Indigenous peoples of Europe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Europeans are the focus of European
Minderheitenrechte in Europa. Handbuch der europäischen Volksgruppen
', Braumüller, (Google Books, snippet view). Als
2006 reprint by Springer
(Amazon, no preview) . The
 The Basques have been found to descend from the population of the late
The Basques have been found to descend from the population of the late
 Iron Age Europe, Iron Age (pre-Migration Period, Great Migrations) populations of Europe known from Greek historiography, Greco-Roman historiography, notably Herodotus, Pliny the Elder, Pliny, Ptolemy and Tacitus:
*Aegean Sea, Aegean: the Greek tribes, Pelasgians, and Anatolians.
*Balkans: the Illyrians (List of ancient tribes in Illyria), Dacians, and Thracians.
*Italian peninsula: the Camunni, Rhaetian people, Rhaetians, Lepontii, Adriatic Veneti, Gauls, Ligurians, Etruscans, Italic peoples and Greeks in Italy, Greek and Phoenician colonies in its neighboring Italian islands.
*Western Europe, Western/Central Europe: the Celts (list of peoples of Gaul, List of Celtic tribes), Rhaetian people, Rhaetians and Swabians, Vistula Veneti, Lugii and Balts.
*Iberian peninsula and Pyrenees : the Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula (Iberians, Celts, Celtiberians, Lusitani, Basques, Turdetani), of the Pyrenean piedmont (geography), piedmont (Aquitani) between the Pyrenees and the Atlantic ocean, and Greek colonisation, Greek and Phoenician colonies, Phoenician coastal Mediterranean colonies.
*Sardinia and Corsica: the ancient Sardinians and Corsicans (also known as Nuragic civilization, Nuragic and Torrean civilization, Torrean peoples), comprising the ''Corsi people, Corsi'', ''Balares'', ''Ilienses'' tribes and Phoenician colonies.
*British Isles: the Celtic tribes in Britain and Ireland and Picts/Priteni.
*Northern Europe: the Baltic Finns, Germanic peoples (list of Germanic peoples) and Normans.
*Sicily: the Italic peoples, Italic Sicels and Morgetes, the Sicani, Elymians and Greek colonisation, Greek and Phoenician colonies.
*Eastern Europe: the Vistula Veneti, Veneti (Early Slavs), Scythians and Sarmatians.
*Armenian Highlands/Anatolia: the Armenians.
Iron Age Europe, Iron Age (pre-Migration Period, Great Migrations) populations of Europe known from Greek historiography, Greco-Roman historiography, notably Herodotus, Pliny the Elder, Pliny, Ptolemy and Tacitus:
*Aegean Sea, Aegean: the Greek tribes, Pelasgians, and Anatolians.
*Balkans: the Illyrians (List of ancient tribes in Illyria), Dacians, and Thracians.
*Italian peninsula: the Camunni, Rhaetian people, Rhaetians, Lepontii, Adriatic Veneti, Gauls, Ligurians, Etruscans, Italic peoples and Greeks in Italy, Greek and Phoenician colonies in its neighboring Italian islands.
*Western Europe, Western/Central Europe: the Celts (list of peoples of Gaul, List of Celtic tribes), Rhaetian people, Rhaetians and Swabians, Vistula Veneti, Lugii and Balts.
*Iberian peninsula and Pyrenees : the Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula (Iberians, Celts, Celtiberians, Lusitani, Basques, Turdetani), of the Pyrenean piedmont (geography), piedmont (Aquitani) between the Pyrenees and the Atlantic ocean, and Greek colonisation, Greek and Phoenician colonies, Phoenician coastal Mediterranean colonies.
*Sardinia and Corsica: the ancient Sardinians and Corsicans (also known as Nuragic civilization, Nuragic and Torrean civilization, Torrean peoples), comprising the ''Corsi people, Corsi'', ''Balares'', ''Ilienses'' tribes and Phoenician colonies.
*British Isles: the Celtic tribes in Britain and Ireland and Picts/Priteni.
*Northern Europe: the Baltic Finns, Germanic peoples (list of Germanic peoples) and Normans.
*Sicily: the Italic peoples, Italic Sicels and Morgetes, the Sicani, Elymians and Greek colonisation, Greek and Phoenician colonies.
*Eastern Europe: the Vistula Veneti, Veneti (Early Slavs), Scythians and Sarmatians.
