Iowa archaeology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
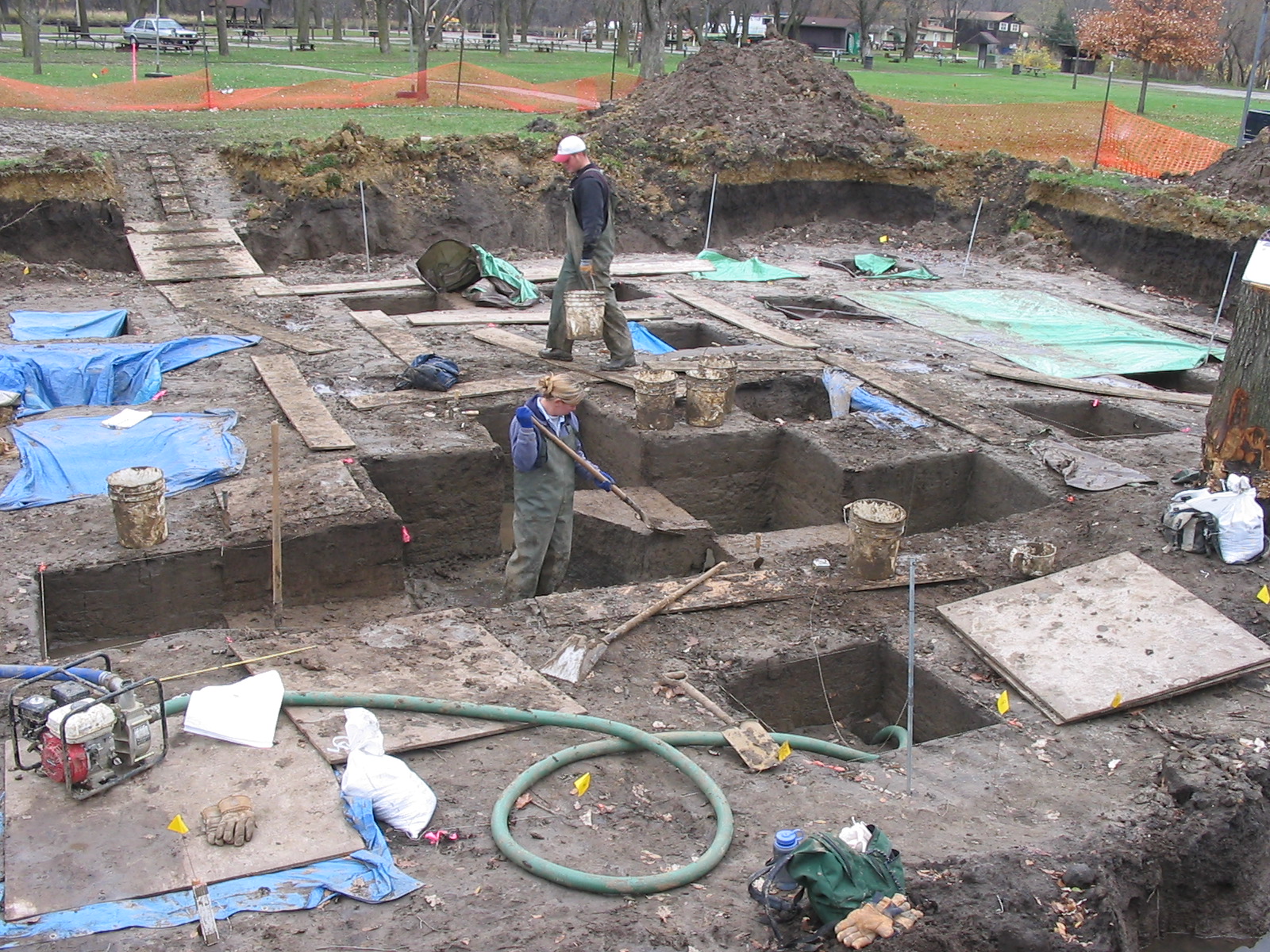 The archaeology of Iowa is the study of the buried remains of
The archaeology of Iowa is the study of the buried remains of
 Archaeologists have studied the prehistory of Iowa since the mid-19th century, when large American Indian mounds were first observed along the Mississippi. Early archaeologists such as S.V. Proudfit and Theodore Lewis documented large sites such as earthworks, mounds, and earthlodges. Truly systematic recording of Iowa sites began with Charles R. Keyes and Ellison Orr’s surveys and excavations beginning in the 1920s. Documenting hundreds of sites, often just before they disappeared under the plow, Keyes’ and Orr’s work led to the formation of the Iowa Archaeological Survey, the
Archaeologists have studied the prehistory of Iowa since the mid-19th century, when large American Indian mounds were first observed along the Mississippi. Early archaeologists such as S.V. Proudfit and Theodore Lewis documented large sites such as earthworks, mounds, and earthlodges. Truly systematic recording of Iowa sites began with Charles R. Keyes and Ellison Orr’s surveys and excavations beginning in the 1920s. Documenting hundreds of sites, often just before they disappeared under the plow, Keyes’ and Orr’s work led to the formation of the Iowa Archaeological Survey, the
 Paleoindian hunters and gatherers were the first occupants of Iowa, entering the state at the end of the
Paleoindian hunters and gatherers were the first occupants of Iowa, entering the state at the end of the
 During the Woodland period, many American Indians in Iowa shifted away from hunting and gathering and used more domesticated plants, although wild food was still important.
