Invasive blood pressure on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Blood pressure (BP) is the
 Various other factors, such as age and
Various other factors, such as age and
 Arterial hypertension can be an indicator of other problems and may have long-term adverse effects. Sometimes it can be an acute problem, for example hypertensive emergency.
Levels of arterial pressure put mechanical stress on the arterial walls. Higher pressures increase heart workload and progression of unhealthy tissue growth (atheroma) that develops within the walls of arteries. The higher the pressure, the more stress that is present and the more atheroma tend to progress and the Myocardium, heart muscle tends to thicken, enlarge and become weaker over time.
Persistent hypertension is one of the risk factors for strokes, myocardial infarction, heart attacks, heart failure, and arterial aneurysms, and is the leading cause of chronic kidney failure. Even moderate elevation of arterial pressure leads to shortened life expectancy. At severely high pressures, mean arterial pressures 50% or more above average, a person can expect to live no more than a few years unless appropriately treated.
In the past, most attention was paid to diastolic pressure; but nowadays it is recognized that both high Systole (medicine), systolic pressure and high pulse pressure (the numerical difference between systolic and diastolic pressures) are also risk factors. In some cases, it appears that a decrease in excessive diastolic pressure can actually increase risk, probably due to the increased difference between systolic and diastolic pressures. If systolic blood pressure is elevated (>140 mmHg) with a normal diastolic blood pressure (<90 mmHg), it is called isolated systolic hypertension and may present a health concern. According to the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Blood Pressure Guidelines, "an {systolic blood pressure] of 130 mm Hg is now considered hypertensive at all ages." This will lead to more diagnoses of hypertension among all ages.
For those with heart valve regurgitation, a change in its severity may be associated with a change in diastolic pressure. In a study of people with heart valve regurgitation that compared measurements two weeks apart for each person, there was an increased severity of aortic insufficiency, aortic and mitral regurgitation when diastolic blood pressure increased, whereas when diastolic blood pressure decreased, there was a decreased severity.
Arterial hypertension can be an indicator of other problems and may have long-term adverse effects. Sometimes it can be an acute problem, for example hypertensive emergency.
Levels of arterial pressure put mechanical stress on the arterial walls. Higher pressures increase heart workload and progression of unhealthy tissue growth (atheroma) that develops within the walls of arteries. The higher the pressure, the more stress that is present and the more atheroma tend to progress and the Myocardium, heart muscle tends to thicken, enlarge and become weaker over time.
Persistent hypertension is one of the risk factors for strokes, myocardial infarction, heart attacks, heart failure, and arterial aneurysms, and is the leading cause of chronic kidney failure. Even moderate elevation of arterial pressure leads to shortened life expectancy. At severely high pressures, mean arterial pressures 50% or more above average, a person can expect to live no more than a few years unless appropriately treated.
In the past, most attention was paid to diastolic pressure; but nowadays it is recognized that both high Systole (medicine), systolic pressure and high pulse pressure (the numerical difference between systolic and diastolic pressures) are also risk factors. In some cases, it appears that a decrease in excessive diastolic pressure can actually increase risk, probably due to the increased difference between systolic and diastolic pressures. If systolic blood pressure is elevated (>140 mmHg) with a normal diastolic blood pressure (<90 mmHg), it is called isolated systolic hypertension and may present a health concern. According to the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Blood Pressure Guidelines, "an {systolic blood pressure] of 130 mm Hg is now considered hypertensive at all ages." This will lead to more diagnoses of hypertension among all ages.
For those with heart valve regurgitation, a change in its severity may be associated with a change in diastolic pressure. In a study of people with heart valve regurgitation that compared measurements two weeks apart for each person, there was an increased severity of aortic insufficiency, aortic and mitral regurgitation when diastolic blood pressure increased, whereas when diastolic blood pressure decreased, there was a decreased severity.
