Inline 6 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The straight-six engine (also referred to as an inline-six engine; abbreviated I6 or L6) is a
The straight-six engine (also referred to as an inline-six engine; abbreviated I6 or L6) is a

 If an appropriate
If an appropriate
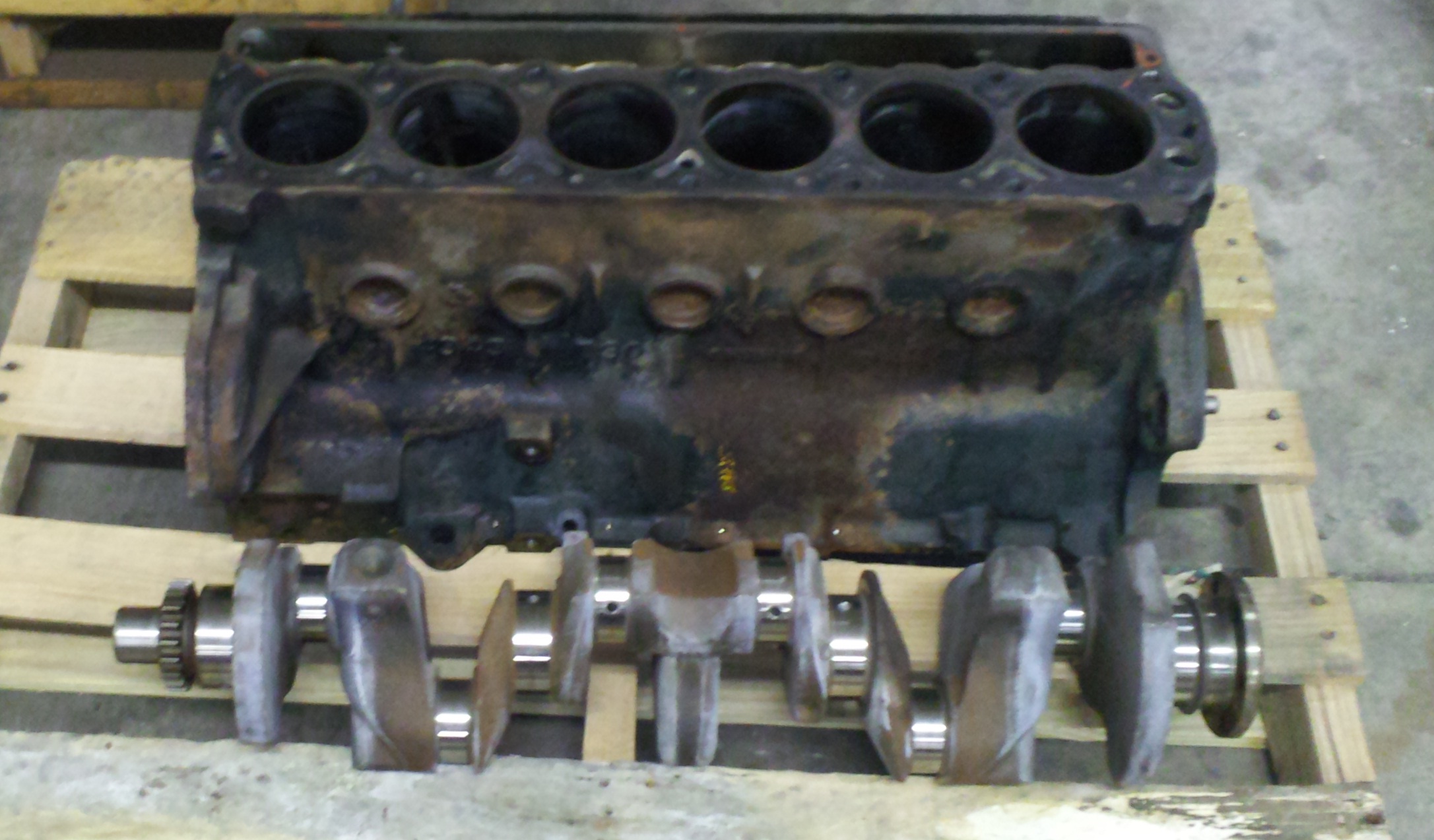


 Alfa Romeo's first production straight-six engine - 6.3 litre flathead petrol engine - was introduced in 1921 in the
Alfa Romeo's first production straight-six engine - 6.3 litre flathead petrol engine - was introduced in 1921 in the
 The straight-six engine (also referred to as an inline-six engine; abbreviated I6 or L6) is a
The straight-six engine (also referred to as an inline-six engine; abbreviated I6 or L6) is a piston engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common feat ...
with six cylinders arranged in a straight line along the crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecti ...
. A straight-six engine has perfect primary and secondary engine balance
Engine balance refers to how the forces (resulting from combustion or rotating/reciprocating components) are balanced within an internal combustion engine or steam engine. The most commonly used terms are ''primary balance'' and ''secondary bala ...
, resulting in fewer vibrations than other designs of six or less cylinders.
Until the mid-20th century, the straight-six layout was the most common design for engines with six cylinders. However, V6 engine
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, Deutz Gasmotoren Fabr ...
s became more common from the 1960s and by the 2000s most straight-six engines had been replaced by V6 engines. An exception to this trend is BMW which has produced automotive straight-six engines from 1933 to the present day.
Characteristics
In terms of packaging, straight-six engines are almost always narrower than aV6 engine
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, Deutz Gasmotoren Fabr ...
or V8 engine
A V8 engine is an eight-cylinder piston engine in which two banks of four cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V8 engine was produced by the French Antoinette company in 1904, developed and u ...
, but longer than straight-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
s, V6s, and most V8s.
