Information Management on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Information management (IM) concerns a cycle of organizational activity: the acquisition of
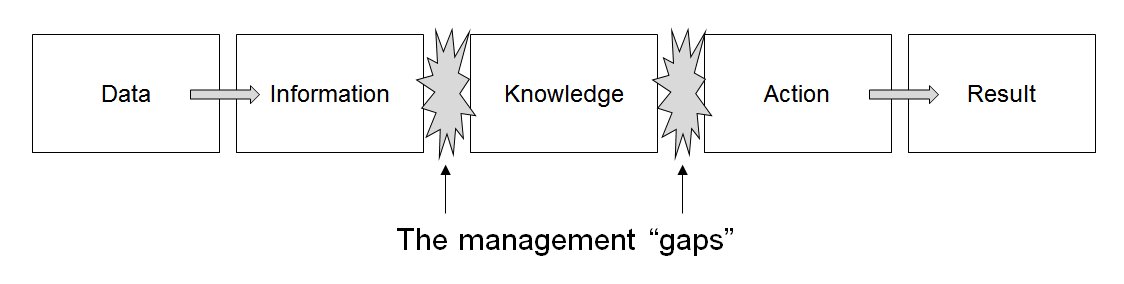 This is often referred to as the DIKAR model: Data, Information, Knowledge, Action and Result,Venkatraman, N., 1996. Managing IT resources as a value center, ''IS Executive Seminar Series, Cranfield School of Management'' it gives a strong clue as to the layers involved in aligning technology and organisational strategies, and it can be seen as a pivotal moment in changing attitudes to information management. The recognition that information management is an investment that must deliver meaningful results is important to all modern organisations that depend on information and good decision-making for their success.Bytheway, A., 2015
This is often referred to as the DIKAR model: Data, Information, Knowledge, Action and Result,Venkatraman, N., 1996. Managing IT resources as a value center, ''IS Executive Seminar Series, Cranfield School of Management'' it gives a strong clue as to the layers involved in aligning technology and organisational strategies, and it can be seen as a pivotal moment in changing attitudes to information management. The recognition that information management is an investment that must deliver meaningful results is important to all modern organisations that depend on information and good decision-making for their success.Bytheway, A., 2015
Investing in Information: the Information Management Body of Knowledge
Geneva: Springer
 Such an information portfolio as this shows how information can be gathered and usefully organised, in four stages:
Stage 1: Taking advantage of public information: recognise and adopt well-structured external schemes of reference data, such as post codes, weather data, GPS positioning data and travel timetables, exemplified in the personal computing press.Ashbrook, D. & Starner, T., 2003. Using GPS to learn significant locations and predict movement across multiple users. ''Personal and Ubiquitous Computing'', 7(5), pp.275–286
Stage 2: Tagging the noise on the
Such an information portfolio as this shows how information can be gathered and usefully organised, in four stages:
Stage 1: Taking advantage of public information: recognise and adopt well-structured external schemes of reference data, such as post codes, weather data, GPS positioning data and travel timetables, exemplified in the personal computing press.Ashbrook, D. & Starner, T., 2003. Using GPS to learn significant locations and predict movement across multiple users. ''Personal and Ubiquitous Computing'', 7(5), pp.275–286
Stage 2: Tagging the noise on the
 ;The information management knowledge areas
The IMBOK is based on the argument that there are six areas of required management competency, two of which (“business process management” and “business information management”) are very closely related.Bytheway, A., 2015. ''Investing in Information: the Information Management Body of Knowledge'', Geneva: Springer,
p29
* Information technology: The pace of change of
;The information management knowledge areas
The IMBOK is based on the argument that there are six areas of required management competency, two of which (“business process management” and “business information management”) are very closely related.Bytheway, A., 2015. ''Investing in Information: the Information Management Body of Knowledge'', Geneva: Springer,
p29
* Information technology: The pace of change of
information
Information is an abstract concept that refers to that which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level information pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed. Any natural process that is not completely random, ...
from one or more sources, the custodianship and the distribution of that information to those who need it, and its ultimate disposal through archiving or deletion.
