List of most massive black holes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This is an ordered list of the most massive black holes so far discovered (and probable candidates), measured in units of
This is an ordered list of the most massive black holes so far discovered (and probable candidates), measured in units of
 A
A
 This is an ordered list of the most massive black holes so far discovered (and probable candidates), measured in units of
This is an ordered list of the most massive black holes so far discovered (and probable candidates), measured in units of solar mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass ...
es (), approximately .
Introduction
 A
A supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical obj ...
(SMBH) is an extremely large black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravitation, gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts t ...
, on the order of hundreds of thousands to billions of solar masses
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass of ...
(), and is theorized to exist in the center of almost all massive galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. ...
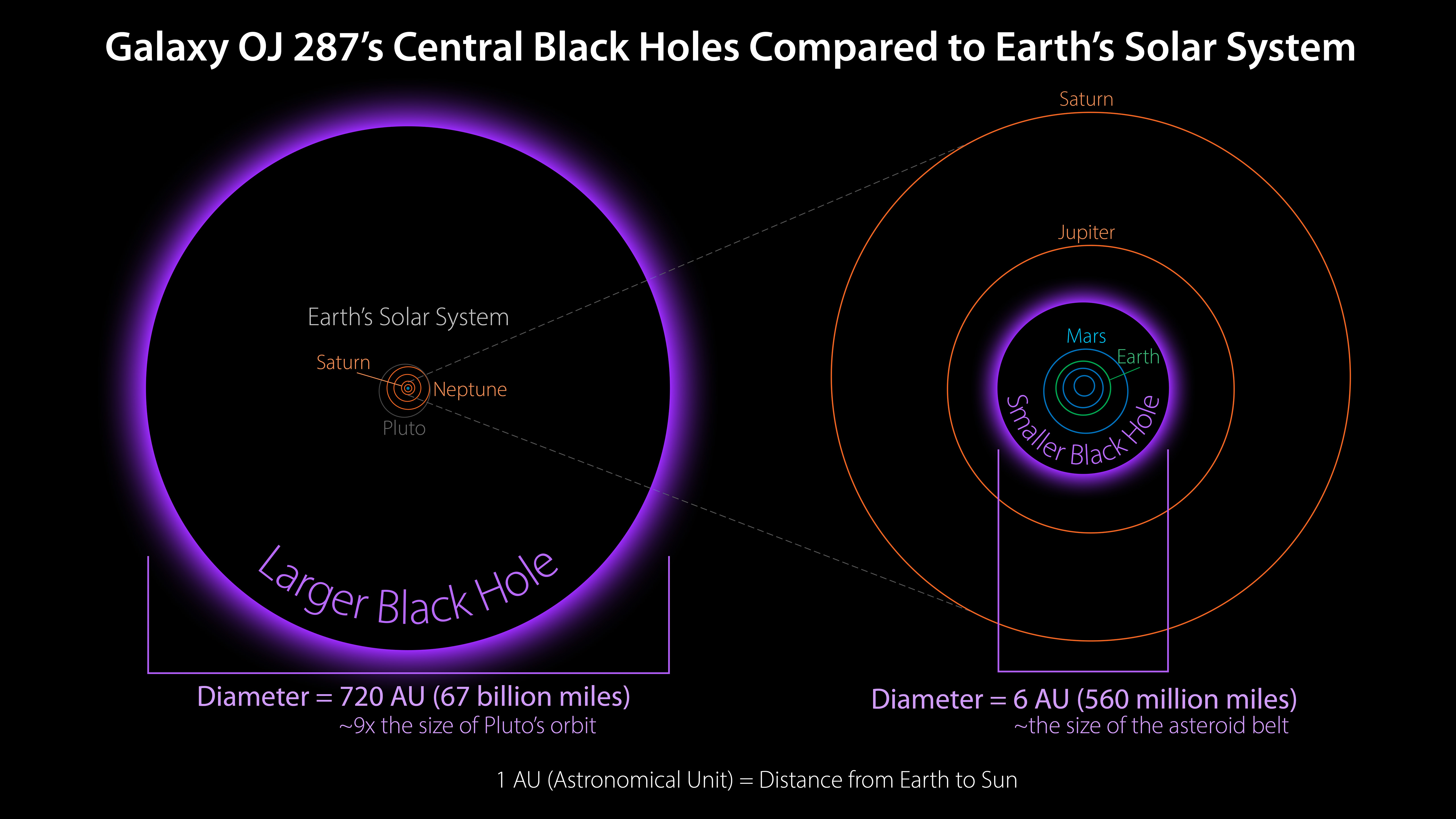
. In some galaxies, there are even binary systems of supermassive black holes, see the OJ 287
OJ 287 is a BL Lac object 3.5 billion light-years from Earth that has produced quasi-periodic optical outbursts going back approximately 120 years, as first apparent on photographic plates from 1891. Seen on photographic plates since at least 18 ...
system. Unambiguous dynamical evidence for SMBHs exists only in a handful of galaxies; these include the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye ...
, the Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way.
It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of .
It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form ...
galaxies M31 and M32, and a few galaxies beyond the Local Group, e.g. NGC 4395
NGC commonly refers to:
* New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars, a catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy
NGC may also refer to:
Companies
* NGC Corporation, name of US electric company Dynegy, Inc. from 1995 to 1998
* Nati ...
. In these galaxies, the mean square (or root mean square
In mathematics and its applications, the root mean square of a set of numbers x_i (abbreviated as RMS, or rms and denoted in formulas as either x_\mathrm or \mathrm_x) is defined as the square root of the mean square (the arithmetic mean of the ...
