List of earthquakes in the Levant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This is a list of earthquakes in the Levant, including
This is a list of earthquakes in the Levant, including
 This is a list of earthquakes in the Levant, including
This is a list of earthquakes in the Levant, including earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
s that either had their epicenter
The epicenter, epicentre () or epicentrum in seismology is the point on the Earth's surface directly above a hypocenter or focus, the point where an earthquake or an underground explosion originates.
Surface damage
Before the instrumental pe ...
in the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
or caused significant damage in the region. As it is now, the list is focused on events which affected the territories of modern-day Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lie ...
, Palestine and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and to some degree the adjacent areas of South Anatolia, Cyprus island and the Sinai Peninsula (modern Turkey, Cyprus, Northern Cyprus and Egypt).
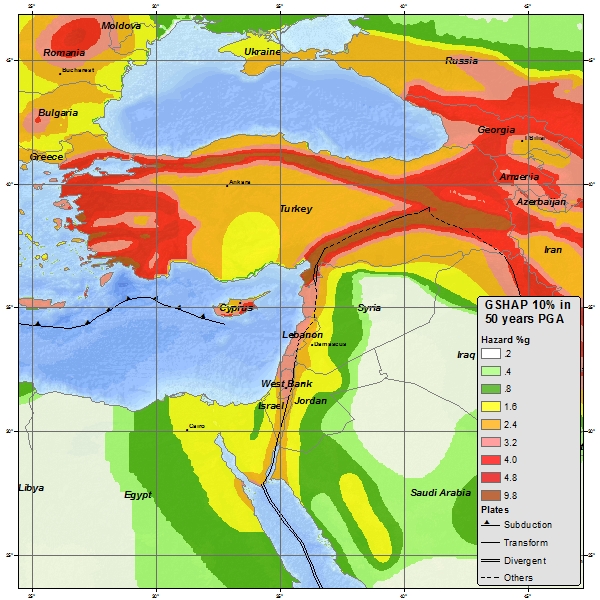
Seismic hazard
TheJordan Rift Valley
The Jordan Rift Valley, also Jordan Valley ''Bīrʿāt haYardēn'', ar, الغور Al-Ghor or Al-Ghawr),, date=November 2022 also called the Syro-African Depression, is an elongated depression located in modern-day Israel, and Jordan. This g ...
is the result of tectonic movements within the Dead Sea Transform
The Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault system, also sometimes referred to as the Dead Sea Rift, is a series of faults that run from the Maras Triple Junction (a junction with the East Anatolian Fault in southeastern Turkey) to the northern end of the ...
(DSF) fault system. The DSF forms the transform boundary
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subductio ...
between the African Plate
The African Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes much of the continent of Africa (except for its easternmost part) and the adjacent oceanic crust to the west and south. It is bounded by the North American Plate and South American Plate ...
to the west and the Arabian Plate
The Arabian Plate is a minor tectonic plate in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres.
It is one of the three continental plates (along with the African and the Indian Plates) that have been moving northward in geological history and colliding ...
to the east. The Golan Heights and all of Transjordan are part of the Arabian Plate, while the Galilee, Judean and Samarian highlands (West Bank), Coastal Plain and Negev along with the Sinai Peninsula are on the African Plate. This tectonic disposition leads to a relatively high seismic activity in the region.
Earthquakes
The region has experienced many earthquakes, the most destructive ones being those of 31 BCE, 363 CE, 749 CE, and 1033 CE. The 1759 events, along with the earlier 1202 Syria earthquake, are likely the strongest historical earthquakes in the region. Some of the earthquakes were also followed by a tsunami - notably in 92 BCE,115 115 may refer to:
* 115 (number), the number
* AD 115, a year in the 2nd century AD
* 115 BC, a year in the 2nd century BC
* 115 (Hampshire Fortress) Corps Engineer Regiment, Royal Engineers, a unit in the UK Territorial Army
* 115 (Leicestershire) ...
, 306, 502, 551, 881
__NOTOC__
Year 881 ( DCCCLXXXI) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Europe
* February 12 – King Charles the Fat, the third son of the late Louis the German, is crowned as Holy Roman Emper ...
, 1202
Year 1202 ( MCCII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Fourth Crusade
* April – May – The bulk of the Crusader army gathers at Venice, alth ...
.
