The International Harvester Company (often abbreviated by IHC, IH, or simply International (
colloq.)) was an American manufacturer of agricultural and construction equipment, automobiles, commercial trucks, lawn and garden products, household equipment, and more. It was formed from the 1902 merger of McCormick Harvesting Machine Company and
Deering Harvester Company
Deering Harvester Company was founded in 1874 by William Deering. In 1902, Deering Harvester Company and McCormick Harvesting Machine Company, along with three smaller agricultural equipment firms (Milwaukee, Plano, and Warder, Bushnell & Glessn ...
and three smaller manufactures: Milwaukee; Plano; and Warder, Bushnell, and Glessner (manufacturers of Champion brand). In the 1980s all divisions were sold off except for International Trucks, which changed its parent company name to Navistar International (NYSE: NAV). Its brands included McCormick, Deering, and later McCormick-Deering, as well as International. Along with the
Farmall and
Cub Cadet tractors, International was also known for the
Scout and
Travelall
The International Harvester Travelall is a model line of vehicles that were manufactured by International Harvester; four generations were produced from 1953 to 1975. Derived from the International light truck line, the Travelall was a truck-base ...
vehicle nameplates.


Given its monumental importance to the building of rural communities the brand continues to have a massive cult following. The International Harvester legacy non-profits host some of the largest agriculture related events in the United States.
Following years of financial and economic decline, International began selling its separate equipment divisions, starting with the sale of the construction division to
Dresser Industries in 1982. In November 1984 IH finalized a deal with
Tenneco to sell the farm equipment division to Tenneco's subsidiary
Case Corporation, and the brand continues as
Case IH which is owned by CNH. The European division exists today as
McCormick Tractors
McCormick Tractors International Ltd. is the agricultural machinery company formed in 2000 when Case IH divested assets in order to gain European Union regulatory approval to merge with New Holland Ag. The initial assets of McCormick bought by A ...
and is owned by
ARGO SpA
ARGO SpA is a family-owned Italian holding company owned by the Morra family that manufactures agricultural machinery. Founded by Valerio Morra in 1980, the company is based in Fabbrico, Emilia-Romagna, Italy. ARGO main products are tractors ...
of Italy. International became solely a truck and engine manufacturer and reorganized as
Navistar International in 1986. Throughout its existence International Harvester was headquartered in
Chicago, Illinois. In 2020 Volkswagen agreed to fully purchase the remaining shares of Navistar.
History
Founding

The roots of International Harvester run to the 1830s, when Virginia inventor
Cyrus Hall McCormick
Cyrus Hall McCormick (February 15, 1809 – May 13, 1884) was an American inventor and businessman who founded the McCormick Harvesting Machine Company, which later became part of the International Harvester Company in 1902. Originally from the ...
perfected his version of a horse-drawn
reaper, which he field-demonstrated in 1831 and for which he received a patent in 1834. Together with his brother
Leander J. McCormick, he moved to Chicago in 1847 to be closer to the Midwestern grain fields and founded the McCormick Harvesting Machine Company. The reaper sold well, partially as a result of savvy and innovative business practices. Their products came onto the market just as the development of railroads offered wide distribution to distant territories. He developed a vast support network to demonstrate field operations. McCormick died in 1884 and his company passed to his son,
Cyrus McCormick, Jr., whose antipathy and incompetence toward organized labor sparked the
Haymarket affair, the origin of
May Day as a labor holiday.

In 1902, the McCormick Harvesting Machine Company and
Deering Harvester Company
Deering Harvester Company was founded in 1874 by William Deering. In 1902, Deering Harvester Company and McCormick Harvesting Machine Company, along with three smaller agricultural equipment firms (Milwaukee, Plano, and Warder, Bushnell & Glessn ...
, along with three smaller agricultural equipment firms (Milwaukee Harvesting Machine Co., Plano Manufacturing Co., and
Warder, Bushnell, and Glessner—manufacturers of Champion brand) merged to create the International Harvester Company.
Banker
J.P. Morgan
JP may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''JP'' (album), 2001, by American singer Jesse Powell
* ''Jp'' (magazine), an American Jeep magazine
* ''Jönköpings-Posten'', a Swedish newspaper
* Judas Priest, an English heavy metal band
* ''Jurassic Par ...
provided the financing. The architect of the merger was
George W. Perkins, one of the Morgan executives about whom Cyrus McCormick described as the "most brilliant negotiator he had ever known."
The new company was valued at $150 million.
In 1919, IH bought the Parlin and Orendorff factory in
Canton, Illinois, a leader in plow manufacturing, renaming it Canton Works. International Harvester was one of the main clients of Product Miniature Company.

Sustained success

In 1926, IH's
Farmall Works built a new plant in
Rock Island, Illinois. By 1930, the 100,000th Farmall was produced. IH next set their sights on introducing a true 'general-purpose' tractor to satisfy the needs of the average American family farmer. The resulting 'letter' series of
Raymond Loewy-designed Farmall tractors in 1939 proved a huge success. IH dominated the market through the 1950s despite stiff competition from
Ford,
Allis Chalmers,
Massey Ferguson and
John Deere.
IH ranked 33rd among United States corporations in the value of World War II production contracts. In 1946 IH acquired a defense plant in
Louisville, Kentucky, which was adapted for production of the Farmall A, B, and the new
340 tractors. It acquired the Metropolitan Body Company of Bridgeport, Connecticut, in 1948. The commercially successful
Metro line of forward control vans and trucks were produced here from 1938 until 1964.
In 1970,
Pacific Trucks was purchased. In 1974, the five-millionth IHC tractor was produced at the Rock Island Farmall plant.
Throughout the 1960s and 1970s, despite good sales, IH's profit margins remained slim. The continual addition of unrelated business lines created a somewhat unwieldy corporate organization. Overly conservative management and a rigid policy of in-house promotion tended to stifle new management strategies and technical innovation. IH faced strong competition and increased production costs, primarily due to labor and government-imposed environmental and safety regulations. In 1974 the 5 millionth International Harvester tractor, a 1066, was manufactured.
Downfall
In 1979 IH named a new CEO,
Archie McCardell
Archie R. McCardell (August 29, 1926 – July 10, 2008) was an American business leader. He was best known for his tenure as chief executive officer, president, and chairman of the board at the International Harvester farm and heavy equipment ...
, who was determined to improve profit margins and drastically cut costs. Unprofitable lines were terminated and factory production was curtailed. By the end of the year, profits were at their highest levels in 10 years but cash reserves were still low. Union members became increasingly irate over these measures and in the spring of 1979, IH prepared to face a strike. On November 1, IH announced McCardell had received a $1.8 million bonus. After he pressed for more concessions from the
United Auto Workers, a
strike was called on November 2, 1979. By the time it ended, the strike had cost the company almost $600 million (over $2
billion today).
