Kapteyn's Star on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kapteyn's Star is a class M1
 Attention was first drawn to what is now known as Kapteyn's Star by the Dutch astronomer
Attention was first drawn to what is now known as Kapteyn's Star by the Dutch astronomer
 Based upon
Based upon  Kapteyn's Star is between one quarter and one third the size and mass of the Sun and has a much cooler
Kapteyn's Star is between one quarter and one third the size and mass of the Sun and has a much cooler
Kapteyn's Star
at SolStations.com. and as a cold
SolStation.com: Kapteyn's Star
Press release on planetary system
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kapteyn's Star M-type main-sequence stars M-type subdwarfs BY Draconis variables High-proper-motion stars Local Bubble Hypothetical planetary systems Pictor (constellation) CD-45 01841
red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
subdwarf
A subdwarf, sometimes denoted by "sd", is a star with luminosity class VI under the Yerkes spectral classification system. They are defined as stars with luminosity 1.5 to 2 magnitudes lower than that of main-sequence stars of the same spectral ...
about 12.83 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s from Earth in the southern constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
Pictor
Pictor is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, located between the star Canopus and the Large Magellanic Cloud. Its name is Latin for Painting, painter, and is an abbreviation of the older name Equuleus Pictoris (the "painter's ...
; it is the closest halo
Halo, halos or haloes usually refer to:
* Halo (optical phenomenon)
* Halo (religious iconography), a ring of light around the image of a head
HALO, halo, halos or haloes may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Video games
* ''Halo'' (franch ...
star to the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
. With a magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
of nearly 9 it is visible through binoculars
Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes (binocular vision) when viewing distant objects. Most binoculars are sized to be held ...
or a telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe ...
.
Its diameter is 30% of the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
's, but its luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic power (light), the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object over time. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a st ...
just 1.2% that of the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
. It may have once been part of the globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of membe ...
Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri (ω Cen, NGC 5139, or Caldwell 80) is a globular cluster in the constellation of Centaurus that was first identified as a non-stellar object by Edmond Halley in 1677. Located at a distance of , it is the largest-known globular clust ...
, itself a likely dwarf galaxy swallowed up by the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye ...
in the distant past. The discovery of two planets— Kapteyn b and Kapteyn c—was announced in 2014, but had a mixed history of rejections and confirmations, until a 2021 study refuted both planets. The "planets" are in fact artifacts of the star's rotation and activity.
History of observations
 Attention was first drawn to what is now known as Kapteyn's Star by the Dutch astronomer
Attention was first drawn to what is now known as Kapteyn's Star by the Dutch astronomer Jacobus Kapteyn
Prof Jacobus Cornelius Kapteyn FRS FRSE LLD (19 January 1851 – 18 June 1922) was a Dutch astronomer. He carried out extensive studies of the Milky Way and was the discoverer of evidence for galactic rotation. Kapteyn was also among the fi ...
in 1898. Under the name CPD-44 612 it was included in the ''Cape photographic Durchmusterung
In astronomy, Durchmusterung or Bonner Durchmusterung (BD) is an astrometric star catalogue of the whole sky, compiled by the Bonn Observatory in Germany from 1859 to 1903. The name comes from ('run-through examination'), a German word used for ...
for the equinox 1875 (−38 to −52)'' by David Gill and Jacobus Cornelius Kapteyn in 1897. This catalogue was based on Gill's observations from the Cape Observatory
South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO) is the national centre for optical and infrared astronomy in South Africa. It was established in 1972. The observatory is run by the National Research Foundation of South Africa. The facility's funct ...
in 1885–1889 and was created in collaboration with Kapteyn. While he was reviewing star charts and photographic plates, Kapteyn noted that a star, previously catalogued in 1873 by B. A. Gould as C.Z. V 243, seemed to be missing. However, Robert T. A. Innes
Robert Thorburn Ayton Innes FRSE FRAS (10 November 1861 – 13 March 1933) was a Scottish astronomer best known for discovering Proxima Centauri in 1915, and numerous binary stars. He was also the first astronomer to have seen the Great January ...