During the Woodland period, many American Indians in Iowa shifted away from hunting and gathering and used more domesticated plants, although wild food was still important.
 In northwestern Iowa, Great Oasis underwent dramatic changes as Mill Creek sites appeared. While Mill Creek has many stylistic similarities with Great Oasis and some Mill Creek sites contain Great Oasis ceramic forms, Mill Creek sites are substantially different. Mill Creek sites became nucleated, often fortified, had a much higher dependence on
In northwestern Iowa, Great Oasis underwent dramatic changes as Mill Creek sites appeared. While Mill Creek has many stylistic similarities with Great Oasis and some Mill Creek sites contain Great Oasis ceramic forms, Mill Creek sites are substantially different. Mill Creek sites became nucleated, often fortified, had a much higher dependence on
 Very large Mississippian centers appeared around AD 1000, with enormous earthen pyramids, palisades, and extreme social hierarchy. The earliest large Mississippian center was
Very large Mississippian centers appeared around AD 1000, with enormous earthen pyramids, palisades, and extreme social hierarchy. The earliest large Mississippian center was
 Protohistoric refers to the period when American Indians were exposed to European trade items and large population shifts occurred because of introduced European diseases and warfare, but there is very little direct written documentation. Explorers such as Marquette and Joliet occasionally documented American Indians along the Mississippi in Iowa, but it was not until the early 19th century that regular written accounts of American Indians in Iowa became common. American Indians in the early Protohistoric period continued many aspects of Oneota culture, but soon almost all indigenous technology disappeared, including ceramics and stone tool production. It was during this period that the
Protohistoric refers to the period when American Indians were exposed to European trade items and large population shifts occurred because of introduced European diseases and warfare, but there is very little direct written documentation. Explorers such as Marquette and Joliet occasionally documented American Indians along the Mississippi in Iowa, but it was not until the early 19th century that regular written accounts of American Indians in Iowa became common. American Indians in the early Protohistoric period continued many aspects of Oneota culture, but soon almost all indigenous technology disappeared, including ceramics and stone tool production. It was during this period that the
 The earliest European forts and settlements were established by traders beginning in the 1680s. Almost none of these ephemeral early historical sites have been located archaeologically.
The earliest European forts and settlements were established by traders beginning in the 1680s. Almost none of these ephemeral early historical sites have been located archaeologically.
human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
within the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to th ...
from the earliest prehistoric through the late historic
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
periods. When the American Indians first arrived in what is now Iowa more than 13,000 years ago, they were hunters and gatherers
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
living in a Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
glacial
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betwe ...
landscape. By the time European explorers visited Iowa, American Indians were largely settled farmers with complex economic, social, and political systems. This transformation happened gradually. During the Archaic period (10,500–2,800 years ago) American Indians adapted to local environments and ecosystems, slowly becoming more sedentary as populations increased. More than 3,000 years ago, during the Late Archaic period, American Indians in Iowa began utilizing domesticated
Domestication is a sustained multi-generational relationship in which humans assume a significant degree of control over the reproduction and care of another group of organisms to secure a more predictable supply of resources from that group. A ...
plants. The subsequent Woodland period saw an increase on the reliance on agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
and social complexity, with increased use of mound
A mound is a heaped pile of earth, gravel, sand, rocks, or debris. Most commonly, mounds are earthen formations such as hills and mountains, particularly if they appear artificial. A mound may be any rounded area of topographically higher ...
s, ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
, and specialized subsistence. During the Late Prehistoric period (beginning about AD 900) increased use of maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
and social changes led to social flourishing and nucleated settlements. The arrival of European trade goods and diseases in the Protohistoric
Protohistory is a period between prehistory and history during which a culture or civilization has not yet developed writing, but other cultures have already noted the existence of those pre-literate groups in their own writings. For example, in ...
period led to dramatic population shifts and economic and social upheaval, with the arrival of new tribes and early European explorers and traders. During the Historical period European traders and American Indians in Iowa gave way to American settlers and Iowa was transformed into an agricultural state.
