K–12 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
K–12, from
 The expression "K–12" is a shortening of
The expression "K–12" is a shortening of
kindergarten
Kindergarten is a preschool educational approach based on playing, singing, practical activities such as drawing, and social interaction as part of the transition from home to school. Such institutions were originally made in the late 18th ce ...
to 12th grade
Twelfth grade, 12th grade, senior year, or grade 12 is the final year of secondary school in most of North America. In other regions, it may also be referred to as class 12 or Year 13. In most countries, students are usually between the ages of 17 ...
, is an American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances i ...
expression that indicates the range of years of publicly supported primary and secondary education
Secondary education or post-primary education covers two phases on the International Standard Classification of Education scale. Level 2 or lower secondary education (less commonly junior secondary education) is considered the second and final pha ...
found in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, which is similar to publicly supported school grades before college in several other countries, such as Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, Australia, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, China, Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula and sharing a land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eas ...
, and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
.
History
U.S. public education was conceived of in the late 18th century. In 1790, Pennsylvania became the first state to require some form of free education for everyone regardless of whether they could afford it. New York passed similar legislation in 1805. In 1820, Massachusetts became the first state to create a tuition-free high school, Boston English. The first K–12 public school systems appeared in the early 19th century. In the 1830s and 1840s, Ohioans were taking a significant interest in the idea of public education. At that point in time, schools were commonly operated independently of each other, with little attempt at uniformity. The Akron School Law of 1847 changed this. The city of Akron unified the operations, curriculum and funding of local schools into a single public school district: In 1849, the state of Ohio enacted a law modeled after the Akron law which extended the idea of school districts to cover the rest of the state. By 1930, all 48 states had passed laws making education compulsory, and in 1965, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA), which committed the federal government to significant ongoing expenditures to each state for the purpose of sustaining local K–12 school systems. The ESEA essentially made K–12 education the law of the land. Since its inception, public K–12 has been debated and subject to several waves of reform throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. In the 1980s, Reagan's 'A Nation at Risk' initiative included provisions requiring public education to be evaluated based on standards, and teacher pay to be based on evaluations. In the 1990s, the Goals 2000 Act and the “Improving America’s Schools” act provided additional federal funding to states to bolster local K–12 systems. This was followed in the 2000s by a rigorous uptick in standards-based evaluations with the No Child Left Behind Act, and the Race to the Top Act. In 2015, President Barack Obama signed theEvery Student Succeeds Act
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) is a US law passed in December 2015 that governs the United States K–12 public education policy. The law replaced its predecessor, the No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB), and modified but did not eliminate pr ...
(ESSA), which returned some power to state governments with respect to evaluations and standards.
Etymology
 The expression "K–12" is a shortening of
The expression "K–12" is a shortening of kindergarten
Kindergarten is a preschool educational approach based on playing, singing, practical activities such as drawing, and social interaction as part of the transition from home to school. Such institutions were originally made in the late 18th ce ...
(K) for 5–6 year olds through twelfth grade
Twelfth grade, 12th grade, senior year, or grade 12 is the final year of secondary school in most of North America. In other regions, it may also be referred to as class 12 or Year 13. In most countries, students are usually between the ages of 17 ...
(12) for 17–18 year-olds, as the first and last grade
Grade most commonly refers to:
* Grade (education), a measurement of a student's performance
* Grade, the number of the year a student has reached in a given educational stage
* Grade (slope), the steepness of a slope
Grade or grading may also ref ...
s,
respectively, of free education
Free education is education funded through government spending or charitable organizations rather than tuition funding. Many models of free higher education have been proposed. Primary school and other comprehensive or compulsory education is fr ...
in these countries. The related term "P–12" is also occasionally used in Australia and the United States to refer to the sum of K–12 plus preschool education
A preschool, also known as nursery school, pre-primary school, or play school or creche, is an educational establishment or learning space offering early childhood education to children before they begin compulsory education at primary schoo ...
.
