded and celebrated at the Louvre. These included the betrothal of Henry of Brabant and Joan of Valois on 21 June 1347, the weddings of Charles of Orléans and Isabella of Valois on 9 November 1389, of ]John of Brittany
John of Brittany (french: Jean de Bretagne; c. 1266 – 17 January 1334), 4th Earl of Richmond, was an English nobleman and a member of the Ducal house of Brittany, the House of Dreux. He entered royal service in England under his uncle Edw ...
and Joan of France on 30 July 1397, of Charles of France and Marie of Anjou on 18 December 1413, of Francis of Nevers and Marguerite of Bourbon-La Marche on 19 January 1538, of Francis of France and Mary Stuart on 19 April 1558, of Duke Charles III of Lorraine and Claude of France
Claude of France (13 October 1499 – 20 July 1524) was Queen of France by marriage to King Francis I. She was also ruling Duchess of Brittany from 1514 until her death in 1524. She was a daughter of King Louis XII of France and his second wife ...
on 19 January 1559; the betrothal of Edward VI of England
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first ...
and Elisabeth of Valois on 20 June 1559; the weddings of Henry of Navarre and Margaret of Valois on 19 August 1572, of François de Bourbon and Jeanne de Coesme on 17 December 1582, of Louis II of Condé (the "Grand Condé") and Claire-Clémence de Maillé on 7 February 1641, of Charles Amadeus of Savoy and Élisabeth de Bourbon
Élisabeth de Bourbon (August 1614 – 19 May 1664) was a granddaughter of King Henry IV of France.
Biography
Élisabeth was born in Paris. Her father was César de Bourbon, Duke of Vendôme, legitimised son of King Henry IV of France and his of ...
on 11 July 1643, of Armand de Bourbon and Anne Marie Martinozzi on 21 February 1654, and of Henri Jules of Condé and Anne Henriette of Bavaria
Anne of the Palatinate known in France as Anne of Bavaria, Princess Palatine (Anne Henriette Julie; 13 March 1648 – 23 February 1723) was a Princess of the Palatinate and Countess Palatine of Simmern by birth and was the wife of Henri Jules ...
on 11 December 1663.[ Another grimmer occasion was just after the assassination of King Henry IV, when the king's coffin was put to lay in state in the of the Lescot Wing.
One of the more recent ceremonial gatherings in the Louvre was a candlelit dinner given in the on 10 April 1957 in honor of ]Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh
Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh (born Prince Philip of Greece and Denmark, later Philip Mountbatten; 10 June 1921 – 9 April 2021) was the husband of Queen Elizabeth II. As such, he served as the consort of the British monarch from E ...
, hosted by French President René Coty
Jules Gustave René Coty (; 20 March 188222 November 1962) was President of France from 1954 to 1959. He was the second and last president of the Fourth French Republic.
Early life and politics
René Coty was born in Le Havre and studied at t ...
at the end of their weeklong visit in Paris. An after-dinner reception was then given in the . A few years later, minister André Malraux started a tradition of public ceremonies in the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
to celebrate recently deceased French cultural luminaries. These were held in honor of Georges Braque
Georges Braque ( , ; 13 May 1882 – 31 August 1963) was a major 20th-century French painter, collagist, draughtsman, printmaker and sculptor. His most notable contributions were in his alliance with Fauvism from 1905, and the role he play ...
on and Le Corbusier
Charles-Édouard Jeanneret (6 October 188727 August 1965), known as Le Corbusier ( , , ), was a Swiss-French architect, designer, painter, urban planner, writer, and one of the pioneers of what is now regarded as modern architecture. He was ...
on , with Malraux delivering the eulogy; of Malraux himself on , with eulogy by prime minister Raymond Barre; and of Pierre Soulages
Pierre Jean Louis Germain Soulages (; 24 December 1919 – 26 October 2022) was a French painter, printmaker, and sculptor. In 2014, President François Hollande of France described him as "the world's greatest living artist." His works are held ...
on , with eulogy by president Emmanuel Macron
Emmanuel Macron (; born 21 December 1977) is a French politician who has served as President of France since 2017. ''Ex officio'', he is also one of the two Co-Princes of Andorra. Prior to his presidency, Macron served as Minister of Econ ...
.
Guest residence for foreign sovereigns and royals
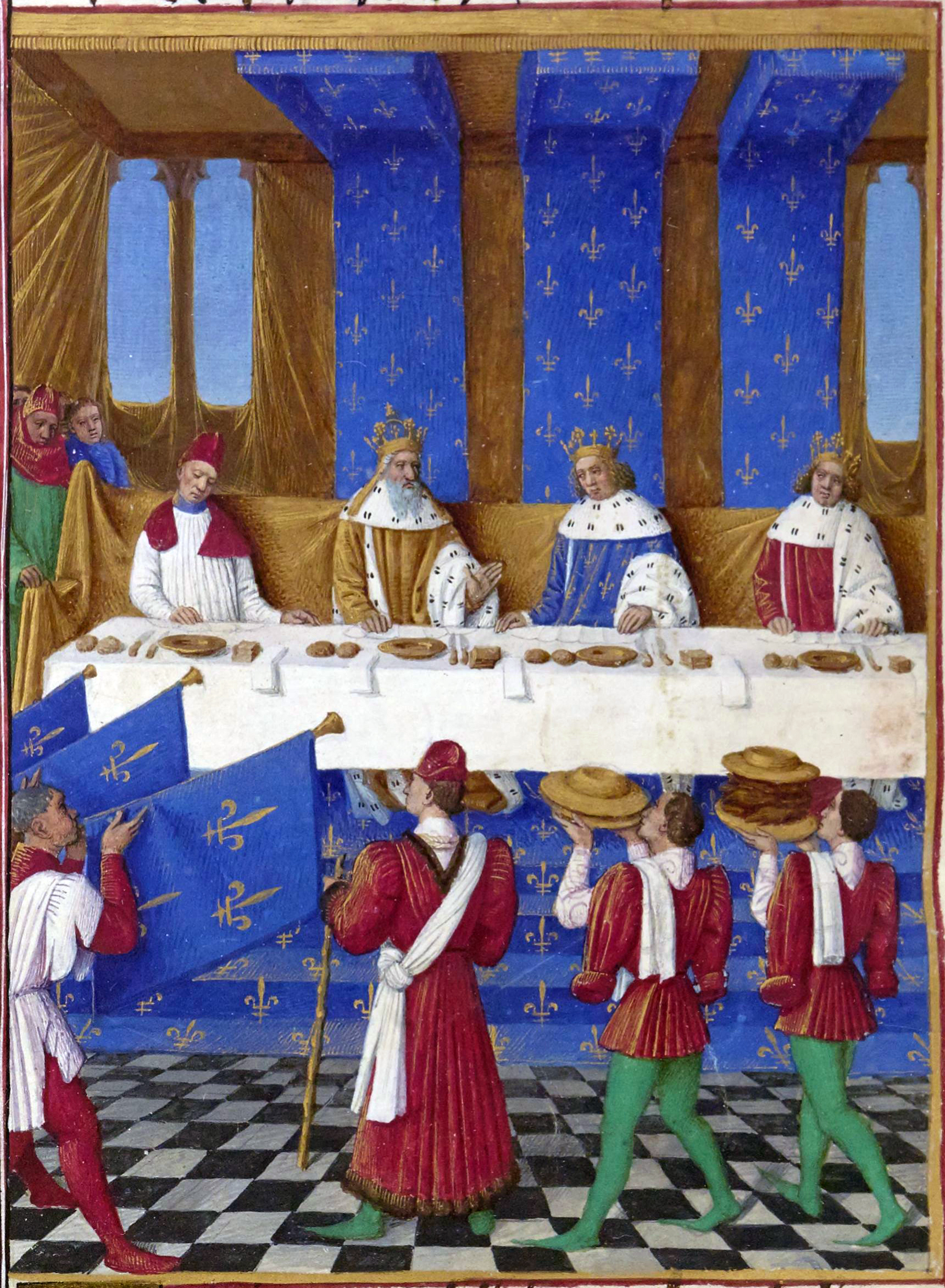 The Louvre was the Parisian home of the Emperors who came to visit France: Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV stayed there in early 1378;
The Louvre was the Parisian home of the Emperors who came to visit France: Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV stayed there in early 1378;[ Byzantine Emperor Manuel II from June 1400 to November 1402, using it as his base for several trips across Europe; ]Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund
Sigismund of Luxembourg (15 February 1368 – 9 December 1437) was a monarch as King of Hungary and Croatia (''jure uxoris'') from 1387, King of Germany from 1410, King of Bohemia from 1419, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1433 until his death in ...