This cycle of information organisation involves a variety of stakeholders, including those who are responsible for assuring the quality, accessibility
Accessibility is the design of products, devices, services, vehicles, or environments so as to be usable by people with disabilities. The concept of accessible design and practice of accessible development ensures both "direct access" (i. ...
and utility
As a topic of economics, utility is used to model worth or value. Its usage has evolved significantly over time. The term was introduced initially as a measure of pleasure or happiness as part of the theory of utilitarianism by moral philosophe ...
of acquired information; those who are responsible for its safe storage and disposal; and those who need it for decision making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either ra ...
. Stakeholders might have rights to originate, change, distribute or delete information according to organisational information management policies.
Information management embraces all the generic concepts of management, including the planning, organizing, structuring, processing, control
Control may refer to:
Basic meanings Economics and business
* Control (management), an element of management
* Control, an element of management accounting
* Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization
* Controlli ...
ling, evaluation and reporting of information activities, all of which is needed in order to meet the needs of those with organisational roles or functions that depend on information. These generic concepts allow the information to be presented to the audience or the correct group of people. After individuals are able to put that information to use, it then gains more value.
Information management is closely related to, and overlaps with, the management of data
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpret ...
, system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and express ...
s, technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scien ...
, processes and – where the availability of information is critical to organisational success – strategy. This broad view of the realm of information management contrasts with the earlier, more traditional view, that the life cycle of managing information is an operational matter that requires specific procedures, organisational capabilities and standards that deal with information as a product or a service.
History
Emergent ideas out of data management
In the 1970s, the management of information largely concerned matters closer to what would now be calleddata management
Data management comprises all disciplines related to handling data as a valuable resource.
Concept
The concept of data management arose in the 1980s as technology moved from sequential processing (first punched cards, then magnetic tape) to ...
: punched cards, magnetic tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic storage made of a thin, magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic film. It was developed in Germany in 1928, based on the earlier magnetic wire recording from Denmark. Devices that use magnet ...
s and other record-keeping media, involving a life cycle of such formats requiring origination, distribution, backup, maintenance and disposal. At this time the huge potential of information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology syste ...
began to be recognised: for example a single chip storing a whole book
A book is a medium for recording information in the form of writing or images, typically composed of many pages (made of papyrus, parchment, vellum, or paper) bound together and protected by a cover. The technical term for this physical ...
, or electronic mail moving messages instantly around the world, remarkable ideas at the time.Evans, C., 1979. ''The Mighty Micro'', London: Victor Gollancz. With the proliferation of information technology and the extending reach of information systems in the 1980s and 1990s,Venkatraman, N., 1994. IT-enabled business transformation: from automation to business scope redefinition. ''Sloan Management Review'', 35(2), pp.73–87 information management took on a new form. Progressive businesses such as British Petroleum transformed the vocabulary of what was then " IT management", so that “ systems analysts” became “business analyst
A business analyst (BA) is a person who processes, interprets and documents business processes, products, services and software through analysis of data. The role of a business analyst is to ensure business efficiency increases through their k ...
s”, “monopoly supply” became a mixture of “ insourcing” and “outsourcing
Outsourcing is an agreement in which one company hires another company to be responsible for a planned or existing activity which otherwise is or could be carried out internally, i.e. in-house, and sometimes involves transferring employees and ...
”, and the large IT function was transformed into “lean teams” that began to allow some agility in the processes that harness information for business benefit.Cross, J. & Earl, M., 1997. Transformation of the IT function at British Petroleum. ''MIS Quarterly'', 21(4), page 403 The scope of senior management
Senior management, executive management, upper management, or a management is generally individuals at the highest level of management of an organization who have the day-to-day tasks of managing that organization—sometimes a company or a corpor ...
interest in information at British Petroleum extended from the creation of value through improved business process
A business process, business method or business function is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks by people or equipment in which a specific sequence produces a service or product (serves a particular business goal) for a parti ...
es, based upon the effective management of information, permitting the implementation of appropriate information systems (or “ applications”) that were operated on IT infrastructure that was outsourced. In this way, information management was no longer a simple job that could be performed by anyone who had nothing else to do, it became highly strategic and a matter for senior management
Senior management, executive management, upper management, or a management is generally individuals at the highest level of management of an organization who have the day-to-day tasks of managing that organization—sometimes a company or a corpor ...
attention. An understanding of the technologies involved, an ability to manage information systems projects and business change
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or buying and selling products (such as goods and services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for profit."
