The long-term heavy consumption of
alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
(
alcohol use disorder
Alcoholism is, broadly, any drinking of alcohol that results in significant mental or physical health problems. Because there is disagreement on the definition of the word ''alcoholism'', it is not a recognized diagnostic entity. Predomin ...
) can cause severe detrimental effects.
intake in large amounts include an increased risk of developing an alcohol use disorder,
malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
,
chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-standing inflammation of the pancreas that alters the organ's normal structure and functions. It can present as episodes of acute inflammation in a previously injured pancreas, or as chronic damage with persistent pa ...
,
erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also called impotence, is the type of sexual dysfunction in which the penis fails to become or stay erect during sexual activity. It is the most common sexual problem in men.Cunningham GR, Rosen RC. Overview of ma ...
,
heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
,
atrial fibrillation,
gastritis
Gastritis is inflammation of the lining of the stomach. It may occur as a short episode or may be of a long duration. There may be no symptoms but, when symptoms are present, the most common is upper abdominal pain (see dyspepsia). Other possi ...
,
stomach ulcer
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
s,
alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also called alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), is a term that encompasses the liver manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with liver fibros ...
, certain types of
dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
, and
several types of cancer. In addition, damage to the
central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
and
peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brai ...
(e.g., painful
peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or or ...
) can occur from chronic heavy alcohol consumption. There is also an increased risk for accidental injuries, for example, those sustained in traffic accidents and falls. Studies show that individuals with heavy substance use have a much higher risk of having other disorders. A cross-sectional observational study found evidence that people who used substances had the highest risk for five of the disorders studied. However, even light and moderate alcohol consumption increase the risk for developing certain types of cancer.
[{{cite web, url=https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/alcohol-consumption-increases-risk-of-breast-and-other-cancers-doctors-say/, title=Alcohol Consumption Increases Risk of Breast and Other Cancers, Doctors Say, author= Cheryl Platzman Weinstock, publisher=]Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it ...
, date=8 November 2017, access-date=13 November 2018, quote=The ASCO statement, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, cautions that while the greatest risks are seen with heavy long-term use, even low alcohol consumption (defined as less than one drink per day) or moderate consumption (up to two drinks per day for men, and one drink per day for women because they absorb and metabolize it differently) can increase cancer risk. In fact, one 2018 study concluded that no level of alcohol consumption is safe, even a little. Among women, light drinkers have a four percent increase
risk of breast cancer, while moderate drinkers have a 23 percent increase in risk of the disease.
[{{cite journal , vauthors=LoConte NK, Brewster AM, Kaur JS, Merrill JK, Alberg AJ , title=Alcohol and Cancer: A Statement of the American Society of Clinical Oncology , journal=J. Clin. Oncol. , volume=36 , issue=1 , pages=83–93 , date=2018 , pmid=29112463 , doi=10.1200/JCO.2017.76.1155, s2cid=25271140 , quote=Clearly, the greatest cancer risks are concentrated in the heavy and moderate drinker categories. Nevertheless, some cancer risk persists even at low levels of consumption. A meta-analysis that focused solely on cancer risks associated with drinking one drink or fewer per day observed that this level of alcohol consumption was still associated with some elevated risk for squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus (sRR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.09 to 1.56), oropharyngeal cancer (sRR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.06 to 1.29), and breast cancer (sRR, 1.05; 95% CI, 1.02 to 1.08), but no discernable associations were seen for cancers of the colorectum, larynx, and liver., url=https://semanticscholar.org/paper/a5733be427514ccea2ced24a6dc692fa0391d80c ]
The long-term use of alcohol is capable of damaging nearly every organ and system in the body. The developing adolescent brain is particularly vulnerable to the toxic effects of alcohol. In addition, the developing fetal brain is also vulnerable, and
fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) may result if pregnant mothers consume alcohol.
While alcohol consumption does not improve overall health,
[{{Cite web, author=Sandee LaMotte, date=2018-08-23, title=No amount of alcohol is good for your overall health, global study says, url=https://www.cnn.com/2018/08/23/health/global-alcohol-study/index.html, access-date=2021-05-21, website=CNN, language=en][{{Cite journal, last1=Burton, first1=Robyn, last2=Sheron, first2=Nick, date=2018-09-22, title=No level of alcohol consumption improves health, url=https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(18)31571-X/abstract, journal=The Lancet, language=English, volume=392, issue=10152, pages=987–988, doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31571-X, issn=0140-6736, pmid=30146328, s2cid=52075453][{{Cite news, title=No Amount Of Alcohol Is Good For Your Health, Global Study Says, url=https://www.npr.org/2018/08/24/641618937/no-amount-of-alcohol-is-good-for-your-health-global-study-claims, access-date=2021-05-21, newspaper=NPR, date=24 August 2018, language=en, last1=Raphelson, first1=Samantha] the inverse relation in
Western culture
Leonardo da Vinci's ''Vitruvian Man''. Based on the correlations of ideal Body proportions">human proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise ''De architectura''.
image:Plato Pio-Cle ...
s between alcohol consumption and cardiovascular disease has been known for over 100 years. Many physicians do not promote alcohol consumption; however, given the many health concerns associated with it, some suggest that alcohol should be regarded as a recreational drug, and promote exercise and good nutrition to combat cardiovascular disease.
[{{Cite journal, last1=Sellman, first1=D, last2=Connor, first2=J, last3=Robinson , first3=G , last4=Jackson, first4=R , title=Alcohol cardio-protection has been talked up., journal=N Z Med J, volume=122, issue=1303, pages=97–101, year=2009, pmid=19851424]
Negative effects include increased risk of
liver disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the si ...
s,
oropharyngeal
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
,
esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include difficulty in swallowing and weight loss. Other symptoms may include pain when swallowing, a hoarse voi ...
and
pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones. There are two main types: acute pancreatitis, and chronic p ...
. Conversely, moderate intake of alcohol may have some beneficial effects on gastritis and
cholelithiasis
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of mig ...
. Chronic alcohol misuse has serious effects on physical and mental health. Chronic excess alcohol intake, or alcohol dependence, can lead to a wide range of
neuropsychiatric
Neuropsychiatry or Organic Psychiatry is a branch of medicine that deals with psychiatry as it relates to neurology, in an effort to understand and attribute behavior to the interaction of neurobiology and social psychology factors. Within neurop ...
or
neurological
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal c ...
impairment,
cardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
disease, liver disease, and
malignant neoplasms
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bl ...
. The psychiatric disorders associated with alcoholism include
major depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introdu ...
,
dysthymia
Dysthymia ( ), also known as persistent depressive disorder (PDD), is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically a disorder primarily of mood, consisting of similar cognitive and physical problems as major depressive disorder, but with l ...
,
depersonalization
Depersonalization can consist of a detachment within the self, regarding one's mind or body, or being a detached observer of oneself. Subjects feel they have changed and that the world has become vague, dreamlike, less real, lacking in significa ...
,
mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a mental and behavioral disorder defined as a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together wi ...
,
hypomania
Hypomania (literally "under mania" or "less than mania") is a mental and behavioural disorder, characterised essentially by an apparently non-contextual elevation of mood (euphoria) that contributes to persistently disinhibited behaviour.
Th ...
,
panic disorder
Panic disorder is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder characterized by reoccurring unexpected panic attacks. Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear that may include palpitations, sweating, shaking, short ...
,
phobias
A phobia is an anxiety disorder defined by a persistent and excessive fear of an object or situation. Phobias typically result in a rapid onset of fear and are usually present for more than six months. Those affected go to great lengths to avoi ...
,
generalized anxiety disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, uncontrollable and often irrational worry about events or activities. Worry often interferes with daily function ...
,
personality disorders
Personality disorders (PD) are a class of mental disorders characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience, exhibited across many contexts and deviating from those accepted by the individual's cultur ...
,
schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social w ...
,
suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and ...
,
neurologic deficits (e.g. impairments of
working memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, ...
,
emotions
Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or displeasure. There is currently no scientific consensus on a definition. ...
,
executive functions
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behavior: selecting and su ...
,
visuospatial abilities and
gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency. ...
and
balance
Balance or balancing may refer to:
Common meanings
* Balance (ability) in biomechanics
* Balance (accounting)
* Balance or weighing scale
* Balance as in equality or equilibrium
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Balance'' (1983 film), a Bulgaria ...
) and
brain damage
Neurotrauma, brain damage or brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating t ...
. There is no evidence that alcohol consumption causes these disorders, but people with these conditions may turn to alcohol as a coping mechanism at a greater rate or frequency than the general population. Alcohol dependence is associated with
hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high b ...
,
coronary heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pl ...
, and
ischemic stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop funct ...
,
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
of the
respiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies g ...
, and also cancers of the
digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
,
liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
,
breast
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues.
In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and sec ...
and
ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
. Heavy drinking is associated with liver disease, such as
cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
. Excessive alcohol consumption can have a negative
impact on aging.
[{{cite journal, author=Stevenson JS, title=Alcohol use, misuse, abuse, and dependence in later adulthood, journal=Annu Rev Nurs Res, volume=23, pages=245–280, year=2005, pmid=16350768, doi=10.1891/0739-6686.23.1.245, s2cid=24586529]
Some nations have introduced
alcohol packaging warning messages
Alcohol packaging warning messages (AWLs) are warning messages that appear on the packaging of alcoholic drinks concerning their health effects. They have been implemented in an effort to enhance the public's awareness of the harmful effects ...
that inform consumers about
alcohol and cancer
Alcohol causes cancers of the oesophagus, liver, breast, colon, oral cavity, rectum, pharynx and laryngeal cancers, and probably causes cancers of the pancreas. Consumption of alcohol in any quantity can cause cancer. The more alcohol is co ...
, and about risk of
fetal alcohol syndrome for women who drink while pregnant.
Mortality effects
A 2016 systematic review and meta-analysis found that moderate ethanol consumption does not prolong life compared with lifetime abstention from ethanol consumption. A systematic analysis of data from the Global Burden of Disease study found that consumption of ethanol increases the risk of cancer and increases the risk of all-cause mortality, and that the level of ethanol consumption that minimizes disease is zero consumption.
[{{cite journal , title=Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 , journal=Lancet , volume= 392, issue= 10152, pages= 1015–1035, date=August 2018 , pmid=30146330 , pmc=6148333 , doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31310-2 , author1=GBD 2016 Alcohol Collaborators ] Some studies have concluded that drinking small quantities of alcohol (less than one drink per day in women and two in men) is associated with a ''decreased'' risk of
heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
,
stroke
A stroke is a disease, medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorr ...
,
diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, and early death.