Historic quakes in Bronze and Iron Ages
* c.1700 BCE - theCanaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
ite palace of Tel Kabri destroyed in a major seismic event
* c.1500/1400 BCE - the city of Jericho
Jericho ( ; ar, أريحا ; he, יְרִיחוֹ ) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank. It is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It is the administrative seat of the Jericho ...
destroyed and abandoned upon a major seismic event
* c.1365 BCE - A supposed violent earthquake that is claimed to have hit Ugarit
)
, image =Ugarit Corbel.jpg
, image_size=300
, alt =
, caption = Entrance to the Royal Palace of Ugarit
, map_type = Near East#Syria
, map_alt =
, map_size = 300
, relief=yes
, location = Latakia Governorate, Syria
, region = ...
in the Bronze Era is based on misinterpreting the evidence, especially Amarna letter 151 which actually only says that half of the royal palaced was destroyed by fire. The layer of destruction of Ugarit supposed to represent archaeological evidence for the catastrophe is now redated to ca. 1250 BCE.
* c.8th century BCE - a major earthquake described in the book of Amos
The Book of Amos is the third of the Twelve Minor Prophets in the Old Testament (Tanakh) and the second in the Greek Septuagint tradition. Amos, an older contemporary of Hosea and Isaiah, Harris, Stephen L., ''Understanding the Bible''. Palo Alt ...
, affecting ancient Kingdom of Israel
The Kingdom of Israel may refer to any of the historical kingdoms of ancient Israel, including:
Fully independent (c. 564 years)
*Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy) (1047–931 BCE), the legendary kingdom established by the Israelites and uniting ...
and Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah ( he, , ''Yəhūdā''; akk, 𒅀𒌑𒁕𒀀𒀀 ''Ya'údâ'' 'ia-ú-da-a-a'' arc, 𐤁𐤉𐤕𐤃𐤅𐤃 ''Bēyt Dāwīḏ'', " House of David") was an Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. C ...
Major earthquakes
* 140 BCE – disastrous earthquake between Tyre and Ptolemais ( Acre/Akko) * 92 BCE – Judean coast hit by tsunamis * 31 BCE – 31 BCE Judea earthquake:epicenter
The epicenter, epicentre () or epicentrum in seismology is the point on the Earth's surface directly above a hypocenter or focus, the point where an earthquake or an underground explosion originates.
Surface damage
Before the instrumental pe ...
in the Jordan Valley, magnitude at least 7; among the largest in 2000 years. Josephus Flavius
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
writes of 30,000 people killed. Damages Emmaus and Straton's Tower (renamed Caesarea
Caesarea () ( he, קֵיסָרְיָה, ), ''Keysariya'' or ''Qesarya'', often simplified to Keisarya, and Qaysaria, is an affluent town in north-central Israel, which inherits its name and much of its territory from the ancient city of Caesar ...
by Herod the Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renova ...
).
* 30–33 CE (all following dates in this list are CE) – An earthquake, identified in the geological strata of the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Ban ...
and by Roman sources, reported by the Gospels
Gospel originally meant the Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words an ...
to have taken place during the crucifixion of Jesus
The crucifixion and death of Jesus occurred in 1st-century Judea, most likely in AD 30 or AD 33. It is described in the four canonical gospels, referred to in the New Testament epistles, attested to by other ancient sources, and consider ...
* 115 – 115 Antioch earthquake
The 115 Antioch earthquake occurred on 13 December 115 AD. It had an estimated magnitude of 7.5 on the surface wave magnitude scale and an estimated maximum intensity of XI (''Extreme'') on the Mercalli intensity scale. Antioch and surrounding a ...
; Yavne and Caesarea are hit by a tsunami
* 130 – strong earthquakes affect among other places Caesarea, Lydda
Lod ( he, לוד, or fully vocalized ; ar, اللد, al-Lidd or ), also known as Lydda ( grc, Λύδδα), is a city southeast of Tel Aviv and northwest of Jerusalem in the Central District of Israel. It is situated between the lower Sheph ...
and Emmaus. Different sources give varying dates: 129, 131
* 306 – tsunami on the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
ine coast. Affects are felt in Caesarea, Tiberias, Jerusalem.
* 363 – the Galilee earthquake. See also next (365 CE) earthquake. The failed attempt of the Jews to rebuild the Jerusalem Temple during the reign of Emperor Julian is connected by some to the earthquake.
