Little Karoo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South
 The only sharp and definite boundary of the Great Karoo is formed by the most inland ranges of
The only sharp and definite boundary of the Great Karoo is formed by the most inland ranges of
 The southern 30– to 50 km-wide strip, north of the Langeberg range, is as arid as the western Lower Karoo, except in the east, where the Langeberg range (arbitrarily) starts to be called the Outeniqua Mountains.
The Little Karoo can only be accessed by road through the narrow defiles cut through the surrounding Cape Fold Mountains by ancient, but still flowing, rivers. A few roads traverse the mountains over passes, the most famous and impressive of which is the Swartberg Pass between Oudtshoorn in the Little Karoo and Prince Albert on the other side of the Swartberg mountains in the Great Karoo. Also, the main road between Oudtshoorn and George, on the coastal plain, crosses the mountains to the south via the Outeniqua Pass. The only exit from the Little Karoo that does not involve crossing a mountain range is through the 150 km-long, narrow Langkloof valley between Uniondale and Humansdorp, near
The southern 30– to 50 km-wide strip, north of the Langeberg range, is as arid as the western Lower Karoo, except in the east, where the Langeberg range (arbitrarily) starts to be called the Outeniqua Mountains.
The Little Karoo can only be accessed by road through the narrow defiles cut through the surrounding Cape Fold Mountains by ancient, but still flowing, rivers. A few roads traverse the mountains over passes, the most famous and impressive of which is the Swartberg Pass between Oudtshoorn in the Little Karoo and Prince Albert on the other side of the Swartberg mountains in the Great Karoo. Also, the main road between Oudtshoorn and George, on the coastal plain, crosses the mountains to the south via the Outeniqua Pass. The only exit from the Little Karoo that does not involve crossing a mountain range is through the 150 km-long, narrow Langkloof valley between Uniondale and Humansdorp, near
 In geological terms, the Karoo Supergroup refers to an extensive and geologically recent (180–310 million years old) sequence of sedimentary and igneous rocks, which is flanked to the south by the
In geological terms, the Karoo Supergroup refers to an extensive and geologically recent (180–310 million years old) sequence of sedimentary and igneous rocks, which is flanked to the south by the
 Karoo Koppies hills are capped by hard, erosion-resistant dolerite sills. This is solidified lava that was forced under high pressure between the horizontal strata of the sedimentary rocks that make up most of the Karoo’s geology. This occurred about 180 million years ago, when huge volumes of lava were extruded over most of Southern Africa and adjoining regions of Gondwana, both on the surface and deep below the surface between the sedimentary strata. Since this massive extrusion of lava, Southern Africa has undergone a prolonged period of erosion, exposing the older, softer rocks, except where they were protected by a cap of dolerite. The genera present include:
*'' Mesosaurus'', aquatic Dwyka carnivore
*'' Bradysaurus'', Beaufort Group herbivore
*'' Owenetta'', Beaufort Group insectivore
*''
Karoo Koppies hills are capped by hard, erosion-resistant dolerite sills. This is solidified lava that was forced under high pressure between the horizontal strata of the sedimentary rocks that make up most of the Karoo’s geology. This occurred about 180 million years ago, when huge volumes of lava were extruded over most of Southern Africa and adjoining regions of Gondwana, both on the surface and deep below the surface between the sedimentary strata. Since this massive extrusion of lava, Southern Africa has undergone a prolonged period of erosion, exposing the older, softer rocks, except where they were protected by a cap of dolerite. The genera present include:
*'' Mesosaurus'', aquatic Dwyka carnivore
*'' Bradysaurus'', Beaufort Group herbivore
*'' Owenetta'', Beaufort Group insectivore
*'' The lava outpourings that ended the Karoo deposition of rocks, not only covered the African surface, and other parts of Gondwana with a 1.6 km thick layer basaltic lava, but it also forced its way, under high pressure, between the horizontal layers of sedimentary rocks belonging to the Ecca and Beaufort groups, to solidify into dolerite sills. The long vertical fissures through which the lava welled up solidified into dikes which resemble the
The lava outpourings that ended the Karoo deposition of rocks, not only covered the African surface, and other parts of Gondwana with a 1.6 km thick layer basaltic lava, but it also forced its way, under high pressure, between the horizontal layers of sedimentary rocks belonging to the Ecca and Beaufort groups, to solidify into dolerite sills. The long vertical fissures through which the lava welled up solidified into dikes which resemble the
 The
The
Accessed 30 April 2014 It starts in the south just north of the Veld#Sandveld and Hardveld, sandveld geographical region, about 250 km north of Cape Town, and continues through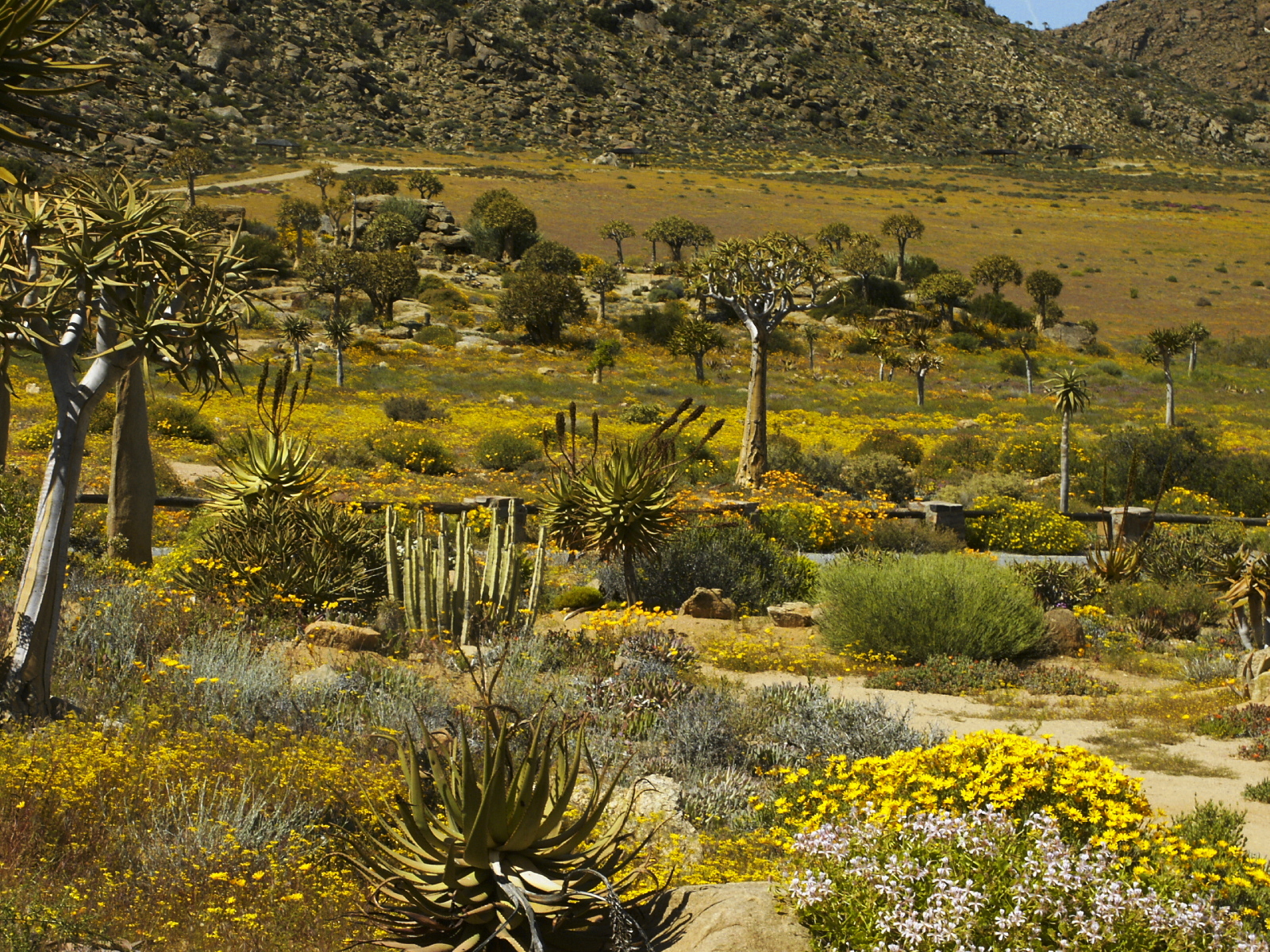 The succulent Karoo biome is dominated by dwarf, leafy-succulent shrubs, and annuals, predominantly
The succulent Karoo biome is dominated by dwarf, leafy-succulent shrubs, and annuals, predominantly
. Accessed 2 May 2014''The Nama Karoo Biome'' . Accessed 2 May 2014 It incorporates nearly the whole of the historical and geographical Great Karoo, but also includes a portion of southern Namibia's Namaqualand, and South Africa's Bushmanland (both local geographical names, not names of biomes). It is the second-largest biome in South Africa, and forms the botanical transition between the Fynbos#Cape Floral Kingdom, fynbos biome to the south and the savannah biome to the north. It is defined primarily by the dominance of dwarf (less than 1 m high) shrubs with a co-dominance of grasses especially towards the north-east and east where it grades into the grassland biome of the highveld and the Eastern Midlands. The shrubs and grasses are deciduous, mainly in response to the irregular rainfall. Much of the Nama Karoo biome is used for sheep and goat farming, providing mutton, wool, and pelts for local and international markets, especially since livestock can frequently be provided with a regular supply of water from boreholes. Overgrazing exacerbates the erosion caused by the violent thunderstorms that occur, infrequently, in the summer. It also promotes the replacement of the grasses by shrubs, especially the less edible varieties such as the threethorn (''