[{{cite journal , last1=O'Keefe , first1=JH , last2=Bhatti , first2=SK, last3=Bajwa, first3=A, last4=DiNicolantonio, first4=JJ, last5=Lavie, first5=CJ, title=Alcohol and cardiovascular health: the dose makes the poison...or the remedy., journal=Mayo Clinic Proceedings, date=March 2014, volume=89, issue=3, pages=382–393, pmid=24582196, doi=10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.11.005] These studies, however, have been replaced by newer studies indicating that even light consumption of alcohol does not improve overall health.
Some of these studies lumped former ethanol drinkers and life-long abstainers into a single group of nondrinkers, hiding the health benefits of life-long abstention from ethanol. Drinking more than this amount actually increases the risk of heart disease,
high blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
,
atrial fibrillation, and
stroke
A stroke is a disease, medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorr ...
.
Risk is greater in younger people due to
binge drinking
Binge drinking, or heavy episodic drinking, is drinking alcoholic beverages with an intention of becoming intoxicated by heavy consumption of alcohol over a short period of time, but definitions ( see below) vary considerably.
Binge drinking i ...
which may result in violence or accidents.
About 3.3 million deaths (5.9% of all deaths) are believed to be due to alcohol each year.
[{{cite web, title=Alcohol Facts and Statistics, url=http://www.niaaa.nih.gov/alcohol-health/overview-alcohol-consumption/alcohol-facts-and-statistics , date=2018, website=National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism , access-date=5 April 2019]
Maximum quantity recommended
{{Further, Recommended maximum intake of alcoholic beverages
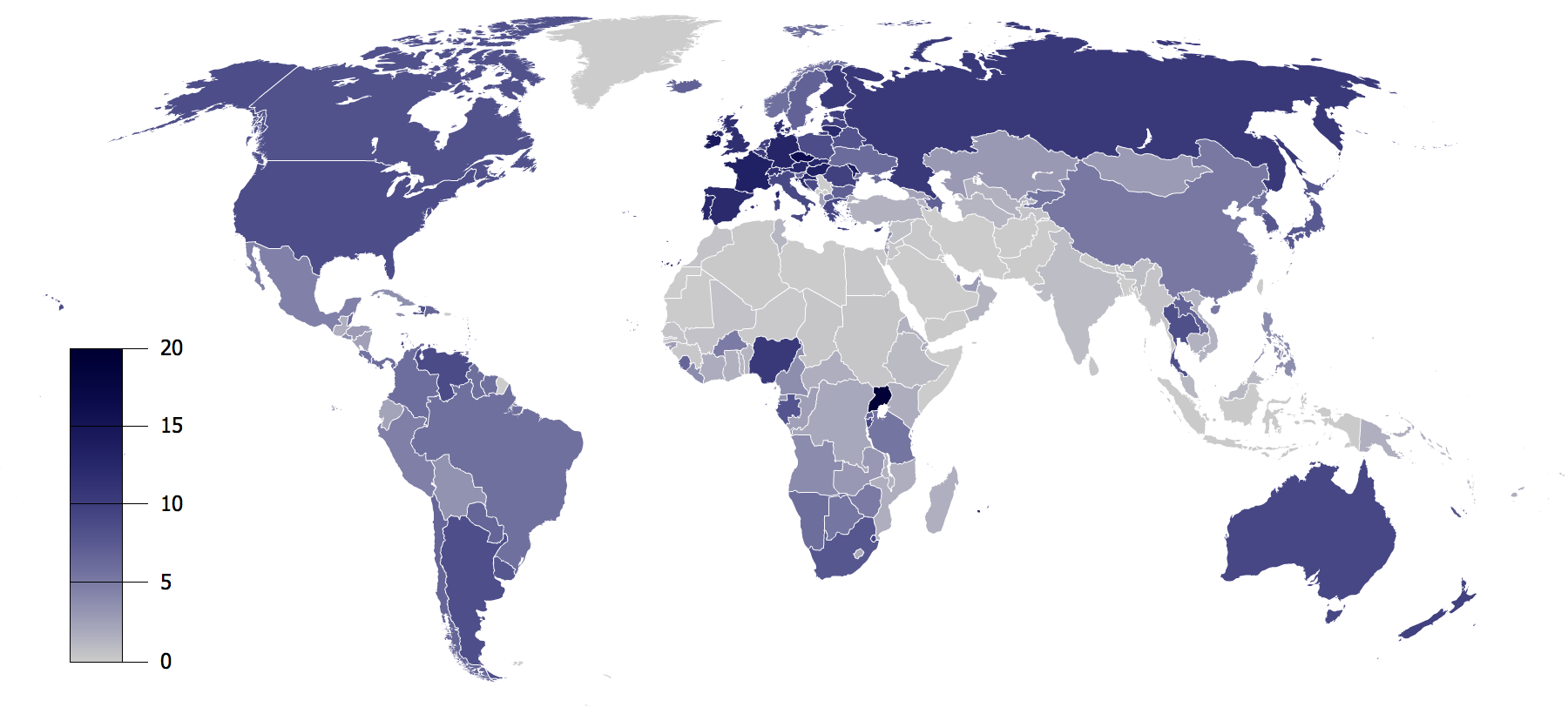
Different countries recommend different maximum quantities. In the UK, the
Chief Medical Officers' recommends men and women drink no more than 14
units per week. A single unit corresponds to 8 g of ethanol. For most countries, the maximum quantity for men is 140 g–210 g per week. For women, the range is 84 g–140 g per week.{{citation needed, date=January 2013 Most countries recommend total abstinence during pregnancy and
lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The proces ...
.
Contradictory large-scale reviews were published in ''
The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823.
The journal publishes original research articles ...
'' in 2018. One reported a "safe" drinking limit of up to seven "standard" drinks per week, equivalent to 100 grams of pure alcohol per week.
[{{Cite journal, vauthors=Wood AM, Kaptoge S, Butterworth AS, Willeit P, et al , date=2018-04-14, title=Risk thresholds for alcohol consumption: combined analysis of individual-participant data for 599 912 current drinkers in 83 prospective studies, url= , journal=The Lancet, language=en, volume=391, issue=10129, pages=1513–1523, doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30134-X, pmid=29676281, pmc=5899998, issn=0140-6736] The other concluded that there is no safe level of alcohol, that "the level of consumption that minimises health loss is zero" and emphasized the need to revise alcohol control policies worldwide in order to reduce overall alcohol consumption.
Alcohol-related death

Over-consumption of alcohol causes many deaths worldwide. The overall mortality from alcohol use was found to be similar to that of the effect of physical inactivity. A review in 2009 found that "the net effect of alcohol consumption on health is detrimental, with an estimated 3.8% of all global deaths and 4.6% of global disability-adjusted life-years attributable to alcohol."
Extensive research of Western cultures has consistently shown increased survival associated with light to moderate alcohol consumption.
A 23-year
prospective study
A prospective cohort study is a longitudinal cohort study that follows over time a group of similar individuals (cohorts) who differ with respect to certain factors under study, to determine how these factors affect rates of a certain outcome. ...
of 12,000 male
British physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
s aged 48–78, found that overall mortality was significantly lower in current drinkers compared to non-drinkers even after correction for ex-drinkers. This benefit was strongest for ischemic heart disease, but was also noted for other vascular disease and respiratory disease. Death rate amongst current drinkers was higher for 'alcohol augmentable' disease such as liver disease and oral cancers, but these deaths were much less common than cardiovascular and respiratory deaths. The lowest mortality rate was found for consumption of 8 to 14 'units' per week. In the UK a unit is defined as 10ml or 8g of pure alcohol. Higher consumption increased overall mortality rate, but not above that of non-drinkers.
[{{cite journal, vauthors=Doll R, Peto R, Boreham J, Sutherland I , title=Mortality in relation to alcohol consumption: a prospective study among male British doctors, journal=Int J Epidemiol, volume=34, issue=1, pages=199–204, date=February 2005, pmid=15647313, doi=10.1093/ije/dyh369] Other studies have found age-dependent mortality risks of low-to-moderate alcohol use: an increased risk for individuals aged 16–34 (due to increased risk of cancers, accidents, liver disease, and other factors), but a decreased risk for individuals ages 55+ (due to lower incidence of ischemic heart disease).
This is consistent with other research that found a J-curve dependency between alcohol consumption and total mortality among middle aged and older men. While the mortality rates of ex-drinkers and heavy drinkers are significantly elevated, the all-cause mortality rates may be 15–18% lower among moderate drinkers. Although the definition of a
drink
A drink or beverage is a liquid intended for human consumption. In addition to their basic function of satisfying thirst, drinks play important roles in human culture. Common types of drinks include plain drinking water, milk, juice, smoothies ...
varies between studies and countries, this meta-analysis found that low levels of alcohol intake, defined as 1–2 drinks per day for women and 2–4 drinks per day for men, was associated with lower mortality than abstainers.
[{{Cite journal, last1=Di Castelnuovo, first1=A., last2=Costanzo, first2=S., last3=Bagnardi, first3=V., last4=Donati, first4=MB., last5=Iacoviello, first5=L., last6=de Gaetano, first6=G., title=Alcohol dosing and total mortality in men and women: an updated meta-analysis of 34 prospective studies, journal=Arch Intern Med, volume=166, issue=22, pages=2437–45, doi=10.1001/archinte.166.22.2437, pmid=17159008, year=2006] This claim was challenged by another study
[{{Cite journal, last1=Fillmore, first1=KM., last2=Stockwell, first2=T., last3=Chikritzhs, first3=T., last4=Bostrom, first4=A., last5=Kerr, first5=W., title=Moderate alcohol use and reduced mortality risk: systematic error in prospective studies and new hypotheses, journal=Ann Epidemiol, volume=17, issue=5 Suppl, pages=S16–23, date=May 2007, doi=10.1016/j.annepidem.2007.01.005, pmid=17478320][{{Cite journal, last1=Chikritzhs, first1=T., last2=Fillmore, first2=K., last3=Stockwell, first3=T., title=A healthy dose of scepticism: four good reasons to think again about protective effects of alcohol on coronary heart disease, journal=Drug Alcohol Rev, volume=28, issue=4, pages=441–4, date=Jul 2009, doi=10.1111/j.1465-3362.2009.00052.x, pmid=19594799, hdl=20.500.11937/8299] that found that in certain low quality studies occasional drinkers or ex-drinkers were included as abstainers, resulting in the increased mortality in that group. However, the J-curve for total and CHD mortality was reconfirmed by studies that took the mentioned confounders into account.
