List of Space Shuttle orbiters on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Space Shuttle orbiter is the
 The
The
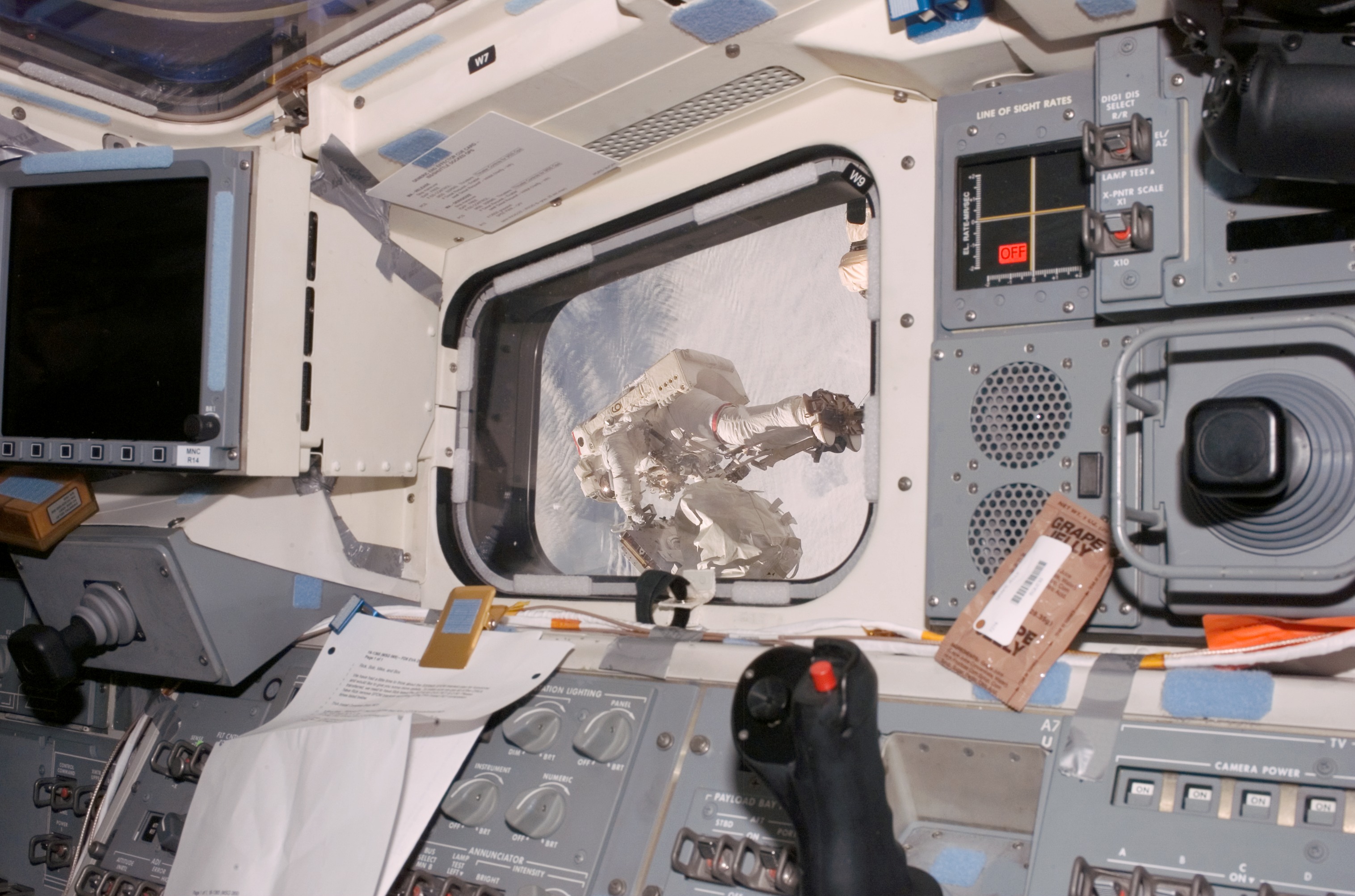
 The orbiter's flight deck or cockpit originally had 2,214 controls and displays, about three times as many as the
The orbiter's flight deck or cockpit originally had 2,214 controls and displays, about three times as many as the
 Three Space Shuttle Main Engines (SSMEs) were mounted on the orbiter's aft fuselage in the pattern of an
Three Space Shuttle Main Engines (SSMEs) were mounted on the orbiter's aft fuselage in the pattern of an
 The orbiters were protected by
The orbiters were protected by
 The Space Shuttle orbiter had three sets of
The Space Shuttle orbiter had three sets of
 The
The  ''Challenger'' established a modified marking scheme for the shuttle fleet that would be matched by ''Discovery'', ''Atlantis'' and ''Endeavour''. The letters "USA" in black above an American flag were displayed on the left wing, with the NASA "worm" logotype in gray centered above the name of the orbiter in black on the right wing. Also, the name of the orbiter was inscribed not on the payload bay doors, but on the forward fuselage just below and behind the cockpit windows. This would make the name visible when the orbiter was photographed in orbit with the doors open. ''Challenger'' also had black tiles on the tip of its vertical stabilizer much like ''Columbia'', which the other orbiters lacked.
In 1983, ''Enterprise'' had its wing markings changed to match ''Challenger'', and the NASA "worm" logotype on the aft end of the payload bay doors was changed from gray to black. Some black markings were added to the nose, cockpit windows and vertical tail to more closely resemble the flight vehicles, but the name "Enterprise" remained on the payload bay doors as there was never any need to open them. ''Columbia'' had its name moved to the forward fuselage to match the other flight vehicles after STS-61-C, during the 1986–1988 hiatus when the shuttle fleet was grounded following the loss of ''Challenger'', but retained its original wing markings until its last overhaul (after
''Challenger'' established a modified marking scheme for the shuttle fleet that would be matched by ''Discovery'', ''Atlantis'' and ''Endeavour''. The letters "USA" in black above an American flag were displayed on the left wing, with the NASA "worm" logotype in gray centered above the name of the orbiter in black on the right wing. Also, the name of the orbiter was inscribed not on the payload bay doors, but on the forward fuselage just below and behind the cockpit windows. This would make the name visible when the orbiter was photographed in orbit with the doors open. ''Challenger'' also had black tiles on the tip of its vertical stabilizer much like ''Columbia'', which the other orbiters lacked.
