List of Guam-related topics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
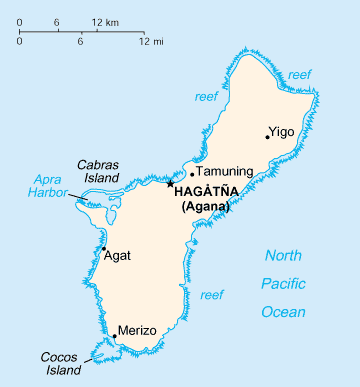
250px, The location of Guam
''U.S. Territories'', Retrieved November 4, 2007. The island's capital is Hagåtña (formerly Agana). Guam is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands. The
 * Pronunciation:
* Common English country name:
* Pronunciation:
* Common English country name:
 * Climate of Guam
* Renewable energy in Guam
*
* Climate of Guam
* Renewable energy in Guam
*
Official Portal for the Island of Guam
Office of the Governor
Congresswoman Madeleine Z. Bordallo, Delegate, U.S. Congress
Guam Customs and Quarantine Agency
Guam Election Commission
Guam Department of Revenue and Taxation
Guam's Original Webpage
; Invasive species
(info from the&nbs
Pacific Island Ecosystems at Risk project (PIER)
Brown tree snake (''Boiga irregularis'') information
from the&nbs
Hawaiian Ecosystems at Risk project (HEAR)
; News
Marianas Variety "Guam's only true independent news source"
''Pacific Daily News'', A Gannett Newspaper
''KUAM'', Guam's Primary News Channel"Pacific News Center - News You Can Trust
; Overviews
''allthingsguam''
A Guam History resource—virtual textbook, virtual workbook and more
Guampedia, Guam's Online Encyclopedia
*
''The World Factbook'' on Guam
Guam Connection
– Guam directory and internet portal. ; Military
Commander, Naval Forces Marianas (COMNAVMAR) Guam
Andersen Air Force Base (AAFB) Guam
; Tourism
Guam Visitors Bureau
Guam Portal
; Others
Guam Chamber of Commerce
National Weather Service - Guam
{{DEFAULTSORT:Guam
Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
The following outline
Outline or outlining may refer to:
* Outline (list), a document summary, in hierarchical list format
* Code folding, a method of hiding or collapsing code or text to see content in outline form
* Outline drawing, a sketch depicting the outer edge ...
is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
:
Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
– organized, unincorporated territory of the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
that comprises the island of Guam in the western North Pacific Ocean
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' i ...
. It is one of five U.S. territories with an established civilian government."USDOI Office of Insular Affairs"''U.S. Territories'', Retrieved November 4, 2007. The island's capital is Hagåtña (formerly Agana). Guam is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands. The
Chamorros
The Chamorro people (; also CHamoru) are the indigenous people of the Mariana Islands, politically divided between the United States territory of Guam and the encompassing Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands in Micronesia. Today, signif ...
, Guam's indigenous inhabitants, first populated the island approximately 4,000 years ago. Discovered by the Spanish expedition of Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the Eas ...
in 1521, the island has a long history of European colonialism beginning in the 16th century, and especially in 1668 with the arrival of Spanish settlers including Padre San Vitores, a Catholic missionary
A missionary is a member of a religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Mi ...
. Guam and the rest of the Mariana Islands were integrated in the Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies ( es , Indias orientales españolas ; fil, Silangang Indiyas ng Espanya) were the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1898, governed for the Spanish Crown from Mexico City and Madri ...
since 1565. The island was a major stopover for Manila Galleons
fil, Galyon ng Maynila
, english_name = Manila Galleon
, duration = From 1565 to 1815 (250 years)
, venue = Between Manila and Acapulco
, location = New Spain (Spanish Empire) ...
sailing from Acapulco, until 1815. Guam was taken over from Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
during the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
in 1898. As the largest island in Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and ...
and the only American-held island in the region before World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Guam was occupied by the Japanese between December 1941 and July 1944. Today, Guam's economy is mainly supported by tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
(primarily from Japan) and U.S. military bases.
General reference
 * Pronunciation:
* Common English country name:
* Pronunciation:
* Common English country name: Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
* Official English country name: The United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
Territory of Guam
* Common endonym(s): List of countries and capitals in native languages
* Official endonym(s): List of official endonyms of present-day nations and states
* Adjectival(s): Guamanian
The Chamorro people (; also CHamoru) are the indigenous people of the Mariana Islands, politically divided between the United States territory of Guam and the encompassing Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands in Micronesia. Today, signifi ...
* Demonym(s):
* Etymology
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the Phonological chan ...
: Name of Guam
* ISO country codes
ISO 3166-1 (''Codes for the representation of names of countries and their subdivisions – Part 1: Country codes'') is a standard defining codes for the names of countries, dependent territories, and special areas of geographical interest. It ...
