Languages of the Philippines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
There are some 120 to 187 languages spoken in the
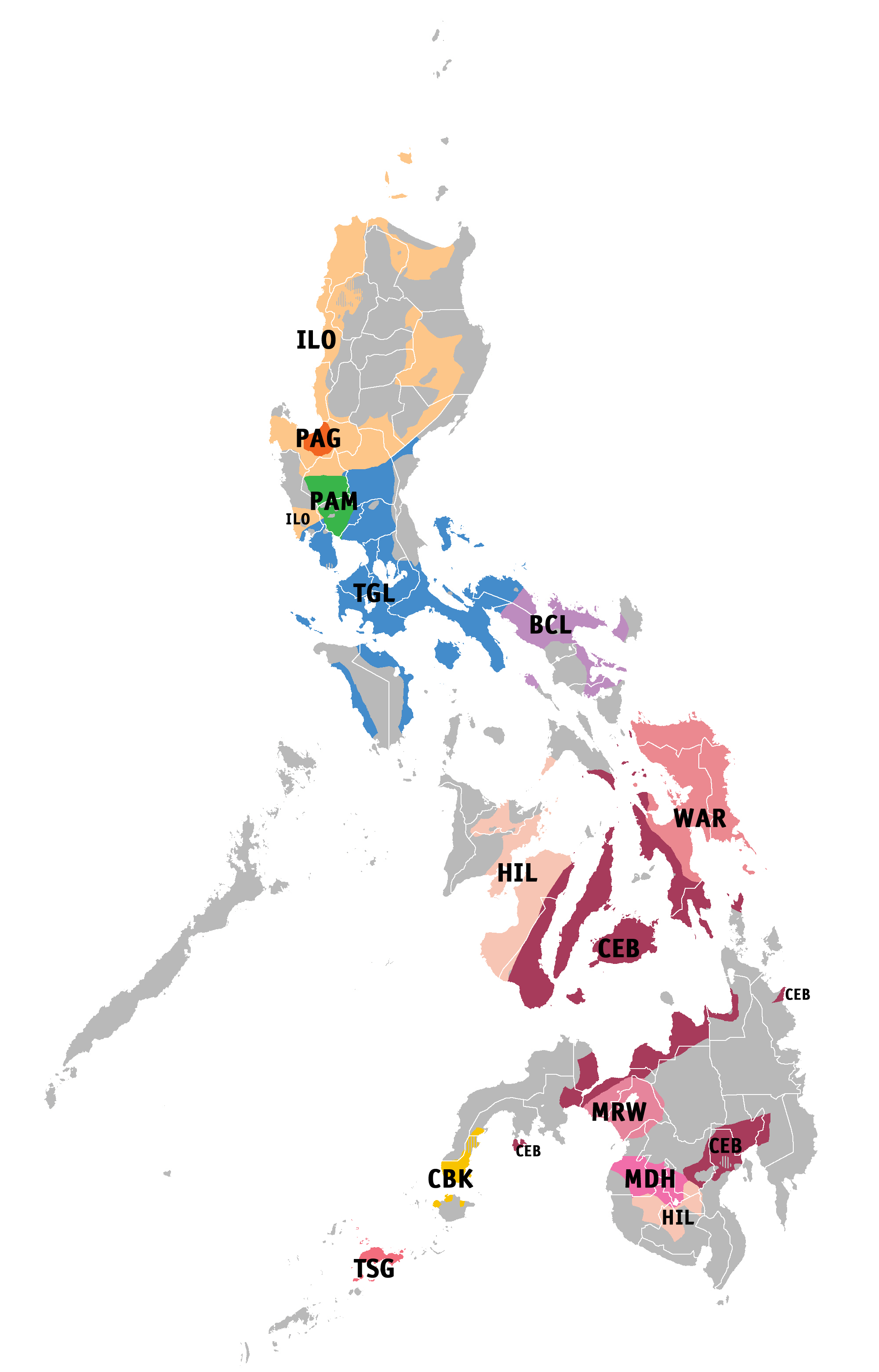
 According to Ethnologue, a total of 182 native languages are spoken in the nation and four languages have been classified as extinct: Dicamay Agta, Katabaga, Tayabas Ayta and Villaviciosa Agta. Except for
According to Ethnologue, a total of 182 native languages are spoken in the nation and four languages have been classified as extinct: Dicamay Agta, Katabaga, Tayabas Ayta and Villaviciosa Agta. Except for
Linguistic map of the Philippines at Muturzikin.com
Ricardo Maria Nolasco on the diversity of languages in the Philippines
Lawrence R. Reid
webpage of Dr. Lawrence A. Reid. Researcher Emeritus of linguistics at the University of Hawai'i at Manoa. Has researched Philippine languages for decades.
Carl Rubino
webpage of Dr. Carl Rubino. A Filipino linguist who has studied Philippine languages.
by Edmundo Farolan Romero, with a brief Philippine poetry anthology in Spanish.
Salita Blog
by Christopher Sundita. A blog about a variety of issues concerning the languages of the Philippines.
Espaniero
An Online Spanish conversation group for Pinoys
The Language Planning Situation in the Philippines
by Andrew González, FSC
kaibigankastila
webpage of the Spanish culture in the Philippines.
On linguistic mutual intolerance in the Philippines
Filipino Translator
Tagalog Translator Online
Online dictionary for translating Tagalog from/to English, including expressions and latest headlines regarding the Philippines.
Linguistic map of the PhilippinesLearn Philippine Languages
a compilation of lessons about languages of the Philippines. {{DEFAULTSORT:Languages of the Philippines Languages of the Philippines,
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, depending on the method of classification. Almost all are Malayo-Polynesian languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast ...
native to the archipelago. A number of Spanish-influenced creole varieties generally called Chavacano
Chavacano or Chabacano is a group of Spanish-based creole language varieties spoken in the Philippines. The variety spoken in Zamboanga City, located in the southern Philippine island group of Mindanao, has the highest concentration of speaker ...
are also spoken in certain communities. The 1987 constitution designates Filipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
, a standardized version of Tagalog, as the national language
A national language is a language (or language variant, e.g. dialect) that has some connection—de facto or de jure—with a nation. There is little consistency in the use of this term. One or more languages spoken as first languages in the te ...
and an official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
along with English. Filipino is regulated by Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino
, logo =
, logo_width =
, logo_caption =
, seal = Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino (KWF).svg
, seal_width =
, seal_caption =
, formed = 1937 (first formation)1991 (reformed)
, preceding1 ...
and serves as a '' lingua franca'' used by Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or othe ...
of various ethnolinguistic backgrounds.