found an uncatalogued star about 15 arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
s away from the absent star's position. It became clear that the star had a very high proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of the observed changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects in the sky, as seen from the center of mass of the Solar System, compared to the abstract background of the more dista ...
of more than 8 arcseconds per year and had moved significantly. Later, CPD-44 612 came to be referred to as Kapteyn's Star although equal credit should be accorded to Robert Innes. At the time of its discovery it had the highest proper motion of any star known, dethroning Groombridge 1830
Groombridge 1830 (also known as 1830 Groombridge or Argelander's Star)Peters, C. A. F.; "On the Parallax of Argelander's Star", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, December 1853, v.50, p.302, is a star in the constellatio ...
. In 1916, Barnard's Star
Barnard's Star is a red dwarf about six light-years from Earth in the constellation of Ophiuchus. It is the fourth-nearest-known individual star to the Sun after the three components of the Alpha Centauri system, and the closest star in the ...
was found to have an even larger proper motion. In 2014, two super-Earth planet candidates in orbit around the star were announced, but later refuted.
Characteristics
 Based upon
Based upon parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects ...
measurements, Kapteyn's Star is from the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
. It came within of the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
about 10,900 years ago and has been moving away since that time. Kapteyn's Star is distinctive in a number of regards: it has a high radial velocity, orbits the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye ...
retrograde, and is the nearest-known halo
Halo, halos or haloes usually refer to:
* Halo (optical phenomenon)
* Halo (religious iconography), a ring of light around the image of a head
HALO, halo, halos or haloes may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Video games
* ''Halo'' (franch ...
star to the Sun. It is a member of a moving group
In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the Observational astronomy, observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space.
Stellar kinematics encompasses the measurement of stellar Velocity, velocities in the Milky W ...
of stars that share a common trajectory through space, named the Kapteyn moving group. Based upon their element abundances, these stars may once have been members of Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri (ω Cen, NGC 5139, or Caldwell 80) is a globular cluster in the constellation of Centaurus that was first identified as a non-stellar object by Edmond Halley in 1677. Located at a distance of , it is the largest-known globular clust ...
, a globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of membe ...
that is thought to be the remnant of a dwarf galaxy
A dwarf galaxy is a small galaxy composed of about 1000 up to several billion stars, as compared to the Milky Way's 200–400 billion stars. The Large Magellanic Cloud, which closely orbits the Milky Way and contains over 30 billion stars, is ...
that merged with the Milky Way. During this process, the stars in the group, including Kapteyn's Star, may have been stripped away as tidal debris.
 Kapteyn's Star is between one quarter and one third the size and mass of the Sun and has a much cooler
Kapteyn's Star is between one quarter and one third the size and mass of the Sun and has a much cooler effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
at about 3500 K, with some disagreement in the exact measurements between different observers. The stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grati ...
is sdM1, which indicates that it is a subdwarf
A subdwarf, sometimes denoted by "sd", is a star with luminosity class VI under the Yerkes spectral classification system. They are defined as stars with luminosity 1.5 to 2 magnitudes lower than that of main-sequence stars of the same spectral ...
with a luminosity lower than that of a main-sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hert ...
star at the same spectral type of M1. The abundance of elements other than hydrogen and helium, what astronomers term the metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the abundance of elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal physical matter in the Universe is either hydrogen or helium, and astronomers use the word ''"metals"'' as a ...
