Lake Van on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lake Van ( tr, Van Gölü; hy, Վանա լիճ, translit=Vana lič̣; ku, Gola Wanê) is the largest lake in
 Lake Van is across at its widest point. It averages deep. Its greatest known depth is . The surface lies above sea level and the shore length is . It covers and contains (has volume of) .
The western portion of the lake is deepest, with a large basin deeper than lying northeast of
Lake Van is across at its widest point. It averages deep. Its greatest known depth is . The surface lies above sea level and the shore length is . It covers and contains (has volume of) .
The western portion of the lake is deepest, with a large basin deeper than lying northeast of
 Land terraces (remnant dry, upper banks from previous shorelines) above the present shore have long been recognized. On a visit in 1898, geologist Felix Oswald noted three raised beaches at 15, 50 and 100 feet (5, 15 and 30 meters) above the lake then, as well as recently drowned trees. Research in the past century has identified many similar terraces, and the lake's level has fluctuated significantly during that time.
As the lake has no outlet, the level over recent millennia rests on inflow and evaporation.
The water level has vacillated greatly. Investigation by a team including Degens in the early 1980s determined that the highest lake levels ( above the current height) had been during the last ice age, about 18,000 years ago. Approximately 9,500 years ago there was a dramatic drop to more than below the present level. This was followed by an equally-dramatic rise around 6,500 years ago.
As a deep lake with no outlet, Lake Van has accumulated great amounts of sediment washed in from surrounding plains and valleys, and occasionally deposited as ash from eruptions of nearby volcanoes.
This layer of sediment is estimated to be up to thick in places, and has attracted climatologists and vulcanologists interested in drilling cores to examine the layered sediments.
In 1989 and 1990, an international team of geologists led by Stephan Kempe from the University of Hamburg retrieved ten sediment cores from depths up to . Although these cores only penetrated the first few meters of sediment, they provided sufficient varves to give proxy climate data for up to 14,570 years BP.
A team of scientists headed by palaeontologist Professor Thomas Litt at the
Land terraces (remnant dry, upper banks from previous shorelines) above the present shore have long been recognized. On a visit in 1898, geologist Felix Oswald noted three raised beaches at 15, 50 and 100 feet (5, 15 and 30 meters) above the lake then, as well as recently drowned trees. Research in the past century has identified many similar terraces, and the lake's level has fluctuated significantly during that time.
As the lake has no outlet, the level over recent millennia rests on inflow and evaporation.
The water level has vacillated greatly. Investigation by a team including Degens in the early 1980s determined that the highest lake levels ( above the current height) had been during the last ice age, about 18,000 years ago. Approximately 9,500 years ago there was a dramatic drop to more than below the present level. This was followed by an equally-dramatic rise around 6,500 years ago.
As a deep lake with no outlet, Lake Van has accumulated great amounts of sediment washed in from surrounding plains and valleys, and occasionally deposited as ash from eruptions of nearby volcanoes.
This layer of sediment is estimated to be up to thick in places, and has attracted climatologists and vulcanologists interested in drilling cores to examine the layered sediments.
In 1989 and 1990, an international team of geologists led by Stephan Kempe from the University of Hamburg retrieved ten sediment cores from depths up to . Although these cores only penetrated the first few meters of sediment, they provided sufficient varves to give proxy climate data for up to 14,570 years BP.