*Armenian Highlands/Anatolia: the Armenians.

 Ethno-linguistic groups that arrived from outside Europe during historical times are:
*Phoenician colonies in the Mediterranean (including regions in
Ethno-linguistic groups that arrived from outside Europe during historical times are:
*Phoenician colonies in the Mediterranean (including regions in

 The earliest accounts of European ethnography date from Classical Antiquity. Herodotus described the Scythians and Thraco-Illyrians. Dicaearchus gave a description of Greece itself, besides accounts of western and northern Europe. His work survives only fragmentarily, but was received by Polybius and others.
Roman Empire period authors include Diodorus Siculus, Strabo and Tacitus. Julius Caesar gives an account of the Celtic tribes of Gaul, while Tacitus describes the Germanic tribes of Magna Germania. A number of authors like Diodorus Siculus, Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias and Sallust depict the ancient Sardinians, Sardinian and Corsicans, Corsican peoples.
The 4th century Tabula Peutingeriana records the names of numerous peoples and tribes.
Ethnographers of Late Antiquity such as Agathias of Myrina Ammianus Marcellinus, Jordanes and Theophylact Simocatta give early accounts of the Slavs, the Franks, the Alamanni and the Goths.
Book IX of Isidore of Seville, Isidore's ''Etymologiae'' (7th century) treats ''de linguis, gentibus, regnis, militia, civibus'' (concerning languages, peoples, realms, war and cities).
Ahmad ibn Fadlan in the 10th century gives an account of the Bolghar and the Rus' peoples.
William Rubruck, while most notable for his account of the Mongols, in his account of his journey to Asia also gives accounts of the Tatars and the Alans.
Saxo Grammaticus and Adam of Bremen give an account of pre-Christian Scandinavia. The ''Chronicon Slavorum'' (12th century) gives an account of the northwestern Slavic tribes.
Gottfried Hensel in his 1741 ''Synopsis Universae Philologiae'' published one of the earliest ethno-linguistic map of Europe, showing the beginning of the ''pater noster'' in the various European languages and scripts.
In the 19th century, ethnicity was discussed in terms of scientific racism, and the ethnic groups of Europe were grouped into a number of "Race (classification of human beings), races", Mediterranean race, Mediterranean, Alpine race, Alpine and Nordic race, Nordic, all part of a larger "Caucasian race, Caucasian" group.
The beginnings of ethnic geography as an academic subdiscipline lie in the period following World War I, in the context of ethnic nationalism, nationalism, and in the 1930s exploitation for the purposes of fascist and Nazi propaganda, so that it was only in the 1960s that ethnic geography began to thrive as a ''bona fide'' academic subdiscipline.
The origins of modern ethnography are often traced to the work of Bronisław Malinowski, who emphasized the importance of fieldwork.
The emergence of population genetics further undermined the categorisation of Europeans into clearly defined racial groups. A 2007 study on the genetic history of Europe found that the most important genetic differentiation in Europe occurs on a line from the north to the south-east (northern Europe to the Balkans), with another east–west axis of differentiation across Europe, separating the indigenous Basques, Sardinians and Sami people, Sami from other European populations.
Despite these stratifications it noted the unusually high degree of European homogeneity: "there is low apparent diversity in Europe with the entire continent-wide samples only marginally more dispersed than single population samples elsewhere in the world."
The earliest accounts of European ethnography date from Classical Antiquity. Herodotus described the Scythians and Thraco-Illyrians. Dicaearchus gave a description of Greece itself, besides accounts of western and northern Europe. His work survives only fragmentarily, but was received by Polybius and others.
Roman Empire period authors include Diodorus Siculus, Strabo and Tacitus. Julius Caesar gives an account of the Celtic tribes of Gaul, while Tacitus describes the Germanic tribes of Magna Germania. A number of authors like Diodorus Siculus, Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias and Sallust depict the ancient Sardinians, Sardinian and Corsicans, Corsican peoples.
The 4th century Tabula Peutingeriana records the names of numerous peoples and tribes.
Ethnographers of Late Antiquity such as Agathias of Myrina Ammianus Marcellinus, Jordanes and Theophylact Simocatta give early accounts of the Slavs, the Franks, the Alamanni and the Goths.