*365 – 365 Crete earthquake
The 365 Crete earthquake occurred at about sunrise on 21 July 365 in the Eastern Mediterranean, with an assumed epicentre near Crete. Geologists today estimate the undersea earthquake to have been a moment magnitude 8.5 or higher. It caused wid ...
triggered a large tsunami that inundated the Nile delta.
* 419 – earthquake causes destruction in Antipatris
Antipatris (, grc, Αντιπατρίς) was a city built during the first century BC by Herod the Great, who named it in honour of his father, Antipater. The site, now a national park in central Israel, was inhabited from the Chalcolithic ...
* 502 – Ptolemais allegedly destroyed (Syriac Syriac may refer to:
*Syriac language, an ancient dialect of Middle Aramaic
*Sureth, one of the modern dialects of Syriac spoken in the Nineveh Plains region
* Syriac alphabet
** Syriac (Unicode block)
** Syriac Supplement
* Neo-Aramaic languages a ...
chronicle of Joshua the Stylite), tsunami hits northern coast, Safed, Latrun (Nicopolis) affected
* 526 – 526 Antioch earthquake
* 551 – 551 Beirut earthquake
The 551 Beirut earthquake occurred on 9 July with an estimated magnitude of about 7.5 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum felt intensity of X (''Extreme'') on the Mercalli intensity scale. It triggered a devastating tsunami which affected ...
affects much of the Middle East, possibly largest event in the Levant. Gush Halav is destroyed. A major tsunami sweeps the coast from Caesarea to Tripoli, Lebanon
Tripoli ( ar, طرابلس/ ALA-LC: ''Ṭarābulus'', Lebanese Arabic: ''Ṭrablus'') is the largest city in northern Lebanon and the second-largest city in the country. Situated north of the capital Beirut, it is the capital of the North Gove ...
* 633 – affects Emmatha in the Yarmouk Valley and possibly nearby Abila of the Decapolis.
* 658 – affects Syria and Palestine. Jerusalem is badly damaged according to the chronicles of Michael the Syrian
Michael the Syrian ( ar, ميخائيل السرياني, Mīkhaʾēl el Sūryani:),( syc, ܡܺܝܟ݂ܳܐܝܶܠ ܣܽܘܪܝܳܝܳܐ, Mīkhoʾēl Sūryoyo), died 1199 AD, also known as Michael the Great ( syr, ܡܺܝܟ݂ܳܐܝܶܠ ܪܰܒ݁ܳܐ, ...
and Theophanes the Confessor
Theophanes the Confessor ( el, Θεοφάνης Ὁμολογητής; c. 758/760 – 12 March 817/818) was a member of the Byzantine aristocracy who became a monk and chronicler. He served in the court of Emperor Leo IV the Khazar before taking ...
.
* 672 – Ascalon, Gaza and Ramla hit by strong earthquake
* 746–749 – a series of earthquakes, often confused into one 749 Galilee earthquake
A devastating earthquake known in scientific literature as the Earthquake of 749 struck on January 18, 749, in areas of the Umayyad Caliphate, with the epicenter in Galilee. The most severely affected areas were parts of Palestine and western Tr ...
. Tiberias, Baysan (Beit She'an
Beit She'an ( he, בֵּית שְׁאָן '), also Beth-shean, formerly Beisan ( ar, بيسان ), is a town in the Northern District of Israel. The town lies at the Beit She'an Valley about 120 m (394 feet) below sea level.
Beit She'an is be ...
) and Hippos
A hippo or hippopotamus is either of two species of large African mammal which live mainly in and near water:
* Hippopotamus
* Pygmy hippopotamus
Hippo or Hippos may also refer to:
Toponymy
* The ancient city of Hippo Regius (modern Annaba, Al ...
were largely destroyed. A large event was centered in the Jordan Valley and had a magnitude of 7.6.
* 808 – An earthquake affects Jerusalem. The Dome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial ...
is severely damaged.
* 846 – The Dome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial ...
is severely damaged by an earthquake.
* 847 – 847 Damascus earthquake
The 847 Damascus earthquake occurred (probably on 24 November) in AD 847. Recent scholarship suggests that the earthquake was part of a multiple earthquake stretching from Damascus to the south, to Antioch in the north and to Mosul in the east. T ...