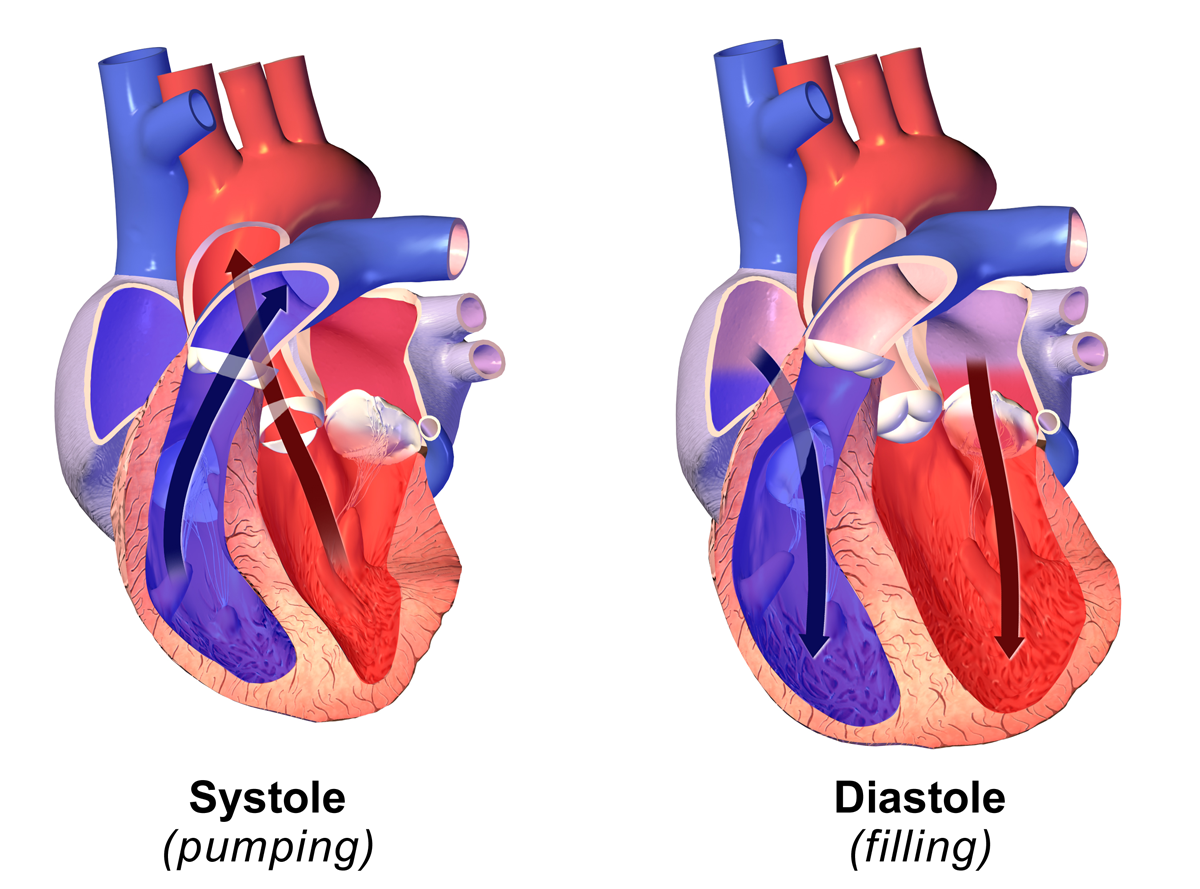
 During each heartbeat, blood pressure varies between a maximum (systolic) and a minimum (diastolic) pressure. The blood pressure in the circulation is principally due to the pumping action of the heart. However, blood pressure is also regulated by neural regulation from the brain (see Hypertension and the brain), as well as osmotic regulation from the kidney. Differences in mean blood pressure drive the flow of blood around the circulation. The rate of mean blood flow depends on both blood pressure and the resistance to flow presented by the blood vessels. In the absence of Fluid statics, hydrostatic effects (e.g. standing), mean blood pressure decreases as the circulating blood moves away from the heart through arteries and capillaries due to Viscosity, viscous losses of energy. Mean blood pressure drops over the whole circulation, although most of the fall occurs along the small arteries and arterioles. Pulsatility also diminishes in the smaller elements of the arterial circulation, although some transmitted pulsatility is observed in capillaries. Gravity affects blood pressure via hydrostatic forces (e.g., during standing), and valves in veins, breathing, and pumping from contraction of skeletal muscles also influence blood pressure, particularly in veins.
During each heartbeat, blood pressure varies between a maximum (systolic) and a minimum (diastolic) pressure. The blood pressure in the circulation is principally due to the pumping action of the heart. However, blood pressure is also regulated by neural regulation from the brain (see Hypertension and the brain), as well as osmotic regulation from the kidney. Differences in mean blood pressure drive the flow of blood around the circulation. The rate of mean blood flow depends on both blood pressure and the resistance to flow presented by the blood vessels. In the absence of Fluid statics, hydrostatic effects (e.g. standing), mean blood pressure decreases as the circulating blood moves away from the heart through arteries and capillaries due to Viscosity, viscous losses of energy. Mean blood pressure drops over the whole circulation, although most of the fall occurs along the small arteries and arterioles. Pulsatility also diminishes in the smaller elements of the arterial circulation, although some transmitted pulsatility is observed in capillaries. Gravity affects blood pressure via hydrostatic forces (e.g., during standing), and valves in veins, breathing, and pumping from contraction of skeletal muscles also influence blood pressure, particularly in veins.
