List of Russian physicians and psychologists on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This list of
This list of






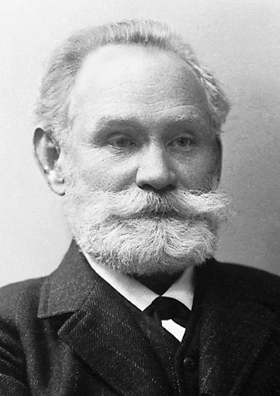


''Memoirs of a Physician''
/ref> *
 This list of
This list of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
n physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
s and psychologist
A psychologist is a professional who practices psychology and studies mental states, perceptual
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the pre ...
s includes the famous physicians and psychologists, medical scientist
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosop ...
s and medical doctors from the Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
, the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
and other predecessor states of Russia. Physicians of all specialties may be listed here.
Alphabetical list
__NOTOC__A
*Nikolai Amosov
Nikolai Mikhailovich Amosov, Doctor of Science, Professor (December 6, 1913 in Olkhovo, Novgorod Governorate, Russian Empire – December 12, 2002 in Kyiv, Ukraine) was a Soviet and Ukrainian doctor of Russian origin, heart surgeon, inventor, bes ...
, prominent cardiovascular surgery
Cardiac surgery, or cardiovascular surgery, is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. It is often used to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, with coronary artery bypass grafting); to corr ...
developer, best-selling author
An author is the writer of a book, article, play, mostly written work. A broader definition of the word "author" states:
"''An author is "the person who originated or gave existence to anything" and whose authorship determines responsibility f ...

B
* Aleksandr Bakulev, prominent cardiovascular surgery developer * Vladimir Bekhterev, neuropathologist, founder of objective psychology, noted the role of thehippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic syste ...
in memory, major contributor to reflexology
Reflexology, also known as zone therapy, is an alternative medical practice involving the application of pressure to specific points on the feet, ears, and hands. This is done using thumb, finger, and hand massage techniques without the use of ...
, studied the Bekhterev’s Disease
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hips ...
*Vladimir Betz
Volodymyr Oleksiyovych Betz( ua, Володи́мир Олексійович Бец) ( – )Kushchayev, Sergiy V., et al. "The Discovery of the Pyramidal Neurons: Volodymyr Betz and a New Era of Neuroscience." JOURNAL OF NEUROSURGERY. Vol. 113. ...
, discovered Betz cells
Betz cells (also known as pyramidal cells of Betz) are giant pyramidal cells (neurons) located within the fifth layer of the grey matter in the primary motor cortex. These neurons are the largest in the central nervous system, sometimes reaching ...
of primary motor cortex
The primary motor cortex (Brodmann area 4) is a Human brain, brain region that in humans is located in the dorsal portion of the frontal lobe. It is the primary cortex, primary region of the motor system and works in association with other motor ...
*Peter Borovsky
Pyotr Fokich Borovsky (russian: Пётр Фоки́ч Боро́вский, 8 June 1863 – 15 December 1932) was Russian and Soviet surgeon and public health administrator of who worked in Tashkent, professor of surgery in Tashkent Medical In ...
, described the causative agent of Oriental sore
The Orient is a term for the East in relation to Europe, traditionally comprising anything belonging to the Eastern world. It is the antonym of ''Occident'', the Western World. In English, it is largely a metonym for, and coterminous with, the c ...
*Sergey Botkin
Sergey Petrovich Botkin (russian: Серге́й Петро́вич Бо́ткин; 5 September 1832 – 12 December 1889) was a famous Russian clinician, therapist, and activist, one of the founders of modern Russian medical science and educati ...
, major therapist
Therapist is a person who offers any kinds of therapy
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis.
As a rule, each therapy has indi ...
and court physician
*Nikolay Burdenko
Nikolay Nilovich Burdenko (russian: Николай Нилович Бурденко; – 11 November 1946) was a Russian Empire and Soviet surgeon, the founder of Russian neurosurgery. He was Surgeon-General of the Red Army (1937–1946), a ...