[{{cite journal , author1=Klatsky Arthur L. , author2=Udaltsova Natalia , year = 2007 , title = Alcohol Drinking and Total Mortality Risk , journal = Ann Epidemiol , volume = 17 , issue = 5, page = 555 , doi=10.1016/j.annepidem.2007.01.014 ][{{Cite journal, last1=Lee, first1=SJ., last2=Sudore, first2=RL., last3=Williams, first3=BA., last4=Lindquist, first4=K., last5=Chen, first5=HL., last6=Covinsky, first6=KE., title=Functional limitations, socioeconomic status, and all-cause mortality in moderate alcohol drinkers, journal=J Am Geriatr Soc, volume=57, issue=6, pages=955–62, date=Jun 2009, doi=10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02184.x, pmid=19473456, pmc=2847409][{{Cite journal, last1=Arriola, first1=L., last2=Martinez-Camblor, first2=P., last3=Larrañaga, first3=N., last4=Basterretxea, first4=M., last5=Amiano, first5=P., last6=Moreno-Iribas, first6=C., last7=Carracedo, first7=R., last8=Agudo, first8=A., last9=Ardanaz, first9=E., title=Alcohol intake and the risk of coronary heart disease in the Spanish EPIC cohort study, journal=Heart, volume=96, issue=2, pages=124–30, date=Jan 2010, doi=10.1136/hrt.2009.173419, pmid=19933099, s2cid=10125924][{{Cite journal, last1=Holahan, first1=CJ., last2=Schutte, first2=KK., last3=Brennan, first3=PL., last4=Holahan, first4=CK., last5=Moos, first5=BS., last6=Moos, first6=RH., title=Late-life alcohol consumption and 20-year mortality, journal=Alcohol Clin Exp Res, volume=34, issue=11, pages=1961–71, date=Nov 2010, doi=10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01286.x, pmid=20735372] There seems to be little discussion of what proportion of individuals classified as abstainers are those already at greater risk of mortality due to chronic conditions and do not or cannot consume alcohol for reasons of health or harmful interactions with medication.
The observed decrease in mortality of light-to-moderate drinkers compared to never drinkers might be partially explained by superior health and social status of the drinking group;
[{{Cite journal, last1=Hansel, first1=B., last2=Thomas, first2=F., last3=Pannier, first3=B., last4=Bean, first4=K., last5=Kontush, first5=A., last6=Chapman, first6=MJ., last7=Guize, first7=L., last8=Bruckert, first8=E., title=Relationship between alcohol intake, health and social status and cardiovascular risk factors in the urban Paris-Ile-De-France Cohort: is the cardioprotective action of alcohol a myth?, journal=Eur J Clin Nutr, volume=64, issue=6, pages=561–8, date=Jun 2010, doi=10.1038/ejcn.2010.61, pmid=20485310, s2cid=4488107, url=https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00537677/file/PEER_stage2_10.1038%252Fejcn.2010.61.pdf ] however, the protective effect of alcohol in light to moderate drinkers remains significant even after adjusting for these confounders.
Additionally, confounders such as underreporting of alcohol intake might lead to the underestimation of how much mortality is reduced in light-to-moderate drinkers.
[{{Cite journal, last1=Klatsky, first1=AL., title=Invited commentary: never, or hardly ever? It could make a difference, journal=Am J Epidemiol, volume=168, issue=8, pages=872–5; discussion 876–7, date=Oct 2008, doi=10.1093/aje/kwn192, pmid=18701441]
A 2010 study confirmed the beneficial effect of moderate alcohol consumption on mortality.
Subjects were grouped into abstainers, light, moderate, and heavy drinkers. The order of mortality rates from lowest to highest were moderate, light, heavy, and abstainers. The increased risk for abstainers was twice the mortality rate as for moderate drinkers. This study specifically sought to control for confounding factors including the problem of ex-drinkers considered as non-drinkers.
According to another study, drinkers with heavy drinking occasions (six or more drinks at a time) have a 57% higher all-cause mortality than drinkers without heavy drinking occasions.
[{{Cite journal, last1=Laatikainen, first1=T., last2=Manninen, first2=L., last3=Poikolainen, first3=K., last4=Vartiainen, first4=E., title=Increased mortality related to heavy alcohol intake pattern, journal=J Epidemiol Community Health, volume=57, issue=5, pages=379–84, date=May 2003, pmid=12700224, pmc=1732462, doi=10.1136/jech.57.5.379]
Mortality is lowest among young abstainers and highest among young heavy drinkers.
According to a 2018 study people who had more than seven and up to 14 standard drinks per week, were likely to have their life expectancy shortened by around 6 months. Those who consumed over 14 drinks and up to 25 per week were likely to have 1–2 years taken off their lifespan, and a consumption of over 25 standard drinks per week correlated with 4–5 fewer years.
In contrast to studies of Western cultures, research in other cultures has yielded some opposite findings. The landmark INTERHEART Study has revealed that alcohol consumption in South Asians was not protective against CAD in sharp contrast to other populations who benefit from it.
[{{cite journal, author1=Joshi, Prashant, author2=Islam, Shofiqul, author3=Pais, Prem, author4=Reddy, Srinath, author5=Dorairaj, Prabhakaran, author6=Kazmi, Khawar, author7=Pandey, Mrigendra Raj, author8=Haque, Sirajul, author9=Mendis, Shanthi, author10=Rangarajan, Sumathy, author11=Yusuf, Salim, title=Risk Factors for Early Myocardial Infarction in South Asians Compared With Individuals in Other Countries, journal=JAMA, date=17 January 2007, volume=297, issue=3, pages=286–294, pmid=17227980, doi=10.1001/jama.297.3.286] In fact Asian Indians who consume alcohol had a 60% higher risk of heart attack which was greater with local spirits (80%) than branded spirits (50%).
[{{cite journal, author1=Roy, A., author2=Prabhakaran, D., author3=Jeemon, P., author4=Thankappan, K.R., author5=Mohan, V., author6=Ramakrishnan, L., author7=Joshi, P., author8=Ahmed, F., author9=Mohan, B.V., author10=Saran, R.K., author11=Sinha, N., author12=Reddy, K.S., title=Impact of alcohol on coronary heart disease in Indian men, journal=Atherosclerosis, date=26 February 2010, volume=210, issue=2, pages=531–535, pmid=20226461, doi=10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.02.033] The harm was observed in alcohol users classified as occasional as well as regular light, moderate, and heavy consumers.
Another large study of 4465 subjects in India also confirmed the possible harm of alcohol consumption on coronary risk in men. Compared to lifetime abstainers, alcohol users had higher blood sugar (2 mg/dl), blood pressure (2 mm Hg) levels, and the HDL-C levels (2 mg/dl) and significantly higher tobacco use (63% vs. 21%).
[
]
Russia
{{Main, Alcoholism in Russia
One study claims that "excessive alcohol consumption in Russia, particularly by men, has in recent years caused more than half of all the deaths at ages 15–54 years." However, there are some difficulties with this study. For instance, the same study also found a protective effect of heavy drinking on breast cancer mortality. This contradicts the well established scientific view that alcohol increases breast cancer risk.[{{Cite journal, last1=Tjønneland, first1=A., last2=Christensen, first2=J., last3=Olsen, first3=A., last4=Stripp, first4=C., last5=Thomsen, first5=BL., last6=Overvad, first6=K., last7=Peeters, first7=PH., last8=van Gils, first8=CH., last9=Bueno-de-Mesquita, first9=HB., display-authors = 8, title=Alcohol intake and breast cancer risk: the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC), journal=Cancer Causes Control, volume=18, issue=4, pages=361–73, date=May 2007, doi=10.1007/s10552-006-0112-9, pmid=17364225, s2cid=21762284] On this account in further correspondence it was advised that "careful interpretation of mortality statistics in relation to alcohol use is needed, taking into account other relevant risk factors, incidence, and survival."[{{Cite journal, last1=Soerjomataram, first1=I., last2=de Vries, first2=E., last3=Coebergh, first3=JW., title=Did alcohol protect against death from breast cancer in Russia?, journal=Lancet, volume=374, issue=9694, pages=975; author reply 975–6, date=Sep 2009, doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61657-3, pmid=19766875, s2cid=46431359]
United Kingdom
A governmental report from Britain has found that "There were 8,724 alcohol-related deaths in 2007, lower than 2006, but more than double the 4,144 recorded in 1991. The alcohol-related death rate was 13.3 per 100,000 population in 2007, compared with 6.9 per 100,000 population in 1991." In Scotland, the NHS estimate that in 2003 one in every 20 deaths could be attributed to alcohol. A 2009 report noted that the death rate from alcohol-related disease was 9,000, a number three times that of 25 years previously.
A UK report came to the result that the effects of low-to-moderate alcohol consumption on mortality are age-dependent. Low-to-moderate alcohol use increases the risk of death for individuals aged 16–34 (due to increased risk of cancers, accidents, liver disease, and other factors), but decreases the risk of death for individuals ages 55+ (due to decreased risk of ischemic heart disease).
A study in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
found that alcohol causes about 4% of cancer cases in the UK (12,500 cases per year).[{{cite web, title=Alcohol and cancer , url=http://info.cancerresearchuk.org/healthyliving/alcohol/ , publisher=]Cancer Research UK
Cancer Research UK (CRUK) is the world's largest independent cancer research organization. It is registered as a charity in the United Kingdom and Isle of Man, and was formed on 4 February 2002 by the merger of The Cancer Research Campaign and t ...
, date=2013-08-22
United States
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georg ...
(CDC) report, "From 2001–2005, there were approximately 79,000 deaths annually attributable to excessive alcohol use. In fact, excessive alcohol use is the 3rd leading lifestyle-related cause of death for people in the United States each year." A 1993 study estimated US deaths through alcohol at 100,000.
Another CDC report from 2001 estimated that medium and high consumption of alcohol led to 75,754 deaths in the United States in 2001. Low consumption of alcohol had some beneficial effects, so a net 59,180 deaths were attributed to alcohol.
Longevity
In 2016, a meta-analysis of 87 studies investigating alcohol use and mortality risk was conducted. The studies analyzed had shown the largest mortality risk reduction in moderate drinkers, but these studies did not correct for confounding variables common with certain abstainers, such as previous alcoholism, and chronic health issues. After adjusting these studies for abstainer biases, no reduction in mortality risk was found for low-volume drinkers. However, there have been individual studies that show abstainers and heavy drinkers have an increased mortality of about 50% over moderate drinkers after adjustment for confounding factors in individuals above the age of 55.