By 1981, the company's finances were at their lowest point ever. The company sold its Payline division of construction equipment to
Dresser Industries in 1982. Further assets were sold to Tenneco, Inc., in 1984.
Following the merger, tractor production at Farmall Works ceased in 1985. Production of the new
Case IH tractors moved to
J.I. Case in Racine, Wisconsin. Production of IH Axial-Flow combines continued at the East Moline, Illinois, factory. The Memphis Works plant was closed. The truck and engine divisions remained and in 1986, Harvester changed the corporate name to
Navistar International Corporation, having sold the International Harvester name to Tenneco. Navistar International Corporation continues to manufacture medium- and heavy-duty trucks, school buses, and engines under the International brand name.
Divisions and products
Agriculture Division

The International Harvester Agricultural Division may have been second to the Truck Division but it was the best-known subsidiary. One of its early products was the Traction Truck, a frame manufactured by Morton Traction Truck Company (later bought by IHC) featuring an IHC engine.
From 1902 to the early 1920s, the McCormick and Deering dealerships kept their original branding with Mogul tractors sold by McCormick and Titan tractors at Deering due to the still-present competitiveness of the former rivals.
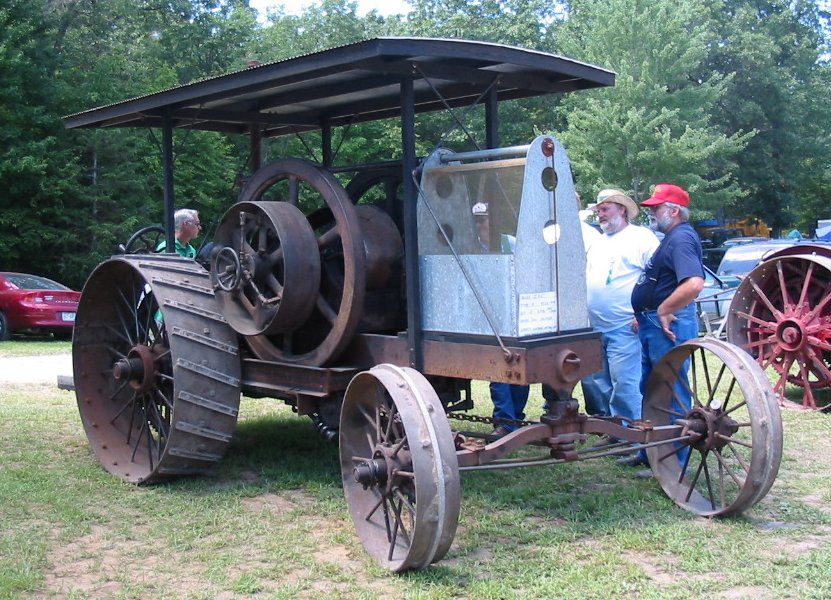

The early tractors
IH produced a range of large gasoline-powered farm tractors under the Mogul and Titan brands. Sold by McCormick dealers, the Type C Mogul was little more than a
stationary engine
A stationary engine is an engine whose framework does not move. They are used to drive immobile equipment, such as pumps, generators, mills or factory machinery, or cable cars. The term usually refers to large immobile reciprocating engines, ...
on a tractor chassis, fitted with friction drive (one speed forward, one reverse).
[Placard at WDM.] Between 1911 and 1914, 862 were built.
These tractors had varied success but the trend going into the mid-1910s was toward "small" and "cheap".
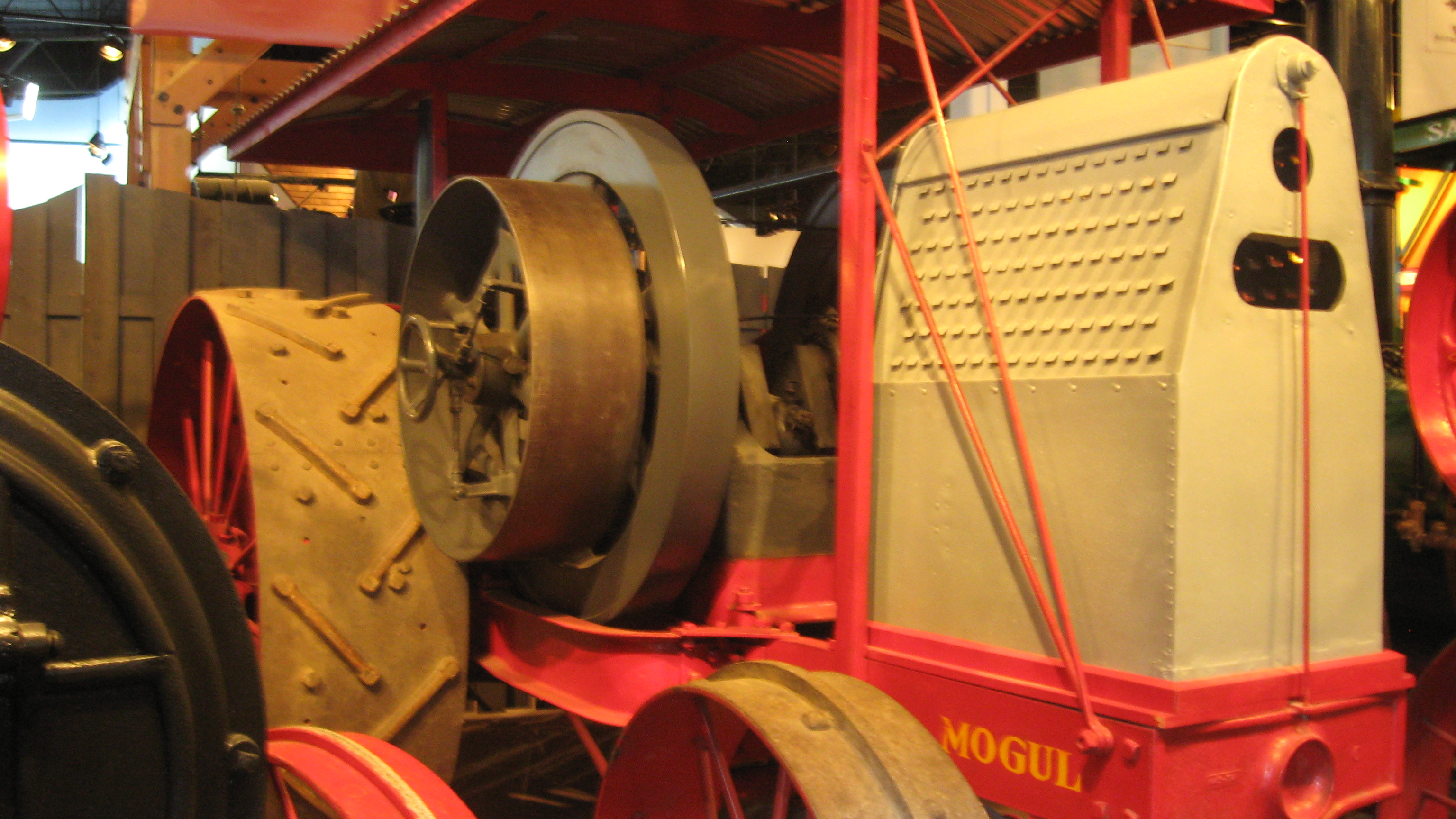
The company's first important
tractors were the 10-20 and 15-30 models. Introduced in 1915, they were primarily used as traction engines to pull plows and for belt work on
threshing machine
A threshing machine or a thresher is a piece of farm equipment that threshes grain, that is, it removes the seeds from the stalks and husks. It does so by beating the plant to make the seeds fall out.