On October 30, 2018, President Rodrigo Duterte signed into law Republic Act 11106, which declares Filipino Sign Language or FSL to be the country's official sign language
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign l ...
and as the Philippine government's official language in communicating with the Filipino Deaf.
While Filipino is used for communication across the country's diverse linguistic groups and in popular culture
Popular culture (also called mass culture or pop culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as, popular art or mass art) and objects that are dominant or prevalent in a ...
, the government operates mostly using English. Including second-language speakers, there are more speakers of Filipino than English in the Philippines. The other regional languages are given official auxiliary status in their respective places according to the constitution but particular languages are not specified. Some of these regional languages are also used in education.
The indigenous scripts of the Philippines (such as the Kulitan
Kulitan (Spanish: ''cúlitan''), also known as súlat Kapampángan and pamagkulit, is one of the various indigenous suyat writing systems in the Philippines. It was used for writing Kapampangan, a language mainly spoken in Central Luzon, until it ...
, Tagbanwa and others) are used very little; instead, Philippine languages are today written in the Latin script
The Latin script, also known as Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern I ...
because of the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
and American colonial experience. Baybayin, though generally not understood, is one of the most well-known of the Philippine indigenous scripts and is used mainly in artistic applications such as on the Philippine banknotes, where the word "Pilipino" is inscribed using the writing system. Additionally, the Arabic script is used in the Muslim areas in the southern Philippines.
Tagalog and Cebuano are the most commonly spoken native languages, together comprising about half of the population of the Philippines. Only Filipino and English are official languages and are taught in schools. This, among other reasons, has resulted in a rivalry between the two language groups.
National and official languages

History
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
was the official language of the country for more than three centuries under Spanish colonial rule, and became the lingua franca of the Philippines in the 19th and early 20th centuries. In 1863, a Spanish decree introduced universal education
Universal access to education is the ability of all people to have equal opportunity in education, regardless of their social class, race, gender, sexuality, ethnic background or physical and mental disabilities. The term is used both in col ...
, creating free public schooling in Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
. It was also the language of the Philippine Revolution, and the 1899 Malolos Constitution
The Political Constitution of 1899 ( es, Constitución Política de 1899), informally known as the Malolos Constitution, was the constitution of the First Philippine Republic. It was written by Felipe Calderón y Roca and Felipe Buencamino as ...
effectively proclaimed it as the official language of the First Philippine Republic
The Philippine Republic ( es, República Filipina), now officially known as the First Philippine Republic, also referred to by historians as the Malolos Republic, was established in Malolos, Bulacan during the Philippine Revolution against ...
. National hero José Rizal wrote most of his works in Spanish. Following the American occupation of the Philippines and the imposition of English, the use of Spanish declined gradually, especially after the 1940s.
Under the U.S. occupation and civil regime, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
began to be taught in schools. By 1901, public education used English as the medium of instruction. Around 600 educators (called "Thomasites
The Thomasites were a group of 600 American teachers who traveled from the United States to the newly occupied territory of the Philippines on the U.S. Army Transport ''Thomas''. The group included 346 men and 180 women, hailing from 43 differe ...
") who arrived in that year aboard the USAT ''Thomas'' replaced the soldiers who also functioned as teachers. The 1935 Constitution added English as an official language alongside Spanish. A provision in this constitution also called for Congress to "take steps toward the development and adoption of a common national language based on one of the existing native languages." On November 12, 1937, the First National Assembly created the National Language Institute. President Manuel L. Quezón
Manuel Luis Quezon y Molina, (; 19 August 1878 – 1 August 1944), also known by his initials MLQ, was a Filipino lawyer, statesman, soldier and politician who served as president of the Commonwealth of the Philippines from 1935 until his de ...
appointed native Waray speaker Jaime C. De Veyra
Jaime Carlos Diaz de Veyra (November 4, 1873 – March 7, 1963) was a Resident Commissioner to the U.S. House of Representatives from the Philippine Islands from 1917 to 1923 and the 1st Governor of Leyte from 1906 to 1907.
Early life
He was ...
to chair a committee of speakers of other regional languages
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
. Their aim was to select a national language among the other regional languages
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
. Ultimately, Tagalog was chosen as the base language on December 30, 1937, on the basis that it was the most widely spoken and developed local language.
In 1939, President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
Manuel L. Quezón
Manuel Luis Quezon y Molina, (; 19 August 1878 – 1 August 1944), also known by his initials MLQ, was a Filipino lawyer, statesman, soldier and politician who served as president of the Commonwealth of the Philippines from 1935 until his de ...
renamed the Tagalog language
Tagalog (, ; ; '' Baybayin'': ) is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by the ethnic Tagalog people, who make up a quarter of the population of the Philippines, and as a second language by the majority. Its standardized form, ...
as ''Wikang Pambansa'' ("national language" in English translation). The language was further renamed in 1959 as ''Pilipino'' by Secretary of
Education Jose Romero. The 1973 constitution declared the Pilipino language to be co-official, along with English, and mandated the development of a national language
A national language is a language (or language variant, e.g. dialect) that has some connection—de facto or de jure—with a nation. There is little consistency in the use of this term. One or more languages spoken as first languages in the te ...
, to be known as ''Filipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
''. In addition, Spanish regained its official status when President Marcos signed Presidential Decree No. 155, s. 1973.
