Intertropical convergence zone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast
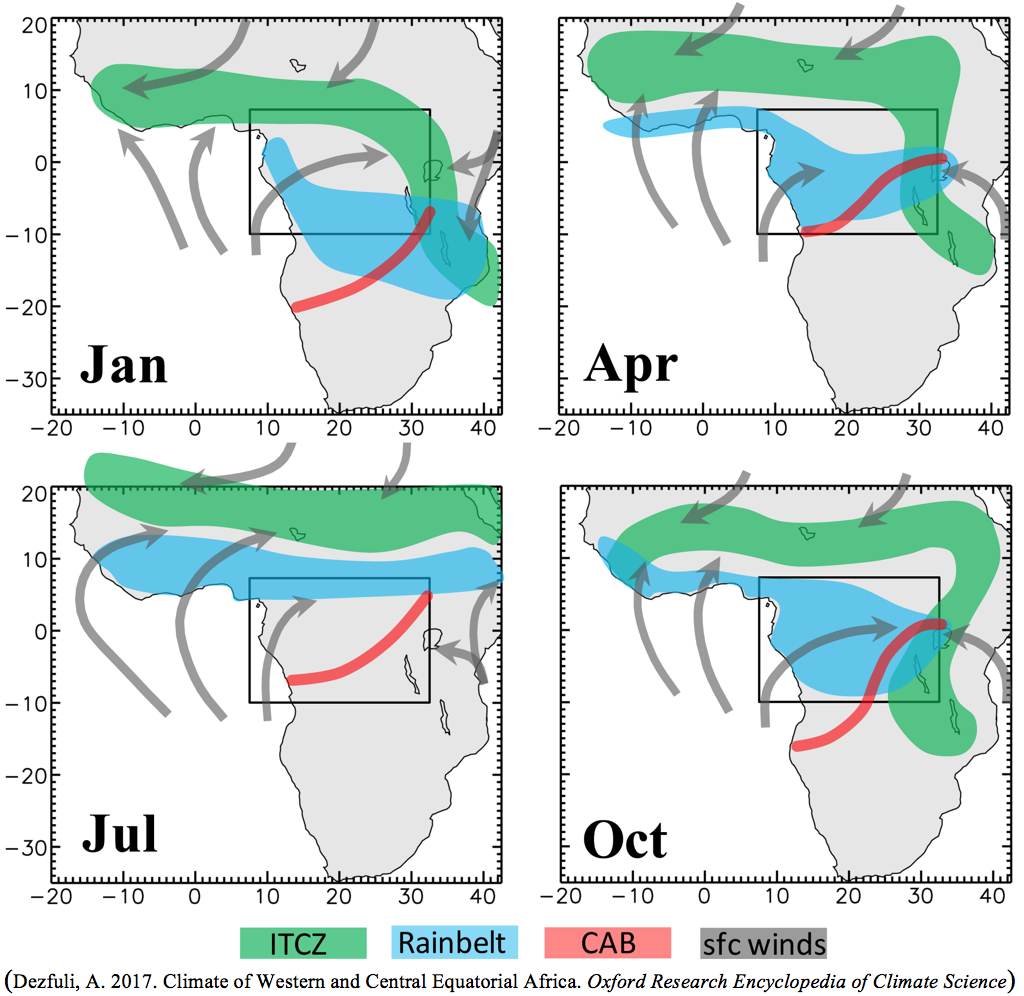 The ITCZ is commonly defined as an equatorial zone where the trade winds converge. Rainfall seasonality is traditionally attributed to the north–south migration of the ITCZ, which follows the sun. Although this is largely valid over the equatorial oceans, the ITCZ and the region of maximum rainfall can be decoupled over the continents. The equatorial precipitation over land is not simply a response to just the surface convergence. Rather, it is modulated by a number of regional features such as local atmospheric jets and waves, proximity to the oceans, terrain-induced convective systems, moisture recycling, and spatiotemporal variability of land cover and albedo.
The ITCZ is commonly defined as an equatorial zone where the trade winds converge. Rainfall seasonality is traditionally attributed to the north–south migration of the ITCZ, which follows the sun. Although this is largely valid over the equatorial oceans, the ITCZ and the region of maximum rainfall can be decoupled over the continents. The equatorial precipitation over land is not simply a response to just the surface convergence. Rather, it is modulated by a number of regional features such as local atmospheric jets and waves, proximity to the oceans, terrain-induced convective systems, moisture recycling, and spatiotemporal variability of land cover and albedo.