, major developer of neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and pe ...
*Konstantin Buteyko
The Buteyko method or Buteyko Breathing Technique is a form of complementary or alternative physical therapy that proposes the use of breathing exercises primarily as a treatment for asthma and other respiratory conditions.
Buteyko asserts that ...
, developed the Buteyko method
The Buteyko method or Buteyko Breathing Technique is a form of complementary or alternative physical therapy that proposes the use of breathing exercises primarily as a treatment for asthma and other respiratory conditions.
Buteyko asserts that ...
for the treatment of asthma and other breathing disorders
C
*Mikhail Chumakov
Mikhail Petrovich Chumakov (russian: Михаи́л Петро́вич Чумако́в) (November 14, 1909 – June 11, 1993) was a Soviet microbiologist and virologist most famous for conducting pivotal large-scale clinical trials that led to l ...
, co-discovered tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infectious disease involving the central nervous system. The disease most often manifests as meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Myelitis and spinal paralysis also occurs. In about one third ...
, co-developed oral polio vaccine
Polio vaccines are vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio). Two types are used: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth (OPV). The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends all chi ...

D
* Livery Darkshevich,neurologist
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal c ...
, described the nucleus of posterior commissure
The posterior commissure (also known as the epithalamic commissure) is a rounded band of white fibers crossing the middle line on the dorsal aspect of the rostral end of the cerebral aqueduct. It is important in the bilateral pupillary light refl ...
*Vladimir Demikhov
Vladimir Petrovich Demikhov (russian: Владимир Петрович Демихов; July 31, 1916 – November 22, 1998) was a Soviet scientist and organ transplantation pioneer, who performed several transplants in the 1940s and 1 ...
, major pioneer of transplantology
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transpo ...
F
*Vladimir Filatov
Vladimir Petrovich Filatov (russian: Владимир Филaтoв, 15 .S. 27February 1875 in Mikhaylovka, Penza Governorate, Russian Empire – 30 October 1956 in Odessa, Ukrainian SSR) was a Russian Empire and Soviet ophthalmologist and surgeo ...
, ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a med ...
, corneal transplantation
Corneal transplantation, also known as corneal grafting, is a surgical procedure where a damaged or diseased cornea is replaced by donated corneal tissue (the graft). When the entire cornea is replaced it is known as penetrating keratoplasty a ...
pioneer
*Svyatoslav Fyodorov
Svyatoslav Nikolayevich Fyodorov (; August 8, 1927 – June 2, 2000) was a Russian ophthalmologist, politician, professor, full member of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. He is considered to be a pioneer o ...
, inventor of radial keratotomy


G
* Pyotr Gannushkin, psychiatrist, pioneer researcher of psychopathies known today aspersonality disorder
Personality disorders (PD) are a class of mental disorders characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience, exhibited across many contexts and deviating from those accepted by the individual's cultu ...
s
*Oleg Gazenko
Oleg Georgievich Gazenko (russian: Олег Георгиевич Газенко; 12 December 1918 – 17 November 2007) was a Russian scientist, general officer in the Soviet Air Force and the former director of the Institute of Biomedical Pr ...
, founder of space medicine
Space medicine is the practice of medicine on astronauts in outer space whereas astronautical hygiene is the application of science and technology to the prevention or control of exposure to the hazards that may cause astronaut ill health. Bot ...
, selected and trained Laika
Laika (russian: link=no, Лайка; – 3 November 1957) was a Soviet space dog who was one of the first animals in space and the first to orbit the Earth. A stray mongrel from the streets of Moscow, she flew aboard the Sputnik 2 space ...
, the first space dog
Bullseye Art was a New York City based art collective that pioneered art and animation on the web. Founded in 1995 by Josh Kimberg, Nick Cogan and Ryan Edwards, the company gained fame for its creation of unique and offbeat interactive cartoon ...
*Georgy Gause
Georgy Frantsevich Gause (russian: Гео́ргий Фра́нцевич Га́узе; December 27, 1910 – May 2, 1986), was a Soviet and Russian biologist and evolutionist, who proposed the competitive exclusion principle, fundamental to the sc ...