 Probably the strangest and most puzzling zoological phenomenon in the Great Karoo was the periodic, unpredictable appearance of massive springbok migrations. These migrations always came from the north, and could either go west towards Namaqualand and the sea, south-west through towns such as
Probably the strangest and most puzzling zoological phenomenon in the Great Karoo was the periodic, unpredictable appearance of massive springbok migrations. These migrations always came from the north, and could either go west towards Namaqualand and the sea, south-west through towns such as  In 1849, a massive herd of springbok, amongst which were intermingled wildebeest, blesbok, quagga, and eland, moved through Beaufort West. Early one morning, the town was awakened to a sound like that of a strong wind, and suddenly the town was filled with animals. They devoured every sprig of foliage in the town and surrounding countryside. The last of the continuously moving herd left the town 3 days later, to disappear towards the west. The Karoo looked as if a fire had swept through it. During these migrations, the plains and hillsides on every side were thickly covered by one vast mass of springbok, packed like sheep in a fold. As far as the eye could see, the landscape was alive with them.
During these migrations, the springbok never ran or trotted. On the whole, they were silent, except for the shudder of their stamping hoofs. Nothing could divert them, and hunters could ride amongst them, shooting them at random, without apparently causing alarm. People could move amongst them and kill them with sticks, or cripple them by seizing a leg and breaking it. Not only people followed these herds for the easy meat they provided, but also lions, leopards,
In 1849, a massive herd of springbok, amongst which were intermingled wildebeest, blesbok, quagga, and eland, moved through Beaufort West. Early one morning, the town was awakened to a sound like that of a strong wind, and suddenly the town was filled with animals. They devoured every sprig of foliage in the town and surrounding countryside. The last of the continuously moving herd left the town 3 days later, to disappear towards the west. The Karoo looked as if a fire had swept through it. During these migrations, the plains and hillsides on every side were thickly covered by one vast mass of springbok, packed like sheep in a fold. As far as the eye could see, the landscape was alive with them.
During these migrations, the springbok never ran or trotted. On the whole, they were silent, except for the shudder of their stamping hoofs. Nothing could divert them, and hunters could ride amongst them, shooting them at random, without apparently causing alarm. People could move amongst them and kill them with sticks, or cripple them by seizing a leg and breaking it. Not only people followed these herds for the easy meat they provided, but also lions, leopards,
 In 1854, Daniel Halladay invented the multibladed
In 1854, Daniel Halladay invented the multibladed  In 1872, construction was started to connect the
In 1872, construction was started to connect the
File:Karoo national park.jpg, The Nuweveld Mountains near
Karoo, South Africa
{{Authority control Geography of South Africa Natural regions of South Africa Namaqualand Physiographic provinces South African English
Khoekhoe
Khoekhoen (singular Khoekhoe) (or Khoikhoi in the former orthography; formerly also '' Hottentots''"Hottentot, n. and adj." ''OED Online'', Oxford University Press, March 2018, www.oed.com/view/Entry/88829. Accessed 13 May 2018. Citing G. S. ...
!Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hard veld") is a semi- desert natural region
A natural region (landscape unit) is a basic geographic unit. Usually, it is a region which is distinguished by its common natural features of geography, geology, and climate.
From the ecological point of view, the naturally occurring flora and ...
of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its extent is also not precisely defined. The Karoo is partly defined by its topography, geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
and climate, and above all, its low rainfall, arid air, cloudless skies, and extremes of heat and cold.Potgieter, D.J. & du Plessis, T.C. (1972) ''Standard Encyclopaedia of Southern Africa''. Vol. 6. pp. 306–307. Nasou, Cape Town.''Reader’s Digest Illustrated Guide to Southern Africa''. (5th Ed. 1993). pp. 78–89. Reader’s Digest Association of South Africa Pty. Ltd., Cape Town. The Karoo also hosted a well-preserved ecosystem hundreds of million years ago which is now represented by many fossils.
The ǃ’Aukarob formed an almost impenetrable barrier to the interior from Cape Town, and the early adventurers, explorers, hunters, and travelers on the way to the Highveld unanimously denounced it as a frightening place of great heat, great frosts, great floods, and great droughts.Palmer, E. (1966) ''The Plains of Camdeboo''. p. 12-13, 120, 126, 140–146. Fontana/ Collins, London. Today, it is still a place of great heat and frosts, and an annual rainfall of between 50 and 250 mm, though on some of the mountains it can be 250 to 500 mm higher than on the plains. However, underground water is found throughout the Karoo, which can be tapped by boreholes, making permanent settlements and sheep farming possible.
The xerophytic
A xerophyte (from Greek ξηρός ''xeros'' 'dry' + φυτόν ''phuton'' 'plant') is a species of plant that has adaptations to survive in an environment with little liquid water, such as a desert such as the Sahara or places in the Alps or t ...
vegetation consists of aloes, mesembryanthemums, crassula
''Crassula'' is a genus of succulent plants containing about 200 accepted species, including the popular jade plant (''Crassula ovata''). They are members of the stonecrop family (Crassulaceae) and are native to many parts of the globe, but cu ...
s, euphorbia
''Euphorbia'' is a very large and diverse genus of flowering plants, commonly called spurge, in the family Euphorbiaceae. "Euphorbia" is sometimes used in ordinary English to collectively refer to all members of Euphorbiaceae (in deference to t ...
s, stapelia
''Stapelia'' is a genus of low-growing, spineless, stem succulent plants, predominantly from South Africa with a few from other parts of Africa. Several Asian and Latin American species were formerly included but they have all now been transfe ...
s, and desert ephemerals, spaced 50 cm or more apart,''The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Micropaedia, Vol. 6. (2007). p. 750. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., Chicago. and becoming very sparse going northwards into Bushmanland and, from there, into the Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for , covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal d ...
