Latter-day Saint movement on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Latter Day Saint movement (also called the LDS movement, LDS restorationist movement, or Smith–Rigdon movement) is the collection of independent church groups that trace their origins to a Christian
The Latter Day Saint movement (also called the LDS movement, LDS restorationist movement, or Smith–Rigdon movement) is the collection of independent church groups that trace their origins to a Christian
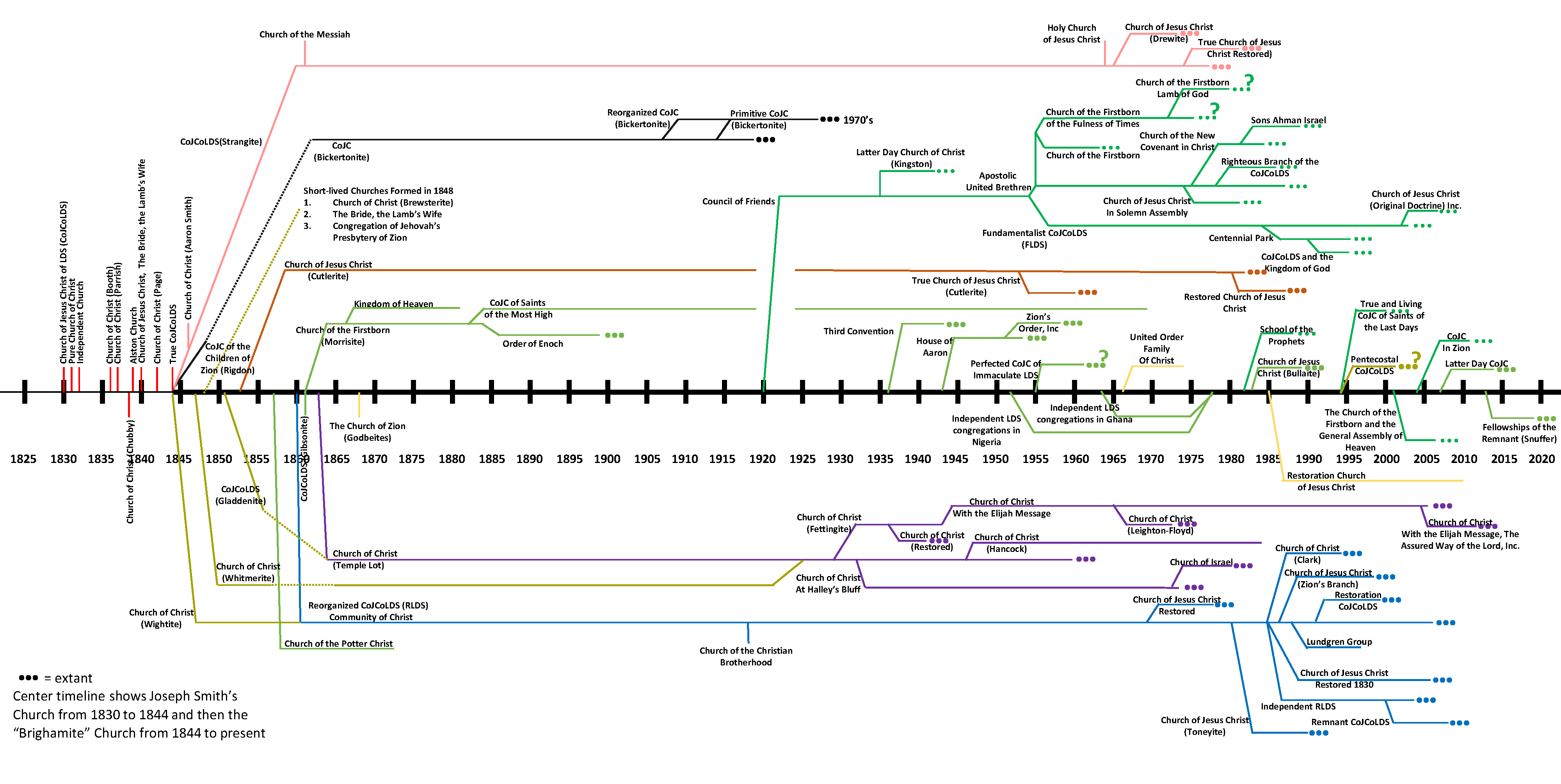
"Dissent and Schism in the Early Church: Explaining Mormon Fissiparousness"
'' Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought'', vol. 28, no. 3 (Fall 1993) pp. 15–39. *. *. *. *Steven L. Shields, ''Divergent Paths of the Restoration: A History of the Latter Day Saint Movement'' Los Angeles: 1990.