 The pulse pressure is the difference between the measured systolic and diastolic pressures,
:::::::::::
The pulse pressure is a consequence of the pulsatile nature of the cardiac output, i.e. the heartbeat. The magnitude of the pulse pressure is usually attributed to the interaction of the stroke volume of the heart, the compliance (ability to expand) of the arterial system—largely attributable to the aorta and large elastic arteries—and the Drag (physics), resistance to flow in the arterial tree.
The pulse pressure is the difference between the measured systolic and diastolic pressures,
:::::::::::
The pulse pressure is a consequence of the pulsatile nature of the cardiac output, i.e. the heartbeat. The magnitude of the pulse pressure is usually attributed to the interaction of the stroke volume of the heart, the compliance (ability to expand) of the arterial system—largely attributable to the aorta and large elastic arteries—and the Drag (physics), resistance to flow in the arterial tree.
/ref> * Renin–angiotensin system (RAS): This system is generally known for its long-term adjustment of arterial pressure. This system allows the kidney to compensate for loss in blood volume or drops in arterial pressure by activating an endogenous vasoconstrictor known as angiotensin II. * Aldosterone release: This steroid hormone is released from the adrenal cortex in response to activation of the renin-angiotensin system, high serum potassium levels, or elevated Adrenocorticotropic hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Renin converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which is converted by Angiotensin-converting enzyme, angiotensin converting enzyme to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II then signals to the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone. Aldosterone stimulates sodium retention and potassium excretion by the kidneys and the consequent salt and water retention increases plasma volume, and indirectly, arterial pressure. Aldosterone may also exert direct pressor effects on vascular smooth muscle and central effects on sympathetic nervous system activity. * Baroreceptors in low pressure receptor zones (mainly in the venae cavae and the pulmonary veins, and in the atrium (heart), atria) result in feedback by regulating the secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH/Vasopressin), renin and aldosterone. The resultant increase in blood volume results in an increased cardiac output by the Frank–Starling law of the heart, in turn increasing arterial blood pressure. These different mechanisms are not necessarily independent of each other, as indicated by the link between the RAS and aldosterone release. When blood pressure falls many physiological cascades commence in order to return the blood pressure to a more appropriate level. # The blood pressure fall is detected by a decrease in blood flow and thus a decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR). # Decrease in GFR is sensed as a decrease in Na+ levels by the macula densa. # The macula densa causes an increase in Na+ reabsorption, which causes water to follow in via osmosis and leads to an ultimate increase in blood plasma, plasma volume. Further, the macula densa releases adenosine which causes constriction of the afferent arterioles. # At the same time, the juxtaglomerular cells sense the decrease in blood pressure and release renin. # Renin converts angiotensinogen (inactive form) to angiotensin I (active form). # Angiotensin I flows in the bloodstream until it reaches the capillaries of the lungs where angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) acts on it to convert it into angiotensin II. # Angiotensin II is a vasoconstrictor that will increase blood flow to the heart and subsequently the preload, ultimately increasing the cardiac output. # Angiotensin II also causes an increase in the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands. # Aldosterone further increases the Na+ and H2O reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule of the nephron. Currently, the RAS is targeted pharmacologically by ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists, also known as angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). The aldosterone system is directly targeted by spironolactone, an aldosterone antagonist. The fluid retention may be targeted by diuretics; the antihypertensive effect of diuretics is due to its effect on blood volume. Generally, the baroreceptor reflex is not targeted in hypertension because if blocked, individuals may experience orthostatic hypotension and fainting.
mm Hg !rowspan=2, Heart rate
beats per minute , - !Systolic !Diastolic , - , Calves , 140 , 70 , 75–146 , - , Cats , 155 , 68 , 100–259 , - , Dogs , 161 , 51 , 62–170 , - , Goats , 140 , 90 , 80–120 , - , Guinea-pigs , 140 , 90 , 240–300 , - , Mice , 120 , 75 , 580–680 , - , Pigs , 169 , 55 , 74–116 , - , Rabbits , 118 , 67 , 205–306 , - , Rats , 153 , 51 , 305–500 , - , Rhesus monkeys , 160 , 125 , 180–210 , - , Sheep , 140 , 80 , 63–210
pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s. Most of this pressure results from the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
pumping blood through the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ...
. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following ...
. It is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, ...
.
Blood pressure is one of the vital signs
Vital signs (also known as vitals) are a group of the four to six most crucial medical signs that indicate the status of the body's vital (life-sustaining) functions. These measurements are taken to help assess the general physical health of a ...
—together with respiratory rate
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute.
Measurement
The respiratory rate in humans is me ...
, heart rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excr ...
, oxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the given temperature. It ca ...