in March and April 1416; and Holy Roman Emperor Charles V
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain ( Castile and Aragon) fr ...
in early January 1540.Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
, where in early February 1649 she learned about the execution of her husband Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
.
In 1717, the was made available to Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
during his visit in Paris, but the Czar preferred to stay in the less grandiose . In 1722, the same apartment became the temporary residence of Infanta Mariana Victoria of Spain
Mariana Victoria of Spain ( pt, Mariana Vitória; 31 March 1718 – 15 January 1781) was an '' Infanta of Spain'' by birth and was later the Queen of Portugal as wife of King Joseph I. She acted as regent of Portugal in 1776–1777, during the l ...
, who was promised to marry the young Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reache ...
(she then moved to Versailles, and in 1725 returned to Spain following the cancelation of the marriage project). This episode remains in the name of the garden in front of the Petite Galerie, known since as the . The courtyard on the other side of the wing, previously known as , was also known as the for much of the 18th century (and later , now ).
In the 1860s, Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A neph ...
decided to create a prestige apartment for visiting sovereigns in the Aile de Flore, close to his own apartment in the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, f ...
. Lefuel designed it with a monumental , the decoration of which he led between 1873 and 1878 even though the monarchy had fallen in the meantime. That project, however, was left unfinished, and in 1901–1902 its richly decorated upper section was repurposed into a room which is now the study gallery of the Louvre's department of graphical arts.
Court house
The Louvre has traditionally not had much of a judiciary role, since royal justice was strongly associated with the much older Palais de la Cité, and local judicial functions under the , including torture and incarceration, were mainly located at the Grand Châtelet. In 1505, as the Châtelet underwent renovation works, its judicial functions were temporarily hosted in the Louvre. Given the castle's prestige it was deemed unsuitable for torture, which was instead carried out during that period in the .
Under Henry IV, the Parlement de Paris was summoned by the king to hold sessions at the Louvre rather than at its traditional venue of the Palais de la Cité.
The Louvre again hosted a judiciary institution when the Conseil d'État was located there between 1824 and 1832. It was awarded the first floor of the Lemercier Wing On the western side of the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
, and remained there until 1832. The painted ceilings of that era, installed in 1827, are still preserved with allegorical themes related to French history and legislation.
The space to the south of the Lescot Wing's Lower Great Hall (now ), created by Pierre Lescot in phases between 1546 and the late 1550s and later remodeled, is known as the . This word, however, refers to its architectural setting, providing a monumental stand for the royal family to watch and dominate the functions held in the Great Hall, and not to a judicial role.
Execution site
 The Louvre was the scene of capital punishment on various occasions. On 4 December 1591,
The Louvre was the scene of capital punishment on various occasions. On 4 December 1591, Charles de Guise
Charles of Lorraine, Duke of Mayenne (26 March 1554 – 3 October 1611), or Charles de Guise, was a French nobleman of the house of Guise and a military leader of the Catholic League, which he headed during the French Wars of Religion, follow ...
had four leaders of the hung from the ceiling of the Lescot Wing's lower main room, now the . During the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
between 21 August 1792 and 11 May 1793, the guillotine was installed on the Place du Carrousel in front of the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, f ...
. It was relocated to the Place de la Concorde
The Place de la Concorde () is one of the major public squares in Paris, France. Measuring in area, it is the largest square in the French capital. It is located in the city's eighth arrondissement, at the eastern end of the Champs-Élysées. ...
(then known as ), first on a one-off basis for the execution of Louis XVI
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was ...
on 21 January 1793, and then permanently in May of the same year.
Entertainment venue
Entertainment performances such as tournaments, games, balls and theater were a core part of court life at the time when the Louvre was a royal residence. On the night of 5 February 1606, a torch-lit carrousel was performed in the Louvre's courtyard between midnight and 5 am, with the monarchs and courtiers watching from their apartments' windows. In 1610, a gladiator-style fight between a man and a lion was organized in the courtyard, which King Henry IV also watched from inside the building. In February 1625 and 1626 respectively, two major ballets burlesques directed by Daniel Rabel were performed in the Louvre's Lower Great Room (now ), with Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crow ...
himself appearing as one of the dancers.
Theatrical representations were particularly significant in the period following the return of the court to the Louvre in 1652. Molière first performed in front of the king in the large first-floor room of the Lescot Wing on 24 October 1658, playing his and . Following that performance's success, he was granted use of a space first in the Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon
The Hôtel du Petit-Bourbon, a former Parisian town house of the House of Bourbon, royal family of Bourbon, was located on the Rive Droite, right bank of the Seine on the rue d'Autriche, between the :en:Louvre Palace, Louvre to the west and the ...
and then, after the latter's demolition to make space for the Louvre Colonnade
The Louvre Colonnade is the easternmost façade of the Palais du Louvre in Paris.
It has been celebrated as the foremost masterpiece of French Architectural Classicism since its construction, mostly between 1667 and 1674. The design, dominated b ...
, at the Palais-Royal
The Palais-Royal () is a former royal palace located in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. The screened entrance court faces the Place du Palais-Royal, opposite the Louvre. Originally called the Palais-Cardinal, it was built for Cardinal R ...
. Molière again performed at the Louvre on 29 January 1664 when he directed , with Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
himself playing a cameo role as an Egyptian, in the main room of the Queen Mother on the ground floor of the Cour Carrée's southern wing. On 17 November 1667, Jean Racine's was created at the Louvre in Louis XIV's presence.
Some lavish entertainment performances left such a mark on collective memory that parts of the Louvre came to be named after them. Thus, the Place du Carrousel preserves the memory of the of 5–6 June 1662, and the Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
is named after the that was first performed there on 13 February 1669.
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
decided to build a new venue for the Paris Opera as part of his project to complete the Louvre and its reunion with the Tuileries. In 1810 Percier and Fontaine planned a new opera house north of what is now the Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
, on a similar footprint to the present-day , with main entrance on the northern side facing the Palais-Royal
The Palais-Royal () is a former royal palace located in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. The screened entrance court faces the Place du Palais-Royal, opposite the Louvre. Originally called the Palais-Cardinal, it was built for Cardinal R ...
