Logic block on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
Re-programmable PLA
. Filed January 11, 1983. Granted April 2, 1985. Retrieved February 5, 2009.Google Patent Search,
Dynamic data re-programmable PLA
. Filed January 11, 1983. Granted June 18, 1985. Retrieved February 5, 2009.
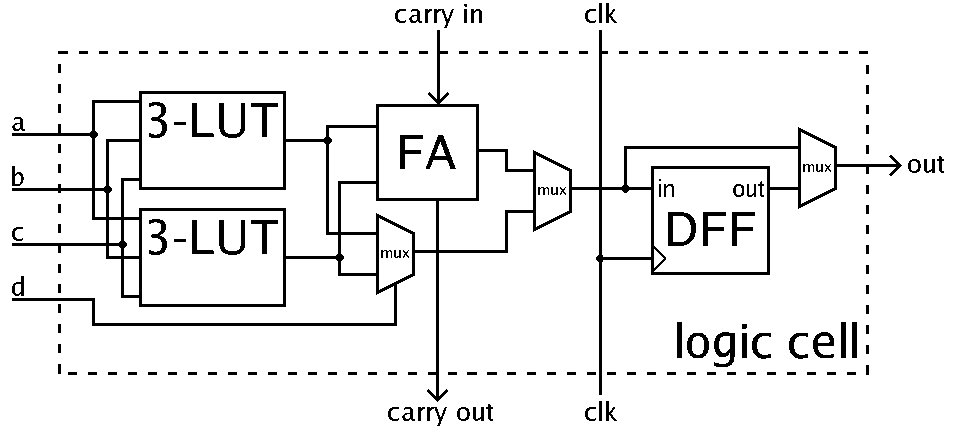 In general, a logic block consists of a few ''logic cells'' (each cell is called an adaptive logic module (ALM), a logic element (LE), slice, etc.). A typical cell consists of a 4-input LUT, a
In general, a logic block consists of a few ''logic cells'' (each cell is called an adaptive logic module (ALM), a logic element (LE), slice, etc.). A typical cell consists of a 4-input LUT, a
FPGA manufacturer claims to beat Moore's Law
" October 27, 2010. Retrieved May 12, 2011. Following the introduction of its 28 nm 7-series FPGAs, Xilinx revealed that several of the highest-density parts in those FPGA product lines will be constructed using multiple dies in one package, employing technology developed for 3D construction and stacked-die assemblies. The technology stacks several (three or four) active FPGA dice side-by-side on a silicon
 Since clock signals (and often other high-
Since clock signals (and often other high-
 Whenever a vertical and a horizontal channel intersect, there is a switch box. In this architecture, when a wire enters a switch box, there are three programmable switches that allow it to connect to three other wires in adjacent channel segments. The pattern, or topology, of switches used in this architecture is the planar or domain-based switch box topology. In this switch box topology, a wire in track number one connects only to wires in track number one in adjacent channel segments, wires in track number 2 connect only to other wires in track number 2 and so on. The figure on the right illustrates the connections in a switch box.
Generally, all the routing channels have the same width (number of wires). Multiple I/O pads may fit into the height of one row or the width of one column in the array.
Whenever a vertical and a horizontal channel intersect, there is a switch box. In this architecture, when a wire enters a switch box, there are three programmable switches that allow it to connect to three other wires in adjacent channel segments. The pattern, or topology, of switches used in this architecture is the planar or domain-based switch box topology. In this switch box topology, a wire in track number one connects only to wires in track number one in adjacent channel segments, wires in track number 2 connect only to other wires in track number 2 and so on. The figure on the right illustrates the connections in a switch box.
Generally, all the routing channels have the same width (number of wires). Multiple I/O pads may fit into the height of one row or the width of one column in the array.
computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, ...
, a logic block or configurable logic block (CLB) is a fundamental building block of field-programmable gate array
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term ''Field-programmability, field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specifi ...
(FPGA) technology. Logic blocks can be configured by the engineer to provide reconfigurable logic gate
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic ga ...
s.
Logic blocks are the most common FPGA architecture, and are usually laid out within a logic block array. Logic blocks require I/O pads (to interface with external signals), and routing channels (to interconnect logic blocks).