Iowa archaeologists
 Archaeologists have studied the prehistory of Iowa since the mid-19th century, when large American Indian mounds were first observed along the Mississippi. Early archaeologists such as S.V. Proudfit and Theodore Lewis documented large sites such as earthworks, mounds, and earthlodges. Truly systematic recording of Iowa sites began with Charles R. Keyes and Ellison Orr’s surveys and excavations beginning in the 1920s. Documenting hundreds of sites, often just before they disappeared under the plow, Keyes’ and Orr’s work led to the formation of the Iowa Archaeological Survey, the
Archaeologists have studied the prehistory of Iowa since the mid-19th century, when large American Indian mounds were first observed along the Mississippi. Early archaeologists such as S.V. Proudfit and Theodore Lewis documented large sites such as earthworks, mounds, and earthlodges. Truly systematic recording of Iowa sites began with Charles R. Keyes and Ellison Orr’s surveys and excavations beginning in the 1920s. Documenting hundreds of sites, often just before they disappeared under the plow, Keyes’ and Orr’s work led to the formation of the Iowa Archaeological Survey, the Iowa Archeological Society
The Iowa Archeological Society is an organization of academic, professional, and amateur archaeologists. It promotes education about Iowa's cultural past, conducts excavations, and encourages ethical collection and recording of archaeological site ...
, and the designation of Effigy Mounds National Monument
Effigy Mounds National Monument preserves more than 200 prehistoric mounds built by pre-Columbian
Mound Builder cultures, mostly in the first millennium CE, during the later part of the Woodland period of pre-Columbian North America.
Numerous ...
. After their deaths in 1951, the Survey was disbanded, and their efforts were continued by the University of Iowa
The University of Iowa (UI, U of I, UIowa, or simply Iowa) is a public research university in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest and largest university in the state. The University of Iowa is organized into 12 col ...
’s Department of Sociology and Anthropology, which formed the Office of the State Archaeologist (OSA) in 1959. The OSA maintains an extensive list of more than 23,000 recorded archaeological sites in Iowa, and conducts survey and excavation across the state. Other institutions conducting archaeological research in Iowa include the State Historical Society of Iowa
The State Historical Society of Iowa (SHSI), a division of the Iowa Department of Cultural Affairs, serves as the official historical repository for the State of Iowa and also provides grants, public education, and outreach about Iowa history a ...
, the Iowa Archeological Society
The Iowa Archeological Society is an organization of academic, professional, and amateur archaeologists. It promotes education about Iowa's cultural past, conducts excavations, and encourages ethical collection and recording of archaeological site ...
, the University of Iowa
The University of Iowa (UI, U of I, UIowa, or simply Iowa) is a public research university in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest and largest university in the state. The University of Iowa is organized into 12 col ...
, Iowa State University
Iowa State University of Science and Technology (Iowa State University, Iowa State, or ISU) is a public land-grant research university in Ames, Iowa. Founded in 1858 as the Iowa Agricultural College and Model Farm, Iowa State became one of the ...
, Grinnell College
Grinnell College is a private liberal arts college in Grinnell, Iowa, United States. It was founded in 1846 when a group of New England Congregationalists established the Trustees of Iowa College.
Grinnell has the fifth highest endowment-to-stu ...
, Luther College, and private archaeological firms. Professional archaeologists in Iowa are represented by the Association of Iowa Archaeologists. Iowa archaeology grew dramatically beginning in the 1960s with the introduction of Cultural Resources Management
In the broadest sense, cultural resource management (CRM) is the vocation and practice of managing heritage assets, and other cultural resources such as contemporary art. It incorporates Cultural Heritage Management which is concerned with traditio ...
legislation that required archaeological survey and excavation at many federal projects in Iowa.
