Leith Hill Place on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Leith Hill in southern England is the highest summit of the
 On the summit of Leith Hill is an 18th-century Gothic tower. In 1764–65 Richard Hull of nearby Leith Hill Place built "Prospect House", later to become known as Leith Hill Tower, with the intention of raising the hill above above sea level. A tower built contemporaneously at the summit of
On the summit of Leith Hill is an 18th-century Gothic tower. In 1764–65 Richard Hull of nearby Leith Hill Place built "Prospect House", later to become known as Leith Hill Tower, with the intention of raising the hill above above sea level. A tower built contemporaneously at the summit of
 Leith Hill was owned by the Evelyn family of Wotton House from the 17th to the early 20th centuries. On the death of Lt. John Evelyn in 1922, the executors of his will were required to raise money to pay
Leith Hill was owned by the Evelyn family of Wotton House from the 17th to the early 20th centuries. On the death of Lt. John Evelyn in 1922, the executors of his will were required to raise money to pay
 Originally a gabled house dating from about 1600, Leith Hill Place was completely refaced in a
Originally a gabled house dating from about 1600, Leith Hill Place was completely refaced in a
 Like the other summits of the
Like the other summits of the
Leith Hill information at the National Trust
* Computer generated summit panorama
NorthSouth
{{Mole Valley Hills of Surrey Marilyns of England National Trust properties in Surrey Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Surrey Towers in Surrey Highest points of English counties Mole Valley
Greensand Ridge
The Greensand Ridge, also known as the Wealden Greensand is an extensive, prominent, often wooded, mixed greensand/sandstone escarpment in south-east England. Forming part of the Weald, a former dense forest in Sussex, Surrey and Kent, it runs ...
, approximately southwest of Dorking
Dorking () is a market town in Surrey in South East England, about south of London. It is in Mole Valley District and the council headquarters are to the east of the centre. The High Street runs roughly east–west, parallel to the Pipp Br ...
, Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant urban areas which form part of the Greater London Built-up Area. ...
and southwest of central London
Central London is the innermost part of London, in England, spanning several boroughs. Over time, a number of definitions have been used to define the scope of Central London for statistics, urban planning and local government. Its characteris ...
. It reaches above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
, and is the second highest point in southeast England
South East England is one of the nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It consists of the counties of Buckinghamshire, East Sussex, Hampshire, the Isle of Wight, Kent, Oxfordshire, Berks ...
, after Walbury Hill
Walbury Hill is a summit of the North Wessex Downs in Berkshire, England. With an elevation of , it is the highest natural point in South East England. On the hill's summit is the Iron Age hill fort of Walbury Camp, whilst the flanks of the hill ...
in southwest Berkshire
Berkshire ( ; in the 17th century sometimes spelt phonetically as Barkeshire; abbreviated Berks.) is a historic county in South East England. One of the home counties, Berkshire was recognised by Queen Elizabeth II as the Royal County of Berk ...
, (which is high). Leith Hill is the highest ground for .
Four areas of woodland surrounding the hill comprise the Leith Hill Site of Special Scientific Interest, although the summit is excluded from this designation.
The nearest railway station is Holmwood station, to the east, served by Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
trains to London Victoria
Victoria station, also known as London Victoria, is a central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station in Victoria, in the City of Westminster, managed by Network Rail. Named after the nearby Victoria Street (not the Q ...
.
Leith Hill Tower
Bredon Hill
Bredon Hill is a hill in Worcestershire, England, south-west of Evesham in the Vale of Evesham. The summit of the hill is in the parish of Kemerton, and it extends over parts of eight other parishes (listed below). The hill is geologically par ...
achieves a similar purpose.
Leith Hill Tower is high and consisted of two rooms "neatly furnished", with a Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
inscription above the door announcing that it had been built not only for his own pleasure, but also for the enjoyment of others. Hull provided visitors with prospect glasses, similar to a small telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe ...
, through which to survey the extensive views towards London and the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
, each some away.
When Hull died in 1772, at his request he was buried under the tower. Following his death, the building was stripped of its contents, doors and windows, and fell into ruin. As a result, the tower was filled with rubble and concrete, and the entrance bricked up.
In 1864, William John Evelyn
William John Evelyn JP DL (27 July 1822 - 26 July 1908) was a British Member of Parliament, landowner and philanthropist. He was MP for Surrey West in 1849 and again for Deptford in 1885.
of nearby Wotton House
Wotton House, Wotton Underwood, Buckinghamshire, England, is a stately home built between 1704 and 1714, to a design very similar to that of the contemporary version of Buckingham House. The house is an example of English Baroque and a Grade I l ...
decided to reopen it, but the concrete made this difficult, and so the additional turreted side-tower was added to allow access to the top of the tower.