In 1983, ''Enterprise'' had its wing markings changed to match ''Challenger'', and the NASA "worm" logotype on the aft end of the payload bay doors was changed from gray to black. Some black markings were added to the nose, cockpit windows and vertical tail to more closely resemble the flight vehicles, but the name "Enterprise" remained on the payload bay doors as there was never any need to open them. ''Columbia'' had its name moved to the forward fuselage to match the other flight vehicles after STS-61-C, during the 1986–1988 hiatus when the shuttle fleet was grounded following the loss of ''Challenger'', but retained its original wing markings until its last overhaul (after  Beginning in 1998, the flight vehicles' markings were modified to incorporate the NASA "meatball" insignia. The "worm" logotype, which the agency had phased out, was removed from the payload bay doors and the "meatball" insignia was added aft of the "United States" text on the lower aft fuselage. The "meatball" insignia was also displayed on the left wing, with the American flag above the orbiter's name, left-justified rather than centered, on the right wing. The three surviving flight vehicles, ''Discovery'', ''Atlantis'' and ''Endeavour'', still bear these markings as museum displays. ''Enterprise'' became the property of the
Beginning in 1998, the flight vehicles' markings were modified to incorporate the NASA "meatball" insignia. The "worm" logotype, which the agency had phased out, was removed from the payload bay doors and the "meatball" insignia was added aft of the "United States" text on the lower aft fuselage. The "meatball" insignia was also displayed on the left wing, with the American flag above the orbiter's name, left-justified rather than centered, on the right wing. The three surviving flight vehicles, ''Discovery'', ''Atlantis'' and ''Endeavour'', still bear these markings as museum displays. ''Enterprise'' became the property of the
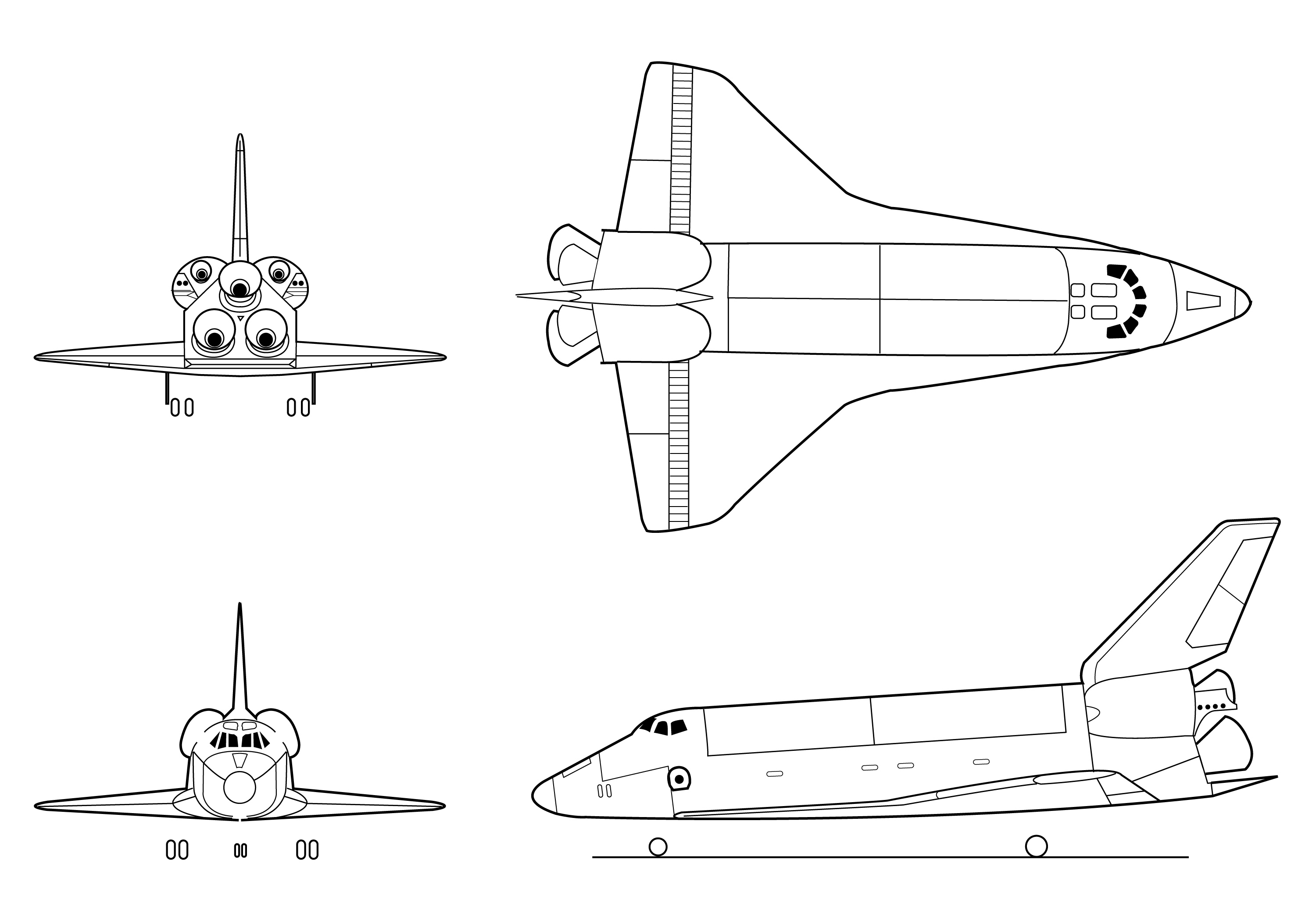 The cargo bay is by , and could transport to , or to the ISS at . The most massive payload launched by the Space Shuttle was the
The cargo bay is by , and could transport to , or to the ISS at . The most massive payload launched by the Space Shuttle was the
 Individual Space Shuttle orbiters were named in honor of antique sailing ships of the navies of the world (though the test orbiter ''Enterprise'', originally to be named "''Constitution''", had its name changed after the ''Star Trek'' starship, itself named after a series of US Navy ships), and they were also numbered using the NASA Orbiter Vehicle designation system. Three of the names had also been given to Apollo spacecraft between 1969 and 1972:
Individual Space Shuttle orbiters were named in honor of antique sailing ships of the navies of the world (though the test orbiter ''Enterprise'', originally to be named "''Constitution''", had its name changed after the ''Star Trek'' starship, itself named after a series of US Navy ships), and they were also numbered using the NASA Orbiter Vehicle designation system. Three of the names had also been given to Apollo spacecraft between 1969 and 1972:
Orbiter Vehicles
*
spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes te ...
component of the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program ...
