Kandalaksha Gulf on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kandalaksha Gulf (, sms, Käddluhtt), fi, Kantalahti) is located in the 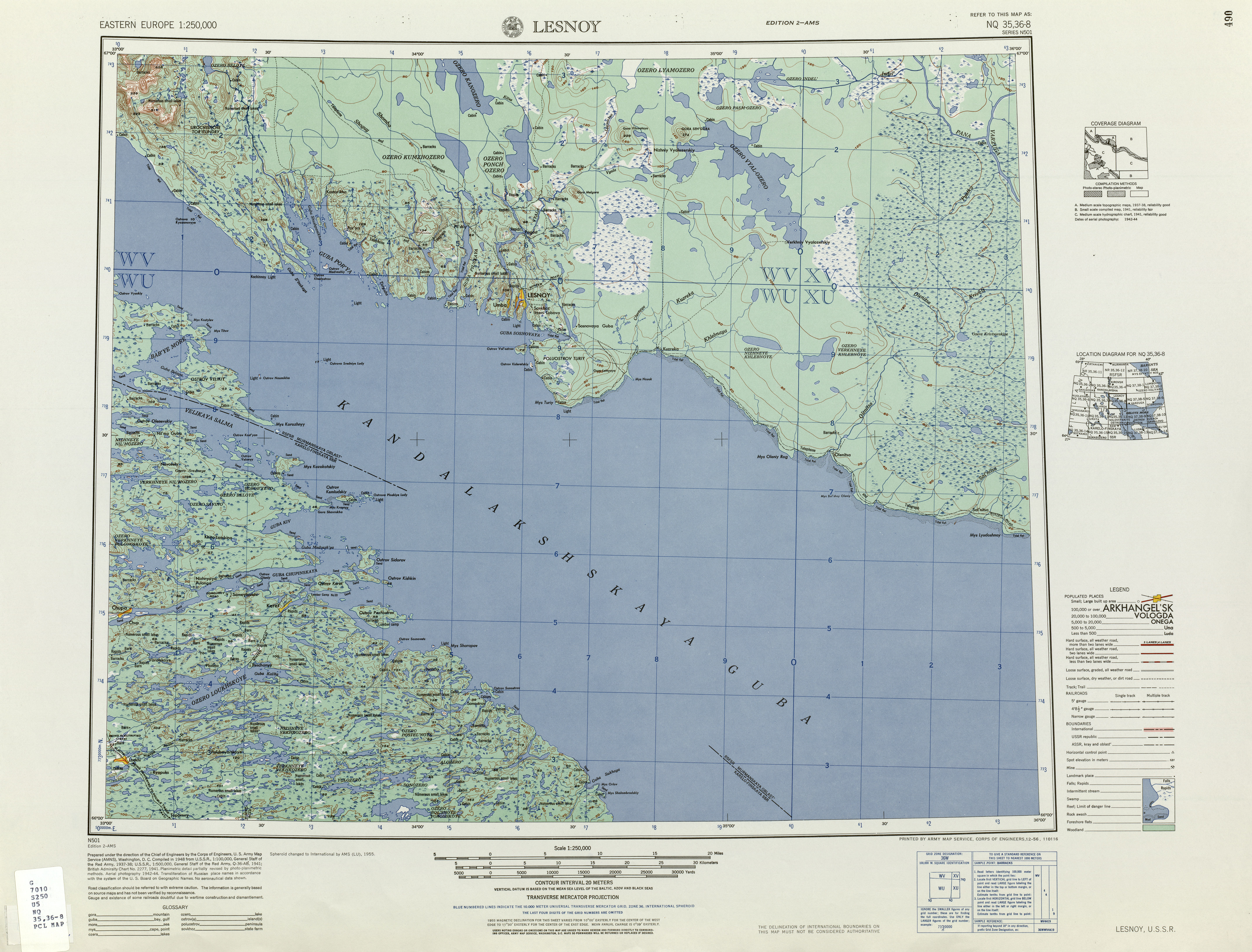 Since
Since
Kandalaksha Nature Reserve (English Summary), and some practical travel information on the City of Kandalaksha, also in English.
{{Authority control Gulfs of the Arctic Ocean Gulfs of Russia Bodies of water of the Republic of Karelia Ramsar sites in Russia Bays of the White Sea Bays of Murmansk Oblast
Republic of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia (russian: Респу́блика Каре́лия, Respublika Kareliya; ; krl, Karjalan tašavalta; ; fi, Karjalan tasavalta; vep, Karjalan Tazovaldkund, Ludic: ''Kard’alan tazavald''), also known as just Karelia (ru ...