 The Latter Day Saint movement (also called the LDS movement, LDS restorationist movement, or Smith–Rigdon movement) is the collection of independent church groups that trace their origins to a Christian
The Latter Day Saint movement (also called the LDS movement, LDS restorationist movement, or Smith–Rigdon movement) is the collection of independent church groups that trace their origins to a Christian Restorationist
Restorationism (or Restitutionism or Christian primitivism) is the belief that Christianity has been or should be restored along the lines of what is known about the apostolic early church, which restorationists see as the search for a purer a ...
movement founded by Joseph Smith in the late 1820s.
Collectively, these churches have over 16 million members, although about 98% belong to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). The predominant theology of the churches in the movement is Mormonism, which sees itself as restoring the early Christian church with additional revelations
Revelation, in religion and theology, is the act of revealing through communication with supernatural entities.
Revelation(s) may also refer to:
* Book of Revelation or simply Revelation, the last book of the New Testament
* Revelation (Latter Da ...
.
A minority of Latter Day Saint adherents, such as members of Community of Christ
The Community of Christ, known from 1872 to 2001 as the Reorganized Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (RLDS), is an American-based international church, and is the second-largest denomination in the Latter Day Saint movement. The churc ...
, have been influenced by Protestant theology while maintaining certain distinctive beliefs and practices including continuing revelation
Continuous revelation or continuing revelation is a theological belief or position that God continues to reveal divine principles or commandments to humanity.
In Christian traditions, it is most commonly associated with the Latter Day Saint mo ...
, an open canon of scripture and building temples
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
. Other groups include the Remnant Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints, which supports lineal succession of leadership from Smith's descendants, and the more controversial Fundamentalist Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints
The Fundamentalist Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints (FLDS Church) is a religious sect of the fundamentalist Mormon denominations whose members practice polygamy. The fundamentalist Mormon movement emerged in the early 20th century, ...
, which defends the practice of polygamy.
Origins
The movement began in western New York during the Second Great Awakening when Smith said that he received visions revealing a new sacred text, the Book of Mormon, which he published in 1830 as a complement to the Bible. Based on the teachings of this book and other revelations, Smith founded aChristian primitivist
Restorationism (or Restitutionism or Christian primitivism) is the belief that Christianity has been or should be restored along the lines of what is known about the Apostolic Age, apostolic early church, which restorationists see as the search ...
church, called the "Church of Christ". The Book of Mormon attracted hundreds of early followers, who later became known as "Mormons", "Latter Day Saints", or just "Saints". In 1831, Smith moved the church headquarters to Kirtland, Ohio, and in 1838 changed its name to the "Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints".
After the church in Ohio collapsed due to a financial crisis and dissensions, in 1838, Smith and the body of the church moved to Missouri. However, they were persecuted and the Latter Day Saints fled to Illinois. After Smith was killed in 1844, a succession crisis A succession crisis is a crisis that arises when an order of succession fails, for example when a king dies without an indisputable heir. It may result in a war of succession.
Examples include (see List of wars of succession):
*Multiple periods dur ...
led to the organization splitting into several groups. The largest of these, the LDS Church, migrated under the leadership of Brigham Young to the Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic basin, endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California ...
(now Utah) and became known for its 19th-century practice of polygamy. The LDS Church officially renounced this practice in 1890, and gradually discontinued it, resulting in Utah Territory becoming a U.S. state. This change resulted in the formation of a number of small sects who sought to maintain polygamy and other 19th-century doctrines and practices, now referred to as " Mormon fundamentalism".