. The driest region of the Karoo, however, is its southwestern corner, between the Great Escarpment and the Cederberg-Skurweberg mountain ranges, called the Tankwa Karoo, which receives only 75 mm of rain annually. The eastern and north-eastern Karoo are often covered by large patches of grassland. The typical Karoo vegetation used to support large game, sometimes in vast herds.Conolly, D. (1992). ''Conolly’s Guide to Southern Africa''. (5th Ed.) pp. 106–117. Conolly Publishers, Scottburgh.
Today, sheep thrive on the xerophytes, though each sheep requires about 4 ha of grazing to sustain itself.
Divisions
The Karoo is divided into the Great Karoo and the Little Karoo. The Little Karoo is delimited in the south by the Outeniqua–Langeberg Mountains that run east-west parallel to the coast, and in the north by the Swartberg Mountain Range that also runs east-west. The Great Karoo lies to the north the Swartberg.Great Karoo
 The only sharp and definite boundary of the Great Karoo is formed by the most inland ranges of
The only sharp and definite boundary of the Great Karoo is formed by the most inland ranges of Cape Fold Mountains
The Cape Fold Belt is a fold and thrust belt of late Paleozoic age, which affected the sequence of Sedimentary rock, sedimentary rock layers of the Cape Supergroup in the southwestern corner of South Africa. It was originally continuous with t ...
to the south and south-west. The extent of the Karoo to the north is vague, fading gradually and almost imperceptibly into the increasingly arid Bushmanland towards the north-west. To the north and north-east, it fades into the savannah and grasslands of Griqualand West
Griqualand West is an area of central South Africa with an area of 40,000 km2 that now forms part of the Northern Cape Province. It was inhabited by the Griqua people – a semi-nomadic, Afrikaans-speaking nation of mixed-race origin, wh ...
and the Highveld.Norman, N., Whitfield, G. (2006) ''Geological Journeys''. p. 206-223, 243–247, 252–273, 300–311. Struik Publishers, Cape Town. The boundary to the east grades into the grasslands of the Eastern Midlands.Grassland biome.
The Great Karoo is itself divided by the Great Escarpment into the Upper Karoo (generally above 1200–1500 m) and the Lower Karoo on the plains below at 700–800 m.
A great many local names, each denoting different subregions of the Great Karoo, exist, some more widely, or more generally, known than others. In the Lower Karoo, going from west to east, they are the Tankwa Karoo, the Moordenaarskaroo, the Koup, the Vlakte, and the Camdeboo Plains. The Hantam, Kareeberge, Roggeveld, and uweveldare the better known subregions of the Upper Karoo, though most of it is simply known as the Upper Karoo, especially in the north.
Little Karoo
The Little Karoo’s boundaries are sharply defined by mountain ranges to the west, north, and south. The road between Uniondale and Willowmore is considered, by convention, to form the approximate arbitrary eastern extremity of the Little Karoo. Its extent is much smaller than that of the Great Karoo. Locally, it is usually called the ''Klein Karoo'', which isAfrikaans
Afrikaans (, ) is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper (i.e., the Hollandic dialect) used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their enslaved people. Afrikaans gra ...
for Little Karoo.
Geography
Great Karoo
The Great Karoo straddles the 30° S parallel on the west of the continent, in a similar position to other semidesert areas on earth, north and south of the equator. It is furthermore in the rainfall shadow of the Cape Fold Mountains along the western coastline. The western "Lower Karoo" (the Tankwa Karoo and Moordenaarskaroo) contain remnants of the Cape Fold Mountains''Geological Map of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland''. (1970). Council for Geoscience, Geological Survey of South Africa. (e.g. the Witteberg and Anysberg Mountains) which give it a moderate hilly appearance, but further east, the Lower Karoo becomes a monotonously flat plain. The "Upper Karoo" has been intruded by dolerite sills (see below),McCarthy, T., Rubridge, B. (2005). ''The Story of Earth and Life. '' p. 89-90, 102–107, 134–136,159–161, 195–211, 248–254. Struik Publishers, Cape Town creating multiple flat-topped hills, or Karoo Koppies, which are iconic of the Great Karoo. The vegetation of the Upper is similar to the Lower Karoo, so few people make a distinction between the two. The main highway (the N1) and railway line from Cape Town to the north enter the Lower Karoo from the Hex River Valley just before Touws River and follow a course about 50 km south of the Great Escarpment up toBeaufort West
Beaufort West (Afrikaans: ''Beaufort-Wes''; Xhosa: ''eBhofolo'') is a town in the Western Cape province in South Africa. It is the largest town in the arid Great Karoo region, and is known as the "Capital of the Karoo". It forms part of the Beau ...
. Thereafter, they gradually ascend the Great Escarpment along a broad valley to Three Sisters on the Central Plateau and the Upper Karoo.
Turning north from the N1 between Touws River and Beaufort West, at Matjiesfontein
Matjiesfontein is a settlement in Central Karoo District Municipality in the Western Cape province of South Africa.
History
The original inhabitants of the region were the Khoikhoi herders and the San hunter gatherers. Following the arrival of ...
, the road ascends the Great Escarpment through the Verlatenkloof Pass to reach Sutherland, at 1456 m above sea level, which is reputedly the coldest town in South Africa with average minimum temperatures of −6.1 °C during winter.Bulpin, T.V. (1992). ''Discovering Southern Africa''. pp. 271–274, 301–314. Discovering Southern Africa Productions, Muizenberg. Parts of the eastern Mpumalangan Highveld do at times experience lower temperatures than Sutherland, but not as consistently as Sutherland does. Snowfalls are not infrequent during the southern winter months. The South African Astronomical Observatory has an emplacement of telescopes about 20 km east of the town, on a small plateau 1798 m above sea level, and is home to the Southern African Large Telescope, the largest optical telescope in the Southern Hemisphere. To the north, still on the Plateau, and 75 km north-west of Carnarvon, seven radio dishes form part of the Square Kilometer Array
The Square Kilometre Array (SKA) is an intergovernmental international radio telescope project being built in Australia (low-frequency) and South Africa (mid-frequency). The combining infrastructure, the Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKA ...
which will, 2500 in total, be scattered in other parts of South Africa and Australia, to survey the southern skies at radio frequencies. Our galaxy, the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
, one of the main targets of this enterprise, is best viewed from the Southern Hemisphere.
The Upper Karoo is indeed an ideal site for an astronomical observatory. This is not only because of the clear skies, absence of artificial lights, and high altitude, but also because it is tectonically completely inactive (meaning that there are no fault lines or volcanoes nearby, and no earth tremors or earthquakes occur, even at great distances).
Little Karoo
The Little Karoo is separated from the Great Karoo by the Swartberg Mountain range. Geographically, it is a 290 km-long valley, only 40–60 km wide, formed by two parallel Cape Fold Mountain ranges, theSwartberg
The Swartberg mountains (''black mountain'' in Afrikaans) are a mountain range in the Western Cape province of South Africa. It is composed of two main mountain chains running roughly east–west along the northern edge of the semi-arid Little ...
to the north, and the continuous Langeberg
The Langeberg Range is a mountain range in the Western Cape province of South Africa. Its highest peak is Keeromsberg at 2,075 m that lies 15 km northeast of the town of Worcester. Some of the highest peaks of the range are located just to ...