, a partially reusable orbital spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, p ...
system that was part of the discontinued Space Shuttle program
The Space Shuttle program was the fourth human spaceflight program carried out by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which accomplished routine transportation for Earth-to-orbit crew and cargo from 1981 to 2011. I ...
. Operated from 1977 to 2011 by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
, the U.S. space agency, this vehicle could carry astronauts and payloads into low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never mor ...
, perform in-space operations, then re-enter the atmosphere and land as a glider
Glider may refer to:
Aircraft and transport Aircraft
* Glider (aircraft), heavier-than-air aircraft primarily intended for unpowered flight
** Glider (sailplane), a rigid-winged glider aircraft with an undercarriage, used in the sport of glidin ...
, returning its crew and any on-board payload to the Earth.
Six orbiters were built for flight: ''Enterprise
Enterprise (or the archaic spelling Enterprize) may refer to:
Business and economics
Brands and enterprises
* Enterprise GP Holdings, an energy holding company
* Enterprise plc, a UK civil engineering and maintenance company
* Enterpris ...
'', '' Columbia'', '' Challenger'', ''Discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discover ...
'', ''Atlantis
Atlantis ( grc, Ἀτλαντὶς νῆσος, , island of Atlas) is a fictional island mentioned in an allegory on the hubris of nations in Plato's works '' Timaeus'' and '' Critias'', wherein it represents the antagonist naval power that b ...
'', and '' Endeavour''. All were built in Palmdale, California, by the Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Western Pennsylvania, the second-most populous city in Pennsylva ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
-based Rockwell International
Rockwell International was a major American manufacturing conglomerate involved in aircraft, the space industry, defense and commercial electronics, components in the automotive industry, printing presses, avionics and industrial products. R ...
company. The first orbiter, ''Enterprise'', made its maiden flight in 1977. An unpowered glider, it was carried by a modified Boeing 747 airliner called the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft
The Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) are two extensively modified Boeing 747 airliners that NASA used to transport Space Shuttle orbiters. One (N905NA) is a 747-100 model, while the other (N911NA) is a short range 747-100SR.
The SCAs were used ...
and released for a series of atmospheric test flights and landings. ''Enterprise'' was partially disassembled and retired after completion of critical testing. The remaining orbiters were fully operational spacecraft, and were launched vertically as part of the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program ...
stack.
''Columbia'' was the first space-worthy orbiter; it made its inaugural flight in 1981. ''Challenger'', ''Discovery'', and ''Atlantis'' followed in 1983, 1984, and 1985 respectively. In 1986, ''Challenger'' was destroyed in an accident shortly after its 10th launch. ''Endeavour'' was built as ''Challenger''s successor, and was first launched in 1992. In 2003, ''Columbia'' was destroyed during re-entry, leaving just three remaining orbiters. ''Discovery'' completed its final flight on March 9, 2011, and ''Endeavour'' completed its final flight on June 1, 2011. ''Atlantis'' completed the final Shuttle flight, STS-135
STS-135 ( ISS assembly flight ULF7) was the 135th and final mission of the American Space Shuttle program. It used the orbiter ''Atlantis'' and hardware originally processed for the STS-335 contingency mission, which was not flown. STS-135 la ...
, on July 21, 2011.
In addition to their crews and payloads, the reusable orbiter carried most of the Space Shuttle System's liquid-propellant rocket system, but both the liquid hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen (LH2 or LH2) is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecular H2 form.
To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point of 33 K. However, for it to be in a fully l ...
fuel and the liquid oxygen
Liquid oxygen—abbreviated LOx, LOX or Lox in the aerospace, submarine and gas industries—is the liquid form of molecular oxygen. It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an app ...
oxidizer
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxid ...
for its three main rocket engines were fed from an external cryogenic propellant tank. Additionally, two reusable solid rocket boosters
A solid rocket booster (SRB) is a large solid propellant motor used to provide thrust in spacecraft launches from initial launch through the first ascent. Many launch vehicles, including the Atlas V, SLS and space shuttle, have used SRBs to giv ...
(SRBs) provided additional thrust for approximately the first two minutes of launch. The orbiters themselves did carry hypergolic propellants for their Reaction Control System
A reaction control system (RCS) is a spacecraft system that uses thrusters to provide attitude control and translation. Alternatively, reaction wheels are used for attitude control. Use of diverted engine thrust to provide stable attitude cont ...
(RCS) thrusters and Orbital Maneuvering System
In spaceflight, an orbital maneuver (otherwise known as a burn) is the use of propulsion systems to change the orbit of a spacecraft.
For spacecraft far from Earth (for example those in orbits around the Sun) an orbital maneuver is called a ' ...
(OMS) engines.
Description
About the size of aMcDonnell Douglas DC-9
The McDonnell Douglas DC-9 is an American five-abreast single-aisle aircraft designed by the Douglas Aircraft Company. It was initially produced by the developer company as the Douglas DC-9 until August 1967 and then by McDonnell Douglas.
Afte ...
, the Space Shuttle orbiter resembled an airplane
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, Propeller (aircraft), propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurat ...
in its design, with a standard-looking fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraf ...
and two double delta
A delta wing is a wing shaped in the form of a triangle. It is named for its similarity in shape to the Greek uppercase letter delta (Δ).
Although long studied, it did not find significant applications until the Jet Age, when it proved suitab ...
wings, both swept wings at an angle of 81 degrees at their inner leading edge
The leading edge of an airfoil surface such as a wing is its foremost edge and is therefore the part which first meets the oncoming air.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 305. Aviation Supplies & Academics, ...
s and 45 degrees at their outer leading edges. The vertical stabilizer
A vertical stabilizer or tail fin is the static part of the vertical tail of an aircraft. The term is commonly applied to the assembly of both this fixed surface and one or more movable rudders hinged to it. Their role is to provide control, s ...
of the orbiter had a leading edge
The leading edge of an airfoil surface such as a wing is its foremost edge and is therefore the part which first meets the oncoming air.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 305. Aviation Supplies & Academics, ...
that was swept back at a 45-degree angle. There were four elevon
Elevons or tailerons are aircraft control surfaces that combine the functions of the elevator (used for pitch control) and the aileron (used for roll control), hence the name. They are frequently used on tailless aircraft such as flying wings. A ...
s mounted at the trailing edge
The trailing edge of an aerodynamic surface such as a wing is its rear edge, where the airflow separated by the leading edge meets.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 521. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 199 ...
s of the delta wings, and the combination rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally air or water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adve ...
and speed brake
In aeronautics, air brakes or speed brakes are a type of flight control surface used on an aircraft to increase the drag on the aircraft. Air brakes differ from spoilers in that air brakes are designed to increase drag while making litt ...
was attached at the trailing edge of the vertical stabilizer
A vertical stabilizer or tail fin is the static part of the vertical tail of an aircraft. The term is commonly applied to the assembly of both this fixed surface and one or more movable rudders hinged to it. Their role is to provide control, s ...