The 1987 Constitution declares Filipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
as the national language of the country. Filipino and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
are the official languages, with the recognition of the regional languages as auxiliary official in their respective regions (though not specifying any particular languages). Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
are to be promoted on an optional and voluntary basis. Filipino also had the distinction of being a national language that was to be "developed and enriched on the basis of existing Philippine and other languages." Although not explicitly stated in the constitution, Filipino is in practice almost completely composed of the Tagalog language as spoken in the capital, Manila; however, organizations such as the University of the Philippines
The University of the Philippines (UP; fil, Pamantasan ng Pilipinas Unibersidad ng Pilipinas) is a state university system in the Philippines. It is the country's national university, as mandated by Republic Act No. 9500 (UP Charter of 200 ...
began publishing dictionaries such as the '' UP Diksyonaryong Filipino'' in which words from various Philippine languages were also included. The present constitution is also the first to give recognition to other regional languages. The constitution also made mention of Spanish and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
, both of which are to be promoted on a voluntary and optional basis.
Republic Act No. 7104, approved on August 14, 1991, created the Commission on the Filipino Language
Filipino (; , ) is an Austronesian language. It is the national language ( / ) of the Philippines, and one of the two official languages of the country, with English. It is a standardized variety of Tagalog based on the native dialect, sp ...
, reporting directly to the President and tasked to undertake, coordinate and promote researches for the development, propagation and preservation of Filipino and other Philippine languages
The Philippine languages or Philippinic are a proposed group by R. David Paul Zorc (1986) and Robert Blust (1991; 2005; 2019) that include all the languages of the Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia—except Sama–Bajaw (languag ...
. On May 13, 1992, the commission issued Resolution 92–1, specifying that Filipino is the
Usage
Filipino is a standardized version of Tagalog, spoken mainly in Metro Manila. Both Filipino and English are used in government, education, print, broadcast media, and business, with third local languages often being used at the same time. Filipino has borrowings from, among other languages, Spanish, English, Arabic, Persian, Sanskrit, Malay, Chinese, Japanese, and Nahuatl. Filipino is an official language of education, but less important than English as a language of publication (except in some domains, likecomic book
A comic book, also called comicbook, comic magazine or (in the United Kingdom and Ireland) simply comic, is a publication that consists of comics art in the form of sequential juxtaposed panels that represent individual scenes. Panels are of ...
s) and less important for academic-scientific-technological discourse. Filipino is used as a lingua franca in all regions of the Philippines as well as within overseas Filipino
An overseas Filipino ( fil, Pilipino sa ibayong-dagat) is a person of full or partial Filipino origin—i.e., people who trace back their ancestry to the Philippines but living or residing outside the country. This term generally applies to b ...
communities, and is the dominant language of the armed forces (except perhaps for the small part of the commissioned officer
An officer is a person who has a position of authority in a hierarchical organization. The term derives from Old French ''oficier'' "officer, official" (early 14c., Modern French ''officier''), from Medieval Latin ''officiarius'' "an officer," f ...
corps from wealthy or upper-middle-class families) and of a large part of the civil service, most of whom are non-Tagalogs.
There are different forms of diglossia
In linguistics, diglossia () is a situation in which two dialects or languages are used (in fairly strict compartmentalization) by a single language community. In addition to the community's everyday or vernacular language variety (labeled ...
that exist in the case of regional languages
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
. Locals may use their mother tongue or the regional lingua franca to communicate amongst themselves, but sometimes switch to foreign languages when addressing outsiders. Another is the prevalence of code-switching
In linguistics, code-switching or language alternation occurs when a speaker alternates between two or more languages, or language varieties, in the context of a single conversation or situation. Code-switching is different from plurilingualis ...
to English when speaking in both their first language and Tagalog.
The Constitution of the Philippines provides for the use of the vernacular languages as official auxiliary languages in provinces where Filipino is not the lingua franca. Filipinos by and large are polyglot
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all Eu ...
s; In the case where the vernacular language is a regional language, Filipinos would speak in Filipino when speaking in formal situations while the regional languages
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
are spoken in non-formal settings. This is evident in major urban areas outside Metro Manila like Camarines Norte
Camarines Norte ( bcl, Amihanan na Camarines; fil, Hilagang Camarines), officially the Province of Camarines Norte, is a province in the Philippines located in the Bicol Region in Luzon. Its capital is Daet. The province borders Quezon to the w ...
in the Bikol-speaking area, and Davao in the Cebuano-speaking area. , the case of Ilocano and Cebuano are becoming more of bilingualism than diglossia due to the publication of materials written in these languages.
The diglossia is more evident in the case of other languages such as Pangasinan, Kapampangan Kapampangan, Capampañgan or Pampangan may refer to:
*Kapampangan people of the Philippines
*Kapampangan language
Kapampangan or Pampangan is an Austronesian language, and one of the eight major languages of the Philippines. It is the primary ...
, Bikol, Waray, Hiligaynon, Sambal
Sambal is an Indonesian chilli sauce or paste, typically made from a mixture of a variety of chilli peppers with secondary ingredients, such as shrimp paste, garlic, ginger, shallot, scallion, palm sugar, and lime juice. ''Sambal'' is an ...
, and Maranao
The Maranao people (Maranao: mәranaw Filipino: ''Maranaw''), also spelled Meranao, Maranaw, and Mëranaw, is the term used by the Philippine government to refer to the southern indigenous people who are the "people of the lake", a predomi ...
, where the written variant of the language is becoming less and less popular to give way to the use of Filipino. Although Philippine laws consider some of these languages as "major languages" there is little, if any, support coming from the government to preserve these languages. This may be bound to change, however, given current policy trends.
There still exists another type of diglossia, which is between the regional languages and the minority languages. Here, we label the regional languages as acrolect
A post-creole continuum (or simply creole continuum) is a dialect continuum of varieties of a creole language between those most and least similar to the superstrate language (that is, a closely related language whose speakers assert or asserted d ...
s while the minority languages as the basilect. In this case, the minority language is spoken only in very intimate circles, like the family or the tribe one belongs to. Outside this circle, one would speak in the prevalent regional language, while maintaining an adequate command of Filipino for formal situations. Unlike the case of the regional languages, these minority languages are always in danger of becoming extinct because of speakers favoring the more prevalent regional language. Moreover, most of the users of these languages are illiterate and as expected, there is a chance that these languages will no longer be revived due to lack of written records.