Before such machines were developed, thr ...
s. The 10-20 and 15-30 had similar Mogul and Titan versions.
Concurrently, IHC purchased a number of smaller competitors. Parlin & Orendorff (P&O Plow) and Chattanooga Plow were purchased in 1919. Other brand names they incorporated include Keystone, D.M. Osborne, Kemp, Meadows, Sterling, Weber, Plano, and
Champion
A champion (from the late Latin ''campio'') is the victor in a challenge, contest or competition. There can be a territorial pyramid of championships, e.g. local, regional / provincial, state, national, continental and world championships, a ...
.
In 1924 IH introduced the
Farmall, a smaller general-purpose tractor, to fend off competition from
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. The company sells automobi ...
's
Fordson
Fordson was a brand name of tractors and trucks. It was used on a range of mass-produced general-purpose tractors manufactured by Henry Ford & Son Inc from 1917 to 1920, by Ford Motor Company (U.S.) and Ford Motor Company Ltd (U.K.) from 19 ...
tractors. Farmall was a leader in the emerging
row-crop tractor segment.

Following the introduction of Farmall, several similarly styled "F Series" models were introduced while the original design continued to be produced as the "Regular."
In 1932, IH produced their first
diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-cal ...
for the McCormick-Deering TD-40
crawler. This engine would start on gasoline and then switch to diesel. Other diesel engines of this era were difficult to start in cold weather and using gasoline allowed the engine to thoroughly warm up first. In 1935, it was used in the WD-40, becoming the first diesel tractor on wheels in North America (the world's first diesel tractor was Germany's Benz-Sendling BS 6 in 1922).
Heavy tractors
The market for industrial tractors grew in the 1930s. The TD-40, the first of IH's heavy-equipment crawlers, was suited for a wide range of environments. As demand for construction equipment grew, so did the competition. The diversification of the agricultural tractor range into genuine construction equipment whetted appetites for further expansion. In 1937 IH engaged designer
Raymond Loewy to revamp its product line and logo. In 1938 the first such model was the TD-65 heavy tractor, later renamed the TD-18.
The letter and standard series
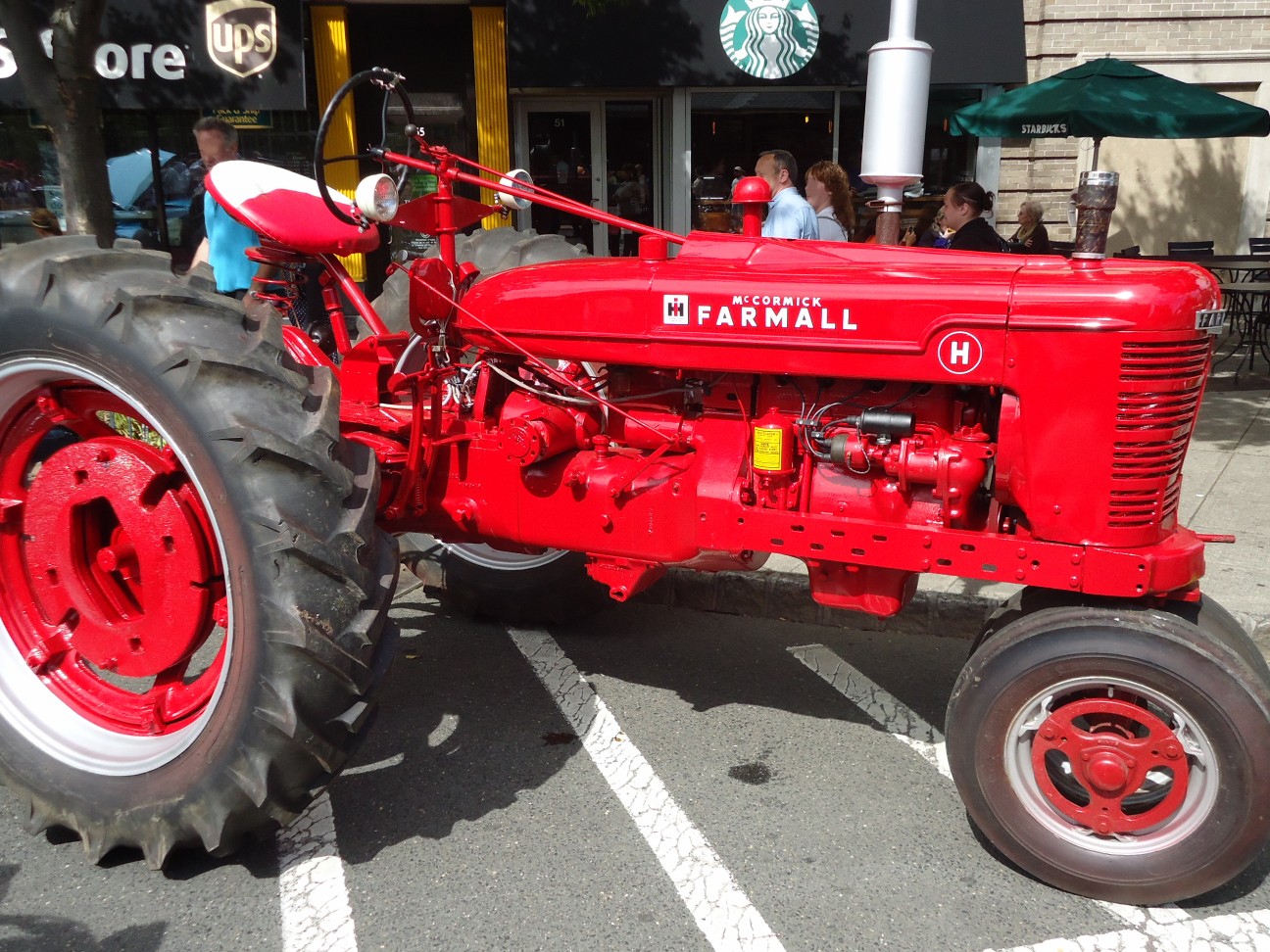

For model year 1939,
Raymond Loewy created the Farmall "letter series" (A, B, BN, C,
H, and M) and the McCormick-Deering "standard series" (W-4, W-6, and W-9). For 1941 the MD model was introduced as the first row crop diesel-powered tractor; over a decade later, IH's largest competitor, John Deere, introduced a diesel option on their row crop models. The letter series tractors were updated to the "super" series in 1953 (with the exception of the A, which had become a "super" in 1947, and the B and BN, which were discontinued in 1948). Many of these tractors (especially the largest, the H, M, and W models) are still in operation on farms today. Especially desirable are the diesel-powered MD, WD-6, and WD-9's.