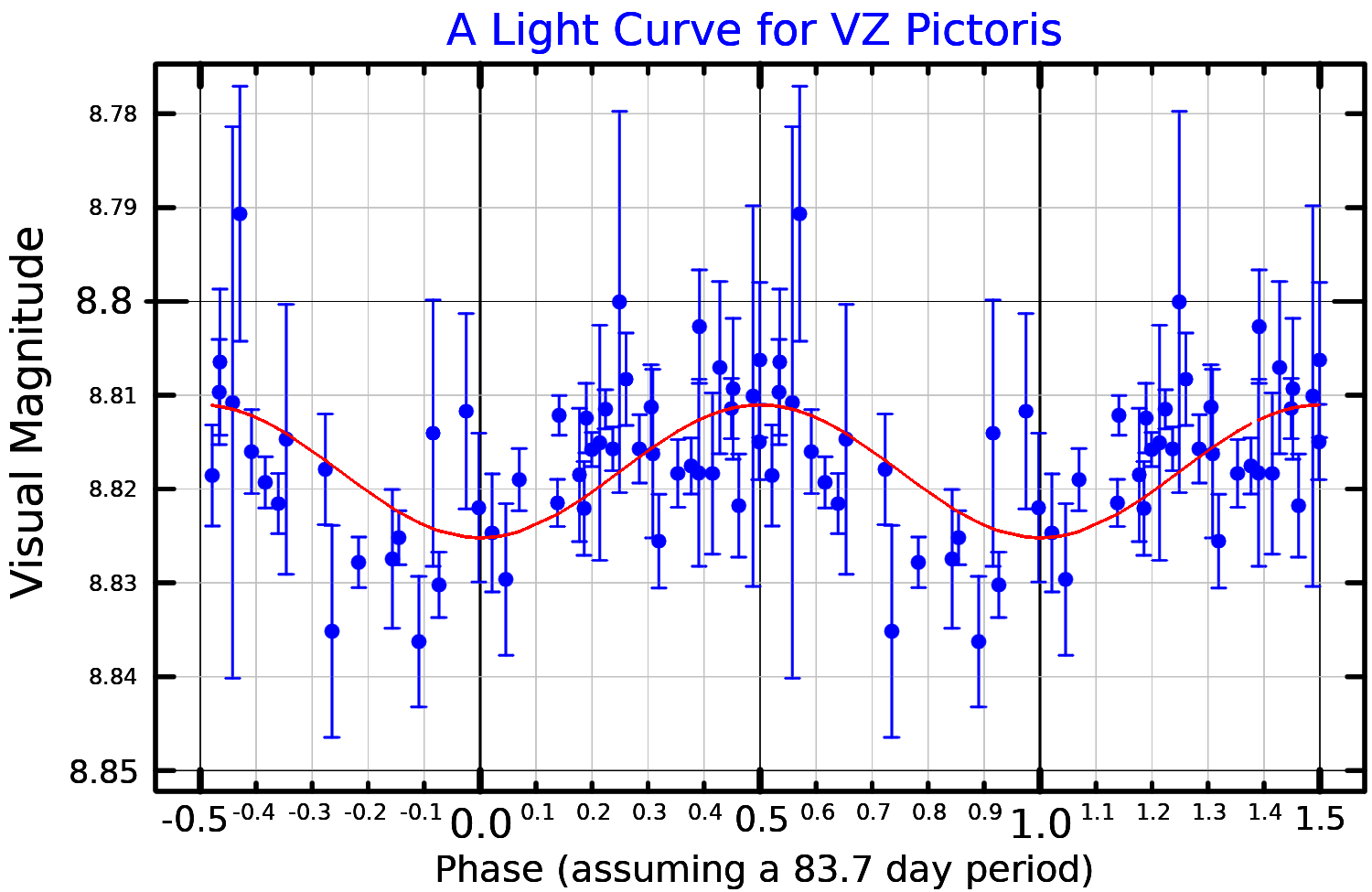
, is about 14% of the abundance in the Sun. It is a variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as ...
of the BY Draconis type with the identifier
An identifier is a name that identifies (that is, labels the identity of) either a unique object or a unique ''class'' of objects, where the "object" or class may be an idea, physical countable object (or class thereof), or physical noncountable ...
