Khowar alphabet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Khowar alphabet is the
 The Khowar language developed during the rule of Mehtar of Chitral State. Since the early twentieth century Khowar has been written in the Khowar alphabet, which is based on the Urdu alphabet and uses the Nasta'liq script. Prior to that, the language was carried on through oral tradition. Today Urdu and English are the official languages and the only major literary usage of Khowar is in both poetry and prose composition. Khowar has also been occasionally written in a version of the Roman script called Roman Khowar since the 1960s. Despite the invention of the Khowar typewriter in 1996, Khowar newsletters and newspapers continued to be published from handwritten scripts by the Khowar authors until the late 1990s. The Monthly Zhang is the first newsletter was the first Khowar
The Khowar language developed during the rule of Mehtar of Chitral State. Since the early twentieth century Khowar has been written in the Khowar alphabet, which is based on the Urdu alphabet and uses the Nasta'liq script. Prior to that, the language was carried on through oral tradition. Today Urdu and English are the official languages and the only major literary usage of Khowar is in both poetry and prose composition. Khowar has also been occasionally written in a version of the Roman script called Roman Khowar since the 1960s. Despite the invention of the Khowar typewriter in 1996, Khowar newsletters and newspapers continued to be published from handwritten scripts by the Khowar authors until the late 1990s. The Monthly Zhang is the first newsletter was the first Khowar
right-to-left
In a script (commonly shortened to right to left or abbreviated RTL, RL-TB or R2L), writing starts from the right of the page and continues to the left, proceeding from top to bottom for new lines. Arabic, Hebrew, Persian, Pashto, Urdu, Kashmir ...
alphabet
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllab ...
used for the Khowar language
Khowar () or Chitrali, is an Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken in Chitral and surrounding areas in Pakistan.
Khowar is the lingua franca of Chitral, and it is also spoken in the Gupis-Yasin and Ghizer districts of Gilgit-Baltistan, as ...
. It is a modification of the Urdu alphabet
The Urdu alphabet (), is the right-to-left alphabet used for Urdu. It is a modification of the Persian script, which is itself a derivative of the Arabic script. The Urdu alphabet has up to 39 or 40 distinct letters with no distinct letter ...
, which is itself a derivative of the Persian alphabet
The Persian alphabet ( fa, الفبای فارسی, Alefbâye Fârsi) is a writing system that is a version of the Arabic script used for the Persian language spoken in Iran (Western Persian) and Afghanistan ( Dari Persian) since the 7th cen ...
and Arabic alphabet and uses the calligraphic Nastaʿlīq script
''Nastaliq'' (; fa, , ), also romanized as ''Nastaʿlīq'', is one of the main calligraphic hands used to write the Perso-Arabic script in the Persian and Urdu languages, often used also for Ottoman Turkish poetry, rarely for Arabic. ''Nas ...
.
History
 The Khowar language developed during the rule of Mehtar of Chitral State. Since the early twentieth century Khowar has been written in the Khowar alphabet, which is based on the Urdu alphabet and uses the Nasta'liq script. Prior to that, the language was carried on through oral tradition. Today Urdu and English are the official languages and the only major literary usage of Khowar is in both poetry and prose composition. Khowar has also been occasionally written in a version of the Roman script called Roman Khowar since the 1960s. Despite the invention of the Khowar typewriter in 1996, Khowar newsletters and newspapers continued to be published from handwritten scripts by the Khowar authors until the late 1990s. The Monthly Zhang is the first newsletter was the first Khowar
The Khowar language developed during the rule of Mehtar of Chitral State. Since the early twentieth century Khowar has been written in the Khowar alphabet, which is based on the Urdu alphabet and uses the Nasta'liq script. Prior to that, the language was carried on through oral tradition. Today Urdu and English are the official languages and the only major literary usage of Khowar is in both poetry and prose composition. Khowar has also been occasionally written in a version of the Roman script called Roman Khowar since the 1960s. Despite the invention of the Khowar typewriter in 1996, Khowar newsletters and newspapers continued to be published from handwritten scripts by the Khowar authors until the late 1990s. The Monthly Zhang is the first newsletter was the first Khowar newspaper
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background.
Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, spor ...
to use ''Nasta’liq'' computer-based composition. There are efforts under way to develop more sophisticated and user-friendly Khowar support on computers and the internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, p ...
. Nowadays, nearly all Khowar newspapers, magazines, journals, and periodicals are composed on computers via various Khowar software programs.
