Light skin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Light skin is a
Light skin is a
 It is generally accepted that dark skin evolved as a protection against the effect of
It is generally accepted that dark skin evolved as a protection against the effect of
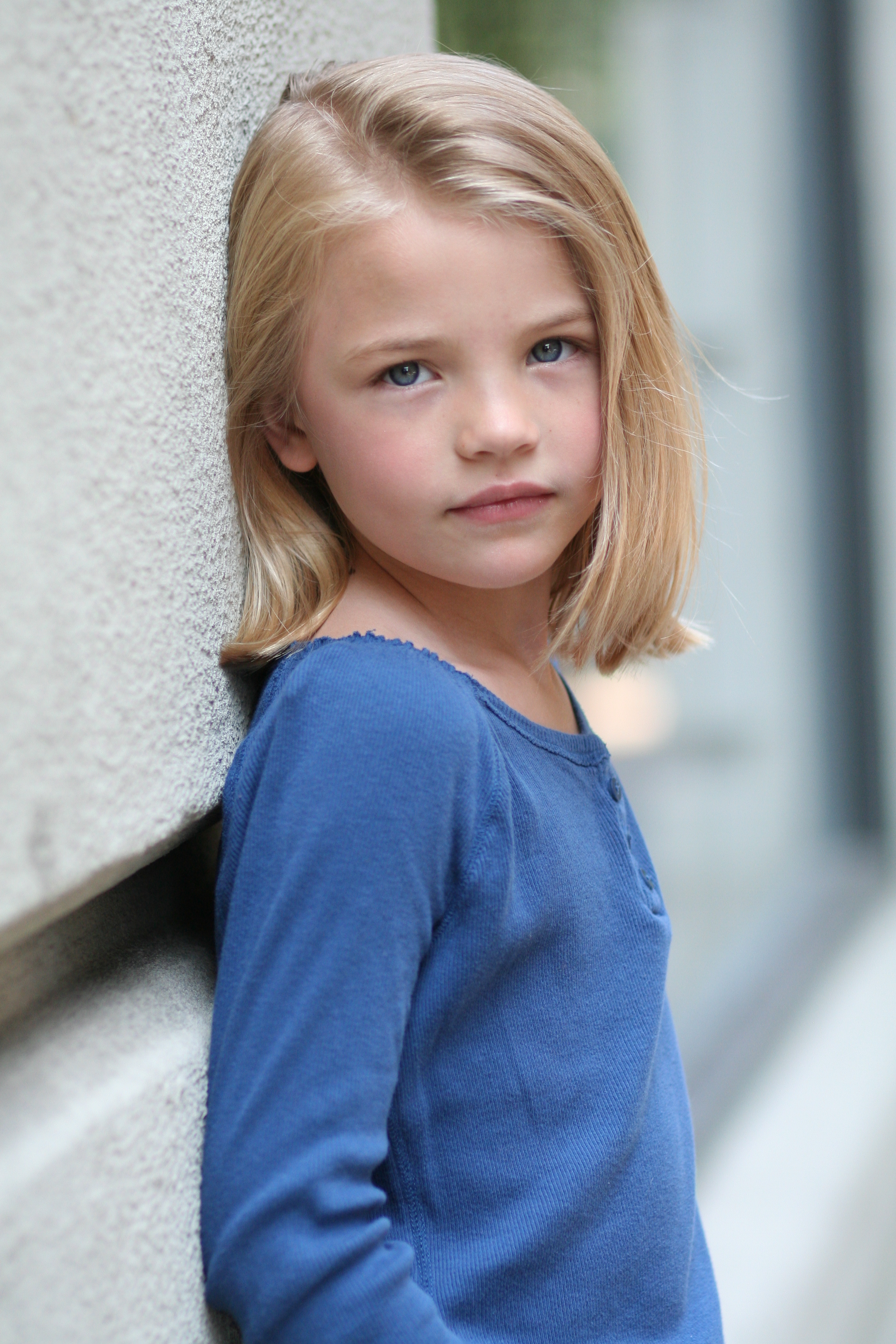

 In the 1960s, biochemist W. Farnsworth Loomis suggested that skin colour is related to the body's need for
In the 1960s, biochemist W. Farnsworth Loomis suggested that skin colour is related to the body's need for 
 Light-skinned people living in high sunlight environments are more susceptible to the harmful UV rays of sunlight because of the lack of
Light-skinned people living in high sunlight environments are more susceptible to the harmful UV rays of sunlight because of the lack of
 Light skin is a
Light skin is a human skin color
Human skin color ranges from the darkest brown to the lightest hues. Differences in skin color among individuals is caused by variation in pigmentation, which is the result of genetics (inherited from one's biological parents and or indiv ...
that has a base level of eumelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the am ...
pigmentation that has adapted to environments of low UV radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiatio ...