. That project, however, was not implemented. Nor was Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A neph ...
's plan in the 1860s to build a large theater room in the Aile de Marsan
The Pavillon de Marsan or Marsan Pavilion was built in the 1660s as the northern end of the Tuileries Palace in Paris, and reconstructed in the 1870s after the Tuileries burned down at the end of the Paris Commune. Following the completion of th ...
as a symmetrical counterpart to the he created in the southern Aile de Flore.
In the 1960s, a theater appears to have operated in the Pavillon de Marsan, known as the . Samuel Beckett's play named ''Play (play), Play'' (french: link=no, Comédie) had its French premiere there on 11 June 1964, directed by Jean-Marie Serreau.
In 1996, the Comédie-Française opened the in the underground spaces of the Carrousel du Louvre
The Carrousel du Louvre is an underground shopping mall in Paris, France, managed by Unibail-Rodamco. The name refers to two nearby sites, the Louvre museum and the Place du Carrousel. The mall contains a famous skylight, ''La Pyramide Inversée'' ...
, its third venue (after its main Palais-Royal
The Palais-Royal () is a former royal palace located in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. The screened entrance court faces the Place du Palais-Royal, opposite the Louvre. Originally called the Palais-Cardinal, it was built for Cardinal R ...
facility and the Théâtre du Vieux-Colombier).
Residence of artists and craftsmen
On 22 December 1608, Henry IV published letters patent heralding his decision to invite hundreds of artists and craftsmen to live and work on the floors under the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
. Simultaneously, Henry established a tapestry factory there, which remained until its transfer to the Gobelins Manufactory in 1671. Creators who lived under the Grande Galerie in the 17th and 18th centuries included Louis Le Vau, Théophraste Renaudot from 1648 to 1653, André Charles Boulle, Jean-Baptiste Pigalle, Augustin Pajou, Maurice Quentin de La Tour, Claude-Joseph Vernet, Carle Vernet, Horace Vernet (who was born there), Jean-Baptiste Greuze, Jean-Honoré Fragonard, and Hubert Robert.Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
and Charles-André van Loo in the Galerie d'Apollon. On 20 August 1801, Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
had the artists and others who lived in the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
all expelled, and in 1806 put a final end to the creators' lodgings under the Grande Galerie.
Royal mint
 In July 1609, Henry IV transferred the Mint (facility), mint to a space the
In July 1609, Henry IV transferred the Mint (facility), mint to a space the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
, from its previous location on the Île de la Cité. The Louvre mint specialized in the production of medals, tokens and commemorative coins, and was correspondingly known as the , whereas common coin kept being produced at the on behind Saint-Germain l'Auxerrois as had been the case since the 13th century.
The Louvre's medals mint was led by prominent artists that included Guillaume Dupré, Jean Varin, and . It closed during the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
but was revived in 1804 by Vivant Denon. By imperial decree of 5 March 1806, it was relocated from the Louvre to the Hôtel des Monnaies, Paris, Hôtel des Monnaies where the had moved in 1775.
Residence of senior courtiers and officials
 In the 17th century, the second floor of the Pavillon du Roi was the home of Charles d'Albert, duc de Luynes until 1621, then of Gaston, Duke of Orléans, and from 1652 of Cardinal Mazarin who also established his nieces in the second-floor attic of the Lescot Wing.. Nicolas Fouquet and his successor
In the 17th century, the second floor of the Pavillon du Roi was the home of Charles d'Albert, duc de Luynes until 1621, then of Gaston, Duke of Orléans, and from 1652 of Cardinal Mazarin who also established his nieces in the second-floor attic of the Lescot Wing.. Nicolas Fouquet and his successor Jean-Baptiste Colbert
Jean-Baptiste Colbert (; 29 August 1619 – 6 September 1683) was a French statesman who served as First Minister of State from 1661 until his death in 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV. His lasting impact on the organization of the country ...
similarly lived on the upper floors of the Pavillon du Roi, above the King's bedchamber.
New prestige apartments for regime dignitaries were created as part of Napoleon III's Louvre expansion. The main one, in the North (Richelieu) Wing, became the apartment of the Finance Minister after 1871, and as such featured prominently in Raymond Depardon's documentary ', shot during the presidential election campaign of then minister Valéry Giscard d’Estaing in early 1974. The apartment was renovated in the early 1990s and is now a part of the Louvre's decorative arts department, known as . Another official apartment was created for the imperial "Great Equerry" () , in the South (Denon) Wing, with entrance through an ornate portico in the . Part of that large apartment was converted in the 1990s into the museum's exhibition space for northern European sculpture, while another part has been used since 1912 as offices for the Louvre's director and their staff. Lefuel also created two successive apartments for the Louvre's director Émilien de Nieuwerkerke, the first in former rooms of the Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture, Académie de peinture, and when these had to be demolished to build the Escalier Daru, on the first floor of the Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
's northern wing.
Several tied cottages still exist in the Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
, including one for the museum's Director. Other apartments in the same pavilion are reserved for senior personnel tasked with the museum's security and maintenance, so that they stay close in case their presence is needed for an emergency.
National printing house
 A first printing workshop appeared in the Louvre in the 1620s. In 1640, superintendent François Sublet de Noyers established it as a royal printing house, the , putting an end to the monarchy's prior practice of subcontracting its printing tasks to individual entrepreneurs such as Robert Estienne. The royal printing house, soon known as , was first led by and his descendants, then by members of the throughout the 18th century until 1792. It was relocated to the Hôtel de Toulouse in 1795, then the in 1809.
In the early 1850s in the early stages of Napoleon III's Louvre expansion, projects were made to relocate the national printing house (then known as ) in the new building of the Louvre, now the Richelieu Wing. These plans were criticized by Ludovic Vitet among others, and were not implemented.
A first printing workshop appeared in the Louvre in the 1620s. In 1640, superintendent François Sublet de Noyers established it as a royal printing house, the , putting an end to the monarchy's prior practice of subcontracting its printing tasks to individual entrepreneurs such as Robert Estienne. The royal printing house, soon known as , was first led by and his descendants, then by members of the throughout the 18th century until 1792. It was relocated to the Hôtel de Toulouse in 1795, then the in 1809.
In the early 1850s in the early stages of Napoleon III's Louvre expansion, projects were made to relocate the national printing house (then known as ) in the new building of the Louvre, now the Richelieu Wing. These plans were criticized by Ludovic Vitet among others, and were not implemented.