Straight-six engines are typically produced in displacements ranging from , however engines ranging in size from the Benelli 750 Sei
The Benelli Sei is a series of motorcycles that were produced by Italian manufacturer Benelli, and masterminded by automotive designer Alejandro de Tomaso, from 1973 to 1989.Benelli 750/900 Performance Portfolio 1973-1989. R. M. Clarke. Brooklands ...
motorcycle engine to the Cummins B Series engine
The Cummins B Series is a family of diesel engines produced by American manufacturer Cummins. In production since 1984, the B series engine family is intended for multiple applications on and off-highway, light-duty, and medium-duty. In the auto ...
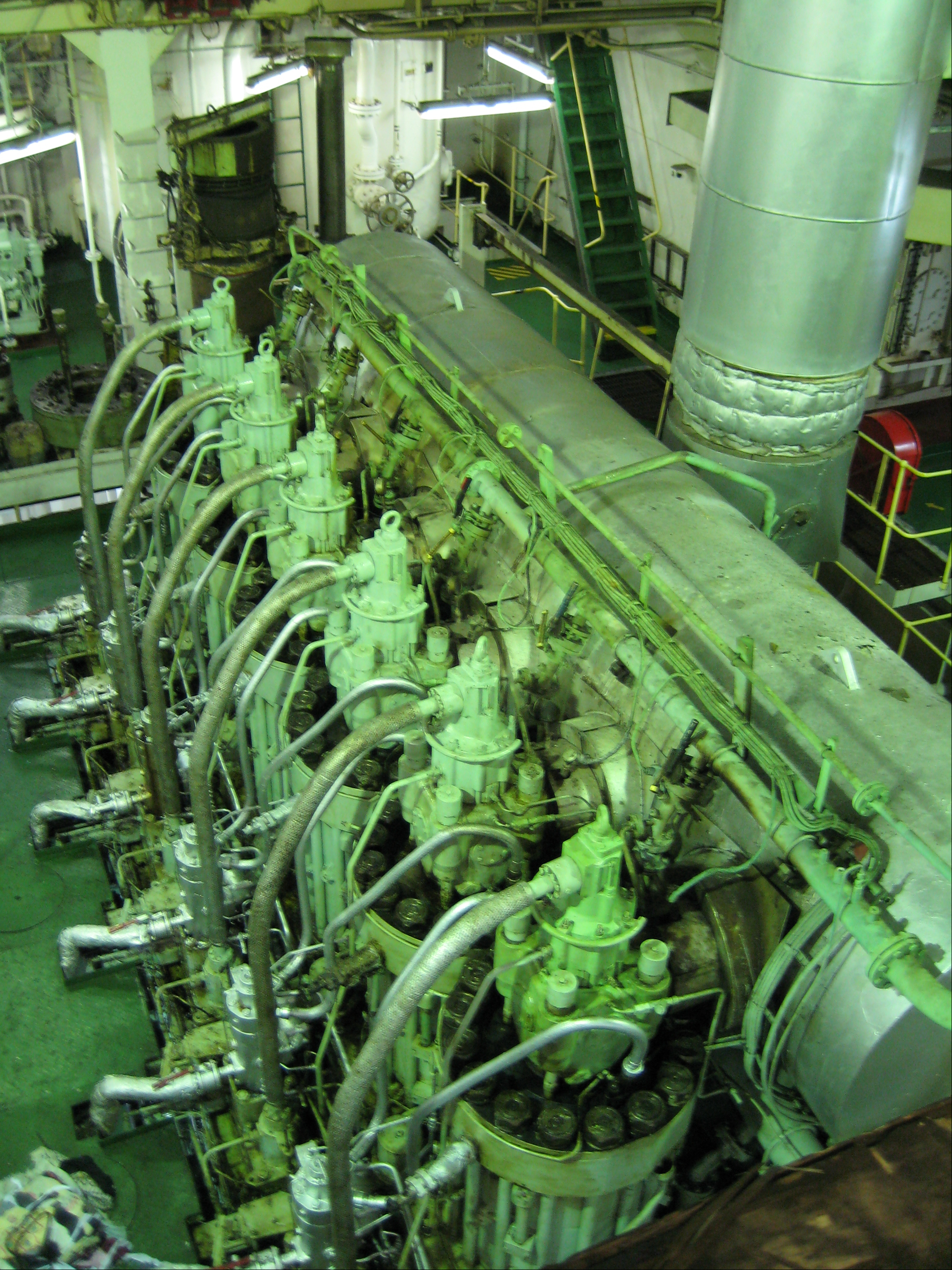
pickup truck engine have also been produced. Due to its well balanced configuration, the straight-six can be scaled up to very large sizes for heavy trucks, locomotives, industrial and marine use.
Engine balance and vibration

 If an appropriate
If an appropriate firing order
The firing order of an internal combustion engine is the sequence of ignition for the cylinders.
In a spark ignition (e.g. gasoline/petrol) engine, the firing order corresponds to the order in which the spark plugs are operated. In a diesel engi ...
is used, a straight-six engine has perfect primary and secondary engine balance
Engine balance refers to how the forces (resulting from combustion or rotating/reciprocating components) are balanced within an internal combustion engine or steam engine. The most commonly used terms are ''primary balance'' and ''secondary bala ...
. The primary balance is due to the front and rear trio of cylinders move in pairs (albeit 360° out of phase), thus cancelling out the rocking motion present in a straight-three engine
A straight-three engine (also called an inline-triple or inline-three) is a three-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
Less common than straight-four engines, straight-three engines have nonethe ...
. The secondary balance is due to the crank throws being arranged in three planes offset at 120°, which results in the non-sinusoidal forces summing to zero for all free forces up until the sixth order.
The engine balance characteristics of a straight-six engine compare favourably with the more common straight-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
s and V6 engine
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, Deutz Gasmotoren Fabr ...
s, which experience significant secondary dynamic imbalance, resulting in engine vibration. As engine reciprocating forces increase with the cube of piston bore, the straight-six is a preferred configuration for large truck engines.