. Light skin is most commonly found amongst the native populations of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
as measured through skin reflectance. People with light skin pigmentation are often referred to as "white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White ...
" or "fair", although these usages can be ambiguous in some countries where they are used to refer specifically to certain ethnic groups or populations.
As populations migrated away from the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also refer ...
into areas of low UV radiation, they developed light skin pigmentation as an evolutionary selection acting against vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of Lipophilicity, fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group ar ...
depletion.
Humans with light skin pigmentation have skin with low amounts of eumelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the am ...
, and possess fewer melanosomes than humans with dark skin
Dark skin is a type of human skin color that is rich in melanin pigments. People with very dark skin are often referred to as "black people", although this usage can be ambiguous in some countries where it is also used to specifically refer to ...
pigmentation. Light skin provides better absorption qualities of ultraviolet radiation. This helps the body to synthesize higher amounts of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of Lipophilicity, fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group ar ...
for bodily processes such as calcium development. Light-skinned people who live near the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also ...
with high sunlight
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when ...
are at an increased risk of folate
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing an ...
depletion. As a consequence of folate depletion, they are at a higher risk of DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
, birth defect
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities ca ...
s, and numerous types of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
s, especially skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. There are three main types of skin cancers: basal-cell skin cancer (BCC) ...
. Humans with darker skin who live further from the tropics have low vitamin D levels, which also can lead to health complications.
The distribution of light-skinned populations is highly correlated with the low ultraviolet radiation levels of the regions inhabited by them. Historically, light-skinned populations almost exclusively lived far from the equator, in high latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
areas with low sunlight intensity. Due to colonization, imperialism, and increased mobility of people between geographical regions in recent centuries, light-skinned populations today are found all over the world.
Evolution
 It is generally accepted that dark skin evolved as a protection against the effect of
It is generally accepted that dark skin evolved as a protection against the effect of UV radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiatio ...
; eumelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the am ...
protects against both folate depletion and direct damage to DNA. This accounts for the dark skin pigmentation of Homo sapiens during their development in Africa; the major migrations out of Africa to colonize the rest of the world were also dark-skinned. It is widely supposed that light skin pigmentation developed due to the importance of maintaining vitamin D3
Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3 and colecalciferol, is a type of vitamin D that is made by the skin when exposed to sunlight; it is found in some foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement.
Cholecalciferol is made in the skin ...
production in the skin. Strong selective pressure
Any cause that reduces or increases reproductive success in a portion of a population potentially exerts evolutionary pressure, selective pressure or selection pressure, driving natural selection. It is a quantitative description of the amount of ...
would be expected for the evolution of light skin in areas of low UV radiation.
Lighter skin tones evolved independently in ancestral populations of north-west and north-east Eurasia, with the two populations diverging around 40,000 years ago. Studies have suggested that the two genes most associated with lighter skin colour in modern Europeans originated in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
and the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
about 22,000 to 28,000 years ago, and were present in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
by 9,000 years ago, where their carriers became associated with the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an inc ...
and the spread of Neolithic farming across Europe. Lighter skin and blond hair also evolved in the Ancient North Eurasian population.
A further wave of lighter-skinned populations across Europe (and elsewhere) is associated with the Yamnaya culture and the Indo-European migrations
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially expl ...
bearing Ancient North Eurasian ancestry and the KITLG allele for blond hair. Furthermore, the SLC24A5 gene linked with light pigmentation in Europeans was introduced into East Africa from Europe over five thousand years ago. These alleles can now be found in the San, Ethiopians
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts o ...
, and Tanzanian populations with Afro-Asiatic ancestry. In the San people, it was acquired from interactions with Eastern African pastoralists. Meanwhile, in the case of north-east Asia and the Americas, a variation of the MFSD12 gene is responsible for lighter skin colour. The modern association between skin tone and latitude is thus a relatively recent development.