Other groups originating within the Latter Day Saint movement followed different paths in Missouri, Illinois, Michigan, and Pennsylvania. For the most part, these groups rejected plural marriage and some of Smith's later teachings. The largest of these, Community of Christ (known previously as the "Reorganized Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints"), was formed in Illinois in 1860 by several groups uniting around Smith's son, Joseph Smith III.
History
The founder of the Latter Day Saint movement was Joseph Smith, and to a lesser extent, during the movement's first two years, Oliver Cowdery. Throughout his life, Smith told of an experience he had as a boy having seen God the Father and Jesus Christ as two separate beings, who told him that the true church of Jesus Christ had been lost and would be restored through him, and that he would be given the authority to organize and lead the true Church of Christ. The Latter Day Saint church was formed on April 6, 1830, consisting of a community of believers in the westernNew York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
towns of Fayette, Manchester, and Colesville. The church was formally organized under the name of the "Church of Christ". By 1834, the church was referred to as the "Church of the Latter Day Saints" in early church publications, and in 1838 Smith announced that he had received a revelation from God that officially changed the name to the "Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints".''Manuscript History of the Church'', LDS Church Archives, book A-1, p. 37; reproduced in Dean C. Jessee Dean Cornell Jessee (born 1929) is a historian of the early Latter Day Saint movement and leading expert on the writings of Joseph Smith Jr.
Biography
Jessee was one of the sons of Phillip Cornell Jessee and Minerva Boss. He was raised in Springvil ...
(comp.) (1989). ''The Papers of Joseph Smith: Autobiographical and Historical Writings'' (Salt Lake City, Utah: Deseret Book) 1:302–303.H. Michael Marquardt and Wesley P. Walters (1994). ''Inventing Mormonism: Tradition and the Historical Record'' (Salt Lake City, Utah: Signature Books) p. 160.
In 1844, William Law and several other Latter Day Saints in church leadership positions publicly denounced Smith's secret practice of polygamy in the ''Nauvoo Expositor
The ''Nauvoo Expositor'' was a newspaper in Nauvoo, Illinois, that published only one issue, on June 7, 1844. Its publication, the destruction of the printed copies (which, according to the Nauvoo Charter, was the legal consequence of a ne ...
'', and formed their own church. The city council of Nauvoo, Illinois
Nauvoo ( ; from the ) is a small city in Hancock County, Illinois, United States, on the Mississippi River near Fort Madison, Iowa. The population of Nauvoo was 950 at the 2020 census. Nauvoo attracts visitors for its historic importance and its ...
, led by Smith, subsequently had the printing press of the ''Expositor'' destroyed. In spite of Smith's later offer to pay damages for destroyed property, critics of Smith and the church considered the destruction heavy-handed. Some called for the Latter Day Saints to be either expelled or destroyed.
Joseph Smith and his brother, Hyrum, the Assistant President of the Church, were both killed by a mob while in a Carthage, Illinois jail
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol (dated, standard English, Australian, and historically in Canada), penitentiary (American English and Canadian English), detention center (or detention centre outside the US), correction center, correc ...
, and several individuals within the church claimed to be the senior surviving authority and appointed successors. These various claims resulted in a succession crisis. Many supported Brigham Young, the president of the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles
A quorum is the minimum number of members of a deliberative assembly (a body that uses parliamentary procedure, such as a legislature) necessary to conduct the business of that group. According to ''Robert's Rules of Order Newly Revised'', the ...
; others Sidney Rigdon, the senior surviving member of the First Presidency. Emma Hale Smith
Emma Hale Smith Bidamon (July 10, 1804 – April 30, 1879) was an American homesteader, the official wife of Joseph Smith, and a prominent leader in the early days of the Latter Day Saint movement, both during Smith's lifetime and afterward as a ...
failed to persuade William Marks, the president of the Presiding High Council
In the Latter Day Saint movement, there are two presiding high councils, one said to be "standing," and the other "traveling." The traveling high council is generally known as the Quorum of Twelve Apostles. Both councils, at least in theory, presid ...
and a Rigdon supporter, to assume leadership and the surviving members of Smith's immediate family remained unaffiliated with any larger body until 1860, when they formed the Reorganized Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints with Joseph's eldest son Joseph Smith III as prophet. These various groups are sometimes referred to under two geographical headings: "Prairie Saints" (those that remained in the Midwest United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
); and "Rocky Mountain Saints" (those who followed Young to what would later become the state of Utah).