Programmable logic blocks were invented by David W. Page and LuVerne R. Peterson, and defined within their 1985 patents.Google Patent Search,Re-programmable PLA
. Filed January 11, 1983. Granted April 2, 1985. Retrieved February 5, 2009.Google Patent Search,
Dynamic data re-programmable PLA
. Filed January 11, 1983. Granted June 18, 1985. Retrieved February 5, 2009.
Applications
An application circuit must be mapped into an FPGA with adequate resources. While the number of logic blocks and I/Os required is easily determined from the design, the number of routing tracks needed may vary considerably even among designs with the same amount of logic. For example, acrossbar switch
In electronics and telecommunications, a crossbar switch (cross-point switch, matrix switch) is a collection of switches arranged in a matrix configuration. A crossbar switch has multiple input and output lines that form a crossed pattern of int ...
requires much more routing than a systolic array
In parallel computer architectures, a systolic array is a homogeneous network of tightly coupled data processing units (DPUs) called cells or nodes. Each node or DPU independently computes a partial result as a function of the data received from i ...
with the same gate count. Since unused routing tracks increase the cost (and decrease the performance) of the part without providing any benefit, FPGA manufacturers try to provide just enough tracks so that most designs that will fit in terms of lookup tables (LUTs) and I/Os can be routed. This is determined by estimates such as those derived from Rent's rule Rent's rule pertains to the organization of computing logic, specifically the relationship between the number of external signal connections to a logic block (i.e., the number of "pins") with the number of logic gates in the logic block, and has bee ...
or by experiments with existing designs.
FPGAs are also widely used for systems validation including pre-silicon validation, post-silicon validation, and firmware development. This allows chip companies to validate their design before the chip is produced in the factory, reducing the time-to-market.
Architecture
 In general, a logic block consists of a few ''logic cells'' (each cell is called an adaptive logic module (ALM), a logic element (LE), slice, etc.). A typical cell consists of a 4-input LUT, a
In general, a logic block consists of a few ''logic cells'' (each cell is called an adaptive logic module (ALM), a logic element (LE), slice, etc.). A typical cell consists of a 4-input LUT, a full adder
An adder, or summer, is a digital circuit that performs addition of numbers. In many computers and other kinds of processors adders are used in the arithmetic logic units (ALUs). They are also used in other parts of the processor, where they are ...
(FA), and a D-type flip-flop (DFF), as shown to the right. The LUTs are in this figure split into two 3-input LUTs. In ''normal mode'' those are combined into a 4-input LUT through the left mux. In ''arithmetic'' mode, their outputs are fed to the FA. The selection of mode is programmed into the middle multiplexer. The output can be either synchronous or asynchronous, depending on the programming of the mux to the right, in the figure example. In practice, entire or parts of the FA are put as functions into the LUTs in order to save space.
Logic blocks typically contain a few ALMs/LEs/slices. ALMs and slices usually contain 2 or 4 structures similar to the example figure, with some shared signals.
Manufacturers have started moving to 6-input LUTs in their high performance parts, claiming increased performance.
3D architecture
To shrink the size and power consumption of FPGAs, vendors such asTabula
Tabula may refer to:
* Tabula (company), a semiconductor company
*Tabula (game), a game thought to be the predecessor to backgammon
* ''Tabula'' (magazine), a magazine published in Tbilisi, Georgia
*Tabula ansata
A tabula ansata or tabella an ...
and Xilinx
Xilinx, Inc. ( ) was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company was known for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and creating the fi ...
have introduced new 3D or stacked architectures.Lawrence Latif, The Inquirer.FPGA manufacturer claims to beat Moore's Law
" October 27, 2010. Retrieved May 12, 2011. Following the introduction of its 28 nm 7-series FPGAs, Xilinx revealed that several of the highest-density parts in those FPGA product lines will be constructed using multiple dies in one package, employing technology developed for 3D construction and stacked-die assemblies. The technology stacks several (three or four) active FPGA dice side-by-side on a silicon
interposer
An interposer is an electrical interface routing between one socket or connection to another. The purpose of an interposer is to spread a connection to a wider pitch or to reroute a connection to a different connection.