Geographic distribution; ultraviolet and vitamin D


 In the 1960s, biochemist W. Farnsworth Loomis suggested that skin colour is related to the body's need for
In the 1960s, biochemist W. Farnsworth Loomis suggested that skin colour is related to the body's need for vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of Lipophilicity, fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group ar ...
. The major positive effect of UV radiation in land-living vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
s is the ability to synthesize vitamin D3
Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3 and colecalciferol, is a type of vitamin D that is made by the skin when exposed to sunlight; it is found in some foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement.
Cholecalciferol is made in the skin ...
from it. A certain amount of vitamin D helps the body to absorb more calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
which is essential for building and maintaining bones, especially for developing embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
s. Vitamin D production depends on exposure to sunlight. Humans living at latitudes far from the equator developed light skin in order to help absorb more vitamin D. People with light ( type II) skin can produce previtamin D3 in their skin at rates 5–10 times faster than dark-skinned ( type V) people.
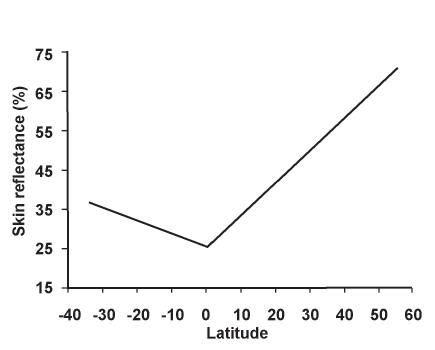
In 1998, anthropologist Nina Jablonski and her husband George Chaplin collected spectrometer data to measure UV radiation levels around the world and compared it to published information on the skin color of indigenous populations of more than 50 countries. The results showed a very high correlation between UV radiation and skin color; the weaker the sunlight was in a geographic region, the lighter the indigenous people's skin tended to be. Jablonski points out that people living above the latitudes of 50 degrees have the highest chance of developing vitamin D deficiency. She suggests that people living far from the equator developed light skin to produce adequate amounts of vitamin D during winter with low levels of UV radiation. Genetic studies suggest that light-skinned humans have been selected for multiple times.

Polar regions, vitamin D, and diet
Polar region
The polar regions, also called the frigid zones or polar zones, of Earth are the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high latitudes are dominated by flo ...
s of the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
receive little UV radiation, and even less vitamin D-producing UVB, for most of the year. These regions were uninhabited by humans until about 12,000 years ago. (In northern Fennoscandia at least, human populations arrived soon after deglaciation.) Areas like Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
and Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
have very low concentrations of ultraviolet radiation, and indigenous populations are all light-skinned.
However, dietary factors may allow vitamin D sufficiency even in dark skinned populations. Many indigenous populations across Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
survive by consuming reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subs ...
, which they follow and herd
A herd is a social group of certain animals of the same species, either wild or domestic. The form of collective animal behavior associated with this is called '' herding''. These animals are known as gregarious animals.
The term ''herd'' i ...
. Reindeer meat, organs, and fat contain large amounts of vitamin D which the reindeer get from eating substantial amounts of lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.polar region
The polar regions, also called the frigid zones or polar zones, of Earth are the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high latitudes are dominated by flo ...
s, like the Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territorie ...
(Eskimos
Eskimo () is an exonym used to refer to two closely related Indigenous peoples: the Inuit (including the Alaska Native Iñupiat, the Greenlandic Inuit, and the Canadian Inuit) and the Yupik (or Yuit) of eastern Siberia and Alaska. A related ...
), retained their dark skin; they ate Vitamin D-rich seafood
Seafood is any form of sea life regarded as food by humans, prominently including fish and shellfish. Shellfish include various species of molluscs (e.g. bivalve molluscs such as clams, oysters and mussels, and cephalopods such as octopus an ...
, such as fish and sea mammal blubber
Blubber is a thick layer of vascularized adipose tissue under the skin of all cetaceans, pinnipeds, penguins, and sirenians.
Description
Lipid-rich, collagen fiber-laced blubber comprises the hypodermis and covers the whole body, except fo ...
.
Furthermore, these people have been living in the far north for less than 7,000 years. As their founding populations lacked alleles for light skin colour, they may have had insufficient time for significantly lower melanin production to have been selected for by nature. "This was one of the last barriers in the history of human settlement," Jablonski states. "Only after humans learned fishing, and therefore had access to food rich in vitamin D, could they settle regions of high latitude
The polar regions, also called the frigid zones or polar zones, of Earth are the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high latitudes are dominated by flo ...