, inventor of gramicidin S and other antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and preventio ...
* Vera Gedroitz, world's first female professor of surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pa ...
*Hans-Werner Gessmann
Hans-Werner Gessmann (born 24 March 1950, in Duisburg) is a German psychologist, founder of humanistic psychodrama and university teacher in Russia, India and Africa, one of the best known psychotherapists worldwide.
Career
Gessmann received a ...
, one of the world's most famous professor of clinical psychology
Clinical psychology is an integration of social science, theory, and clinical knowledge for the purpose of understanding, preventing, and relieving psychologically based distress or dysfunction and to promote subjective well-being and persona ...
, founder of humanistic psychodrama psychotherapy
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of psychological methods, particularly when based on regular personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase happiness, and overcome pro ...
* Yuliya Gippenreyter, researcher in experimental psychology, family therapy and neuro-linguistic programming
* Ilya Gruzinov, found that vocal folds
In humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speec ...
are the source of phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defin ...
H
* Waldemar Haffkine, invented the first vaccines againstcholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium '' Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting an ...
and bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium ('' Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as wel ...

I
* Gavriil Ilizarov, invented Ilizarov apparatus, developed distraction osteogenesisK
* Nikolai Korotkov, inventedauscultatory blood pressure measurement
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" ...
, pioneer of vascular surgery
Vascular surgery is a surgical subspecialty in which diseases of the vascular system, or arteries, veins and lymphatic circulation, are managed by medical therapy, minimally-invasive catheter procedures and surgical reconstruction. The specialt ...
* Sergey Korsakov, studied the effects of alcoholism
Alcoholism is, broadly, any drinking of alcohol that results in significant mental or physical health problems. Because there is disagreement on the definition of the word ''alcoholism'', it is not a recognized diagnostic entity. Predomi ...
on the nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes ...
, described Korsakoff's syndrome
Korsakoff syndrome (KS) is a disorder of the central nervous system characterized by amnesia, deficits in explicit memory, and confabulation. This neurological disorder is caused by a deficiency of thiamine (vitamin B1) in the brain, and it ...
, introduced paranoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy c ...
concept
* Aleksei Kozhevnikov, neurologist and psychiatrist, described the epilepsia partialis continua
Epilepsia partialis continua is a rare type of brain disorder in which a patient experiences recurrent motor epileptic seizures that are focal (hands and face), and recur every few seconds or minutes for extended periods (days to years). It is som ...

L
* Aleksey Leontyev, founder of activity theory in psychology *Peter Lesgaft
Peter Franzevich Lesgaft (russian: Пётр Францевич Лесгафт) (21 September 1837 – 1909) was a Russian teacher, anatomist, physician and social reformer. He was the founder of the modern system of physical education and medical-p ...
, founder of the modern system of physical education
Physical education, often abbreviated to Phys Ed. or P.E., is a subject taught in schools around the world. It is usually taught during primary and secondary education, and encourages psychomotor learning by using a play and movement explorat ...
in Russia
* Andrey Yevgenyevich Lichko, adolescent psychiatrist
*Alexander Luria
Alexander Romanovich Luria (russian: Алекса́ндр Рома́нович Лу́рия, p=ˈlurʲɪjə; 16 July 1902 – 14 August 1977) was a Soviet neuropsychologist, often credited as a father of modern neuropsychology. He develope ...
, co-developer of activity theory and cultural-historical psychology Cultural-historical psychology is a branch of psychological theory and practice associated with Lev Vygotsky and Alexander Luria and their Circle, who initiated it in the mid-1920s–1930s.Yasnitsky, A., van der Veer, R., & Ferrari, M. (Eds.) (2014) ...
, major researcher of aphasia
Aphasia is an inability to comprehend or formulate language because of damage to specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine but aphasia due to stroke is estimated to be 0.1–0.4% in ...
M
* Ilya Mechnikov, pioneer researcher ofimmune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
, probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria- host i ...
and phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is ...