Book IX of Isidore of Seville, Isidore's ''Etymologiae'' (7th century) treats ''de linguis, gentibus, regnis, militia, civibus'' (concerning languages, peoples, realms, war and cities).
Ahmad ibn Fadlan in the 10th century gives an account of the Bolghar and the Rus' peoples.
William Rubruck, while most notable for his account of the Mongols, in his account of his journey to Asia also gives accounts of the Tatars and the Alans.
Saxo Grammaticus and Adam of Bremen give an account of pre-Christian Scandinavia. The ''Chronicon Slavorum'' (12th century) gives an account of the northwestern Slavic tribes.
Gottfried Hensel in his 1741 ''Synopsis Universae Philologiae'' published one of the earliest ethno-linguistic map of Europe, showing the beginning of the ''pater noster'' in the various European languages and scripts.
In the 19th century, ethnicity was discussed in terms of scientific racism, and the ethnic groups of Europe were grouped into a number of "Race (classification of human beings), races", Mediterranean race, Mediterranean, Alpine race, Alpine and Nordic race, Nordic, all part of a larger "Caucasian race, Caucasian" group.
The beginnings of ethnic geography as an academic subdiscipline lie in the period following World War I, in the context of ethnic nationalism, nationalism, and in the 1930s exploitation for the purposes of fascist and Nazi propaganda, so that it was only in the 1960s that ethnic geography began to thrive as a ''bona fide'' academic subdiscipline.
The origins of modern ethnography are often traced to the work of Bronisław Malinowski, who emphasized the importance of fieldwork.
The emergence of population genetics further undermined the categorisation of Europeans into clearly defined racial groups. A 2007 study on the genetic history of Europe found that the most important genetic differentiation in Europe occurs on a line from the north to the south-east (northern Europe to the Balkans), with another east–west axis of differentiation across Europe, separating the indigenous Basques, Sardinians and Sami people, Sami from other European populations.
Despite these stratifications it noted the unusually high degree of European homogeneity: "there is low apparent diversity in Europe with the entire continent-wide samples only marginally more dispersed than single population samples elsewhere in the world."

 The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of Europeans.
The member states of the Council of Europe in 1995 signed the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities. The broad aims of the convention are to ensure that the signatory states respect the rights of national minorities, undertaking to combat discrimination, promote equality, preserve and develop the culture and identity of national minorities, guarantee certain freedoms in relation to access to the media, minority languages and education and encourage the participation of national minorities in public life. The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities defines a national minority implicitly to include minorities possessing a territorial identity and a distinct cultural heritage. By 2008, 39 member states had signed and ratified the convention, with the notable exception of France.
The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of Europeans.
The member states of the Council of Europe in 1995 signed the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities. The broad aims of the convention are to ensure that the signatory states respect the rights of national minorities, undertaking to combat discrimination, promote equality, preserve and develop the culture and identity of national minorities, guarantee certain freedoms in relation to access to the media, minority languages and education and encourage the participation of national minorities in public life. The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities defines a national minority implicitly to include minorities possessing a territorial identity and a distinct cultural heritage. By 2008, 39 member states had signed and ratified the convention, with the notable exception of France.
 Many non-European ethnic groups and nationalities have migrated to Europe over the centuries. Some arrived centuries ago. However, the vast majority arrived more recently, mostly in the 20th and 21st centuries. Often, they come from former colonies of the British, Dutch, French, Portuguese and Spanish empires.
*Ethnic groups in the Middle East, Western Asians
**Turkish people, Turks: There were 10 million Turks living in Western Europe and the Balkans in 1997 (excluding Northern Cyprus and Turkey). By 2010 there was up to 15 million Turks living in the European Union (i.e. excluding Turkish communities in Turkey as well as several Balkan countries and former USSR countries which are not in the EU). According to Dr Araks Pashayan 10 million "Turks in Europe, Euro-Turks" alone were living in Germany, France, the Netherlands and Belgium in 2012. In addition, there is 500,000 Turks in the UK (2011 estimate), 500,000 in Austria (2011 estimate) 150,000 in Sweden, 120,000 in Switzerland, 70,000 in Denmark (2008 estimate), as well as growing communities in Italy, Liechtenstein, Lichtenstein, Finland and
Many non-European ethnic groups and nationalities have migrated to Europe over the centuries. Some arrived centuries ago. However, the vast majority arrived more recently, mostly in the 20th and 21st centuries. Often, they come from former colonies of the British, Dutch, French, Portuguese and Spanish empires.