A team of scientists headed by palaeontologist Professor Thomas Litt at the
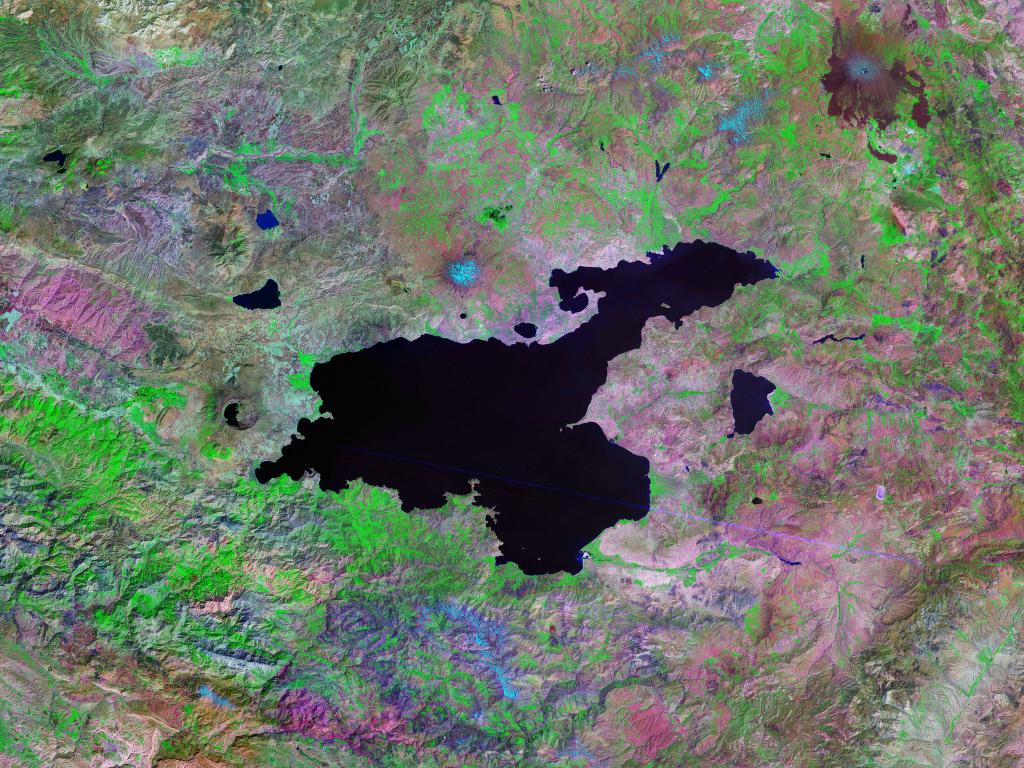 Similar but smaller fluctuations have been seen recently. The level of the lake rose by at least during the 1990s, drowning much agricultural land, and (after a brief period of stability and then retreat) seems to be rising again. The level rose approximately in the 10 years immediately prior to 2004.
Similar but smaller fluctuations have been seen recently. The level of the lake rose by at least during the 1990s, drowning much agricultural land, and (after a brief period of stability and then retreat) seems to be rising again. The level rose approximately in the 10 years immediately prior to 2004.
 Prior to 2018, the only fish known to live in the
Prior to 2018, the only fish known to live in the
 Tushpa, the capital of
Tushpa, the capital of
 Alp Arslan divided the conquered eastern portions of the Byzantine empire among his Turcoman generals, with each ruled as a hereditary
Alp Arslan divided the conquered eastern portions of the Byzantine empire among his Turcoman generals, with each ruled as a hereditary
Van Gölü canavarı gerçek mi? 131 yıl önce Osmanlı gazetesinde manşet olmuş
mynet. 22 April 2020.
 Lake Van occasionally hosts several
Lake Van occasionally hosts several
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
. It lies in the far east of Turkey, in the provinces of Van and Bitlis in the Armenian highlands. It is a saline soda lake
A soda lake or alkaline lake is a lake on the strongly alkaline side of neutrality, typically with a pH value between 9 and 12. They are characterized by high concentrations of carbonate salts, typically sodium carbonate (and related salt complex ...
, receiving water from many small streams that descend from the surrounding mountains. It is one of the world's few endorheic lake
An endorheic lake (also called a sink lake or terminal lake) is a collection of water within an endorheic basin, or sink, with no evident outlet. Endorheic lakes are generally saline as a result of being unable to get rid of solutes left in the l ...
s (a lake having no outlet) of size greater than and has 38% of the country's surface water (including rivers). A volcanic eruption blocked its original outlet in prehistoric times. It is situated at above sea level. Despite the high altitude and winter highs below , high salinity usually prevents it from freezing; the shallow northern section can freeze, but rarely.
Hydrology and chemistry
 Lake Van is across at its widest point. It averages deep. Its greatest known depth is . The surface lies above sea level and the shore length is . It covers and contains (has volume of) .