 The South Pacific convergence zone (SPCZ) is a reverse-oriented, or west-northwest to east-southeast aligned, trough extending from the west Pacific warm pool southeastwards towards French Polynesia. It lies just south of the equator during the Southern Hemisphere warm season, but can be more extratropical in nature, especially east of the International Date Line. It is considered the largest and most important piece of the ITCZ, and has the least dependence upon heating from a nearby
The South Pacific convergence zone (SPCZ) is a reverse-oriented, or west-northwest to east-southeast aligned, trough extending from the west Pacific warm pool southeastwards towards French Polynesia. It lies just south of the equator during the Southern Hemisphere warm season, but can be more extratropical in nature, especially east of the International Date Line. It is considered the largest and most important piece of the ITCZ, and has the least dependence upon heating from a nearby
 Tropical cyclogenesis depends upon low-level vorticity as one of its six requirements, and the ITCZ fills this role as it is a zone of wind change and speed, otherwise known as horizontal wind shear. As the ITCZ migrates to tropical and subtropical latitudes and even beyond during the respective hemisphere's summer season, increasing Coriolis force makes the formation of
Tropical cyclogenesis depends upon low-level vorticity as one of its six requirements, and the ITCZ fills this role as it is a zone of wind change and speed, otherwise known as horizontal wind shear. As the ITCZ migrates to tropical and subtropical latitudes and even beyond during the respective hemisphere's summer season, increasing Coriolis force makes the formation of
NOAA. What are the doldrums? National Ocean Service website, https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/doldrums.html, 01/07/20 Even today, leisure and competitive sailors attempt to cross the zone as quickly as possible as the erratic weather and wind patterns may cause unexpected delays.
The ITCZ in Africa
via the University of South Carolina
A Shifting Band of Rain
from March 2011 ''
Duane E. Waliser and Catherine Gautier, 1993: A Satellite-derived Climatology of the ITCZ. ''J. Climate'', 6, 2162–2174.
{{Authority control Tropical meteorology Atmospheric dynamics Geography terminology Nautical terminology
 The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisp ...
converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal equator though its specific position varies seasonally. When it lies near the geographic Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also ...
, it is called the near-equatorial trough. Where the ITCZ is drawn into and merges with a monsoonal circulation, it is sometimes referred to as a monsoon trough, a usage that is more common in Australia and parts of Asia.
Meteorology
The ITCZ was originally identified from the 1920s to the 1940s as the ''Intertropical Front'' (''ITF''), but after the recognition in the 1940s and the 1950s of the significance of wind field convergence intropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
weather production, the term ''Intertropical Convergence Zone'' (''ITCZ'') was then applied.
The ITCZ appears as a band of clouds, usually thunderstorms, that encircle the globe near the Equator. In the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
, the trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisp ...
move in a southwestward direction from the northeast, while in the Southern Hemisphere, they move northwestward from the southeast. When the ITCZ is positioned north or south of the Equator, these directions change according to the Coriolis effect imparted by Earth's rotation. For instance, when the ITCZ is situated north of the Equator, the southeast trade wind changes to a southwest wind as it crosses the Equator. The ITCZ is formed by vertical motion largely appearing as convective
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the ...
activity of thunderstorms driven by solar heating, which effectively draw air in; these are the trade winds. The ITCZ is effectively a tracer of the ascending branch of the Hadley cell and is wet. The dry descending branch is the horse latitudes.
The location of the ITCZ gradually varies with the seasons, roughly corresponding with the location of the thermal equator. As the heat capacity of the oceans is greater than air over land, migration is more prominent over land. Over the oceans, where the convergence zone
A convergence zone in meteorology is a region in the atmosphere where two prevailing flows meet and interact, usually resulting in distinctive weather conditions.
This causes a mass accumulation that eventually leads to a vertical movement an ...
is better defined, the seasonal cycle is more subtle, as the convection is constrained by the distribution of ocean temperatures. Sometimes, a double ITCZ forms, with one located north and another south of the Equator, one of which is usually stronger than the other. When this occurs, a narrow ridge of high pressure forms between the two convergence zones.