- Outeniqua range to the south. The northern strip of the valley, within 10–20 km from the foot of the Swartberg mountains is least karoo-like, in that it is a well-watered area both from the rain and the many streams that cascade down the mountain, or through narrow defiles in the Swartberg from the Great Karoo. The main towns of the region are situated along this northern strip of the Little Karoo: Montagu, Barrydale, Ladismith
Ladismith is a town and agricultural centre in the western Little Karoo region of South Africa's Western Cape province.
Geography
It is situated adjacent to a series of fertile, irrigated valleys, at an elevation of 550 m above sea level, at ...
, Calitzdorp
Calitzdorp is a town on the Western side of the Little or Klein Karoo in the Western Cape Province
The Western Cape is a province of South Africa, situated on the south-western coast of the country. It is the fourth largest of the nine provi ...
, Oudtshoorn, and De Rust, as well as such well-known mission stations such as Zoar, Amalienstein, and Dysselsdorp.
 The southern 30– to 50 km-wide strip, north of the Langeberg range, is as arid as the western Lower Karoo, except in the east, where the Langeberg range (arbitrarily) starts to be called the Outeniqua Mountains.
The Little Karoo can only be accessed by road through the narrow defiles cut through the surrounding Cape Fold Mountains by ancient, but still flowing, rivers. A few roads traverse the mountains over passes, the most famous and impressive of which is the Swartberg Pass between Oudtshoorn in the Little Karoo and Prince Albert on the other side of the Swartberg mountains in the Great Karoo. Also, the main road between Oudtshoorn and George, on the coastal plain, crosses the mountains to the south via the Outeniqua Pass. The only exit from the Little Karoo that does not involve crossing a mountain range is through the 150 km-long, narrow Langkloof valley between Uniondale and Humansdorp, near
The southern 30– to 50 km-wide strip, north of the Langeberg range, is as arid as the western Lower Karoo, except in the east, where the Langeberg range (arbitrarily) starts to be called the Outeniqua Mountains.
The Little Karoo can only be accessed by road through the narrow defiles cut through the surrounding Cape Fold Mountains by ancient, but still flowing, rivers. A few roads traverse the mountains over passes, the most famous and impressive of which is the Swartberg Pass between Oudtshoorn in the Little Karoo and Prince Albert on the other side of the Swartberg mountains in the Great Karoo. Also, the main road between Oudtshoorn and George, on the coastal plain, crosses the mountains to the south via the Outeniqua Pass. The only exit from the Little Karoo that does not involve crossing a mountain range is through the 150 km-long, narrow Langkloof valley between Uniondale and Humansdorp, near Plettenberg Bay
Plettenberg Bay, nicknamed Plet or Plett, is the primary town of the Bitou Local Municipality in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. As of the census of 2001, there were 29,149 population. It was originally named Bahia Formosa ("beautifu ...
.
Geology of the Karoo
The Great Karoo
 In geological terms, the Karoo Supergroup refers to an extensive and geologically recent (180–310 million years old) sequence of sedimentary and igneous rocks, which is flanked to the south by the
In geological terms, the Karoo Supergroup refers to an extensive and geologically recent (180–310 million years old) sequence of sedimentary and igneous rocks, which is flanked to the south by the Cape Fold Mountains
The Cape Fold Belt is a fold and thrust belt of late Paleozoic age, which affected the sequence of Sedimentary rock, sedimentary rock layers of the Cape Supergroup in the southwestern corner of South Africa. It was originally continuous with t ...
, and to the north by the more ancient Ventersdorp Lavas, the Transvaal Supergroup and Waterberg Supergroup. It covers two-thirds of South Africa and extends in places to 8000 m below the land surface, constituting an immense volume of rocks which was formed, geologically speaking, in a short period of time.
Although almost the whole of the Great Karoo is situated on Karoo Supergroup rocks, the geological Karoo rocks extend over a very much larger area, both within South Africa and Lesotho, but also beyond its borders and onto other continents that formed part of Gondwana.
Geological history of the Karoo Supergroup
The Karoo Supergroup was formed in a vast inland basin starting 320 million years ago, at a time when that part of Gondwana which would eventually become Africa, lay over the South Pole. Icebergs that had calved off the glaciers and ice sheets to the north deposited a 1 km-thick layer of mud containingdropstones
Dropstones are isolated fragments of rock found within finer-grained water-deposited sedimentary rocks or pyroclastic beds. They range in size from small pebbles to boulders. The critical distinguishing feature is that there is evidence that the ...
of varying origins and sizes into this basin. This became the Dwyka Group consisting primarily of tillite
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
, the lowermost layer of the Karoo Supergroup. As Gondwana drifted northwards, the basin turned into an inland sea with extensive swampy deltas along its northern shores. The peat in these swamps eventually turned into large deposits of coal which are mined in KwaZulu-Natal and on the Highveld. This 3 km-thick layer is known as the Ecca Group
The Ecca Group is the second of the main subdivisions of the Karoo Supergroup of geological strata in southern Africa. It mainly follows conformably after the Dwyka Group in some sections, but in some localities overlying unconformably over much ...
, which is overlain by the 5.6 km-thick Beaufort Group, laid down on a vast plain with Mississippi-like rivers depositing mud from an immense range of mountains to the south. Ancient reptiles and amphibians prospered in the wet forests, and their remains have made the Karoo famous amongst palaeontologists. The first of these Karoo fossils was discovered in 1838 by Scots-born Andrew Geddes Bain
Andrew Geddes Bain (baptised 11 June 1797 – 20 October 1864), was a South African geologist, road engineer, palaeontologist and explorer.
Life history
The only child of Alexander Bain and Jean Geddes, both of whom died when Bain was still a ...
at a road cutting near Fort Beaufort. He sent his specimens to the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
, where fellow Scotsman Robert Broom recognised the Karoo fossils' mammal-like characteristics in 1897.
After the Beaufort period, Southern Africa (still part of Gondwana) became an arid sand desert with only ephemeral rivers and pans. These sands consolidated to form the Stormberg Group, the remnants of which are found only in the immediate vicinity of Lesotho. Several dinosaur nests, containing eggs, some with dinosaur fetal skeletons in them, have been found in these rocks, near what had once been a swampy pan.Weishampel, David B; et al (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Early Jurassic, Africa)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 535–536. .
Finally, about 180 million years ago, volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
activity took place on a titanic scale, which brought an end to a flourishing reptile evolution. These genera represent some of the extinct, mainly predinosaur, animals of the Karoo:
 Karoo Koppies hills are capped by hard, erosion-resistant dolerite sills. This is solidified lava that was forced under high pressure between the horizontal strata of the sedimentary rocks that make up most of the Karoo’s geology. This occurred about 180 million years ago, when huge volumes of lava were extruded over most of Southern Africa and adjoining regions of Gondwana, both on the surface and deep below the surface between the sedimentary strata. Since this massive extrusion of lava, Southern Africa has undergone a prolonged period of erosion, exposing the older, softer rocks, except where they were protected by a cap of dolerite. The genera present include:
*'' Mesosaurus'', aquatic Dwyka carnivore
*'' Bradysaurus'', Beaufort Group herbivore
*'' Owenetta'', Beaufort Group insectivore
*''
Karoo Koppies hills are capped by hard, erosion-resistant dolerite sills. This is solidified lava that was forced under high pressure between the horizontal strata of the sedimentary rocks that make up most of the Karoo’s geology. This occurred about 180 million years ago, when huge volumes of lava were extruded over most of Southern Africa and adjoining regions of Gondwana, both on the surface and deep below the surface between the sedimentary strata. Since this massive extrusion of lava, Southern Africa has undergone a prolonged period of erosion, exposing the older, softer rocks, except where they were protected by a cap of dolerite. The genera present include:
*'' Mesosaurus'', aquatic Dwyka carnivore
*'' Bradysaurus'', Beaufort Group herbivore
*'' Owenetta'', Beaufort Group insectivore
*''Procolophon
''Procolophon'' is a genus of lizard-like procolophonid parareptiles that first appeared in the Early Triassic (Induan) of South Africa, Brazil, and Antarctica. It persisted through the Permian–Triassic extinction event, but went extinct in ...