, and body temperature
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
—that healthcare professional
A health professional, healthcare professional, or healthcare worker (sometimes abbreviated HCW) is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physician (s ...
s use in evaluating a patient's health
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World Health Organiza ...
. Normal resting blood pressure, in an adult is approximately systolic over diastolic, denoted as "120/80 mmHg". Globally, the average blood pressure, age standardized, has remained about the same since 1975 to the present, at approx. 127/79 mmHg in men and 122/77 mmHg in women, although these average data mask significantly diverging regional trends.
Traditionally, a health-care worker measured blood pressure non-invasive
A medical procedure is defined as ''non-invasive'' when no break in the skin is created and there is no contact with the mucosa, or skin break, or internal body cavity beyond a natural or artificial body orifice. For example, deep palpation and p ...
ly by auscultation (listening) through a stethoscope for sounds in one arm's artery as the artery is squeezed, closer to the heart, by an aneroid gauge
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressu ...
or a mercury-tube sphygmomanometer
A sphygmomanometer ( ), a blood pressure monitor, or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure blood pressure, composed of an inflatable cuff to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff in a controlled manner, and a mercury ...
. Auscultation is still generally considered to be the gold standard of accuracy for non-invasive blood pressure readings in clinic. However, semi-automated methods have become common, largely due to concerns about potential mercury toxicity, although cost, ease of use and applicability to ambulatory blood pressure
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) measures blood pressure at regular intervals. It is believed to be able to reduce the white coat hypertension effect in which a patient's blood pressure is elevated during the examination process due to ...
or home blood pressure measurements have also influenced this trend. Early automated alternatives to mercury-tube sphygmomanometers were often seriously inaccurate, but modern devices validated to international standards achieve an average difference between two standardized reading methods of 5 mm Hg or less, and a standard deviation of less than 8 mm Hg. Most of these semi-automated methods measure blood pressure using oscillometry (measurement by a pressure transducer in the cuff of the device of small oscillations of
intra-cuff pressure accompanying heartbeat-induced changes in the volume of each pulse).
Blood pressure is influenced by cardiac output, systemic vascular resistance, blood volume, arterial stiffness
Arterial stiffness occurs as a consequence of biological aging and arteriosclerosis. Inflammation plays a major role in arteriosclerosis development, and consequently it is a major contributor in large arteries stiffening. Increased arterial stif ...
and varies depending of patient's situation, emotional state, activity, and relative health or disease state. In the short term, blood pressure is regulated
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. Fo ...
by baroreceptors, which act via the brain to influence the nervous and the endocrine systems.
Blood pressure that is too low is called hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dia ...
, pressure that is consistently too high is called hypertension, and normal pressure is called normotension. Both hypertension and hypotension have many causes and may be of sudden onset or of long duration. Long-term hypertension is a risk factor for many diseases, including stroke, heart disease, and kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
. Long-term hypertension is more common than long-term hypotension.
Classification, normal and abnormal values
Systemic arterial pressure
The risk of cardiovascular disease increases progressively above 115/75 mmHg, below this level there is limited evidence. Observational studies demonstrate that people who maintain arterial pressures at the low end of these pressure ranges have much better long-term cardiovascular health. There is an ongoing medical debate over what is the optimal level of blood pressure to target when using drugs to lower blood pressure with hypertension, particularly in older people. The table shows the 2018 classification of office (or clinic) blood pressure by The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Similar thresholds had been adopted by the American Heart Association for adults who are 18 years and older, but in November 2017 the American Heart Association announced revised definitions for blood pressure categories that increased the number of people considered to have high blood pressure. Blood pressure fluctuates from minute to minute and normally shows a circadian rhythm over a 24-hour period, with highest readings in the early morning and evenings and lowest readings at night. Loss of the normal fall in blood pressure at night is associated with a greater future risk of cardiovascular disease and there is evidence that night-time blood pressure is a stronger predictor of cardiovascular events than day-time blood pressure. Blood pressure varies over longer time periods (months to years) and this variability predicts adverse outcomes. Blood pressure also changes in response to temperature, noise, emotionalstress
Stress may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition
* Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase ...
, consumption of food or liquid, dietary factors, physical activity, changes in posture (such as standing-up), drugs, and disease. The variability in blood pressure and the better predictive value of ambulatory blood pressure measurements has led some authorities, such as the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the UK, to advocate for the use of ambulatory blood pressure as the preferred method for diagnosis of hypertension.
 Various other factors, such as age and
Various other factors, such as age and sex
Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing animal or plant produces male or female gametes. Male plants and animals produce smaller mobile gametes (spermatozoa, sperm, pollen), while females produce larger ones ( ova, of ...