In addition to Filipino and English, other languages have been proposed as additional nationwide languages. Among the most prominent proposals are Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, and Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
.
Indigenous languages
 According to Ethnologue, a total of 182 native languages are spoken in the nation and four languages have been classified as extinct: Dicamay Agta, Katabaga, Tayabas Ayta and Villaviciosa Agta. Except for
According to Ethnologue, a total of 182 native languages are spoken in the nation and four languages have been classified as extinct: Dicamay Agta, Katabaga, Tayabas Ayta and Villaviciosa Agta. Except for English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, Chavacano
Chavacano or Chabacano is a group of Spanish-based creole language varieties spoken in the Philippines. The variety spoken in Zamboanga City, located in the southern Philippine island group of Mindanao, has the highest concentration of speaker ...
and varieties of Chinese
Chinese, also known as Sinitic, is a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family consisting of hundreds of local varieties, many of which are not mutually intelligible. Variation is particularly strong in the more mountainous southeast of ma ...
(Hokkien
The Hokkien () variety of Chinese is a Southern Min language native to and originating from the Minnan region, where it is widely spoken in the south-eastern part of Fujian in southeastern mainland China. It is one of the national languages ...
, Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
and Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
), all of the languages belong to the Malayo-Polynesian
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeas ...
branch of the Austronesian language family.
There are 4 indigenous languages with more than 5 million native speakers:
* Tagalog
* Cebuano
* Ilocano
* Hiligaynon
and 7 with 1 million to 5 million native speakers:
* Bikol
* Waray
* Kapampangan Kapampangan, Capampañgan or Pampangan may refer to:
*Kapampangan people of the Philippines
*Kapampangan language
Kapampangan or Pampangan is an Austronesian language, and one of the eight major languages of the Philippines. It is the primary ...
* Pangasinan
* Maguindanao
* Maranao
The Maranao people (Maranao: mәranaw Filipino: ''Maranaw''), also spelled Meranao, Maranaw, and Mëranaw, is the term used by the Philippine government to refer to the southern indigenous people who are the "people of the lake", a predomi ...
* Tausug
One or more of these is spoken natively by more than 90% of the population.
A Philippine language sub-family identified by Robert Blust
Robert A. Blust (; ; May 9, 1940 – January 5, 2022) was an American linguist who worked in several areas, including historical linguistics, lexicography and ethnology. He was Professor of Linguistics at the University of Hawaii at Mānoa. Blus ...
includes languages of north Sulawesi and the Yami language
Yami language (), also known as Tao language (), is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken by the Tao people of Orchid Island, 46 kilometers southeast of Taiwan. It is a member of the Ivatan dialect continuum.
Yami is known as 'human speech' by i ...
of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, but excludes the Sama–Bajaw languages
The Sama–Bajaw languages are a well established group of languages spoken by the Sama-Bajau peoples of the Philippines, Indonesia and Malaysia. They are mainly spoken on Borneo and the Sulu Archipelago between Borneo and Mindanao.
Languages ...
of the Tawi-Tawi
Tawi-Tawi, officially the Province of Tawi-Tawi ( tl, Lalawigan ng Tawi-Tawi; Tausug: ''Wilaya' sin Tawi-Tawi''; Sinama: ''Jawi Jawi/Jauih Jauih''), is an island province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim ...
islands, as well as a couple of North Bornean languages
The Greater North Borneo languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The subgroup covers languages that are spoken throughout much of Borneo (excluding the southeastern area where the Greater Barito languages are spok ...
spoken in southern Palawan
Palawan (), officially the Province of Palawan ( cyo, Probinsya i'ang Palawan; tl, Lalawigan ng Palawan), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in t ...
.
Eskayan is an artificial auxiliary language created as the embodiment of a Bohol
Bohol (), officially the Province of Bohol ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Bohol; tl, Lalawigan ng Bohol), is an island province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas region, consisting of the island itself and 75 minor surrounding islands. It ...
nation in the aftermath of the Philippine–American War. It is used by about 500 people.
A theory that the indigenous scripts of Sumatra, Sulawesi and the Philippines are descended from an early form of the Gujarati script
The Gujarati script (, transliterated: ) is an abugida for the Gujarati language, Kutchi language, and various other languages. It is a variant of the Devanagari script differentiated by the loss of the characteristic horizontal line running abo ...
was presented at the 2010 meeting of the Berkeley Linguistics Society.
Mutual intelligibility
Philippine languages are often referred to by Filipinos asdialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a ...
s, partly as a relic of the inaccurate vocabulary used in literature during the American period (1898–1946). While there are indeed many hundreds of dialects in the Philippines, they represent variations of no fewer than 120 distinct languages, and many of these languages maintain greater differences than those between established European languages like French and Spanish.
The vast differences between the languages can be seen in the following translations of what has been asserted to be the Philippine national proverb:
Dialectal variation
The amount of dialectal variation varies from language to language. Languages like Tagalog, Kapampangan and Pangasinan are known to have very moderate dialectal variation. For the languages of theBicol Region
Bicol, known formally as the Bicol Region or colloquially as Bicolandia ( bcl, Rehiyon kan Bikol; Rinconada Bikol: ''Rehiyon ka Bikol''; Waray Sorsogon, Masbateño: ''Rehiyon san Bikol''; tl, Rehiyon ng Bikol), is an administrative region of ...
, however, there is great dialectal variation. There are cities and towns which have their own dialects and varieties. Below is the sentence "Were you there at the market for a long time?" translated into certain varieties of Bikol. The translation is followed by dialect and corresponding language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
, and a city/town in Bicol where they are spoken. The final translation is in Tagalog.
* Haloy ka duman sa saod? (Standard Coastal Bikol, a dialect of Central Bikol
Central Bikol commonly called Bikol Naga, also known simply as Bikol, is an Austronesian language spoken by the Bicolanos, primarily in the Bicol Region of southern Luzon, Philippines. It is spoken in the northern and western part of Camarines ...
; Canaman, Camarines Sur
Canaman, officially the Municipality of Canaman ( bcl, Banwaan kan Canaman; tl, Bayan ng Canaman) is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 36,205 people.
Can ...
