List of the oldest universities on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
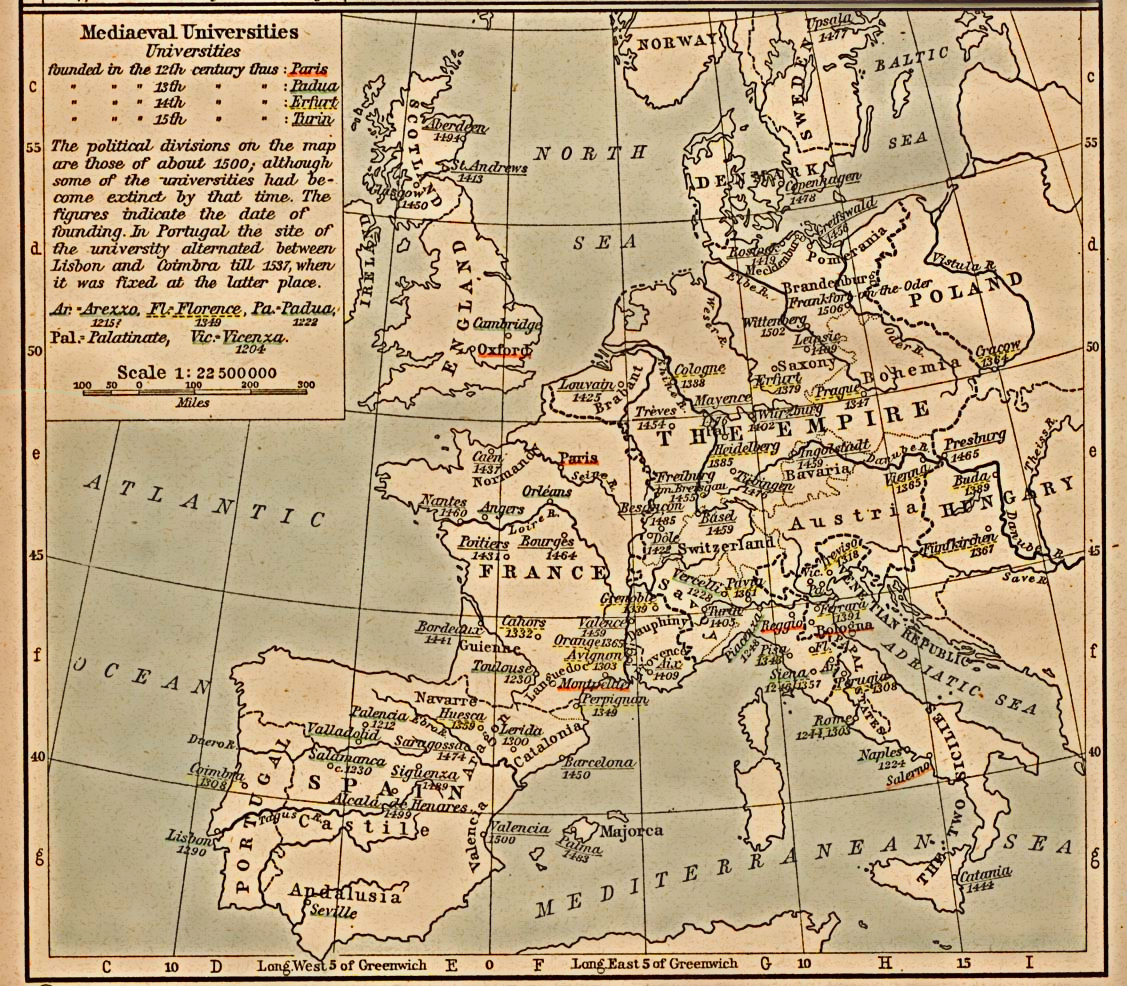
 This article contains a list of the oldest existing universities in continuous operation in the world. Inclusion in this list is determined by the date at which the educational institute first met the traditional definition of a university used by academic historians although it may have existed as a different kind of institution before that time. This definition limits the term "university" to institutions with distinctive structural and legal features that developed in Europe, and which make the university form different from other institutions of higher learning in the pre-modern world, even though these may sometimes now be referred to popularly as universities. Thus, to be included in the list below, the university must have been founded before 1500 in Europe or be the oldest university derived from the medieval European model in a country or region. It must also be still in operation, with institutional continuity retained throughout its history. So some early universities, most notably the University of Paris (founded around the beginning of the thirteenth century), which was abolished by the Revolution in 1793, are excluded. Some institutions re-emerge, but with new foundations, such as the modern University of Paris, which came into existence in 1896 after the ''Louis Liard law'' disbanded
This article contains a list of the oldest existing universities in continuous operation in the world. Inclusion in this list is determined by the date at which the educational institute first met the traditional definition of a university used by academic historians although it may have existed as a different kind of institution before that time. This definition limits the term "university" to institutions with distinctive structural and legal features that developed in Europe, and which make the university form different from other institutions of higher learning in the pre-modern world, even though these may sometimes now be referred to popularly as universities. Thus, to be included in the list below, the university must have been founded before 1500 in Europe or be the oldest university derived from the medieval European model in a country or region. It must also be still in operation, with institutional continuity retained throughout its history. So some early universities, most notably the University of Paris (founded around the beginning of the thirteenth century), which was abolished by the Revolution in 1793, are excluded. Some institutions re-emerge, but with new foundations, such as the modern University of Paris, which came into existence in 1896 after the ''Louis Liard law'' disbanded

 This article contains a list of the oldest existing universities in continuous operation in the world. Inclusion in this list is determined by the date at which the educational institute first met the traditional definition of a university used by academic historians although it may have existed as a different kind of institution before that time. This definition limits the term "university" to institutions with distinctive structural and legal features that developed in Europe, and which make the university form different from other institutions of higher learning in the pre-modern world, even though these may sometimes now be