The western portion of the lake is deepest, with a large basin deeper than lying northeast of
Lake Van is across at its widest point. It averages deep. Its greatest known depth is . The surface lies above sea level and the shore length is . It covers and contains (has volume of) .
The western portion of the lake is deepest, with a large basin deeper than lying northeast of Tatvan
Tatvan ( ) is a city on the western shore of Lake Van. It is the chief city of Tatvan District within Bitlis Province in eastern Turkey, and has about 96,000 inhabitants. The current Mayor is Mehmet Emin Geylani ( AKP).
The district is fully Kurd ...
and south of Ahlat. The eastern arms of the lake are shallower. The Van-Ahtamar portion shelves gradually, with a maximum depth of about on its northwest side where it joins the rest of the lake. The Erciş arm is much shallower, mostly less than , with a maximum depth of about .
The lake water is strongly alkaline ( pH 9.7–9.8) and rich in sodium carbonate and other salts. Some is extracted in salt evaporation pond
A salt evaporation pond is a shallow artificial salt pan designed to extract salts from sea water or other brines. The Salt pans are shallow and large of size because it will be easier for sunlight to travel and reach the sea water. Natural sal ...
s alongside, used in or as detergents.
Geology
Lake Van is primarily a tectonic lake, formed more than 600,000 years ago by the gradual subsidence of a large block of the earth's crust due to movement on several major faults that run through this portion of Eastern Anatolia. The lake's southern margin demarcates: a metamorphic rock zone of the Bitlis Massif and volcanic strata of the Neogene and Quaternary periods. The deep, western portion of the lake is an antidome basin in a tectonic depression. This was formed bynormal Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson
* ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keith Rennie, and Andrew Airlie
* ''Norma ...
and strike-slip faulting and thrusting.
The lake's proximity to the Karlıova Triple Junction
The Karlıova Triple Junction is a geologic triple junction of three tectonic plates: the Anatolian Plate, the Eurasian Plate and the Arabian Plate.
The Karlıova Triple Junction is found where the east-west trending North Anatolian Fault inters ...
has led to molten fluids of the Earth's mantle accumulating in the strata beneath, still driving gradual change. Dominating the lake's northern shore is the stratovolcano Mount Süphan
Mount Süphan ( tr, Süphan Dağı, ku, Sîpanê Xelatê, hy, Սիփան, Sipan) is a stratovolcano located in eastern Turkey, immediately north of Lake Van. It is the second highest volcano in Turkey, with an elevation of , and has the third h ...
. The broad crater of a second, dormant volcano, Mount Nemrut
Mount Nemrut or Nemrud ( tr, Nemrut Dağı; ku, Çiyayê Nemrûdê; hy, Նեմրութ լեռ; Greek: Όρος Νεμρούτ) is a mountain in southeastern Turkey, notable for the summit where a number of large statues are erected around what ...
, is close to the western tip of the lake. There is hydrothermal activity throughout the region.
For much of its history, until the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
, Lake Van has had an outlet towards the southwest. However, the level of this threshold has varied over time, as the lake has been blocked by successive lava flows from Nemrut volcano westward towards the Muş Plain. This threshold has then been lowered at times by erosion.
Bathymetry
The first acoustic survey of Lake Van was performed in 1974. Kempe and Degens later identified three physiographic provinces comprising the lake: *a lacustrine shelf (27% of the lake) from the shore to a clear gradient change *a steeper lacustrine slope (63%) *a deep, relatively flat basin province (10%) in the western center of the lake. The deepest part of the lake is the Tatvan basin, which is almost completely bounded by faults.Prehistoric lake levels
 Land terraces (remnant dry, upper banks from previous shorelines) above the present shore have long been recognized. On a visit in 1898, geologist Felix Oswald noted three raised beaches at 15, 50 and 100 feet (5, 15 and 30 meters) above the lake then, as well as recently drowned trees. Research in the past century has identified many similar terraces, and the lake's level has fluctuated significantly during that time.
As the lake has no outlet, the level over recent millennia rests on inflow and evaporation.
