List of impact craters on Earth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
This list of
"A possible tektite strewn field in the Argentinian Pampa"
''Science'', volume 296, issue 5570, pp. 1109–12 However, there is some uncertainty regarding its origins and age, with some sources giving it as < 10 ka while the EID gives a broader < 100 ka. The Kaali impacts (c. 2000 BC) during the For the Rio Cuarto craters, 2002 research suggests they may actually be aeolian structures. The EID gives a size of about for Campo del Cielo, but other sources quote .
For the Rio Cuarto craters, 2002 research suggests they may actually be aeolian structures. The EID gives a size of about for Campo del Cielo, but other sources quote .
"Australasian tektites found in Guangxi Province, China"
in Proceedings of the 30th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, March 1999Glass, Billy P.; Pizzuto, James E.; (1994
"Geographic variation in Australasian microtektite concentrations: Implications concerning the location and size of the source crater"
''Journal of Geophysical Research'', vol. 99, no. E9, 19075–81, September 1994
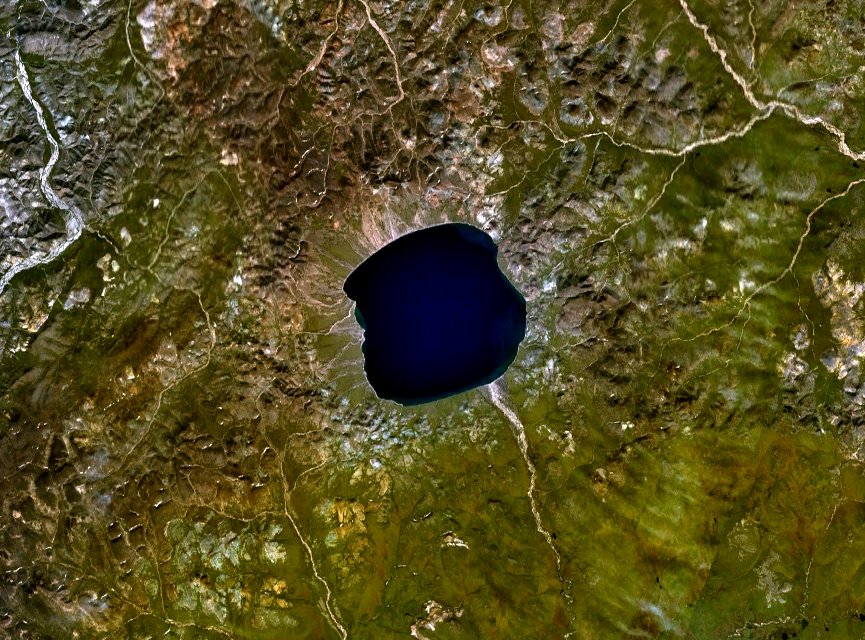

 From between 1 and 10 million years ago, and with a diameter of 5 km or more. If uncertainties regarding its age are resolved, then the largest in the last 10 million years would be the Karakul crater which is listed in EID with an age of less than 5 Ma, or the
From between 1 and 10 million years ago, and with a diameter of 5 km or more. If uncertainties regarding its age are resolved, then the largest in the last 10 million years would be the Karakul crater which is listed in EID with an age of less than 5 Ma, or the
impact crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact crater ...
s on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
contains a selection of the 190 confirmed craters given in the Earth Impact Database as of 2017.
To keep the lists manageable, only the largest craters within a time period are included. Alphabetical lists for different continents can be found under Craters by continent below.
Confirmed impact craters listed by size and age
These features were caused by the collision ofmeteor
A meteoroid () is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as mi ...
s (consisting of large fragments of asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. ...
s) or comets
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ar ...
(consisting of ice, dust particles and rocky fragments) with the Earth. For eroded or buried craters, the stated diameter typically refers to the best available estimate of the original rim diameter, and may not correspond to present surface features. Time units are either in ka (thousands) or Ma (millions) of years.