, also influence a person's blood pressure. Differences between left-arm and right-arm blood pressure measurements tend to be small. However, occasionally there is a consistent difference greater than 10 mmHg which may need further investigation, e.g. for peripheral arterial disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is an abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. When narrowing occurs in the heart, it is called coronary artery disease, and in the brain, it is called cerebrovascular disea ...
, obstructive arterial disease or aortic dissection
Aortic dissection (AD) occurs when an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of severe chest or ...
.
There is no accepted diagnostic standard for hypotension, although pressures less than 90/60 are commonly regarded as hypotensive. In practice blood pressure is considered too low only if symptoms are present.
Systemic arterial pressure and age
Fetal blood pressure
Inpregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
, it is the fetal heart and not the mother's heart that builds up the fetal blood pressure to drive blood through the fetal circulation. The blood pressure in the fetal aorta is approximately 30 mmHg at 20 weeks of gestation, and increases to approximately 45 mmHg at 40 weeks of gestation.
The average blood pressure for full-term infants:
* Systolic 65–95 mmHg
* Diastolic 30–60 mmHg
Childhood
In children, the normal ranges for blood pressure are lower than for adults and depend on height. Reference blood pressure values have been developed for children in different countries, based on the distribution of blood pressure in children of these countries.Aging adults
In adults in most societies, systolic blood pressure tends to rise from early adulthood onward, up to at least age 70; diastolic pressure tends to begin to rise at the same time but to start to fall earlier in mid-life, approximately age 55. Mean blood pressure rises from early adulthood, plateauing in mid-life, while pulse pressure rises quite markedly after the age of 40. Consequently, in many older people, systolic blood pressure often exceeds the normal adult range, if the diastolic pressure is in the normal range this is termed isolated systolic hypertension. The rise in pulse pressure with age is attributed to increased stiffness of the arteries. An age-related rise in blood pressure is not considered healthy and is not observed in some isolated unacculturated communities.Systemic venous pressure
Blood pressure generally refers to the arterial pressure in the systemic circulation. However, measurement of pressures in the venous system and the pulmonary vessels plays an important role inintensive care medicine
Intensive care medicine, also called critical care medicine, is a medical specialty that deals with seriously or critically ill patients who have, are at risk of, or are recovering from conditions that may be life-threatening. It includes pro ...
but requires invasive measurement of pressure using a catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgi ...
.
Venous pressure is the vascular pressure in a vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenat ...
or in the atria of the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon diox ...
. It is much lower than arterial pressure, with common values of 5 mmHg in the right atrium and 8 mmHg in the left atrium.
Variants of venous pressure include:
* Central venous pressure, which is a good approximation of right atrial pressure, which is a major determinant of right ventricular end diastolic volume. (However, there can be exceptions in some cases.)
* The jugular venous pressure (JVP) is the indirectly observed pressure over the venous system. It can be useful in the differentiation of different forms of heart disease, heart and lung disease.
* The portal venous pressure is the blood pressure in the portal vein. It is normally 5–10 mmHg
Pulmonary pressure
Normally, the pressure in the pulmonary artery is about 15 mmHg at rest. Increased blood pressure in the capillaries of the lung causes pulmonary hypertension, leading to interstitial edema if the pressure increases to above 20 mmHg, and to pulmonary edema at pressures above 25 mmHg.Mean systemic pressure
If the heart is stopped, blood pressure falls, but it does not fall to zero. The remaining pressure measured after cessation of the heart beat and redistribution of blood throughout the circulation is termed the mean systemic pressure or mean circulatory filling pressure; typically this is proximally ~7mm Hg.Disorders of blood pressure
Disorders of blood pressure control include Hypertension, high blood pressure, Hypotension, low blood pressure, and blood pressure that shows excessive or maladaptive fluctuation.High blood pressure
Low blood pressure
Blood pressure that is too low is known ashypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dia ...
. This is a medical concern if it causes signs or symptoms, such as dizziness, fainting, or in extreme cases, shock (circulatory), circulatory shock.
Causes of low arterial pressure include:
* Sepsis
* Hemorrhage – blood loss
* Cardiogenic shock
* Neurally Mediated Hypotension, Neurally mediated hypotension (or reflex syncope)
* Toxins including toxic doses of blood pressure medicine
* Hormone, Hormonal abnormalities, such as Addison's disease
* Eating disorders, particularly anorexia nervosa and bulimia
Orthostatic hypotension
A large fall in blood pressure upon standing (persistent systolic/diastolic blood pressure decrease of >20/10 mm Hg) is termed orthostatic hypotension (postural hypotension) and represents a failure of the body to compensate for the effect of gravity on the circulation. Standing results in an increased Hydrostatics, hydrostatic pressure in the blood vessels of the lower limbs. The consequent distension of the veins below the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm (venous pooling) causes ~500 ml of blood to be relocated from the chest and upper body. This results in a rapid decrease in central blood volume and a reduction of ventricular Preload (cardiology), preload which in turn reduces stroke volume, and mean arterial pressure. Normally this is compensated for by multiple mechanisms, including activation of the autonomic nervous system which increasesheart rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excr ...