The water level has vacillated greatly. Investigation by a team including Degens in the early 1980s determined that the highest lake levels ( above the current height) had been during the last ice age, about 18,000 years ago. Approximately 9,500 years ago there was a dramatic drop to more than below the present level. This was followed by an equally-dramatic rise around 6,500 years ago.
As a deep lake with no outlet, Lake Van has accumulated great amounts of sediment washed in from surrounding plains and valleys, and occasionally deposited as ash from eruptions of nearby volcanoes.
This layer of sediment is estimated to be up to thick in places, and has attracted climatologists and vulcanologists interested in drilling cores to examine the layered sediments.
In 1989 and 1990, an international team of geologists led by Stephan Kempe from the University of Hamburg retrieved ten sediment cores from depths up to . Although these cores only penetrated the first few meters of sediment, they provided sufficient varves to give proxy climate data for up to 14,570 years BP.
A team of scientists headed by palaeontologist Professor Thomas Litt at the
Land terraces (remnant dry, upper banks from previous shorelines) above the present shore have long been recognized. On a visit in 1898, geologist Felix Oswald noted three raised beaches at 15, 50 and 100 feet (5, 15 and 30 meters) above the lake then, as well as recently drowned trees. Research in the past century has identified many similar terraces, and the lake's level has fluctuated significantly during that time.
As the lake has no outlet, the level over recent millennia rests on inflow and evaporation.
The water level has vacillated greatly. Investigation by a team including Degens in the early 1980s determined that the highest lake levels ( above the current height) had been during the last ice age, about 18,000 years ago. Approximately 9,500 years ago there was a dramatic drop to more than below the present level. This was followed by an equally-dramatic rise around 6,500 years ago.
As a deep lake with no outlet, Lake Van has accumulated great amounts of sediment washed in from surrounding plains and valleys, and occasionally deposited as ash from eruptions of nearby volcanoes.
This layer of sediment is estimated to be up to thick in places, and has attracted climatologists and vulcanologists interested in drilling cores to examine the layered sediments.
In 1989 and 1990, an international team of geologists led by Stephan Kempe from the University of Hamburg retrieved ten sediment cores from depths up to . Although these cores only penetrated the first few meters of sediment, they provided sufficient varves to give proxy climate data for up to 14,570 years BP.
A team of scientists headed by palaeontologist Professor Thomas Litt at the University of Bonn
The Rhenish Friedrich Wilhelm University of Bonn (german: Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn) is a public research university located in Bonn, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It was founded in its present form as the ( en, Rhine ...
has applied for funding from the International Continental Scientific Drilling Program
The International Continental Scientific Drilling Program is a multinational program to further and fund geosciences in the field of Continental Scientific Drilling. Scientific drilling is a critical tool in understanding of Earth processes and s ...
(ICDP) for an akin deeper-drilling project. This expects to find it "stores the climate history of the last 800,000 years—an incomparable treasure house of data which we want to tap for at least the last 500,000 years." A test drilling in 2004 detected evidence of 15 volcanic eruptions in the past 20,000 years.
Recent lake level change
 Similar but smaller fluctuations have been seen recently. The level of the lake rose by at least during the 1990s, drowning much agricultural land, and (after a brief period of stability and then retreat) seems to be rising again. The level rose approximately in the 10 years immediately prior to 2004.
Similar but smaller fluctuations have been seen recently. The level of the lake rose by at least during the 1990s, drowning much agricultural land, and (after a brief period of stability and then retreat) seems to be rising again. The level rose approximately in the 10 years immediately prior to 2004.
Climate
It is in the highest and largestregion
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
of Turkey, which has a Mediterranean-influenced humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
. Average temperatures in July are between 22 and 25 °C, and in January between −3 °C to −12 °C. On some cold winter nights the temperature has reached −30 °C.
The lake, particularly on urban townscape shore tempers the climate, in the city of Van, where the average temperature in July is 22.5 °C, and in January −3.5 °C. The average annual rainfall in the basin, ranges from 400 to 700 mm.Матвеев: Турция �то значительно ниже установленной позже корректной цифры в 161,2 метра
Ecology
 Prior to 2018, the only fish known to live in the
Prior to 2018, the only fish known to live in the brackish water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
of Lake Van was ''Chalcalburnus tarichi
''Alburnus tarichi'', known as the tarek, pearl mullet, Van fish or Van shah kuli, is a species of cyprinid fish, found only in Turkey, where it is the only fish known to inhabit Lake Van. It is endemic to the Lake Van basin. It is locally known ...