Cardiovascular system
{{main, Alcohol and cardiovascular disease
Alcohol has been found to have anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where t ...
properties.[{{cite journal, vauthors=Mennen LI, Balkau B, Vol S, Cacès E, Eschwège E , title=Fibrinogen: a possible link between alcohol consumption and cardiovascular disease? DESIR Study Group, journal=Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, volume=19, issue=4, pages=887–892, date=1999, pmid=10195914 , url=http://atvb.ahajournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10195914, doi=10.1161/01.atv.19.4.887] Thrombosis
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (th ...
is lower among moderate drinkers than abstainers. A meta-analysis of randomized trials found that alcohol consumption in moderation decreases serum levels of fibrinogen, a protein that promotes clot formation, while it increases levels of tissue type plasminogen activator, an enzyme that helps dissolve clots. These changes were estimated to reduce coronary heart disease risk by about 24%. Another meta-analysis in 2011 found favorable changes in HDL cholesterol, adiponectin, and fibrinogen associated with moderate alcohol consumption. A systematic review based on 16,351 participants showed J-shaped curve for the overall relationship between cardiovascular mortality and alcohol intake. Maximal protective effect was shown with 5–10 g of alcohol consumption per day and the effect was significant up to 26 g/day alcohol consumption. Serum levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a putative marker of inflammation and predictor of CHD (coronary heart disease) risk, are lower in moderate drinkers than in those who abstain from alcohol, suggesting that alcohol consumption in moderation might have anti-inflammatory effects.[{{Cite journal, last1=Albert, first1=MA, last2=Glynn, first2=RJ, last3=Ridker, first3=PM, title=Alcohol consumption and plasma concentration of C-reactive protein, journal=Circulation, volume=107, issue=3, pages=443–447, date=2003, doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000045669.16499.EC, pmid=12551869, s2cid=323583][{{Cite journal, last1=Stewart, first1=SH, last2=Mainous, first2=AG, last3=Gilbert, first3=G, title=Relation between alcohol consumption and C-reactive protein levels in the adult US population, url=http://www.jabfm.org/cgi/reprint/15/6/437.pdf, journal=J Am Board Fam Pract, volume=15, issue=6, pages=437–442, year=2002, pmid=12463288][{{Cite journal, last1=Imhof, first1=A, last2=Froehlich, first2=M, last3=Brenner, first3=H, last4=Boeing, first4=H, last5=Pepys, first5=MB, last6=Koenig, first6=W., title=Effect of alcohol consumption on systemic markers of inflammation, journal=Lancet, volume=357, issue=9258, pages=763–767, date=2001, doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04170-2, pmid=11253971, s2cid=8046780] Data from one prospective study suggest that, among men with initially low alcohol consumption ({{cite journal , vauthors=Sesso HD, Stampfer MJ, Rosner B, Hennekens CH, Manson JE, Gaziano JM , title=Seven-Year Changes in Alcohol Consumption and Subsequent Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Men , journal=Arch Intern Med , volume=160 , issue=17 , pages=2605–2612 , year=2000 , doi=10.1001/archinte.160.17.2605 , pmid=10999974
Despite epidemiological evidence, many have cautioned against recommendations for the use of alcohol for health benefits. A physician from the
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
labeled such alcohol promotion as "ridiculous and dangerous". One reviewer noted, "Despite the wealth of observational data, it is not absolutely clear that alcohol reduces cardiovascular risk, because no randomized controlled trials have been performed. Alcohol should never be recommended to patients to reduce cardiovascular risk as a substitute for the well-proven alternatives of appropriate diet, exercise, and drugs."
[{{Cite journal, last1=Vogel, first1=RA, title=Alcohol, heart disease, and mortality: a review., journal=Rev Cardiovasc Med, volume=3, issue=1, pages=7–13, year=2002, pmid=12439349] It has been argued that the health benefits from alcohol are at best debatable and may have been exaggerated by the
alcohol industry, with investigators holding that alcohol should be regarded as a recreational drug with potentially serious adverse effects on health and should not be promoted for cardio-protection.
Peripheral arterial disease
A prospective study published in 1997 found "moderate alcohol consumption appears to decrease the risk of PAD in apparently healthy men." In a large population-based study, moderate alcohol consumption was inversely associated with peripheral arterial disease in women but not in men. But when confounding by smoking was considered, the benefit extended to men. The study concluded "an inverse association between alcohol consumption and peripheral arterial disease was found in nonsmoking men and women."
Intermittent claudication
A study found that moderate consumption of alcohol had a protective effect against
intermittent claudication
Intermittent claudication, also known as vascular claudication, is a symptom that describes muscle pain on mild exertion (ache, cramp, numbness or sense of fatigue), classically in the calf muscle, which occurs during exercise, such as walking, an ...
. The lowest risk was seen in men who drank 1 to 2 drinks per day and in women who drank half to 1 drink per day.
Heart attack and stroke
Drinking in moderation has been found to help those who have had a
heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
survive it. However, excessive alcohol consumption leads to an increased risk of
heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
. A review of the literature found that half a drink of alcohol offered the best level of protection. However, they noted that at present there have been no randomised trials to confirm the evidence which suggests a protective role of low doses of alcohol against heart attacks. There is an increased risk of
hypertriglyceridemia
Hypertriglyceridemia is the presence of high amounts of triglycerides in the blood. Triglycerides are the most abundant fatty molecule in most organisms. Hypertriglyceridemia occurs in various physiologic conditions and in various diseases, and ...
,
cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. ...
,
hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high b ...
, and
stroke
A stroke is a disease, medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorr ...
if three or more
standard drinks of alcohol are taken per day. A systematic review reported that reducing alcohol intake lowers blood pressure in a dose-dependent manner in heavy drinkers. For people who drank two or fewer drinks per day, no difference was found.
Cardiomyopathy
Large amount of alcohol over the long term can lead to alcoholic
cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. ...
. Alcoholic cardiomyopathy presents in a manner clinically identical to idiopathic
dilated cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Co ...
, involving hypertrophy of the musculature of the heart that can lead to congestive heart failure.
[{{Cite journal , last1=Awtry, first1=EH , last2=Philippides , first2=GJ, title=Alcoholic and cocaine-associated cardiomyopathies., journal=Prog Cardiovasc Dis, volume=52, issue=4, pages=289–299, year=2010 , doi=10.1016/j.pcad.2009.11.004, pmid=20109599]
Hematologic diseases
Alcoholics may have
anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
from several causes; they may also develop
thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients a ...
from direct toxic effect on
megakaryocytes, or from
hypersplenism.
Atrial fibrillation
Alcohol consumption increases the risk of
atrial fibrillation, a type of abnormal heart rhythm. This remains true even at moderate levels of consumption.
Nervous system

Chronic heavy alcohol consumption impairs brain development, causes
alcohol dementia
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
,
brain shrinkage
Neurotrauma, brain damage or brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating t ...
,
physical dependence
Physical dependence is a physical condition caused by chronic use of a tolerance-forming drug, in which abrupt or gradual drug withdrawal causes unpleasant physical symptoms. Physical dependence can develop from low-dose therapeutic use of certai ...
,
alcoholic polyneuropathy
Alcoholic polyneuropathy is a neurological disorder in which peripheral nerves throughout the body malfunction simultaneously. It is defined by axonal degeneration in neurons of both the sensory and motor systems and initially occurs at the dista ...
(also known as 'alcohol leg'), increases neuropsychiatric and cognitive disorders and causes distortion of the
brain chemistry
Neurochemistry is the study of chemicals, including neurotransmitters and other molecules such as psychopharmaceuticals and neuropeptides, that control and influence the physiology of the nervous system. This particular field within neuroscience e ...
. At present, due to poor study design and methodology, the literature is inconclusive on whether moderate alcohol consumption increases the risk of dementia or decreases it. Evidence for a protective effect of low to moderate alcohol consumption on age-related cognitive decline and dementia has been suggested by some research; however, other research has not found a protective effect of low to moderate alcohol consumption.
[{{Cite journal, last1=Panza, first1=F., last2=Capurso, first2=C., last3=D'Introno, first3=A., last4=Colacicco, first4=AM., last5=Frisardi, first5=V.
, last6=Lorusso, first6=M., last7=Santamato, first7=A., last8=Seripa, first8=D., last9=Pilotto, first9=A., display-authors = 8, title=Alcohol drinking, cognitive functions in older age, predementia, and dementia syndromes., journal=J Alzheimers Dis, volume=17, issue=1, pages=7–31, date=May 2009, doi=10.3233/JAD-2009-1009, pmid=19494429] Some evidence suggests that low to moderate alcohol consumption may speed up brain volume loss.
[{{Cite journal, last1=Verbaten, first1=MN., title=Chronic effects of low to moderate alcohol consumption on structural and functional properties of the brain: beneficial or not?, journal=Hum Psychopharmacol, volume=24, issue=3, pages=199–205, date=Apr 2009, doi=10.1002/hup.1022, pmid=19330800, s2cid=205924421] Chronic consumption of alcohol may result in increased plasma levels of the toxic amino acid
homocysteine
Homocysteine is a non-proteinogenic α-amino acid. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene bridge (-CH2-). It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group. In th ...
; which may explain alcohol withdrawal seizures, alcohol-induced brain atrophy and alcohol-related cognitive disturbances. Alcohol's impact on the nervous system can also include disruptions of
memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remember ...
and
learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of lea ...
(''see
Effects of alcohol on memory
Ethanol is the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages. It is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid that acts as a central nervous system depressant. Ethanol can impair different types of memory.
Mode of actions
Effects on the hippoca ...
''), such as resulting in a
blackout phenomenon.
Strokes
Epidemiological studies of middle-aged populations generally find the relationship between alcohol intake and the risk of stroke to be either U- or J-shaped.
[{{Cite journal, last1=Di Castelnuovo, first1=A., last2=Costanzo, first2=S., last3=di Giuseppe, first3=R., last4=de Gaetano, first4=G., last5=Iacoviello, first5=L., title=Alcohol consumption and cardiovascular risk: mechanisms of action and epidemiologic perspectives., journal=Future Cardiol, volume=5, issue=5, pages=467–77, date=Sep 2009, doi=10.2217/fca.09.36, pmid=19715411][{{Cite journal, last1=Klatsky, first1=AL., title=Alcohol and cardiovascular diseases., journal=Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther, volume=7, issue=5, pages=499–506, date=May 2009, doi=10.1586/erc.09.22, pmid=19419257, s2cid=23782870][{{Cite journal, last1=Galimanis, first1=A., last2=Mono, first2=ML., last3=Arnold, first3=M., last4=Nedeltchev, first4=K., last5=Mattle, first5=HP., title=Lifestyle and stroke risk: a review., journal=Current Opinion in Neurology, volume=22, issue=1, pages=60–8, date=Feb 2009, doi=10.1097/WCO.0b013e32831fda0e, pmid=19155763, s2cid=22619761][{{Cite journal, last1=O'Keefe, first1=JH., last2=Bybee, first2=KA., last3=Lavie, first3=CJ., title=Alcohol and cardiovascular health: the razor-sharp double-edged sword, journal=J Am Coll Cardiol, volume=50, issue=11, pages=1009–14, date=Sep 2007, doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2007.04.089, pmid=17825708, s2cid=42462804 ] There may be very different effects of alcohol based on the type of stroke studied. The predominant form of stroke in Western cultures is ischemic, whereas non-western cultures have more hemorrhagic stroke. In contrast to the beneficial effect of alcohol on ischemic stroke, consumption of more than two drinks per day increases the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. The National Stroke Association estimates this higher amount of alcohol increases stroke risk by 50%. "For stroke, the observed relationship between alcohol consumption and risk in a given population depends on the proportion of strokes that are hemorrhagic. Light-to-moderate alcohol intake is associated with a lower risk of ischemic stroke which is likely to be, in part, causal. Hemorrhagic stroke, on the other hand, displays a
log-linear relationship with alcohol intake."
