Larissa (moon) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Larissa, also known as Neptune VII, is the fifth-closest inner satellite of
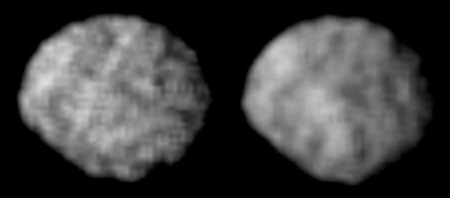 The fourth-largest satellite of Neptune, Larissa is irregular (non-spherical) in shape and appears to be heavily cratered, with no sign of any geological modification. It is likely that Larissa, like the other satellites inward of
The fourth-largest satellite of Neptune, Larissa is irregular (non-spherical) in shape and appears to be heavily cratered, with no sign of any geological modification. It is likely that Larissa, like the other satellites inward of
 Larissa has only been visited by ''
Larissa has only been visited by ''
Larissa Profile
b
NASA's Solar System Exploration
(by Scott S. Sheppard) {{DEFAULTSORT:Larissa (Moon) Moons of Neptune 19810524 M
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
. It is named after Larissa
Larissa (; el, Λάρισα, , ) is the capital and largest city of the Thessaly region in Greece. It is the fifth-most populous city in Greece with a population of 144,651 according to the 2011 census. It is also capital of the Larissa regiona ...
, a lover of Poseidon
Poseidon (; grc-gre, Ποσειδῶν) was one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and myth, god of the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, he was venerated as ...
(Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
) in Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities o ...
and eponymous nymph
A nymph ( grc, νύμφη, nýmphē, el, script=Latn, nímfi, label=Modern Greek; , ) in ancient Greek folklore is a minor female nature deity. Different from Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature, are ...
of the city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
in Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thes ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
.
Discovery
It was first discovered by Harold J. Reitsema,William B. Hubbard
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Eng ...
, Larry A. Lebofsky and David J. Tholen, based on fortuitous ground-based stellar occultation
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden from the observer by another object that passes between them. The term is often used in astronomy, but can also refer to any situation in which an object in the foreground blocks ...
observations on May 24, 1981, given the temporary designation S/1981 N 1 and announced on May 29, 1981. The moon was recovered and confirmed to be the only object in its orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
during the ''Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, '' Voyager 1'', ...
'' flyby in 1989 after which it received the additional designation S/1989 N 2 on August 2, 1989. The announcement by Stephen P. Synnott
Stephen P. Synnott (born 1946) is an American astronomer and Voyager scientist at JPL, and expert in spacecraft optical navigation techniques. He has discovered several natural satellites of outer Solar System planets such as Metis, Puck, Lariss ...
spoke of “10 frames taken over 5 days”, which gives a recovery date sometime before July 28. The name was given on September 16, 1991.
Characteristics
 The fourth-largest satellite of Neptune, Larissa is irregular (non-spherical) in shape and appears to be heavily cratered, with no sign of any geological modification. It is likely that Larissa, like the other satellites inward of
The fourth-largest satellite of Neptune, Larissa is irregular (non-spherical) in shape and appears to be heavily cratered, with no sign of any geological modification. It is likely that Larissa, like the other satellites inward of Triton
Triton commonly refers to:
* Triton (mythology), a Greek god
* Triton (moon), a satellite of Neptune
Triton may also refer to:
Biology
* Triton cockatoo, a parrot
* Triton (gastropod), a group of sea snails
* ''Triton'', a synonym of ''Triturus'' ...
, is a rubble pile
In astronomy, a rubble pile is a celestial body that is not a monolith, consisting instead of numerous pieces of rock that have coalesced under the influence of gravity. Rubble piles have low density because there are large cavities between the ...
re-accreted from fragments of Neptune's original satellites, which were disrupted by perturbations from Triton soon after that moon's capture into a very eccentric initial orbit.
Larissa's orbit is nearly circular and lies below Neptune's synchronous orbit A synchronous orbit is an orbit in which an orbiting body (usually a satellite) has a period equal to the average rotational period of the body being orbited (usually a planet), and in the same direction of rotation as that body.
Simplified meanin ...
radius, so it is slowly spiralling inward due to tidal deceleration and may eventually impact Neptune's atmosphere, or break up into a planetary ring
A ring system is a disc or ring, orbiting an astronomical object, that is composed of solid material such as dust and moonlets, and is a common component of satellite systems around giant planets. A ring system around a planet is also known ...
upon passing its Roche limit due to tidal stretching, similarly to how Triton
Triton commonly refers to:
* Triton (mythology), a Greek god
* Triton (moon), a satellite of Neptune
Triton may also refer to:
Biology
* Triton cockatoo, a parrot
* Triton (gastropod), a group of sea snails
* ''Triton'', a synonym of ''Triturus'' ...
will eventually collide with Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
or break into a planetary ring
A ring system is a disc or ring, orbiting an astronomical object, that is composed of solid material such as dust and moonlets, and is a common component of satellite systems around giant planets. A ring system around a planet is also known ...
.
Exploration
 Larissa has only been visited by ''
Larissa has only been visited by ''Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, '' Voyager 1'', ...
''. The probe was able to get photographs of Larissa, showing its cratered surface.
Notes
References
External links
Larissa Profile
b
NASA's Solar System Exploration
(by Scott S. Sheppard) {{DEFAULTSORT:Larissa (Moon) Moons of Neptune 19810524 M