Two-stroke engines
An even-firing six cylindertwo-stroke
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of ...
engine requires ignitions at 60° intervals or else it would run with simultaneous ignitions and be no smoother than a triple
Triple is used in several contexts to mean "threefold" or a " treble":
Sports
* Triple (baseball), a three-base hit
* A basketball three-point field goal
* A figure skating jump with three rotations
* In bowling terms, three strikes in a row
* ...
in power delivery. As such, it also requires crank throws at 60° such designs appear to have been limited to diesel engines such as the Detroit 71 series and some marine engines, as well as outboard motors.
Some of the 120 possible crankshaft configurations have useful properties, but all of them have a rocking imbalance of some kind which may or may not require a balance shaft, depending on the application. This is because the six pistons with six unique phases cannot be "paired" as in the four-stroke case. The Detroit engines used a configuration that, once the primary rocking couple was balanced out, was also perfectly balanced at all other rocking couples until 6th-order. Mercury came to use a configuration that canceled only the primary rocking couple and was run without a balancer.
The reciprocating masses of all configurations are still imbalanced at only 6th-order and up in their plane of motion, but the balance of kinetic energy exchange between pistons has improved to a residual 6th-order-and-up inertial torque oscillation compared with the four-stroke design being imbalanced at 3rd-order and up.
Crankshaft

Crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecti ...
s for straight-six engines usually have either four main bearing
Main may refer to:
Geography
* Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
...
s (i.e. a bearing in between each pair of crankpin
A crankpin or crank pin, also known as a rod bearing journal, is a mechanical device in an engine which connects the crankshaft to the connecting rod for each cylinder. It has a cylindrical surface, to allow the crankpin to rotate relative to the ...
s and one at each end) or seven main bearings (i.e. a bearing between every crankpin):
* Larger engines and diesel engines typically use seven bearings, in order to minimise crankshaft flex. When an engine is subject to high loads at low engine speeds, the greater distance between main bearings causes increased crankshaft flex. Modern high-compression engines subject the crankshaft to greater bending loads from higher peak gas pressures, requiring the crankthrows to have greater support from adjacent bearings, so it is now common for straight-six engines to use seven main bearings.
* Smaller and high-performance engines typically use four bearings, since having fewer main journals increases the torsional stiffness of the crankshaft. At high engine speeds, the lack of torsional stiffness can make the seven main bearing design susceptible to torsional flex and potential breakage. Any torsional flex in the crankshaft is compounded by the torsional flex of the camshaft
A camshaft is a shaft that contains a row of pointed cams, in order to convert rotational motion to reciprocating motion. Camshafts are used in piston engines (to operate the intake and exhaust valves), mechanically controlled ignition systems ...
s for the rear cylinders, since the camshafts are quite long and subject to torsional flex. At high engine speeds, the combination of camshaft and crankshaft flex results in inaccurate timing of the valve openings which in the worst case can cause the valves and pistons to collide with catastrophic results.
Usage in cars
The first production straight-six engine was introduced in the Dutch '' Spyker 60 HP'' racing car in 1903. Straight-six engines increased in popularity in the years after and by 1909, there were approximately 80 manufacturers using it (including 62 in the United Kingdom). Prior to the 1950s,V6 engine
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, Deutz Gasmotoren Fabr ...
s were rarely used, due to the poorer engine balance
Engine balance refers to how the forces (resulting from combustion or rotating/reciprocating components) are balanced within an internal combustion engine or steam engine. The most commonly used terms are ''primary balance'' and ''secondary bala ...
of V6 engines compared to straight-six engines. Since the 1980s, however, the shorter length of V6 engines has seen most manufacturers replace straight-six engines with V6 engines. An exception to this trend is German brand BMW, which has always used a straight-six layout for its six-cylinder engines.
Since 2017, a small reversal of the trend of switching to V6 engines has occurred, due to the ability to create a modular engine family of straight-four and straight-six engines sharing many components. Examples include the 2017–present Mercedes-Benz M256 engine
The Mercedes-Benz M256 engine is a turbocharged straight-six engine produced since 2017, when it was first introduced on the W222 S450. It replaces the previous M276 V6 engine, and is Mercedes' first straight-six engine since the M104 engine.
...
, the 2019–present Jaguar Land Rover Ingenium engines (AJ300 and AJ300D versions), the 2021–present Stellantis Hurricane engine and the 2022–present Mazda Skyactiv-X and Skyactiv-D engines.
Europe

 Alfa Romeo's first production straight-six engine - 6.3 litre flathead petrol engine - was introduced in 1921 in the
Alfa Romeo's first production straight-six engine - 6.3 litre flathead petrol engine - was introduced in 1921 in the Alfa Romeo G1
The Alfa Romeo G1 (1921–23) was an Italian automobile.
It was the first all-new design from Alfa Romeo after the end of the A.L.F.A. brand. The car was designed by A.L.F.A. pioneer Giuseppe Merosi as the factory's new luxury vehicle while he s ...
luxury car. A overhead valve
An overhead valve (OHV) engine, sometimes called a ''pushrod engine'', is a piston engine whose valves are located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier flathead engines, where the valves were located be ...
design was introduced in the 1922 Alfa Romeo RL sports car and an overhead camshaft
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine where the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion cha ...
design was used in the 1927 Alfa Romeo 6C sports car and various racing cars from 1927-1954. The last Alfa Romeo model using a straight-six was the 1961-1969 Alfa Romeo 2600 executive car, before the company switched to V6 engines.