The letter and standard series of tractors was produced until 1954 and was a defining product in IH history.
In 1947, the smallest tractor in the Farmall line was introduced, the
Cub. With a 60-cu. in., four-cylinder engine and a 69-inch wheelbase, the Cub was aimed at small farms which had previously relied on horse-drawn equipment. Like the
various John Deere L/LA/LI models, one of the "mechanization-resistant" markets it hoped to penetrate was the small one-mule family farms of the rural American
Deep South, but the Cub also sold to owners of larger farms needing a second tractor. Production of the Cub commenced at the newly acquired and updated Farmall Works-Louisville plant (formerly the wartime
Curtiss-Wright Aircraft factory in
Louisville, Kentucky). Selling for $545 in 1947, the Cub proved extremely popular and its design continued largely unchanged mechanically until 1979.
For 1955 in IH tractors, the numbered "hundred series" was offered. Although given slightly different styling and few new features, they were still updates to the models introduced in 1939. The only new tractor in the 1955 lineup was the 300 Utility. In 1957 power was increased in some models and the 230 Utility was introduced.
Heavy tractors: the 1950s
IH would sell 38,000 TD-18 series tractors between 1938 and 1958. The TD-18 would be replaced by an upgraded TD-18A in 1949 and 181/182 variants in 1955. In 1958 the TD-20 crawler was introduced.
60 Series recall
In July 1958, IH launched a major campaign to introduce a new line of tractors, the 60 series. At the
Hinsdale, Illinois, Testing Farm, IH entertained over 12,000 dealers from over 25 countries. The series included the first-of-its-kind six-cylinder 460 and 560 tractors. Unfortunately just a year later, these models were recalled due to final drive component failures. They had not been updated since 1939 and would fail rapidly under the stress of the more powerful 60-series engines. Some customers lost faith in IH and migrated to John Deere's New Generation of Power tractors introduced in 1960.
1960s

Throughout the 1960s, IH introduced new tractors and new sales techniques. As producing tractors was the lifeblood of the company, IH would have to remain competitive in this field. They both succeeded and failed at this goal but farming was about to change. In 1963, IH introduced the 706 and 806 tractors. Until the 88 series, all numbered seies tractors followed a simple numbering system. The first 2-3 digits was the horsepower rating, and the last number was the number of cylinders, so a 1486 was rated 148 hp and had a 6 cyl. engine, while the 1468 had 146 hp and a v8 engine. In 1964, IH made its four-millionth tractor, an 806. In 1965, IH introduced its first two-wheel-drive tractor, the 1206. Another option became available in 1965 for the 706, 806, and the new 1206: a factory-installed cab (made by Stopler Allen Co.), often called the "ice cream box" due to its shape. It could be equipped with a fan and heater. By 1967, over 100,000 models 706, 806, and 1206 were built. The 276 was also built at this time, becoming popular for smaller farms with tighter lanes and fields due to its lighter weight.
In 1967 was the introduction of the bigger and more powerful 56 series tractors as replacements for the popular "06" series. These new models included the 656, 756, the 856, and the 1256. The "ice cream box" cab was still an option. In 1969 IH introduced the 1456 Turbo at . Also that year, the 826 was introduced with the option of gearshift or hydrostatic
transmissions. The "ice cream box" cab was dropped and replaced with a new "custom" cab made by Exel Industries which could be equipped with factory air-conditioning, heat, and an AM radio. Another milestone was the 1970 introduction of the 1026 Hydro, basically a hydrostatic version of the 1256 and at that time the most powerful hydrostatic transmission tractor made in the US with .
1970s
In 1971, IH introduced the 66 series line. The new models included the 766, the 966, the 1066 turbo, the 1466 Turbo, and the 1468 V-8. The 4166 4WD was also introduced. The 966 and 1066 were available with Hydro or gearshift transmissions and the choice of two-post
roll over protection structures (ROPs) or two different cabs, the "custom" and the "deluxe". Both could be equipped with air conditioning, heat, and AM-FM radios.
In 1972, the 666 replaced the long-running 656, the 1568 V-8 replaced the 1468, and the 1566 and the 4366 4WD were introduced. Also later that year, four-post ROPs replaced two-post; the "custom" cab was dropped and the "deluxe" cab was now painted red instead of white. Due to horsepower confusions, the 966 and 1066 Hydro models were restriped; the Hydro 100 and the 666 Hydro became the Hydro 70. On February 1, 1974, at 9:00 am, the five-millionth tractor came off the assembly line at the Farmall Plant in Illinois. IH was the first tractor manufacturer to accomplish this.
Also in 1973, IH officially dropped the "Farmall" name from its tractor. This ended an era that began with the first Farmall "Regular" back in 1924.
The 4568 V-8 4WD was introduced in 1975. In 1976, the entire tractor line got a new paint job and decal pattern. No longer were the side panels all white with chrome and black decals: they were now all red with a black-striped sticker. This was done to clear inventory for the forthcoming Pro Ag Line.
In September 1976, IH released their 86 series Pro Ag Line. The models included the 786, the 886, the 986, the 186 Hydro, the 1086, the 1486 and the 1586. These new tractors had a new cab dubbed the Control Center that came standard with air conditioning, heat, and several radio-CB options. The driver sat well ahead of the rear axle and the fuel tank was mounted behind the cab over the rear axle. This increased balance and ride. Also in 1976, the 686 along with the "86" series four-wheel-drives were introduced, including the 4186, 4386, 4586, and 4786.
In 1977, International Harvester introduced the first Axial-Flow rotary combine. This machine, produced at
East Moline, Illinois
East Moline is a city in Rock Island County, Illinois, United States. The population was 21,374 at the 2020 census. East Moline is part of the Quad Cities, along with the cities of Rock Island, Moline, and the Iowa cities of Davenport and Be ...
, was the first generation of over 30 years of Axial-Flow combines.
In 1979, IH introduced two all-new tractors: the 3388 and 3588, known as the 2+2 4WD line. These tractors were the result of taking two 1086 rear ends and hooking them together with a transfer case. A year later, the 3788 was introduced. Although these tractors performed well in the field, they never sold well.
1980s
As the 1980s began, IH faced a stable economy, yet an unknown fate. In September 1981, IH announced at a dealership meeting the new "50 Series" of tractors, which included the 5088, the 5288 and the 5488. IH also released the "30 series", which included the 3088, the 3288, the 3488 Hydro, and the 3688. These new tractors proved once again that IH was innovative. Designed and styled by IH industrial designer Gregg Montgomery (Montgomery Design International), the new stylish design of the 50 and 30 series changed the look of tractors from that time forward. IH spent over $29 million to develop this new series, and the result was the last great lineup of tractors from International Harvester.