'', Beaufort Group omnivore
*''Diictodon
''Diictodon'' is an extinct genus of pylaecephalid dicynodont. These mammal-like synapsids lived during the Late Permian period, approximately 255 million years ago. Fossils have been found in the ''Cistecephalus'' Assemblage Zone of the Mad ...
'', Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last ...
synapsid
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptil ...
*''Rubidgea
''Rubidgea'' is a genus of gorgonopsid from the upper Permian of South Africa and Tanzania, containing the species ''Rubidgea atrox''. The generic name ''Rubidgea'' is sometimes believed to be derived from the surname of renowned Karoo paleontolo ...
'', Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last ...
predator
*'' Lystrosaurus'', Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
herbivorous therapsid
*''Thrinaxodon
''Thrinaxodon'' is an extinct genus of cynodonts, most commonly regarded by its species ''T. liorhinus'' which lived in what are now South Africa and Antarctica during the Early Triassic. ''Thrinaxodon'' lived just after the Permian–Triassic m ...
'', Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
carnivorous therapsid
*''Euparkeria
''Euparkeria'' (; meaning "Parker's good animal", named in honor of W.K. Parker) is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Middle Triassic of South Africa. It was a small reptile that lived between 245-230 million years ago, and was close to ...
'', archosaur
*''Massospondylus
''Massospondylus'' ( ; from Greek, (massōn, "longer") and (spondylos, "vertebra")) is a genus of sauropodomorph dinosaur from the Early Jurassic. (Hettangian to Pliensbachian ages, ca. 200–183 million years ago). It was described by S ...
'', late Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
to early Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
herbivorous, bipedal dinosaur
*''Megazostrodon
''Megazostrodon'' is an extinct genus of basal mammaliaforms belonging to the order Morganucodonta. It is approximately 200 million years old.
'', early mammal
 The lava outpourings that ended the Karoo deposition of rocks, not only covered the African surface, and other parts of Gondwana with a 1.6 km thick layer basaltic lava, but it also forced its way, under high pressure, between the horizontal layers of sedimentary rocks belonging to the Ecca and Beaufort groups, to solidify into dolerite sills. The long vertical fissures through which the lava welled up solidified into dikes which resemble the
The lava outpourings that ended the Karoo deposition of rocks, not only covered the African surface, and other parts of Gondwana with a 1.6 km thick layer basaltic lava, but it also forced its way, under high pressure, between the horizontal layers of sedimentary rocks belonging to the Ecca and Beaufort groups, to solidify into dolerite sills. The long vertical fissures through which the lava welled up solidified into dikes which resemble the Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic gro ...
from the air.
From about 150 million years ago the South African surface has been subjected to an almost uninterrupted period of erosion, particularly during the past 20 million years, shaving off many kilometers of sediments. This exposed the dolerite sills, which were more resistant to erosion than the Karoo sediments, forming one of the most characteristic features of the Karoo landscape, namely the flat topped hills, called "Karoo Koppies".
Geology of the Little Karoo
The geology of the Little Karoo bears no resemblance to that of the Great Karoo (see the diagram on the left, of a NS geological cross-section through the Little and Great Karoos). The valley is an integral part of the Cape Fold Mountain Belt, with the two ranges on either side composed of extremely hard, erosion-resistant, quartziticsandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
belonging to the 450- to 510-million-year-old Table Mountain Group (i.e. the oldest layer of the Cape Supergroup). The valley floor is covered, in the main, by the next (younger) layer of the Supergroup, namely the much softer Bokkeveld shales. The dolerite of the Great Karoo did not penetrate these rocks, so Karoo Koppies are not seen in the Little Karoo.
The Little Karoo contains two other geological features that give the landscape a special character. During the erosion of the African interior following the bulging of the continent during the massive lava outpourings that ended the Karoo sedimentation 180 million years ago, some of the eroded material was trapped in the valleys of the Cape Fold Mountains, especially during the Cretaceous period
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of t ...
, about to years ( Ma) ago. These "Enon Conglomerates", as they are known, were deposited by high energy, fast flowing rivers, and are found between Calitzdorp and Oudtshoorn, where they form the strikingly red "Redstone Hills".Van Deventer, L. & McLennan, B. (eds) (2010). "The Little Karoo" in ''South Africa by Road, a Regional Guide''. p. 58-61. Struik Publishers, Cape Town.
The second special geological feature that marks the Little Karoo is the 300 km-long fault line along the southern edge of the Swartberg Mountains. The Swartberg Mountains were lifted up along this fault, to such an extent that in the Oudtshoorn region, the rocks that form the base of the Cape Supergroup are exposed. These are locally known as the Cango Group, but are probably continuous with the Malmesbury Group that forms the base of Table Mountain
Table Mountain ( naq, Huriǂoaxa, lit= sea-emerging; af, Tafelberg) is a flat-topped mountain forming a prominent landmark overlooking the city of Cape Town in South Africa. It is a significant tourist attraction, with many visitors using the ...
on the Cape Peninsula, and similar outcrops in the Western Cape
The Western Cape is a province of South Africa, situated on the south-western coast of the country. It is the fourth largest of the nine provinces with an area of , and the third most populous, with an estimated 7 million inhabitants in 2020 ...
. In the Little Karoo, the outcrop is composed of limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
, into which an underground stream has carved the impressively extensive Cango Caves
The Cango Caves are located in Precambrian limestones at the foothills of the Swartberg range near the town of Oudtshoorn, in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. The principal cave is one of the country's finest, best known, and most pop ...
.
Karoo flora
 The
The World Wildlife Fund
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the Wo ...
has classified the Great Karoo and Little Karoo as almost entirely within two of what they consider South Africa’s eight botanical biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
s,
they have coined their biomes succulent Karoo and the Nama Karoo
Nama Karoo is a xeric shrubland ecoregion located on the central plateau of South Africa and Namibia. It occupies most of the interior of the western half of South Africa and extends into the southern interior of Namibia.
Climate
The climate t ...
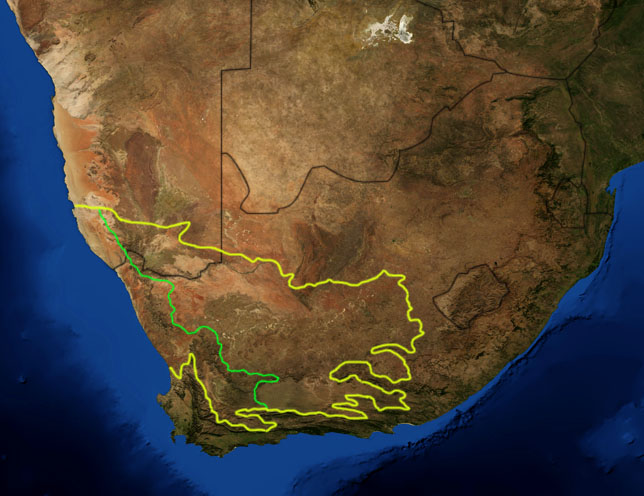
, although both, like the geological Karoo Supergroup, are more extensive than the geographical or historical Karoo described in South African atlases and guide books (compare the map on the right with the map at the beginning of the article).''The Times Comprehensive Atlas of the World''. (1999) p. 90. Times Books Group, London.