Mercedes-Benz's history of straight-six engines began with the 1913 Mercedes D.I
The Mercedes D.I (also known as the Type E6F) was a six-cylinder, water-cooled, SOHC valvetrain inline engine developed in Germany for use in aircraft in 1913. Developing 75 kW (100 hp), it powered many German military aircraft during t ...
aircraft engine. The first automotive straight-six engine was the 1924-1929 ''Daimler M836'' 3.9 litre petrol engine. Following World War 2, Mercedes resumed production of straight-six engines with the 1951 introduction of the Mercedes-Benz M180 overhead camshaft engine. In 1985, the Mercedes-Benz OM603 3.0 litre diesel straight-six engine was introduced. In 1996, the company replaced its petrol straight-sixes with a series V6 engines, although the company continued to produce diesel straight-six engines. Production of petrol straight-six engines resumed in 2017 with the introduction of the Mercedes-Benz M256 turbocharged DOHC engine.
Opel began production of straight-six engines in 1927 with a 1.8 litre flathead petrol engine used by the Opel 8/40 PS. The displacement of this engine was expanded as it was used in later models such as the Opel Kapitän
The Opel Kapitän is a luxury car made in several different generations by the German car manufacturer Opel from 1938 until 1970.
Kapitän (1938–1940)
The Kapitän was the last new Opel model to appear before the outbreak of the Second ...
and Opel Admiral, with later versions switching to an overhead valve (pushrod) design. In 1968, the straight-six versions of the Opel CIH engine were introduced, initially using a single overhead camshaft (SOHC) with some later versions using double overhead camshafts (DOHC). Production of the Opel CIH engine continued until 1993, when it was replaced by a V6 engine.
Volvo began production of straight-six engines with the 1929-1958 Penta DB
Penta DB was an engine model produced by AB Pentaverken. The 1929 introduced engine was a side-valve engine with a cast-iron block and seven main bearings, and the first straight-6 engine used in Volvos. Four other variants followed after. Thes ...
flathead petrol engines. The company resumed production in 1969 with the Volvo B30 overhead valve petrol engine, followed by the straight-six versions of the Volvo Modular Engine
The Volvo Modular Engine is a family of straight-four, straight-five, and straight-six automobile piston engines that was produced by Volvo Cars in Skövde, Sweden from 1990 until 2016. All engines feature an aluminum engine block and aluminum ...
introduced in 1995 and then the Volvo SI6 engine
The SI6 (Short Inline 6) is a family of straight-six engines developed by Volvo and used by Land Rover and Volvo.
History
Volvo designed the SI6 ("short inline 6") straight-6 automobile engine for use in 2007 models. An evolution of the compan ...
introduced in 2006. Several models (such as the 1998-2006 Volvo S80
The Volvo S80 is an executive car produced by the Swedish manufacturer Volvo Cars from 1998 to 2016 across two generations. It took the place of the rear-wheel-drive S90 as Volvo's flagship sedan.
The first generation (1998–2006) was made a ...
) used the uncommon design of a transversely-mounted straight-six engine. Production of Volvo straight-six engines ceased in 2015.
BMW's first product was the 1917 BMW IIIa
BMW IIIa was an inline six-cylinder SOHC valvetrain, water-cooled aircraft engine, the first-ever engine produced by Bayerische Flugzeugwerke AG, who, at the time, were exclusively an aircraft engine manufacturer. Its success laid the foundatio ...
straight-six aircraft engine. The company began production of automotive straight-six engines in 1933 with the BMW M78
The BMW M78 is an overhead valve straight-six petrol engine which was produced from 1933 to 1950. It is the first straight-6 automobile engine produced by BMW, an engine layout which has been a key feature of the brand for many years since.
The M ...
petrol engine, a 1.2 litre overhead valve design which evolved over the years into the BMW M337
The BMW M337 is a straight-6 OHV petrol engine installed at a slanted angle which was produced in three variants (M337/1, M337/2 and M337/3) from 1952-1958. Built to power BMW's first new car after World War II, the M337 engine was a replacement ...
(produced until 1958). Production of straight-six engines resumed in 1968 with the BMW M30 single overhead camshaft engine, which was produced for 27 years and used in various models. The 1978-1989 BMW M88
The BMW M88 is a straight-6 DOHC petrol engine which was produced from 1978 to 1989. It is based on the DOHC version of the BMW M49 engine, which was used in the BMW 3.0CSi racing cars.
The M88 was produced alongside the BMW M30 engine, as th ...
engine was a double overhead camshaft design which was introduced in the BMW M1
The BMW M1 (model code E26) is a mid-engined sports car produced by German automotive manufacturer BMW from 1978 until 1981.
In the late 1970s, Italian automobile manufacturer Lamborghini entered into an agreement with BMW to build a producti ...
mid-engine sport car. BMW's introduction of turbocharged straight-six engines (aside from the low-volume variants of the M30 engine in the 1980s) was the 2006 BMW N54 and production of naturally aspirated engines ceased in 2015. , the BMW B58 turbocharged straight-six engine remains in production, along with its higher performance BMW S58
The BMW B58 is a turbocharged straight-six engine, which began production in 2015. The B58 replaced the N55 and was launched in the F30 340i.
The B58 is part of BMW's new modular engine family, each engine using a displacement of per cylinde ...
variants.
United Kingdom
Rolls-Royce's first straight-six engine was a 6.0 litre IOE petrol engine which was used in the 1905Rolls-Royce 30 hp
The Rolls-Royce 30 hp was one of four cars to be produced as a result of an agreement of 23 December 1904 between Charles Rolls and Henry Royce. Badged as a Rolls-Royce, the 30 hp was produced during 1905 and 1906 by Royce's company, ...
luxury car. This car was replaced by the 1906-1926 Rolls-Royce Silver Ghost
The Rolls-Royce Silver Ghost name refers both to a car model and one specific car from that series.