Academic and educational facility

 In the late 17th century, the Louvre started to become the seat of the French royal academies. First, in 1672 Colbert allowed the Académie Française to meet on the ground floor of the Pavillon du Roi, in the Guards' Room of the former Queen Mother's apartment. Soon the Académie moved to the ground floor of the Lemercier Wing On the Cour Carrée, and also maintained its library there. The Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres, Académie des Inscriptions joined it in nearby rooms. The Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture had been established in the Grande Galerie until 1661, and returned to the Louvre in 1692, establishing itself in the Salon Carré and the nearby wing built by Le Vau on the , next to the where a number of the king's paintings were kept. The Académie royale d'architecture moved to the Queen's apartment (in the southern wing of the Cour Carrée) in 1692. After a fire in 1740 it moved to the ground floor of the north wing. The
In the late 17th century, the Louvre started to become the seat of the French royal academies. First, in 1672 Colbert allowed the Académie Française to meet on the ground floor of the Pavillon du Roi, in the Guards' Room of the former Queen Mother's apartment. Soon the Académie moved to the ground floor of the Lemercier Wing On the Cour Carrée, and also maintained its library there. The Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres, Académie des Inscriptions joined it in nearby rooms. The Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture had been established in the Grande Galerie until 1661, and returned to the Louvre in 1692, establishing itself in the Salon Carré and the nearby wing built by Le Vau on the , next to the where a number of the king's paintings were kept. The Académie royale d'architecture moved to the Queen's apartment (in the southern wing of the Cour Carrée) in 1692. After a fire in 1740 it moved to the ground floor of the north wing. The Académie des Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French scientific research. It was at ...
also moved to the Louvre in the 1690s, and in 1699 moved from the ground-floor to the former king's room, namely the , the (antechamber) and the former (now which was partitioned at that time. The , a diplomats' training school, took over in the 1710s the large room on the third floor of the Pavillon de l'Horloge
The Pavillon de l’Horloge ("Clock Pavilion"), also known as the Pavillon Sully, is a prominent architectural structure located in the center of the western wing of the Cour Carrée of the Palais du Louvre in Paris. Since the late 19th century ...
(now partitioned into offices).
From 1725, the Salon Carré, recently vacated with the return to Spain of the child Mariana Victoria, was used by the Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture for its yearly exhibition, which took from it its name of ''Salon (Paris), Salon''. From 1763, the Académie also overtook the Galerie d'Apollon.
During the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
, all academies were deemed to be fatally tainted by the Ancien régime associations and terminated on 8 August 1793. Barely more than two years later, however, they were recreated as the Institut de France on 24 October 1795, ceremonially inaugurated in the Lescot Wing's ground-floor room (the Louvre's ) on 4 April 1796. On 20 March 1805 Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
decided to relocate the Institut from the Louvre to its current seat at the former Collège des Quatre-Nations, which had been closed in 1791.
The ''Salon (Paris), Salon'' restarted on a yearly basis in the Salon Carré, until the French Revolution of 1848, Revolution of 1848. That year, the Louvre's energetic new director Philippe-Auguste Jeanron had it relocated to the Tuileries, so that the Salon Carré could be fully devoted to the museum's permanent exhibition. From 1857 the salon moved on from there to the newly built Palais de l'Industrie.
The École du Louvre was created in 1882 with the mission to "extract from the collections the knowledge they contain, and to train curators, missionaries and excavators". The school's curriculum originally focused on archaeology but soon expanded to related disciplines, such as art history and museography. In the early years, the school's sessions were held in the in two rooms of the former apartment of the great equerry, with entrance from the quayside. A large underground classroom, the named after art historian and Louvre curator Louis Courajod, was built in 1932 on architect Albert Ferran's design under the . It was replaced in the 1990s by the still larger , also underground on the northern end of the Carrousel du Louvre
The Carrousel du Louvre is an underground shopping mall in Paris, France, managed by Unibail-Rodamco. The name refers to two nearby sites, the Louvre museum and the Place du Carrousel. The mall contains a famous skylight, ''La Pyramide Inversée'' ...
. The former was then transformed into exhibition rooms in which the Louvre's Coptic art collection is now displayed, including the architectonic pieces from Bawit.
Museum
Securities exchange
The national securities exchange (or ) was located at the Louvre between 10 May 1795 and 9 September 1795, in Anne of Austria's former summer apartment on the ground floor of the Petite Galerie.
Administrative office building
During the Ancien Régime, administrative staff numbers in the machinery of government remained small and were dwarfed by the number of courtiers and domestic servants. That changed in the 19th century as the administrative arms of the state became increasingly significant, and the Louvre as a quintessential government building reflected that new reality. The installation of the Conseil d'État in the Lemercier Wing between 1824 and 1832 was a first step, since that body has administrative as well as judiciary competencies.
The office footprint within the Louvre increased considerably with Napoleon III's Louvre expansion, Napoleon III's expansion. The new North (Richelieu) Wing included offices for use by various ministries:
* Plans were made for the short-lived (1858–1860) to be located in the and the adjacent wing to the west, but that department was terminated before the office space was made available;[
* The was separated from the in 1860, and located in the spaces previously reserved for the Algeria Ministry;][
* The , created in early 1870, was also briefly located in the northern wing;][
On 29 May 1871, a mere few days after the Tuileries' fire, France's government head ]Adolphe Thiers
Marie Joseph Louis Adolphe Thiers ( , ; 15 April 17973 September 1877) was a French statesman and historian. He was the second elected President of France and first President of the French Third Republic.
Thiers was a key figure in the July Rev ...
attributed all administrative offices and barracks space in the Louvre's northern wing to the Ministry of the Economy and Finance (France), French Finance Ministry, whose buildings on the other side of the rue de Rivoli had been entirely destroyed. The Finance Ministry remained there for more than a century, until the late 1980s. A meeting of finance ministers of the Group of Seven countries, hosted at the Louvre on 22 February 1987, gave its name to the Louvre Accord.
Further west, projects were made in the 1880s to relocate the Court of Audit (France), National Court of Audit () – whose previous offices in the Palais d'Orsay, where the Musée d'Orsay now stands, had also been burned down – in the which had just been reconstructed and expanded by Lefuel. Only archives of the Court were deposited there in 1884, however,[ and these spaces were eventually attributed in 1897 to what is now the Musée des Arts Décoratifs.
The Minister of the Overseas (France), Ministry of Colonies was installed in the Flore Wing from 1893 to 1909. The museum then planned to expand into the Flore Wing but that was thwarted during World War I as the facility was used by the wartime bond issuance service. The Finance Ministry, together with the it created in 1933, remained there and stayed until 1961.
The Louvre museum itself keeps offices in various parts of the building, e.g. in the former apartment of the Great Equerry (museum direction), on the top floors of the ]Pavillon de l'Horloge
The Pavillon de l’Horloge ("Clock Pavilion"), also known as the Pavillon Sully, is a prominent architectural structure located in the center of the western wing of the Cour Carrée of the Palais du Louvre in Paris. Since the late 19th century ...
,[ and in part of the ]entresol
A mezzanine (; or in Italian, a ''mezzanino'') is an intermediate floor in a building which is partly open to the double-height ceilinged floor below, or which does not extend over the whole floorspace of the building, a loft with non-sloped w ...
under the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
.
City Hall of Paris
After the Hôtel de Ville, Paris, Paris City Hall was arsoned at the end of the Commune in May 1871, the Municipal Council of Paris and Prefect of the Seine first moved to the Luxembourg Palace across the Seine, but they had to leave that building in 1878 as the Senate (France), French Senate prepared to move back from their previous temporary location in the Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, u ...
, and relocated for several years in the of the Louvre. The new City Hall was formally inaugurated on 13 July 1882 but it took significantly longer to finish the interior works, with some ceremonial rooms only completed in 1906. While in the Louvre the Municipal Council's meetings were held in Napoleon III's unfinished of the , from 1878 to 1883. The left the Louvre in 1887 to its current City Hall location. The offices of the Prefecture and apartment of Préfet Eugène Poubelle remained in the Pavillon de Flore until 1893, when they were replaced by the Ministry of Colonies, despite a 1883 order () that had transferred the entire to the museum.