'' or Pearl Mullet ( tr, inci kefali), a Cyprinid
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family. It includes the carps, the true minnows, and relatives like the barbs and barbels. Cyprinidae is the largest and most diverse fish family and the largest ver ...
fish related to chub and dace
A dace is a small fish that can be one of many different species. The unmodified name is usually a reference to the common dace (''Leuciscus leuciscus''). This, like most fish called "daces", belongs to the family Cyprinidae, mostly in subfamily ...
, which is caught during the spring floods. In May and June, these fish migrate from the lake to less alkaline water, spawning either near the mouths of the rivers feeding the lake or in the rivers themselves. After spawning season it returns to the lake. In 2018, a new species of fish, which is deemed as ''Oxynoemacheilus ercisianus
''Oxynoemacheilus ercisianus'', the Van loach, is a species of stone loach endemic to the Lake Van
Lake Van ( tr, Van Gölü; hy, Վանա լիճ, translit=Vana lič̣; ku, Gola Wanê) is the largest lake in Turkey. It lies in the far east ...
'', has been discovered inside a microbialite
Microbialite is a benthic sedimentary deposit made of carbonate mud (particle diameter < 5 μm) that is formed with the mediation of microbes. The constituent carbonate mud is a type of
.
103 species of phytoplankton have been recorded in the lake including cyanobacteria, flagellates, diatoms, green algae, and brown algae
Brown algae (singular: alga), comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and p ...
. 36 species of zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
have also been recorded including Rotatoria, Cladocera
The Diplostraca or Cladocera, commonly known as water fleas, are a superorder of small crustaceans that feed on microscopic chunks of organic matter (excluding some predatory forms).
Over 1000 species have been recognised so far, with many more ...
, and Copepoda
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have p ...
in the lake.
In 1991, researchers reported the discovery of tall microbialites in the lake. These are solid towers on the lake bed formed by coccoid cyanobacteria ('' Pleurocapsa'' group) these create mats of aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral, one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate, (the other forms being the minerals calcite and vaterite). It is formed by biological and physical processes, including pre ...
that combine with calcite precipitating out of the lake water.
The region hosts the rare Van cat breed of cat, having – among other things – an unusual fascination with water. The lake is mainly surrounded by fruit orchards and grain fields, interspersed by some non-agricultural trees.
Lake Van monster
According to legend, the lake hosts the mysterious Lake Van Monster that lurks below the surface, 30 to 40 ft long with brown scaly skin, an elongated reptilian head and flippers. Apart from some amateur photographs and videos, there is no physical evidence to prove its existence. The profile resembles an extinct mosasaurus orbasilosaurus
''Basilosaurus'' (meaning "king lizard") is a genus of large, predatory, prehistoric archaeocete whale from the late Eocene, approximately 41.3 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). First described in 1834, it was the first archaeocete and prehistor ...
.
History
 Tushpa, the capital of
Tushpa, the capital of Urartu
Urartu (; Assyrian: ',Eberhard Schrader, ''The Cuneiform inscriptions and the Old Testament'' (1885), p. 65. Babylonian: ''Urashtu'', he, אֲרָרָט ''Ararat'') is a geographical region and Iron Age kingdom also known as the Kingdom of V ...
, near the shores, on the site of what became medieval Van's castle, west of present-day Van city. The ruins of the medieval city of Van are still visible below the southern slopes of the rock on which Van Castle stands.
In 2017, archaeologists from Van Yüzüncü Yil University and a team of independent divers who were exploring Lake Van reported the discovery of a large underwater fortress spanning roughly one kilometer. The team estimates that this fortress was constructed during the Urartian period, based on their visual assessments. The archaeologists believe that the fortress, along with other parts of the ancient city that surrounded it at the time, had slowly become submerged over the millennia by the gradually rising lake.