[{{Cite journal, last1=Emberson, first1=JR., last2=Bennett, first2=DA., title=Effect of alcohol on risk of coronary heart disease and stroke: causality, bias, or a bit of both?, journal=Vasc Health Risk Manag, volume=2, issue=3, pages=239–49, year=2006, pmid=17326330, pmc=1993990, doi=10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.3.239]
Brain
{{main, Long-term impact of alcohol on the brain
Alcohol misuse is associated with widespread and significant brain
lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classif ...
s. Alcohol related brain damage is not only due to the direct toxic effects of alcohol; alcohol withdrawal, nutritional deficiency, electrolyte disturbances, and liver damage are also believed to contribute to alcohol-related brain damage.
[{{Cite journal, doi=10.1111/j.1530-0277.1998.tb04389.x, last1=Neiman, first1=J., title=Alcohol as a risk factor for brain damage: neurologic aspects, journal=Alcohol Clin Exp Res, volume=22, issue=7 Suppl, pages=346S–351S, date=Oct 1998, pmid=9799959]
Cognition and dementia
Excessive alcohol intake is associated with impaired
prospective memory Prospective memory is a form of memory that involves remembering to perform a planned action or recall a planned intention at some future point in time.McDaniel, M. A., & Einstein, G. O. (2007). ''Prospective memory: An overview and synthesis of an ...
. This impaired cognitive ability leads to increased failure to carry out an intended task at a later date, for example, forgetting to lock the door or to post a letter on time. The higher the volume of alcohol consumed and the longer consumed, the more severe the impairments.
[{{Cite journal, doi=10.2174/1874473710801010036, last1=Heffernan, first1=TM, title=The impact of excessive alcohol use on prospective memory: a brief review., journal=Curr Drug Abuse Rev, volume=1, issue=1, pages=36–41, date=2008, pmid=19630703] One of the organs most sensitive to the toxic effects of chronic alcohol consumption is the brain. In the United States approximately 20% of admissions to mental health facilities are related to alcohol-related cognitive impairment, most notably alcohol-related dementia. Chronic excessive alcohol intake is also associated with serious cognitive decline and a range of neuropsychiatric complications. The elderly are the most sensitive to the toxic effects of alcohol on the brain. There is some inconclusive evidence that small amounts of alcohol taken in earlier adult life is protective in later life against cognitive decline and dementia. However, a study concluded, "Our findings suggest that, despite previous suggestions, moderate alcohol consumption does not protect older people from cognitive decline."
Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome
Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome (WKS) is the combined presence of Wernicke encephalopathy (WE) and Korsakoff syndrome. Due to the close relationship between these two disorders, people with either are usually diagnosed with WKS as a single syndrom ...
is a manifestation of
thiamine
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient, that cannot be made in the body. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thi ...
deficiency, usually as a secondary effect of alcohol misuse. The syndrome is a combined manifestation of two eponymous disorders,
Korsakoff's Psychosis and
Wernicke's encephalopathy. Wernicke's encephalopathy is the acute presentation of the syndrome and is characterised by a
confusion
In medicine, confusion is the quality or state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion" al state while Korsakoff's psychosis main
symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showi ...
s are
amnesia
Amnesia is a deficit in memory caused by brain damage or disease,Gazzaniga, M., Ivry, R., & Mangun, G. (2009) Cognitive Neuroscience: The biology of the mind. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. but it can also be caused temporarily by the use ...
and
executive dysfunction. "
Banana bag
A banana bag (or rally pack) is a bag of IV fluids containing vitamins and minerals. The bags typically contain thiamine, folic acid, and magnesium sulfate, and are usually used to correct nutritional deficiencies or chemical imbalances in the hu ...
s", intravenous fluid containers containing vitamins and minerals (bright yellow due to the vitamins), can be used to mitigate these outcomes.
[{{cite book, title=Principles of Psychopharmacology for Mental Health Professionals, author1=Jeffrey E Kelsey , author2=D Jeffrey Newport , author3=Charles B Nemeroff , name-list-style=amp , chapter=Alcohol Use Disorders, pages=196–197, publisher=Wiley-Interscience, year=2006, isbn= 978-0-471-79462-2]
Essential tremor
Essential tremor
Essential tremor (ET), also called benign tremor, familial tremor, and idiopathic tremor, is a medical condition characterized by involuntary rhythmic contractions and relaxations ( oscillations or twitching movements) of certain muscle groups in ...
s—or, in the case of essential tremors on a background of family history of essential tremors, familial tremors—can be temporarily relieved in up to two-thirds of patients by drinking small amounts of alcohol.
Ethanol is known to activate aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) and inhibit N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptors, which are both implicated in essential tremor pathology and could underlie the ameliorative effects. Additionally, the effects of ethanol have been studied in different animal essential tremor models. (For more details on this topic, see
Essential tremor
Essential tremor (ET), also called benign tremor, familial tremor, and idiopathic tremor, is a medical condition characterized by involuntary rhythmic contractions and relaxations ( oscillations or twitching movements) of certain muscle groups in ...
).
Sleep
{{main, Alcohol use and sleep
Chronic use of alcohol used to induce sleep can lead to
insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder in which people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, ...
: frequent moving between sleep stages occurs, with awakenings due to headaches and
diaphoresis. Stopping chronic alcohol misuse can also lead to profound disturbances of sleep with vivid dreams. Chronic alcohol misuse is associated with
NREM stage 3 and 4 sleep as well as suppression of
REM sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream ...
and REM sleep fragmentation. During withdrawal REM sleep is typically exaggerated as part of a
rebound effect.
[{{Cite book, last1=Lee-chiong, first1=Teofilo, title=Sleep Medicine: Essentials and Review, date=24 April 2008, publisher=Oxford University Press, USA, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=s1F_DEbRNMcC&pg=PT105, isbn=978-0-19-530659-0, page=105]
Mental health effects
High rates of
major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Intro ...
occur in heavy drinkers. Whether it is more true that major depressive disorder causes self-medicating alcohol use, or the increased incidence of the disorder in people with an alcohol use disorder is caused by the drinking, is not known though some evidence suggests drinking causes the disorder. Alcohol misuse is associated with a number of mental health disorders and alcoholics have a very high
suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and ...
rate. A study of people hospitalized for suicide attempts found that those who were alcoholics were 75 times more likely to go on to successfully commit suicide than non-alcoholic suicide attempts. In the general alcoholic population the increased risk of suicide compared to the general public is 5-20 times greater. About 15 percent of alcoholics commit suicide, the most common methods being overdosing and cutting/scratching. There are high rates of suicide attempts, self-harm, suicidal ideation, and self-harm ideation in people with substance dependence who have been hospitalized. Use of other illicit drugs is also associated with an increased risk of
suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and ...
. About 33 percent of suicides in the under 35s are correlated with alcohol or other substance misuse.
Social skills
A social skill is any competence facilitating interaction and communication with others where social rules and relations are created, communicated, and changed in verbal and nonverbal ways. The process of learning these skills is called soci ...
are significantly impaired in people that have alcoholism due to the neurotoxic effects of alcohol on the brain, especially the
prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA ...
area of the brain. The social skills that are impaired by
alcohol use disorder
Alcoholism is, broadly, any drinking of alcohol that results in significant mental or physical health problems. Because there is disagreement on the definition of the word ''alcoholism'', it is not a recognized diagnostic entity. Predomin ...
include impairments in perceiving facial emotions,
prosody perception problems and
theory of mind
In psychology, theory of mind refers to the capacity to understand other people by ascribing mental states to them (that is, surmising what is happening in their mind). This includes the knowledge that others' mental states may be different fro ...
deficits; the ability to understand humor is also impaired in people with an alcohol use disorder.
[{{cite journal, vauthors=Uekermann J, Daum I , title=Social cognition in alcoholism: a link to prefrontal cortex dysfunction?, journal=Addiction, volume=103, issue=5, pages=726–35, date=May 2008, pmid=18412750, doi=10.1111/j.1360-0443.2008.02157.x]
Studies have shown that alcohol dependence relates directly to
cravings and
irritability
Irritability (also called as crankiness) is the excitatory ability that living organisms have to respond to changes in their environment. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessi ...
. Another study has shown that alcohol use is a significant predisposing factor towards
antisocial behavior
Antisocial may refer to:
Sociology, psychiatry and psychology
* Anti-social behaviour
*Antisocial personality disorder
*Psychopathy
*Conduct disorder
Law
*Anti-social Behaviour Act 2003
*Anti-Social Behaviour Order
*Crime and Disorder Act 1998
* ...
in children.
[{{cite journal , vauthors=Young R, Sweeting H, West P , title=A longitudinal study of alcohol use and antisocial behaviour in young people , journal=Alcohol Alcohol. , volume=43 , issue=2 , pages=204–14 , year=2008 , pmid=17977868 , doi=10.1093/alcalc/agm147 , pmc=2367698] Depression, anxiety and panic disorder are disorders commonly reported by alcohol dependent people. Alcoholism is associated with dampened activation in brain networks responsible for emotional processing (''e.g.'' the
amygdala
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex ver ...
and
hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic syste ...
). Evidence that the mental health disorders are often induced by alcohol misuse via distortion of brain neurochemistry is indicated by the improvement or disappearance of symptoms that occurs after prolonged abstinence, although problems may worsen in early withdrawal and recovery periods. Psychosis is secondary to several alcohol-related conditions including acute intoxication and withdrawal after significant exposure.
[{{EMedicine, med, 3113, Alcohol-Related Psychosis] Chronic alcohol misuse can cause psychotic type symptoms to develop, more so than with other illicit substances. Alcohol misuse has been shown to cause an 800% increased risk of
psychotic disorder
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior ...
s in men and a 300% increased risk of psychotic disorders in women which are not related to pre-existing psychiatric disorders. This is significantly higher than the increased risk of psychotic disorders seen from cannabis use making alcohol misuse a very significant cause of psychotic disorders. Approximately 3 percent of people who are alcohol dependent experience psychosis during acute intoxication or withdrawal. Alcohol-related psychosis may manifest itself through a
kindling mechanism. The mechanism of alcohol-related psychosis is due to distortions to neuronal membranes,
gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. T ...
, as well as
thiamin
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient, that cannot be made in the body. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of t ...
deficiency. It is possible in some cases that excessive alcohol use, via a kindling mechanism, can cause the development of a chronic substance-induced psychotic disorder, i.e.
schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social w ...
. The effects of an alcohol-related psychosis include an increased risk of depression and suicide as well as psychosocial impairments.