Today, the vast majority (over 98 percent) of Latter Day Saints belong to the LDS Church, which reports over 16 million members worldwide. The second-largest denomination is the Missouri-based Community of Christ, which reports 252,000 members. Small denominations that trace their origins to Rigdon, James Strang, or other associates of Smith's still exist, and several fundamentalist sects which separated from the LDS Church after it rejected plural marriage in 1890 claim tens of thousands of members.
Historically, the different denominations within the Latter Day Saint movement have been hostile towards or dismissive of one another; this is largely because each group claims to be the sole legitimate continuation of the one true church established by Smith in 1830.
Beliefs
''Saint''-designation of members
The beliefs within the LDS Church with regard to saints are similar but not quite the same as the Protestant tradition. In the New Testament, saints are all those who have entered into the Christian covenant of baptism. The qualification "latter-day" refers to the doctrine that members are living in the "latter days", before theSecond Coming of Christ
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messi ...
, and is used to distinguish the members of the church, which considers itself the restoration of the ancient Christian church. Members are therefore often referred to as " Latter-day Saints" or "LDS", and among themselves, "saints".
Restoration
The Latter Day Saint movement classifies itself within Christianity, but as a distinct restored dispensation. Latter Day Saints hold that a Great Apostasy began in Christianity not long after the ascension of Jesus, (see also: 2 Thessalonians 2:3) marked with the corruption of Christian doctrine by Greek and other philosophies, and followers dividing into different ideological groups. Additionally, Latter Day Saints claim the martyrdom of theapostles
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary, from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to send off". The purpose of such sending ...
led to a loss of priesthood authority to administer the church and its ordinances.
According to Latter Day Saint churches, God re-established the early Christian
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish d ...
church as found in the New Testament through Joseph Smith. In particular, Latter Day Saints believe that angels such as Peter, James
James is a common English language surname and given name:
*James (name), the typically masculine first name James
* James (surname), various people with the last name James
James or James City may also refer to:
People
* King James (disambiguat ...
, John, and John the Baptist appeared to Smith and others and bestowed various priesthood authorities on them. Thus, Smith and his successors are considered modern prophets who receive revelation from God to guide the church.
Theology
Most members of Latter Day Saint churches are adherents to Mormonism, a theology based on Joseph Smith's later teachings and further developed by Brigham Young, James Strang and others who claimed to be Smith's successors. The term ''Mormon'' derives from the Book of Mormon, and most of these adherents refer to themselves as Latter Day Saints or Mormons. Mormonism and Christianity have a complex theological, historical, and sociological relationship. Mormons express the doctrines of Mormonism using standard biblical terminology, and claim to have similar views about the nature of Jesus' atonement, resurrection, and Second Coming as traditional Christianity. Nevertheless, Mormons agree with non-Mormons that their view of God is significantly different from the trinitarian view of theNicene Creed
The original Nicene Creed (; grc-gre, Σύμβολον τῆς Νικαίας; la, Symbolum Nicaenum) was first adopted at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. In 381, it was amended at the First Council of Constantinople. The amended form is a ...
of the 4th century.
Mormons consider the Bible as scripture and have also adopted additional scriptures. Mormons not only practice baptism and celebrate the eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
but also participate in religious rituals not practiced in traditional Christianity. Although the various branches of Christianity have diverse views about the nature of salvation, the Mormon view is particularly distinct.
Focusing on differences, some Christians consider Mormonism "non-Christian"; members of the LDS Church, focusing on similarities, are offended at being so characterized. Mormons do not accept non-Mormon baptism. Mormons regularly proselytize individuals actually or nominally within the Christian tradition, and some Christians, especially evangelicals
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide Interdenominationalism, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being "bor ...