VZ Pictoris. This means that the luminosity of the star changes because of magnetic activity
A stellar magnetic field is a magnetic field generated by the motion of conductive plasma inside a star. This motion is created through convection, which is a form of energy transport involving the physical movement of material. A localized magn ...
in the chromosphere
A chromosphere ("sphere of color") is the second layer of a star's atmosphere, located above the photosphere and below the solar transition region and corona. The term usually refers to the Sun's chromosphere, but not exclusively.
In the Su ...
coupled with rotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
moving the resulting star spot
Starspots are stellar phenomena, so-named by analogy with sunspots.
Spots as small as sunspots have not been detected on other stars, as they would cause undetectably small fluctuations in brightness. The commonly observed starspots are in gene ...
s into and out of the line of sight with respect to the Earth.
Search for planets
In 2014, Kapteyn's Star was announced to host two planets, Kapteyn b and Kapteyn c. Kapteyn b was described as the oldest-known potentiallyhabitable planet
Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and maintain environments hospitable to life. Life may be generated directly on a planet or satellite endogenously or be transferred to it from a ...
, estimated to be 11 billion years old, while Kapteyn c was described as beyond the host star's habitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), or simply the habitable zone, is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressure.J. F. Kas ...
,at SolStations.com.
Super-Earth
A super-Earth is an extrasolar planet with a mass higher than Earth's, but substantially below those of the Solar System's ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, which are 14.5 and 17 times Earth's, respectively.
The term "super-Earth" refers only to ...
. However, Robertson et al. (2015) noted that the orbital period of Kapteyn b is an integer fraction (1/3) of their estimated stellar rotation period and thus the planetary signal is most likely an artifact of stellar activity. The authors did not rule out the existence of Kapteyn c, calling for further observation. Guinan et al. (2016) (as well as earlier authors) found a lower value for the stellar rotation, which lended support to the original planetary finding.
In 2021, a new analysis found no evidence for either planet, and found that the observed radial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the temporal rate of change, rate of change of the distance or Slant range, range between the two points. It is e ...
signals are in fact artifacts of the star's rotation and activity, after the rotational period of the star was refined, with a rotational period very similar to that of candidate c.
The purported planets were thought to be close to a 5:2 period commensurability, but resonances could not be confirmed. Dynamical integration of the orbits suggested that the pair of planets are in a dynamical state called apsidal co-rotation, which usually implies that the system is dynamically stable over long time scales. Guinan et al. (2016) suggested that the present day star could potentially support life on Kapteyn b, but that the planet's atmosphere may have been stripped away when the star was young (~0.5 Gyr) and highly active. The announcement of the planetary system was accompanied by a science-fiction short-story, "Sad Kapteyn", written by writer Alastair Reynolds
Alastair Preston Reynolds (born 13 March 1966) is a Welsh science fiction author. He specialises in hard science fiction and space opera. He spent his early years in Cornwall, moved back to Wales before going to Newcastle University, where he s ...
.
See also
*List of nearest stars
This list covers all known stars, brown dwarfs, and sub-brown dwarfs within of the Sun. So far, 131 such objects have been found, of which only 22 are bright enough to be visible without a telescope. The visible light needs to reach or exce ...
* Stars named after people
Over the past few centuries, a small number of stars have been named after individual people. It is common in astronomy for objects to be given names, in accordance with accepted astronomical naming conventions. Most stars have not been given Prope ...
References
Further reading
*. *. *. *. *.External links
SolStation.com: Kapteyn's Star
Press release on planetary system
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kapteyn's Star M-type main-sequence stars M-type subdwarfs BY Draconis variables High-proper-motion stars Local Bubble Hypothetical planetary systems Pictor (constellation) CD-45 01841
0191
0191 is the UK telephone dialling code used by Newcastle, Durham, Sunderland and other nearby areas in the north east of England.
Areas covered
Numbering in the 0191 area is officially divided into three distinct areas, each with their own batc ...
033793
024186
Pictoris, VZ