[ However, moderate wine drinking has been shown to lower the risk for depression.
While ]alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
initially helps social phobia or panic symptoms, with longer term alcohol misuse can often worsen social phobia symptoms and can cause panic disorder to develop or worsen, during alcohol intoxication and especially during the alcohol withdrawal syndrome
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) is a set of symptoms that can occur following a reduction in alcohol use after a period of excessive use. Symptoms typically include anxiety, shakiness, sweating, vomiting, fast heart rate, and a mild fever. Mo ...
. This effect is not unique to alcohol but can also occur with long-term use of drugs which have a similar mechanism of action to alcohol such as the benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, ...
, which are sometimes prescribed as tranquilizers to people with alcohol problems. Approximately half of patients attending mental health services for conditions including anxiety disorders
Anxiety disorders are a cluster of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal function are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause physi ...
such as panic disorder
Panic disorder is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder characterized by reoccurring unexpected panic attacks. Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear that may include palpitations, sweating, shaking, short ...
or social phobia
Social anxiety disorder (SAD), also known as social phobia, is an anxiety disorder characterized by sentiments of fear and anxiety in social situations, causing considerable distress and impaired ability to function in at least some aspects o ...
have alcohol or benzodiazepine dependence
Benzodiazepine dependence defines a situation in which one has developed one or more of either tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, drug seeking behaviors, such as continued use despite harmful effects, and maladaptive pattern of substance use, accord ...
. It was noted that every individual has an individual sensitivity level to alcohol or sedative hypnotic drugs and what one person can tolerate without ill health another will have very ill health and that even moderate drinking can cause rebound anxiety
The rebound effect, or rebound phenomenon, is the emergence or re-emergence of symptoms that were either absent or controlled while taking a medication, but appear when that same medication is discontinued, or reduced in dosage. In the case of re ...
syndromes and sleep disorders. A person who is experiencing the toxic effects of alcohol will not benefit from other therapies or medications as they do not address the root cause of the symptoms.
Addiction to alcohol, as with any addictive substance tested so far, has been correlated with an enduring reduction in the expression of GLT1 ( EAAT2) in the nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hyp ...
and is implicated in the drug-seeking behavior expressed nearly universally across all documented addiction syndromes. This long-term dysregulation of glutamate transmission is associated with an increase in vulnerability to both relapse-events after re-exposure to drug-use triggers as well as an overall increase in the likelihood of developing addiction to other reinforcing drugs. Drugs which help to re-stabilize the glutamate system such as N-acetylcysteine have been proposed for the treatment of addiction to cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Am ...
, nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and '' Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is use ...
, and alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
.[{{cite journal , vauthors = McClure EA, Gipson CD, Malcolm RJ, Kalivas PW, Gray KM , title = Potential role of N-acetylcysteine in the management of substance use disorders , journal = CNS Drugs , volume = 28 , issue = 2 , pages = 95–106 , year = 2014 , pmid = 24442756 , pmc = 4009342 , doi = 10.1007/s40263-014-0142-x ]
The effect on depression and returning to drinking among individuals with alcohol dependence has always been controversial. Studies show that after doing a study on men and women hospitalized for alcohol dependence the likelihood of returning to drinking with depression is extremely high. A diagnosis of major depression at entry into an inpatient treatment for alcohol dependence showed shorter times to first drink and also relapse in both women and men.
Digestive system and weight gain
{{see also, Alcohol and weight, Alcoholic liver disease, Alcoholic hepatitis, Fatty liver, Cirrhosis
The impact of alcohol on weight-gain is contentious: some studies find no effect, others find decreased or increased effect on weight gain.
Alcohol use increases the risk of chronic gastritis
Gastritis is inflammation of the lining of the stomach. It may occur as a short episode or may be of a long duration. There may be no symptoms but, when symptoms are present, the most common is upper abdominal pain (see dyspepsia). Other possi ...
(stomach inflammation);[{{cite book, author=]National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), as part of the U.S. National Institutes of Health, supports and conducts biomedical and behavioural research on the causes, consequences, treatment, and prevention of alcoholism
...
(NIAAA), title=Health risks and benefits of alcohol consumption, journal=Alcohol Res Health, volume=24, issue=1, pages=5–11, year=2000, pmid=11199274, pmc=6713002, url=http://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/arh24-1/05-11.pdf, doi=10.4135/9781412963855.n839, isbn=9781412941860[{{cite journal, vauthors=Bode C, Bode JC, title=Alcohol's role in gastrointestinal tract disorders, journal=Alcohol Health Res World, volume=21, issue=1, pages=76–83, year=1997, pmid=15706765, pmc=6826790, url=https://webapps.ou.edu/alcohol/docs/12EtohGastroinstestinalTractDisorders76.pdf, url-status=dead, archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060902085657/https://webapps.ou.edu/alcohol/docs/12EtohGastroinstestinalTractDisorders76.pdf, archive-date=2006-09-02] it is one cause of cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
, hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes ( jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal ...
, and pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones. There are two main types: acute pancreatitis, and chronic p ...
in both its chronic and acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse ef ...
forms.
Metabolic syndrome
A national survey (NHANES) conducted in the U.S. concluded, "Mild to moderate alcohol consumption is associated with a lower prevalence of the metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndro ...
, with a favorable influence on lipids, waist circumference, and fasting insulin. This association was strongest among whites and among beer and wine drinkers." Similarly, a national survey conducted in Korea reported a J-curve association between alcohol intake and metabolic syndrome: "The results of the present study suggest that the metabolic syndrome is negatively associated with light alcohol consumption (1–15 g alcohol/d) in Korean adults," but risk increased at higher alcohol consumption.
Gallbladder effects
Research has found that drinking reduces the risk of developing gallstones
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of mi ...
. Compared with alcohol abstainers, the relative risk of gallstone disease, controlling for age, sex, education, smoking, and body mass index, is 0.83 for occasional and regular moderate drinkers (< 25 ml of ethanol per day), 0.67 for intermediate drinkers (25-50 ml per day), and 0.58 for heavy drinkers. This inverse association was consistent across strata of age, sex, and body mass index." Frequency of drinking also appears to be a factor. "An increase in frequency of alcohol consumption also was related to decreased risk. Combining the reports of quantity and frequency of alcohol intake, a consumption pattern that reflected frequent intake (5–7 days/week) of any given amount of alcohol was associated with a decreased risk, as compared with nondrinkers. In contrast, infrequent alcohol intake (1–2 days/week) showed no significant association with risk."
A large self-reported study published in 1998 found no correlation between gallbladder disease and multiple factors including smoking, alcohol consumption, hypertension, and coffee consumption. A retrospective study from 1997 found vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) ...
(ascorbic acid
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) ...
) supplement use in drinkers was associated with a lower prevalence of gallbladder disease, but this association was not seen in non-drinkers.
Liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also called alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), is a term that encompasses the liver manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with liver fibros ...
is a major public health problem. For example, in the United States up to two million people have alcohol-related liver disorders.[ Chronic heavy alcohol consumption can cause ]fatty liver
Fatty liver disease (FLD), also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Complica ...
, cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
, and alcoholic hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis (inflammation of the liver) due to excessive intake of alcohol. Patients typically have a history of at least 10 years of heavy alcohol intake, typically 8-10 drinks per day. It is usually found in association with ...
. Treatment options are limited and consist of most importantly discontinuing alcohol consumption. In cases of severe liver disease, the only treatment option may be a liver transplant from alcohol abstinent donors. Research is being conducted into the effectiveness of anti-TNF
A TNF inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that suppresses the physiologic response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which is part of the inflammatory response. TNF is involved in autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ...
s. Certain complementary medications, e.g., milk thistle and silymarin, appear to offer some benefit.[{{cite journal, vauthors=Barve A, Khan R, Marsano L, Ravindra KV, McClain C , title=Treatment of alcoholic liver disease, journal=Ann Hepatol, volume=7, issue=1, pages=5–15, year=2008, pmid=18376362, url=http://www.stopdrinkingexpert.com/pdf/ijms.pdf, doi=10.1016/S1665-2681(19)31883-6] Alcohol is a leading cause of liver cancer
Liver cancer (also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy) is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary (starts in liver) or secondary (meaning cancer which has spread from elsewhere to th ...
in the Western world, accounting for 32-45% of hepatic cancers. Up to half a million people in the United States develop alcohol-related liver cancer.
Pancreatitis
Alcohol misuse is a leading cause of both acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. Causes in order of frequency include: 1) a gallstone impacted in the common bile duct beyond the point where the pancreatic duct joins it; 2) heavy alcohol use; 3) systemic disea ...
and chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-standing inflammation of the pancreas that alters the organ's normal structure and functions. It can present as episodes of acute inflammation in a previously injured pancreas, or as chronic damage with persistent pa ...
. Alcoholic pancreatitis can result in severe abdominal pain and may progress to pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a mass. These cancerous cells have the ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of pancr ...
.
Chronic pancreatitis often results in intestinal malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a variety ...
, and can result in diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
.
Body composition
Alcohol affects the nutritional state of the chronic drinkers. It can decrease food consumption and lead to malabsorption. It can create imbalance in the skeletal muscle mass and cause muscle wasting. Chronic consumption alcohol can also increase breakdown of important proteins in our body which can affect gene expression.
Oral and dental implications
Fetal alcohol syndrome
The frequency, time, and amount of alcohol consumption during pregnancy can cause various dental anomalies in children with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS). Not only does it increase the chance of children developing cleft lip and palate, newborns will tend to show agenesis, maxillary overjet, crowded incisors, anterior open bite and diastemas. These dental and maxillofacial changes are thought to be caused by the teratogenic effects of alcohol on the fetus in which FAS causes an alteration in the MSX1 and MSX2 genes. Both genes play an important part in the maxillary process's fusion and odontogenic formation.{{citation needed, date=April 2022
Oral cancer
The consumption of alcohol alone is not associated with an increased risk of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC); however, the synergistic consumption of alcohol and tobacco is positively associated with the occurrence of (OSCC), and significantly increases an individual's risk. Studies confirm that alcohol dissolves the lipid component of epithelium and increases the permeability, amplifying the toxicity of carcinogenic components of tobacco. Limiting the overall consumption of the two has shown to reduce the risk of OSCC by three-fourth. The knowledge provided is useful for better understanding the differences in the effect of the combined consumption of alcohol and tobacco, in the development of OSCC.
Alcohol consumption has frequently been associated with an increased risk of oral cancer in current literature. Studies have found that people that consume alcohol were two times more likely to develop oral cancer in comparison to people who did not. The mechanisms in which alcohol acts as a carcinogen within the oral cavity are currently not fully understood. It is thought to be a multifactorial disease which then gives rise to a cancerous lesion. Many theories have become apparent in research, including alcohol being responsible for high estrogen and androgen levels, specifically in women, which may facilitate the alcohol-related immunodeficiency and/or immunosuppression that causes carcinogenesis. Therefore, immediate cessation of the habit of alcohol consumption can aid in decreasing the risk of oral cancer.