Armenian kingdoms
The lake was the centre of theArmenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
kingdom of Ararat from about 1000 BC, afterwards of the Satrapy of Armenia
The Satrapy of Armenia (Old Persian: 𐎠𐎼𐎷𐎡𐎴 or 𐎠𐎼𐎷𐎡𐎴𐎹 ), a region controlled by the Orontid dynasty (570–201 BC), was one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC that later became an ind ...
, Kingdom of Greater Armenia, and the Armenian Kingdom of Vaspurakan
Vaspurakan (, Western Armenian pronunciation: ''Vasbouragan'') was the eighth province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, which later became an independent kingdom during the Middle Ages, centered on Lake Van. Located in what is now southeaster ...
.
Along with Lake Sevan
Lake Sevan ( hy, Սևանա լիճ, Sevana lich) is the largest body of water in both Armenia and the Caucasus region. It is one of the largest freshwater high-altitude (alpine) lakes in Eurasia. The lake is situated in Gegharkunik Province, ...
in today's Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
and Lake Urmia
Lake Urmia;
az, اۇرمۇ گؤلۆ, script=Arab, italic=no, Urmu gölü;
ku, گۆلائوو رمیەیێ, Gola Ûrmiyeyê;
hy, Ուրմիա լիճ, Urmia lich;
arc, ܝܡܬܐ ܕܐܘܪܡܝܐ is an endorheic salt lake in Iran. The lake is l ...
in today's Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Van was one of the three great lakes of the Armenian Kingdom, referred to as ''the seas of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
'' (in ancient Assyrian sources: "tâmtu ša mât Nairi" (Upper Sea of Nairi
Nairi ( classical hy, Նայիրի, ''Nayiri'', reformed: Նաիրի, ''Nairi''; , also ''Na-'i-ru'') was the Akkadian name for a region inhabited by a particular group (possibly a confederation or league) of tribal principalities in the Armen ...
), the Lower Sea being Lake Urmia
Lake Urmia;
az, اۇرمۇ گؤلۆ, script=Arab, italic=no, Urmu gölü;
ku, گۆلائوو رمیەیێ, Gola Ûrmiyeyê;
hy, Ուրմիա լիճ, Urmia lich;
arc, ܝܡܬܐ ܕܐܘܪܡܝܐ is an endorheic salt lake in Iran. The lake is l ...
). Over time, the lake was known by various Armenian names, including hy, Վանա լիճ (Lake of Van), Վանա ծով (Sea of Van), Արճեշի ծով (Sea of Arčeš), Բզնունեաց ծով (Sea of Bznunik), Ռշտունեաց ծով (Sea of Rshtunik), and Տոսպայ լիճ (Lake of Tosp).
East Roman Empire
By the 11th century the lake was on the border between the East Roman Empire, with its capital atConstantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
, and the Turko-Persian Seljuk Empire, with its capital at Isfahan. In the uneasy peace between the two empires, local Armenian-Byzantine landowners employed Turcoman gazi
A ''ghazi'' ( ar, غازي, , plural ''ġuzāt'') is an individual who participated in ''ghazw'' (, '' ''), meaning military expeditions or raiding. The latter term was applied in early Islamic literature to expeditions led by the Islamic prophe ...
s and Byzantine akritai
The ''Akritai'' ( el, , singular: ''Akritēs'', ) is a term used in the Byzantine Empire in the 9th–11th centuries to denote the frontier soldiers guarding the Empire's eastern border, facing the Muslim states of the Middle East. Their exploits, ...
for protection. The Greek-speaking Byzantines called the lake ''Thospitis limne'' ( gkm, Θωσπῖτις λίμνη).
In the second half of the 11th century Emperor Romanus IV Diogenes
Romanos IV Diogenes (Greek: Ρωμανός Διογένης), Latinized as Romanus IV Diogenes, was a member of the Byzantine military aristocracy who, after his marriage to the widowed empress Eudokia Makrembolitissa, was crowned Byzantine Em ...
launched a campaign to re-conquer Armenia and head off growing Seljuk control. Diogenes and his large army crossed the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
and confronted a much smaller Seljuk force led by Alp Arslan at the Battle of Manzikert, north of Lake Van on 26 August 1071. Despite their greater numbers, the cumbersome Byzantine force was defeated by the more mobile Turkish horsemen and Diogenes was captured.