Many technology-related innovations were used in the new series. A computer monitoring system (Sentry) was developed, and IH became the first manufacturer to add a computer to a farm tractor. Other innovations included a "Z" shift pattern, an 18-speed synchronized transmission, a forward air-flow cooling system which sucked air from above the hood and blew it out the front grille, "Power Priority" three-pump hydraulic system, color-coded hydraulic lines and controls, and a new rear-hitch system. The 50 Series had an unprecedented three-year or 2,500-hour engine and drive-train warranty, which later became an industry standard. Although no new sales records were set, IH sold a respectable number of these tractors during their short production time. IH also released the "60 series 2+2s" and planned on making the "Super 70 series" 2+2s, but only a handful of these exist today. On May 14, 1985, the last IH tractor rolled off the factory line, a 5488 FWA.
In the late 1970s, IH entered a deal with Spain's
Enasa to build diesel engines there as ''Internacional de Motores''. After a downturn in the market coupled to problems with Spain's entry into the
European Economic Community threatened the profitability of this project, International Harvester withdrew in 1982.
In return for being allowed to escape all conditions of the
joint venture
A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties, generally characterized by shared ownership, shared returns and risks, and shared governance. Companies typically pursue joint ventures for one of four reasons: to acces ...
, IH lost their up-front investment in the engine plant and ended up selling British truck manufacturer
Seddon Atkinson (which had belonged to IH since 1974) to Enasa in 1983.
Brand names of the agriculture division

IH over the years used a number of brand names to market their tractor and harvesting products:
*International (1902–1985)
*Titan (1910–1924)
*Mogul (1911–1924)
*McCormick–Deering (1922–1947)
*McCormick (1947–1958)
*Farmall (1924–1973)
*Fairway (1924–1938)
*Electrall (1954–1956)
*Cub (1947-1985)
Other agricultural products
Along with the prominent tractor division, IH also sold several different types of farm-related equipment, such as
balers,
cultivator
A cultivator is a piece of agricultural equipment used for secondary tillage. One sense of the name refers to frames with ''teeth'' (also called ''shanks'') that pierce the soil as they are dragged through it linearly. It also refers to ma ...
s,
combines (self-propelled and pull behind), combine heads,
corn sheller
{{more sources, date=May 2016
A corn sheller is a hand-held device or a piece of machinery to shell corn kernels off the cob for feeding to livestock or for other uses.
History
The modern corn sheller is commonly attributed to Lester E. Denison ...
s,
cotton pickers,
manure spreader
A manure spreader or muck spreader or honey wagon is an agricultural machine used to distribute manure over a field as a fertilizer. A typical (modern) manure spreader consists of a trailer towed behind a tractor with a rotating mechanism driven ...
s, hay rakes,
crop dusters,
disk harrows, elevators, feed grinders, hammer mills, hay conditioners, milking machines, planters, mills, discs, plows, and miscellaneous equipment.
Also produced were twine,
stationary engine
A stationary engine is an engine whose framework does not move. They are used to drive immobile equipment, such as pumps, generators, mills or factory machinery, or cable cars. The term usually refers to large immobile reciprocating engines, ...
s and
wagons.
Earthmoving division
IH built up its earthmoving division over a period of time, buying companies and acquiring technology. Its heavy tractor range was an established offering, however IH wanted to offer innovative new construction technology. Significant moves included the purchase of the Frank G Hough company
which produced an iconic machine called a PayLoader, and the purchase of French company Yumbo, which produced hydraulic excavators.
Between 1956 and 1982 IH developed and sold a range of off-road
dump trucks, which were known commercially as
'PayHaulers'.
International manufactured and sold an extensive range of
heavy equipment. In 1974 IH renamed this division the 'Payline' division.
Payloaders
The original payloader model was literally a tractor which had forks welded to the front. Frank Hough was the man who invented the concept and Hough's company worked closely with IH until it was purchased in 1952. The terminology came to mean any type of front loader machine, and loaders were manufactured in a number of varieties, included wheeled and track loaders, rear wheel loaders or an articulated steering design.
PayScrapers
In the early 1950s contractors worldwide began using motor scrapers as a means of shifting dirt. IH had a hole in its product range; it did not offer a motor scraper product to the market. One of IH's suppliers, a company named Heil Earthmovers, manufactured a range of scrapers called 'Heiliners.'
Rather than spend money on R&D and enter the market at a later date, in 1953 IH bought Heil's road machinery division, incorporating a range of motor and towed scrapers.
Attachments: blades, buckets, rippers and compaction equipment
IH International had a supply agreement for its heavy tractor attachments with a
company called
Bucyrus-Erie. Amongst a variety of attachment solutions Bucyrus-Erie made a range of cable and hydraulically operated blades which fitted International-Harvester track type tractors.
IH purchased the blades range from Bucyrus-Erie in the 1950s and absorbed these into its machinery division.
IH also purchased attachments for the tractor range from Isaacson, including logging arches and dozer blades. Carrying on with its expansion IH purchased Isaacson's attachments division in 1952.
Electrall
The Electrall system was introduced in 1954; it was a short-lived attempt to market electrically operated farm equipment and accessories. The system, co-developed with
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable ene ...
, consisted of a 208
V three-phase alternating-current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which ...
generator connected with electric cables to the device to be powered. The generator could even power a household. A 10 kW Electrall generator was an option on the Farmall 400 tractor, and a 12.5 kW
PTO-driven version was made. The possible applications of Electrall power were many, but few made it to market. IH marketing materials showed a haybaler being Electrall powered. One of the more novel applications of the Electrall was a device to electrocute insects in the field at night (basically like a modern-day
bug zapper, but on a larger scale).
Road vehicles
Light duty trucks
IH is often remembered as a maker of relatively successful and innovative "light" lines of vehicles, competing directly against the
Big Three. The most common were
pickup trucks. IH made light trucks from 1907 to 1975, beginning with the Model A Auto Wagon (sometimes called the "Auto Buggy").
Production commenced in February 1907 at IH's McCormick Works in Chicago, although production was moved to
Akron, Ohio
Akron () is the fifth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and is the county seat of Summit County. It is located on the western edge of the Glaciated Allegheny Plateau, about south of downtown Cleveland. As of the 2020 Census, the city ...
, in October that year.
[ Powered by a horizontally opposed, air-cooled twin around , it was a right-hand-drive model popular in rural areas for high ground clearance on the poor roads typical of the era. It featured a rear seat convertible to a carrier bed. The Auto Wagon was renamed the Motor Truck in 1910, and was a forerunner to the successful modern pickup truck. They were called IHC until 1914, when the 'International' name was first applied.][ The final light line truck was made on May 5, 1975.