)
* Aloy ka duman sa saod? (Magarao, a variety of Coastal Bikol; Magarao, Camarines Sur
Magarao, officially the Municipality of Magarao ( bcl, Banwaan kan Magarao; tl, Bayan ng Magarao), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 26,742 people.
Ma ...
)
* Huray ka doon sa saod? ( Northern Catanduanes Bicolano or ''Pandan Bikol''; Pandan, Catanduanes
Pandan, officially the Municipality of Pandan, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Catanduanes, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 21,473 people.
History
Formerly the town site was located some two kil ...
)
* Naawat ka duman sa saod? ( Southern Catanduanes Bikol or ''Virac Bikol'', a dialect of Coastal Bikol; Virac, Catanduanes
Virac, officially the Municipality of Virac, is a 1st class municipality and capital of the province of Catanduanes, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 76,520 people.
It is most populous and fifth largest in land ...
)
* Naəban ikā sadtō sāran? (Rinconada Bikol
Rinconada Bikol or simply Rinconada, spoken in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines, is one of several languages that compose the Inland Bikol (or Southern Bicol) group of the Bikol languages, Bikol macrolanguage. It belongs to the Austron ...
; Iriga City
Iriga, officially the City of Iriga ( Rinconada Bikol: ''Syudad ka Iriga''; bcl, Siyudad nin Iriga; fil, Lungsod ng Iriga), is component city in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of ...
)
* Nauban ikā sadtō sāran? (Rinconada Bikol
Rinconada Bikol or simply Rinconada, spoken in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines, is one of several languages that compose the Inland Bikol (or Southern Bicol) group of the Bikol languages, Bikol macrolanguage. It belongs to the Austron ...
; Nabua, Camarines Sur
Nabua, officially the Municipality of Nabua (Rinconada Bikol: ''Banwāan ka Nabua''; Tagalog: ''Bayan ng Nabua''), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 8 ...
)
* Uban ika adto sa saod? (Libon, Albay Bikol; Libon, Albay
Libon, officially the Municipality of Libon ( bcl, Banwaan kan Libon; tl, Bayan ng Libon), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Albay, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 75,073 people.
Libon has a land a ...
)
* Naëǧëy ika adto sa saran? (Buhinon, Albay Bikol; Buhi, Camarines Sur
Buhi, officially the Municipality of Buhi ( Buhinon: ''Banwaan nya Buhi''; Rinconada Bikol: ''Banwāan ka Buhi''; Tagalog: ''Bayan ng Buhi''), is a 1st class world class municipality in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines. According to th ...
)
* Ëlëy ka idto sa sëd? (West Miraya Bikol, Albay Bikol; Oas, Albay
Oas, officially the Municipality of Oas ( bcl, Banwaan kan Oas; tl, Bayan ng Oas), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Albay, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 66,084 people.
Etymology
There are two ...
)
* Na-alõy ika idto sa sâran/merkado?(West Miraya Bikol, Albay Bikol; Polangui, Albay
Polangui, officially the Municipality of Polangui ( bcl, Banwaan kan Polangui; tl, Bayan ng Polangui), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Albay, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of people.
Etymology ...
)
* Naulay ka didto sa saran? (East Miraya Bikol, Albay Bikol; Daraga, Albay
Daraga, officially the Municipality of Daraga ( bcl, Banwaan kan Daraga; tl, Bayan ng Daraga), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Albay, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 133,893.
The municipality is ...
)
* Dugay ka didto sa merkado? (Ticao, Masbateño; Monreal, Masbate
Monreal, officially the Municipality of Monreal, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Masbate, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 25,164 people.
It is located on the northern part of Ticao Island.
Geogra ...
)
* Awat ka didto sa plasa? (Gubat, Southern Sorsogon; Gubat, Sorsogon
Gubat, officially the Municipality of Gubat ( Gubatnon: ''Bungto san Gubat''; war, Bungto han Gubat, tl, Bayan ng Gubat), is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Sorsogon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of ...
)
* Awát ka didto sa rilansi? (Bulan, Southern Sorsogon Language, Southern Sorsogon; Bulan, Sorsogon)
* Matagal ka na ba roon sa palengke? ( Tagalog)
Comparison chart
Below is a chart of Philippine languages. While there have been misunderstandings on which ones should be classified as ''language'' and which ones should be classified as ''dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a ...
'', the chart confirms that most have similarities, yet are not mutually comprehensible. These languages are arranged according to the regions they are natively spoken (from north to south, then east to west).
There is a language spoken by the Tao people (also known as Yami) of Orchid Island of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
which is not included in the language of the Philippines. Their language, Yami language, Tao (or Yami) is part of the Batanic languages which includes Ivatan language, Ivatan, Babuyan, and Itbayat of the ''Batanes''.
Native speakers
Below are the number of Filipinos who speak the following 20 languages as a native language based on the 2010 Philippine census by the Philippine Statistics Authority.Negrito languages
Language vitality
2010 UNESCO designation
Endangered and extinct languages in the Philippines are based on the 3rd world volume released by UNESCO in 2010. Degree of endangerment (UNESCO standard) * ''Safe'': language is spoken by all generations; intergenerational transmission is uninterrupted * ''Vulnerable'': most children speak the language, but it may be restricted to certain domains (e.g., home) * ''Definitely endangered'': children no longer learn the language as mother tongue in the home * ''Severely endangered'': language is spoken by grandparents and older generations; while the parent generation may understand it, they do not speak it to children or among themselves * ''Critically endangered'': the youngest speakers are grandparents and older, and they speak the language partially and infrequently * ''Extinct'': there are no speakers left. These languages are included in the Atlas if presumably extinct since the 1950s ;Vulnerable languages ;Definitely endangered ;Severely endangered ;Critically endangered ;Extinct2014 North Dakota study
In a separate study by Thomas N. Headland, the Summer Institute of Linguistics in Dallas, and the University of North Dakota called ''Thirty Endangered Languages in the Philippines'', the Philippines has 32 endangered languages, but 2 of the listed languages in the study are written with 0 speakers, noting that they are extinct or probably extinct. All of the listed languages are Negrito languages, the oldest languages in the Philippines.Proposals to conserve Philippine languages
There have been numerous proposals to conserve the many languages of the Philippines. According to the Komisyon ng Wikang Filipino, there are 135 ethnolinguistic groups in the country, each having their own distinct Philippine language. Among the proposals include (1) ''"establishing a dictionary & sentence construction manual"'' for each of the 135 living languages in the country, (2) ''"video documentation"'' of all Philippine languages, (3) ''"revival of the ancient scripts of the Philippines"'' where each ethnic group's own script shall be revived and used in schools along with the currently-used Roman script in communities where those script/s used to be known, (4) ''"teaching of ethnic mother languages first"'' in homes and schools before the teaching of Filipino and foreign languages (English, Spanish, and/or Arabic), and (5) ''"using the ethnic mother language and script first in public signs"'' followed by Filipino and foreign languages (English, Spanish, and/or Arabic) and scripts, for example, using Cebuano first followed by Filipino and English underneath the sign. Currently, only the fourth proposal has been made by the national government of the Philippines. A National Script bill has been filed in Congress in support of the third and fifth proposal, however, the bill only mandates the usage of the ancient script compatible with the national language, which is Filipino.Major immigrant languages
French language, French, German language, German,Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
, Chinese language, Chinese (Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin), Korean language, Korean, and Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
are taught in some public and private schools.