Paleoindian (13,500–10,500 years ago)
 Paleoindian hunters and gatherers were the first occupants of Iowa, entering the state at the end of the
Paleoindian hunters and gatherers were the first occupants of Iowa, entering the state at the end of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
glacial period. At the time the state was covered by tundra, conifer forests, and deciduous forests. Areas immediately north of Des Moines extending to Minnesota were covered by the receding Des Moines Lobe, a large glacier system. Highly mobile, their sites are scattered across Iowa and are noted for their large stone points. While Paleoindians were traditionally viewed as big game hunters, more recent research suggests much of their subsistence was derived from small game and wild plants. Paleoindian points are found throughout Iowa, but almost no intact Paleoindian sites have been excavated, probably because they were ephemeral and are now either destroyed by plowing or are very deeply buried in river valleys.
Clovis and other Early Paleoindian
The oldest artifacts found in Iowa are Clovis points, large lanceolate points found occasionally in all parts of the state except for the Des Moines Lobe. Possible sources of game were giant Pleistocene megafauna, including mammoth, mastodon, and giant forms of bison, all of which are now extinct. While widespread, only two Clovis sites have been excavated in Iowa. The Rummells-Maske site is a Clovis site in Cedar County; unfortunately, this site was damaged by plowing, although 20 points and point fragments were recovered. The Carlisle Clovis Cache Site inWarren County Warren County is the name of fourteen counties in the USA. Some are named after General Joseph Warren, who was killed in the Battle of Bunker Hill in the American Revolutionary War:
* Warren County, Georgia
* Warren County, Illinois
* Warren County ...
contained 38 unfinished stone tools that appear to date to the Clovis period, but these results have not yet been published.
Other Iowa Early Paleoindian points include Gainey, a point that appears to be intermediate between Clovis and Folsom. Gainey points were also recovered at Rummells-Maske. While Folsom point
Folsom points are projectile points associated with the Folsom tradition of North America. The style of tool-making was named after the Folsom site located in Folsom, New Mexico, where the first sample was found in 1908 by George McJunkin within t ...
s are found throughout Iowa, especially western Iowa, none have been excavated in a well-preserved site.
Dalton and other Late Paleoindian
At the beginning of the glacial-freeHolocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
Epoch, humans in Iowa utilized projectile point found throughout the mid-continent, including Dalton
Dalton may refer to:
Science
* Dalton (crater), a lunar crater
* Dalton (program), chemistry software
* Dalton (unit) (Da), the atomic mass unit
* John Dalton, chemist, physicist and meteorologist
Entertainment
* Dalton (Buffyverse), minor ch ...
, Fayette, Agate Basin, and Hell Gap. Humans were still highly mobile, and by this time most of the Pleistocene megafauna had gone extinct. As with the Early Paleoindian period, no intact Late Paleoindian sites have been excavated in Iowa.
Archaic Period
The Archaic is the longest period of Iowa prehistory, lasting about 8,000 years. Overall, populations appear to have increased in Iowa during the Archaic, despite a changing climate. During this time American Indians transitioned from highly mobile hunters and gatherers with large ranges towards a focus on local resources and ecosystems. Domesticated plants appeared in Iowa towards the end of the Archaic.Early Archaic (10,500–7,500 years ago)
During the Early Archaic period regional variation in point forms is seen in Iowa, and Indians adapted to more localized forms of hunting and gathering while probably maintaining seasonal movements from camp to camp. Common stone tool types are Corner-notched St. Charles points and Thebes Knives. Soon Hardin and Kirk points appear in Iowa as well. Excavated Early Archaic sites in Iowa include the Soldow Site, Horizons IIIa and II of the Cherokee Sewer Site,Anderson, Duane C., and Holmes A. Semken, Jr. (eds.) (1980) ''The Cherokee Excavations: Holocene Ecology and Human Adaptations in Northwestern Iowa.'' Academic Press, New York and the Simonsen Site.Middle Archaic (7,500–5,000 years ago)
Temperatures rose in the mid-continent during the Middle Archaic, a warming trend known as theHypsithermal
The Holocene Climate Optimum (HCO) was a warm period that occurred in the interval roughly 9,000 to 5,000 years ago BP, with a thermal maximum around 8000 years BP. It has also been known by many other names, such as Altithermal, Climatic Optimu ...
. Grasslands expanded east, forests became less common, and many Iowa lakes shrank or disappeared. Humans responded by diversifying their subsistence strategy: eastern Iowa saw a shift towards river resources, and western Iowa towards Plains resources. Excavated sites in eastern and central Iowa include the Brash Site, the Gast Spring Site, and the Ed’s Meadow Site. Western Iowa sites include the Turin Site, Horizon I of the Cherokee Sewer Site, and the Pony Creek Site.
