Industrial CT scanning on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Industrial computed tomography (CT) scanning is any computer-aided tomographic process, usually
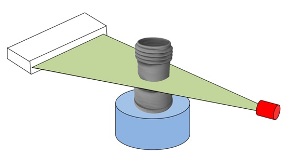 ''Line beam scanning'' is the traditional process of industrial CT scanning.Hofmann, J., Flisch, A., Obrist, A., Adaptive CT scanning-mesh based optimisation methods for industrial X-ray computer tomography applications. NDT&E International (37), 2004, pp. 271–278. X-rays are produced and the beam is
''Line beam scanning'' is the traditional process of industrial CT scanning.Hofmann, J., Flisch, A., Obrist, A., Adaptive CT scanning-mesh based optimisation methods for industrial X-ray computer tomography applications. NDT&E International (37), 2004, pp. 271–278. X-rays are produced and the beam is 

X-ray computed tomography
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 ...
, that uses irradiation
Irradiation is the process by which an object is exposed to radiation. The exposure can originate from various sources, including natural sources. Most frequently the term refers to ionizing radiation, and to a level of radiation that will serve ...
to produce three-dimensional internal and external representations of a scanned object. Industrial CT scanning has been used in many areas of industry for internal inspection of components. Some of the key uses for industrial CT scanning have been flaw detection, failure analysis, metrology, assembly analysis and reverse engineering applications. Just as in medical imaging, industrial imaging includes both nontomographic radiography (industrial radiography
Industrial radiography is a modality of non-destructive testing that uses ionizing radiation to inspect materials and components with the objective of locating and quantifying defects and degradation in material properties that would lead to the ...
) and computed tomographic radiography (computed tomography).
Types of scanners
 ''Line beam scanning'' is the traditional process of industrial CT scanning.Hofmann, J., Flisch, A., Obrist, A., Adaptive CT scanning-mesh based optimisation methods for industrial X-ray computer tomography applications. NDT&E International (37), 2004, pp. 271–278. X-rays are produced and the beam is
''Line beam scanning'' is the traditional process of industrial CT scanning.Hofmann, J., Flisch, A., Obrist, A., Adaptive CT scanning-mesh based optimisation methods for industrial X-ray computer tomography applications. NDT&E International (37), 2004, pp. 271–278. X-rays are produced and the beam is collimated
A collimated beam of light or other electromagnetic radiation has parallel rays, and therefore will spread minimally as it propagates. A perfectly collimated light beam, with no divergence, would not disperse with distance. However, diffraction p ...
to create a line. The X-ray line beam is then translated across the part and data is collected by the detector. The data is then reconstructed to create a 3-D volume rendering
In scientific visualization and computer graphics, volume rendering is a set of techniques used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set, typically a 3D scalar field.
A typical 3D data set is a group of 2D slice imag ...
of the part.
In ''cone beam scanning'', the part to be scanned is placed on a rotary table. As the part rotates, the cone of X-rays produce a large number of 2D images that are collected by the detector. The 2D images are then processed to create a 3D volume rendering
In scientific visualization and computer graphics, volume rendering is a set of techniques used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set, typically a 3D scalar field.
A typical 3D data set is a group of 2D slice imag ...
of the external and internal geometries of the part.

History
Industrial CT scanning technology was introduced in 1972 with the invention of the CT scanner for medical imaging byGodfrey Hounsfield
Sir Godfrey Newbold Hounsfield (28 August 1919 – 12 August 2004) was an English electrical engineer who shared the 1979 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine with Allan MacLeod Cormack for his part in developing the diagnostic technique of X ...
. The invention earned him a Nobel Prize in medicine, which he shared with Allan McLeod Cormack. Many advances in CT scanning have allowed for its use in the industrial field for metrology in addition to the visual inspection primarily used in the medical field (medical CT scan).
Analysis and inspection techniques
Various inspection uses and techniques include part-to-CAD comparisons, part-to-part comparisons, assembly and defect analysis, void analysis, wall thickness analysis, and generation of CAD data. The CAD data can be used for reverse engineering, geometric dimensioning and tolerance analysis, and production part approval.Assembly
One of the most recognized forms of analysis using CT is for assembly, or visual analysis. CT scanning provides views inside components in their functioning position, without disassembly. Some software programs for industrial CT scanning allow for measurements to be taken from the CT dataset volume rendering. These measurements are useful for determining the clearances between assembled parts or the dimension of an individual feature.
Void, crack and defect detection
Traditionally, determining defects, voids and cracks within an object would require destructive testing. CT scanning can detect internal features and flaws displaying this information in 3D without destroying the part. Industrial CT scanning (3D X-ray) is used to detect flaws inside a part such as porosity, an inclusion, or a crack. It has been also used to detect the origin and propagation of damages in concrete. Metal casting and moulded plastic components are typically prone to porosity because of cooling processes, transitions between thick and thin walls, and material properties. Void analysis can be used to locate, measure, and analyze voids inside plastic or metal components.Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing analysis
Traditionally, without destructive testing, full metrology has only been performed on the exterior dimensions of components, such as with acoordinate-measuring machine
A coordinate measuring machine (CMM) is a device that measures the geometry of physical objects by sensing discrete points on the surface of the object with a probe. Various types of probes are used in CMMs, the most common being mechanical and l ...
(CMM) or with a vision system to map exterior surfaces. Internal inspection methods would require using a 2D X-ray of the component or the use of destructive testing. Industrial CT scanning allows for full non-destructive metrology. With unlimited geometrical complexity, 3D printing
3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer co ...
allows for complex internal features to be created with no impact on cost, such features are not accessible using traditional CMM. The first 3D printed artefact that is optimised for characterisation of form using computed tomography CT
Image-based finite element methods
Image-based finite element method converts the 3D image data from X-ray computed tomography directly into meshes for finite element analysis. Benefits of this method include modelling complex geometries (e.g. composite materials) or accurately modelling "as manufactured" components at the micro-scale.See also
*Industrial radiography
Industrial radiography is a modality of non-destructive testing that uses ionizing radiation to inspect materials and components with the objective of locating and quantifying defects and degradation in material properties that would lead to the ...
* Cone beam computed tomography
Cone beam computed tomography (or CBCT, also referred to as C-arm CT, cone beam volume CT, flat panel CT or Digital Volume Tomography (DVT)) is a medical imaging technique consisting of X-ray computed tomography where the X-rays are divergent, f ...
* PCB reverse engineering
Reverse engineering of Printed circuit boards (sometimes called “cloning”, or PCB RE) is the process of generating fabrication and design data for an existing circuit board, either closely or exactly replicating its functionality.
Obtaining ...
, an application of industrial CT
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Industrial Ct Scanning Tomography Materials science Microtomography Microtechnology Nondestructive testing Reverse engineering Articles containing video clips