Following the early success with the Auto Buggy, International released their K and KB series trucks in the mid-1940s. They were more simplistic than other trucks released in that era. This was followed by the L Series in 1949, which was replaced by the R Series in 1952, followed by the S line (a name re-used later for IH's larger medium-duty trucks) in 1955. In 1957, to celebrate IH's ]golden anniversary
A golden jubilee marks a 50th anniversary. It variously is applied to people, events, and nations.
Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, golden jubilee refers the 50th anniversary year of the separation from Pakistan and is called in Bengali language, ...
as a truck manufacturer, this was replaced by the new A line. 'A' stands for anniversary. With light modifications to its appearance, but more serious changes under the shell (and a number of new names), this design continued in production until replaced by the 1100D in late 1969, which looked very similar to the Scout which was already in production.International Harvester Auto-Buggy The International Harvester Auto-Buggy is a two-cylinder, air-cooled motor car made by International Harvester Corporation. First announced in February 1907, the Auto-Buggy was dropped from their range of products in early 1912, but the Auto Wagon ...
File:'27 International stakebed.jpg, 1927 International one-ton stakebed
File:1954 International R110 Truck.JPG, 1954 R110 series pickup
File:1956 international pickup.jpg, 1957 A series pickup
File:IHC TRUCK.jpg, 1965 International D1000 Travelette 4x4
File:1975 International 150 Pick-Up (29146707494).jpg, 1975 International 150
Sport-utility vehicles
One of the company's light-duty vehicles was the Travelall
The International Harvester Travelall is a model line of vehicles that were manufactured by International Harvester; four generations were produced from 1953 to 1975. Derived from the International light truck line, the Travelall was a truck-base ...
, which was similar in concept to the Chevrolet Suburban
The Chevrolet Suburban is a series of automobiles built by the Chevrolet division of General Motors. The name started in 1934 for the 1935 U.S. model year, making it the longest continuously used automobile nameplate in production. It has trad ...
. The Travelette
The Travelette is a sub-model of the International Harvester series of light-duty pickup trucks that was produced from 1957 to 1975. The Travelette was the first factory-production, 6 passenger, crew-cab pickup truck, made by any United States man ...
was a crew cab, available in two- or four-wheel drive
Four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, refers to a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer ca ...
. A three-door version was available starting in 1957, and a four-door version was available starting in 1961. The 1961 Travelette four-door (crewcab) was the first six-passenger, four-door truck of its time.
The Scout, first introduced in 1961,
Motorhomes
In the 1970s, motorhomes were manufactured using IHC engines and bare chassis. Most of the bodies were constructed of fiberglass.
Commercial trucks (Truck and Engine Division)
International Harvester was an early manufacturer of medium- and heavy-duty trucks. Although based upon truck chassis, IH also became the leading manufacturer of the chassis portion of body-on-chassis conventional (type C) school buses. In 1962, IH offered the International Harvester Loadstar
The International Loadstar is a series of trucks that were produced by International Harvester from 1962 to 1978. The first product line of the company developed specifically as a medium-duty truck, the Loadstar was slotted between C-Line picku ...
which became the premier medium-duty truck. In 1978, IH offered the International Harvester S-Series
The International S series is a range of trucks that was manufactured by International Harvester (later Navistar International
Navistar, Inc is an American holding company created in 1986 as the successor to International Harvester. Navis ...
, which replaced the Loadstar in 1979.
With the truck and engine divisions remaining following the 1985 sale of the agricultural division, International Harvester Company changed their corporate name to Navistar International in 1986. Today, Navistar International's subsidiary, International Truck and Engine Corporation, manufactures and markets trucks and engines under the International brand name. From 1983 to 2010, Ford Motor Company offered International V8 diesel engines in heavy-duty pickup trucks, vans, and SUVs (using the Power Stroke name after 1994).
1960s
In 1961, the DCO-400 "Emeryville" model line was expanded with a conventional; officially named the D-400, the model line shared its cab with the COE and was the first International conventional produced with a tilting hood.
In 1962, International began to phase out the R-line series of trucks (dating to 1953). In place of a comprehensive model line ranging from half-ton pickup trucks to its largest Class 8 trucks, International introduced two purpose-built model lines for commercial use. Slotted above its Light Line pickup trucks, the Loadstar was a medium-duty conventional-cab truck.
1970s
In 1970, International split the CO Loadstar into its own product line, dubbed the Cargostar. As part of a model update, the Cargostar received a larger grille and wider cab over its predecessor. Competing directly against the Ford C-Series, the Cargostar was a medium-duty truck fitted with both gasoline and diesel engines (shared with the Loadstar conventional).
1971 marked the end of the "Emeryville" product lines, as the DC-400 Transtar 400 was replaced by the Transtar 4200/4300. Developed as a Class 8 highway tractor, the Transtar 4200/4300 introduced an all-new cab that would be used for International heavy-duty trucks through 1999. Competing against a wide range of manufacturers, the Transtar conventional was offered in both short and long-hood configurations for both regional and long-distance shipping.
In 1972, the Paystar 5000 series was introduced, replacing the 210/230 and M-series trucks (dating to 1952). Developed for severe-service use (primarily construction and related applications), the Paystar shared its cab with the Transtar, using a heavier-duty chassis, steel fenders, and a flat-panel hood.International S-series
The International S series is a range of trucks that was manufactured by International Harvester (later Navistar International) from 1977 to 2001. Introduced to consolidate the medium-duty IHC Loadstar and heavy-duty IHC Fleetstar into a sing ...
was introduced, consolidating the Fleetstar and Loadstar into a single model range. While less comprehensive than the product ranges of the 1930s to the 1950s, the S-series product line included medium-duty, heavy-duty, severe-service, and highway trucks (along with a new generation of the Schoolmaster bus chassis) from the Class 5 to Class 8 size ranges. At its 1977 launch, the S-series was introduced to replace the Fleetstar, with lighter-duty models phased in to replace the Loadstar during 1979.
1980s
In 1981, International introduced the CO9670, replacing the Transtar II. Sharing only the trapezoidal grille with the previous Transtar II, the CO9670 was designed with a larger cab with improved visibility and improved access (larger windshield, shared doors with the Transtar/Paystar conventional); to increase fuel economy, the Cummins KTA diesel was replaced by a turbocharged Cummins N-series I6.
Overseas subsidiaries
Australia

Australian Army designs
International Harvester Australia, a subsidiary of the US manufacturer, had a long relationship with the Australian Army
The Australian Army is the principal land warfare force of Australia, a part of the Australian Defence Force (ADF) along with the Royal Australian Navy and the Royal Australian Air Force. The Army is commanded by the Chief of Army (CA), who ...
with the US-designed AS series trucks in the early 1950s. The AS164 4x2 used as a tractor unit and the 4x2 AS161 used as a trayback troop transport
The association between International Harvester Australia and the Australian Army developed and in conjunction with the Army Design Establishment of the Australian Commonwealth Department of Supply, designed and constructed a range of trucks for the Australian Army. With the body loosely based upon the design of cab 13 of the Canadian Military Pattern truck, the first prototype built in 1959 was the International Truck Cargo Ton General Service, Australian No.1 Mk1. which was followed by the Mk2 prototype. A variant with a midmounted, 20,000-lb winch, resulted in the first production model, the Mk3 entering service in 1963 – just in time for Australia's entry into the Vietnam War.