Having a business name does not separat ...
well, and a willingness to align technology and business strategies all became necessary.Ward, J. & Peppard, J., 2002. ''Strategic Planning for Information Systems'' (3rd Edition), Chichester: Wiley
Positioning information management in the bigger picture
In the transitional period leading up to the strategic view of information management, Venkatraman (a strong advocate of this transition and transformation,Venkatraman, N., 1994. IT-enabled business transformation: from automation to business scope redefinition. ''Sloan Management Review'', 35(2), pp.73–87. proffered a simple arrangement of ideas that succinctly brought together the managements of data, information, andknowledge
Knowledge can be defined as awareness of facts or as practical skills, and may also refer to familiarity with objects or situations. Knowledge of facts, also called propositional knowledge, is often defined as true belief that is distin ...
(see the figure)) argued that:
* Data that is maintained in IT infrastructure has to be ''interpreted'' in order to render information.
* The information in our information systems has to be ''understood'' in order to emerge as knowledge.
* Knowledge allows managers to ''take effective decisions''.
* Effective decisions have to lead to ''appropriate actions''.
* Appropriate actions are expected to deliver ''meaningful results''.
 This is often referred to as the DIKAR model: Data, Information, Knowledge, Action and Result,Venkatraman, N., 1996. Managing IT resources as a value center, ''IS Executive Seminar Series, Cranfield School of Management'' it gives a strong clue as to the layers involved in aligning technology and organisational strategies, and it can be seen as a pivotal moment in changing attitudes to information management. The recognition that information management is an investment that must deliver meaningful results is important to all modern organisations that depend on information and good decision-making for their success.Bytheway, A., 2015
This is often referred to as the DIKAR model: Data, Information, Knowledge, Action and Result,Venkatraman, N., 1996. Managing IT resources as a value center, ''IS Executive Seminar Series, Cranfield School of Management'' it gives a strong clue as to the layers involved in aligning technology and organisational strategies, and it can be seen as a pivotal moment in changing attitudes to information management. The recognition that information management is an investment that must deliver meaningful results is important to all modern organisations that depend on information and good decision-making for their success.Bytheway, A., 2015Investing in Information: the Information Management Body of Knowledge
Geneva: Springer
Theoretical background
Behavioural and organisational theories
It is commonly believed that good information management is crucial to the smooth working of organisations, and although there is no commonly acceptedtheory
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may ...
of information management ''per se'', behavioural and organisational theories help. Following the behavioural science theory of management, mainly developed at Carnegie Mellon University and prominently supported by March and Simon, most of what goes on in modern organizations is actually information handling and decision making. One crucial factor in information handling and decision making is an individual's ability to process information and to make decisions under limitations that might derive from the context: a person's age, the situational complexity, or a lack of requisite quality in the information that is at hand – all of which is exacerbated by the rapid advance of technology and the new kinds of system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and express ...
that it enables, especially as the social web emerges as a phenomenon that business cannot ignore. And yet, well before there was any general recognition of the importance of information management in organisations, March and Simon March, J.G. & Simon, H.A., 1958. ''Organizations'', Wiley argued that organizations have to be considered as cooperative systems, with a high level of information processing and a vast need for decision making at various levels. Instead of using the model of the " economic man", as advocated in classical theory see Opp, K.-D., 1985. Sociology and economic man. ''Zeitschrift für die gesamte Staatswissenschaft/Journal of Institutional and Theoretical Economics'', pp.213–243 they proposed "administrative man
Administration may refer to:
Management of organizations
* Management, the act of directing people towards accomplishing a goal
** Administrative Assistant, traditionally known as a Secretary, or also known as an administrative officer, administ ...