Arabic
Arabic is used by some Filipino Muslims in both a liturgical language, liturgical and instructional capacity since the arrival of Islam in the Philippines, Islam and establishment of several Sultanates in the 14th century. Along with Malay language, Malay, Arabic was the '' lingua franca'' of the Malay Archipelago among Muslim traders and the Malay aristocracy. The 1987 Constitution mandates that Arabic (along with Spanish) is to be promoted on an optional and voluntary basis. Arabic is taught for free and is promoted in some Islamic centres predominantly in the southernmost parts of Philippines. It is used primarily in religious activities and education (such as in a ''madrasa'' or Islamic school) and rarely for official events or daily conversation. In this respect, its function and use is somewhat like the traditional roles of Latin and Spanish in Catholic Church in the Philippines, Filipino Catholicism ''vis-à-vis'' other currently spoken languages. Islamic schools in Mindanao teach Modern Standard Arabic in their curriculum.English
The first significant exposure of Filipinos to the English language occurred in 1762 when the British Occupation of Manila, British invaded Manila during the Seven Years' War, but this was a brief episode that had no lasting influence. English later became more important and widespread during American Colonial Period (Philippines), American rule between 1898 and 1946, and remains anofficial language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
of the Philippines.
On August 22, 2007, three Malolos City regional trial courts in Bulacan decided to use Filipino, instead of English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, in order to promote the national language. Twelve stenographers from Branches 6, 80 and 81, as model courts, had undergone training at Marcelo H. del Pilar College of Law of Bulacan State University College of Law following a directive from the Supreme Court of the Philippines. De la Rama said it was the dream of former Chief Justice Reynato Puno to implement the program in other areas such as Laguna (province), Laguna, Cavite, Quezon, Quezón, Nueva Écija, Batangas, Rizal, and Metro Manila.
English is used in official documents of business, government, the legal system, medicine, the sciences and as a medium of instruction. Filipinos prefer textbooks for subjects like calculus, physics, chemistry, biology, etc., written in English rather than Filipino. However, the topics are usually taught, even in colleges, in Tagalog or the local language. By way of contrast, native languages are often heard in colloquial and domestic settings, spoken mostly with family and friends. The use of English attempts to give an air of formality, given its use in school, government and various ceremonies. A percentage of the media such as cable television and newspapers are also in English; major television networks such as ABS-CBN and GMA Network, GMA and all AM radio stations broadcast primarily in Filipino, as well as government-run stations like People's Television Network, PTV and the Philippine Broadcasting Service. However, a 2009 article by a UNICEF worker reported that the level of spoken English language in the Philippines was poor. The article reported that aspiring Filipino teachers score the lowest in English out of all of the subjects on their licensing exams.
A large influx of English (American English) words have been assimilated into Tagalog and the other native languages called Taglish or Bislish. There is a debate, however, on whether there is diglossia or bilingualism, between Filipino and English. Filipino is also used both in formal and informal situations. Though the masses would prefer to speak in Filipino, government officials tend to speak in English when performing government functions. There is still resistance to the use of Filipino in courts and the drafting of national statutes.
In parts of Mindanao, English and Tagalog blend with Cebuano to form "Davao Tagalog".
Hokkien
Diplomatic ties with the Ming dynasty among some established states or kingdoms in Luzon and direct interactions and trade overall within the archipelago as a whole may go as far back as the early 10th century. Standard Chinese, Mandarin Chinese is the medium of instruction and subject matter being taught for Chinese school#Chinese language, Chinese class in List of Chinese schools in the Philippines, Chinese schools in the Philippines. However, the Lan nang, Lan-nang-ue variant of Hokkien Min Chinese, Chinese is the majority household and heritage language of the Overseas Chinese, overseas Chinese Filipino, Chinese in the Philippines, who for generations originally mostly trace roots from Minnan region, Southern Fujian (pronounced locally as Fukkien or Hokkien) province in Mainland China, China. Othervarieties of Chinese
Chinese, also known as Sinitic, is a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family consisting of hundreds of local varieties, many of which are not mutually intelligible. Variation is particularly strong in the more mountainous southeast of ma ...
such as Yue Chinese (especially Taishanese or Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
), Teochew dialect, Teochew, and Hakka Chinese, Hakka are spoken among a minority of Chinese Filipinos whose ancestral roots trace all the way back from the Guangdong or Guangxi provinces of Northern and southern China, Southern China. Most Chinese Filipinos raised in the Philippines, especially those of families of who have lived in the Philippines for multiple generations, are typically able and usually primarily speak Philippine English and/or Filipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
( Tagalog) and/or other Regions of the Philippines, regional Philippine languages
The Philippine languages or Philippinic are a proposed group by R. David Paul Zorc (1986) and Robert Blust (1991; 2005; 2019) that include all the languages of the Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia—except Sama–Bajaw (languag ...