Originally named the " 40/50 h.p." the chassis was first made at Royce's Manchester works, with production moving to Derby in July 1908, ...
, which switched to a flathead (side-valve) design for its straight-six engine.
In 1906, the '' Standard Six'' luxury car was introduced, powered by a 20 hp straight-six petrol engine. Standard's engines were also used in several cars built by SS Cars and its successor Jaguar, such as the 1932 SS 1
The SS 1 (the top of its radiator says 'SS One') is a British two-door sports saloon and tourer built by Swallow Coachbuilding Company in Foleshill, Coventry, England. It was first presented to the public at the 1931 London Motor Show. In ...
sports car, the 1936 SS Jaguar 100 and the 1938 Jaguar 3½ Litre sports saloon/coupe and the 1948 Jaguar Mark V luxury car.
The 1927 Rover Two-litre
The Rover Two-litre was a mid-size luxury open tourer, saloon or limousine produced from 1927 by the Rover Company of Coventry and available through to 1932. As usual the chassis was also available to coach builders.
The 16hp Two-litre was ...
luxury car introduced the company's IOE straight-six petrol engine. This engine was used in various Rover models until the Rover P5
The Rover P5 series are large saloon and coupé automobiles that were produced by Rover from 1958 until 1973. The models were marketed under the names Rover 3 Litre, Rover 3.5 Litre and Rover 3½ Litre.
The P5 was a larger car than the P4 w ...
was discontinued in 1973, and in various Land Rover models from the 1961 Land Rover Series IIA until 1980 Land Rover Series III
The Land Rover series I, II, and III (commonly referred to as ''series'' Land Rovers, to distinguish them from later models) are compact British off-road vehicles, produced by the Rover Company since 1948, and later by British Leyland. Though ...
.
The 1928 Austin 20/6 luxury car introduced Austin's flathead straight-six petrol engine. The 1938-1939 Austin Twenty-Eight used an enlarged version of this engine. This was replaced by the Austin D-Series engine
The Austin D and K series engines are a straight-six engine made by the British Austin Motor Company between 1939 and 1968. It was developed initially for the lorry market; but was used in a number of automobiles in its later life. It was an over ...
, an overhead valve engine initially designed for trucks, which was used in passenger cars from 1947-1968 (along with several Jensen Motors
Jensen Motors Limited was a British manufacturer of sports cars and commercial vehicles in West Bromwich, England. Brothers Alan and Richard Jensen gave the new name, Jensen Motors Limited, to the commercial body and sports car body making bu ...
models from 1946-1962). The overhead valve BMC C-Series was used by various BMC brands from 1954-1971, followed by the 2.2 litre version of the BMC E-Series overhead camshaft engine, which was produced from 1970-1982.
The 1930-1936 Wolseley Hornet six lightweight car was powered by a 1.3-1.6 litre overhead camshaft straight-six petrol engine.
The 1931-1932 MG F-type tourers, 1932-1934 MG K-type sports cars and 1934-1936 MG N-type
The MG N-type Magnette is a sports car that was produced by MG from October 1934 to 1936. The car was developed from the K-Type and L-Type but had a new chassis that broke away in design from the simple ladder type used on the earlier cars of ...
sports cars were powered by an overhead camshaft straight-six petrol engine.
During the mid-1930s, the Riley MPH
The Riley MPH is a small production, two-seat sports car made between 1934 and 1935 by the Riley company of Coventry, England. Very few were made, and examples are now highly sought after.
The chassis, with half-elliptic springs and rigid axle ...
sports car and ''Riley Kestrel 6'' saloon were produced in small numbers and were powered by dual overhead camshaft straight-six petrol engine.
The 1947 Bristol 400 luxury car was powered by an overhead valve straight-six petrol engine based on the design of the BMW M328
The BMW M328 is an overhead valve straight-six petrol engine which was produced from 1936 to 1940. It was a high-performance development of the BMW M78 engine that was produced alongside the M78.
Compared with the M78, the M328 has an aluminium ...
engine. This engine remained in use until the Bristol 406
The Bristol 406 was a luxury car produced between 1958 and 1961 by British manufacturer Bristol Aeroplane Co. Their cars were constructed to very high engineering standards and were intended to be long-lasting to justify their very high price. ...
was discontinued in 1961.
The dual overhead camshaft Jaguar XK6 engine
The Jaguar XK is an inline 6-cylinder dual overhead camshaft (DOHC) engine produced by Jaguar Cars between 1949 and 1992. Introduced as a 3.4-litre, it earned fame on both the road and track, being produced in five displacements between 2 ...
petrol engine was produced from 1948-1992 in the Jaguar XK120 sports car. Introduced as a 3.4-litre, it was used both in passenger cars and racing cars, being produced in displacements of 2.4 to 4.2-litres. The XK6 engine was followed by the AJ6 and AJ16 engines, which were produced from 1984-1996, before being replaced by a Ford-derived V6 engine.
The 1948-1959 Lagonda straight-6 dual overhead camshaft petrol engine was used in various cars from Aston Martin and Lagonda. This engine's successor was the Tadek Marek-designed straight-six used in the DB4 (1958), DB5 (1963), DB6 (1965) and DBS (1967).
The Ford Zephyr 6 overhead valve engine was used in the ''Ford Zephyr'' executive car and several other models from 1951-1966.
The Triumph I6 overhead valve straight-six petrol engine was produced from 1960-1977 and debuted in the Triumph TR5
The Triumph TR5 is a sports car built by the Triumph Motor Company in Coventry, England, between August 1967 and September 1968.
Visually similar to the Michelotti-designed TR4 roadster it was derived from,TR for Triumph, Chris Harvey, the ...
sports car. The Leyland PE166 engine was loosely based on the Triumph design and was produced from 1977-1986.