Sculpture garden
While the Louvre is rich with architectural sculpture, its position in the midst of a bustling city neighborhood was long unfavorable to the display of freestanding sculpture, with few exceptions that included the temporary display of a colossal statue of Vulcan (mythology), Vulcan in the Louvre's courtyard during Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V's visit in 1540.[ In the early 17th century, a bronze sculpture by Francesco Bordoni was erected at the center of the Queen's garden (), now to the south of the Pavillon du Roi.
During the 19th century, the Louvre's open spaces multiplied and the public taste for sculpture and monuments simultaneously increased. An early project was made in the late 1820s to place the Great Sphinx of Tanis in the center of the ]Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Const ...
, but was not implemented.
Instead, on 28 October 1845 an equestrian statue of Ferdinand Philippe, Duke of Orléans was placed on that spot, itself a second cast of a monument by Carlo Marochetti erected in Algiers earlier that year. But that did not last long, and the statue was relocated to Versailles shortly after the French Revolution of 1848, Revolution of 1848 (it was moved again in 1971 to its present location at the Château d'Eu). In the early Second Empire, plans were made to erect equestrian statues of Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
in the Cour Carrée and Charlemagne and Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
respectively in the two squares of the Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
. A plaster model of Auguste Clésinger's equestrian Francis I was placed in the Cour Carrée between December 1855 to February 1856, when it was transferred to the Crystal Palace on Sydenham Hill in London. On 15 January 1863 Clésinger was also tasked to create the statue of Charlemagne, on which he worked until 1871. The statue of Napoleon was commissioned on 26 August 1862 from then-prominent sculptor Jean-Baptiste Claude Eugène Guillaume, Eugène Guillaume, who apparently only produced several small-scale models.
Sculpted monuments mushroomed around the Louvre in the late 19th and early 20th century. Most of them were removed in 1933 on the initiative of Education Minister Anatole de Monzie, due to changing tastes:
* Marble monument to François Boucher by Jean-Paul Aubé (1890), in the , removed in 1933 and now at the Municipal Museum in Longwy
* Equestrian statue of Diego Velázquez by Emmanuel Frémiet (1892), in the , relocated in 1933 to the Casa de Velázquez in Madrid and destroyed during the Spanish Civil War
* Marble version of the group titled , a celebration of the resistance of Belfort during the Franco-Prussian War by Antonin Mercié
Marius Jean Antonin Mercié (October 30, 1845 in Toulouse – December 12, 1916 in Paris), was a French sculptor, medallist and painter.
Biography
Mercié entered the École des Beaux-Arts, Paris, and studied under Alexandre Falguière and Fr ...
, installed in 1894 in the Carrousel Garden
The Tuileries Garden (french: Jardin des Tuileries, ) is a public garden located between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. Created by Catherine de' Medici as the garden of the Tuileries Palace ...
, removed in 1933 and now at Fort Mont-Valérien
* Marble statue of Ernest Meissonier by Antonin Mercié
Marius Jean Antonin Mercié (October 30, 1845 in Toulouse – December 12, 1916 in Paris), was a French sculptor, medallist and painter.
Biography
Mercié entered the École des Beaux-Arts, Paris, and studied under Alexandre Falguière and Fr ...
(1895), in the , removed in 1966 and relocated in 1980 in the at Poissy
* Monument to Auguste Raffet by Emmanuel Frémiet (1896), in the , bronze parts melted in the early 1940s during the Paris in World War II, German occupation, the rest removed in 1966Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
, dubbed the "campo santo".[
* ''Pierre Puget, Puget'', marble by François-Léon Sicard (1910), since 1933 on in Marseille
* ''Nicolas Poussin, Poussin'', marble by Constant Roux (1911), since 1934 in Les Andelys
* ''Jules Hardouin-Mansart, Hardouin-Mansart'', bronze by Ernest Henri Dubois (1908), since the 1930s at the of Les Invalides
* ''Antoine Watteau, Watteau'', marble by Henri-Édouard Lombard (1909), since 1937 in front of the Musée des Beaux-Arts de Valenciennes
* ''Jean-Antoine Houdon, Houdon'', marble by Paul Gasq (1909), since 1935 in Lisieux
* ''Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot, Corot'', marble by François-Raoul Larche (1908), since 1935 in Ville-d'Avray
Two more memorials, of François Rude, Rude by Sicard and Jean-Baptiste-Siméon Chardin, Chardin by Larche, were commissioned but not completed.][ All these sculptures, except Landowski's ''Sons of Cain'', were also removed in 1933. Ségoffin's group was transferred to the southern French town of Saint-Gaudens, Haute-Garonne, Saint-Gaudens in 1935, and melted down during World War II. Landowski's ''Sons of Cain'' was eventually moved in 1984 to its current location on the of the Tuileries Garden.
In the eastern octagonal garden, an , by Paul Wayland Bartlett, was erected in 1908. This initiative had been sponsored in 1899 by American diplomat Robert John Thompson in gratitude of the French gift of the Statue of Liberty, and originally intended for a dedication at Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de Lafayette, Lafayette's grave at the Picpus Cemetery during the Exposition Universelle (1900), Exposition Universelle of 1900. In preparation for the Grand Louvre remodeling, the Lafayette monument was moved in 1985 to its current location on the Cours-la-Reine.
In 1964, Culture Minister André Malraux decided to install in the ]Carrousel Garden
The Tuileries Garden (french: Jardin des Tuileries, ) is a public garden located between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. Created by Catherine de' Medici as the garden of the Tuileries Palace ...
21 bronze sculptures by Aristide Maillol which had been donated to the French state by the sculptor's former model and muse, Dina Vierny, including casts of ''Air (Maillol), Air'', ''Action in Chains'', ''The Mountain (Maillol), The Mountain'', and ''La Rivière (Maillol), The River''. The Maillol statues were rearranged during the overhaul of the garden in the 1990s.
Most recently, as part of the Grand Louvre project designed by I. M. Pei, a cast made in lead in 1986 of the marble Equestrian statue of Louis XIV (Bernini), Equestrian statue of Louis XIV by Gian Lorenzo Bernini
Gian Lorenzo (or Gianlorenzo) Bernini (, , ; Italian Giovanni Lorenzo; 7 December 159828 November 1680) was an Italian sculptor and architect. While a major figure in the world of architecture, he was more prominently the leading sculptor of his ...
has been placed in the Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
, in front of the Louvre Pyramid
The Louvre Pyramid (Pyramide du Louvre) is a large glass and metal structure designed by the Chinese-American architect I. M. Pei. The pyramid is in the main courtyard (Cour Napoléon) of the Louvre Palace in Paris, surrounded by three smalle ...
and marking the end of Paris's . This was intended as a tribute to Bernini's past role as architect of the Louvre in 1664–1666, even though his plans were not executed.