, or the code-switching
In linguistics, code-switching or language alternation occurs when a speaker alternates between two or more languages, or language varieties, in the context of a single conversation or situation. Code-switching is different from plurilingualis ...
or code-mixing of these, such as Taglish or Bislish, but Philippine Hokkien is typically or occasionally used within Chinese Filipino households privately amongst family or acts a heritage language among descendants of such. Hokaglish is the code-switching equivalent of the above languages.
As with Spanish, many native languages have co-opted numerous List of loanwords in Tagalog#Hokkien, loanwords from Chinese, in particular words that refer to Philippine cuisine, cuisine, household objects, and Philippine kinship kinship terminology, terminology.
Japanese
The Japanese first came to the Philippines around the 11th century CE, the first country they emigrated to, as well as in waves from the 15th century (as depicted in the Boxer Codex) 17th century, late 19th century, 1900s, 1930s, and the 1940s. There is a small Japanese community and a school for Japanese in Metro Manila due to the number of Japanese companies. Also there is a large community of Japanese and Japanese descendants in Laguna province, Baguio, and in the Davao Region. Davao City is a home to a large population of Japanese descendants. Japanese laborers were hired by American companies like the National Fiber Company (NAFCO) in the first decades of the 20th century to work in abaca plantations. Japanese were known for their hard work and industry. During World War II, Japanese schools were present in Davao City.Korean
Korean is mainly spoken by the expatriates from South Korea and people born in the Koreans in the Philippines, Philippines with Korean ancestry. The Korean language has been added under the Department of Education (Philippines), Department of Education (DepEd) Special Program in Foreign Language (SPFL) curriculum, together with Spanish, French, German, Chinese, and Japanese.Malay
Malay is spoken as a second language by a minority of the Tausūg people, Tausug, Sama-Bajau, and Yakan people, Yakan peoples in the southernmost parts of the Philippines, from Zamboanga Peninsula (geographical region), Zamboanga down toTawi-Tawi
Tawi-Tawi, officially the Province of Tawi-Tawi ( tl, Lalawigan ng Tawi-Tawi; Tausug: ''Wilaya' sin Tawi-Tawi''; Sinama: ''Jawi Jawi/Jauih Jauih''), is an island province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim ...
. It is also spoken as a daily language by the Malaysians and Indonesians who have settled, or do business in the Philippines. It is also spoken in southern Palawan
Palawan (), officially the Province of Palawan ( cyo, Probinsya i'ang Palawan; tl, Lalawigan ng Palawan), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in t ...
to some extent. It is not spoken among the Maranao people, Maranao and Maguindanao people, Maguindanao peoples. Brunei, Malaysia, Indonesia and the southern Philippines are largely Islamic and the liturgical language of Islam is Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
, but the vast majority of Muslims in the Philippines have little practical knowledge of Arabic beyond limited religious terminology.
The Malay language, along with Philippine languages belonging to the Malayo-Polynesian language family, has also had an immense influence on many languages spoken in the Philippines. This is because Old Malay used to be the lingua franca throughout the archipelago, a good example of this is Magellan's translator Enrique using Malay to converse with the native ''Sugbuanon'' (Cebuano people, Cebuano) during this time period.
An example of Old Malay language, Old Malay spoken in Philippine history can be seen in the language of the 10th century Laguna Copperplate Inscription.
When the Spanish had first arrived in the Philippines in the 16th century, Old Malay was spoken among the aristocracy.
It is believed that Ferdinand Magellan's slave Enrique of Malacca could converse with the local leaders in Cebu Island, confirming to Magellan his arrival in Southeast Asia.
Today, Indonesian language, Indonesian is taught as a foreign language in the Department of Linguistics and Asian Languages in the University of the Philippines
The University of the Philippines (UP; fil, Pamantasan ng Pilipinas Unibersidad ng Pilipinas) is a state university system in the Philippines. It is the country's national university, as mandated by Republic Act No. 9500 (UP Charter of 200 ...
. Also, the Indonesian School in Davao City teaches the language to preserve the culture of Indonesian immigrants there. The Indonesian Embassy in Manila also offers occasional classes for Filipinos and foreigners.
Since 2013, the Indonesian Embassy in the Philippines has given basic Indonesian language training to members of the Armed Forces of the Philippines.
In an interview, Department of Education (Philippines), Department of Education Secretary Armin Luistro said that the country's government should promote Indonesian language, Indonesian and Malaysian language, Malaysian, which are both related to Filipino and other Philippine languages. Thus, the possibility of offering it as an optional subject in public schools is being studied.
South Asian languages
Since pre-Spanish times, there have been small Indian communities in the Philippines. Indians tend to be able to speak Tagalog and the other native languages, and are often fluent in English. Among themselves, Sindhi language, Sindhi and Punjabi language, Punjabi are used. Urdu language, Urdu is spoken among the Pakistani community. Only few South Asians, such as Pakistani, as well as the recent newcomers like speakers of Tamil language, Tamil, Nepali language, Nepali and Marathi language, Marathi retain their own respective languages.Spanish
Spanish language in the Philippines, Spanish was introduced in the islands after 1565, when the Spanish conquistador Miguel López de Legazpi set sail from Mexico and founded the first Spanish settlement on Cebú. Though its usage is not as widespread as before, Spanish has had a significant influence in the various local Philippine languages such as providing numerous loan words. Several Spanish-based creole language varieties collectively known as Chabacano have also emerged. The current 1987 constitution makes mention of Spanish in which it provides that Spanish (along with Arabic) is to be promoted on an optional and voluntary basis. In 1593, the first printing press in the Philippine islands was founded and it released the first (albeit polyglot) book, the ''Doctrina Christiana'' that same year. In the 17th century, Spanish religious orders founded the first universities in the Philippines, some of which are considered the oldest in Asia. During colonial rule through Mexico, Spanish was the language of education, trade, politics, and religion, and by the 19th century, became the colony's lingua franca although it was mainly used by the educated Filipinos. In 1863, a Spanish decree introduced a system of public education, creating free public schooling in Spanish. In the 1890s, the Philippines had a prominent group of Spanish-speaking scholars called the Ilustrados, such as José Rizal. Some of these scholars participated in the Philippine Revolution and later in the struggle against American occupation. Both theMalolos Constitution
The Political Constitution of 1899 ( es, Constitución Política de 1899), informally known as the Malolos Constitution, was the constitution of the First Philippine Republic. It was written by Felipe Calderón y Roca and Felipe Buencamino as ...
and the ''Lupang Hinirang'' (national anthem) were written in Spanish.