" as an alternative, based on their argumentation about the cognitive limits of rationality. Additionally they proposed the notion of satisficing, which entails searching through the available alternatives until an acceptability threshold is met - another idea that still has currency.Winter, S.G., 2000. The satisficing principle in capability learning. ''Strategic Management Journal'', 21(10-11), pp.981–996
Economic theory
In addition to the organisational factors mentioned by March and Simon, there are other issues that stem from economic and environmental dynamics. There is the cost of collecting and evaluating the information needed to take a decision, including the time and effort required.Hedberg, Bo (1981), "How organizations learn and unlearn", in: Nyström, P.C. & Starbuck, W.H., ''Handbook of Organizational Design'', Oxford University Press The transaction cost associated with information processes can be high. In particular, established organizational rules and procedures can prevent the taking of the most appropriate decision, leading to sub-optimum outcomes .Mackenzie K.D. (1978), ''Organizational Structures'', AHM Publishing CorporationMullins, L.J (1993), ''Management and Organizational Behaviours'', 3rd ed., Pitman Publishing This is an issue that has been presented as a major problem with bureaucratic organizations that lose the economies of strategic change because of entrenched attitudes.Wigand, Rolf T., Picot, Arnold and Reichwald, Ralf (1997), ''Information, Organization and Management: Expanding Markets and Corporate Boundaries'', Wiley & SonsStrategic information management
Background
According to the Carnegie Mellon School an organization's ability to process information is at the core of organizational and managerial competency, and an organization's strategies must be designed to improve information processing capability Cyert, R.M. & March, J.G., 1959. A behavioural theory of organizational objectives. ''Modern Organization Theory'', Wiley, New York, pp.76–90 and as information systems that provide that capability became formalised and automated, competencies were severely tested at many levels.Morton, M.S.S., 1991. ''The corporation of the 1990s: Information technology and organizational transformation'', Oxford University Press It was recognised that organisations needed to be able to learn and adapt in ways that were never so evident before Senge, P.M., 1990. ''The fifth discipline'', Doubleday and academics began to organise and publish definitive works concerning the strategic management of information, and information systems.Earl, M.J., 1989. ''Management Strategies for Information Technology'', Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Prentice-Hall, Inc. Concurrently, the ideas ofbusiness process
A business process, business method or business function is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks by people or equipment in which a specific sequence produces a service or product (serves a particular business goal) for a parti ...
management Hammer, M. & Champy, J., 2009. ''Reengineering the Corporation: Manifesto for Business Revolution'', A, Zondervan and knowledge management
Knowledge management (KM) is the collection of methods relating to creating, sharing, using and managing the knowledge and information of an organization. It refers to a multidisciplinary approach to achieve organisational objectives by making ...
Nonaka, I. & Takeuchi, H., 1995. ''The knowledge creating company: how Japanese companies create the dynamics of innovation'', New York, NY, USA: Oxford University Press although much of the optimistic early thinking about business process redesign
Business process re-engineering (BPR) is a business management strategy originally pioneered in the early 1990s, focusing on the analysis and design of workflows and business processes within an organization. BPR aims to help organizations fund ...
has since been discredited in the information management literature.Belmiro, T., Gardiner, P. & Simmons, J., 1997. Business process re-engineering—A discredited vocabulary? ''International Journal of Information Management'', 17(1), pp.21–33 In the strategic studies field, it is considered of the highest priority the understanding of the information environment, conceived as the aggregate of individuals, organizations, and systems that collect, process, disseminate, or act on information. This environment consists of three interrelated dimensions which continuously interact with individuals, organizations, and systems. These dimensions are the physical, informational, and cognitive.Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, U.S. Army (2012). Information Operations. Joint Publication 3-13. Joint Doctrine Support Division, 116 Lake View Parkway, Suffolk, VA., p. 18.