Alcohol-based mouthwashes used to be very common and can still be purchased for use today. Correlation in the presence of alcohol in mouthwashes with development of oral and pharyngeal cancer is unknown due to lack of evidence. However, it has been suggested that acetaldehyde, the first metabolite of ethanol, plays a role in the carcinogenesis of alcohol in oral cancer. Acetaldehyde, has been found to increase when in the salivary medium after an alcoholic beverage has been consumed and could possibly occur with alcohol-based mouthwashes as well, posing as a possible risk factor for oral cancer. However, more research must be conducted regarding these theories.
Periodontitis
Alcohol Consumption is associated with a higher risk of Periodontitis, an inflammatory disease of the gums around the teeth. There was also found to be a dose-response relationship in which the risk of periodontitis increased by 0.4% for each 1g/day in alcohol consumption. Mechanisms explaining the relationship between the two are still unclear however, several explanations have been suggested. One explanation is the weakening of neutrophil activity by alcohol consumption which potentially leads to bacterial overgrowth and increased bacterial penetration subsequently leading to periodontal inflammation and periodontal disease. Characteristics of the disease include shrinkage of gingival height and increased mobility of teeth which may exfoliate if the disease continues to progress. A patient's consumption of alcohol needs to be monitored to estimate the risk of periodontitis, but further well-designed cohort studies are needed to reaffirm theses results.
Cleft lip and palate
Various maternal behavioral factors have been known to increase the risk of oral clefts such as folate deficiency, antiepileptic drugs, smoking, and alcohol consumption. Even though alcohol is known to be a folic acid antagonist, there is no significant correlation between mild to moderate consumption of alcohol during pregnancy and the risk of oral clefts. However, as a baby's palate and lip develop during the first trimester of the pregnancy (first 12 weeks), mothers should be aware to avoid drinking during this time. Research on the correlation between heavy drinking and orofacial cleft is still necessary for confirmation.
Other systems
Respiratory system
Chronic alcohol ingestion can impair multiple critical cellular functions in the lungs. These cellular impairments can lead to increased susceptibility to serious complications from lung disease. Recent research cites alcoholic lung disease as comparable to liver disease in alcohol-related mortality. Alcoholics have a higher risk of developing acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin colo ...
(ARDS) and experience higher rates of mortality from ARDS when compared to non-alcoholics. In contrast to these findings, a large prospective study
A prospective cohort study is a longitudinal cohort study that follows over time a group of similar individuals (cohorts) who differ with respect to certain factors under study, to determine how these factors affect rates of a certain outcome. ...
has shown a protective effect of moderate alcohol consumption on respiratory mortality.
Kidney stones
Research indicates that drinking beer or wine is associated with a lower risk of developing kidney stones
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a calculus (medicine), solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the ...
.
Sexual function
{{Main, Alcohol and sex
Low to moderate alcohol consumption is shown to have protective effect for men's erectile function. Several reviews and meta-analyses
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting m ...
of existing literature show that low to moderate alcohol consumption significantly decrease erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also called impotence, is the type of sexual dysfunction in which the penis fails to become or stay erect during sexual activity. It is the most common sexual problem in men.Cunningham GR, Rosen RC. Overview of ma ...
risk.
Men's sexual behaviors can be affected dramatically by high alcohol consumption. Both chronic and acute alcohol consumption have been shown in most studies
(but not all) to inhibit testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
production in the testes. This is believed to be caused by the metabolism of alcohol reducing the NAD+/NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an aden ...
ratio both in the liver and the testes; since the synthesis of testosterone requires NAD+, this tends to reduce testosterone production.
Long term excessive intake of alcohol can lead to damage to the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
and the peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brai ...
resulting in loss of sexual desire and impotence in men. This is caused by reduction of testosterone from ethanol-induced testicular atrophy
Testicular atrophy is a medical condition in which one or both testicles (or "testes") diminish in size and may be accompanied by reduced testicular function. Testicular atrophy is not related to the temporary shrinkage of the surrounding scrotum, ...
, resulting in increased feminisation of males and is a clinical feature of alcohol abusing males who have cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
of the liver.[{{cite journal, vauthors=Yoshitsugu M, Ihori M , title=Endocrine disturbances in liver cirrhosis—focused on sex hormones, language=ja, journal=Nippon Rinsho, volume=55, issue=11, pages=3002–6, date=November 1997, pmid=9396303]
Hormonal imbalance
Excessive alcohol intake can result in hyperoestrogenisation. It has been speculated that alcoholic beverages may contain estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
-like compounds. In men, high levels of estrogen can lead to testicular
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosteron ...
failure and the development of feminine traits including development of male breasts, called gynecomastia
Gynecomastia (also spelled gynaecomastia) is the abnormal non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in males due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Updated by Brent Wisse ( ...
.[{{Cite journal, last1=Weiss, first1=JR., last2=Moysich, first2=KB., last3=Swede, first3=H., title=Epidemiology of male breast cancer, journal=Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, volume=14, issue=1, pages=20–6, date=Jan 2005, doi=10.1158/1055-9965.20.14.1 , url=http://cebp.aacrjournals.org/content/14/1/20.long, pmid=15668471, s2cid=9667914 ] In women, increased levels of estrogen due to excessive alcohol intake have been related to an increased risk of breast cancer.
Diabetes mellitus
A meta-analysis determined the dose-response relationships by sex and end point using lifetime abstainers as the reference group. A U-shaped relationship was found for both sexes. Compared with lifetime abstainers, the relative risk (RR) for type 2 diabetes among men was most protective when consuming 22 g/day alcohol and became deleterious at just over 60 g/day alcohol. Among women, consumption of 24 g/day alcohol was most protective, and became deleterious at about 50 g/day alcohol.{{citation needed, date=April 2019 A systematic review on intervention studies in women also supported this finding. It reported that alcohol consumption in moderation improved insulin sensitivity among women.
The way in which alcohol is consumed (i.e., with meals or binge drinking) affects various health outcomes. It may be the case that the risk of diabetes associated with heavy alcohol consumption is due to consumption mainly on the weekend as opposed to the same amount spread over a week.[{{cite journal, title=Alcohol as a Risk Factor for Type 2 Diabetes , pmc=2768203 , pmid=19875607 , doi=10.2337/dc09-0227 , volume=32 , issue=11 , year=2009 , journal=Diabetes Care , pages=2123–2132 , vauthors=Baliunas DO, Taylor BJ, Irving H, Roerecke M, Patra J, Mohapatra S, Rehm J] In the United Kingdom "advice on weekly consumption is avoided".{{citation needed, date=April 2019 A twenty-year twin study from Finland reported that moderate alcohol consumption may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes in men and women. However, binge drinking and high alcohol consumption was found to increase the risk of type 2 diabetes in women.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Regular consumption of alcohol is associated with an increased risk of gouty arthritis and a decreased risk of rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are inv ...
. Two recent studies report that the more alcohol consumed, the lower the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Among those who drank regularly, the one-quarter who drank the most were up to 50% less likely to develop the disease compared to the half who drank the least.
The researchers noted that moderate alcohol consumption also reduces the risk of other inflammatory processes such as cardiovascular disease. Some of the biological mechanisms by which ethanol reduces the risk of destructive arthritis and prevents the loss of bone mineral density (BMD), which is part of the disease process.
A study concluded, "Alcohol either protects from RA or, subjects with RA curtail their drinking after the manifestation of RA". Another study found, "Postmenopausal women who averaged more than 14 alcoholic drinks per week had a reduced risk of rheumatoid arthritis..."
Osteoporosis
Moderate alcohol consumption is associated with higher bone mineral density
Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optical ...
in postmenopausal women. "...Alcohol consumption significantly decreased the likelihood f_osteoporosis.html" ;"title="osteoporosis.html" ;"title="f osteoporosis">f osteoporosis">osteoporosis.html" ;"title="f osteoporosis">f osteoporosis" "Moderate alcohol intake was associated with higher BMD in postmenopausal elderly women." "Social drinking is associated with higher bone mineral density in men and women [over 45]." However, heavy alcohol use is associated with bone loss.[{{Cite journal, last1=Ronis, first1=MJ., last2=Wands, first2=JR., last3=Badger, first3=TM., last4=de la Monte, first4=SM., last5=Lang, first5=CH., last6=Calissendorff, first6=J., title=Alcohol-induced disruption of endocrine signaling., journal=Alcohol Clin Exp Res, volume=31, issue=8, pages=1269–85, date=Aug 2007, doi=10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00436.x, pmid=17559547][{{Cite journal, last1=Peer, first1=KS., last2=Newsham, first2=KR., title=A case study on osteoporosis in a male athlete: looking beyond the usual suspects., journal=Orthop Nurs, volume=24, issue=3, pages=193–9; quiz 200–1, year=2005, pmid=15928528, doi=10.1097/00006416-200505000-00007 , s2cid=23377405]
Skin
Chronic excessive alcohol use is associated with a wide range of skin disorders including urticaria
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and does not leave any long-last ...
, porphyria cutanea tarda
Porphyria cutanea tarda is the most common subtype of porphyria. The disease is named because it is a porphyria that often presents with skin manifestations later in life. The disorder results from low levels of the enzyme responsible for the fift ...
, flushing, cutaneous stigmata of cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
, psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to comple ...
, pruritus
Itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant ...
, seborrheic dermatitis, and rosacea
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, enlarg ...
.
A 2010 study concluded, "Nonlight beer intake is associated with an increased risk of developing psoriasis among women. Other alcoholic beverages did not increase the risk of psoriasis in this study."
Immune system
Bacterial infection
Excessive alcohol consumption seen in people with an alcohol use disorder is a known risk factor for developing pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
.{{citation needed, date=November 2021
Common cold
A study on the common cold found that "Greater numbers of alcoholic drinks (up to three or four per day) were associated with decreased risk for developing colds because drinking was associated with decreased illness following infection. However, the benefits of drinking occurred only among nonsmokers. ... Although alcohol consumption did not influence risk of clinical illness for smokers, moderate alcohol consumption was associated with decreased risk for nonsmokers."
Another study concluded, "Findings suggest that wine intake, especially red wine, may have a protective effect against common cold. Beer, spirits, and total alcohol intakes do not seem to affect the incidence of common cold."
Cancer
{{Main, Alcohol and cancer
In 1988, the International Agency for Research on Cancer
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC; french: Centre International de Recherche sur le Cancer, CIRC) is an intergovernmental agency forming part of the World Health Organization of the United Nations.
Its role is to conduct and ...