; coined the term "gerontology
Gerontology ( ) is the study of the social, cultural, psychological, cognitive, and biological aspects of aging. The word was coined by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov in 1903, from the Greek , ''geron'', "old man" and , ''-logia'', "study of". The fi ...
", Nobel Prize in Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, according ...
winner
* Lazar Minor, neurologist, described Minor's disease
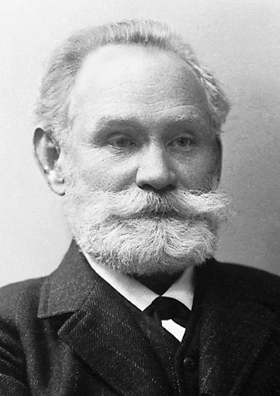
N
*Pyotr Nikolsky Pyotr Vasilyevich Nikolsky (russian: Пётр Васи́льевич Нико́льский; September 13 [ O.S. September 1] 1858 – March 13, 1940) was a Russian dermatologist. He was born in Usman in the Russian Empire and ear ...
, dermatologist
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medica ...
, discoverer of Nikolsky's sign
Nikolsky's sign is a clinical dermatological sign, named after Pyotr Nikolsky (1858–1940), a Russian physician who trained and worked in the Russian Empire. The sign is present when slight rubbing of the skin results in exfoliation of the outermo ...
*Raissa Nitabuch
Raissa Nitabuch (born 1859) was a Russian pathologist who is known for her histological studies of the human placenta. The layer of fibrin that was thought to separate the uterine decidua from the fetoplacental trophoblast after birth was named th ...
, pathologist, the first to describe the spiral arteries
Spiral arteries are small arteries which temporarily supply blood to the endometrium of the uterus during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
In histology, identifying the presence of these arteries is one of the most useful techniques in i ...
which connect the uterine and placental blood flow during pregnancy.
O
* Alexey Olovnikov, predicted existence oftelomerase
Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds a species-dependent telomere repeat sequence to the 3' end of telomeres. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of the chromosomes of most euk ...
, suggested the telomere hypothesis of aging
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes. Although there are different architectures, telomeres, in a broad sense, are a widespread genetic feature m ...
and the telomere relations to cancer
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes. Although there are different architectures, telomeres, in a broad sense, are a widespread genetic feature mos ...

P
*Ivan Pavlov
Ivan Petrovich Pavlov ( rus, Ива́н Петро́вич Па́влов, , p=ɪˈvan pʲɪˈtrovʲɪtɕ ˈpavləf, a=Ru-Ivan_Petrovich_Pavlov.ogg; 27 February 1936), was a Russian and Soviet experimental neurologist, psychologist and physio ...
, founder of modern physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemic ...
, the first to research classical conditioning
Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent stimulus (e.g. food) is paired with a previously neutral stimulus (e.g. a triangle). It also refers to the lear ...
, influenced comparative psychology
Comparative psychology refers to the scientific study of the behavior and mental processes of non-human animals, especially as these relate to the phylogenetic history, adaptive significance, and development of behavior. Research in this area addr ...
and behaviorism
Behaviorism is a systematic approach to understanding the behavior of humans and animals. It assumes that behavior is either a reflex evoked by the pairing of certain antecedent stimuli in the environment, or a consequence of that individual ...
by his works on reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus.
Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs ...
es, Nobel Prize in Medicine winner
*Nikolay Pirogov
Nikolay Ivanovich Pirogov (Russian: Никола́й Ива́нович Пирого́в; — ) was a Russian scientist, medical doctor, pedagogue, public figure, and corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Sciences (1847), one of the ...
, pioneer of ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again ...
anaesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), a ...
and modern field surgery
Battlefield medicine, also called field surgery and later combat casualty care, is the treatment of wounded combatants and non-combatants in or near an area of combat. Civilian medicine has been greatly advanced by procedures that were first ...