, myocardial contractility and systemic arterial vasoconstriction to preserve blood pressure and elicits Vein, venous vasoconstriction to decrease venous Compliance (physiology), compliance. Decreased venous compliance also results from an intrinsic Myogenic mechanism, myogenic increase in venous smooth muscle tone in response to the elevated pressure in the veins of the lower body. Other compensatory mechanisms include the veno-arteriolar axon reflex, the 'Skeletal-muscle pump, skeletal muscle pump' and 'Venous return curve, respiratory pump'. Together these mechanisms normally stabilize blood pressure within a minute or less. If these compensatory mechanisms fail and arterial pressure and blood rate of fluid flow, flow decrease beyond a certain point, the perfusion of the brain becomes critically compromised (i.e., the blood supply is not sufficient), causing lightheadedness, dizziness, weakness or Syncope (medicine), fainting. Usually this failure of compensation is due to disease, or drugs that affect the sympathetic nervous system. A similar effect is observed following the experience of excessive gravitational forces (G-loading), such as routinely experienced by aerobatic or combat pilots 'G-force, pulling Gs' where the extreme hydrostatic pressures exceed the ability of the body's compensatory mechanisms.
Variable or fluctuating blood pressure
Some fluctuation or variation in blood pressure is normal. Variations in pressure that are significantly greater than the norm are associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease brain small vessel disease, and dementia independent of the average blood pressure level. Recent evidence from clinical trials has also linked variation in blood pressure to mortality, stroke, heart failure, and cardiac changes that may give rise to heart failure. These data have prompted discussion of whether excessive variation in blood pressure should be treated, even among normotensive older adults. Older individuals and those who had received blood pressure medications are more likely to exhibit larger fluctuations in pressure, and there is some evidence that different antihypertensive agents have different effects on blood pressure variability; whether these differences translate to benefits in outcome is uncertain.Physiology

 During each heartbeat, blood pressure varies between a maximum (systolic) and a minimum (diastolic) pressure. The blood pressure in the circulation is principally due to the pumping action of the heart. However, blood pressure is also regulated by neural regulation from the brain (see Hypertension and the brain), as well as osmotic regulation from the kidney. Differences in mean blood pressure drive the flow of blood around the circulation. The rate of mean blood flow depends on both blood pressure and the resistance to flow presented by the blood vessels. In the absence of Fluid statics, hydrostatic effects (e.g. standing), mean blood pressure decreases as the circulating blood moves away from the heart through arteries and capillaries due to Viscosity, viscous losses of energy. Mean blood pressure drops over the whole circulation, although most of the fall occurs along the small arteries and arterioles. Pulsatility also diminishes in the smaller elements of the arterial circulation, although some transmitted pulsatility is observed in capillaries. Gravity affects blood pressure via hydrostatic forces (e.g., during standing), and valves in veins, breathing, and pumping from contraction of skeletal muscles also influence blood pressure, particularly in veins.
During each heartbeat, blood pressure varies between a maximum (systolic) and a minimum (diastolic) pressure. The blood pressure in the circulation is principally due to the pumping action of the heart. However, blood pressure is also regulated by neural regulation from the brain (see Hypertension and the brain), as well as osmotic regulation from the kidney. Differences in mean blood pressure drive the flow of blood around the circulation. The rate of mean blood flow depends on both blood pressure and the resistance to flow presented by the blood vessels. In the absence of Fluid statics, hydrostatic effects (e.g. standing), mean blood pressure decreases as the circulating blood moves away from the heart through arteries and capillaries due to Viscosity, viscous losses of energy. Mean blood pressure drops over the whole circulation, although most of the fall occurs along the small arteries and arterioles. Pulsatility also diminishes in the smaller elements of the arterial circulation, although some transmitted pulsatility is observed in capillaries. Gravity affects blood pressure via hydrostatic forces (e.g., during standing), and valves in veins, breathing, and pumping from contraction of skeletal muscles also influence blood pressure, particularly in veins.
Hemodynamics
A simple view of the hemodynamics of systemic arterial pressure is based around mean arterial pressure (MAP) and pulse pressure. Most influences on blood pressure can be understood in terms of their effect on cardiac output, Vascular resistance, systemic vascular resistance, orarterial stiffness
Arterial stiffness occurs as a consequence of biological aging and arteriosclerosis. Inflammation plays a major role in arteriosclerosis development, and consequently it is a major contributor in large arteries stiffening. Increased arterial stif ...