The 1972-1977 TVR 2500M sports car was powered by the aforementioned Triumph I6 engine. Then from 1999-2007, TVR's own TVR Speed Six dual overhead camshaft engine was used in several of the company's sports cars.
United States
The 1906-1908 Ford Model K luxury car used a straight-six petrol engine and was the only Ford six-cylinder passenger car engine until to the 1940s. The Ford flathead I6 was produced from 1941-1951, followed by the Ford OHV I6 overhead valve engine from 1952-1964, then the Ford Thriftpower Six overhead valve engine from 1960-1982 and the Ford 240 I6 from 1965-1972. The Ford straight-sixes were replaced by V6 engines for passenger cars in the mid 1970s, however a version of the straight-six engine remained in production for SUVs, vans and trucks until 1996. In 1908, theOldsmobile Model Z
The Oldsmobile Model Z was the company's first top-level passenger car produced under the Oldsmobile brand before they became a division of General Motors in 1908. The Model Z was created and engineered after Mr. Olds left the company but before ...
was powered a flathead straight-six petrol engine, which was produced until 1912 (in the Oldsmobile Limited
The Oldsmobile Limited was an top-level passenger car produced by GM's Oldsmobile Division in 1910, offered as an upgraded replacement to the Oldsmobile Model Z when it was discontinued in 1909. The Oldsmobile Limited was very large and expensive ...
luxury car) in displacements of , and . Oldsmobile's next straight-six engine was introduced in the 1913 Oldsmobile Six
The Oldsmobile Six, also known as the Model 53, 54 and 55 (1913-1915) then a brief cancellation until it reappeared as the Model 37, 37A and 37B (1917-1921) was a top level sedan along with the Oldsmobile Series 40 junior vehicle produced by GM's ...
luxury car, initially with a displacement of , followed by a displacement of for the 1917-1921 Oldsmobile Model 37 luxury car. The later generations of the Oldsmobile Straight-6 also used a flathead design, from its introduction in the 1923 Oldsmobile Model 30 luxury car until it was replaced in 1950 by Oldsmobile's V8 engine.
The 1913-1929 Oakland Six luxury car was powered by a flathead petrol engine produced in displacements of and . In 1926, the Pontiac Six was introduced as a lower cost version of the Oakland six, powered by the Pontiac Split-Head Six flathead engine, which used two cylinder heads. This engine was replaced by the 1941-1954 Pontiac flathead six. The unrelated Pontiac OHV 6 overhead valve engine was produced in 1964-1965, based on a Chevrolet design. Pontiac's final straight-six engine was the 1966-1969 Pontiac OHC 6 overhead camshaft engine, which was replaced by Chevrolet's straight-six engine and Buick's V6 engine.
a
The overhead valve Buick Straight-6 petrol engine was introduced in the 1914 Buick Six
The Buick Six was a top level automobile produced by GM's Buick Division which was first introduced in 1914, and was the senior vehicle to the Buick Series B Four. It was an all new platform which was shared with the Oldsmobile Six and was the ...
luxury car and was produced until 1930. Buick did not produce another six-cylinder engine until they introduced a V6 engine in 1962.
The 1916-1926 Hudson Super Six
The Hudson Super Six Coach is an automobile which was first manufactured by the Hudson Motor Car Company of Detroit, Michigan in 1916. The first model was kept in production until 1928. The nameplate was revived for a rebadged Essex (automobile), ...
was powered by a straight-six petrol engine. This was followed by an IOE version in 1916. The 1951 Hudson Hornet
The Hudson Hornet is a full-sized automobile that was manufactured by Hudson Motor Car Company of Detroit, Michigan from 1951 until 1954, when Nash-Kelvinator and Hudson merged to form American Motors Corporation (AMC). Hudson automobiles co ...
introduced a flathead straight-six engine, which remained in production until Hudson was shuttered in 1957.
In 1924, Chrysler began production of a straight six version of the Chrysler flathead petrol engine. This was replaced by the 1959-2000 Chrysler Slant-6 overhead valve straight-six petrol engine, which was so named due to the 30-degree angle used to reduce the height of the engine (with the trade-off of a wider engine). The Slant-6 was released in the Dodge Dart
Dodge Dart is a line of automobiles marketed by Dodge from the 1959 to 1976 model years in North America, with production extended to later years in various other markets.
The Dart name originally appeared on a 1956 Chrysler show car featuring ...
economy car and used in many models until it was replaced by a V6 engine after 30 years in production.
The Chevrolet Stovebolt overhead valve straight-six petrol engine was introduced in 1929 as a replacement for the brand's straight-four engines and was produced in displacements of , and . The second generation of this engine family - often referred to as the Blue Flame
''Blue Flame'' is a rocket-powered land speed racing vehicle that was driven by Gary Gabelich and achieved a world land speed record on Bonneville Salt Flats in Utah on October 23, 1970. The vehicle set the FIA world record for the flying mi ...
engine - was produced from 1937-1962 in displacements of , and . This was followed by the 1962-1988 Chevrolet Turbo-Thrift engine
The Chevrolet Turbo-Thrift engine is a straight-six produced from 1962 to 2001 by the Chevrolet Division of General Motors. The entire series of engines was commonly called ''Turbo-Thrift'', although the name was first used on the 230 cubic inch v ...
(also using an overhead valve design), which was replaced by various General Motors V6 engines.
The 1952-2006 AMC Straight-6 petrol engine initially used a flathead design, before being upgraded to an overhead valve design in 1956. The engine blocks were noted for their sturdiness and used in some racing cars; a turbocharged racing engine based on the AMC Straight-6 engine block produced and competed in the 1978 Indianapolis 500 race. The final application for the AMC Straight-6 engine was the 2006 Jeep Wrangler (TJ), after which it was replaced by a V6 engine.