File:Bain News Service, Statue of Lafayette in the courtyard of the Louvre, Paris, France - Library of Congress.tif , Lafayette Monument in the Cour Napoléon, early 20th century
File:Paul Landowsky - Die Söhne Kains 1900 - Paris, Cour du Carrousel 1968.jpg , Landowski's ''Sons of Cain'' in the Cour Napoléon, 1968
File:Les Trois Grâces by Aristide Maillol (Tuileries) 11.jpg, Maillol's ''Les Trois Grâces''
File:L'Air by Aristide Maillol, Tuileries garden, Paris 11 August 2015.jpg, Maillol's ''L'Air''
File:Jardin du Carrousel du Louvre.jpg, Maillol's ''Ile-de-France''
File:Monument aux morts de Port-Vendres by Aristide Maillol (Tuileries) 02.jpg, Maillol's ''Monument aux morts de Port-Vendres''
File:Louis XIV Bernin réplique Cour Napoléon Louvre.jpg, Bernini's ''Louis XIV'' in the Cour Napoléon
Research facility
 The was created in 1932 to support research on paintings and leverage new analysis techniques. In 1968 it became the , with a national mandate but still located at the Louvre. In 1998, this laboratory merged with the to form the Center for Research and Restoration of Museums of France (C2RMF), located in the
The was created in 1932 to support research on paintings and leverage new analysis techniques. In 1968 it became the , with a national mandate but still located at the Louvre. In 1998, this laboratory merged with the to form the Center for Research and Restoration of Museums of France (C2RMF), located in the Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
.
Dining and shopping venue
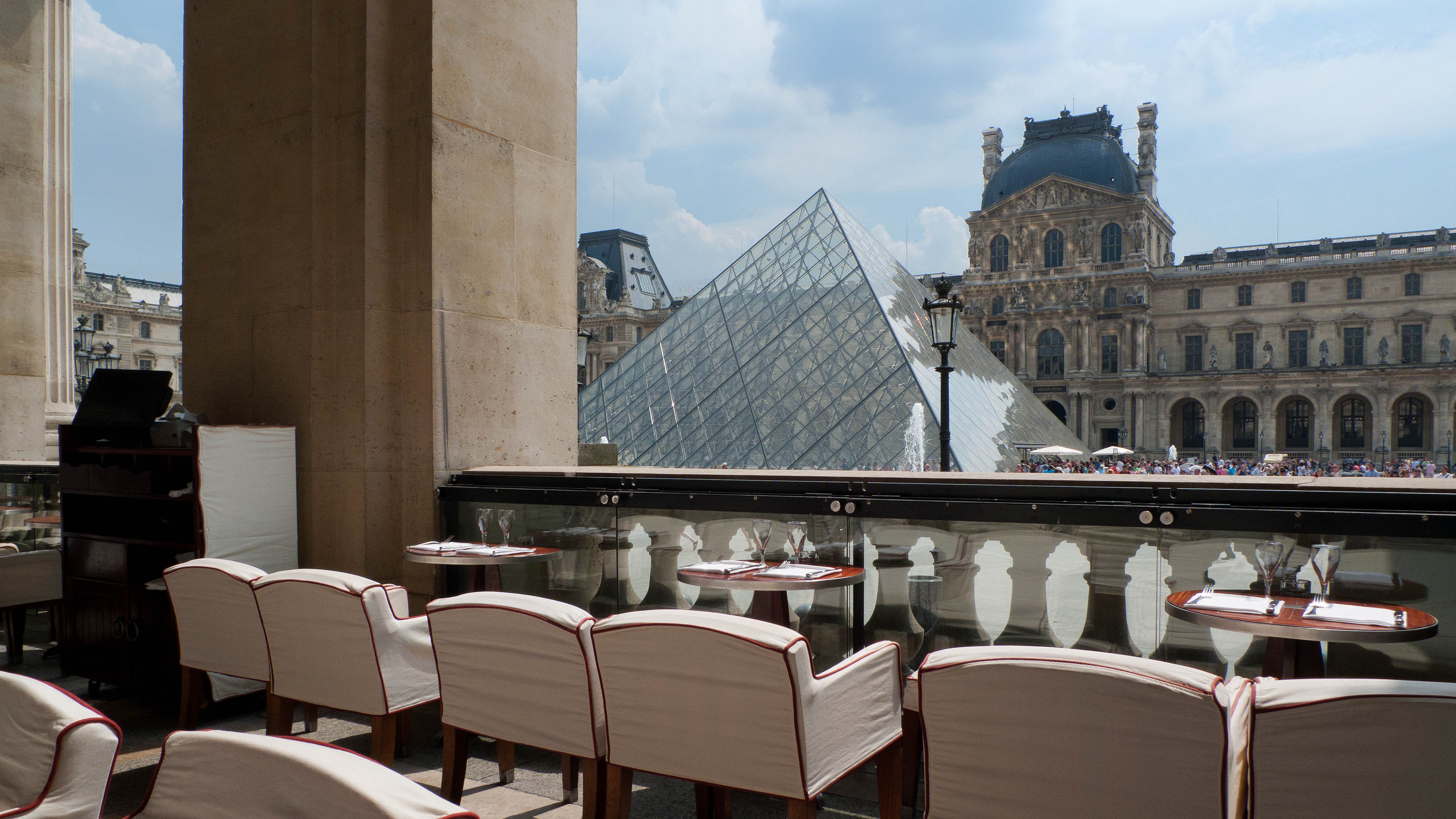 The Louvre palace is host to several restaurants and cafés. As of 2021, the most prominent is the , opened in 1994 in the Richelieu Wing with a terrace on the
The Louvre palace is host to several restaurants and cafés. As of 2021, the most prominent is the , opened in 1994 in the Richelieu Wing with a terrace on the Cour Napoléon
The expansion of the Louvre under Napoleon III in the 1850s, known at the time and until the 1980s as the Nouveau Louvre or Louvre de Napoléon III, was an iconic project of the Second French Empire and a centerpiece of its ambitious transforma ...
, named after the Louvre's nearby and designed by It was created by restaurateur on a Concession (contract), concession contract from the museum.Aile de Marsan
The Pavillon de Marsan or Marsan Pavilion was built in the 1660s as the northern end of the Tuileries Palace in Paris, and reconstructed in the 1870s after the Tuileries burned down at the end of the Paris Commune. Following the completion of th ...
with a terrace on the Carrousel Garden
The Tuileries Garden (french: Jardin des Tuileries, ) is a public garden located between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. Created by Catherine de' Medici as the garden of the Tuileries Palace ...
, designed by Joseph Dirand and replacing a previous restaurant on the same spot, . A high-end restaurant named opened in 1989 on the mezzanine of the Hall Napoléon, under the Louvre Pyramid
The Louvre Pyramid (Pyramide du Louvre) is a large glass and metal structure designed by the Chinese-American architect I. M. Pei. The pyramid is in the main courtyard (Cour Napoléon) of the Louvre Palace in Paris, surrounded by three smalle ...
, and was operated by chef Yves Pinard; its inaugural event was the dinner of the 15th G7 summit.Carrousel du Louvre
The Carrousel du Louvre is an underground shopping mall in Paris, France, managed by Unibail-Rodamco. The name refers to two nearby sites, the Louvre museum and the Place du Carrousel. The mall contains a famous skylight, ''La Pyramide Inversée'' ...
shopping mall is home to fast food outlets grouped in one of the first food courts in Paris, opened in 1993 and rebranded in 2009 as .
From 1608 to 1806, the ground floor of the Grande Galerie
The Grande Galerie, in the past also known as the Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Waterside Gallery), is a wing of the Louvre Palace, perhaps more properly referred to as the Aile de la Grande Galerie (Grand Gallery Wing), since it houses the longest ...
hosted a number of shops in which artists and artisans peddled their creations. They were closed by order of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
. Aside from museum shops, the Louvre experienced a revival of retail commercial activity with the opening in 1993 of the Carrousel du Louvre
The Carrousel du Louvre is an underground shopping mall in Paris, France, managed by Unibail-Rodamco. The name refers to two nearby sites, the Louvre museum and the Place du Carrousel. The mall contains a famous skylight, ''La Pyramide Inversée'' ...
shopping mall, whose largest slot was initially leased by a Virgin Megastores, Virgin Megastore until 2012, and by Printemps since 2014. France's first Apple Store was also located there and operated from 2009 to 2018.