(the inverse of arterial compliance). Cardiac output is the product of stroke volume and heart rate. Stroke volume is influenced by 1) the End-diastolic volume, end diastolic volume or filling pressure of the ventricle acting via the Frank–Starling law, Frank Starling mechanism—this is influenced by blood volume; 2) Myocardial contractility, cardiac contractility; and 3) afterload, the impedance to blood flow presented by the circulation. In the short-term, the greater the blood volume, the higher the cardiac output. This has been proposed as an explanation of the relationship between high dietary salt intake and increased blood pressure; however, responses to increased dietary sodium intake vary between individuals and are highly dependent on autonomic nervous system responses and the renin–angiotensin system, changes in Plasma osmolality, plasma osmolarity may also be important. In the longer-term the relationship between volume and blood pressure is more complex. In simple terms, systemic vascular resistance is mainly determined by the caliber of small arteries and arterioles. The resistance attributable to a blood vessel depends on its radius as described by the Hagen–Poiseuille equation, Hagen-Poiseuille's equation (resistance∝1/radius4). Hence, the smaller the radius, the higher the resistance. Other physical factors that affect resistance include: vessel length (the longer the vessel, the higher the resistance), blood viscosity (the higher the viscosity, the higher the resistance) and the number of vessels, particularly the smaller numerous, arterioles and capillaries. The presence of a severe arterial stenosis increases resistance to flow, however this increase in resistance rarely increases systemic blood pressure because its contribution to total systemic resistance is small, although it may profoundly decrease downstream flow. Substances called vasoconstrictors reduce the caliber of blood vessels, thereby increasing blood pressure. Vasodilators (such as nitroglycerin) increase the caliber of blood vessels, thereby decreasing arterial pressure. In the longer term a process termed remodeling also contributes to changing the caliber of small blood vessels and influencing resistance and reactivity to vasoactive agents. Reductions in capillary density, termed capillary rarefaction, may also contribute to increased resistance in some circumstances.
In practice, each individual's autonomic nervous system and other systems regulating blood pressure, notably the kidney, respond to and regulate all these factors so that, although the above issues are important, they rarely act in isolation and the actual arterial pressure response of a given individual can vary widely in the short and long term.
Mean arterial pressure
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) is the average of blood pressure over acardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following ...
and is determined by the cardiac output (CO), systemic vascular resistance (SVR), and central venous pressure (CVP):
:::::::::::
In practice, the contribution of CVP (which is small) is generally ignored and so
:::::::::::
MAP is often estimated from measurements of the systolic pressure, and the diastolic pressure, using the equation:
where ''k'' = 0.333 although other values for ''k'' have been advocated.
Pulse pressure
Regulation of blood pressure
The endogenous, Homeostasis, homeostatic regulation of arterial pressure is not completely understood, but the following mechanisms of regulating arterial pressure have been well-characterized: * Baroreceptor reflex: Baroreceptors in the high pressure receptor zones detect changes in arterial pressure. These baroreceptors send signals ultimately to the medulla oblongata, medulla of the brain stem, specifically to the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM). The medulla, by way of the autonomic nervous system, adjusts the mean arterial pressure by altering both the force and speed of the heart's contractions, as well as the systemic vascular resistance. The most important arterial baroreceptors are located in the left and right carotid sinuses and in the aortic arch.Archived version 2009-10-03/ref> * Renin–angiotensin system (RAS): This system is generally known for its long-term adjustment of arterial pressure. This system allows the kidney to compensate for loss in blood volume or drops in arterial pressure by activating an endogenous vasoconstrictor known as angiotensin II. * Aldosterone release: This steroid hormone is released from the adrenal cortex in response to activation of the renin-angiotensin system, high serum potassium levels, or elevated Adrenocorticotropic hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Renin converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which is converted by Angiotensin-converting enzyme, angiotensin converting enzyme to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II then signals to the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone. Aldosterone stimulates sodium retention and potassium excretion by the kidneys and the consequent salt and water retention increases plasma volume, and indirectly, arterial pressure. Aldosterone may also exert direct pressor effects on vascular smooth muscle and central effects on sympathetic nervous system activity. * Baroreceptors in low pressure receptor zones (mainly in the venae cavae and the pulmonary veins, and in the atrium (heart), atria) result in feedback by regulating the secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH/Vasopressin), renin and aldosterone. The resultant increase in blood volume results in an increased cardiac output by the Frank–Starling law of the heart, in turn increasing arterial blood pressure. These different mechanisms are not necessarily independent of each other, as indicated by the link between the RAS and aldosterone release. When blood pressure falls many physiological cascades commence in order to return the blood pressure to a more appropriate level. # The blood pressure fall is detected by a decrease in blood flow and thus a decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR). # Decrease in GFR is sensed as a decrease in Na+ levels by the macula densa. # The macula densa causes an increase in Na+ reabsorption, which causes water to follow in via osmosis and leads to an ultimate increase in blood plasma, plasma volume. Further, the macula densa releases adenosine which causes constriction of the afferent arterioles. # At the same time, the juxtaglomerular cells sense the decrease in blood pressure and release renin. # Renin converts angiotensinogen (inactive form) to angiotensin I (active form). # Angiotensin I flows in the bloodstream until it reaches the capillaries of the lungs where angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) acts on it to convert it into angiotensin II. # Angiotensin II is a vasoconstrictor that will increase blood flow to the heart and subsequently the preload, ultimately increasing the cardiac output. # Angiotensin II also causes an increase in the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands. # Aldosterone further increases the Na+ and H2O reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule of the nephron. Currently, the RAS is targeted pharmacologically by ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists, also known as angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). The aldosterone system is directly targeted by spironolactone, an aldosterone antagonist. The fluid retention may be targeted by diuretics; the antihypertensive effect of diuretics is due to its effect on blood volume. Generally, the baroreceptor reflex is not targeted in hypertension because if blocked, individuals may experience orthostatic hypotension and fainting.