, proselytize Mormons. The LDS Church has a formal missionary program with nearly 70,000 missionaries, with 15 training centers and 407 missions worldwide. A prominent scholarly view is that Mormonism is a form of Christianity, but is distinct enough from traditional Christianity so as to form a new religious tradition, much as Christianity has roots in but is a distinct religion from Judaism..
The Mormonism that originated with Smith in the 1820s shared strong similarities with some elements of 19th-century Protestant Christianity including the necessity of baptism, emphasis on family, and central doctrine on Christ as a means to salvation. However, beginning with his accounts of the First Vision in the 1830s and 1840s, Smith—who said that Christ had told him not to join any existing church—departed significantly from traditional Christianity, claiming all churches of his day were part of a Great Apostasy that had lost the authority to direct Christ's church. Mormonism does not characterize itself as a Protestant religion, as Smith taught that he had received revelation direct from Christ to restore his original church. Mormons believe that God, through Smith and his successors, restored these truths and doctrinal clarifications, and, initiating a new heavenly dispensation, restored the original church and Christianity taught by Jesus. For example, Smith rejected the Nicene
The original Nicene Creed (; grc-gre, Σύμβολον τῆς Νικαίας; la, Symbolum Nicaenum) was first adopted at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. In 381, it was amended at the First Council of Constantinople. The amended form is a ...
doctrine of the Trinity as of one body and substance, with no "body, parts, or passions", and instead taught that the Godhead
Godhead (from Middle English ''godhede'', "godhood", and unrelated to the modern word "head"), may refer to:
* Deity
* Divinity
* Conceptions of God
* In Abrahamic religions
** Godhead in Judaism, the unknowable aspect of God, which lies beyo ...
included God, the Eternal Father, also known as Elohim
''Elohim'' (: ), the plural of (), is a Hebrew word meaning "gods". Although the word is plural, in the Hebrew Bible it usually takes a singular verb and refers to a single deity, particularly (but not always) the God of Israel. At other times ...
; his only-begotten son in the flesh, Jesus Christ, also known as Jehovah
Jehovah () is a Latinization of the Hebrew , one vocalization of the Tetragrammaton (YHWH), the proper name of the God of Israel in the Hebrew Bible/ Old Testament. The Tetragrammaton is considered one of the seven names of God in Judais ...
, the savior and redeemer of the world; and the Holy Ghost or Holy Spirit, an individual personage of spirit whose influence can be felt in many places at once. Further, Smith taught that the essence of all humans is co-eternal with God and that humans, as the spirit offspring of God the Father, have the potential to become like God. The LDS Church, the largest Mormon denomination, while acknowledging its differences with mainstream Christianity, often focuses on its commonalities, which are many, the most important of which is that Christ is the savior of the world and that he suffered for the world's sins so that the penitent can return to live in heaven.
A small fraction of Latter Day Saints, most notably those within Community of Christ, the second largest Latter Day Saint denomination, follow a traditional Protestant theology. Community of Christ views God in trinitarian terms, and reject the distinctive theological developments they believe to have been developed later in Mormonism.
Denominations

See also
*Criticism of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) has been subject to criticism and sometimes discrimination since its early years in New York and Pennsylvania. In the late 1820s, criticism centered around the claim by Joseph Smith ...
*Temple Riders
The Temple Riders is a Mormon motorcycle club
A motorcycle club is a group of individuals whose primary interest and activities involve motorcycles. A motorcycle group can range as clubbed groups of different bikes or bikers who own same mode ...
Notes
References
*. *Danny L. Jorgensen Danny Lynn Jorgensen (born 1951) is an American professor at the Department of Religious Studies of the University of South Florida, for which he also served as chair from 1999 to 2006.
Jorgensen's research interests include Sociology of Culture, ...
"Dissent and Schism in the Early Church: Explaining Mormon Fissiparousness"
'' Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought'', vol. 28, no. 3 (Fall 1993) pp. 15–39. *. *. *. *Steven L. Shields, ''Divergent Paths of the Restoration: A History of the Latter Day Saint Movement'' Los Angeles: 1990.
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Latter Day Saint Movement Christian new religious movements Joseph Smith Mormon studies