(Centre International de Recherche sur le Cancer) of the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
classified alcohol as a Group 1 carcinogen, stating "There is sufficient evidence for the carcinogenicity of alcoholic beverages in humans.... Alcoholic beverages are carcinogenic to humans (Group 1)." The U.S. Department of Health & Human Services' National Toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating e ...
Program in 2000 listed alcohol as a ''known carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive sub ...
''.
It was estimated in 2006 that "3.6% of all cancer cases worldwide are related to alcohol drinking, resulting in 3.5% of all cancer deaths."[{{Cite journal, vauthors=Boffetta P, Hashibe M, La Vecchia C, Zatonski W, Rehm J , title=The burden of cancer attributable to alcohol drinking , journal=International Journal of Cancer , volume=119 , issue=4 , pages=884–7 , date=August 2006 , pmid=16557583 , doi=10.1002/ijc.21903, hdl=2434/22728 , s2cid=14938863 ] A European study from 2011 found that one in 10 of all cancers in men and one in 33 in women were caused by past or current alcohol intake. The World Cancer Research Fund
World Cancer Research Fund International is a not-for-profit association related to cancer prevention research related to diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the del ...
panel report ''Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity and the Prevention of Cancer: a Global Perspective'' finds the evidence "convincing" that alcoholic drinks increase the risk of the following cancers: mouth, pharynx and larynx, oesophagus, colorectum (men), breast (pre- and postmenopause).[WCR]
World Cancer Research Fund / American Institute for Cancer Research. Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and the Prevention of Cancer: a Global Perspective. Washington DC: AICR, 2007
{{webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130523121425/http://eprints.ucl.ac.uk/4841/1/4841.pdf , date=2013-05-23
Even light and moderate alcohol consumption increases cancer risk in individuals, especially with respect to squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus, oropharyngeal cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer (OPC), also known as oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) and tonsil cancer, is a disease in which abnormal cells with the potential to both grow locally and spread to other parts of the body are found in the oral ca ...
, and breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or ...
.Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3 CHO, sometimes abbreviated by chemists as MeCHO (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the ...
, a metabolic product of alcohol, is suspected to promote cancer. Typically the liver eliminates 99% of acetaldehyde produced. However, liver disease and certain genetic enzyme deficiencies result in high acetaldehyde levels. Heavy drinkers who are exposed to high acetaldehyde levels due to a genetic defect in alcohol dehydrogenase
Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) () are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to NA ...
have been found to be at greater risk of developing cancers of the upper gastrointestinal tract and liver. A review in 2007 found "convincing evidence that acetaldehyde... is responsible for the carcinogenic effect of ethanol... owing to its multiple mutagenic effects on DNA." Acetaldehyde can react with DNA to create DNA adducts including the Cr-Pdg adduct. This Cr-PdG adduct "is likely to play a central role in the mechanism of alcoholic beverage related carcinogenesis."
Alcohol's effect on the fetus
{{main, Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
Fetal alcohol syndrome or FAS is a birth defect
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities ca ...
that occurs in the offspring of women who drink alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
during pregnancy. More risks than benefits according to a survey of current knowledge. Alcohol crosses the placental barrier and can stunt fetal growth or weight, create distinctive facial stigmata, damaged neurons
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa ...
and brain structures, and cause other physical, mental, or behavioural problems. Fetal alcohol exposure is the leading known cause of intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation, Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signif ...
in the Western world. Alcohol consumption during pregnancy is associated with brain insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
and insulin-like growth factor resistance.
Short term-term effects of alcoholism on family and children
Children raised in alcoholic families have the potential to suffer emotional distress as they move into their own committed relationships. These children are at a higher risk for divorce and separation, unstable marital conditions and fractured families.[{{cite journal, last1=Kearns-Bodkin, first1=Jill N., last2=Leonard, first2=Kenneth E., title=Relationship Functioning Among Adult Children of Alcoholics, journal=Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, pages=941–950, date=November 2008, pmc=2583382, pmid=18925353, volume=69, issue=6, doi=10.15288/jsad.2008.69.941] Feelings of depression and antisocial behaviors experienced in early childhood frequently contribute to marital conflict and domestic violence. Women are more likely than men to be victims of alcohol-related domestic violence.[{{cite journal , last1=Finger , first1=Brent , last2=Kachadourian , first2=Lorig K. , last3=Molnar , first3=Danielle S. , last4=Eiden , first4=Rina D. , last5=Edwards , first5=Ellen P. , last6=Leonard , first6=Kenneth E. , title=Alcoholism, associated risk factors, and harsh parenting among fathers: Examining the role of marital aggression , journal=Addictive Behaviors , date=June 2010 , volume=35 , issue=6 , pages=541–548 , doi=10.1016/j.addbeh.2009.12.029, pmid=20153586 , pmc=3824378 ][{{Cite journal, last=Sher, first=K, title=Characteristics of Children of Alcoholics: Putative Risk Factors, Substance Use and Abuse, and Psychopathology, journal=Journal of Abnormal Psychology, volume=100 , issue = 4 , pages=427–448, doi=10.1037/0021-843x.100.4.427, year=1991, pmid=1757657][{{Cite journal, last=Gerhant, first=A., title=Personality Traits in Alcohol-Dependent Individuals in the Context of Childhood Abuse, journal= Psychiatria Polska, volume=50 , issue = 5 , pages=973–987, doi=10.12740/pp/60346, pmid=27992890, year=2016][{{Cite journal , doi = 10.15288/jsad.2013.74.674, pmid = 23948526, pmc = 3749310, title = Impact of Fathers' Alcohol Problems on the Development of Effortful Control in Early Adolescence, journal = Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, volume = 74, issue = 5, pages = 674–683, year = 2013, last1 = Adkison, first1 = Sarah E., last2 = Grohman, first2 = Kerry, last3 = Colder, first3 = Craig R., last4 = Leonard, first4 = Kenneth, last5 = Orrange-Torchia, first5 = Toni, last6 = Peterson, first6 = Ellen, last7 = Eiden, first7 = Rina D.]
Children of alcoholics often incorporate behaviors learned as children into their marital relationships. These behaviors lead to poor parenting practices. For example, adult children of alcoholics may simultaneously express love and rejection toward a child or spouse. This is known as insecure attachment
Attachment theory is a psychological, evolutionary and ethological theory concerning relationships between humans. The most important tenet is that young children need to develop a relationship with at least one primary caregiver for norm ...
.fear of abandonment
Emotional abandonment is a subjective emotional state in which people feel undesired, left behind, insecure, or discarded. People experiencing emotional abandonment may feel at a loss. They may feel like they have been cut off from a crucial so ...
.
Economic impact from long-term consumption of alcohol
There is currently no consistent approach to measuring the economic impact of alcohol consumption.[{{Cite journal, last1=Verhaeghe, first1=Nick, last2=Lievens, first2=Delfine, last3=Annemans, first3=Lieven, last4=Vander Laenen, first4=Freya, last5=Putman, first5=Koen, date=2017-01-18, title=Methodological Considerations in Social Cost Studies of Addictive Substances: A Systematic Literature Review, journal=Frontiers in Public Health, volume=4, pages=295, doi=10.3389/fpubh.2016.00295, issn=2296-2565, pmc=5241275, pmid=28149834, doi-access=free] The economic burden such as direct, indirect, and intangible cost of diseases can be estimated through cost-of-illness studies. Direct costs are estimated through prevalence and incidence studies, while indirect costs are estimated through the human capital
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial ...
method, the demographic method, and the friction cost method.Alcohol dependence
Alcohol dependence is a previous (DSM-IV and ICD-10) psychiatric diagnosis in which an individual is physically or psychologically dependent upon alcohol (also chemically known as ethanol).
In 2013, it was reclassified as alcohol use disorder ...
has a far reaching impact on health outcomes. A study conducted in Germany in 2016 found the economic burden for those dependent on alcohol was 50% higher than those who were not. In the study, over half of the economic cost was due to lost productivity, and only 6% was due to alcohol treatment programs. The economic cost was mostly borne by individuals between 30 and 49 years old. In another study conducted with data from eight European countries, 77% of alcohol dependent patients had psychiatric and somatic co-morbidity, which in turn increased systematic healthcare and economic cost. Alcohol consumption can also affect the immune system and produce complications in people with HIV, pneumonia, and tuberculosis.
Indirect costs due to alcohol dependence are significant. The biggest indirect cost comes from lost productivity, followed by premature mortality. Men with alcohol dependence in the U.S. have lower labor force participation by 2.5%, lower earnings by 5.0%, and higher absenteeism by 0.5–1.2 days. Female binge drinkers have higher absenteeism by 0.4–0.9 days. Premature mortality is another large contributor to indirect costs of alcohol dependence. In 2004, 3.8% of global deaths were attributable to alcohol (6.3% for men and 1.1% for women). Those under 60 years old have much higher prevalence in global deaths attributable to alcohol at 5.3%.
In general, indirect costs such as premature mortality due to alcohol dependence, loss of productivity due to absenteeism and presenteeism, and cost of property damage and enforcement, far exceed the direct health care and law enforcement costs. Aggregating the economic cost from all sources, the impact can range from 0.45 to 5.44% of a country's gross domestic product (GDP). The wide range is due to inconsistency in measurement of economic burden, as researchers in some studies attributed possible positive effects from long term alcohol consumption.[{{Cite web, url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/252250147, title=The Social Costs of Drug Abuse in Australia in 1988 and 1992 (PDF Download Available), website=ResearchGate, language=en, access-date=2017-09-17]
See also
* Short-term effects of alcohol consumption
The short-term effects of alcohol (more specifically ethanol) consumption range from a decrease in anxiety and motor skills and euphoria at lower doses to intoxication (drunkenness), to stupor, unconsciousness, anterograde amnesia (memory "blac ...
* Alcohol and suicide
* Self-medication on CNS depressants (alcohol)
* Self-medicated effectiveness on alcohol
References
{{Reflist
External links
{{Medical resources
, ICD10 = {{ICD10, F, 10, , f, 10.1
Alcohol, Other Drugs, and Health: Current Evidence. Boston University/National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism Journal
(NHS)
{{alcohealth
{{Psychoactive substance use
{{DEFAULTSORT:Long-Term Effects Of Alcohol
Long
Alc
 Different countries recommend different maximum quantities. In the UK, the Chief Medical Officers' recommends men and women drink no more than 14 units per week. A single unit corresponds to 8 g of ethanol. For most countries, the maximum quantity for men is 140 g–210 g per week. For women, the range is 84 g–140 g per week.{{citation needed, date=January 2013 Most countries recommend total abstinence during pregnancy and
Different countries recommend different maximum quantities. In the UK, the Chief Medical Officers' recommends men and women drink no more than 14 units per week. A single unit corresponds to 8 g of ethanol. For most countries, the maximum quantity for men is 140 g–210 g per week. For women, the range is 84 g–140 g per week.{{citation needed, date=January 2013 Most countries recommend total abstinence during pregnancy and