referred to popularly as universities. Thus, to be included in the list below, the university must have been founded before 1500 in Europe or be the oldest university derived from the medieval European model in a country or region. It must also be still in operation, with institutional continuity retained throughout its history. So some early universities, most notably the University of Paris (founded around the beginning of the thirteenth century), which was abolished by the Revolution in 1793, are excluded. Some institutions re-emerge, but with new foundations, such as the modern University of Paris, which came into existence in 1896 after the ''Louis Liard law'' disbanded
This article contains a list of the oldest existing universities in continuous operation in the world. Inclusion in this list is determined by the date at which the educational institute first met the traditional definition of a university used by academic historians although it may have existed as a different kind of institution before that time. This definition limits the term "university" to institutions with distinctive structural and legal features that developed in Europe, and which make the university form different from other institutions of higher learning in the pre-modern world, even though these may sometimes now be referred to popularly as universities. Thus, to be included in the list below, the university must have been founded before 1500 in Europe or be the oldest university derived from the medieval European model in a country or region. It must also be still in operation, with institutional continuity retained throughout its history. So some early universities, most notably the University of Paris (founded around the beginning of the thirteenth century), which was abolished by the Revolution in 1793, are excluded. Some institutions re-emerge, but with new foundations, such as the modern University of Paris, which came into existence in 1896 after the ''Louis Liard law'' disbanded Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's University of France system.
The word ''university'' is derived from the la, universitas magistrorum et scholarium, which approximately means "community of teachers and scholars". The University of Bologna in Bologna, Italy, where teaching began around 1088 and which was organised into a university in the late twelfth century, is the world's oldest university in continuous operation, and the first university in the sense of a higher-learning and degree-awarding institute.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f. The origin of many medieval universities
A medieval university was a corporation organized during the Middle Ages for the purposes of higher education. The first Western European institutions generally considered to be universities were established in present-day Italy (including the ...
can be traced back to the Catholic cathedral schools or monastic schools, which appeared as early as the 6th century and were run for hundreds of years as such before their formal establishment as universities in the high medieval period
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 1500 ...
.
Ancient higher-learning institutions, such as those of ancient Greece, ancient Persia, ancient Rome, Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
, ancient China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapte ...