10 ka or less
Less than ten thousand years old, and with a diameter of or more. The EID lists fewer than ten such craters, and the largest in the last 100,000 years (100 ka) is the Rio Cuarto crater inArgentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
.Bland, Phil A.; de Souza Filho, C. R.; Timothy Jull, A. J.; Kelley, Simon P.; Hough, Robert Michael; Artemieva, N. A.; Pierazzo, E.; Coniglio, J.; Pinotti, Lucio; Evers, V.; Kearsley, Anton; (2002)"A possible tektite strewn field in the Argentinian Pampa"
''Science'', volume 296, issue 5570, pp. 1109–12 However, there is some uncertainty regarding its origins and age, with some sources giving it as < 10 ka while the EID gives a broader < 100 ka. The Kaali impacts (c. 2000 BC) during the
Nordic Bronze Age
The Nordic Bronze Age (also Northern Bronze Age, or Scandinavian Bronze Age) is a period of Scandinavian prehistory from c. 2000/1750–500 BC.
The Nordic Bronze Age culture emerged about 1750 BC as a continuation of the Battle Axe culture (th ...
may have influenced Estonian and Finnish mythology, the Campo del Cielo
Campo del Cielo refers to a group of iron meteorites and the area in Argentina where they were found. The site straddles the provinces of Chaco and Santiago del Estero, located north-northwest of Buenos Aires, Argentina and approximately south ...
(c. 2000 BC) could be in the legends of some Native American tribes, while Henbury (c. 2200 BC) has figured in Australian Aboriginal
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait I ...
oral traditions.
 For the Rio Cuarto craters, 2002 research suggests they may actually be aeolian structures. The EID gives a size of about for Campo del Cielo, but other sources quote .
For the Rio Cuarto craters, 2002 research suggests they may actually be aeolian structures. The EID gives a size of about for Campo del Cielo, but other sources quote .
10 ka to 1 Ma
From between 10 thousand years and one million years ago, and with a diameter of less than : From between ten thousand years and one million years ago, and with a diameter of or more. The largest in the last one million years is theZhamanshin crater
Zhamanshin is a meteorite crater in Kazakhstan. It is in diameter and the age is estimated to be 900,000 ± 100,000 years (Pleistocene). The crater is exposed at the surface.