Seljuk Empire
 Alp Arslan divided the conquered eastern portions of the Byzantine empire among his Turcoman generals, with each ruled as a hereditary
Alp Arslan divided the conquered eastern portions of the Byzantine empire among his Turcoman generals, with each ruled as a hereditary bey
Bey ( ota, بك, beğ, script=Arab, tr, bey, az, bəy, tk, beg, uz, бек, kz, би/бек, tt-Cyrl, бәк, translit=bäk, cjs, пий/пек, sq, beu/bej, sh, beg, fa, بیگ, beyg/, tg, бек, ar, بك, bak, gr, μπέης) is ...
lik, under overall sovereignty of the Seljuq Empire
The Great Seljuk Empire, or the Seljuk Empire was a high medieval, culturally Turko-Persian, Sunni Muslim empire, founded and ruled by the Qïnïq branch of Oghuz Turks. It spanned a total area of from Anatolia and the Levant in the west to t ...
. Alp Arslan gave the region around Lake Van to his commander Sökmen el-Kutbî, who set up his capital at Ahlat on the western side of the lake. The dynasty of Shah-Armens
The Shah-Armens (lit. 'Kings of Armenia', tr, Ermenşahlar), also known as Ahlatshahs (lit. 'Rulers of Ahlat', tr, Ahlatşahlar), was a Turkoman Sunni Muslim Anatolian beylik founded after the Battle of Manzikert (1071) and centred in Ahlat on t ...
, also known as ''Sökmenler'', ruled this area from 1085 to 1192.
The Ahlatshahs were succeeded by the Ayyubid dynasty.
Ottoman Empire
Following the disintegration of the Seljuq-ruled Sultanate of Rum, Lake Van and its surroundings were conquered by theIlkhanate
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm ...
Mongols, and later switched hands between the Ottoman Empire and Safavid Iran until Sultan Selim I
Selim I ( ota, سليم الأول; tr, I. Selim; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute ( tr, links=no, Yavuz Sultan Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite las ...
took control for good.
Reports of the Lake Van Monster surfaced in the late 1800s and gained popularity. A news article was published by ''Saadet Gazetesi'' issue number 1323, dated 28 Shaban 1306 Hijri year
The Hijri year ( ar, سَنة هِجْريّة) or era ( ''at-taqwīm al-hijrī'') is the era used in the Islamic lunar calendar. It begins its count from the Islamic New Year in which Muhammad and his followers migrated from Mecca to Yathr ...
, corresponding to 29 April 1889 during the reign of Sultan Abdul Hamid II.mynet. 22 April 2020.
Architecture
Near the Van Fortress and the southern shore, onAkdamar Island
Akdamar Island ( tr, Akdamar Adası, ku, Girava Axtamarê), also known as Aghtamar ( hy, Աղթամար, translit=Aġt’amar) or Akhtamar ( hy, Ախթամար, translit=Axt’amar), is the second largest of the four islands in Lake Van, in east ...
lies the 10th century Cathedral of the Holy Cross, Aghtamar
The Cathedral of the Holy Cross ( hy, Սուրբ Խաչ եկեղեցի, translit=Surp Khachʿ egeghetsʿi, tr, Akdamar Kilisesi or ) on Aghtamar Island, in Lake Van in eastern Turkey, is a medieval Armenian Apostolic cathedral, built as a palat ...
( hy, Սուրբ Խաչ, Surb Khach), which served as a royal church to the kingdom of Vaspurakan
Vaspurakan (, Western Armenian pronunciation: ''Vasbouragan'') was the eighth province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, which later became an independent kingdom during the Middle Ages, centered on Lake Van. Located in what is now southeaster ...
. The ruins of Armenian monasteries also exist on the other three islands of Lake Van: Lim, Arter, and Ktuts. The area around Lake Van was also the home to a large number Armenian monasteries, among the most prominent of these being the 10th century Narekavank and the 11th century Varagavank, the former now destroyed.