ITCZ over oceans vs. land
 The ITCZ is commonly defined as an equatorial zone where the trade winds converge. Rainfall seasonality is traditionally attributed to the north–south migration of the ITCZ, which follows the sun. Although this is largely valid over the equatorial oceans, the ITCZ and the region of maximum rainfall can be decoupled over the continents. The equatorial precipitation over land is not simply a response to just the surface convergence. Rather, it is modulated by a number of regional features such as local atmospheric jets and waves, proximity to the oceans, terrain-induced convective systems, moisture recycling, and spatiotemporal variability of land cover and albedo.
The ITCZ is commonly defined as an equatorial zone where the trade winds converge. Rainfall seasonality is traditionally attributed to the north–south migration of the ITCZ, which follows the sun. Although this is largely valid over the equatorial oceans, the ITCZ and the region of maximum rainfall can be decoupled over the continents. The equatorial precipitation over land is not simply a response to just the surface convergence. Rather, it is modulated by a number of regional features such as local atmospheric jets and waves, proximity to the oceans, terrain-induced convective systems, moisture recycling, and spatiotemporal variability of land cover and albedo.
South Pacific convergence zone
 The South Pacific convergence zone (SPCZ) is a reverse-oriented, or west-northwest to east-southeast aligned, trough extending from the west Pacific warm pool southeastwards towards French Polynesia. It lies just south of the equator during the Southern Hemisphere warm season, but can be more extratropical in nature, especially east of the International Date Line. It is considered the largest and most important piece of the ITCZ, and has the least dependence upon heating from a nearby
The South Pacific convergence zone (SPCZ) is a reverse-oriented, or west-northwest to east-southeast aligned, trough extending from the west Pacific warm pool southeastwards towards French Polynesia. It lies just south of the equator during the Southern Hemisphere warm season, but can be more extratropical in nature, especially east of the International Date Line. It is considered the largest and most important piece of the ITCZ, and has the least dependence upon heating from a nearby land mass
A landmass, or land mass, is a large region or area of land. The term is often used to refer to lands surrounded by an ocean or sea, such as a continent or a large island. In the field of geology, a landmass is a defined section of continent ...
during the summer than any other portion of the monsoon trough. The southern ITCZ in the southeast Pacific and southern Atlantic, known as the SITCZ, occurs during the Southern Hemisphere fall between 3° and 10° south of the equator east of the 140th meridian west longitude during cool or neutral El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) patterns. When ENSO reaches its warm phase, otherwise known as El Niño, the tongue of lowered sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface temperature, is the ocean temperature close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air mas ...
s due to upwelling off the South American continent disappears, which causes this convergence zone to vanish as well.
Effects on weather
Variation in the location of the intertropical convergence zone drastically affects rainfall in many equatorial nations, resulting in the wet and dry seasons of the tropics rather than the cold and warm seasons of higher latitudes. Longer term changes in the intertropical convergence zone can result in severedrought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
s or flooding in nearby areas.
In some cases, the ITCZ may become narrow, especially when it moves away from the equator; the ITCZ can then be interpreted as a front along the leading edge of the equatorial air. There appears to be a 15 to 25-day cycle in thunderstorm activity along the ITCZ, which is roughly half the wavelength of the Madden–Julian oscillation (MJO).
Within the ITCZ the average winds are slight, unlike the zones north and south of the equator where the trade winds feed. As trans-equator sea voyages became more common, sailors in the eighteenth century named this belt of calm ''the doldrums'' because of the calm, stagnant, or inactive winds.
Role in tropical cyclone formation
 Tropical cyclogenesis depends upon low-level vorticity as one of its six requirements, and the ITCZ fills this role as it is a zone of wind change and speed, otherwise known as horizontal wind shear. As the ITCZ migrates to tropical and subtropical latitudes and even beyond during the respective hemisphere's summer season, increasing Coriolis force makes the formation of
Tropical cyclogenesis depends upon low-level vorticity as one of its six requirements, and the ITCZ fills this role as it is a zone of wind change and speed, otherwise known as horizontal wind shear. As the ITCZ migrates to tropical and subtropical latitudes and even beyond during the respective hemisphere's summer season, increasing Coriolis force makes the formation of tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dep ...
s within this zone more possible. Surges of higher pressure from high latitudes can enhance tropical disturbances along its axis. In the north Atlantic and the northeastern Pacific oceans, tropical waves move along the axis of the ITCZ causing an increase in thunderstorm activity, and clusters of thunderstorms can develop under weak vertical wind shear.