Chronological plan of the construction of the Louvre
The oldest part of the above-ground Louvre is the southwest corner of the square block that faces the center of Paris to the east. This corner section, consisting of the Lescot Wing (1) and the north side of the western part of the south wing (2), was designed and constructed in the 16th century by Pierre Lescot, who replaced the corresponding wings of the medieval Louvre (not shown). Later that century, the Petite Galerie (4) was added, connecting the Louvre to the section of the wall of Charles V which ran along the north bank of the Seine toward the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, f ...
(3, 5, 8, 11, 14; destroyed by fire in 1871). Around 1600, during the reign of Henry IV, the wall along the river was replaced with the Grande Galerie (6, 7), which provided a covered passage from the Louvre to Tuileries Palace and later was the first part of the Louvre to become a museum. The Lescot Wing was expanded north with the Lemercier Wing (9) under Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crow ...
, and in the second half of the 17th century, during the reign of Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
, the Petite Galerie was enlarged (10, 13) and the remaining wings around the Square Court (12, 16) were constructed, but not totally completed until the first part of the 19th century under Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, who also added the Arc du Carrousel (17) and parts of the north wing (17) along the rue de Rivoli. Later in the 19th century, the north wing was slightly extended (18) by Louis XVIII
Louis XVIII (Louis Stanislas Xavier; 17 November 1755 – 16 September 1824), known as the Desired (), was King of France from 1814 to 1824, except for a brief interruption during the Hundred Days in 1815. He spent twenty-three years in ...
. From 1852 to 1857, Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A neph ...
connected the north wing to the buildings surrounding the Square Court with the Richelieu Wing (19, north part) and enlarged the Grande Galerie with the Denon Wing (19, south part). In 1861–1870 his architect Hector Lefuel carried out further work, replacing the Pavillon de Flore
The Pavillon de Flore, part of the Palais du Louvre in Paris, France, stands at the southwest end of the Louvre, near the Pont Royal. It was originally constructed in 1607–1610, during the reign of Henry IV, as the corner pavilion betw ...
and the western section of the Grande Galerie (7) and adding the Pavillon des Sessions (20, also known as the Pavillon des États). In 1874–1880 he replaced the Pavillon de Marsan (15) and extended the south facade of the adjacent Marsan Wing (21).
Photo gallery
File:Paris - The Musee Du Louvre main hall by night - 2884.jpg, French sculpture in the Cour Marly in the renovated Richelieu wing of the Grand Louvre, viewed toward the west
File:Cour Carrée, Louvre Museum, 2 April 2009.jpg, Panoramic view of the Cour Carrée, from the central courtyard fountain toward the west
File:Louvre Cour Carrée June 2010.jpg, The Cour Carrée of the "Old Louvre" looking west (Left to right: Aile Lescot, Pavillon Sully (de l'Horloge), Aile Lemercier)
File:Louvre20081008.jpg, The Louvre Palace looking west across the Cour Napoleon and the Louvre Pyramid
The Louvre Pyramid (Pyramide du Louvre) is a large glass and metal structure designed by the Chinese-American architect I. M. Pei. The pyramid is in the main courtyard (Cour Napoléon) of the Louvre Palace in Paris, surrounded by three smalle ...
File:Pavillon de Flore from the Tuileries Garden, Paris 5 November 2019.jpg, Pavillon de Flore as seen from the Tuileries Garden
See also
* Palais de la Cité
* Versailles Palace
Notes
References
* Ayers, Andrew (2004). ''The Architecture of Paris''. Stuttgart; London: Edition Axel Menges. .
* Ballon, Hilary (1991). ''The Paris of Henri IV: Architecture and Urbanism''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT Press. .
* Berger, Robert W. (1993). ''The Palace of the Sun: The Louvre of Louis XIV''. University Park: The Pennsylvania State University Press. .
* Adolphe Berty, Berty, Adolphe (1868). ''Topographie historique du vieux Paris. Région du Louvre et des Tuileries. Tome 2''. Paris: Imprimerie Impériale
Copy
at Gallica.
* Bezombes, Dominique, editor (1994). ''The Grand Louvre: History of a Project''. Paris: Moniteur. .
* Biasini, Émile; Lebrat, Jean; Bezombes, Dominique; Vincent, Jean-Michel (1989). ''The Grand Louvre: A Museum Transfigured 1981–1993''. Paris: Electa Moniteur. .
* Blunt, Anthony; Beresford, Richard (1999). ''Art and architecture in France, 1500–1700''. New Haven: Yale University Press. .
* Bresc-Bautier, Genevieve (1995). ''The Louvre: An Architectural History''. New York: The Vendome Press. .
* Briggs, Keith (2008)
"The Domesday Book castle LVVRE"
''Journal of the English Place-Name Society'', vol. 40, pp. 113–118. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
* Christ, Yvan (1949). ''Le Louvre et les Tuileries : Histoire architecturale d'un double palais''. [Paris]: Éditions "Tel". .
* Edwards, Henry Sutherland (1893). ''Old and New Paris: Its History, Its People, and Its Places''. Paris: Cassell
View
at Google Books. Retrieved 30 April 2008.
* Hanser, David A. (2006). ''Architecture of France''. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. .
* Hautecoeur, Louis (1940). ''Histoire du Louvre: Le Château – Le Palais – Le Musée, des origines à nos jours, 1200–1940'', 2nd edition. Paris: Administration provisoire d'imprimerie. .
* Lowry, Bates (1956). ''Palais du Louvre, 1528–1624: The Development of a Sixteenth-Century Architectural Complex'' (thesis/dissertation). University of Chicago.
ProQuest
* Mignot, Claude (1999). ''The Pocket Louvre: A Visitor's Guide to 500 Works''. New York: Abbeville Press. .
* Ochterbeck, Cynthia Clayton, editor (2009). ''The Green Guide Paris'', pp. 168–201. Greenville, South Carolina: Michelin Maps and Guides. .
* Sauval, Henri (1724). ''Histoire et recherches des antiquités de la ville de Paris'', vol. 2, Paris: C. Moette and J. Chardon
Copy
at Google Books.
* Sturdy, David (1995). ''Science and social status: the members of the Académie des sciences 1666–1750''. Woodbridge, Suffolk, U.K.: Boydell Press.
Preview
at Google Books.