Interposer comes from t ...
– a single piece of silicon that carries passive interconnect. The multi-die construction also allows different parts of the FPGA to be created with different process technologies, as the process requirements are different between the FPGA fabric itself and the very high speed 28 Gbit/s serial transceivers. An FPGA built in this way is called a ''heterogeneous FPGA''.http://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/white_papers/wp380_Stacked_Silicon_Interconnect_Technology.pdf
External I/O
fan-out
In digital electronics, the fan-out is the number of gate inputs driven by the output of another single logic gate.
In most designs, logic gates are connected to form more complex circuits. While no logic gate input can be fed by more than one ...
signals) are normally routed via special-purpose dedicated routing networks (i.e. global buffers) in commercial FPGAs, they and other signals are separately managed.
For this example architecture, the locations of the FPGA logic block pins are shown to the right.
Each input is accessible from one side of the logic block, while the output pin can connect to routing wires in both the channel to the right and the channel below the logic block.
Each logic block output pin can connect to any of the wiring segments in the channels adjacent to it.
Similarly, an I/O pad can connect to any one of the wiring segments in the channel adjacent to it. For example, an I/O pad at the top of the chip can connect to any of the W wires (where W is the channel width) in the horizontal channel immediately below it.
Routing
Generally, the FPGA routing is unsegmented. That is, each wiring segment spans only one logic block before it terminates in a switch box. By turning on some of the programmable switches within a switch box, longer paths can be constructed. For higher speed interconnect, some FPGA architectures use longer routing lines that span multiple logic blocks.Hard blocks
Modern FPGA families expand upon the above capabilities to include higher level functionality fixed into the silicon. Having these common functions embedded into the silicon reduces the area required and gives those functions increased speed compared to building them from primitives. Examples of these include multipliers, generic DSP blocks, embedded processors, high speed I/O logic and embedded memories. Higher-end FPGAs can contain high speed multi-gigabit transceivers and ''hard IP cores'' such as processor cores,Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1 ...
media access control
In IEEE 802 LAN/MAN standards, the medium access control (MAC, also called media access control) sublayer is the layer that controls the hardware responsible for interaction with the wired, optical or wireless transmission medium. The MAC sublay ...
lers, PCI/PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common ...
controllers, and external memory controllers. These cores exist alongside the programmable fabric, but they are built out of transistors instead of LUTs so they have ASIC level performance and power consumption while not consuming a significant amount of fabric resources, leaving more of the fabric free for the application-specific logic. The multi-gigabit transceivers also contain high performance analog input and output circuitry along with high-speed serializers and deserializers, components which cannot be built out of LUTs. Higher-level PHY layer functionality such as line coding may or may not be implemented alongside the serializers and deserializers in hard logic, depending on the FPGA.
Clock signals
Most of the circuitry built inside of an FPGA is synchronous circuitry that requires a clock signal. FPGAs contain dedicated global and regional routing networks for clock and reset so they can be delivered with minimal skew. FPGAs generally contain analogphase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a ...
and/or delay-locked loop components to synthesize new clock frequencies and attenuate jitter
In electronics and telecommunications, jitter is the deviation from true periodicity of a presumably periodic signal, often in relation to a reference clock signal. In clock recovery applications it is called timing jitter. Jitter is a signific ...
. Complex designs can use multiple clocks with different frequency and phase relationships, each forming separate clock domains. These clock signals can be generated locally by an oscillator or they can be recovered from a high speed serial data stream. Care must be taken when building clock domain crossing
In digital electronic design a clock domain crossing (CDC), or simply clock crossing, is the traversal of a signal in a synchronous digital circuit from one clock domain into another. If a signal does not assert long enough and is not registered, ...
circuitry to avoid metastability. FPGAs generally contain block RAMs that are capable of working as dual port RAMs with different clocks, aiding in the construction of building FIFOs and dual port buffers that connect differing clock domains.
See also
*Altera
Altera Corporation was a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015.
The main product lines from Altera were the flagship Stratix series, mid-ran ...
References
{{Programmable Logic Gate arrays