) velocities of the stars or gas rises as ~1/r near the center, indicating a central point
Point or points may refer to:
Places
* Point, Lewis, a peninsula in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland
* Point, Texas, a city in Rains County, Texas, United States
* Point, the NE tip and a ferry terminal of Lismore, Inner Hebrides, Scotland
* Point ...
mass. In all other galaxies observed to date, the rms velocities are flat, or even falling, toward the center, making it impossible to state with certainty that a supermassive black hole is present. Nevertheless, it is commonly accepted that the center of nearly every galaxy contains a supermassive black hole. The reason for this assumption is the M–sigma relation
The M–sigma (or ''M''–''σ'') relation is an empirical correlation between the stellar velocity dispersion ''σ'' of a galaxy bulge and the mass M of the supermassive black hole at its center.
The ''M''–''σ'' relation was first presented i ...
, a tight (low scatter) relation between the mass of the hole in the ~10 galaxies with secure detections, and the velocity dispersion
In astronomy, the velocity dispersion (''σ'') is the statistical dispersion of velocity, velocities about the Arithmetic mean, mean velocity for a group of astronomical objects, such as an open cluster, globular cluster, galaxy, galaxy cluster, or ...
of the stars in the bulges of those galaxies. This correlation, although based on just a handful of galaxies, suggests to many astronomers a strong connection between the formation of the black hole and the galaxy itself.
Although SMBHs are currently theorized to exist in almost all massive galaxies, more massive black holes are rare; with only fewer than several dozen having been discovered to date. There is extreme difficulty in determining the mass of a particular SMBH, and so they still remain in the field of open research. SMBHs with accurate masses are limited only to galaxies within the Laniakea Supercluster
The Laniakea Supercluster (; Hawaiian for "open skies" or "immense heaven") is the galaxy supercluster that is home to the Milky Way and approximately 100,000 other nearby galaxies. It was defined in September 2014, when a group of astronom ...
and to active galactic nuclei
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not prod ...
.
Another problem for this list is the method used in determining the mass. Such methods, such as broad emission-line reverberation mapping
Reverberation mapping (or Echo mapping) is an astrophysics, astrophysical technique for measuring the structure of the broad-line region (BLR) around a supermassive black hole at the center of an active galaxy, and thus estimating the hole's mass. ...
(BLRM), Doppler measurements, velocity dispersion
In astronomy, the velocity dispersion (''σ'') is the statistical dispersion of velocity, velocities about the Arithmetic mean, mean velocity for a group of astronomical objects, such as an open cluster, globular cluster, galaxy, galaxy cluster, or ...
, and the aforementioned M–sigma relation have not yet been well established. Most of the time, the masses derived from the given methods contradict each other's values.
This list contains supermassive black holes with known masses, determined at least to the order of magnitude. Some objects in this list have two citations, like 3C 273; one from Bradley M. Peterson ''et al.'' using the BLRM method, and the other from Charles Nelson using III�5007 value and velocity dispersion. Note that this list is very far from complete, as the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-spectral imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project began in 2000 a ...
(SDSS) alone detected quasars
A quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is pronounced , and sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. This emission from a galaxy nucleus is powered by a supermassive black hole with a mass ranging ...
, which likely may be the homes of billion-solar-mass black holes. In addition, there are several hundred citations for black hole measurements not yet included on this list. Despite this, the majority of well-known black holes above 1 billion are shown. Messier galaxies with precisely known black holes are all included.
New discoveries suggest that many black holes, dubbed 'stupendously large', may exceed 100 billion or even 1 trillion solar masses.
List
Due to the very large numbers involved, listed black holes here have their mass values in scientific notation (numbers multiplied to powers of 10). Values with uncertainties are written in parentheses when possible. Note that different entries in this list have different methods and systematics in obtaining their mass values, and hence different levels of confidence in their masses. These methods are specified in their notes.See also
*List of largest cosmic structures
This is a list of the largest cosmic structures so far discovered. The unit of measurement used is the light-year (distance traveled by light in one Julian year; approximately 9.46 trillion kilometres).
This list includes superclusters, galaxy ...
* List of largest galaxies
This is a list of largest galaxies known, sorted by order of increasing major axis diameters. The unit of measurement used is the light-year (approximately 9.46 kilometers).
Overview
Galaxies are vast collections of stars, planets, nebulae an ...
* List of least massive black holes
* List of most massive exoplanets
Below is a list of the largest exoplanets so far discovered, in terms of physical size, ordered by radius.
Caveats
This list of extrasolar objects may and will change over time because of inconsistency between journals, different methods used ...
* List of most massive neutron stars
* List of most massive stars
This is a list of the most massive stars that have been discovered, in solar masses ().
Uncertainties and caveats
Most of the masses listed below are contested and, being the subject of current research, remain under review and subject to consta ...
* List of the most distant astronomical objects
This article documents the most distant astronomical objects discovered and verified so far, and the time periods in which they were so classified.
For comparisons with the light travel distance of the astronomical objects listed below, the age of ...
* Lists of astronomical objects
This is a list of lists, grouped by type of astronomical object.
Solar System
* List of Solar System objects
* List of gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System
* List of Solar System objects most distant from the Sun
* List of So ...
References
{{portal bar, Astronomy, Physics, Space, Star *Black holes
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can def ...
Black holes, Most massive
Black holes
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can def ...
Heaviest or most massive things