A five-ton 6×6 version was to follow with three major variants the Truck Cargo 5 Ton with winch F1 which replaced the Mk3 in Vietnam service.
The F2 a tipper version that replaced the International Harvester AB160 "teaspoon Tipper" in both Vietnam and Borneo theatres of operations.
The F5 wrecker with a lack of 4×4 ton trucks available because of the Vietnam War, the Mk3 was supplemented with further 4×4 production with the updated Mk4 version which shared the cab with the 6×6 variants Production of The Australian No.1. range of trucks were produced until 1973. The Mk3, Mk4, F1, F2 and F5 saw service until the late 1980s.
ACCO
The Australian designed and built International Australian A-line Cab Over (AACO) was first produced in the late 1960s and later in 1972 the Australian C-line Cab Over (ACCO) . The ACCO is a cab over engine
Cab-over, also known as cab over engine (COE), cab forward (U.S.), flat nose (Canada), or forward control (UK), is a body style of truck, bus, or van that has a vertical front, "flat face" or a semi-hood, with the cab of the truck sitting ab ...
type truck and has been offered in 4x2, 4x4, 6x2, 6x4, 8x4, and 10x4 configurations. Engines used have been Cummins
Cummins Inc. is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and distributes engines, filtration, and power generation products. Cummins also services engines and related equipment, including fuel systems, controls, air ...
, Caterpillar, Detroit Diesel, Perkins, Neuss or GMC with Road-Ranger or Allison transmissions and Rockwell differentials. The ACCO range were built to order, serving private operators, fire departments, military services, and municipal departments across Australia and New Zealand. The ACCO became the most popular product of International Harvester in Australia. The ACCO was discontinued in November 2019 and replaced by a locally built European designed ACCO, under the ownership of Iveco.
File:Old Truck With Generator Loaded Up.jpg, International ACCO
File:EF2878.jpg, NZFS 1969 C1800 Butterbox ACCO
Brazilian subsidiary
International Harvester Máquinas S.A. was established with Brazilian government support as part of a project to develop a vehicle industry there. Their first product was the International S-184 heavy truck.
Home products
Home appliances
 Although best known for farm equipment, IH produced home appliances for farmers and nonfarmers alike. This included refrigeration equipment such as refrigerators,
Although best known for farm equipment, IH produced home appliances for farmers and nonfarmers alike. This included refrigeration equipment such as refrigerators, air conditioners
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C or AC, is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment (sometimes referred to as 'comfort cooling') and in some cases also strictly controlling ...
, and freezers. IH had a refrigeration division of its own, as did other vehicle manufacturers of the time: Ford had Philco, Chrysler had Airtemp
The history of Chrysler involves engineering innovations, high finance, wide alternations of profits and losses, various mergers and acquisitions, and multinationalization. Chrysler, a large automobile manufacturer, was founded in the 1920s and ...
, General Motors had Frigidaire, Nash-Kelvinator Corporation (and then American Motors) had Kelvinator, Studebaker had the Franklin Appliance Company, and Crosley had Crosley
Crosley was a small, independent American manufacturer of subcompact cars, bordering on microcars. At first called the Crosley Corporation and later Crosley Motors Incorporated, the Cincinnati, Ohio, firm was active from 1939 to 1952, int ...
.
The IH appliance division had originally been developed to manufacture commercial-grade items to farmers, most of whom had just received electricity by way of the many electrification projects in the U.S. before and after World War II. Among the offerings were milk coolers and walk-in freezers for produce and meat. Later on, IH courted the farmer's wife with kitchen refrigerators available in the latest designer styles. The IH spokeswoman for these products was Irma Harding, a factory trademark. These products were introduced in 1947 and sold for less than 10 years. The refrigeration division was sold to Whirlpool Corporation in 1955. Since the duration of production was short, IH appliances are rare today.
Lawn and garden
 IH branched out into the home lawn and garden business in 1961 with its line of Cub Cadet equipment, which included riding and walk-behind lawn mowers and snow blowers. Also produced were compost shredders, rotary tillers, Cadet garden tractors, and power washers.
The Cub Cadet line was sold to MTD Products in 1981.
IH branched out into the home lawn and garden business in 1961 with its line of Cub Cadet equipment, which included riding and walk-behind lawn mowers and snow blowers. Also produced were compost shredders, rotary tillers, Cadet garden tractors, and power washers.
The Cub Cadet line was sold to MTD Products in 1981.
Other products
Defense
IH manufactured light, medium, and heavy vehicles for military use. Examples include a Metro van sold to the Czechoslovakian Army in 1938, M5 Tractor
The M5 13 ton High Speed Tractor was a World War II era artillery tractor that was used by the US Army from 1942 to tow medium field artillery pieces.
Design
The M5 High Speed Tractor was a fully-tracked artillery tractor designed to tow arti ...
s and 2.5-ton M-5H-6 trucks for the US Navy and Marines in 1942, and around 3,500 2.5 ton M-5-6-318 cargo trucks provided mostly to the Soviet Union and China.
Weapons
In early 1951, the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, ...
through the Springfield Armory contracted International Harvester to produce M1 rifles, and from 1953 to 1956 IH produced 337,623 rifles in total, according to the Army Ordnance Department.
HT-341
In 1959, International Harvester created a jet turbine-powered tractor called the International HT-341. It was donated to the Smithsonian Institution in 1967.
See also
*Farmall tractor
Farmall was a model name and later a brand name for tractors manufactured by International Harvester (IH), an American truck, tractor, and construction equipment company. The Farmall name was usually presented as McCormick-Deering Farmall and ...
* Farmall Cub
* High wheeler
* International Harvester Scout
* "International Harvester" song
*List of International Harvester/Navistar engines
The International Harvester Company (IHC) has been building its own proprietary truck engines since the introduction of their first truck in 1907. International tended to use proprietary diesel engines. In the 1970s, IHC built the DVT 573 V-8 die ...
*List of International Harvester vehicles
This is a list of the various vehicles and machines produced by the International Harvester company.