Late Archaic (5,000–2,800 years ago)
In the Late Archaic the climate became more similar to modern with the end of theHypsithermal
The Holocene Climate Optimum (HCO) was a warm period that occurred in the interval roughly 9,000 to 5,000 years ago BP, with a thermal maximum around 8000 years BP. It has also been known by many other names, such as Altithermal, Climatic Optimu ...
. The number of Late Archaic Sites increased in Iowa, perhaps reflective of increased populations allowed by climate change and new subsistence strategies. The Late Archaic sees the first indication of mound building in Iowa, as well as direct evidence of domesticated plants, and large, long-term settlements. The Red Ocher Culture appeared in northeast Iowa, associated with copper artifacts and mound building. Numerous Late Archaic sites have been excavated in eastern Iowa, some showing the gradual adaptation of cultigen
A cultigen () or cultivated plant is a plant that has been deliberately altered or selected by humans; it is the result of artificial selection. These plants, for the most part, have commercial value in horticulture, agriculture or forestry. Beca ...
s, including squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
, little barley, marsh elder, and barnyard grass. Sites with evidence for early cultigens in Iowa include the Edgewater Park Site
The Edgewater Park Site is a 3,800-year-old Late Archaic campsite situated along the Iowa River in Coralville, Iowa, United States. Plant remains recovered from the site suggest the inhabitants were in the earliest stages of adapting domesticat ...
in Coralville, the Gast Spring Site, and the Sand Run Slough West Site. In western Iowa, Late Archaic sites are common, however large bison killing or processing sites are less common than before, and there is little evidence for the use of domesticated plants.
Woodland Period
Ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
, the bow and arrow, burial mounds
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built ...
, and evidence of political and social hierarchy became common at Woodland sites in Iowa.
Early Woodland (800 BC–200 BC)
The Early Woodland period saw the introduction of ceramics to Iowa, including Marion Thick and Black Sand types. Marion Thick may have originated with the nucleated Late Archaic cultures of the Upper Midwest, and was widespread in distribution. Early Woodland Indians in eastern Iowa built large burial mounds in the Mississippi River region, and participated in long-distance trade of exotic raw material. This long-distance trade may have been the forerunner of the later Havanna- Hopewell trading sphere. In north-central Iowa, Early Woodland peoples appear to have interacted more directly with the Prairie Lakes region ofMinnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
. Numerous Early Woodland sites have been excavated in Iowa, including the Gast Spring Site, and many sites which have not been formally published.
Middle Woodland (200 BC–400 AD)
The Middle Woodland Indians of eastern Iowa participated at the edge of the Havana and Hopewell interaction networks. This cultural connection to the East is seen in the construction of large mounds, earthworks, and the trade of exotic goods over very long distances. There were several large earthwork enclosures in Iowa along the Mississippi that date to the Middle Woodland period, but none in the interior of the state, indicating Iowa is the western edge of Havana-Hopewell influence. The Toolesboro Mound Group in Louisa County included a large octagonal earthen enclosure that covered several acres; earthworks of this style are indicative of the monumental construction once seen inHavana, Illinois
Havana is a city in Mason County, Illinois, United States. The population was 3,301 at the 2010 census, and 3,040 at a 2018 estimate. It is the county seat of Mason County.
History
Havana was a major ancient American settlement two thousand years ...
along the Illinois River and sites in the Ohio River drainage including Chillicothe and Newark, Ohio. Hopewell trading networks were quite extensive, with obsidian from the Yellowstone
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
area, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
from Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
, and shells from the Gulf Coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South, is the coast, coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The list of U.S. states and territories by coastline, coastal states that have a shor ...
appearing in Middle Woodland Iowa sites. Sites in eastern Iowa appeared to nucleate, vacating much of the hinterlands. Western Iowa appears to have been not directly involved in this exchange network, and the Havana-Hopewell flourishing did not extend much above the Kansas City area of the Missouri River.