, the first to perform anaesthesia in the field conditions, invented a number of surgical operations
* Viktor Protopopov, founder of his own pathophysiological school of thought, namesake of Protopopov's syndrome
R
* Leonid Rogozov, performed anappendectomy
An appendectomy, also termed appendicectomy, is a surgical operation in which the vermiform appendix (a portion of the intestine) is removed. Appendectomy is normally performed as an urgent or emergency procedure to treat complicated acute appe ...
on himself during the 6th Soviet Antarctic Expedition
The Soviet Antarctic Expedition (SAE or SovAE) (russian: Советская антарктическая экспедиция, САЭ, ''Sovetskaya antarkticheskaya ekspeditsiya'') was part of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute of the S ...
, a famous case of self-surgery
* Grigory Rossolimo, pioneer of child neuropsychology
Neuropsychology is a branch of psychology concerned with how a person's cognition and behavior are related to the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Professionals in this branch of psychology often focus on how injuries or illnesses of t ...
* Vladimir Roth, neuropathologist, described meralgia paraesthetica

S
*Ivan Sechenov
Doctor Ivan Mikhaylovich Sechenov (russian: Ива́н Миха́йлович Се́ченов; , Tyoply Stan (now Sechenovo) near Simbirsk, Russia – , Moscow), was a Russian psychologist, physiologist, and medical scientist.
The very fa ...
, founder of electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek , ''ēlektron'', "amber" etymology of "electron"">Electron#Etymology">etymology of "electron" , ''physis'', "nature, origin"; and , ''-logia'') is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of bi ...
and neurophysiology
Neurophysiology is a branch of physiology and neuroscience that studies nervous system function rather than nervous system architecture. This area aids in the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological diseases. Historically, it has been dominated ...
, author of the classic work ''Reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus.
Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs ...
es of the Brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
''
* Vladimir Serbsky, founder of forensic psychiatry
Forensic psychiatry is a subspeciality of psychiatry and is related to criminology. It encompasses the interface between law and psychiatry. According to the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law, it is defined as "a subspecialty of psychiat ...
in Russia
* Nikolay Sklifosovskiy, prominent 19th-century field surgeon
A combat medic, or healthcare specialist, is responsible for providing emergency medical treatment at a point of wounding in a combat or training environment, as well as primary care and health protection and evacuation from a point of injur ...
* Victor Skumin, first to describe a previously unknown disease, now called Skumin syndrome (a disorder of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
of some patient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other heal ...
s after a prosthetic heart valve)
*Lina Stern
Lina Solomonovna Stern (or Shtern; russian: Лина Соломоновна Штерн; 26 August 1878 – 7 March 1968) was a Soviet biochemist, physiologist and humanist whose medical discoveries saved thousands of lives at the fronts of Worl ...
, pioneer researcher of blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system where ne ...
U
* Fyodor Uglov, oldest practicing surgeon in history * Igor Ursov, phthisiatrist, the inventor ofintravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
intermittent bactericidal
A bactericide or bacteriocide, sometimes abbreviated Bcidal, is a substance which kills bacteria. Bactericides are disinfectants, antiseptics, or antibiotics.
However, material surfaces can also have bactericidal properties based solely on the ...
tuberculosis therapy
V
*Alexander Varshavsky
Alexander Jacob Varshavsky (russian: link=no, Александр Яковлевич Варшавский; born 8 November 1946) is a Russian-American biochemist, noted for his discovery of the N-end rule of ubiquitination. A native of Moscow, he ...
, researched ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Fo ...
ation, Wolf Prize in Medicine
The Wolf Prize in Medicine is awarded annually by the Wolf Foundation in Israel. It is one of the six Wolf Prizes established by the Foundation and awarded since 1978; the others are in Agriculture, Chemistry, Mathematics, Physics and Arts. The ...
winner
*Vikenty Veresayev
Vikenty Vikentyevich Smidovich (16 January 1867 – 3 June 1945), better known by his pen name Vikenty Vikentyevich Veresaev, (russian: Вике́нтий Вике́нтьевич Вереса́ев) was a Russian and Soviet writer, translat ...