Description
It is believed that the Zhamanshin crater is the site of ...
in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
and has been described as being capable of producing a nuclear-like winter.
However, the currently unknown source of the enormous Australasian strewnfield (c. 780 ka) could be a crater about across.Povenmire, Harold; Liu, W.; Xianlin, Luo; (1999"Australasian tektites found in Guangxi Province, China"
in Proceedings of the 30th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, March 1999Glass, Billy P.; Pizzuto, James E.; (1994
"Geographic variation in Australasian microtektite concentrations: Implications concerning the location and size of the source crater"
''Journal of Geophysical Research'', vol. 99, no. E9, 19075–81, September 1994
1 Ma to 10 Ma

 From between 1 and 10 million years ago, and with a diameter of 5 km or more. If uncertainties regarding its age are resolved, then the largest in the last 10 million years would be the Karakul crater which is listed in EID with an age of less than 5 Ma, or the
From between 1 and 10 million years ago, and with a diameter of 5 km or more. If uncertainties regarding its age are resolved, then the largest in the last 10 million years would be the Karakul crater which is listed in EID with an age of less than 5 Ma, or the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Eltanin impact (2.5 Ma) into the
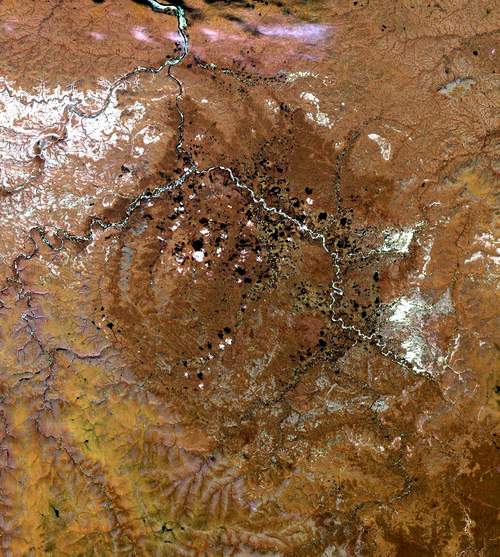





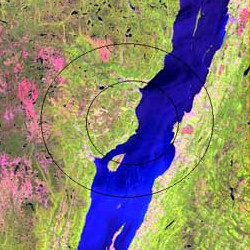
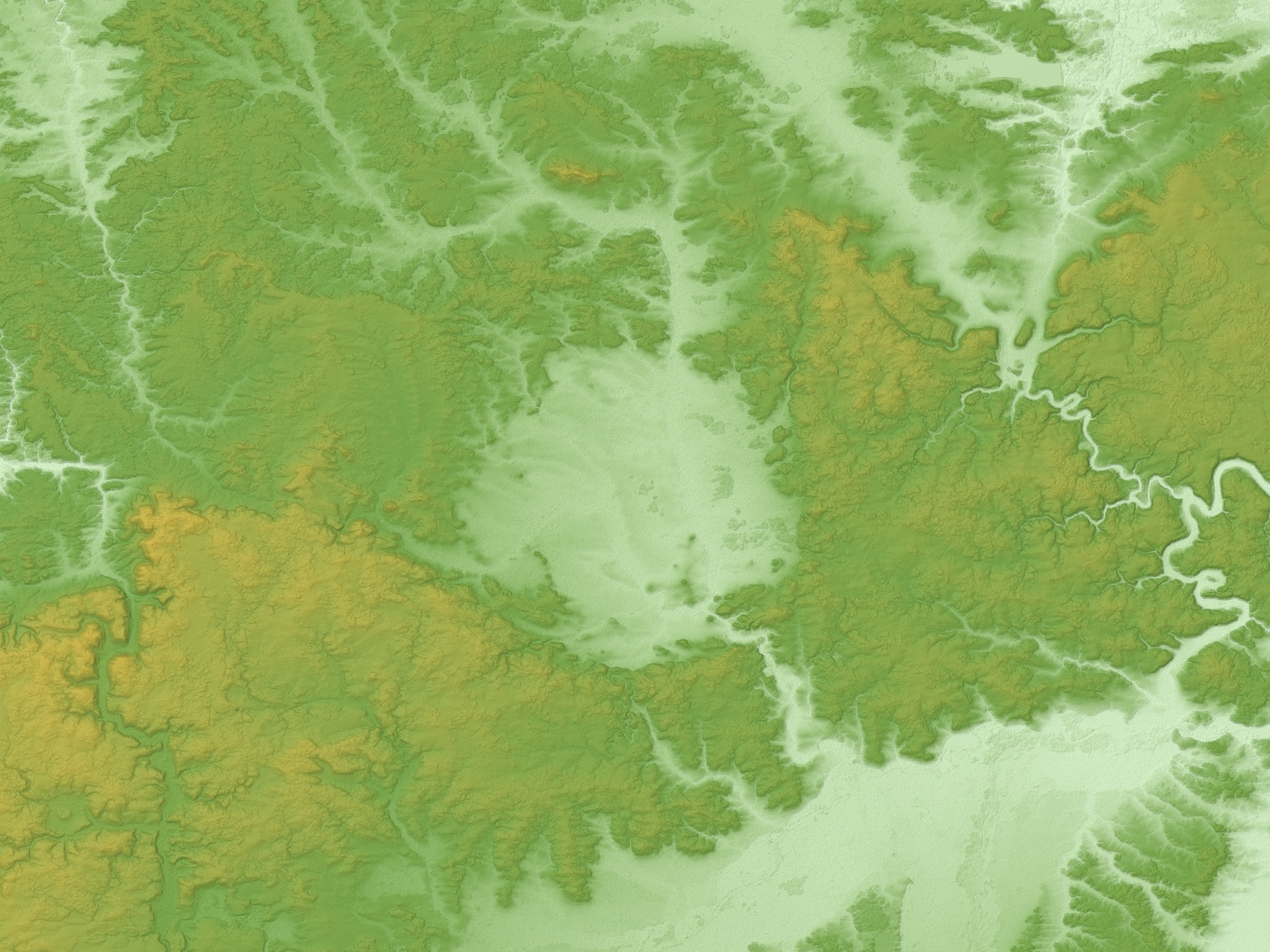
"Geophysical characterization of two circular structures at Bajada del Diablo (Patagonia, Argentina): Indication of impact origin"
''Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors'', vol. 192, pp. 21–34 with the small but well-funded
Impact Database
(formerly Suspected Earth Impact Sites list) maintained by David Rajmon fo
US
Impact Meteor Crater Viewer
Google Maps Page with Locations of Meteor Craters around the world {{DEFAULTSORT:Impact craters on Earth Lists of coordinates
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
has been suggested as contributing to the glaciations and cooling during the Pliocene.