. These, along with a movable body flap located underneath the main engines, controlled the orbiter during later stages of reentry
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the ...
.
Attitude control system
 The
The Reaction Control System
A reaction control system (RCS) is a spacecraft system that uses thrusters to provide attitude control and translation. Alternatively, reaction wheels are used for attitude control. Use of diverted engine thrust to provide stable attitude cont ...
(RCS) was composed of 44 small liquid-fueled rocket
A liquid-propellant rocket or liquid rocket utilizes a rocket engine that uses liquid propellants. Liquids are desirable because they have a reasonably high density and high specific impulse (''I''sp). This allows the volume of the propellant ta ...
thrusters and their very sophisticated fly-by-wire
Fly-by-wire (FBW) is a system that replaces the conventional manual flight controls of an aircraft with an electronic interface. The movements of flight controls are converted to electronic signals transmitted by wires, and flight control ...
flight control system
A conventional fixed-wing aircraft flight control system consists of flight control surfaces, the respective cockpit controls, connecting linkages, and the necessary operating mechanisms to control an aircraft's direction in flight. Aircraft ...
, which utilized computationally intensive digital Kalman filter
For statistics and control theory, Kalman filtering, also known as linear quadratic estimation (LQE), is an algorithm that uses a series of measurements observed over time, including statistical noise and other inaccuracies, and produces estima ...
ing. This control system carried out the usual attitude control
Attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of an aerospace vehicle with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc.
Controlling vehicle ...
along the pitch, roll, and yaw axes during all of the flight phases of launching, orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
ing, and re-entry. This system also executed any needed orbital maneuvers, including all changes in the orbit's altitude, orbital plane
The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies. Three non-collinear points in space suffice to determine an orbital plane. A common example would be the positions of the centers of a massive body (host) an ...
, and eccentricity
Eccentricity or eccentric may refer to:
* Eccentricity (behavior), odd behavior on the part of a person, as opposed to being "normal"
Mathematics, science and technology Mathematics
* Off-Centre (geometry), center, in geometry
* Eccentricity (g ...
. These were all operations that required more thrust and impulse
Impulse or Impulsive may refer to:
Science
* Impulse (physics), in mechanics, the change of momentum of an object; the integral of a force with respect to time
* Impulse noise (disambiguation)
* Specific impulse, the change in momentum per uni ...
than mere attitude control.
The forward rockets of the Reaction Control System, located near the nose of the Space Shuttle orbiter, included 14 primary and two vernier RCS rockets. The aft RCS engines were located in the two Orbital Maneuvering System
In spaceflight, an orbital maneuver (otherwise known as a burn) is the use of propulsion systems to change the orbit of a spacecraft.
For spacecraft far from Earth (for example those in orbits around the Sun) an orbital maneuver is called a ' ...
(OMS) pods at the rear of the orbiter, and these included 12 primary (PRCS) and two vernier (VRCS) engines in each pod. The PRCS system provided the pointing control of the Orbiter, and the VRCS was used for fine maneuvering during the rendezvous, docking, and undocking maneuvers with the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ( ...
, or formerly with the Russian Mir space station
''Mir'' (russian: Мир, ; ) was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to&n ...
. The RCS also controlled the attitude of the orbiter during most of its re-entry into the Earth's atmosphere – until the air became dense enough that the rudder, elevons and body flap became effective.
The orbiter's OMS and RCS fuel is monomethyl hydrazine (CH3NHNH2), and the oxidizer is dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4). This particular propellant combination is extremely reactive and spontaneously ignites on contact (hypergolic) with each other. This chemical reaction (4CH3NHNH2 + 5N2O4 → 9N2 + 4CO2 + 12H2O) occurs within the engine's combustion chamber. The reaction products are then expanded and accelerated in the engine bell to provide thrust. Due to their hypergolic characteristics these two chemicals are easily started and restarted without an ignition source, which makes them ideal for spacecraft maneuvering systems.
During the early design process of the orbiter, the forward RCS thrusters were to be hidden underneath retractable doors, which would open once the orbiter reached space. These were omitted in favor of flush-mounted thrusters for fear that the RCS doors would remain stuck open and endanger the crew and orbiter during re-entry.
Pressurized cabin

 The orbiter's flight deck or cockpit originally had 2,214 controls and displays, about three times as many as the
The orbiter's flight deck or cockpit originally had 2,214 controls and displays, about three times as many as the Apollo command module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother shi ...
. The crew cabin consisted of the flight deck, the mid-deck, and the utility area. The uppermost of these was the flight deck, in which sat the Space Shuttle's commander and pilot, with up to two mission specialists seated behind them. The mid-deck, which was below the flight deck, had three more seats for the rest of the crew members.
The galley, toilet, sleep locations, storage lockers, and the side hatch for entering and exiting the orbiter were also located on the mid-deck, as well as the airlock
An airlock, air-lock or air lock, often abbreviated to just lock, is a compartment with doors which can be sealed against pressure which permits the passage of people and objects between environments of differing pressure or atmospheric compo ...
. The airlock had an additional hatch into the payload bay. This airlock allowed two or three astronauts, wearing their Extravehicular Mobility Unit
The Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) is an independent anthropomorphic spacesuit that provides environmental protection, mobility, life support, and communications for astronauts performing extravehicular activity (EVA) in Earth orbit. Introduc ...
(EMU) space suits, to depressurize before a walk in space (EVA
Eva or EVA may refer to:
* Eva (name), a feminine given name
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional characters
* Eva (Dynamite Entertainment), a comic book character by Dynamite Entertainment
* Eva (''Devil May Cry''), Dante's mother in t ...