Measurement
Arterial pressure is most commonly measured via asphygmomanometer
A sphygmomanometer ( ), a blood pressure monitor, or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure blood pressure, composed of an inflatable cuff to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff in a controlled manner, and a mercury ...
, which uses the height of a column of mercury, or an aneroid gauge
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressu ...
, to reflect the blood pressure by auscultation. The most common automated blood pressure measurement technique is based on the Blood pressure measurement#Oscillometric, oscillometric method. Fully automated oscillometric measurement has been available since 1981. This principle has recently been used to measure blood pressure with a smartphone. Measuring pressure Invasive blood pressure, invasively, by penetrating the arterial wall to take the measurement, is much less common and usually restricted to a hospital setting.
Novel methods to measure blood pressure without penetrating the arterial wall, and without applying any pressure on patient's body are currently being explored. So-called cuffless measurements, these methods open the door to more comfortable and acceptable blood pressure monitors. An example is a cuffless blood pressure monitor at the wrist that uses only optical sensors.
One common problem in office blood pressure measurement in the United States is terminal digit preference. According to one study, approximately 40% of recorded measurements ended with the digit zero, whereas "without bias, 10%–20% of measurements are expected to end in zero" Therefore, addressing digit preference is a key issue for improving blood pressure measurement accuracy.
In animals
Blood pressure levels in non-human mammals may vary depending on the species. Heart rate differs markedly, largely depending on the size of the animal (larger animals have slower heart rates). The giraffe has a distinctly high arterial pressure of about 190 mm Hg, enabling blood perfusion through the -long neck to the head. In other species subjected to orthostatic blood pressure, such as Arboreal locomotion, arboreal snakes, blood pressure is higher than in non-arboreal snakes. A heart near to the head (short heart-to-head distance) and a long tail with tight integument favor blood perfusion to the head. As in humans, blood pressure in animals differs by age, sex, time of day, and environmental circumstances: measurements made in laboratories or under anesthesia may not be representative of values under free-living conditions. Rats, mice, dogs and rabbits have been used extensively to study the regulation of blood pressure. {, class="wikitable sortable" , +Blood pressure and heart rate of various mammals !rowspan=2, Species !colspan=2, Blood pressuremm Hg !rowspan=2, Heart rate
beats per minute , - !Systolic !Diastolic , - , Calves , 140 , 70 , 75–146 , - , Cats , 155 , 68 , 100–259 , - , Dogs , 161 , 51 , 62–170 , - , Goats , 140 , 90 , 80–120 , - , Guinea-pigs , 140 , 90 , 240–300 , - , Mice , 120 , 75 , 580–680 , - , Pigs , 169 , 55 , 74–116 , - , Rabbits , 118 , 67 , 205–306 , - , Rats , 153 , 51 , 305–500 , - , Rhesus monkeys , 160 , 125 , 180–210 , - , Sheep , 140 , 80 , 63–210
Hypertension in cats and dogs
Hypertension in cats and dogs is generally diagnosed if the blood pressure is greater than 150 mm Hg (systolic), although Sighthound, sight hounds have higher blood pressures than most other dog breeds; a systolic pressure greater than 180 mmHg is considered abnormal in these dogs.References
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Blood Pressure Blood pressure, Cardiovascular physiology Mathematics in medicine Pressure Articles containing video clips