Under U.S. rule, the English language began to be promoted instead of Spanish. The use of Spanish began to decline as a result of the introduction of English into the public schools as a language of instruction. The 1935 constitution establishing the Philippine Commonwealth designated both English and Spanish as official languages. The 1950 census stated that Filipinos who spoke Spanish as a first or second language made up only 6% of the population. In 1990, the census reported that the number had dwindled to just 2,500. A 2012 survey estimates that while around 1 million people can speak Spanish with varying degrees of competency, only around 439,000 people can speak the language at a native level.
Spanish briefly lost its status as an official language upon promulgation of the 1973 constitution but regained official status two months later when President Marcos signed Presidential Decree No. 155. In the 1987 constitution, Spanish is designated as an "optional and voluntary language" but does not mention it as an "official language". Spanish was dropped as a college requirement during Corazón Aquino's administration. Former president Gloria Macapagal Arroyo, a third-language Spanish speaker, introduced legislation to re-establish the instruction of Spanish in 2009 in the state education system. Today, the language is still spoken by Filipino-Spanish mestizos and Spanish families who are mainly concentrated in Metro Manila, Iloilo City, Iloilo and Cebu City, Cebu. It remains an optional subject in some academic institutions, such as the University of Santo Tomás in Manila and the University of San Carlos in Cebu. Most foreign language study takes place in Grades 9–12, where over a third of the students study a foreign language. Spanish is the most popular language, studied by about 28% of all secondary school students,
followed by French with 11%, and German with 3%. At the primary level, over 6% of the students study foreign languages, again with Spanish leading the list at 4.5% followed by French with 1.5%, and German and Japanese each with 0.2% of enrollments.
Many historical documents, land titles, and works of literature are written in Spanish and are still not translated into Filipino languages, despite the fact that some such as land titles have legal value. Spanish, through colonization has contributed the largest number of List of loanwords in Tagalog#Spanish, loanwords and expressions in Tagalog, Cebuano, and other Philippine languages. The ''Academia Filipina de la Lengua Española'' (Philippine Academy of the Spanish Language), established in 1924, is a founding member of the Association of Academies of the Spanish Language; an association of the various Spanish academies of the world which cooperate in the standardizing and promotion of the Spanish language. Among its past and present academics are former President Arroyo, former Foreign Affairs Secretary Alberto Romulo, and Archbishop of Cebú Cardinal Ricardo Vidal.
Spanish creoles
There are several Spanish-based creole languages in the Philippines, collectively calledChavacano
Chavacano or Chabacano is a group of Spanish-based creole language varieties spoken in the Philippines. The variety spoken in Zamboanga City, located in the southern Philippine island group of Mindanao, has the highest concentration of speaker ...
. These may be split into two major geographical groups:
* In Luzon:
** ''Chavacano#Caviteño / Ternateño, Caviteño'' (Chabacano de Cavite), spoken in Cavite City, Cavite.
** ''Chavacano#Caviteño / Ternateño, Ternateño'' (Chabacano de Barra), spoken in Ternate, Cavite, Ternate, Cavite.
** ''Chavacano#Ermitaño, Ermitaño'' (Chabacano de Ermita), formerly spoken in Ermita, Manila but is now language extinction, extinct. The last reported speakers were a woman and her grandson during the 1980s and 1990s.
* In Mindanao:
** ''Chavacano, Zamboangueño Chavacano'' (Chabacano de Zamboanga / Zamboangueño Chavacano), spoken in Zamboanga City, Zamboanga Sibugay, Zamboanga del Sur, Zamboanga del Norte, Basilan, Sulu, Tawi-Tawi
Tawi-Tawi, officially the Province of Tawi-Tawi ( tl, Lalawigan ng Tawi-Tawi; Tausug: ''Wilaya' sin Tawi-Tawi''; Sinama: ''Jawi Jawi/Jauih Jauih''), is an island province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim ...
and Semporna, Sabah, Malaysia (360,000 native speakers-Zamboanga City alone as per 2000 census, making it the most spoken form and known form of Chavacano)
** ''Chavacano, Cotabateño'' (Chabacano de Cotabato), spoken in Cotabato
** ''Chavacano, Davaoeño Abakay'' (Chabacano de Davao), spoken in Davao City
See also
* Filipino alphabet * Filipino orthography *Philippine languages
The Philippine languages or Philippinic are a proposed group by R. David Paul Zorc (1986) and Robert Blust (1991; 2005; 2019) that include all the languages of the Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia—except Sama–Bajaw (languag ...
* List of English words of Philippine origin
References
Notes
General references
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * *External links
Linguistic map of the Philippines at Muturzikin.com
Ricardo Maria Nolasco on the diversity of languages in the Philippines
Lawrence R. Reid
webpage of Dr. Lawrence A. Reid. Researcher Emeritus of linguistics at the University of Hawai'i at Manoa. Has researched Philippine languages for decades.
Carl Rubino
webpage of Dr. Carl Rubino. A Filipino linguist who has studied Philippine languages.
by Edmundo Farolan Romero, with a brief Philippine poetry anthology in Spanish.
Salita Blog
by Christopher Sundita. A blog about a variety of issues concerning the languages of the Philippines.
Espaniero
An Online Spanish conversation group for Pinoys
The Language Planning Situation in the Philippines
by Andrew González, FSC
kaibigankastila
webpage of the Spanish culture in the Philippines.
On linguistic mutual intolerance in the Philippines
Filipino Translator
Tagalog Translator Online
Online dictionary for translating Tagalog from/to English, including expressions and latest headlines regarding the Philippines.
Linguistic map of the Philippines
a compilation of lessons about languages of the Philippines. {{DEFAULTSORT:Languages of the Philippines Languages of the Philippines,