Hazards
Thunderstorms along the Intertropical Convergence Zone played a role in the loss of Air France Flight 447, which leftRio de Janeiro–Galeão International Airport
Rio or Río is the Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, and Maltese word for "river". When spoken on its own, the word often means Rio de Janeiro, a major city in Brazil.
Rio or Río may also refer to:
Geography Brazil
* Rio de Janeiro
* Rio do Sul, a ...
on Sunday, 31 May 2009, at about 7:00 p.m. local time (6:00 p.m. EDT or 10:00 p.m. UTC) and had been expected to land at Charles de Gaulle Airport
Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport (french: Aéroport de Paris-Charles-de-Gaulle, ), also known as Roissy Airport or simply Paris CDG, is the principal airport serving the French capital, Paris ( and its metropolitan area), and the largest inter ...
near Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
on Monday, 1 June 2009, at 11:15 a.m. (5:15 a.m. EDT or 9:15 a.m. UTC). The aircraft crashed with no survivors while flying through a series of large ITCZ thunderstorms, and ice forming rapidly on airspeed sensors was the precipitating cause for a cascade of human errors which ultimately doomed the flight. Most aircraft flying these routes are able to avoid the larger convective
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the ...
cells without incident.
In the Age of Sail
The Age of Sail is a period that lasted at the latest from the mid-16th (or mid- 15th) to the mid-19th centuries, in which the dominance of sailing ships in global trade and warfare culminated, particularly marked by the introduction of nava ...
, to find oneself becalmed in this region in a hot and muggy climate could mean death when wind was the only effective way to propel ships across the ocean. Calm periods within the doldrums could strand ships for days or weeks.NOAA. What are the doldrums? National Ocean Service website, https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/doldrums.html, 01/07/20 Even today, leisure and competitive sailors attempt to cross the zone as quickly as possible as the erratic weather and wind patterns may cause unexpected delays.
In literature
The doldrums are notably described inSamuel Taylor Coleridge
Samuel Taylor Coleridge (; 21 October 177225 July 1834) was an English poet, literary critic, philosopher, and theologian who, with his friend William Wordsworth, was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lak ...
's poem ''The Rime of the Ancient Mariner
''The Rime of the Ancient Mariner'' (originally ''The Rime of the Ancyent Marinere'') is the longest major poem by the English poet Samuel Taylor Coleridge, written in 1797–1798 and published in 1798 in the first edition of '' Lyrical Ball ...
'' (1798) and also provide a metaphor for the initial state of boredom and indifference of Milo, the child hero of Norton Juster's classic children's novel ''The Phantom Tollbooth
''The Phantom Tollbooth'' is a children's fantasy adventure novel written by Norton Juster, with illustrations by Jules Feiffer, first published in 1961. The story follows a bored young boy named Milo who unexpectedly receives a magic tollboo ...
''. It is also cited in the book Wind, Sand and Stars
''Wind, Sand and Stars'' (French title: ''Terre des hommes'', literally "Land of Men") is a memoir by the French aristocrat aviator-writer Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, and a winner of several literary awards.
It was first published in France in ...
.
See also
* Asymmetry of the Intertropical Convergence Zone * Monsoon trough *Chemical equator
The chemical equator term and concept was coined in 2008 when researchers from University of York discovered a distinct divide between the polluted air and haze over Indonesia from the largely uncontaminated atmosphere over Australia. This divide ...
* Roaring Forties
* Horse latitudes
*Polar front
In meteorology, the polar front is the weather front boundary between the polar cell and the Ferrel cell around the 60° latitude, near the polar regions, in both hemisphere. At this boundary a sharp gradient in temperature occurs between the ...
Notes
External links
The ITCZ in Africa
via the University of South Carolina
A Shifting Band of Rain
from March 2011 ''
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it ...
''Duane E. Waliser and Catherine Gautier, 1993: A Satellite-derived Climatology of the ITCZ. ''J. Climate'', 6, 2162–2174.
{{Authority control Tropical meteorology Atmospheric dynamics Geography terminology Nautical terminology