Aligning technology and business strategy with information management
Venkatraman has provided a simple view of the requisite capabilities of an organisation that wants to manage information well – the DIKAR model (see above). He also worked with others to understand how technology and business strategies could be appropriately aligned in order to identify specific capabilities that are needed.Henderson, J.C. & Venkatraman, N., 1993. Strategic alignment: leveraging information technology for transforming organizations. ''IBM Systems Journal'', 32(1), pp.4–16 This work was paralleled by other writers in the world of consulting,Zachman, J. A. (1987). A framework for information systems architecture. ''IBM Systems Journal'', 26(3), 590–616 practice Cross, J., 1995. IT outsourcing : British Petroleum's competitive approach. ''Harvard Business Review'', 73(3), p.94 and academia.Ward, J. & Daniel, E., 2005. ''Benefits Management: Delivering Value from IS and IT Investments'', Chichester: WileyA contemporary portfolio model for information
Bytheway has collected and organised basic tools and techniques for information management in a single volume. At the heart of his view of information management is a portfolio model that takes account of the surging interest in external sources of information and the need to organise un-structured information external so as to make it useful (see the figure). Such an information portfolio as this shows how information can be gathered and usefully organised, in four stages:
Stage 1: Taking advantage of public information: recognise and adopt well-structured external schemes of reference data, such as post codes, weather data, GPS positioning data and travel timetables, exemplified in the personal computing press.Ashbrook, D. & Starner, T., 2003. Using GPS to learn significant locations and predict movement across multiple users. ''Personal and Ubiquitous Computing'', 7(5), pp.275–286
Stage 2: Tagging the noise on the
Such an information portfolio as this shows how information can be gathered and usefully organised, in four stages:
Stage 1: Taking advantage of public information: recognise and adopt well-structured external schemes of reference data, such as post codes, weather data, GPS positioning data and travel timetables, exemplified in the personal computing press.Ashbrook, D. & Starner, T., 2003. Using GPS to learn significant locations and predict movement across multiple users. ''Personal and Ubiquitous Computing'', 7(5), pp.275–286
Stage 2: Tagging the noise on the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet.
Documents and downloadable media are made available to the network through web ...
: use existing schemes such as post code
A postal code (also known locally in various English-speaking countries throughout the world as a postcode, post code, PIN or ZIP Code) is a series of letters or digits or both, sometimes including spaces or punctuation, included in a postal a ...
s and GPS data or more typically by adding “tags”, or construct a formal ontology
In metaphysics, ontology is the philosophy, philosophical study of being, as well as related concepts such as existence, Becoming (philosophy), becoming, and reality.
Ontology addresses questions like how entities are grouped into Category ...
that provides structure. Shirky provides an overview of these two approaches.Shirky, C., 2005. Shirky: Ontology is Overrated -- Categories, Links, and Tags. ''Clay Shirky's Writings About the Internet''. Available at: http://shirky.com/writings/ontology_overrated.html ccessed May 23, 2013/ref>
Stage 3: Sifting and analysing: in the wider world the generalised ontologies that are under development extend to hundreds of entities and hundreds of relations between them and provide the means to elicit meaning from large volumes of data. Structured data in databases works best when that structure reflects a higher-level information model – an ontology, or an entity-relationship model.Noy, N.F., McGuinness, D.L. & others, 2001. Ontology development 101: A guide to creating your first ontology, ''Stanford knowledge systems laboratory technical report KSL-01-05 and Stanford medical informatics technical report SMI-2001-0880''
Stage 4: Structuring and archiving: with the large volume of data available from sources such as the social web and from the miniature telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', "remote", an ...
systems used in personal health management
Health administration, healthcare administration, healthcare management or hospital management is the field relating to leadership, management, and administration of public health systems, health care systems, hospitals, and hospital networks ...
, new ways to archive and then trawl data for meaningful information. Map-reduce methods, originating from functional programming
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by applying and composing functions. It is a declarative programming paradigm in which function definitions are trees of expressions tha ...