External links
*
*
A virtual visit of the Louvre
{{Coord, 48, 51, 40, N, 2, 20, 11, E, region:FR_type:landmark, display=title
Louvre Palace,
Châteaux in Paris
Castles in Île-de-France
Royal residences in France, Louvre
 The Louvre Palace (french: link=no, Palais du Louvre, ), often referred to simply as the Louvre, is an iconic French palace located on the Right Bank of the
The Louvre Palace (french: link=no, Palais du Louvre, ), often referred to simply as the Louvre, is an iconic French palace located on the Right Bank of the 
 Beyond the name of the palace itself, the toponymy of the Louvre can be treacherous. Partly because of the building's long history and links to changing politics, different names have applied at different times to the same structures or rooms. For example, what used to be known in the 17th and 18th centuries the or is now generally referred to as
Beyond the name of the palace itself, the toponymy of the Louvre can be treacherous. Partly because of the building's long history and links to changing politics, different names have applied at different times to the same structures or rooms. For example, what used to be known in the 17th and 18th centuries the or is now generally referred to as  On the southern side of the
On the southern side of the  In 1190 King Philip II of France, who was about to leave for the
In 1190 King Philip II of France, who was about to leave for the  In 1624,
In 1624,  After the definitive departure of the royal court for Versailles in 1682, the Louvre became occupied by multiple individuals and organizations, either by royal favor or simply
After the definitive departure of the royal court for Versailles in 1682, the Louvre became occupied by multiple individuals and organizations, either by royal favor or simply  A tall was planned in 1884 and erected in 1888 in front of the two gardens on what is now the ''Cour Napoléon''. That initiative carried heavy political symbolism, since Gambetta was widely viewed as the founder of the Third Republic, and his outsized celebration in the middle of Napoleon III's landmark thus affirmed the final victory of
A tall was planned in 1884 and erected in 1888 in front of the two gardens on what is now the ''Cour Napoléon''. That initiative carried heavy political symbolism, since Gambetta was widely viewed as the founder of the Third Republic, and his outsized celebration in the middle of Napoleon III's landmark thus affirmed the final victory of  Aside from the interior refurbishment of the
Aside from the interior refurbishment of the  Charles V was renowned for his interest in books (thus his moniker "" which translates as "learned" as well as "wise"), and in 1368 established a library of about 900 volumes on three levels inside the northwestern tower of the Louvre, then renamed from to . The next year he appointed , one of his officials, as the librarian. This action has been widely viewed as foundational, transitioning from the kings' prior practice of keeping books as individual objects to organizing a collection with proper cataloguing; as such, Charles V's library is generally considered a precursor to the
Charles V was renowned for his interest in books (thus his moniker "" which translates as "learned" as well as "wise"), and in 1368 established a library of about 900 volumes on three levels inside the northwestern tower of the Louvre, then renamed from to . The next year he appointed , one of his officials, as the librarian. This action has been widely viewed as foundational, transitioning from the kings' prior practice of keeping books as individual objects to organizing a collection with proper cataloguing; as such, Charles V's library is generally considered a precursor to the  The Louvre was the Parisian home of the Emperors who came to visit France: Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV stayed there in early 1378; Byzantine Emperor Manuel II from June 1400 to November 1402, using it as his base for several trips across Europe;
The Louvre was the Parisian home of the Emperors who came to visit France: Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV stayed there in early 1378; Byzantine Emperor Manuel II from June 1400 to November 1402, using it as his base for several trips across Europe;  The Louvre was the scene of capital punishment on various occasions. On 4 December 1591,
The Louvre was the scene of capital punishment on various occasions. On 4 December 1591,  In July 1609, Henry IV transferred the Mint (facility), mint to a space the
In July 1609, Henry IV transferred the Mint (facility), mint to a space the  In the 17th century, the second floor of the Pavillon du Roi was the home of Charles d'Albert, duc de Luynes until 1621, then of Gaston, Duke of Orléans, and from 1652 of Cardinal Mazarin who also established his nieces in the second-floor attic of the Lescot Wing.. Nicolas Fouquet and his successor
In the 17th century, the second floor of the Pavillon du Roi was the home of Charles d'Albert, duc de Luynes until 1621, then of Gaston, Duke of Orléans, and from 1652 of Cardinal Mazarin who also established his nieces in the second-floor attic of the Lescot Wing.. Nicolas Fouquet and his successor  A first printing workshop appeared in the Louvre in the 1620s. In 1640, superintendent François Sublet de Noyers established it as a royal printing house, the , putting an end to the monarchy's prior practice of subcontracting its printing tasks to individual entrepreneurs such as Robert Estienne. The royal printing house, soon known as , was first led by and his descendants, then by members of the throughout the 18th century until 1792. It was relocated to the Hôtel de Toulouse in 1795, then the in 1809.
In the early 1850s in the early stages of Napoleon III's Louvre expansion, projects were made to relocate the national printing house (then known as ) in the new building of the Louvre, now the Richelieu Wing. These plans were criticized by Ludovic Vitet among others, and were not implemented.
A first printing workshop appeared in the Louvre in the 1620s. In 1640, superintendent François Sublet de Noyers established it as a royal printing house, the , putting an end to the monarchy's prior practice of subcontracting its printing tasks to individual entrepreneurs such as Robert Estienne. The royal printing house, soon known as , was first led by and his descendants, then by members of the throughout the 18th century until 1792. It was relocated to the Hôtel de Toulouse in 1795, then the in 1809.
In the early 1850s in the early stages of Napoleon III's Louvre expansion, projects were made to relocate the national printing house (then known as ) in the new building of the Louvre, now the Richelieu Wing. These plans were criticized by Ludovic Vitet among others, and were not implemented.

 In the late 17th century, the Louvre started to become the seat of the French royal academies. First, in 1672 Colbert allowed the Académie Française to meet on the ground floor of the Pavillon du Roi, in the Guards' Room of the former Queen Mother's apartment. Soon the Académie moved to the ground floor of the Lemercier Wing On the Cour Carrée, and also maintained its library there. The Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres, Académie des Inscriptions joined it in nearby rooms. The Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture had been established in the Grande Galerie until 1661, and returned to the Louvre in 1692, establishing itself in the Salon Carré and the nearby wing built by Le Vau on the , next to the where a number of the king's paintings were kept. The Académie royale d'architecture moved to the Queen's apartment (in the southern wing of the Cour Carrée) in 1692. After a fire in 1740 it moved to the ground floor of the north wing. The
In the late 17th century, the Louvre started to become the seat of the French royal academies. First, in 1672 Colbert allowed the Académie Française to meet on the ground floor of the Pavillon du Roi, in the Guards' Room of the former Queen Mother's apartment. Soon the Académie moved to the ground floor of the Lemercier Wing On the Cour Carrée, and also maintained its library there. The Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres, Académie des Inscriptions joined it in nearby rooms. The Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture had been established in the Grande Galerie until 1661, and returned to the Louvre in 1692, establishing itself in the Salon Carré and the nearby wing built by Le Vau on the , next to the where a number of the king's paintings were kept. The Académie royale d'architecture moved to the Queen's apartment (in the southern wing of the Cour Carrée) in 1692. After a fire in 1740 it moved to the ground floor of the north wing. The  The was created in 1932 to support research on paintings and leverage new analysis techniques. In 1968 it became the , with a national mandate but still located at the Louvre. In 1998, this laboratory merged with the to form the Center for Research and Restoration of Museums of France (C2RMF), located in the
The was created in 1932 to support research on paintings and leverage new analysis techniques. In 1968 it became the , with a national mandate but still located at the Louvre. In 1998, this laboratory merged with the to form the Center for Research and Restoration of Museums of France (C2RMF), located in the  The Louvre palace is host to several restaurants and cafés. As of 2021, the most prominent is the , opened in 1994 in the Richelieu Wing with a terrace on the
The Louvre palace is host to several restaurants and cafés. As of 2021, the most prominent is the , opened in 1994 in the Richelieu Wing with a terrace on the