Cars, SUVs, vans, and pickup trucks Cars
* Auto Buggy / Auto Wagon 1907-1916
Sport-Utility Vehicles Scout
* Scout 80 (1960–1965)
**80 Cam ...
* Lee Klancher
References
Further reading
*
* Pripps, Robert N.; Morland, Andrew (photographer) (1993) ''Farmall Tractors: History of International McCormick-Deering Farmall Tractors'' (Farm Tractor Color History Series, Osceola, WI, USA: MBI), ISBN 978-0-87938-763-1
* Winder, Gordon M. (2016) ''The American Reaper: Harvesting Networks and Technology, 1830-1910'' (Routledge, ISBN 9781317045151)
External links
International Harvester ForumInternational Harvester DigestThe Binder Planet: all IH light trucks technical resource websiteMcCormick – International Harvester CollectionOld International Harvester Truck Special Interest GroupTrucks1970s International 4030 Yard Crane Tractor
{{Authority control
*
1902 establishments in Illinois
1985 disestablishments in Illinois
Agricultural machinery manufacturers of the United States
Defunct bus manufacturers of the United States
Defunct companies based in Illinois
Defunct motor vehicle manufacturers of the United States
Defunct truck manufacturers of the United States
Emergency services equipment makers
Former components of the Dow Jones Industrial Average
Fulton County, Illinois
Home appliance manufacturers of the United States
Iveco trucks
Manufacturing companies based in Chicago
Vehicle manufacturing companies established in 1902
Vehicle manufacturing companies disestablished in 1985
Navistar International
Pickup trucks
Tractor manufacturers of the United States
Truck manufacturers of the United States
Brass Era vehicles
Highwheeler
1900s cars
1910s cars
 The roots of International Harvester run to the 1830s, when Virginia inventor
The roots of International Harvester run to the 1830s, when Virginia inventor  In 1902, the McCormick Harvesting Machine Company and
In 1902, the McCormick Harvesting Machine Company and 
 In 1926, IH's Farmall Works built a new plant in Rock Island, Illinois. By 1930, the 100,000th Farmall was produced. IH next set their sights on introducing a true 'general-purpose' tractor to satisfy the needs of the average American family farmer. The resulting 'letter' series of Raymond Loewy-designed Farmall tractors in 1939 proved a huge success. IH dominated the market through the 1950s despite stiff competition from Ford, Allis Chalmers, Massey Ferguson and John Deere.
IH ranked 33rd among United States corporations in the value of World War II production contracts. In 1946 IH acquired a defense plant in Louisville, Kentucky, which was adapted for production of the Farmall A, B, and the new 340 tractors. It acquired the Metropolitan Body Company of Bridgeport, Connecticut, in 1948. The commercially successful Metro line of forward control vans and trucks were produced here from 1938 until 1964.
In 1970, Pacific Trucks was purchased. In 1974, the five-millionth IHC tractor was produced at the Rock Island Farmall plant.
Throughout the 1960s and 1970s, despite good sales, IH's profit margins remained slim. The continual addition of unrelated business lines created a somewhat unwieldy corporate organization. Overly conservative management and a rigid policy of in-house promotion tended to stifle new management strategies and technical innovation. IH faced strong competition and increased production costs, primarily due to labor and government-imposed environmental and safety regulations. In 1974 the 5 millionth International Harvester tractor, a 1066, was manufactured.
In 1926, IH's Farmall Works built a new plant in Rock Island, Illinois. By 1930, the 100,000th Farmall was produced. IH next set their sights on introducing a true 'general-purpose' tractor to satisfy the needs of the average American family farmer. The resulting 'letter' series of Raymond Loewy-designed Farmall tractors in 1939 proved a huge success. IH dominated the market through the 1950s despite stiff competition from Ford, Allis Chalmers, Massey Ferguson and John Deere.
IH ranked 33rd among United States corporations in the value of World War II production contracts. In 1946 IH acquired a defense plant in Louisville, Kentucky, which was adapted for production of the Farmall A, B, and the new 340 tractors. It acquired the Metropolitan Body Company of Bridgeport, Connecticut, in 1948. The commercially successful Metro line of forward control vans and trucks were produced here from 1938 until 1964.
In 1970, Pacific Trucks was purchased. In 1974, the five-millionth IHC tractor was produced at the Rock Island Farmall plant.
Throughout the 1960s and 1970s, despite good sales, IH's profit margins remained slim. The continual addition of unrelated business lines created a somewhat unwieldy corporate organization. Overly conservative management and a rigid policy of in-house promotion tended to stifle new management strategies and technical innovation. IH faced strong competition and increased production costs, primarily due to labor and government-imposed environmental and safety regulations. In 1974 the 5 millionth International Harvester tractor, a 1066, was manufactured.
 The International Harvester Agricultural Division may have been second to the Truck Division but it was the best-known subsidiary. One of its early products was the Traction Truck, a frame manufactured by Morton Traction Truck Company (later bought by IHC) featuring an IHC engine.
From 1902 to the early 1920s, the McCormick and Deering dealerships kept their original branding with Mogul tractors sold by McCormick and Titan tractors at Deering due to the still-present competitiveness of the former rivals.
The International Harvester Agricultural Division may have been second to the Truck Division but it was the best-known subsidiary. One of its early products was the Traction Truck, a frame manufactured by Morton Traction Truck Company (later bought by IHC) featuring an IHC engine.
From 1902 to the early 1920s, the McCormick and Deering dealerships kept their original branding with Mogul tractors sold by McCormick and Titan tractors at Deering due to the still-present competitiveness of the former rivals. The company's first important tractors were the 10-20 and 15-30 models. Introduced in 1915, they were primarily used as traction engines to pull plows and for belt work on
The company's first important tractors were the 10-20 and 15-30 models. Introduced in 1915, they were primarily used as traction engines to pull plows and for belt work on  IH over the years used a number of brand names to market their tractor and harvesting products:
*International (1902–1985)
*Titan (1910–1924)
*Mogul (1911–1924)
*McCormick–Deering (1922–1947)
*McCormick (1947–1958)
*Farmall (1924–1973)
*Fairway (1924–1938)
*Electrall (1954–1956)
*Cub (1947-1985)
IH over the years used a number of brand names to market their tractor and harvesting products:
*International (1902–1985)
*Titan (1910–1924)
*Mogul (1911–1924)
*McCormick–Deering (1922–1947)
*McCormick (1947–1958)
*Farmall (1924–1973)
*Fairway (1924–1938)
*Electrall (1954–1956)
*Cub (1947-1985)
 Although best known for farm equipment, IH produced home appliances for farmers and nonfarmers alike. This included refrigeration equipment such as refrigerators,
Although best known for farm equipment, IH produced home appliances for farmers and nonfarmers alike. This included refrigeration equipment such as refrigerators,  IH branched out into the home lawn and garden business in 1961 with its line of Cub Cadet equipment, which included riding and walk-behind lawn mowers and snow blowers. Also produced were compost shredders, rotary tillers, Cadet garden tractors, and power washers.
The Cub Cadet line was sold to MTD Products in 1981.
IH branched out into the home lawn and garden business in 1961 with its line of Cub Cadet equipment, which included riding and walk-behind lawn mowers and snow blowers. Also produced were compost shredders, rotary tillers, Cadet garden tractors, and power washers.
The Cub Cadet line was sold to MTD Products in 1981.