Succulent Karoo biome
The succulent Karoo biome runs along the West Coast, from approximately Lamberts Bay northwards to over 200 km into southernNamibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
.''Succulent Karoo''Accessed 30 April 2014 It starts in the south just north of the Veld#Sandveld and Hardveld, sandveld geographical region, about 250 km north of Cape Town, and continues through
Namaqualand
Namaqualand (khoekhoe: "Nama-kwa" meaning Nama Khoe people's land) is an arid region of Namibia and South Africa, extending along the west coast over and covering a total area of . It is divided by the lower course of the Orange River into ...
, the Richtersveld, immediately south of the Orange River, and on into the Namaqualand or Namaland region of southern Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
. None of these regions is ever referred to, either geographically or locally, as "Karoo". However, it has a major extension inland into the Tankwa Karoo and Moordenaarskaroo regions of the Lower Karoo, and adjoining Upper Karoo region of the geographic Great Karoo. It also occurs to the south, in part of the Breede River Valley
Breede River Valley is a region of Western Cape Province, South Africa known for being the largest fruit and wine producing valley in the Western Cape, as well as South Africa's leading race-horse breeding area. It is part of the Boland borderin ...
, as the Robertson Karoo
Robertson Karoo is a semi-arid vegetation type, restricted to sections of the Breede River Valley, Western Cape Province, South Africa. It is a subtype of Succulent Karoo (geographically an extension of the "Little Karoo") and is characterised by ...
. From here, it continues eastwards into the western half of the Little Karoo.
 The succulent Karoo biome is dominated by dwarf, leafy-succulent shrubs, and annuals, predominantly
The succulent Karoo biome is dominated by dwarf, leafy-succulent shrubs, and annuals, predominantly Asteraceae
The family Asteraceae, alternatively Compositae, consists of over 32,000 known species of flowering plants in over 1,900 genera within the order Asterales. Commonly referred to as the aster, daisy, composite, or sunflower family, Compositae w ...
, popularly known as Namaqualand daisies, which put on spectacular flower displays covering vast stretches of the landscape in the southern spring-time (August–September) after good rains in the winter. Grasses are uncommon, making most of the biome unsuitable for grazing. The low rainfall, in fact, discourages most forms of agriculture. An exception is the thriving ostrich-farming industry in the Little Karoo, which is heavily dependent on supplementary feeding with lucerne. The difference between the succulent Karoo biome and the Nama Karoo biome is that the former receives the little rain that falls as cyclonic rainfall in winter, which has less erosive power than the infrequent but violent summer thunderstorms of the Nama Karoo. Frost is also less common in the succulent Karoo biome than in the Nama Karoo biome. The number of mainly succulent plant species is very high for an arid area of this size anywhere in the world.
Nama Karoo biome
The Nama Karoo biome is located entirely on the central plateau mostly at altitudes between 1000 and 1500 m.''The Nama Karoo Biome''. Accessed 2 May 2014''The Nama Karoo Biome'' . Accessed 2 May 2014 It incorporates nearly the whole of the historical and geographical Great Karoo, but also includes a portion of southern Namibia's Namaqualand, and South Africa's Bushmanland (both local geographical names, not names of biomes). It is the second-largest biome in South Africa, and forms the botanical transition between the Fynbos#Cape Floral Kingdom, fynbos biome to the south and the savannah biome to the north. It is defined primarily by the dominance of dwarf (less than 1 m high) shrubs with a co-dominance of grasses especially towards the north-east and east where it grades into the grassland biome of the highveld and the Eastern Midlands. The shrubs and grasses are deciduous, mainly in response to the irregular rainfall. Much of the Nama Karoo biome is used for sheep and goat farming, providing mutton, wool, and pelts for local and international markets, especially since livestock can frequently be provided with a regular supply of water from boreholes. Overgrazing exacerbates the erosion caused by the violent thunderstorms that occur, infrequently, in the summer. It also promotes the replacement of the grasses by shrubs, especially the less edible varieties such as the threethorn (''
Rhigozum trichotomum
''Rhigozum trichotomum'' is a shrub that is native to Namibia and South Africa. It is found mainly in the Nama Karoo and is listed on the SANBI red list as 'safe' (LC). It is a woody perennial shrub
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a ...
''), bitterbos ('' Chrysocoma ciliata''), and sweet thorn ('' Acacia karroo''). However, there are few rare or Red Data Book plant species in the Nama Karoo biome.
Karoo fauna
Great Karoo
The Great Karoo used to support a large variety of antelope (particularly thespringbok
The springbok (''Antidorcas marsupialis'') is a medium-sized antelope found mainly in south and southwest Africa. The sole member of the genus ''Antidorcas'', this bovid was first described by the German zoologist Eberhard August Wilhelm ...
), the quagga
The quagga ( or ) (''Equus quagga quagga'') is a subspecies of the plains zebra that was endemic to South Africa until it was hunted to extinction in the late 19th century. It was long thought to be a distinct species, but early genetic ...
, and other large game, especially on the grassy flats in the east. Francois Le Vaillant, the famous French explorer, naturalist, and ornithologist, who traveled through the Great Karoo in the 1780s, killed a hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extan ...
in the Great Fish River in the Karoo (and ate its foot for breakfast). He also recorded that he saw the spoor of a rhinoceros near Cranemere, in the Camdeboo Plains (eastern Lower Karoo). Elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
tusks have been found by farmers in the Camdeboo district, but no records exist of any having been seen alive in that region.
The quagga roamed the Karoo in great numbers together with wildebeest and ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There ...
es, which always seemed to accompany them. These quagga seemed gentle and easy to domesticate. (A pair of quagga was used to draw a horse carriage through London, more for curiosity than for any superiority the quagga might have had over a horse.) They were consequently also easy prey for hunters, who hunted them for sport rather than their meat. By the middle of the 1800s, they were almost extinct, and in 1883, the last one died in an Amsterdam zoo.
 Probably the strangest and most puzzling zoological phenomenon in the Great Karoo was the periodic, unpredictable appearance of massive springbok migrations. These migrations always came from the north, and could either go west towards Namaqualand and the sea, south-west through towns such as
Probably the strangest and most puzzling zoological phenomenon in the Great Karoo was the periodic, unpredictable appearance of massive springbok migrations. These migrations always came from the north, and could either go west towards Namaqualand and the sea, south-west through towns such as Beaufort West
Beaufort West (Afrikaans: ''Beaufort-Wes''; Xhosa: ''eBhofolo'') is a town in the Western Cape province in South Africa. It is the largest town in the arid Great Karoo region, and is known as the "Capital of the Karoo". It forms part of the Beau ...
, or south through the Camdeboo district. These vast herds moved steadily and inexorably across the plains, trampling all before them, including their own kind. Le Vaillant gave the first eyewitness account of such a migration in 1782. He rode through the herd filling the Plains of Camdeboo, seeing neither the beginning nor end of the moving mass.
 In 1849, a massive herd of springbok, amongst which were intermingled wildebeest, blesbok, quagga, and eland, moved through Beaufort West. Early one morning, the town was awakened to a sound like that of a strong wind, and suddenly the town was filled with animals. They devoured every sprig of foliage in the town and surrounding countryside. The last of the continuously moving herd left the town 3 days later, to disappear towards the west. The Karoo looked as if a fire had swept through it. During these migrations, the plains and hillsides on every side were thickly covered by one vast mass of springbok, packed like sheep in a fold. As far as the eye could see, the landscape was alive with them.