." Additionally, in the spring, Inuit would receive high levels of UV radiation as reflection from the snow, and their relatively darker skin then protects them from the sunlight.
Earlier hypotheses
Two other main hypotheses have been put forward to explain the development of light skin pigmentation: resistance to cold injury, and genetic drift; now both of them are considered unlikely to be the main mechanism behind the evolution of light skin. The resistance to cold injury hypothesis claimed that dark skin was selected against in cold climates far from the equator and in higher altitudes as dark skin was more affected byfrostbite
Frostbite is a skin injury that occurs when exposed to extreme low temperatures, causing the freezing of the skin or other tissues, commonly affecting the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin areas. Most often, frostbite occurs in t ...
. It has been found that reaction of the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
to extreme cold climates has actually more to do with other aspects, such as the distribution of connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
and distribution of fat, and with the responsiveness of peripheral capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
to differences in temperature, and not with pigmentation.
The supposition that dark skin evolved in the absence of selective pressure was put forward by the ''probable mutation effect'' hypothesis. The main factor initiating the development of light skin was seen as a consequence of genetic mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
without an evolutionary selective pressure
Any cause that reduces or increases reproductive success in a portion of a population potentially exerts evolutionary pressure, selective pressure or selection pressure, driving natural selection. It is a quantitative description of the amount of ...
. The subsequent spread of light skin was thought to be caused by assortive mating and sexual selection contributed to an even lighter pigmentation in females. Doubt has been cast on this hypothesis, as more random patterns of skin coloration would be expected in contrast to the observed structural light skin pigmentation in areas of low UV radiation. The clinal (gradual) distribution of skin pigmentation observable in the Eastern hemisphere, and to a lesser extent in the Western hemisphere, is one of the most significant characteristics of human skin pigmentation. Increasingly lighter skinned populations are distributed across areas with incrementally lower levels of UV radiation.
Genetic associations
Variations in the ''KITL'' gene have been positively associated with about 20% of melanin concentration differences between African and non-African populations. One of the alleles of the gene has an 80% occurrence rate in Eurasian populations. The ''ASIP'' gene has a 75–80% variation rate among Eurasian populations compared to 20–25% in African populations. Variations in the '' SLC24A5'' gene account for 20–25% of the variation between dark and light skinned populations of Africa, and appear to have arisen as recently as within the last 10,000 years. The Ala111Thr or rs1426654 polymorphism in the coding region of the SLC24A5 gene reaches fixation inEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, but is found across the globe, particularly among populations in Northern Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
, the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004 ...
, West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes ...
, Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
and South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
.
Biochemistry
Melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
is a derivative of the amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the G ...
. Eumelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the am ...
is the dominant form of melanin found in human skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to m ...
. Eumelanin protects tissues and DNA from radiation damage by UV light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
. Melanin is produced in specialized cells called melanocyte
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea),
the inner ear,
vaginal epithelium, meninges,
bones,
and hear ...
s, which are found in the lowest level of the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rel ...
. Melanin is produced inside small membrane-bound packages called melanosomes. Humans with naturally occurring light skin have varied amounts of smaller and sparsely distributed eumelanin and its lighter-coloured relative, pheomelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the am ...
. The concentration of pheomelanin varies highly within populations from individual to individual, but it is more commonly found among lightly pigmented Europeans, East Asians, and Native Americans.
For the same body region, individuals, independently of skin colour, have the same amount of melanocytes (however variation between different body parts is substantial), but organelles which contain pigments, called melanosomes, are smaller and less numerous in light-skinned humans.
For people with very light skin, the skin gets most of its colour from the bluish-white connective tissue in the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided ...
and from the haemoglobin associated blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
cells circulating in the capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
of the dermis. The colour associated with the circulating haemoglobin becomes more obvious, especially in the face, when arterioles dilate and become tumefied with blood as a result of prolonged physical exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic s ...
or stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of t ...
(usually embarrassment
Embarrassment or awkwardness is an emotional state that is associated with mild to severe levels of discomfort, and which is usually experienced when someone commits (or thinks of) a socially unacceptable or frowned-upon act that is witnessed ...
or anger
Anger, also known as wrath or rage, is an intense emotional state involving a strong uncomfortable and non-cooperative response to a perceived provocation, hurt or threat.
A person experiencing anger will often experience physical effects, su ...
). Up to 50% of UVA can penetrate deeply into the dermis in persons with light skin pigmentation with little protective melanin pigment.