Late Woodland (400–1250 AD)
The Late Woodland Period was once considered to be relatively unimportant and uninteresting compared to earlier and later periods, but recent research shows unexpected cultural complexity. Late Woodland sites are more dispersed than Middle Woodland sites, but they are apparently more numerous. Gone are the complex earthworks and long-distance trade networks, but this does not appear to be a cultural collapse, since Late Woodland sites and artifact types overlap with and transition from Middle Woodland sites. Technical changes of the Late Woodland include the use of true arrow heads, thinner and larger ceramics with less elaborate decorations, and the adaptation of new crops, includingmaize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
. Numerous regional variations and phases have been defined in Iowa, based in large extent on differences of ceramic form and decoration. Excavations at Late Woodland sites are common, some of these sites showing surprising complexity. The Gast Farm Site excavations revealed a complex settlement associated with a midden of refuse 100 m in diameter. Large storage and food processing pits, trash middens, and other features were excavated. Occupants utilized acorns, other nuts and fruits, goosefoot, little barley, maygrass, sunflower, fish, birds, deer, muskrat, and turtle. There was little evidence of long-distance trade. The Rainbow and M.A.D. sites provide a glimpse into the Late Archaic of western Iowa. At Rainbow, a large house was excavated, showing evidence of reuse and possible joint occupation by two families. Mound building became more common during the Late Woodland Period, large groups of mounds appeared including the Slinde Mound Group, and the Fish Farm Mound Group.
Effigy Mounds
The Late Woodland in Iowa is perhaps best known foreffigy mounds
An effigy mound is a raised pile of earth built in the shape of a stylized animal, symbol, religious figure, human, or other figure. The Effigy Moundbuilder culture is primarily associated with the years 550-1200 CE during the Late Woodland Peri ...
, large, low mounds shaped like animals such as birds and bears. Effigy mounds are distributed across southern Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, northern Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
, and northeast Iowa. A large concentration of mounds in several groups is preserved at Effigy Mounds National Monument
Effigy Mounds National Monument preserves more than 200 prehistoric mounds built by pre-Columbian
Mound Builder cultures, mostly in the first millennium CE, during the later part of the Woodland period of pre-Columbian North America.
Numerous ...
. Like most mounds in Iowa, excavation reveals that these mounds were commonly used as sacred burial locations but contain few artifacts. Recent ground-penetrating radar survey of selected mounds at Effigy Mounds National Monument reveal that many are badly disturbed, but others appear to be comparatively intact. The Folkert Mound Group in central Iowa contains an enigmatic cruciform mound that may or may not be astronomically aligned.
Late Prehistoric (900–1600)

Maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
appears to have been the catalyst for change in the Late Prehistoric period in Iowa. While maize had been a minor crop in the Woodland Period, many archaeologists believe new varieties of maize were introduced to the region that produced higher yields, allowing for a population boom. This increase in population, combined with the potential for surplus and growing tensions over control of territory, appears to have led to large nucleated settlements throughout the eastern U.S. Although this manifested itself earliest along the Mississippi south of Iowa, the earliest Late Prehistoric cultures appeared in the western part of the state.
Great Oasis (ca. 900–1100)
Great Oasis sites appeared in the Missouri River drainage, and have attributes of both Late Woodland and Late Prehistoric cultures. Great Oasis cultures extended through the eastern Plains from Iowa to South Dakota. Developing independently from the eastern Mississippian cultures, Great Oasis sites display large sites along major stream terraces, increased reliance on agriculture combined with hunting and gathering, substantial pit earth lodges, and a transition from Late Woodland to Late Prehistoric ceramic forms. Overall, Great Oasis appears to have been a regional adaptation of new forms of farming and settlement patterns, including seasonal occupation of different ecological zones, that includes aspects of Late Woodland and the subsequent Middle Missouri Tradition.Mill Creek and Glenwood (1100–1300)
 In northwestern Iowa, Great Oasis underwent dramatic changes as Mill Creek sites appeared. While Mill Creek has many stylistic similarities with Great Oasis and some Mill Creek sites contain Great Oasis ceramic forms, Mill Creek sites are substantially different. Mill Creek sites became nucleated, often fortified, had a much higher dependence on
In northwestern Iowa, Great Oasis underwent dramatic changes as Mill Creek sites appeared. While Mill Creek has many stylistic similarities with Great Oasis and some Mill Creek sites contain Great Oasis ceramic forms, Mill Creek sites are substantially different. Mill Creek sites became nucleated, often fortified, had a much higher dependence on maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
and bison hunting, show substantial evidence of long-distance trade, and appear to have been occupied year-round. The Phipps and Chan-Ya-Ta sites are classic examples. Glenwood culture
The Glenwood Culture was a population of Indigenous peoples of North America prior to historical times. The culture is recognized as an eastern extension of the Nebraska Phase of the Woodland period, and was not a Mississippian culture.