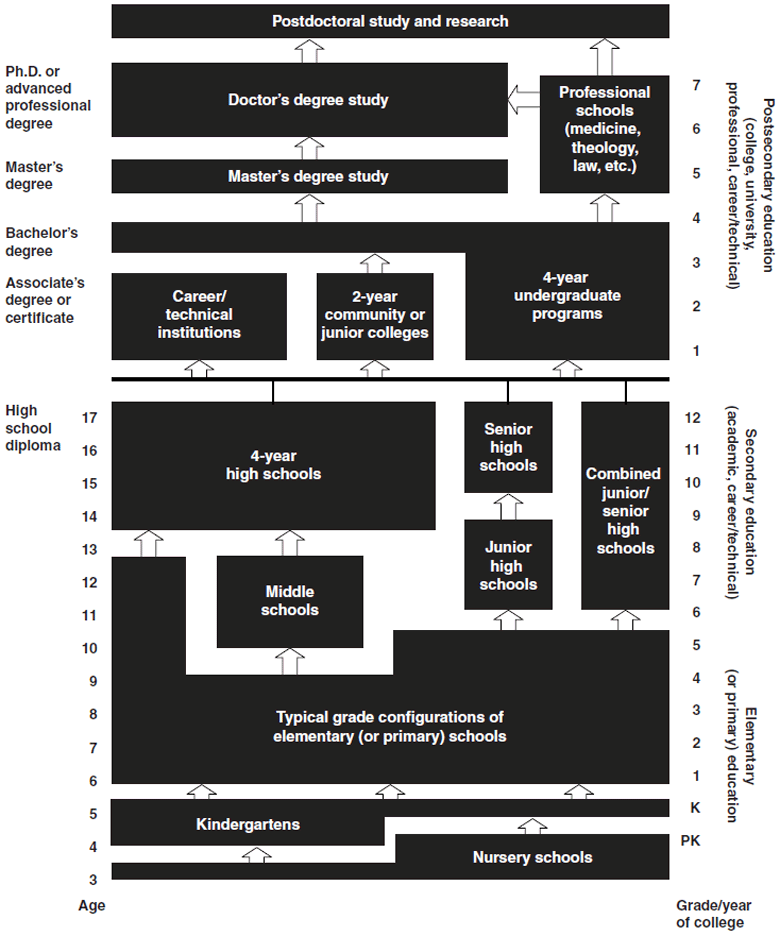
The image at the right illustrates the education system in the United States. The table shows the progression of the education system starting with the basic K–12 system then progressing through post-secondary education. K–14 refers to K–12 plus two years of post-secondary where training was received from vocational-technical institutions or community or junior colleges. K-16 is 12 years of compulsory education plus a 4-year undergrad program. The K numbers refer to the years of educational attainment and continues to progress upward accordingly depending on the degree being sought.
Usage
The term is often used as a kind of shorthand to collectively refer to the entirety of primary and secondary education, as it is much easier than having to say one is referring in the aggregate to elementary, middle, and high school education. However, it is rare for a school district to actually teach all K–12 grades at one unified school campus. Even the smallest school districts try to maintain, at a minimum, a two-tier distinction between an elementary school (K–8) and a high school (9–12). The term is often used in school website URLs, generally appearing before thecountry code top-level domain
A country code top-level domain (ccTLD) is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, sovereign state, or dependent territory identified with a country code. All ASCII ccTLD identifiers are two letters long, and all ...
(or in the United States, the state top-level domain). The terms "PK–12", "PreK–12", or "Pre-K–12" are sometimes used to add pre-kindergarten.
It is also used by American multinationals selling into the educational sector, such as Dell where UK customers are presented with this as a market segment choice.
P–12
In Australia, P–12 is sometimes used in place of K–12, particularly inQueensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
, where it is used as an official term in the curriculum framework. P–12 schools serve children for the thirteen years from prep
PowerPC Reference Platform (PReP) was a standard system architecture for PowerPC-based computer systems (as well as a reference implementation) developed at the same time as the PowerPC processor architecture. Published by IBM in 1994, it allo ...
until Year 12, without including the separate kindergarten component. In Canada (Nova Scotia) P–12 is used commonly in place of K–12 and serves students from grade Primary through 12.
K–14, K–16, K–18 and K–20
K–14 education also includescommunity college
A community college is a type of educational institution. The term can have different meanings in different countries: many community colleges have an "open enrollment" for students who have graduated from high school (also known as senior se ...
s (the first two years of university). K–16 education adds a four-year undergraduate university degree. For simplicity purposes education shorthand was created to denote specific education levels of achievement. This shorthand is commonly used in articles, publications and educational legislation. The following list contains the most commonly found shorthand descriptors:
* P–14: Pre-school to associate degree
* P–16: Pre-school to bachelor's degree
* P–18: Pre-school to master's degree
* P–20: Pre-school to graduate degree
* K–14: Kindergarten to associate degree
* K–16: Kindergarten to bachelor's degree
* K–18: Kindergarten to master's degree
* K–20: Kindergarten to graduate degree
The Career Technical Education (CTE) Unit of the California Community College Economic Development and Workforce Preparation Division focuses on program coordination and advocacy, policy development and coordination with K–18 workforce preparation and career and technical education systems.
The ASCCC Chancellor's Office Career Technical Education (CTE) Unit of the Economic Development and Workforce Preparation Division focuses on program coordination and advocacy, policy development and coordination with K–18 workforce preparation and career and technical education systems. Responsible for the implementation of the Vocational and Technical Education Act (VTEA), managing and coordinating activities that impact other interagency and intra-agency objectives. In addition, the CTE Unit is also responsible for the development, dissemination, and implementation of the California State Plan and the annual performance reports.
Further reference to K–18 education can be found in this publication by Ann Diver-Stamnes and Linda Catelli in chapter 4 "College/University Partnership Projects for Instituting Change and Improvement in K–18 Education".
See also
*Day care
Child care, otherwise known as day care, is the care and supervision of a child or multiple children at a time, whose ages range from two weeks of age to 18 years. Although most parents spend a significant amount of time caring for their child(r ...
* All-through school
Notes
References
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:K-12 Educational years Educational stages Education in the United States