), and also to repressurize and re-enter the orbiter at the conclusion of the EVA.
The utility area was located under the floor of the mid-deck and contained air and water tanks in addition to the carbon dioxide scrubbing system.
Propulsion
 Three Space Shuttle Main Engines (SSMEs) were mounted on the orbiter's aft fuselage in the pattern of an
Three Space Shuttle Main Engines (SSMEs) were mounted on the orbiter's aft fuselage in the pattern of an equilateral triangle
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each oth ...
. These three liquid-fueled engines could be swiveled 10.5 degrees vertically and 8.5 degrees horizontally during the rocket-powered ascent of the orbiter in order to change the direction of their thrust. Hence, they steered the entire Space Shuttle, as well as providing rocket thrust towards orbit. The aft fuselage also housed three auxiliary power unit
An auxiliary power unit (APU) is a device on a vehicle that provides energy for functions other than propulsion. They are commonly found on large aircraft and naval ships as well as some large land vehicles. Aircraft APUs generally produce 115& ...
s (APU). The APUs chemically converted hydrazine fuel from a liquid state
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, ...
to a gas state
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or co ...
, powering a hydraulic pump which supplied pressure for all of the hydraulic system, including the hydraulic sub-system that pointed the three main liquid-fueled rocket engines, under computerized flight control
A conventional fixed-wing aircraft flight control system consists of flight control surfaces, the respective cockpit controls, connecting linkages, and the necessary operating mechanisms to control an aircraft's direction in flight. Aircraft e ...
. The hydraulic pressure generated was also used to control all of the orbiter's flight control surfaces
Aircraft flight control surfaces are aerodynamic devices allowing a pilot to adjust and control the aircraft's flight attitude.
Development of an effective set of flight control surfaces was a critical advance in the development of aircraft. Ea ...
(the elevons, rudder, speed brake, etc.), to deploy the landing gear of the orbiter, and to retract the umbilical hose connection doors located near the rear landing gear, which supplied the orbiter's SSMEs with liquid hydrogen and oxygen from the external tank.
Two Orbital Maneuvering System
In spaceflight, an orbital maneuver (otherwise known as a burn) is the use of propulsion systems to change the orbit of a spacecraft.
For spacecraft far from Earth (for example those in orbits around the Sun) an orbital maneuver is called a ' ...
(OMS) thrusters were mounted in two separate removable pods on the orbiter's aft fuselage, located between the SSMEs and the vertical stabilizer. The OMS engines provided significant thrust for course orbital maneuvers, including insertion, circularization, transfer, rendezvous, deorbit, abort to orbit, and to abort once around. At lift-off, two solid rocket boosters
A solid rocket booster (SRB) is a large solid propellant motor used to provide thrust in spacecraft launches from initial launch through the first ascent. Many launch vehicles, including the Atlas V, SLS and space shuttle, have used SRBs to giv ...
(SRBs) were used to take the vehicle to an altitude of roughly 140,000 feet.
Electrical power
Electric power for the orbiter'ssubsystem
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and expresse ...
s was provided by a set of three hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells which produced 28 volt DC power and was also converted into 115 volt 400 Hz AC three-phase electric power
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ) is a common type of alternating current used in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system employing three wires (or four including an optional neutral ...
(for systems that used AC power). These provided power to the entire Shuttle stack (including the SRBs and ET) from T-minus 3m30s up through the end of the mission. The hydrogen and oxygen for the fuel cells was kept in pairs of cryogenic storage tanks in the mid-fuselage underneath the payload bay liner, and a variable number of such tanks could be installed (up to five) depending on the requirements of the mission. The three fuel cells were capable of generating 21 kilowatts of power continuously (or a 15-minute peak of 36 kilowatts) with the orbiter consuming an average of about 14 kilowatts of that power (leaving 7 kilowatts for the payload).
Additionally, the fuel cells provided potable water for the crew during the mission.
Computer systems
The orbiter's computer system consisted of five identical IBM AP-101avionics
Avionics (a blend of ''aviation'' and ''electronics'') are the electronic systems used on aircraft. Avionic systems include communications, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems, and the hundreds of systems that are fit ...
computers, which redundantly controlled the vehicle's on-board systems. The specialized HAL/S programming language was used for orbiter systems.
Thermal protection
 The orbiters were protected by
The orbiters were protected by Thermal Protection System
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the entr ...
(TPS) materials (developed by Rockwell Space Systems) inside and out, from the orbiter's outer surface to the payload bay. The TPS protected it from the cold soak of in space to the heat of re-entry.
Structure
The orbiter's structure was made primarily fromaluminium alloy
An aluminium alloy (or aluminum alloy; see spelling differences) is an alloy in which aluminium (Al) is the predominant metal. The typical alloying elements are copper, magnesium, manganese, silicon, tin, nickel and zinc. There are two principa ...
, although the engine thrust structure was made from titanium alloy
Titanium alloys are alloys that contain a mixture of titanium and other chemical elements. Such alloys have very high tensile strength and toughness (even at extreme temperatures). They are light in weight, have extraordinary corrosion resista ...
. The later orbiters (''Discovery'', ''Atlantis'' and ''Endeavour'') substituted graphite epoxy for aluminum in some structural elements in order to reduce weight. The windows were made of aluminum silicate
Aluminium silicate (or aluminum silicate) is a name commonly applied to chemical compounds which are derived from aluminium oxide, Al2O3 and silicon dioxide, SiO2 which may be anhydrous or hydrated, naturally occurring as minerals or synthetic. ...
glass and fused silica
Fused quartz, fused silica or quartz glass is a glass consisting of almost pure silica (silicon dioxide, SiO2) in amorphous (non- crystalline) form. This differs from all other commercial glasses in which other ingredients are added which ch ...
glass, and comprised an internal pressure pane, a optical pane, and an external thermal pane. The windows were tinted with the same ink used to make American banknotes.
Landing gear
 The Space Shuttle orbiter had three sets of
The Space Shuttle orbiter had three sets of landing gear
Landing gear is the undercarriage of an aircraft or spacecraft that is used for takeoff or landing. For aircraft it is generally needed for both. It was also formerly called ''alighting gear'' by some manufacturers, such as the Glenn L. Martin ...
which emerged downwards through doors in the heat shield. As a weight-saving measure, the gear could not be retracted once deployed. Since any premature extension of the landing gear would very likely have been catastrophic (as it opened through the heat shield layers), the landing gear could only be lowered by manual controls, and not by any automatic system.