The 1962-1973 Jeep Tornado overhead camshaft straight-six engine was introduced in the Willys Jeep Station Wagon. At the time of its introduction, the Tornado engine had the lowest specific fuel consumption of an American gasoline (petrol) engine. The Tornado engine was replaced by the AMC Straight-6 engine.
In 2001, General Motors resumed production of straight-six engines with the Vortec 4200 dual overhead camshaft petrol engine. This engine was used in various SUV models until 2009. Also, the Duramax Straight-6 turbocharged diesel engine has been available in several General Motors SUV and light truck models since 2020.
Asia
The Toyota Type A was an overhead valve petrol engine which was based on the ''Chevrolet Stovebolt'' engine and produced from 1935-1947. This was followed by the first generation Toyota F overhead valve engine, which was produced from 1949-1975, which in turn was followed by the 2F version from 1975-1988 and the fuel-injected 3F / 3FE version from 1988-1992. This was replaced by the dual overhead camshaftToyota FZ engine
The Toyota FZ engine was a 24-valve, DOHC straight-6 internal combustion engine manufactured by Toyota to replace the F-series engine. It was used primarily in SUVs because of its large displacement, smoothness, ruggedness and torque.
Technical ...
, which was produced from 1993-2008. Produced alongside these engines was the single overhead camshaft Toyota M engine
Toyota Motor Corporation's M family of engines were a longitudinally mounted straight-6 engine design. They were used from the 1960s through the 1990s. All M family engines were OHC designs. While the M family was born with a chain-driven single c ...
, which was introduced in 1965 and produced over seven generations (the final being the ''7M-GTE'' version) until 1993. The M engine was replaced by the dual overhead camshaft Toyota JZ engine
The Toyota JZ engine family is a series of inline-6 automobile engines produced by Toyota Motor Corporation. As a replacement for the M-series inline-6 engines, the JZ engines were 24-valve DOHC engines in 2.5- and 3.0-litre versions.
1JZ
T ...
, which was produced from 1990-2007 and is arguably Toyota's best-known straight-six engine. Toyota's third line of straight-six engines was the 2.0 litre Toyota G engine, which was released as a single overhead camshaft engine in 1979 and upgraded to dual overhead camshafts before production ended in 2008.
Nissan's first straight-six engine was the 1950-1952 Nissan NAK flathead petrol engine, which continued in various forms until production of the Nissan P engine ended in 2003. The 1963-1965 Nissan K overhead valve petrol engine was used in the Nissan Cedric Special 50 luxury car. Using a similar design, the Nissan H30 engine was used in several luxury cars form 1965-1989. In 1966, Nissan began production of the six-cylinder versions of the Nissan L single overhead camshaft engine, which was produced until 2009. The 1985-2004 Nissan RB engine, used in the Nissan Skyline
The is a brand of automobile originally produced by the Prince Motor Company starting in 1957, and then by Nissan after the two companies merged in 1967. After the merger, the Skyline and its larger counterpart, the Nissan Gloria, were sold i ...
and several other cars, was produced in single overhead camshaft and dual overhead camshaft configurations until it was replaced by a V6 engine. The Nissan TB overhead valve engine was introduced in 1987 and produced alongside the other straight-six engines.
The six-cylinder versions of the Prince G engine
The Prince G-series engine was the company's only straight-four and straight-six engines which began production in 1955. A number of variations were made, with both OHV and OHC heads. A diesel four-cylinder with was also built, called the D-6 ...
were introduced in 1963 and remained in production until 1969, three years after Prince's merger with Nissan. The 1969-1973 Nissan S20 dual overhead camshaft engine (used in the Nissan Fairlady
The Datsun Sports (called Datsun Fairlady in the Japanese and Australian markets), was a series of roadsters produced by Nissan in the 1960s. The series was a predecessor to the Z-car in the Fairlady line, and offered a competitor to the Europea ...
and first generation of the Nissan Skyline GT-R
The is a sports car based on the Nissan Skyline range. The first cars named "Skyline GT-R" were produced between 1969 and 1972 under the model code KPGC10, and were successful in Japanese touring car racing events. This model was followed by ...
) was based on the Prince G engine.
Mitsubishi produced six-cylinder versions of the Mitsubishi KE engine from 1963-1970, as well as the rare six-cylinder versions of the Mitsubishi 6G34 version of the single overhead camshaft "Saturn" engine from 1970-1976.
The 2000-2006 Daewoo Magnus
The Daewoo Magnus is a mid-sized sedan developed and manufactured by Daewoo for model years 2000-2006 under a single generation, and marketed globably by GM Daewoo and other General Motors divisions, as well as GMDAT stake holder Suzuki. Develo ...
(also called the Chevrolet Evanda, Chevrolet Epica, Holden Epica or Suzuki Verona) was powered by the ''Daewoo XK6'' straight-six petrol engine, which is one of few straight-six engines to be used in a transverse engine
A transverse engine is an engine mounted in a vehicle so that the engine's crankshaft axis is perpendicular to the direction of travel. Many modern front-wheel drive vehicles use this engine mounting configuration. Most rear-wheel drive vehicle ...
front-wheel drive car.
Australia
From the 1950s to the 2010s, many cars produced in Australia were powered by a straight-six engine. Holden's first car, the 1948Holden 48-215
The Holden 48-215 is a mid-size sedan which was produced by the Australian automaker Holden between November 1948 and October 1953. A coupe utility derivative, coded as the 50-2106 and marketed as the Holden Coupe Utility, was produced from J ...
sedan, was powered by the Holden 'grey' motor, an overhead valve petrol engine. This engine was replaced by the Holden 'red' motor, which was produced from 1963-1980 and in turn followed by the 1980-1984 Holden 'blue' motor. The final locally-produced Holden straight-six was the 1984-1986 Holden 'black' motor, which was initially replaced by the Japanese-built Nissan RB30 engine, before Holden switched to a locally-built V6 engine.