During these migrations, the springbok never ran or trotted. On the whole, they were silent, except for the shudder of their stamping hoofs. Nothing could divert them, and hunters could ride amongst them, shooting them at random, without apparently causing alarm. People could move amongst them and kill them with sticks, or cripple them by seizing a leg and breaking it. Not only people followed these herds for the easy meat they provided, but also lions, leopards,
In 1849, a massive herd of springbok, amongst which were intermingled wildebeest, blesbok, quagga, and eland, moved through Beaufort West. Early one morning, the town was awakened to a sound like that of a strong wind, and suddenly the town was filled with animals. They devoured every sprig of foliage in the town and surrounding countryside. The last of the continuously moving herd left the town 3 days later, to disappear towards the west. The Karoo looked as if a fire had swept through it. During these migrations, the plains and hillsides on every side were thickly covered by one vast mass of springbok, packed like sheep in a fold. As far as the eye could see, the landscape was alive with them.
During these migrations, the springbok never ran or trotted. On the whole, they were silent, except for the shudder of their stamping hoofs. Nothing could divert them, and hunters could ride amongst them, shooting them at random, without apparently causing alarm. People could move amongst them and kill them with sticks, or cripple them by seizing a leg and breaking it. Not only people followed these herds for the easy meat they provided, but also lions, leopards, cheetah
The cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus'') is a large cat native to Africa and central Iran. It is the fastest land animal, estimated to be capable of running at with the fastest reliably recorded speeds being , and as such has evolved specialized ...
s, African wild dogs, hyenas, and jackal
Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed ...
s preyed on them.
No one knew how, why, or where these migrations started, nor where they ended, nor did anyone know if these animals ever returned to where they had started. The migrations were always unidirectional, from north of the Great Karoo.
Great locust swarms also frequently invaded or arose in the Great Karoo, and still occur from time to time today.
The riverine rabbit, a critically endangered animal, lives exclusively in seasonal river basins and a very particular set of scrubland in the central semiarid region in the Karoo. It is hunted by falconiformes
The order Falconiformes () is represented by the extant family Falconidae (falcons and caracaras) and a handful of enigmatic Paleogene species. Traditionally, the other bird of prey families Cathartidae (New World vultures and condors), Sagitt ...
and Verreaux's eagles. Its numbers have been consistently lowering due to destruction of its habitat. They are unique relative to similar species through how they are polygamous and how each female can only produce one or two offspring per year.
The introduction of the windpump to tap the Great Karoo’s underground water resources in the late 1800s made permanent human habitation and sheep farming possible over large parts of the Great Karoo for the first time. As a result, the teeming number of large antelope in the Karoo has dwindled into insignificance, and with them, the large carnivores have all but disappeared. Today, the caracal (7–19 kg),Stuart, C. & Stuart, T (2007). ''Field Guide to Mammals of Southern Africa'' p. 136, 170, 176. Struik, Cape Town black-backed jackal (6–10 kg), Verreaux's eagle (3.0–5.8 kg) and the martial eagle (3.0–6.2 kg)Hockey, P.A.R., Dean, W.R.J. & Ryan, P.G. (2005). ''Roberts Birds of Southern Africa''. (7th Edition). p. 531, 497. Trustees of the John Voelcker Bird Book Fund, Cape Town. are arguably the largest predators likely to be seen in the Great Karoo today. Leopards
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus ''Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
(20–90 kg) do occur, especially in the mountains, but are very secretive, so are rarely seen. Many of the animals that formerly inhabited the Karoo in large numbers, including lions, have been reintroduced to the area in nature reserves and game farms.
Little Karoo
As in the Great Karoo, antelope and other big game inhabited the Little Karoo in the past. However, the dominant zebra was not the quagga, but the Cape mountain zebra, (''Equus zebra zebra'') which is adapted for life on rugged, mountainous terrain. Their hooves are harder and faster-growing than those of Burchell’s zebra (''Equus quagga burchellii''), which lives on the plains.Moodley, Y. & Harley, E.H. (2006) Population structuring in mountain zebra (''Equus zebra''):the molecular consequences of divergent histories. ''Conservation Genetics''. The two species are, therefore, rarely seen in the same habitat. The quagga is closely related to Burchell's zebra, and appears also to have been confined to the plains. The mountain zebra occurred in the mountain regions of the Cape Fold Belt and along the southern portion of the Great Escarpment. Thus, they were endemic to, amongst others, the western Lower Karoo and the Little Karoo. However, they were hunted to near extinction, leaving fewer than 100 individuals by the 1930s. Conservation efforts since then brought their numbers up to 1200 by 1998, mainly by concentrating these zebra in nature reserves and protected areas, the most well-known of these being the Mountain Zebra National Park near Cradock in the Great Karoo. Cape mountain zebras are still found in protected areas managed by Cape Nature, including the Kamanassie and Gamkaberg Nature Reserves. The ostrich is found throughout Africa, but the most handsome specimens came from the Little Karoo, where the dry weather, but plentiful water in the streams formed an ideal habitat for these large, flightless birds. Here, they grow to over 2 m in height, and weigh over 100 kg. The male’s feathers have been prized by many cultures in Africa, Europe, and Asia over thousands of years. In the 1860s, a farmer in theGraaff-Reinet
Graaff-Reinet is a town in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. It is the oldest town in the province. It is also the sixth-oldest town in South Africa, after Cape Town, Stellenbosch, Simon's Town, Paarl and Swellendam. The town was the ...
district was apparently the first person to demonstrate that the ostrich could successfully be domesticated, bred in captivity, and the eggs hatched in incubators, while still producing the magnificent feathers. This idea was quickly adopted by farmers in the Little Karoo, where they started growing lucerne as the birds' favorite food. During 1880, no less than 74,000 kg of feathers were exported, and in 1904, it passed the 210,000-kg mark.
The First World War brought about a slump in the ostrich feather market, but the industry recovered in later years, when not only the feathers were sought after, but also ostrich leather, and its meat, which is very tasty, and a major export item. Today, several farms can be visited by tourists, near Oudtshoorn, the center of the ostrich industry.
Modern history
Great Karoo
The first European settlers landed in the Cape of Good Hope in 1652, and between 1659 and 1664, made several unsuccessful attempts to penetrate the Great Karoo from the south-west. The Europeans who first entered the Great Karoo did so from the south-east (traveling north from Algoa Bay), which is slightly less arid than the western Karoo. These were the '' trekboers'' of the mid-1700s, who led a nomadic existence, enduring great hardships in the relentless aridity, the intense heat (such that even their dogs could not walk on the scorching ground and had to be lifted into the overcrowded wagons), and the bitter cold in winter, especially at night. Before that time, the only inhabitants were the Khoe-speaking clans migrating through the area, and !Ui-speaking peoples, who lived in small family groups and, it is believed, remained largely in their own "territories", killing their own game, and gathering bulbs and roots and drinking from a spring or other water source within their territory. Sometimes these territories were very large and the family group moved from one part to the other. Their only domestic animals were dogs. The Ntu-speaking agriculturalists to the east of the Great Karoo did not occupy this arid region due to the scarce rainfall which prevented the farming of cattle.windpump
A windpump is a type of windmill which is used for pumping water.
Windpumps were used to pump water since at least the 9th century in what is now Afghanistan, Iran and Pakistan. The use of wind pumps became widespread across the Muslim world an ...
(windmill) in the USA. It was perfected in 1883, and soon South Africa (and elsewhere) produced them in large numbers. These windpumps transformed the Great Karoo, making permanent settlement and stock farming (predominantly sheep) possible over large parts of the Karoo for the first time. Like the Karoo Koppie, the multibladed windpump became an iconic feature of the Great Karoo.
Sheep farming and the fencing off of the land have meant that antelope numbers have dwindled significantly, and with them, the big carnivores. Leopards still occur in the mountains, but lions now only occur in nature reserves, where they have been recently reintroduced into the Great Karoo.
 In 1872, construction was started to connect the
In 1872, construction was started to connect the Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with t ...