*Ethnic groups in the Middle East, Western Asians
**Turkish people, Turks: There were 10 million Turks living in Western Europe and the Balkans in 1997 (excluding Northern Cyprus and Turkey). By 2010 there was up to 15 million Turks living in the European Union (i.e. excluding Turkish communities in Turkey as well as several Balkan countries and former USSR countries which are not in the EU). According to Dr Araks Pashayan 10 million "Turks in Europe, Euro-Turks" alone were living in Germany, France, the Netherlands and Belgium in 2012. In addition, there is 500,000 Turks in the UK (2011 estimate), 500,000 in Austria (2011 estimate) 150,000 in Sweden, 120,000 in Switzerland, 70,000 in Denmark (2008 estimate), as well as growing communities in Italy, Liechtenstein, Lichtenstein, Finland and  **Romani people, Romani (Gypsies): approx. 4 or 10 million (although estimates vary widely), dispersed throughout Europe but with large numbers concentrated in the Balkans area, they are of ancestral South Asian and European descent, originating from the North India, northern regions of the
**Romani people, Romani (Gypsies): approx. 4 or 10 million (although estimates vary widely), dispersed throughout Europe but with large numbers concentrated in the Balkans area, they are of ancestral South Asian and European descent, originating from the North India, northern regions of the
 Medieval notions of a relation of the peoples of Europe are expressed in terms of genealogy of mythical founders of the individual groups.
The Europeans were considered the descendants of Japheth from early times, corresponding to the division of the known world into T and O map, three continents, the descendants of Shem peopling Asia and those of Ham, son of Noah, Ham peopling Roman North Africa, Africa. Identification of Europeans as "Japhetites" is also reflected in early suggestions for terming the
Medieval notions of a relation of the peoples of Europe are expressed in terms of genealogy of mythical founders of the individual groups.
The Europeans were considered the descendants of Japheth from early times, corresponding to the division of the known world into T and O map, three continents, the descendants of Shem peopling Asia and those of Ham, son of Noah, Ham peopling Roman North Africa, Africa. Identification of Europeans as "Japhetites" is also reflected in early suggestions for terming the
 Since the High Middle Ages, most of Europe has been dominated by Christianity. There are three major denominations: Roman Catholic, Protestant and Eastern Orthodox, with Protestantism restricted mostly to Northern Europe, and Orthodoxy to Eastern Europe, East and South Slavs, South Slavic regions, Romania, Moldova, Greece, and Georgia (country), Georgia. The Armenian Apostolic Church, part of the Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Church, is also in Europe – another branch of Christianity (world's oldest National Church). Catholicism, while typically centered in Western Europe, also has a very significant following in Central Europe (especially among the Germanic peoples, Germanic, West Slavs, Western Slavic and Hungarians, Hungarian peoples/regions) as well as in Ireland (with some in Great Britain).
Christianity has been the dominant religion shaping European culture for at least the last 1700 years.Cambridge University Historical Series, ''An Essay on Western Civilization in Its Economic Aspects'', p.40: Hebraism, like Hellenism, has been an all-important factor in the development of Western Civilization; Judaism, as the precursor of Christianity, has indirectly had had much to do with shaping the ideals and morality of western nations since the christian era.Caltron J.H Hayas, ''Christianity and Western Civilization'' (1953), Stanford University Press, p.2: That certain distinctive features of our Western civilization — the civilization of western Europe and of America— have been shaped chiefly by Judaeo – Graeco – Christianity, Catholic and Protestant.Horst Hutter, University of New York, ''Shaping the Future: Nietzsche's New Regime of the Soul And Its Ascetic Practices'' (2004), p.111:three mighty founders of Western culture, namely Socrates, Jesus, and Plato.Fred Reinhard Dallmayr, ''Dialogue Among Civilizations: Some Exemplary Voices'' (2004), p.22: Western civilization is also sometimes described as "Christian" or "Judaeo- Christian" civilization. Modern philosophical thought has very much been influenced by Christian philosophers such as St Thomas Aquinas and Erasmus, and throughout most of its history, Europe has been nearly equivalent to Christian culture. The Christian culture was the predominant force in Western culture, western civilization, guiding the course of philosophy, art, and science. The notion of "Europe" and the "Western World" has been intimately connected with the concept of "Christendom, Christianity and Christendom" many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity.