The characteristic of fair skin, red hair
Red hair (also known as orange hair and ginger hair) is a hair color found in one to two percent of the human population, appearing with greater frequency (two to six percent) among people of Northern or Northwestern European ancestry and ...
, and freckling is associated with high amount of pheomelanin, little amounts of eumelanin. This phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (biology), morphology or physical form and structure, its Developmental biology, developmental proc ...
is caused by a loss-of-function
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosi ...
mutation in the melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) gene. However, variations in the MC1R gene sequence only have considerable influence on pigmentation in populations where red hair and extremely fair skin is prevalent. The gene variation's primary effect is to promote eumelanin synthesis at the expense of pheomelanin synthesis, although this contributes to very little variation in skin reflectance between different ethnic groups. Melanocytes from light skin cells cocultured with keratinocyte
Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells.
Basal cells in the basal layer (''stratum basale'') of the skin are sometimes referre ...
s give rise to a distribution pattern characteristic of light skin.
Freckles usually only occur in people with very lightly pigmented skin. They vary from very dark to brown in colour and develop a random pattern on the skin of the individual. Solar lentigines, the other types of freckles, occur among old people regardless of skin colour. People with very light skin ( types I and II) make very little melanin in their melanocytes, and have very little or no ability to produce melanin in the stimulus of UV radiation. This can result in frequent sunburns and a more dangerous, but invisible, damage done to connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
and DNA underlying the skin. This can contribute to premature aging and skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. There are three main types of skin cancers: basal-cell skin cancer (BCC) ...
. The strongly red appearance of lightly pigmented skin as a response to high UV radiation levels is caused by the increased diameter, number, and blood flow of the capillaries.
People with moderately pigmented skin ( Types III-IV) are able to produce melanin in their skin in response to UVR. Normal tanning is usually delayed as it takes time for the melanins to move up in the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rel ...
. Heavy tanning does not approach the photoprotective effect against UVR-induced DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
compared to naturally occurring dark skin
Dark skin is a type of human skin color that is rich in melanin pigments. People with very dark skin are often referred to as "black people", although this usage can be ambiguous in some countries where it is also used to specifically refer to ...
, however it offers great protection against seasonal variations in UVR. Gradually developed tan in the spring prevents sunburns in the summer. This mechanism is almost certainly the evolutionary reason behind the development of tanning behaviour.
Health implications
Skin pigmentation is an evolutionary adaptation to the various UV radiation levels around the world. There are health implications of light-skinned people living in environments of high UV radiation. Various cultural practices increase problems related to health conditions of light skin, for examplesunbathing
Sun tanning or tanning is the process whereby skin color is darkened or tanned. It is most often a result of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or from artificial sources, such as a tanning lamp found in indoor tanning b ...
among the light-skinned.
Advantages in low sunlight
Humans with light skin pigmentation living in low sunlight environments experience increasedvitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of Lipophilicity, fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group ar ...
synthesis compared to humans with dark skin pigmentation due to the ability to absorb more sunlight. Almost every part of the human body, including the skeleton, the immune system, and brain requires vitamin D. Vitamin D production in the skin begins when UV radiation penetrates the skin and interacts with a cholesterol-like molecule produce pre-vitamin D3. This reaction only occurs in the presence of medium length UVR, UVB. Most of the UVB and UVC rays are destroyed or reflected by ozone, oxygen, and dust in the atmosphere. UVB reaches the Earth's surface in the highest amounts when its path is straight and goes through a little layer of atmosphere.
The farther a place is from the equator, the less UVB is received, and the potential to produce of vitamin D is diminished. Some regions far from the equator do not receive UVB radiation at all between autumn and spring. Vitamin D deficiency does not kill its victims quickly, and generally does not kill at all. Rather it weakens the immune system, the bones, and compromises the body's ability to fight uncontrolled cell division which results in cancer. A form of vitamin D is a potent cell growth inhibitor; thus chronic deficiencies of vitamin D seem to be associated with higher risk of certain cancers. This is an active topic of cancer research and is still debated.
With the increase of vitamin D synthesis, there is a decreased incidence of conditions that are related to common vitamin D deficiency conditions of people with dark skin pigmentation living in environments of low UV radiation: rickets
Rickets is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children, and is caused by either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stunted growth, bone pain, large forehead, and trouble sleeping. Complications ma ...
, osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone a ...