's coastal railway system with the diamond fields in Kimberley, The new line started in Worcester and entered the Lower Karoo through the Hex River valley, where it followed a course almost midway between the Swartberg Mountains to the south and the Great Escarpment to the north. Along the way, it passed through the quaint Victorian village of Matjiesfontein
Matjiesfontein is a settlement in Central Karoo District Municipality in the Western Cape province of South Africa.
History
The original inhabitants of the region were the Khoikhoi herders and the San hunter gatherers. Following the arrival of ...
, with the historic Lord Milner Hotel, which is still operational today. The railway reached this point in 1878, before proceeding to Beaufort West at the foot of the Great Escarpment. From there, it reached the top of the African Plateau near Three Sisters along a valley with such a low gradient that passengers were (and still are) hardly aware that they were ascending the Great Escarpment. From there it continued through the Upper Karoo, to De Aar, and crossed the Orange River at Hopetown
Hopetown is a town which lies at the edge of the Great Karoo in South Africa's Northern Cape province. It is situated on an arid slope leading down to the Orange River. The first diamond discovered in South Africa, the Eureka Diamond, was fo ...
, where South Africa’s first diamond, the Eureka Diamond, was found. The Orange River, at this point, forms the local unofficial boundary between the Great Karoo and the Highveld.
The line reached Kimberley in 1885, and has since been extended via Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label= Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalaha ...
(then Bechuanaland) to reach Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and ...
and Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are t ...
(when they were still known as South and North Rhodesia), and branch lines have been constructed to Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
and Port Elizabeth through a hub at De Aar, in the Great Karoo. Further branch lines were later built from points further north to Bloemfontein
Bloemfontein, ( ; , "fountain of flowers") also known as Bloem, is one of South Africa's three capital cities and the capital of the Free State province. It serves as the country's judicial capital, along with legislative capital Cape To ...
, Durban
Durban ( ) ( zu, eThekwini, from meaning 'the port' also called zu, eZibubulungwini for the mountain range that terminates in the area), nicknamed ''Durbs'',Ishani ChettyCity nicknames in SA and across the worldArticle on ''news24.com'' from ...
, and, of course, to Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu and xh, eGoli ), colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a megacity, and is one of the 100 largest urban areas in the world. According to Dem ...
.
During the Second Anglo-Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
of 1899–1902, three Republican commando
Royal Marines from 40 Commando on patrol in the Sangin">40_Commando.html" ;"title="Royal Marines from 40 Commando">Royal Marines from 40 Commando on patrol in the Sangin area of Afghanistan are pictured
A commando is a combatant, or operativ ...
units, reinforced by the sympathizers ("rebels") from the Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with t ...
, conducted widespread operations throughout the Karoo. Countless skirmishes took place in the region, with the Calvinia magisterial district, in particular, contributing a significant number of fighters to the Republican cause. Fought both conventionally and as a guerrilla struggle over the Karoo's vast expanses, it was a bloody war of attrition wherein both sides used newly developed technologies to their advantage. Numerous abandoned blockhouses can still be seen at strategic locations, especially along the railway line, throughout the Great Karoo. A prime example still "guards" a bridge over the Buffels River, to the east of the town of Laingsburg, in the Lower Karoo, between Matjiesfontein and Beaufort West.
Recently, nature reserves and game farms have been established in many parts of the Great Karoo, turning what was once regarded as a forbiddingly desolate and unattractive geographical barrier into a tourist destination.
Little Karoo
This area was explored by European settlers in the late 17th century, who encountered the Khoisan people as the original inhabitants of this area. The latter called the Swartberg Mountains ''kango'' meaning "a place rich in water". TheCango Caves
The Cango Caves are located in Precambrian limestones at the foothills of the Swartberg range near the town of Oudtshoorn, in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. The principal cave is one of the country's finest, best known, and most pop ...
in the Swartberg Mountains are named after this Khoisan word.
The Little Karoo, and especially Oudtshoorn, became synonymous with the ostrich-feather industry in the 1880s. The resulting "feather millionaires" built Victorian "Feather Palaces" all over town, using the red rocks belonging to the Enon Conglomerate, and related Kirkwood Formation, to build them. These grand red palaces and other buildings in Oudtshoorn can still be admired today.
A railway line was built to connect Calitzdorp and Oudtshoorn, to Willowmore and from there, via Klipplaat, to Port Elizabeth, from where the ostrich feathers from the Little Karoo’s ostrich farms could be exported to Europe. That line is no longer in use today.
The Swartberg Pass was built, with convict labor, between 1881 and 1888 by Thomas Bain, son of the famous Andrew Geddes Bain
Andrew Geddes Bain (baptised 11 June 1797 – 20 October 1864), was a South African geologist, road engineer, palaeontologist and explorer.
Life history
The only child of Alexander Bain and Jean Geddes, both of whom died when Bain was still a ...
, who built Bain's Kloof Pass and many others in the Western Cape. The main motivation for building the pass was to provide an all-weather road connection between the southern Great Karoo, and Oudtshoorn (and from there to the sea). The two alternative roads, through the Meiringspoort and the Seweweekspoort defiles, were subject to periodic flooding, after heavy thunderstorms in the Great Karoo. The Swartberg Pass is not tarred and can be treacherously slippery after rain. It also becomes impassable after heavy snowfalls on the mountain, a not infrequent occurrence in winter.
Karoo in literature
Poet Thomas Hardy wrote of the Karoo in his 1899 poem "Drummer Hodge" (or "The Dead Drummer").Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
, in his 1901 poem "Bridge-Guard in the Karroo", evoked the loneliness experienced by blockhouse soldiers at Ketting station on the Dwyka River while guarding the Karoo railway track, a lifeline during the South African War. The poem was first published in The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' (f ...
of 5 June 1901.
Beaufort West
Beaufort West (Afrikaans: ''Beaufort-Wes''; Xhosa: ''eBhofolo'') is a town in the Western Cape province in South Africa. It is the largest town in the arid Great Karoo region, and is known as the "Capital of the Karoo". It forms part of the Beau ...
File:Karoo National Park.jpg, The Lower Karoo
File:Valley of Desolation 02 (3547568381).jpg, The Valley of Desolation near Graaff-Reinet
Graaff-Reinet is a town in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. It is the oldest town in the province. It is also the sixth-oldest town in South Africa, after Cape Town, Stellenbosch, Simon's Town, Paarl and Swellendam. The town was the ...
File:Karoo Koppies.png, Typical Karoo koppies near Cradock
File:Farmhouse in the Northern Cape (Karoo).jpg, Farmhouse in the Tankwa Karoo.
See also
* People of the Karoo *Karoo National Park
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hard veld") is a semi- desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its ...
* Mountain Zebra National Park
*Camdeboo National Park
The Camdeboo National Park is located in the Karoo and almost completely surrounds the Eastern Cape town of Graaff-Reinet
Graaff-Reinet is a town in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. It is the oldest town in the province. It is als ...
*Tankwa Karoo National Park
Tankwa Karoo National Park is a national park in South Africa. The park lies about 70 km due west of Sutherland near the border of the Northern Cape and Western Cape, in one of the most arid regions of South Africa, with areas receiving ...
*Karoo District Municipality
Pixley ka Seme is one of the five districts of the Northern Cape province of South Africa. The seat of Pixley ka Seme is De Aar. The majority (77%) of its 186,351 people speak Afrikaans as first language (2011 Census). The district code is DC7. ...
* Central Karoo District Municipality
* Karoo Ice Age
References
External links
* *http://www.karoospace.co.zaKaroo, South Africa
{{Authority control Geography of South Africa Natural regions of South Africa Namaqualand Physiographic provinces South African English