Similarly, since the Shuttle landed at high speed and could not abort its landing attempt, the gear had to deploy reliably on the first try every time. The gear were unlocked and deployed by triple redundant hydraulics, with the gear doors actuated by mechanical linkages to the gear strut. If all three hydraulic systems failed to release the landing gear uplocks within one second of the release command, pyrotechnic charges automatically cut the lock hooks and a set of springs deployed the gear.
During landing, the Shuttle nose wheel could be steered with the rudder pedals in the cockpit. During the construction of , an improved nose wheel steering system was developed which allowed easier and more effective nose wheel steering. After ''Endeavour'' roll-out, the system was installed on the other shuttles during their overhauls in the early 1990s.
Lack of navigational lights
The Space Shuttle orbiter did not carry anti-collision lights, navigational lights, orlanding lights
Landing lights are lights, mounted on aircraft, that illuminate the terrain and runway ahead during takeoff and landing, as well as being used as a collision avoidance measure against other aircraft and bird strikes.
Overview
Almost all moder ...
, because the orbiter always landed in areas that had been specially cleared by both the Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic ...
(FAA) and the U.S. Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Sign ...
. The orbiter always landed at either Edwards Air Force Base, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
or at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility
The Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) also known as Launch and Landing Facility (LLF) is an airport located on Merritt Island in Brevard County, Florida, United States. It is a part of the Kennedy Space Center and was used by Space Shuttle for ...
, Florida, except STS-3
STS-3 was NASA's third Space Shuttle mission, and was the third mission for the Space Shuttle ''Columbia''. It launched on March 22, 1982, and landed eight days later on March 30, 1982. The mission, crewed by Jack R. Lousma and C. Gordon Ful ...
at the White Sands Space Harbor
White Sands Space Harbor (WSSH) is a spaceport in New Mexico that was formerly used as a Space Shuttle runway, a test site for rocket research, and the primary training area used by NASA for Space Shuttle pilots practicing approaches and landin ...
in New Mexico. Similar special clearances (no-fly zones) were also in effect at potential emergency landing sites, such as in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
during all launches.
When an orbiter landing was carried out at night, the runway was always strongly illuminated with light from floodlights
A floodlight is a broad-beamed, high-intensity artificial light. They are often used to illuminate outdoor playing fields while an outdoor sports event is being held during low-light conditions. More focused kinds are often used as a stage ...
and spotlights on the ground, making landing lights on the orbiter unnecessary and also an unneeded spaceflight weight load. A total of 26 landings took place at night, the first being STS-8
STS-8 was the eighth NASA Space Shuttle mission and the third flight of the Space Shuttle ''Challenger''. It launched on August 30, 1983, and landed on September 5, 1983, conducting the first night launch and night landing of the Space Shuttl ...
in September 1983.
Markings and insignia
typeface
A typeface (or font family) is the design of lettering that can include variations in size, weight (e.g. bold), slope (e.g. italic), width (e.g. condensed), and so on. Each of these variations of the typeface is a font.
There are thousands o ...
used on the Space Shuttle orbiter was Helvetica
Helvetica (originally Neue Haas Grotesk) is a widely used sans-serif typeface developed in 1957 by Swiss typeface designer Max Miedinger and Eduard Hoffmann.
Helvetica is a neo-grotesque design, one influenced by the famous 19th century (1890s) ...
.
The prototype orbiter ''Enterprise'' originally had a flag of the United States on the upper surface of the left wing and the letters "USA" in black on the right wing. The name "Enterprise" in black was painted on the payload bay doors just above the forwardmost hinge and behind the crew module; on the aft end of the payload bay doors was the NASA "worm" logotype in gray. Underneath the rear of the payload bay doors on the side of the fuselage just above the wing was the text "United States" in black with a flag of the United States ahead of it.
The first operational orbiter, ''Columbia'', originally had the same markings as ''Enterprise'', although the letters "USA" on the right wing were slightly larger and spaced farther apart. ''Columbia'' also had black tiles which ''Enterprise'' lacked on its forward RCS module, around the cockpit windows, and on its vertical stabilizer. ''Columbia'' also had distinctive black chines on the forward part of its upper wing surfaces, which none of the other orbiters had.
STS-93
STS-93 in 1999 marked the 95th launch of the Space Shuttle, the 26th launch of ''Columbia'', and the 21st night launch of a Space Shuttle. Eileen Collins became the first female shuttle Commander on this flight. Its primary payload was the Chan ...
), and its unique black chines for the remainder of its operational life.
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ...
in 1985 and was no longer under NASA's control when these changes were made, hence the prototype orbiter still has its 1983 markings and still has its name on the payload bay doors.
Retirement
With the end of the Shuttle program, plans were made to place the three remaining Space Shuttle orbiters on permanent display. NASA Administrator Charles F. Bolden Jr. announced the disposition location of the orbiters on April 12, 2011, the 50th anniversary of the first human space flight and the 30th anniversary of thefirst flight
The maiden flight, also known as first flight, of an aircraft is the first occasion on which it leaves the ground under its own power. The same term is also used for the first launch of rockets.
The maiden flight of a new aircraft type is alw ...
of ''Columbia''. ''Discovery'' went to the Smithsonian's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center
The Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, also called the Udvar-Hazy Center, is the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum (NASM)'s annex at Washington Dulles International Airport in the Chantilly area of Fairfax County, Virginia. It holds numerous ...
, replacing ''Enterprise'' which was moved to the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum
The ''Intrepid'' Sea, Air & Space Museum is an American military and maritime history museum in New York City with a collection of museum ships. It is located at Pier 86 at 46th Street, along the Hudson River, in the Hell's Kitchen neighborh ...
in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
. ''Endeavour'' went to the California Science Center
The California Science Center (sometimes spelled California ScienCenter) is a state agency and museum located in Exposition Park, Los Angeles, next to the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County and the University of Southern California. ...
in Los Angeles arriving on October 14, 2012. ''Atlantis'' went to the Kennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC, originally known as the NASA Launch Operations Center), located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten field centers. Since December 1968 ...
Visitor Complex on November 2, 2012. Hundreds of other shuttle artifacts will be put on display at various other museums and educational institutions around the U.S.