Culture
...
sites in southwest Iowa near the Missouri River appear to be unrelated to the earlier Great Oasis sites, and are notable for their large earthlodge sites. Glenwood sites appear to have been more oriented in lifeways and trade with the Central Plains Tradition cultures to the west than with the Mississippian cultures to the southeast. Around 1300 AD Mill Creek and Glenwood sites in Iowa disappeared, replaced by the rapidly spreading Oneota cultures.
Oneota (1250–1700)
 Very large Mississippian centers appeared around AD 1000, with enormous earthen pyramids, palisades, and extreme social hierarchy. The earliest large Mississippian center was
Very large Mississippian centers appeared around AD 1000, with enormous earthen pyramids, palisades, and extreme social hierarchy. The earliest large Mississippian center was Cahokia
The Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site ( 11 MS 2) is the site of a pre-Columbian Native American city (which existed 1050–1350 CE) directly across the Mississippi River from modern St. Louis, Missouri. This historic park lies in south- ...
, east of St. Louis
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which e ...
. Cahokia appears to have dominated trade in the upper Mississippi, with satellite or closely aligned settlements as far as Aztalan in Wisconsin. In Iowa, there is little evidence of Mississippian occupation, and the Late Woodland lasts longer in the east than in the west. This is puzzling, given the proximity to Mississippian cultures; it is possible that the nearby presence of the large, hierarchal Mississippian trading network inhibited local development. After the decline of the Cahokia network after AD 1250 the local Late Woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the ''plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (se ...
populations expanded in complexity, developing large nucleated villages and their own trading network, known as Upper Mississippian
The Upper Mississippian cultures were located in the Upper Mississippi basin and Great Lakes region of the American Midwest. They were in existence from approximately A.D. 1000 until the Protohistoric and early Historic periods (approximately A. ...
Oneota
Oneota is a designation archaeologists use to refer to a cultural complex that existed in the eastern plains and Great Lakes area of what is now occupied by the United States from around AD 900 to around 1650 or 1700. Based on classification de ...
. Oneota, named by Charles Keyes for a river in northeast Iowa, was a large cultural manifestation that covered the Upper Midwest at the edge of the Mississippian cultures. Oneota sites are easily identifiable by the globular, shell-tempered pots, which typically have strap handles and incised designs. Pots of this kind were well designed for the cooking of porridge and foods made from the various cultivated foods of the area. Important Oneota sites in Iowa include Kingston, Mckinney, Christenson, Blood Run, Hartley Fort, the Lane Enclosure, three sites in downtown Des Moines, and sites along the Upper Iowa River, including several large earthwork enclosures. After the decline of the Mill Creek and Glenwood cultures in western Iowa, Oneota cultures appeared across the state. It is widely accepted that the Oneota were the ancestors of modern American Indian tribes associated with Iowa, including the Ioway
The Iowa, also known as Ioway, and the Bah-Kho-Je or Báxoje (English: grey snow; Chiwere: Báxoje ich'é) are a Native American Siouan people. Today, they are enrolled in either of two federally recognized tribes, the Iowa Tribe of Oklahoma an ...
, Ho-Chunk (Winnebago), Otoe
The Otoe (Chiwere: Jiwére) are a Native American people of the Midwestern United States. The Otoe language, Chiwere, is part of the Siouan family and closely related to that of the related Iowa, Missouria, and Ho-Chunk tribes.
Historically, t ...
, Missouria
The Missouria or Missouri (in their own language, Niúachi, also spelled Niutachi) are a Native American tribe that originated in the Great Lakes region of what is now the United States before European contact.May, John D"Otoe-Missouria"''Oklaho ...
, and Omaha.
Protohistoric (1600–1800)
 Protohistoric refers to the period when American Indians were exposed to European trade items and large population shifts occurred because of introduced European diseases and warfare, but there is very little direct written documentation. Explorers such as Marquette and Joliet occasionally documented American Indians along the Mississippi in Iowa, but it was not until the early 19th century that regular written accounts of American Indians in Iowa became common. American Indians in the early Protohistoric period continued many aspects of Oneota culture, but soon almost all indigenous technology disappeared, including ceramics and stone tool production. It was during this period that the
Protohistoric refers to the period when American Indians were exposed to European trade items and large population shifts occurred because of introduced European diseases and warfare, but there is very little direct written documentation. Explorers such as Marquette and Joliet occasionally documented American Indians along the Mississippi in Iowa, but it was not until the early 19th century that regular written accounts of American Indians in Iowa became common. American Indians in the early Protohistoric period continued many aspects of Oneota culture, but soon almost all indigenous technology disappeared, including ceramics and stone tool production. It was during this period that the Meskwaki
The Meskwaki (sometimes spelled Mesquaki), also known by the European exonyms Fox Indians or the Fox, are a Native American people. They have been closely linked to the Sauk people of the same language family. In the Meskwaki language, th ...