The Ahlatshahs left a large number of historic headstones
A headstone, tombstone, or gravestone is a stele or marker, usually stone, that is placed over a grave. It is traditional for burials in the Christian, Jewish, and Muslim religions, among others. In most cases, it has the deceased's nam ...
in and around the town of Ahlat. Local administrators are currently trying to have the tombstones included in UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
's World Heritage List
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
, where they are currently listed tentatively.
Transportation
The railway connecting Turkey andIran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
was built in the 1970s, sponsored by CENTO
The Middle East Treaty Organization (METO), also known as the Baghdad Pact and subsequently known as the Central Treaty Organization (CENTO), was a military alliance of the Cold War. It was formed in 24 February 1955 by Iran, Iraq, Pakistan, Tur ...
. It uses a train ferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry railway vehicles. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the front and/or rear to give access to the wharves. In the United States, train ...
(ferry for decanted passengers) across between the cities Tatvan
Tatvan ( ) is a city on the western shore of Lake Van. It is the chief city of Tatvan District within Bitlis Province in eastern Turkey, and has about 96,000 inhabitants. The current Mayor is Mehmet Emin Geylani ( AKP).
The district is fully Kurd ...
and Van, rather than building tracks around rugged terrain. This limits passenger capacity. In May 2008 talks started between Turkey and Iran to replace the ferry with a double-track electrified railway.
In December 2015 the new generation of train ferries
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry railway vehicles. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the front and/or rear to give access to the wharves. In the United States, train f ...
operated by the Turkish State Railways
The State Railways of the Republic of Turkey ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti Devlet Demiryolları), abbreviated as TCDD, is a government-owned national railway company responsible with the ownership and maintenance of railway infrastructure in Turkey ...
, the largest of their kind in Turkey, entered service in Lake Van.
Ferit Melen Airport abuts Van. Turkish Airlines
Turkish Airlines ( Turkish: ''Türk Hava Yolları'') is the national flag carrier airline of Turkey. , it operates scheduled services to 340 destinations in Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas, making it the largest mainline carrier in the ...
, AnadoluJet
AnadoluJet is a brand of Turkish Airlines operating as a regional airline. It operates domestic flights as well as flights to Northern Cyprus, Western Europe and Western Asia for its parent company.
History
The brand was created on 23 April 200 ...
, Pegasus Airlines
Pegasus Airlines ( tr, Pegasus Hava Taşımacılığı A.Ş.) (), sometimes stylized as Flypgs, is a Turkish low-cost carrier headquartered in the Kurtköy area of Pendik, Istanbul with bases at several Turkish airports.
History
On 1 Decemb ...
, and SunExpress are the airlines which have regular flights.
Sports
water sports
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a s ...
, sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, windsurfer, or kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (land yacht) over a chosen cou ...
, and inshore powerboat racing
Inshore powerboat racing is a form of water-based motorsport using powerboats in sheltered or inland stretches of water, including lakes, rivers, docks and sheltered bays. It is often referred to as circuit powerboat racing because of the freque ...
events, such as the UIM World Offshore 225 Championship's IOC Van Grand Prix, and the Van Lake Festival.
Islands
*Adır Island
Adır Island ( tr, Adır Adası) or Lim Island ( hy, Լիմ կղզի ''Lim kghzi'', ku, Girava Lîm), is the largest island in Lake Van, located in the North East part of the lake. During the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was ...
*Akdamar Island
Akdamar Island ( tr, Akdamar Adası, ku, Girava Axtamarê), also known as Aghtamar ( hy, Աղթամար, translit=Aġt’amar) or Akhtamar ( hy, Ախթամար, translit=Axt’amar), is the second largest of the four islands in Lake Van, in east ...
*Çarpanak Island
Çarpanak Island ( tr, Çarpanak Adası) or Ktuts or Ktouts ( hy, Կտուց կղզի ''Ktuts kghzi''), is a small island in Lake Van. It is now uninhabited, but formerly contained an Armenian monastery called Ktuts. The ruins of it can still b ...
* Kuş Island
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control Eastern Anatolia Region Van Van Van Landforms of Van Province Landforms of Bitlis Province Van