One of the Crew Compartment Trainer Flight and mid-deck training hardware is on display at the National Museum of the U.S. Air Force
The National Museum of the United States Air Force (formerly the United States Air Force Museum) is the official museum of the United States Air Force located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, northeast of Dayton, Ohio. The NMUSAF is the ...
, while the other is on display at the JSC. The Full Fuselage Trainer, which includes the payload bay and aft section but no wings, is on display at the Museum of Flight
The Museum of Flight is a private non-profit air and space museum in the Seattle metropolitan area. It is located at the southern end of King County International Airport (Boeing Field) in the city of Tukwila, immediately south of Seattle. ...
in Seattle, Washington
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region ...
. The Mission Simulation and Training Facility's Shuttle Mission Simulator Fixed Base Simulator originally went to the Adler Planetarium
The Adler Planetarium is a public museum in Chicago, Illinois, dedicated to astronomy and astrophysics. It was founded in 1930 by local businessman Max Adler. Located on the northeastern tip of Northerly Island on Lake Michigan in the city, th ...
in Chicago, Illinois
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
but was later transferred to the Stafford Air & Space Museum in Weatherford, Oklahoma
Weatherford is a city in Custer County, Oklahoma, United States. The population was 10,833 at the 2010 census.
Geography
Weatherford is located at (35.5384097, -98.6872467). The elevation is 1,634 feet (498 m). According to the United States ...
. The Motion Base Simulator was transferred to the Texas A&M
Texas A&M University (Texas A&M, A&M, or TAMU) is a public, land-grant, research university in College Station, Texas. It was founded in 1876 and became the flagship institution of the Texas A&M University System in 1948. As of late 2021, T ...
Aerospace Engineering Department in College Station, Texas
College Station is a city in Brazos County, Texas, Brazos County, Texas, situated in East-Central Texas in the heart of the Brazos Valley, towards the eastern edge of the region known as the Texas Triangle. It is northwest of Houston and east-n ...
, and the Guidance and Navigation Simulator went to the Wings of Dreams Aviation Museum in Starke, Florida. NASA also made approximately 7,000 TPS tiles available to schools and universities.
Shuttle Orbiter Specifications (OV-105)
 The cargo bay is by , and could transport to , or to the ISS at . The most massive payload launched by the Space Shuttle was the
The cargo bay is by , and could transport to , or to the ISS at . The most massive payload launched by the Space Shuttle was the Chandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources 1 ...
in 1999 at , including its Inertial Upper Stage
The Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), originally designated the Interim Upper Stage, was a two-stage, solid-fueled space launch system developed by Boeing for the United States Air Force beginning in 1976 for raising payloads from low Earth orbit to ...
(IUS) and support equipment. The Shuttle was capable of returning approximately of cargo to Earth.
The orbiter's maximum glide ratio
In aerodynamics, the lift-to-drag ratio (or L/D ratio) is the lift generated by an aerodynamic body such as an aerofoil or aircraft, divided by the aerodynamic drag caused by moving through air. It describes the aerodynamic efficiency under giv ...
/ lift-to-drag ratio
In aerodynamics, the lift-to-drag ratio (or L/D ratio) is the lift generated by an aerodynamic body such as an aerofoil or aircraft, divided by the aerodynamic drag caused by moving through air. It describes the aerodynamic efficiency under gi ...
varied considerably with speed, ranging from 1:1 at hypersonic speed
In aerodynamics, a hypersonic speed is one that exceeds 5 times the speed of sound, often stated as starting at speeds of Mach 5 and above.
The precise Mach number at which a craft can be said to be flying at hypersonic speed varies, since ind ...
s, 2:1 at supersonic speed
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound ( Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times ...
s, and reaching 4.5:1 at subsonic speeds during approach and landing.
Fleet
 Individual Space Shuttle orbiters were named in honor of antique sailing ships of the navies of the world (though the test orbiter ''Enterprise'', originally to be named "''Constitution''", had its name changed after the ''Star Trek'' starship, itself named after a series of US Navy ships), and they were also numbered using the NASA Orbiter Vehicle designation system. Three of the names had also been given to Apollo spacecraft between 1969 and 1972:
Individual Space Shuttle orbiters were named in honor of antique sailing ships of the navies of the world (though the test orbiter ''Enterprise'', originally to be named "''Constitution''", had its name changed after the ''Star Trek'' starship, itself named after a series of US Navy ships), and they were also numbered using the NASA Orbiter Vehicle designation system. Three of the names had also been given to Apollo spacecraft between 1969 and 1972: Apollo 11
Apollo 11 (July 16–24, 1969) was the American spaceflight that first landed humans on the Moon. Commander Neil Armstrong and lunar module pilot Buzz Aldrin landed the Apollo Lunar Module ''Eagle'' on July 20, 1969, at 20:17 UTC, ...
Command Module ''Columbia'', Apollo 15 Command Module ''Endeavour'', and Apollo 17 Lunar Module ''Challenger''.
While all of the orbiters were externally practically identical, they had minor differences in their interiors. New equipment for the Orbiters was installed in the same order that they underwent maintenance work, and the newer orbiters were constructed by Rockwell International, under NASA supervision, with some more advanced, lighter in weight, structural elements. Thus, the newer orbiters (''Discovery'', ''Atlantis'' and ''Endeavour'') had slightly more cargo capacity than ''Columbia'' or ''Challenger''.
The Space Shuttle orbiters were assembled at Rockwell's assembly facility in Palmdale, California, at the federally owned Plant 42
United States Air Force Plant 42 is a classified aircraft manufacturing plant owned by the United States Air Force in the Antelope Valley, about from downtown Los Angeles. It is also used by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (N ...
complex.
Orbiter Vehicle Designation
EachNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program ...
designation was composed of a prefix and suffix separated by a dash. The prefix for operational shuttles is OV, for Orbiter Vehicle. The suffix is composed of two parts: the series and the vehicle number; "0" was used for non-flight ready orbiters, and "1" was used for flight-ready orbiters. The vehicle number is sequentially assigned within the series, beginning with 1. Therefore, there can never be an OV-100 as it would read "Orbiter Vehicle Series 1 Vehicle 0". Many proposals to build a second generation of orbiters, externally compatible with the current system but internally new, refer to them as "OV-200" or "OV-2xx" in order to differentiate them from the "first generation", the OV-100s. This terminology is informal, and it is unlikely that any Shuttle-derived vehicle built will be given such designation. ''Challenger'' was originally intended to be used as a Structural Test Article (STA), rather than a flight-capable orbiter; as such, the numbering was changed when it was rebuilt. ''Enterprise'', on the other hand, was intended to be rebuilt into a flight-capable orbiter; it was found to be cheaper to rebuild STA-099 than OV-101, so it remained unflown. The designations were not altered, despite these changes in plans. An "OV-106" designation was given to the set of structural components manufactured to replace those used in the construction of ''Endeavour''; however, the contract for these was canceled shortly afterwards, and they were never completed. The "096" and "097" designators were given to structural test articles that were canceled, but while they exist in some NASA records, the NASA History Office has no official record of STA-096 and STA-097.