At the top of the tower there is a viewpoint indicator to commemorate Walker Miles, whose work in the early days of the Rambler's movement contributed to the formation of The Ramblers
The Ramblers is the trading name of the Ramblers Association, Great Britain's leading walking charity. The Ramblers is also a membership organisation with around 100,000 members and a network of volunteers who maintain and protect the path ...
of Great Britain. It has been claimed that on a clear day, 13 counties can be seen from the top of Leith Hill Tower.
The tower was fully restored by the National Trust
The National Trust, formally the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, is a charity and membership organisation for heritage conservation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland, there is a separate and ...
in 1984. This restoration included the removal of rubble and concrete, fitting safety features such as a handrail in the narrow staircase, and converting the lower portion of the tower into a servery. Following restoration, the mobile phone operator Cellnet installed a first-generation transmitter station (Base site) into one of the tower rooms, feeding single vertical antennas on the tower roof dressed to look like flag poles.
Leith Hill Tower is open to the public every day from 10:00 am until 3:00 pm on weekdays and 9:00 am to 5:00 pm on weekends, every day of the year except Christmas Day
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year, ...
, with a comprehensive display explaining the history of the tower.
History
 Leith Hill was owned by the Evelyn family of Wotton House from the 17th to the early 20th centuries. On the death of Lt. John Evelyn in 1922, the executors of his will were required to raise money to pay
Leith Hill was owned by the Evelyn family of Wotton House from the 17th to the early 20th centuries. On the death of Lt. John Evelyn in 1922, the executors of his will were required to raise money to pay death duties
An inheritance tax is a tax paid by a person who inherits money or property of a person who has died, whereas an estate tax is a levy on the estate (money and property) of a person who has died.
International tax law distinguishes between an es ...
and they therefore offered the Tower and the surrounding five acres of Leith Hill for sale. After a campaign, organised in part by the Commons and Footpath Preservation Society, the land was bought by Wilfred James MacAndrew (a resident of Reigate and former co-owner of the shipping company MacAndrew & Co) and donated to the National Trust.
Leith Hill Place
 Originally a gabled house dating from about 1600, Leith Hill Place was completely refaced in a
Originally a gabled house dating from about 1600, Leith Hill Place was completely refaced in a Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and ...
style about 1760 by Richard Hull. It was bought in 1847 by Josiah Wedgwood III
Josiah "Joe" Wedgwood III (12 January 1795–11 March 1880), a grandson of the English potter Josiah Wedgwood.
Wedgwood was the eldest son of Josiah Wedgwood II and his wife Elizabeth Allen. He was born nine days after the death of his gran ...
and remained in the family until his grandson, the composer Ralph Vaughan Williams
Ralph Vaughan Williams, (; 12 October 1872– 26 August 1958) was an English composer. His works include operas, ballets, chamber music, secular and religious vocal pieces and orchestral compositions including nine symphonies, written over ...
, who had been brought up there and eventually inherited it from his brother, immediately gave it to the National Trust
The National Trust, formally the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, is a charity and membership organisation for heritage conservation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland, there is a separate and ...
on his brother's death in 1944. Subsequently, it was leased from the Trust by his cousins Sir Ralph Wedgwood
Sir Ralph Lewis Wedgwood, 1st Baronet, (; 2 March 1874 – 5 September 1956) was the Chief Officer of the London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) for 16 years from its inauguration in 1923. He was chairman of the wartime Railway Executive Commit ...
and then Sir John Wedgwood, later becoming a boarding house for a nearby sixth form college, Hurtwood House
Hurtwood House is a 15–19 mixed, independent boarding school and sixth form in, Surrey, England.
Synopsis
Founded in 1970 by Richard Jackson, the main house is an Edwardian mansion set in in the Surrey Hills. The intern students, aged 1 ...
.
The house was opened to the public by the National Trust in 2013 and now serves as a memorial to Ralph Vaughan Williams. Josiah Wedgwood's widow
A widow (female) or widower (male) is a person whose spouse has Death, died.
Terminology
The state of having lost one's spouse to death is termed ''widowhood''. An archaic term for a widow is "relict," literally "someone left over". This word ...
, born Caroline Darwin, created a rhododendron
''Rhododendron'' (; from Ancient Greek ''rhódon'' "rose" and ''déndron'' "tree") is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants in the heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are nati ...
wood there, now open to the public.