, ancient India and the Islamic world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
, are not included in this list owing to their cultural, historical, structural and legal differences from the medieval European university from which the modern university evolved.Rüegg, Walter: "Foreword. The University as a European Institution", in: ''A History of the University in Europe. Vol. 1: Universities in the Middle Ages'', Cambridge University Press, 1992, , pp. XIX–XX.
Medieval origins
The university as aninstitution
Institutions are humanly devised structures of rules and norms that shape and constrain individual behavior. All definitions of institutions generally entail that there is a level of persistence and continuity. Laws, rules, social conventions a ...
was historically rooted in medieval society, which it in turn influenced and shaped. Academic historian Walter Rüegg asserts that:
Modern spread
From the early modern period onwards, the university spread from the medieval Latin West across the globe, eventually replacing all other higher-learning institutions and becoming the preeminent institution for higher education everywhere. The process occurred in the following chronological order:Rüegg, Walter (ed.): ''Geschichte der Universität in Europa'', 3 vols., C.H. Beck, München 1993, * Southern and Western Europe (from the 11th or 12th century) * Central and Northern Europe (from the 14th or 15th century) * Americas (from the 16th century) * Australia (from the 19th century) * Asia and Africa (from the 19th or 20th century), with the exception of the Philippines, where the University of Santo Tomas was established in the 17th century.Founded as universities before 1500
This list includesmedieval universities
A medieval university was a corporation organized during the Middle Ages for the purposes of higher education. The first Western European institutions generally considered to be universities were established in present-day Italy (including the ...
that were founded before 1500 and which have retained institutional continuity since then (excluding not only those that ceased to exist, but also those that merged into or split away to an institution which is regarded as newly established). Several of these have been closed for brief periods: for example the University of Siena was closed 18051815 during the Napoleonic wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, and non-German speaking universities in the Czech Republic and Poland were closed during Nazi occupation, 1939–1945.
Universities are dated from when, according to scholars, they first met the definition of a university. In cases such as the universities of Bologna and Oxford which trace their history back to teaching in individual schools prior to their formation into a university, or which existed in another form prior to being a university, the date in the list below is thus later than the date given by the institutions for their foundation.
Oldest universities by country or region after 1500 still in operation
The majority of European countries had universities by 1500. Many universities were established at institutes of learning such as schools and colleges that may have been founded significantly earlier but were not classed as universities upon their foundation; this is normally described in the notes for that institution. In some countries (particularly the US and those influenced by its culture), degree-granting higher education institutions that would normally be called universities are instead called colleges, in this case both the oldest institution that would normally be regarded as a university and the oldest institution (if different) to actually be called a university are given. In many parts of the world the first university to have a presence was an institution based elsewhere (often the University of London via the affiliation of a local college); where this is different from the first locally established university both are given.Africa
Asia
Europe
While Europe had 143 universities in 1789, the Coalition Wars took a heavy toll, reducing the number to 83 by 1815. The universities of France were abolished and over half of the universities in both Germany and Spain were destroyed. By the mid 19th century, Europe had recovered to 98 universities.Latin America and the Caribbean
North America
In the United States, thecolonial colleges
The colonial colleges are nine institutions of higher education chartered in the Thirteen Colonies before the United States of America became a sovereign nation after the American Revolution. These nine have long been considered together, notably ...
awarded degrees from their foundation, but none were formally named as universities prior to the American Revolution, leading to various claims to be the first university in the United States. The earliest Canadian institutions were founded as colleges, without degree awarding powers, and gained degree granting authority and university status later.
Oceania
See also
* List of oldest Islamic seminaries * List of medieval universities *List of oldest institutions in continuous operation
This article contains a list of the oldest existing social institutions in continuous operation, by year of foundation, in the world. Inclusion in this list is determined by the date at which the entity met the traditional definition of an institu ...
References
Notes
Citations
{{DEFAULTSORT:Oldest Universities In Continuous Operation Lists of universities and colleges Lists of education-related superlatives Oldest things