Test article
Operational orbiters
* '' Columbia'' was first launched on April 12, 1981. On February 1, 2003, ''Columbia'' disintegrated during re-entry on its 28th spaceflight. * '' Challenger'' was first launched on April 4, 1983. On January 28, 1986, it disintegrated 73 seconds after launch on its 10th mission. * ''Discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discover ...
'' was first launched on August 30, 1984. It flew 39 missions, and was NASA's "Return to Flight" vehicle, following the accidental destructions of ''Challenger'' and ''Columbia''. ''Discovery'' completed its last mission, STS-133
STS-133 ( ISS assembly flight ULF5) was the 133rd mission in NASA's Space Shuttle program; during the mission, Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' docked with the International Space Station. It was ''Discoverys 39th and final mission. The mission l ...
, in March 2011. It is currently on display at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, near Dulles International Airport
Washington Dulles International Airport , typically referred to as Dulles International Airport, Dulles Airport, Washington Dulles, or simply Dulles ( ), is an international airport in the Eastern United States, located in Loudoun County and F ...
.
* ''Atlantis
Atlantis ( grc, Ἀτλαντὶς νῆσος, , island of Atlas) is a fictional island mentioned in an allegory on the hubris of nations in Plato's works '' Timaeus'' and '' Critias'', wherein it represents the antagonist naval power that b ...
'' was first launched on October 3, 1985. It flew 33 spaceflights including the final Space Shuttle mission, STS-135
STS-135 ( ISS assembly flight ULF7) was the 135th and final mission of the American Space Shuttle program. It used the orbiter ''Atlantis'' and hardware originally processed for the STS-335 contingency mission, which was not flown. STS-135 la ...
, in July 2011.
* '' Endeavour'' was first launched on May 7, 1992. It flew 25 spaceflights, the final being STS-134
STS-134 ( ISS assembly flight ULF6) was the penultimate mission of NASA's Space Shuttle program and the 25th and last spaceflight of . This flight delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer and an ExPRESS Logistics Carrier to the Internationa ...
, launched May 16, 2011.
Mockups
In addition to the test articles and orbiters produced for use in the Shuttle program, there are also various mockup replicas on display throughout the United States: * ''Adventure'', a full-scale replica of an orbiter mid-deck and flight deck, also at Space Center Houston. * '' America'', a full-scale replica of an orbiter for an attraction of the same name atSix Flags Great America
Six Flags Great America is a amusement park located in Gurnee, Illinois, within the northern Chicago metropolitan area. The amusement park originally opened as Marriott's Great America on May 29, 1976, as one of two theme parks built by the ...
in Gurnee, Illinois
Gurnee ( ) is a village in Lake County, Illinois, United States. Its population was 30,706 as of the 2020 census. It borders the city of Waukegan, and is a popular tourist attraction within the Chicago metropolitan area.
Best known for being t ...
and had authentic thermal tiles used in the shuttle missions. It was disassembled and removed in 2009.
* ''Independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the statu ...
'', formerly ''Explorer'', a full-scale replica of the entire orbiter at the Johnson Space Center's visitor facility, Space Center Houston
Space Center Houston is a science museum that serves as the official visitor center of NASA Johnson Space Center in Houston. It was designated a Smithsonian Affiliate museum in 2014. The organization is owned by NASA, and operated under a con ...
, in Houston, Texas atop of the Shuttle Carrying Aircraft, NASA 905.
* '' Inspiration (California)'', a nearly full-scale replica of an orbiter (lacking a left-wing, vertical stabilizer, and payload bay doors) displayed in a tent at the Columbia Memorial Space Center.
* ''Inspiration (Florida)'', bearing the same name as the Californian mockup, is a full-scale replica of an orbiter formerly outside the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame
The United States Astronaut Hall of Fame, located inside the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex Heroes & Legends building on Merritt Island, Florida, honors American astronauts and features the world's largest collection of their personal memora ...
. It was subsequently sold by NASA to LVX and transported to the Shuttle Landing Facility
The Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) also known as Launch and Landing Facility (LLF) is an airport located on Merritt Island in Brevard County, Florida, United States. It is a part of the Kennedy Space Center and was used by Space Shuttle for ...
for refurbishment and modifications in 2016.
* ''Resolution!'', a full-scale replica of an orbiter crew-compartment, originally built to house an amateur flight simulator but later intended for use by Kennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC, originally known as the NASA Launch Operations Center), located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten field centers. Since December 1968 ...
firefighters to practice rescue techniques. Now abandoned and nearly destroyed by nature and neglect.
Flight statistics
Flight history timeline
See also
*Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program ...
for programme history and description of operations
* Buran programme
The ''Buran'' program (russian: Буран, , "Snowstorm", "Blizzard"), also known as the "VKK Space Orbiter program" (russian: ВКК «Воздушно-Космический Корабль», lit=Air and Space Ship), was a Soviet and later R ...
* Dream Chaser
Dream Chaser is an American reusable lifting-body spaceplane being developed by Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) Space Systems. Originally intended as a crewed vehicle, the Dream Chaser Space System is set to be produced after the cargo vari ...
Notes
References
External links
Orbiter Vehicles
*
Historic American Engineering Record
Heritage Documentation Programs (HDP) is a division of the U.S. National Park Service (NPS) responsible for administering the Historic American Buildings Survey (HABS), Historic American Engineering Record (HAER), and Historic American Landscapes ...
(HAER) documentation, filed under Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center, 2101 NASA Parkway, Houston, Harris County, TX:
**
**
**
**
{{Authority control
Tailless delta-wing aircraft
Glider aircraft
Orbiter
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to spaceflight, fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth ...
Crewed spacecraft
Spaceplanes
NASA spacecraft
Reusable spacecraft