, Russian/Soviet doctor, author of ''Memoirs of a Physician''/ref> *
Luka Voyno-Yasenetsky
Luke of Simferopol (Luke, russian: Архиепи́скоп Лука́, born Valentin Felixovich Voyno-Yasenetsky, russian: Валенти́н Фе́ликсович Во́йно-Ясене́цкий; April 27 or May 9, 1877 in Kerch – June 11, ...
, founder of purulent
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collect ...
surgery, saint
*Lev Vygotsky
Lev Semyonovich Vygotsky (russian: Лев Семёнович Выго́тский, p=vɨˈɡotskʲɪj; be, Леў Сямёнавіч Выго́цкі, p=vɨˈɡotskʲɪj; – June 11, 1934) was a Soviet psychologist, known for his work on ps ...
, founder of cultural-historical psychology Cultural-historical psychology is a branch of psychological theory and practice associated with Lev Vygotsky and Alexander Luria and their Circle, who initiated it in the mid-1920s–1930s.Yasnitsky, A., van der Veer, R., & Ferrari, M. (Eds.) (2014) ...
, major contributor to child development
Child development involves the Human development (biology), biological, developmental psychology, psychological and emotional changes that occur in human beings between birth and the conclusion of adolescence. Childhood is divided into 3 stages o ...
and psycholinguistics
Psycholinguistics or psychology of language is the study of the interrelation between linguistic factors and psychological aspects. The discipline is mainly concerned with the mechanisms by which language is processed and represented in the mind ...
, introduced zone of proximal development
The zone of proximal development (ZPD) is a concept in educational psychology. It represents the distance between what a learner is capable of doing unsupported, and what they can only do supported. It is the range where they are capable only with ...
and cultural mediation Cultural mediation describes a profession that studies the cultural differences between people, using the data in problem solving.
It is one of the fundamental mechanisms of distinctly human Developmental psychology, development according to cultura ...
concepts
W
*Josias Weitbrecht Josias Weitbrecht (russian: Иосия Вейтбрехт, born 6 November 1702 in Schorndorf, died 28 February 1747 in St. Petersburg) was a German professor of medicine and anatomy in Russia.
Life and career
After his studies at the University ...
, first to describe the construction and function of intervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to h ...
s
Y
* Sergei Yudin, inventor of cadaveric blood transfusionZ
* Alexander Zaporozhets, developmental psychologist, collaborator of Vygotsky, Luria, and Leontiev, once head of theKharkov School of Psychology
{{Use dmy dates, date=October 2015
The Kharkov school of psychology (''Харьковская психологическая школа'') is a tradition of developmental psychological research conducted in the paradigm of Lev Vygotsky's "sociocult ...
* Bluma Zeigarnik, psychiatrist, discovered the Zeigarnik effect
Named after Lithuanian-Soviet psychologist Bluma Zeigarnik, in psychology the Zeigarnik effect occurs when an activity that has been interrupted may be more readily recalled. It postulates that people remember unfinished or interrupted tasks bett ...
, founded experimental psychopathology
Psychopathology is the study of abnormal cognition, behaviour, and experiences which differs according to social norms and rests upon a number of constructs that are deemed to be the social norm at any particular era.
Biological psychopathol ...
See also
*List of physicians
This is a list of famous physicians in history.
Chronological lists
Ancient physicians
30th century BCE to 4th century CE
* List of ancient physicians
Post-classical physicians
5th century CE to 15th century CE
* List of post-classical ph ...
* Psychiatry in the Soviet Union
*List of Russian scientists Polymaths
*Karl Ernst von Baer, polymath naturalist, formulated the geological Baer's law on river erosion and embryological Baer's laws, founder of the Russian Entomological Society, co-founder of the Russian Geographical Society
*Alexander Boro ...
*List of Russian inventors
This is a list of inventors from the Russian Federation, Soviet Union, Russian Empire, Tsardom of Russia and Grand Duchy of Moscow, including both ethnic Russians and people of other ethnicities.
This list also includes those who were born in Rus ...
*Science and technology in Russia
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Russian physicians and psychologists, list of Physicians and psychologistsRussians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
Russian psychologists, list of