Lion of Amphipolis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

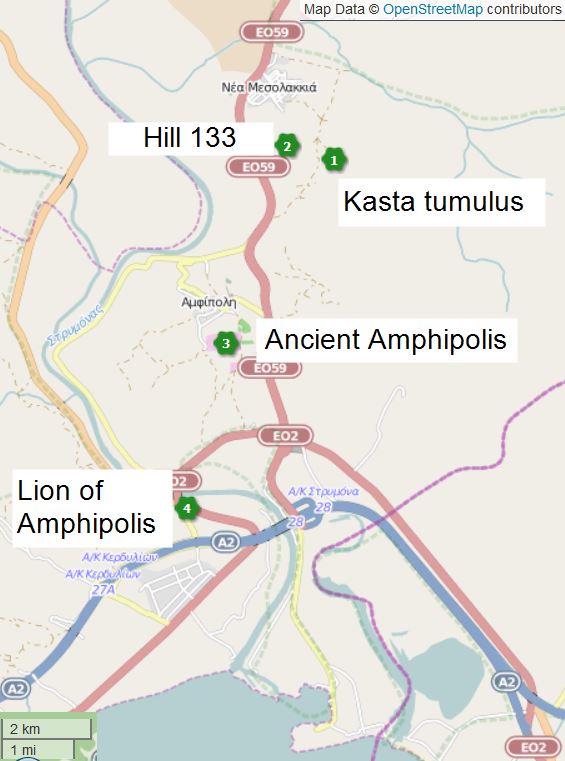 The Lion of Amphipolis () is a 4th-century BC tomb sculpture near
The Lion of Amphipolis () is a 4th-century BC tomb sculpture near
The Lion of Amphipolis by Oscar Broneer
{{Greek Macedonia 4th-century BC Greek sculptures Ancient Amphipolis Sculptures of lions

 The Lion of Amphipolis () is a 4th-century BC tomb sculpture near
The Lion of Amphipolis () is a 4th-century BC tomb sculpture near Amphipolis
Amphipolis ( ell, Αμφίπολη, translit=Amfipoli; grc, Ἀμφίπολις, translit=Amphipolis) is a municipality in the Serres regional unit, Macedonia, Greece. The seat of the municipality is Rodolivos. It was an important ancient Gr ...
, Macedonia, northern Greece
Northern Greece ( el, Βόρεια Ελλάδα, Voreia Ellada) is used to refer to the northern parts of Greece, and can have various definitions.
Administrative regions of Greece
Administrative term
The term "Northern Greece" is widely used ...
. According to Oscar Broneer __NOTOC__
Oscar Theodore Broneer (December 28, 1894 – February 22, 1992) was a prominent Swedish American educator and archaeologist known in particular for his work on Ancient Greece. He is most associated with his discovery of the Temple of Ist ...
and archaeologist Dimitris Lazaridis, the first person excavating in the area in the 1960s, it was set up in honour of Laomedon of Mytilene
Laomedon (Greek: Λαoμέδων ὁ Μυτιληναῖος; lived during the 4th century BC) was a Greek military commander, native of Mytilene and son of Larichus. He was one of Alexander the Great's generals, and appears to have enjoyed a high ...
, an important general of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, king of Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an Classical antiquity, ancient monarchy, kingdom on the periphery of Archaic Greece, Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. Th ...
.
It is now located about 1km outside the south gate of the ancient city.
History
The discovery of the monument is connected to the modern history ofGreek Macedonia
Macedonia (; el, Μακεδονία, Makedonía ) is a geographic and former administrative region of Greece, in the southern Balkans. Macedonia is the largest and Greek geographic region, with a population of 2.36 million in 2020. It is ...
, as the first parts of it were found initially by Greek soldiers during the First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
in 1912–13 when they drained the Strymonas river bed (where the stone from the Lion’s plinth had been used in a dam in or after the Roman period) to build the modern bridge.The Lion of Amphipolis, A research by the 28th Ephorate of Prehistoric and Classical Antiquities https://www.archaeology.wiki/blog/2013/04/01/the-lion-of-amphipolis/ They were followed by British soldiers a few years later in 1916, during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, who also discovered significant parts of the monument while building fortifications at the bridge. The British tried to steal the pieces, but a Bulgarian attack prevented their plans.
In the early 1930s, during works for draining part of Lake Kerkini nearby, there was a discovery of an ancient bridge and close to it in the river mud further, very large pieces of the marble lion. In 1937, and thanks to Lincoln MacVeagh
Lincoln MacVeagh (October 1, 1890January 15, 1972) was a United States soldier, diplomat, businessman, and archaeologist. He served a long career as the United States ambassador to several countries during difficult times.
MacVeagh family
The ...
, the US ambassador in Greece at the time, there was a private initiative along with support and funds from the Greek government to restore the Lion of Amphipolis, which eventually came to be in its current form. The whole process has been documented thoroughly by Oscar Broneer __NOTOC__
Oscar Theodore Broneer (December 28, 1894 – February 22, 1992) was a prominent Swedish American educator and archaeologist known in particular for his work on Ancient Greece. He is most associated with his discovery of the Temple of Ist ...
in his book ''The Lion of Amphipolis'' published in 1941.
Description
Although in seated position, the lion is larger and bulkier than the one erected atChaeronea
Chaeronea (English: or ; el, Χαιρώνεια , ) is a village and a former municipality in Boeotia, Greece, located about 35 kilometers east of Delphi. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Livadeia, of which ...
and has a height of more than 4 m in its main body. Taking into account the base, it is taller than 8 m. The head has a width of 2 m. Its craftsmanship shows a work of the 5th or first half of 4th century BC. As to when it was erected, there is no agreement between experts as there is no mention of it in ancient sources.
References
External links
The Lion of Amphipolis by Oscar Broneer
{{Greek Macedonia 4th-century BC Greek sculptures Ancient Amphipolis Sculptures of lions