: GU, GUM, 316
* ISO region codes
ISO 3166-2 is part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and defines codes for identifying the principal subdivisions (e.g., provinces or states) of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1. The ...
: See ISO 3166-2:GU
* Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
country code top-level domain
A country code top-level domain (ccTLD) is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, sovereign state, or dependent territory identified with a country code. All ASCII ccTLD identifiers are two letters long, and all ...
: .gu
.gu is the Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost poin ...
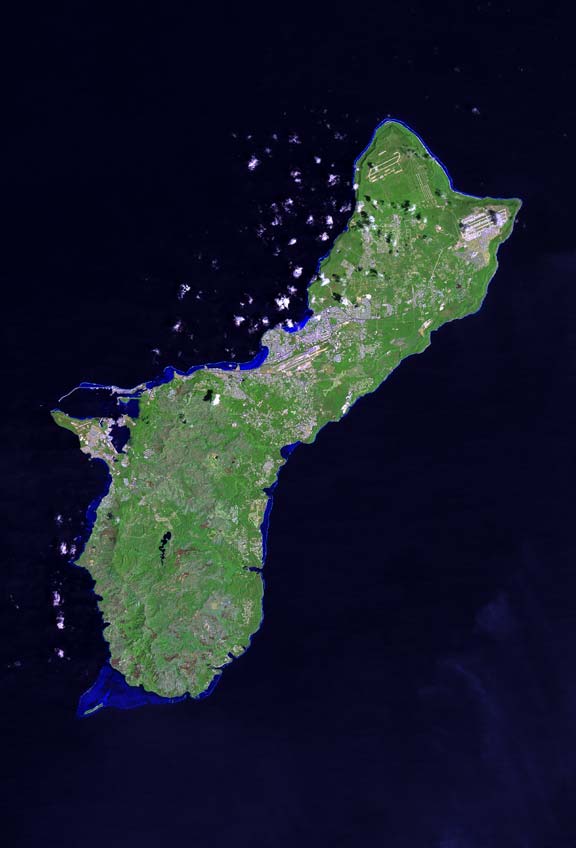
Geography of Guam

Geography of Guam
Guam is a U.S. territory in the western Pacific Ocean, at the boundary of the Philippine Sea. It is the southernmost and largest member of the Mariana Islands archipelago, which is itself the northernmost group of islands in Micronesia. The closes ...
* Guam is: a United States territory
* Location:
** Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
** Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
*** North Pacific
**** Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
***** Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and ...
** Time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it ...
: Chamorro Standard Time
The Chamorro Time Zone, formerly the Guam Time Zone, is a United States time zone which observes standard time ten hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC+10:00). The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 150th m ...
(UTC+10
UTC+10:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +10:00. This time is used in:
As standard time (year-round)
''Principal cities: Brisbane, Gold Coast, Vladivostok, Khabarovsk, Port Moresby, Dededo, Saipan''
North Asia
*Russia – ...
)
** Extreme points of Guam
*** High: Mount Lamlam
Mount Lamlam (meaning ''lightning'' in Chamoru) is a peak on the United States island of Guam. It is located near the village of Agat ( north), in the south-west of the island.
Rising to above sea level, the distance from the peak to the bottom ...
– 11,377 meters above Challenger Deep
The Challenger Deep is the deepest-known point of the seabed of Earth, with a depth of by direct measurement from deep-diving submersibles, remotely operated underwater vehicles and benthic landers, and (sometimes) slightly more by sonar bathym ...
*** Low: North Pacific Ocean
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' i ...
0 m
** Land boundaries: ''none''
** Coastline:
* Population of Guam: 173,000 – 179th most populous country
*
* Area of Guam:
* Atlas of Guam
Environment of Guam
 * Climate of Guam
* Renewable energy in Guam
*
* Climate of Guam
* Renewable energy in Guam
* Geology of Guam
The geology of Guam formed as a result of mafic, felsic and intermediate composition volcanic rocks erupting below the ocean, building up the base of the island in the Eocene, between 33.9 and 56 million years ago. The island emerged above the wate ...
* Protected areas of Guam
** Biosphere reserves in Guam
** National parks of Guam
* Superfund sites in Guam
* Wildlife of Guam
** Fauna of Guam
*** Birds of Guam
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight s ...
*** Mammals of Guam
Natural geographic features of Guam
* Beaches in Guam * Islands of Guam * Lakes of Guam * Mountains of Guam ** Volcanoes in Guam * Rivers of Guam ** Waterfalls of Guam * Valleys of Guam * World Heritage Sites in Guam: NoneRegions of Guam
* Regions of GuamEcoregions of Guam
* List of ecoregions in GuamAdministrative divisions of Guam
None=Municipalities of Guam
= * Capital of Guam: Hagåtña * Cities of GuamDemography of Guam
* Demographics of GuamGovernment and politics of Guam
Politics of Guam
Guam is a two-party presidential representative democracy, in which the Governor is the head of government. Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States, with policy relations between Guam and the US under the jurisdic ...