* 881 – 881 Acre earthquake. An earthquake on the Levantine coast leads to a tsunami at Acre
The acre is a unit of land area used in the imperial and US customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong (66 by 660 feet), which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, of a square mile, 4,840 square ...
* 1015 – The dome of the Dome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial ...
collapses due to an earthquake.
* 1016 – Jerusalem, Jaffa and the region around are affected
* 1033–34 – 1033 Jordan Rift Valley earthquake
An earthquake struck the Jordan Rift Valley on December 5, 1033 and caused extreme devastation in the Levant region. It was part of a sequence of four strong earthquakes in the region between 1033 AD and 1035 AD. Scholars have estimated the momen ...
: a series of earthquakes which are felt for 40 days destroys Ramla, Jericho and Nablus 70,000 deaths.
* 1063 – a large earthquake hits the Levantine littoral. Acre is badly damaged
* 1068 – ground-rupturing event
Event may refer to:
Gatherings of people
* Ceremony, an event of ritual significance, performed on a special occasion
* Convention (meeting), a gathering of individuals engaged in some common interest
* Event management, the organization of ev ...
in Wadi Arabah
The Arabah, Araba or Aravah ( he, הָעֲרָבָה, ''hāʿĂrāḇā''; ar, وادي عربة, ''Wādī ʿAraba''; lit. "desolate and dry area") is a loosely defined geographic area south of the Dead Sea basin, which forms part of the bord ...
. Ramla was totally destroyed and lay abandoned for four years after losing some 15,000–25,000 inhabitants in the earthquake.
* 1070 – a large earthquake centered in the Beqaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important ...
affects Palestine
* 1091 – coastal towns affected, city towers collapse
* 1138 – 1138 Aleppo earthquake
The 1138 Aleppo earthquake was among the deadliest earthquakes in history. Its name was taken from the city of Aleppo, in northern Syria, where the most casualties were sustained. The earthquake also caused damage and chaos to many other places i ...
* 1157 – 1157 Hama earthquake
The 1157 Hama earthquake occurred on 12 August after a year of foreshocks. Its name was taken from the city of Hama, in west-central Syria (then under the Seljuk rule), where the most casualties were sustained. In eastern Syria, near the Euphrates ...
* 1170 – 1170 Syria earthquake
The 1170 Syria earthquake was one of the largest earthquakes to hit Syria. It occurred early in the morning of 29 June 1170. It formed part of a sequence of large earthquakes that propagated southwards along the Dead Sea Transform, starting with t ...
: Caesarea damaged by tremor
* 1202 – 1202 Syria earthquake, one of the largest seismic events in written history. It resulted in nearly a million fatalities in the region, including fires and tsunamis
* 1261 – between Akko and Tripoli islands disappear under the sea
* 1660 – Tiberias hit by an earthquake.
* 1752 – coast of Syria and Palestine hit by strong earthquake
* 1759 – Near East earthquakes of 1759
The Near East earthquakes of 1759 were a series of devastating earthquakes that shook a large portion of the Levant in October and November of that year. This geographical crossroads in the Eastern Mediterranean were at the time under the rule o ...
, likely among the strongest historical earthquakes in the region.
* 1822 - 1822 Aleppo earthquake
* 1834 – 1834 Jerusalem earthquake The 1834 Jerusalem earthquake occurred on 13 May during the first few days of the Peasants' revolt in Palestine against Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt. The earthquake's epicenter was in the Jerusalem area. After a brief lull, fighting resumed the next day. ...
: Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Hebron are affected
* 1837 – Galilee earthquake of 1837
The Galilee earthquake of 1837, often called the Safed earthquake, shook the Galilee on January 1 and is one of a number of moderate to large events that have occurred along the Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault system that marks the boundary of t ...
, known as the Safed earthquake. The Roum fault, and its extension south to the Sea of Galilee, were sources of the event
*1856 – 1856 Heraklion earthquake
The 1856 Heraklion earthquake, also known as the Crete earthquake or Rhodes earthquake occurred on the morning of October 12 at 02:45 am local time. This extremely catastrophic earthquake had an estimated magnitude of 7.7 to 8.3 at a depth of appr ...
: although the earthquake had an epicenter off the Greek island of Crete, shaking was severe in Cairo, Israel, Palestine and in North Africa. Some people were killed in the Nile delta and Cairo due to collapsing buildings.