, numerous cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
types (including colon and breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or ...
), and immune system malfunctioning. Vitamin D promotes the production of cathelicidin, which helps to defend humans' bodies against fungal, bacterial, and viral infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
s, including flu. When exposed to UVB, the entire exposed area of body's skin of a relatively light skinned person is able to produce between 10 and 20000 IU of vitamin D.
Disadvantages in high sunlight
 Light-skinned people living in high sunlight environments are more susceptible to the harmful UV rays of sunlight because of the lack of
Light-skinned people living in high sunlight environments are more susceptible to the harmful UV rays of sunlight because of the lack of melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
produced in the skin. The most common risk that comes with high exposure to sunlight is the increased risk of sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and animals include: red or reddish skin that is h ...
s. This increased risk has come along with the cultural practice of sunbathing, which is popular among light-skinned populations. This cultural practice to gain tanned skin if not regulated properly can lead to sunburn, especially among very lightly-skinned humans. The overexposure to sunlight also can lead to basal cell carcinoma, which is a common form of skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. There are three main types of skin cancers: basal-cell skin cancer (BCC) ...
.
Another health implication is the depletion of folate within the body, where the overexposure to UV light can lead to megaloblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of macrocytic anemia. An anemia is a red blood cell defect that can lead to an undersupply of oxygen. Megaloblastic anemia results from inhibition of DNA synthesis during red blood cell production. When DNA synth ...
. Folate deficiency in pregnant women can be detrimental to the health of their newborn babies in the form of neural tube defects, miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemica ...
s, and spina bifida
Spina bifida (Latin for 'split spine'; SB) is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the spine and the membranes around the spinal cord during early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, men ...
, a birth defect in which the backbone and spinal canal do not close before birth. The peak of neural tube defect occurrences is the highest in the May–June period in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
. Folate is needed for DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritan ...
in dividing cells and deficiency can lead to failures of normal embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
and spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubu ...
.
Individuals with lightly pigmented skin who are repeatedly exposed to strong UV radiation, experience faster aging of the skin, which shows in increased wrinkling and anomalies of pigmentation. Oxidative damage causes the degradation of protective tissue in the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided ...
, which confers the strength of the skin. It has been postulated that white women may develop wrinkle
A wrinkle, also known as a rhytid, is a fold, ridge or crease in an otherwise smooth surface, such as on skin or fabric. Skin wrinkles typically appear as a result of ageing processes such as glycation, habitual sleeping positions, loss of ...
s faster after menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often d ...
than black women because they are more susceptible to the lifetime damage of the sun throughout life. Dr. Hugh S. Taylor, of Yale School of Medicine
The Yale School of Medicine is the graduate medical school at Yale University, a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. It was founded in 1810 as the Medical Institution of Yale College and formally opened in 1813.
The primary te ...
, concluded that the study could not prove the findings but they suspect the underlying cause. Light-coloured skin has been suspected to be one of the contributing factors that promote wrinkling.
See also
*White people
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view.
Description of populations as ...
*Dark skin
Dark skin is a type of human skin color that is rich in melanin pigments. People with very dark skin are often referred to as "black people", although this usage can be ambiguous in some countries where it is also used to specifically refer to ...
*Olive skin
Olive skin is a human skin colour spectrum. It is often associated with pigmentation in the Type III to Type IV and Type V ranges of the Fitzpatrick scale. It generally refers to light or moderate tan skin, and it is often described as having ...
*High yellow
High yellow, occasionally simply yellow (dialect: yaller, yella), is a term used to describe a light-skinned person of white and black ancestry. It is also used as a slang for those thought to have "yellow undertones". The term was in common use ...
*Skin whitening
Skin whitening, also known as skin lightening and skin bleaching, is the practice of using chemical substances in an attempt to lighten the skin or provide an even skin color by reducing the melanin concentration in the skin. Several chemicals ha ...
*Albinism
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albino.
Varied use and interpretation of the term ...
*Blond
Blond (male) or blonde (female), also referred to as fair hair, is a hair color characterized by low levels of the dark pigment eumelanin. The resultant visible hue depends on various factors, but always has some yellowish color. The color ...
*Red hair
Red hair (also known as orange hair and ginger hair) is a hair color found in one to two percent of the human population, appearing with greater frequency (two to six percent) among people of Northern or Northwestern European ancestry and ...
* Albinism in humans
References
{{Skin colors Skin pigmentation