(Fox) and Sauk appeared in eastern Iowa, displaced from their homelands in the east. Important protohistoric sites include Milford; Blood Run; Gillett Grove; and Iowaville.
Historical (1800–present)
 The earliest European forts and settlements were established by traders beginning in the 1680s. Almost none of these ephemeral early historical sites have been located archaeologically.
The earliest European forts and settlements were established by traders beginning in the 1680s. Almost none of these ephemeral early historical sites have been located archaeologically. Julien Dubuque
Julien Dubuque (January 1762 – 24 March 1810) was a Canadian of Norman origin from the area of Champlain, Quebec who arrived near what now is known as Dubuque, Iowa, which was named after him. He was one of the first European men to settle in t ...
’s Mines of Spain settlement and adjacent Meskwaki village occupied in the late 18th century and early 19th century, has been the subject of numerous archaeological surveys. Fort Madison (1808–1813), the first American settlement and the first American fort in Iowa, was partially excavated in 1965. American settlement began in earnest in the 1830s, and the official removal of American Indians from Iowa was completed by 1852. Several of these historical sites have been excavated, including Gilbert’s Trading Post. and Fort Atkinson. Archaeologists have also studied historical American settlements, including excavations at the Plum Grove Historic House
Plum Grove is a historic house located in Iowa City, United States. Plum Grove was the retirement home of Gov. Robert Lucas and the childhood home of the author Eleanor Hoyt Brainerd.
History
Built in 1844, Lucas lived there with his wife, F ...
, the Buxton
Buxton is a spa town in the Borough of High Peak, Derbyshire, England. It is England's highest market town, sited at some above sea level.Iowa Archaeological Society
* Indians of Iowa
*
Iowa Office of the State Archaeologist Website
Iowa Archaeological Society Website
Association of Iowa Archaeologists Website
Department of Anthropology, University of Iowa Website
Department of Anthropology, Iowa State University Website
Department of Anthropology, Grinnell College Website
Department of Anthropology, Luther College Website
{{Good article History of indigenous peoples of North America Pre-Columbian cultural areas Pre-statehood history of Iowa Protected areas of Iowa Former Native American populated places in the United States Clovis sites Archaic period in North America Mound builders (people) Woodland period Mississippian culture Ruins in the United States fr:Pointes de flèches de la période Clovis
Geology of Iowa
The geography of Iowa includes the study of bedrock, landforms, rivers, geology, paleontology and urbanisation of the U.S. state of Iowa. The state covers an area of 56,272.81 sq mi (145,746 km2).
Bedrock features
Iowa's bedrock geology ge ...
*History of Iowa
Native Americans in the United States resided in what is now Iowa for thousands of years. The written history of Iowa begins with the proto-historic accounts of Native Americans by explorers such as Marquette and Joliet in the 1680s. Until the ea ...
*State Historical Society of Iowa
The State Historical Society of Iowa (SHSI), a division of the Iowa Department of Cultural Affairs, serves as the official historical repository for the State of Iowa and also provides grants, public education, and outreach about Iowa history a ...
* Iowa Historic Preservation Alliance
*Effigy Mounds National Monument
Effigy Mounds National Monument preserves more than 200 prehistoric mounds built by pre-Columbian
Mound Builder cultures, mostly in the first millennium CE, during the later part of the Woodland period of pre-Columbian North America.
Numerous ...
References
External links
Iowa Office of the State Archaeologist Website
Iowa Archaeological Society Website
Association of Iowa Archaeologists Website
Department of Anthropology, University of Iowa Website
Department of Anthropology, Iowa State University Website
Department of Anthropology, Grinnell College Website
Department of Anthropology, Luther College Website
{{Good article History of indigenous peoples of North America Pre-Columbian cultural areas Pre-statehood history of Iowa Protected areas of Iowa Former Native American populated places in the United States Clovis sites Archaic period in North America Mound builders (people) Woodland period Mississippian culture Ruins in the United States fr:Pointes de flèches de la période Clovis