Geology
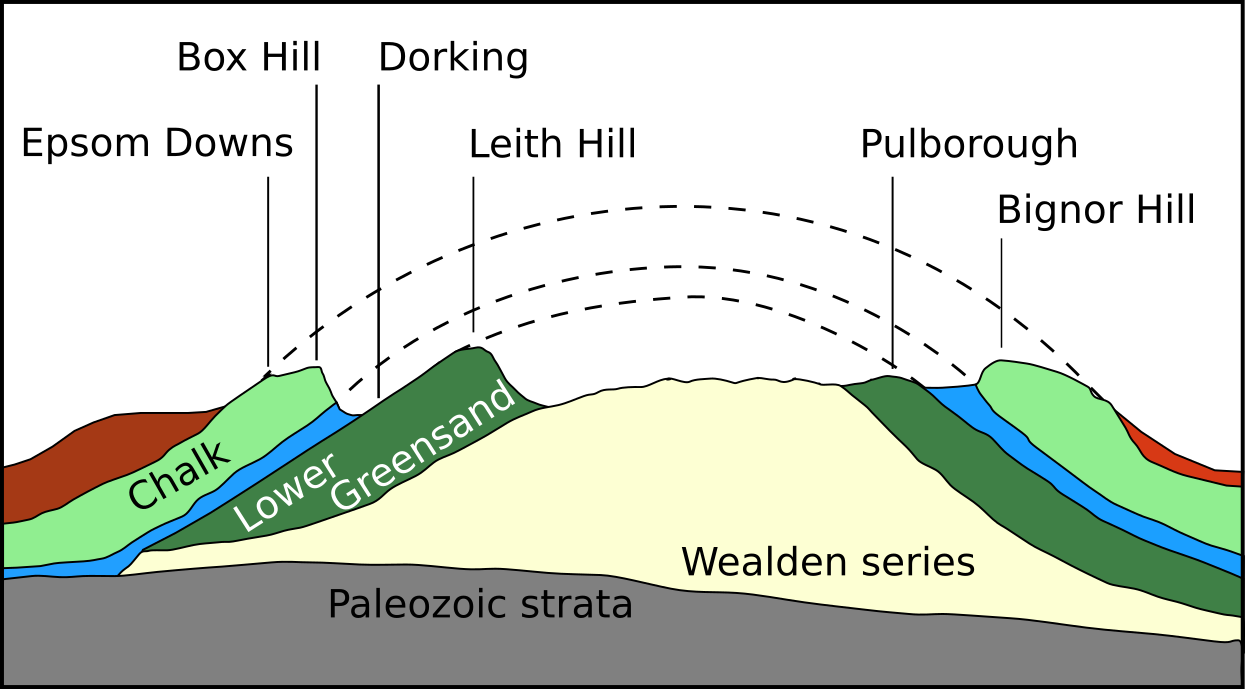
 Like the other summits of the
Like the other summits of the Greensand Ridge
The Greensand Ridge, also known as the Wealden Greensand is an extensive, prominent, often wooded, mixed greensand/sandstone escarpment in south-east England. Forming part of the Weald, a former dense forest in Sussex, Surrey and Kent, it runs ...
in the south of Surrey, the rock of which Leith Hill is composed, is primarily the Lower Greensand, overlaid with a harder layer of chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a prec ...
. The greensand was deposited in the early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
, most likely in a shallow sea with low oxygen levels. Over the subsequent 50 million years, other strata were deposited on top of the Lower Greensand, including Gault clay
The Gault Formation is a geological formation of stiff blue clay deposited in a calm, fairly deep-water marine environment during the Lower Cretaceous Period (Upper and Middle Albian). It is well exposed in the coastal cliffs at Copt Point in ...
and the chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Chalk ...
of the North and South Downs.
Following the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
, the sea covering the south of England began to retreat and the land was pushed higher. The Weald (the area covering modern-day south Surrey, south Kent, north Sussex and east Hampshire) was lifted by the same geological processes that created the Alps, resulting in an anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the ...
which stretched across the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
to the Artois region of northern France. Initially an island, this dome-like structure was drained by the ancestors of the rivers which today cut through the North and South Downs (including the Mole
Mole (or Molé) may refer to:
Animals
* Mole (animal) or "true mole", mammals in the family Talpidae, found in Eurasia and North America
* Golden moles, southern African mammals in the family Chrysochloridae, similar to but unrelated to Talpida ...
, Wey and Arun). The dome was eroded away over the course of the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
, exposing the strata beneath and resulting in the escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escar ...
s of the Downs and the Greensand Ridge.
Search for oil
A site on an ancient lane going up the hill was originally chosen by an oil company for exploratory drilling, however due to an active protest campaign and various legal objections raised by local groups and environmentalists, the lease on the land from theForestry Commission
The Forestry Commission is a non-ministerial government department responsible for the management of publicly owned forests and the regulation of both public and private forestry in England.
The Forestry Commission was previously also respon ...
expired before the drilling could start. The Minister for Environment subsequently decided not to renew the lease due to concerns of the effect it would have on nearby ancient woodland. The oil company has since stated it intends to find a new site from which to explore the same prospect. Locals have stated that they will continue to oppose this.
Geodesy
Leith Hill Tower was the origin (meridian) of the 6 inch and 1:2500 Ordnance Survey maps of Surrey.References
Notes
External links
Leith Hill information at the National Trust
* Computer generated summit panorama
North
{{Mole Valley Hills of Surrey Marilyns of England National Trust properties in Surrey Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Surrey Towers in Surrey Highest points of English counties Mole Valley