* Form of government: presidential representative democracy
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy, is a type of democracy where elected people represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies function as some type of represe ...
* Capital of Guam: Hagåtña
* Elections in Guam
* Political parties in Guam
Branches of the government of Guam
Government of Guam
The Government of Guam (GovGuam) is a presidential representative democratic system, whereby the President is the head of state and the Governor is head of government, and of a multi-party system. Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory ...
Executive branch of the government of Guam
*Head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
: President of United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
* Head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, ...
: Governor of Guam
* Cabinet of Guam
Legislative branch of the government of Guam
* Legislature of Guam (unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multi ...
)
Judicial branch of the government of Guam
Court system of Guam *Supreme Court of Guam
The Supreme Court of Guam is the highest judicial body of the United States territory of Guam. The Court hears all appeals from the Superior Court of Guam and exercises original jurisdiction only in cases where a certified question is submitted ...
Foreign relations of Guam
* Diplomatic missions in GuamInternational organization membership
The United States Territory of Guam is a member of: *International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
(IOC)
* Secretariat of the Pacific Community
The Pacific Community (PC), formerly the South Pacific Commission (SPC), is an international development organisation governed by 27 members, including 22 Pacific island countries and territories. The organisation's headquarters are in Nouméa, ...
(SPC)
* Universal Postal Union
The Universal Postal Union (UPU, french: link=no, Union postale universelle), established by the Treaty of Bern of 1874, is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to ...
(UPU)
Law and order in Guam
Law of Guam *Cannabis in Guam
Cannabis in Guam has been legal for medical use since 2015 and legal for recreational use since April 2019. Guam was the first United States Territory to legalize medical marijuana, passing via a ballot referendum in 2014.
The 2012 UNODC ''Worl ...
* Constitution of Guam
The Guam Organic Act of 1950, ( ''et seq.'', ) is a United States federal law that redesignated the island of Guam as an unincorporated territory of the United States, established executive, legislative, and judicial branches, and transferred fe ...
* Crime in Guam
* Human rights in Guam
** LGBT rights in Guam
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Guam have improved significantly in recent years. Same-sex sexual activity has not been criminalized since 1978, and same-sex marriage has been allowed since June 2015. The U.S. territory n ...
** Freedom of religion in Guam
* Law enforcement in Guam
Local government in Guam
Local government in GuamHistory of Guam
History of Guam
The history of Guam starts with the early arrival around 2000 BC of Austronesian people known today as the Chamorro Peoples. The CHamorus then developed a "pre-contact" society, that was Spanish Empire, colonized by the Spanish in the 17th centu ...
* Timeline of the history of Guam
* Current events of Guam
History of Guam, by period
*Geology of Guam
The geology of Guam formed as a result of mafic, felsic and intermediate composition volcanic rocks erupting below the ocean, building up the base of the island in the Eocene, between 33.9 and 56 million years ago. The island emerged above the wate ...
*Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
** Chamorro people
* First European contact, 1521–1668
***On March 6, 1521, three Spanish ships under the command of Fernão de Magalhães
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese people, Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the Magellan expeditio ...
(Ferdinand Magellan) land on the Island of Guam after a seemingly endless eleven week voyage across the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
. Magalhães names the archipelago '' Las Isles de las Velas Latinas'' (The Islands of the Latine Sails). When the Spaniards refuse to pay for supplies, natives take iron from the ships. Magalhães renames the archipelago '' Las Islas de los Ladrones'' (The Islands of the Thieves).
*Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies ( es , Indias orientales españolas ; fil, Silangang Indiyas ng Espanya) were the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1898, governed for the Spanish Crown from Mexico City and Madri ...
, 1565–(1668–1898)–1899
** Diego Luis de San Vitores leads the colonization of Guam, renaming the Chamorro archipelago '' Islas Marianas'' in honor of his patroness, Queen Mariana of Austria
Mariana of Austria ( es, Mariana de Austria) or Maria Anna (24 December 163416 May 1696) was Queen of Spain as the second wife of her uncle Philip IV of Spain from their marriage in 1649 until Philip died in 1665. She was then appointed regent f ...
**The Spanish-Chamorro Wars (1670-1683 on Guam) pacifies CHamoru resistance and solidifies Spanish control
**Guam becomes a major stopover for Spanish galleons en route to Manila, from Acapulco. A number of coastal forts are built to protect these ships, including Fort Soledad
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
and Fort San Jose in Umatac.
*Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
, April 23 – August 12, 1898
**Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
declares war on the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, April 23, 1898
**United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
capture of Guam
The Capture of Guam was a bloodless engagement between the United States and Spain during the Spanish–American War. The U.S. Navy sent a single cruiser, , to capture the island of Guam, then under Spanish control. However, the Spanish garri ...
, June 20–21, 1898
**Treaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
, December 10, 1898
*United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
Territory of Guam, since December 10, 1898
**World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, June 28, 1914 – November 11, 1918
***United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
enters Great War on April 6, 1917
**World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, September 1, 1939 – September 2, 1945
***United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
enters Second World War on December 8, 1941
*** Battle of Guam of 1941
*** Battle of Guam of 1944
** Cold War, March 5, 1946 – December 25, 1991
**Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
, June 25, 1950 – July 27, 1953
**Guam Organic Act
The Guam Organic Act of 1950, ( ''et seq.'', ) is a United States federal law that redesignated the island of Guam as an unincorporated territory of the United States, established executive, legislative, and judicial branches, and transferred fed ...
, August 1, 1950
Culture of Guam
Culture of Guam * Architecture of Guam * Cuisine of Guam * Festivals in Guam * Languages of Guam * Media in Guam * National symbols of Guam ** Coat of arms of Guam **Flag of Guam
The flag of the United States territory of Guam was adopted on February 9, 1948. The territorial flag is dark blue with a narrow red border on all sides (border was a later addition). The red border represents the blood spilled in World War II and ...
** National anthem of Guam
* People of Guam
* Public holidays in Guam
* Records of Guam
* Religion in Guam
** Christianity in Guam
** Hinduism in Guam
** Islam in Guam
** Judaism in Guam
** Sikhism in Guam
* World Heritage Sites in Guam: None
Art in Guam
* Art in Guam * Literature of Guam * Music of Guam * Television in Guam * Theatre in GuamSports in Guam
Sports in Guam * Football in Guam * Guam at the OlympicsEconomy and infrastructure of Guam
Economy of Guam
The economy of Guam depends mainly on US military spending and on tourist revenue. Over the past 20 years, the tourist industry grew rapidly, creating a construction boom for new hotels, golf courses and other tourist amenities. More than 1.1 ...
* Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 150th (one hundred and fiftieth)
* Agriculture in Guam
* Banking in Guam
** National Bank of Guam
* Communications in Guam
Though Guam is a United States territory, some U.S. long-distance plans and courier services list Guam as an international location. As a result of Guam's being added to the North American Numbering Plan (NANP) in 1997, calls made to the U.S., Can ...
** Internet in Guam
* Companies of Guam
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared go ...
* Currency of Guam: Dollar
Dollar is the name of more than 20 currencies. They include the Australian dollar, Brunei dollar, Canadian dollar, Hong Kong dollar, Jamaican dollar, Liberian dollar, Namibian dollar, New Taiwan dollar, New Zealand dollar, Singapore dollar, ...
** ISO 4217: USD
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
* Energy in Guam
** Energy policy of Guam
** Oil industry in Guam
* Mining in Guam
* Tourism in Guam
* Guam Stock Exchange
Infrastructure of Guam
* Health care in Guam *Transportation in Guam
The United States territory of Guam has no railways or freeways, nor does it have a merchant marine. The largest port is Apra Harbor, which serves almost all commercial traffic including cruise, cargo and fishing vessels. There are smaller harbo ...
** Airports in Guam
** Rail transport in Guam
** Roads in Guam
*** Highways in Guam
Education in Guam
*Education in Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
** Schools in Guam
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compul ...
** Colleges and universities in Guam
See also
*Topic overview: **Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
** Index of Guam-related articles
*
*
*
*
References
External links
; GovernmentOfficial Portal for the Island of Guam
Office of the Governor
Congresswoman Madeleine Z. Bordallo, Delegate, U.S. Congress
Guam Customs and Quarantine Agency
Guam Election Commission
Guam Department of Revenue and Taxation
Guam's Original Webpage
; Invasive species
(info from the&nbs
Pacific Island Ecosystems at Risk project (PIER)
Brown tree snake (''Boiga irregularis'') information
from the&nbs
Hawaiian Ecosystems at Risk project (HEAR)
; News
Marianas Variety "Guam's only true independent news source"
''Pacific Daily News'', A Gannett Newspaper
''KUAM'', Guam's Primary News Channel
; Overviews
''allthingsguam''
A Guam History resource—virtual textbook, virtual workbook and more
Guampedia, Guam's Online Encyclopedia
*
''The World Factbook'' on Guam
Guam Connection
– Guam directory and internet portal. ; Military
Commander, Naval Forces Marianas (COMNAVMAR) Guam
Andersen Air Force Base (AAFB) Guam
; Tourism
Guam Visitors Bureau
Guam Portal
; Others
Guam Chamber of Commerce
National Weather Service - Guam
{{DEFAULTSORT:Guam
Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...