10 Ma or more
Craters with diameter or more are all older than 10 Ma, except possibly Karakul, , whose age is uncertain. There are more than forty craters of such size. The largest two within the last hundred million years have been linked to two extinction events: Chicxulub for the Cretaceous–Paleogene and the Popigai impact for theEocene–Oligocene extinction event
The Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, also called the Eocene-Oligocene transition or ''Grande Coupure'', is the transition between the end of the Eocene and the beginning of the Oligocene, an extinction event and faunal turnover occurring betwe ...
.







Craters by continent
, the Earth Impact Database (EID) contains 190 confirmed craters. (As of 2022, no update has yet been made to the database.) The table below is arranged by the continent's percentage of the Earth's land area, and where Asian and Russian craters are grouped together per EID convention. The global distribution of known impact structures apparently shows a surprising asymmetry,Prezzi, Claudia B.; Orgeira, María Julia; Acevedo, Rogelio D.; Ponce, Juan Federico; Martinez, Oscar; Rabassa, Jorge O.; Corbella, Hugo; Vásquez, Carlos; González-Guillot, Mauricio; Subías, Ignacio; (2011)"Geophysical characterization of two circular structures at Bajada del Diablo (Patagonia, Argentina): Indication of impact origin"
''Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors'', vol. 192, pp. 21–34 with the small but well-funded
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an continent having a ''large'' percentage of confirmed craters. It is suggested this situation is an artifact, highlighting the importance of intensifying research in less studied areas like Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
, South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
and elsewhere.
Links in the column "Continent" will give a list of craters for that continent.
See also
*Bolide
A bolide is normally taken to mean an exceptionally bright meteor, but the term is subject to more than one definition, according to context. It may refer to any large crater-forming body, or to one that explodes in the atmosphere. It can be a ...
s
* Earth Impact Database
* Extinction event
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp change in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. I ...
* Impact event
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or ...
s
* Impact Field Studies Group The Impact Field Studies Group (IFSG) was a scientific organization emphasizing geologic field research of suspected and confirmed sites of impact craters and impact structures. The group is composed of researchers, professionals and students invol ...
* List of possible impact structures on Earth
* '' Traces of Catastrophe'', 1998 book from Lunar and Planetary Institute
The Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI) is a scientific research institute dedicated to study of the Solar System, its formation, evolution, and current state. The Institute is part of the Universities Space Research Association (USRA) and is sup ...
– comprehensive reference on impact crater science
* Giant-impact hypothesis
The giant-impact hypothesis, sometimes called the Big Splash, or the Theia Impact, suggests that the Moon formed from the ejecta of a collision between the proto-Earth and a Mars-sized planet, approximately 4.5 billion years ago, in the Had ...
Notes
References
External links
Impact Database
(formerly Suspected Earth Impact Sites list) maintained by David Rajmon fo
US
Impact Meteor Crater Viewer
Google Maps Page with Locations of Meteor Craters around the world {{DEFAULTSORT:Impact craters on Earth Lists of coordinates