Isotopes of boron on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
[] , p , Subsequently decays by double proton emission to for a net reaction of → + 3 , (3/2−) , , , - , Has 1 halo nucleus, halo proton , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 3 , , , Beta decay, β+ α , , 2+ , , , - , style="text-indent:1em" , , colspan="3" style="text-indent:2em" , , , , , 0+ , , , - , , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 4 , , , p , , Immediately decays into two α particles, for a net reaction of → 2 + , 3/2− , , , - , One of the few stable odd-odd nuclei , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 5 , , colspan=3 align=center, Stable , 3+ , colspan=2 align=center, ref name="Atomic Weight of Boron2"> , - , , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 6 , , colspan=3 align=center, Stable , 3/2− , colspan=2 align=center, ref name="Atomic Weight of Boron2" /> , - , style="text-indent:1em" , , colspan="3" style="text-indent:2em" , , , , , 1/2+, (3/2+) , , , - , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2 style="text-align:center" , 5 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:center" , 7 , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , β− () , , rowspan=2, 1+ , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , - , β−α () , Immediately decays into two α particles, for a net reaction of → 3 + , - , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2 style="text-align:center" , 5 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:center" , 8 , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , β− () , , rowspan=2, 3/2− , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , - , β−n () , , - , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3 style="text-align:center" , 5 , rowspan=3 style="text-align:center" , 9 , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , β− () , , rowspan=3, 2− , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , - , β−n () , , - , β−2n ?Decay mode shown is energetically allowed, but has not been experimentally observed to occur in this nuclide. , ? , - , style="text-indent:1em" , , colspan="3" style="text-indent:2em" , , , IT ? , , 0+ , , , - , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3 style="text-align:center" , 5 , rowspan=3 style="text-align:center" , 10 , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , β−n () , , rowspan=3, 3/2− , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , - , β− (< ) , , - , β−2n (< ) , , - , , style=text-align:center , 5 , style=text-align:center , 11 , , >
Boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the '' boron group'' it has t ...
(5B) naturally occurs as isotopes
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers ( mass numbers ...
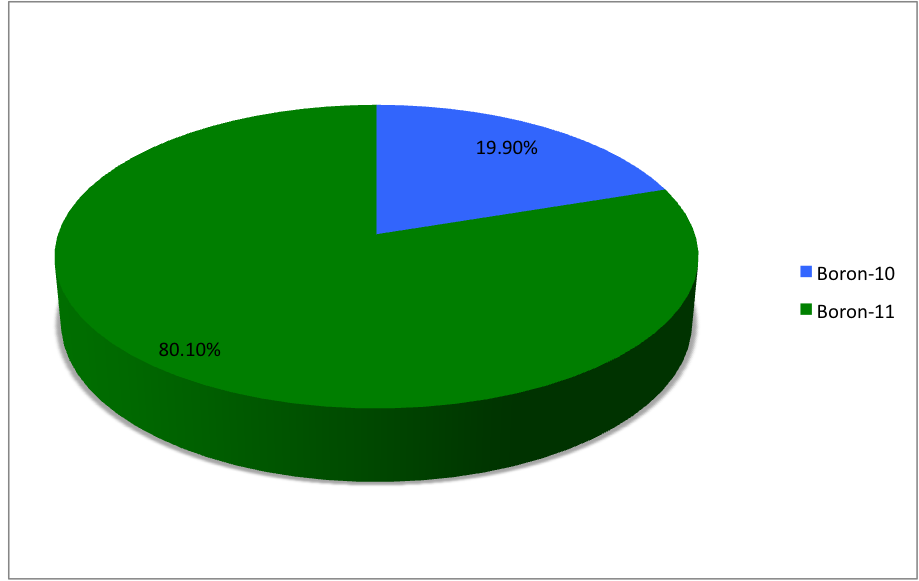
and , the latter of which makes up about 80% of natural boron. There are 13 radioisotopes
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
that have been discovered, with mass numbers from 7 to 21, all with short half-lives
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
, the longest being that of , with a half-life of only and with a half-life of . All other isotopes have half-lives shorter than . Those isotopes with mass below 10 decay into helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic ta ...
(via short-lived isotopes of beryllium
Beryllium (4Be) has 11 known isotopes and 3 known isomers, but only one of these isotopes () is stable and a primordial nuclide. As such, beryllium is considered a monoisotopic element. It is also a mononuclidic element, because its other isot ...
for and ) while those with mass above 11 mostly become carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
.

List of isotopes
, - , ?This isotope has not yet been observed; given data is inferred or estimated from periodic trends. , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 1 , , p-unstable , 2p? , ? , 2−# , , , - , , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 2 , ,[] , p , Subsequently decays by double proton emission to for a net reaction of → + 3 , (3/2−) , , , - , Has 1 halo nucleus, halo proton , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 3 , , , Beta decay, β+ α , , 2+ , , , - , style="text-indent:1em" , , colspan="3" style="text-indent:2em" , , , , , 0+ , , , - , , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 4 , , , p , , Immediately decays into two α particles, for a net reaction of → 2 + , 3/2− , , , - , One of the few stable odd-odd nuclei , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 5 , , colspan=3 align=center, Stable , 3+ , colspan=2 align=center, ref name="Atomic Weight of Boron2"> , - , , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 6 , , colspan=3 align=center, Stable , 3/2− , colspan=2 align=center, ref name="Atomic Weight of Boron2" /> , - , style="text-indent:1em" , , colspan="3" style="text-indent:2em" , , , , , 1/2+, (3/2+) , , , - , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2 style="text-align:center" , 5 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:center" , 7 , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , β− () , , rowspan=2, 1+ , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , - , β−α () , Immediately decays into two α particles, for a net reaction of → 3 + , - , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2 style="text-align:center" , 5 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:center" , 8 , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , β− () , , rowspan=2, 3/2− , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , - , β−n () , , - , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3 style="text-align:center" , 5 , rowspan=3 style="text-align:center" , 9 , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , β− () , , rowspan=3, 2− , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , - , β−n () , , - , β−2n ?Decay mode shown is energetically allowed, but has not been experimentally observed to occur in this nuclide. , ? , - , style="text-indent:1em" , , colspan="3" style="text-indent:2em" , , , IT ? , , 0+ , , , - , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3 style="text-align:center" , 5 , rowspan=3 style="text-align:center" , 10 , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , β−n () , , rowspan=3, 3/2− , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , - , β− (< ) , , - , β−2n (< ) , , - , , style=text-align:center , 5 , style=text-align:center , 11 , , >