, are a more recent way of eliciting information from large archival datasets that is becoming interesting to regular businesses that have very large data resources to work with, but it requires advanced multi-processor resources.Chu, C. et al., 2007. Map-reduce for machine learning on multicore. ''Advances in neural information processing systems'', 19, p.281
Competencies to manage information well
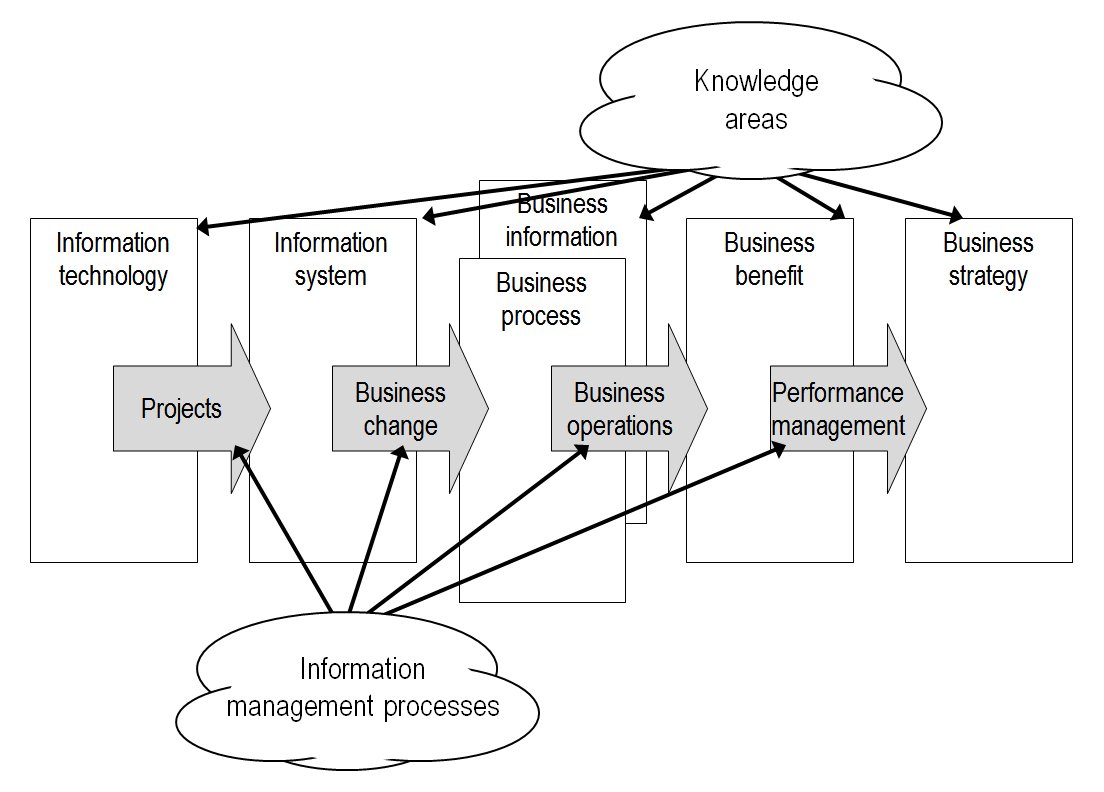
In 2004, the management system " Information Management Body of Knowledge" was first published on the World Wide WebIMBOK, 2004. ''The Information Management Body of Knowledge''. Available at: http://www.imbok.org ccessed May 12, 2015/ref> and set out to show that the required management competencies to derive real benefits from an investment in information are complex and multi-layered. The framework model that is the basis for understanding competencies comprises six “knowledge” areas and four “process” areas: ;The information management knowledge areas
The IMBOK is based on the argument that there are six areas of required management competency, two of which (“business process management” and “business information management”) are very closely related.Bytheway, A., 2015. ''Investing in Information: the Information Management Body of Knowledge'', Geneva: Springer,
p29
* Information technology: The pace of change of
;The information management knowledge areas
The IMBOK is based on the argument that there are six areas of required management competency, two of which (“business process management” and “business information management”) are very closely related.Bytheway, A., 2015. ''Investing in Information: the Information Management Body of Knowledge'', Geneva: Springer,
p29
* Information technology: The pace of change of technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scien ...
and the pressure to constantly acquire the newest technological products can undermine the stability of the infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
that supports systems, and thereby optimises business process
A business process, business method or business function is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks by people or equipment in which a specific sequence produces a service or product (serves a particular business goal) for a parti ...
es and delivers benefits. It is necessary to manage the “ supply side” and recognise that technology is, increasingly, becoming a commodity
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
The price of a co ...
.Carr, N., 2003. IT doesn't matter. In ''Wringing real value from IT''. HBR OnPoint, pp. 3–10
* Information system: While historically information systems were developed in-house, over the years it has become possible to acquire most of the software systems that an organisation needs from the software package industry. However, there is still the potential for competitive advantage
In business, a competitive advantage is an attribute that allows an organization to outperform its competitors.
A competitive advantage may include access to natural resources, such as high-grade ores or a low-cost power source, highly skilled ...
from the implementation of new systems ideas that deliver to the strategic intentions of organisations.