Ford produced straight-six engines for the longest time of any Australian manufacturer. In 1960, the Ford Falcon
Ford Falcon is an automobile nameplate applied to several vehicles worldwide.
* Ford Falcon (North America), an automobile produced by Ford from 1960 to 1970.
* Ford Falcon (Argentina), a car built by Ford Argentina from 1962 until 1991.
* For ...
large sedan was introduced with a locally-built version of the American Ford Straight-6 overhead valve engine. In 1998, these engines were upgraded to a single overhead camshaft design. This was followed in 2002 by the Ford Barra dual overhead camshaft engine in 2002, which was produced in both naturally aspirated and turbocharged versions. The Ford Barra engine remained in use until Ford Australia ceased local production in 2016.
The Chrysler Valiant was introduced in 1962, powered by the American Chrysler Slant 6. In 1970, the Valiant switched over to the Chrysler Hemi-6 overhead valve engine, an Australia-only engine that was produced until Chrysler Australia ceased production of large cars in 1981.
The 1962-1965 Austin Freeway and Wolseley 24/80
The Wolseley 24/80 is an automobile produced by British Motor Corporation (Australia) from May 1962 to October 1965,BMC E-series overhead camshaft engines, which were introduced in the 1970 Austin Kimberley / Austin Tasman front-wheel drive sedans, which were produced until 1972. This engine was upsized to a 2.6 L displacement in 1973 and used
 From 1964-1967, Honda produced several
From 1964-1967, Honda produced several
Leyland P76
The Leyland P76 is a large car that was produced by Leyland Australia, the Australian subsidiary of British Leyland. Featuring what was described at the time as the "standard Australian wheelbase of 111 inches", it was intended to provide the c ...
and the Morris Marina
The Morris Marina is a front-engined, rear-wheel-drive small family car that was manufactured by the Austin-Morris division of British Leyland from 1971 until 1980. It served to replace the Morris Minor in the Morris product line, which ...
large cars until 1975.
Usage in motorcycles
 From 1964-1967, Honda produced several
From 1964-1967, Honda produced several Grand Prix motorcycle racing
Grand Prix motorcycle racing is the premier class of motorcycle road racing events held on road circuits sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de Motocyclisme (FIM). Independent motorcycle racing events have been held since the start ...
motorcycles powered by straight-six versions of the Honda RC petrol racing engine; these versions were designated the '3RC164', 'RC165', 'RC166' and Honda RC174
The Honda RC174 was a racing motorcycle built by Honda for the 350 cc class of Grand Prix motorcycle racing in the 1967 season. Based on the 250 cc class Honda RC166, it had less than 300 cc, yet won seven out of the eight races ...
. The unrelated road-use Honda CBX was produced from 1978-1982 and was powered by a dual overhead camshaft petrol engine.
The 1973-1989 Benelli Sei
The Benelli Sei is a series of motorcycles that were produced by Italian manufacturer Benelli, and masterminded by automotive designer Alejandro de Tomaso, from 1973 to 1989.Benelli 750/900 Performance Portfolio 1973-1989. R. M. Clarke. Brooklands ...
series was the first road-use motorcycle to use a straight-six engine. Initially released with a single overhead camshaft petrol engine, in 1979 it was upgraded to a engine.
The 1979-1989 Kawasaki Z1300
The Kawasaki Z1300 is a standard motorcycle unusual for its large-displacement ''1,300 cc'' straight-six engine made by Kawasaki from 1979 to 1989.
Performance
Kawasaki Z1300's length is 89.1 inches, and its width is 30.9 inches, its heig ...
roadster motorcycle was powered by a dual overhead camshaft petrol engine.
From 2011–present, the BMW K1600 series of touring motorcycles have been powered by a dual overhead camshaft petrol engine.
Usage in trucks
Straight-six engines used in trucks include: * 5.9 and 6.7 litre versions of the 1984–present Cummins B Series turbocharged diesel engine * General Motors' 2002-2009 Vortec 4200 naturally-aspirated petrol engineDiesel engines
Automotive engines
Straight-six engines used in automobiles include: * 1978-1995 Volkswagen D24 naturally-aspirated engine and the 1982-1992 Volkswagen D24T turbocharged engine * 1986-1997 Mercedes-Benz OM603 engine - produced in naturally-aspirated and turbocharged variants * BMW's line of diesel engines consists of theBMW M21
The BMW M21 is a straight-six diesel engine developed by the Bavarian engine manufacturer BMW. It has swirl chamber injection and is based on the M20 petrol engine and was produced for BMW by the Upper Austrian Steyr engine plant from 1983 to ...
(introduced in 1981) through to the current BMW B57 engine
* 1985-2009 Nissan RD (naturally-aspirated and turbocharged variants) and 1987-2007 Nissan TD42 (turbocharged) engines
Industrial-use and truck engines
* various Toyota engines from 1956-present * Cummins B Series (5.9 and 6.7 litre versions) from 1984-present * industrial and truck engines from MAN Truck & Bus,Scania
Scania, also known by its native name of Skåne (, ), is the southernmost of the historical provinces (''landskap'') of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous with Skån ...
and Yuchai
See also
*Flat-six engine
A flat-six engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-six, is a six-cylinder piston engine with three cylinders on each side of a central crankshaft. The most common type of flat-six engine is the boxer-six engine, where each pair of opposed cy ...
* V6 engine
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, Deutz Gasmotoren Fabr ...
* VR6 engine
VR6 engines are V6 piston engines with a narrow angle between the cylinder banks and a single cylinder head covering both banks of cylinders.
Volkswagen Group introduced the first VR6 engine in 1991 and VR6 engines currently remain in producti ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Straight-Six Engine 6