, and Murmansk Oblast
Murmansk Oblast (russian: Му́рманская о́бласть, p=ˈmurmənskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ, r=Murmanskaya oblast, ''Murmanskaya oblast''; Kildin Sami: Мурман е̄ммьне, ''Murman jemm'ne'') is a federal subject (an oblast) o ...
in northwestern Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
. Forming the north-western corner of the White Sea
The White Sea (russian: Белое море, ''Béloye móre''; Karelian and fi, Vienanmeri, lit. Dvina Sea; yrk, Сэрако ямʼ, ''Serako yam'') is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is s ...
, it is one of four large bays and gulfs of this sea, the others being the Onega Bay
The Onega Bay (russian: Онежская губа, Онежский залив) is located in the Republic of Karelia and Arkhangelsk Oblast in Northwestern Russia, west of the city of Arkhangelsk. It is the southernmost of four large bays and g ...
(south-west), the Dvina Bay
The Dvina Bay (russian: Двинская Губа) is located in Arkhangelsk Oblast in Northwestern Russia. It is one of four large bays and gulfs of the White Sea, the others being the Mezen Bay, the Onega Bay, and the Kandalaksha Gulf. The tw ...
(south), and the Mezen Bay (south east).
The Kola Peninsula
The Kola Peninsula (russian: Кольский полуостров, Kolsky poluostrov; sjd, Куэлнэгк нёа̄ррк) is a peninsula in the extreme northwest of Russia, and one of the largest peninsulas of Europe. Constituting the bulk ...
lies north of the Kandalaksha Gulf. The city of Kandalaksha is located at the northern tip of the gulf; the new oil port Vitino, some 10 km to the south. There are hundreds of skerries in the gulf. The gulf is shallow, reaching 300 meters on its western side. In 1976, the upper reaches of the gulf were designated a Ramsar wetland of international importance
This is the list of Wetlands of International Importance as defined by the Ramsar Convention for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands, recognizing the fundamental ecological functions of wetlands and their economic, cultural, scientif ...
, notably as a breeding ground for migratory waterfowl such as the sea duck
The sea ducks (''Mergini'') are a tribe of the duck subfamily of birds, the Anatinae. The taxonomy of this group is incomplete. Some authorities separate the group as a subfamily, while others remove some genera. Most species within the group sp ...
.
Kandalaksha Nature Reserve ( Кандалакшский заповедник) includes parts of the coastline and many of the islands in the gulf. It is one of Russia's oldest nature reserves, established in 1932.
 Since
Since deglaciation Deglaciation is the transition from full glacial conditions during ice ages, to warm interglacials, characterized by global warming and sea level rise due to change in continental ice volume. Thus, it refers to the retreat of a glacier, an ice shee ...
the rate of post-glacial rebound
Post-glacial rebound (also called isostatic rebound or crustal rebound) is the rise of land masses after the removal of the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, which had caused isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound ...
in the Kandalaksha Gulf has varied. Since the White Sea
The White Sea (russian: Белое море, ''Béloye móre''; Karelian and fi, Vienanmeri, lit. Dvina Sea; yrk, Сэрако ямʼ, ''Serako yam'') is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is s ...
connected to the World's oceans uplift along southern coast of the gulf has totaled 90 m. In the interval 9,500–5,000 years ago uplift rate was of 9–13 mm/ yr. Prior to the Atlantic period uplift rate had decreased to 5–5.5 mm/yr, to then rise briefly before arriving at the present uplift rate is of 4 mm/yr.
See also
*Gandvik In Norse mythology, Gandvík is a dangerous sea, known as the "Bay of Serpents" because of its tortuous shape.
The 12th-13th century Dane Saxo Grammaticus stated that Gandvik was an old name for the Baltic Sea (a name misspelt Grandvik in some tra ...
* White Sea Rift System
The White Sea Rift System is a complex of rifts manifested as numerous individual grabens located chiefly in the White Sea but including onshore areas and a strip of the Barents Sea. The rifts run in a subparallel manner from northwest to southea ...
References
External links
Kandalaksha Nature Reserve (English Summary), and some practical travel information on the City of Kandalaksha, also in English.
{{Authority control Gulfs of the Arctic Ocean Gulfs of Russia Bodies of water of the Republic of Karelia Ramsar sites in Russia Bays of the White Sea Bays of Murmansk Oblast