* Business processes and Business information: Information system
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, information systems are composed by four components: task, people ...
s are applied to business process
A business process, business method or business function is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks by people or equipment in which a specific sequence produces a service or product (serves a particular business goal) for a parti ...
es in order to improve them, and they bring data to the business that becomes useful as business information. Business process management is still seen as a relatively new idea because it is not universally adopted, and it has been difficult in many cases; business ''information'' management is even more of a challenge.Belmiro, T.R. et al., 2000. Are BPR practitioners really addressing business processes? ''International Journal of Operations & Production Management'', 20(10), pp.1183–1203Davenport, T.H. & Short, J., 2003. Information technology and business process redesign. ''Operations management: critical perspectives on business and management'', 1, p.97
* Business benefit: What are the benefits that we are seeking? It is necessary not only to be brutally honest about what ''can'' be achieved, but also to ensure the active management and assessment of benefit delivery. Since the emergence and popularisation of the Balanced scorecardKaplan, R. & Norton, D., 1996. ''The balanced scorecard - translating stragegy into action'', Boston MA: Harvard University Press there has been huge interest in business performance management but not much serious effort has been made to relate business performance management to the benefits of information technology investments and the introduction of new information system
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, information systems are composed by four components: task, people ...
s until the turn of the millennium
A millennium (plural millennia or millenniums) is a period of one thousand years, sometimes called a kiloannus, kiloannum (ka), or kiloyear (ky). Normally, the word is used specifically for periods of a thousand years that begin at the starting ...
.
* Business strategy: Although a long way from the workaday issues of managing information in organisations, strategy in most organisations simply has to be informed by information technology and information systems opportunities, whether to address poor performance or to improve differentiation and competitiveness. Strategic analysis tools such as the value chain
A value chain is a progression of activities that a firm operating in a specific industry performs in order to deliver a valuable product (i.e., good and/or service) to the end customer. The concept comes through business management and was f ...
and critical success factor Critical success factor (CSF) is a management term for an element that is necessary for an organization or project to achieve its mission. To achieve their goals they need to be aware of each key success factor (KSF) and the variations between the ...
analysis are directly dependent on proper attention to the information that is (or could be) managed
;The information management processes
Even with full capability and competency within the six knowledge areas, it is argued that things can still go wrong. The problem lies in the migration of ideas and information management value from one area of competency to another. Summarising what Bytheway explains in some detail (and supported by selected secondary references):Bytheway, A., 2015. ''Investing in Information: the Information Management Body of Knowledge'', Geneva: Springer,
p31
* Projects: Information technology is without value until it is engineered into information systems that meet the needs of the business by means of good project management
Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. T ...
.Schwalbe, K., 2013. ''Information technology project management'', Cengage Learning
* Business change: The best information systems succeed in delivering benefits through the achievement of change within the business systems, but people do not appreciate change that makes new demands upon their skills in the ways that new information systems often do. Contrary to common expectations, there is some evidence that the public sector
The public sector, also called the state sector, is the part of the economy composed of both public services and public enterprises. Public sectors include the public goods and governmental services such as the military, law enforcement, inf ...
has succeeded with information technology induced business change
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or buying and selling products (such as goods and services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for profit."
Having a business name does not separat ...
.Scholl, H.J., 2005. E-government-induced business process change (BPC): An empirical study of current practices. ''International Journal of Electronic Government Research'' (IJEGR), 1(2), pp.27–49
* Business operations: With new systems in place, with business process
A business process, business method or business function is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks by people or equipment in which a specific sequence produces a service or product (serves a particular business goal) for a parti ...
es and business information improved, and with staff finally ready and able to work with new processes, then the business can get to work, even when new systems extend far beyond the boundaries of a single business.Saeed, K.A., Malhotra, M.K. & Grover, V., 2005. Examining the Impact of Interorganizational Systems on Process Efficiency and Sourcing Leverage in Buyer–Supplier Dyads. ''Decision Sciences'', 36(3), pp.365–396
* Performance management: Investment
Investment is the dedication of money to purchase of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.
In finance, the purpose of investing is ...
s are no longer solely about financial results, financial success must be balanced with internal efficiency, customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction (often abbreviated as CSAT) is a term frequently used in marketing. It is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation. Customer satisfaction is defined as "the number of ...
, and with organisational learning and development.
Summary
There are always many ways to see a business, and the information management viewpoint is only one way. It is important to remember that other areas of business activity will also contribute to strategy – it is not only good information management that moves a business forwards.Corporate governance
Corporate governance is defined, described or delineated in diverse ways, depending on the writer's purpose. Writers focused on a disciplinary interest or context (such as accounting, finance, law, or management) often adopt narrow definitions ...