Nasta'liq
The Nasta'liq calligraphic writing style began as a Persian mixture of scripts Naskh and Ta'liq. Nasta'liq is more cursive and flowing than its Naskh counterpart.Alphabet
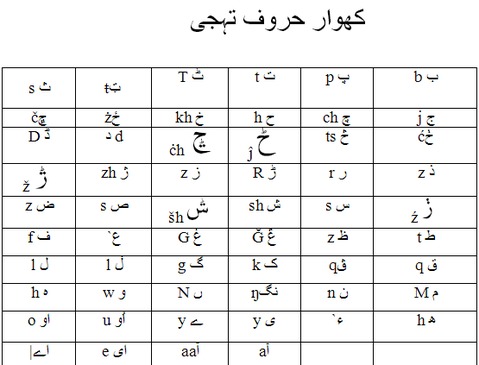
A list of the letters of the Khowar alphabet and their pronunciation is given below. Khowar contains many historical spellings from Arabic and Persian, and therefore has many irregularities. The Arabic letters ''yaa'' and ''haa'' both have two variants in Khowar: one of the ''yaa'' variants is used at the ends of words for the sound , and one of the ''haa'' variants is used to indicate the aspirated andbreathy voiced
Breathy voice (also called murmured voice, whispery voice, soughing and susurration) is a phonation in which the vocal folds vibrate, as they do in normal (modal) voicing, but are adjusted to let more air escape which produces a sighing-like ...
consonants. The retroflex consonant
A retroflex ( /ˈɹɛtʃɹoːflɛks/), apico-domal ( /əpɪkoːˈdɔmɪnəl/), or cacuminal () consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the h ...
s needed to be added as well; this was accomplished by placing a superscript (''to'e'') above the corresponding dental consonant
A dental consonant is a consonant articulated with the tongue against the upper teeth, such as , . In some languages, dentals are distinguished from other groups, such as alveolar consonants, in which the tongue contacts the gum ridge. Dental ...
s. Several letters which represent distinct consonants in Arabic are conflated in Persian, and this has carried over to Khowar. Some of the original Arabic letters are not used in Khowar.
This is the list of the Khowar letters, giving the consonant pronunciation. Many of these letters also represent vowel sounds.
Vowels
Vowel
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (len ...
s in Khowar are represented by letters that are also considered consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced w ...
s. Many vowel sounds can be represented by one letter. Confusion can arise, but context is usually enough to figure out the correct sound.
Vowel chart
This is a list of Khowar vowels found in the initial, medial, and final positions.Short vowels
Short vowel
In linguistics, vowel length is the perceived length of a vowel sound: the corresponding physical measurement is duration. In some languages vowel length is an important phonemic factor, meaning vowel length can change the meaning of the word, ...
s ("a", "i", "u") are represented by marks above and below a consonant.
''Alif''
Alif (ا) is the first letter of the Khowar alphabet, and it is used exclusively as a vowel. At the beginning of a word, alif can be used to represent any of the short vowels, e.g. ابدار abdar, اسم ism, اردو Urdu. Also at the beginning, an alif (ا) followed by either wā'o (و) or ye (ی) represents a long vowel sound. However, wā'o (و) or ye (ی) alone at the beginning represents a consonant. Alif also has a variant, call alif madd (آ). It is used to represent a long "ā" at the beginning of a word, e.g. آپک āpak, آدیمزاد ādmzaad. At the middle or end of a word, long ā is represented simply by ''alif'' (ا), e.g. باغ bāgh, آرام ārām.''Wā'o''
Wā'o is used to render the vowels "ū", "o", and "au". It also renders the consonants "w" and 'v', but many people get confused between these two sounds.''Ye''
Ye is divided into two variants: choṭī ye and baṛī ye. ''Choṭī ye'' (ی) is written in all forms exactly as in Persian. It is used for the long vowel "ī" and the consonant "y". ''Baṛī ye'' (ے) is used to render the vowels "e" and "ai" ( and respectively). ''Baṛī ye'' is distinguished in writing from choṭī ye only when it comes at the end of a word.Use of specific letters
Retroflex letters
Retroflex consonant
A retroflex ( /ˈɹɛtʃɹoːflɛks/), apico-domal ( /əpɪkoːˈdɔmɪnəl/), or cacuminal () consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the h ...
s were not present in the Persian alphabet
The Persian alphabet ( fa, الفبای فارسی, Alefbâye Fârsi) is a writing system that is a version of the Arabic script used for the Persian language spoken in Iran (Western Persian) and Afghanistan ( Dari Persian) since the 7th cen ...
, and therefore had to be created specifically for Khowar. This was accomplished by placing a superscript ط (''to'e'') above the corresponding dental consonant
A dental consonant is a consonant articulated with the tongue against the upper teeth, such as , . In some languages, dentals are distinguished from other groups, such as alveolar consonants, in which the tongue contacts the gum ridge. Dental ...
s.
''Do chashmī he''
The letter ''do chashmī he'' (ھ) is used in native Hindustānī words, for aspiration and breathy voice. The consonants are sometimes classified as separate letters, although they are digraphs.References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Khowar Alphabet Khowar language Arabic alphabets for South Asian languages