*1872 – 1872 Amik earthquake: At least 1,800 people were killed during an 7.2 (MSK 64 = XI) quake in the Amik Valley
The Amik Valley ( tr, Amik Ovası; ar, ٱلْأَعْمَاق, al-ʾAʿmāq) is located in the Hatay Province, close to the city of Antakya (Antioch on the Orontes River) in the southern part of Turkey. Along with Dabiq in northwestern Syria, ...
. This earthquake is believed to have generated 50 km of surface rupture on the Amanos Fault.
* 1927 – 1927 Jericho earthquake
The 1927 Jericho earthquake was a devastating event that shook Mandatory Palestine and Transjordan on July 11 at . The epicenter of the earthquake was in the northern area of the Dead Sea. The cities of Jerusalem, Jericho, Ramle, Tiberias, and Na ...
. The epicenter was in the northern area of the Dead Sea. Jerusalem, Jericho, Ramle, Tiberias and Nablus were heavily damaged and at least 500 were estimated to have been killed. The death toll in Jerusalem included more than 130 people and around 450 were injured. About 300 houses collapsed or were severely damaged to the point of not being usable. The earthquake caused heavy damage to the domes of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
and the al-Aqsa Mosque
Al-Aqsa Mosque (, ), also known as Jami' Al-Aqsa () or as the Qibli Mosque ( ar, المصلى القبلي, translit=al-Muṣallā al-Qiblī, label=none), and also is a congregational mosque located in the Old City of Jerusalem. It is situate ...
, the Dome of the Rock being badly damaged. The earthquake was especially severe in Nablus where it destroyed around 300 buildings, including the Mosque of Victory and the historic parts of the Great Mosque of Nablus. The death toll in Nablus included more than 150 people and around 250 were injured. In Jericho, a number of houses collapsed, including several relatively new hotels in one of which three female tourists from India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
were killed. Ramla
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
and Tiberias were also heavily damaged.
* 1955 - 1955 Alexandria earthquake
The 1955 Alexandria earthquake occurred on September 12 at 06:09 UTC. The epicenter was located in the eastern Mediterranean, offshore of Alexandria, Egypt. The earthquake had a magnitude of Ms 6.3.
Damage was reported in the Nile Delta between ...
caused damage in the Nile Delta and left at least 18 dead.
* 1969 - 1969 Sharm El Sheikh earthquake
The 1969 Sharm El Sheikh earthquake occurred on March 31 off the southern Sinai Peninsula in northeastern Egypt. The epicenter was located near Shadwan island, southwest of the city of Sharm El Sheikh, at the confluence of the Red Sea and the Gul ...
affecting the southern Sinai peninsula
Minor earthquakes (below 6.0)
* 1898 – Haifa damaged by earthquake * 1956 – Chim earthquake: In the south of Lebanon in the Chouf District; 6,000 homes destroyed, and another 17,000 damaged; 136 persons killed. Magnitude - 5.3-5.5 Mw. * 2008 – A 5.1 earthquake shook South Lebanon, causing ten injuries, power outages and some building damage on February 15. Of several hundred responses to the USGS' "Did you feel it?" system, three reports from northern coastal Israel indicated that a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (''Strong'') was observed there. The oblique-slip shock was also felt lightly in Jerusalem, Nicosia, and Amman. * 2020 – A series of 4.7 earthquakes occurred at a depth of 20 kilometers in the eastern Mediterranean nearBurj Islam
Burj Islam ( ar, برج اسلام) is a village in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Latakia Governorate, located north of Latakia. Nearby localities include Salib al-Turkman to the north, al-Shabatliyah to the northeast, Ayn a ...
, Syria.
* 2022 – An earthquake registering slightly more than 4.1 just over a mile below the surface, centered northeast of Beit She'an
Beit She'an ( he, בֵּית שְׁאָן '), also Beth-shean, formerly Beisan ( ar, بيسان ), is a town in the Northern District of Israel. The town lies at the Beit She'an Valley about 120 m (394 feet) below sea level.
Beit She'an is be ...
, south of the Sea of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee ( he, יָם כִּנֶּרֶת, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ar, بحيرة طبريا), also called Lake Tiberias, Kinneret or Kinnereth, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest ...
, is felt throughout Israel; no injuries or damage are reported.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Earthquakes In the Levant Lists of earthquakes