, human resource management
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture ...
, product development and marketing
Marketing is the process of exploring, creating, and delivering value to meet the needs of a target market in terms of goods and services; potentially including selection of a target audience; selection of certain attributes or themes to emph ...
will all have an important role to play in strategic ways, and we must not see one domain of activity alone as the sole source of strategic success. On the other hand, corporate governance, human resource management, product development and marketing are all dependent on effective information management, and so in the final analysis our competency to manage information well, on the broad basis that is offered here, can be said to be predominant.
Operationalising information management
Managing requisite change
Organizations are often confronted with many information management challenges and issues at theoperational level
In the field of military theory, the operational level of war (also called operational art, as derived from russian: оперативное искусство, or operational warfare) represents the level of command that connects the details of ...
, especially when organisational change is engendered. The novelty of new systems architectures and a lack of experience with new styles of information management requires a level of organisational change management
Change management (sometimes abbreviated as CM) is a collective term for all approaches to prepare, support, and help individuals, teams, and organizations in making organizational change. It includes methods that redirect or redefine the use ...
that is notoriously difficult to deliver. As a result of a general organisational reluctance to change, to enable new forms of information management, there might be (for example): a shortfall in the requisite resources, a failure to acknowledge new classes of information and the new procedures that use them, a lack of support from senior management leading to a loss of strategic vision, and even political manoeuvring that undermines the operation of the whole organisation.Knights, D. & Murray, F., 1994. ''Managers Divided'', Chichester: John Wiley However, the implementation of new forms of information management should normally lead to operational benefits.
The early work of Galbraith
In early work, taking an information processing view of organisation design, Jay Galbraith has identified five tactical areas to increase information processing capacity and reduce the need for information processing.Galbraith, J.R., 1977. ''Organization design'', Addison Wesley * Developing, implementing, and monitoring all aspects of the “environment” of an organization. * Creation of slack resources so as to decrease the load on the overallhierarchy
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
of resources and to reduce information processing relating to overload.
* Creation of self-contained tasks with defined boundaries and that can achieve proper closure, and with all the resource
Resource refers to all the materials available in our environment which are technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally sustainable and help us to satisfy our needs and wants. Resources can broadly be classified upon thei ...
s at hand required to perform the task.
* Recognition of lateral relations that cut across functional units, so as to move decision power to the process instead of fragmenting it within the hierarchy
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
.
* Investment in vertical information systems that route information flows for a specific task (or set of tasks) in accordance to the applied business logic.
The matrix organisation
The lateral relations concept leads to an organizational form that is different from the simple hierarchy, the “ matrix organization”. This brings together the vertical (hierarchical) view of an organisation and the horizontal (product or project) view of the work that it does visible to the outside world. The creation of a matrix organization is one management response to a persistent fluidity of external demand, avoiding multifarious and spurious responses to episodic demands that tend to be dealt with individually.See also
* Balanced scorecard *Business process
A business process, business method or business function is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks by people or equipment in which a specific sequence produces a service or product (serves a particular business goal) for a parti ...
* Content management
* Data management
Data management comprises all disciplines related to handling data as a valuable resource.
Concept
The concept of data management arose in the 1980s as technology moved from sequential processing (first punched cards, then magnetic tape) to ...
* Information excellence
* Information Management Body of Knowledge
* Information Resources Management Journal
* Information system
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, information systems are composed by four components: task, people ...
* Information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology syste ...
* Journal of Global Information Management
* Knowledge management
Knowledge management (KM) is the collection of methods relating to creating, sharing, using and managing the knowledge and information of an organization. It refers to a multidisciplinary approach to achieve organisational objectives by making ...
* Master of Information Management
* Project management
Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. T ...
* Records management
Records management, also known as records and information management, is an organizational function devoted to the management of information in an organization throughout its life cycle, from the time of creation or receipt to its eventual dispos ...
* Strategic management
In the field of management, strategic management involves the formulation and implementation of the major goals and initiatives taken by an organization's managers on behalf of stakeholders, based on consideration of resources and an assessme ...
References
External links
{{Authority control Information Information technology Information systems Works about information