Christianity is still the largest religion in Europe; according to a 2011 survey, 76.2% of Europeans considered themselves Christians. Also according to a study on Religiosity in the European Union in 2012, by Eurobarometer, Christianity is the largest religion in the European Union, accounting for 72% of the European Union, EU's population. As of 2010 Catholics were the largest Christians, Christian group in Europe, accounting for more than 48% of European Christians. The second-largest Christian group in Europe were the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox, who made up 32% of European Christians. About 19% of European Christians were part of the Protestant tradition. Russia is the largest Christian country in Europe by population, followed by Germany and Italy.
Islam has some tradition in the Balkans and the
Since the High Middle Ages, most of Europe has been dominated by Christianity. There are three major denominations: Roman Catholic, Protestant and Eastern Orthodox, with Protestantism restricted mostly to Northern Europe, and Orthodoxy to Eastern Europe, East and South Slavs, South Slavic regions, Romania, Moldova, Greece, and Georgia (country), Georgia. The Armenian Apostolic Church, part of the Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Church, is also in Europe – another branch of Christianity (world's oldest National Church). Catholicism, while typically centered in Western Europe, also has a very significant following in Central Europe (especially among the Germanic peoples, Germanic, West Slavs, Western Slavic and Hungarians, Hungarian peoples/regions) as well as in Ireland (with some in Great Britain).
Christianity has been the dominant religion shaping European culture for at least the last 1700 years.Cambridge University Historical Series, ''An Essay on Western Civilization in Its Economic Aspects'', p.40: Hebraism, like Hellenism, has been an all-important factor in the development of Western Civilization; Judaism, as the precursor of Christianity, has indirectly had had much to do with shaping the ideals and morality of western nations since the christian era.Caltron J.H Hayas, ''Christianity and Western Civilization'' (1953), Stanford University Press, p.2: That certain distinctive features of our Western civilization — the civilization of western Europe and of America— have been shaped chiefly by Judaeo – Graeco – Christianity, Catholic and Protestant.Horst Hutter, University of New York, ''Shaping the Future: Nietzsche's New Regime of the Soul And Its Ascetic Practices'' (2004), p.111:three mighty founders of Western culture, namely Socrates, Jesus, and Plato.Fred Reinhard Dallmayr, ''Dialogue Among Civilizations: Some Exemplary Voices'' (2004), p.22: Western civilization is also sometimes described as "Christian" or "Judaeo- Christian" civilization. Modern philosophical thought has very much been influenced by Christian philosophers such as St Thomas Aquinas and Erasmus, and throughout most of its history, Europe has been nearly equivalent to Christian culture. The Christian culture was the predominant force in Western culture, western civilization, guiding the course of philosophy, art, and science. The notion of "Europe" and the "Western World" has been intimately connected with the concept of "Christendom, Christianity and Christendom" many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity.
Christianity is still the largest religion in Europe; according to a 2011 survey, 76.2% of Europeans considered themselves Christians. Also according to a study on Religiosity in the European Union in 2012, by Eurobarometer, Christianity is the largest religion in the European Union, accounting for 72% of the European Union, EU's population. As of 2010 Catholics were the largest Christians, Christian group in Europe, accounting for more than 48% of European Christians. The second-largest Christian group in Europe were the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox, who made up 32% of European Christians. About 19% of European Christians were part of the Protestant tradition. Russia is the largest Christian country in Europe by population, followed by Germany and Italy.
Islam has some tradition in the Balkans and the
Online article
* *
Full text on google books
*
Online version
* part I: Europe, pp. 1–100. * * *Panikos Panayi, ''Outsiders: A History of European Minorities'' (London: Hambledon Press, 1999) * * * * * * * * *
Ethnic Power Relations (EPR) Atlas
' *Ron Balsdon,
The Cultural Mosaic of the European Union: Why National Boundaries and the Cultures Inside Still Matter
'
Migration Policy Institute – Country and Comparative Data
* * {{Western world Ethnic groups in Europe,
ethnology
Ethnology (from the grc-gre, ἔθνος, meaning 'nation') is an academic field that compares and analyzes the characteristics of different peoples and the relationships between them (compare cultural, social, or sociocultural anthropology). ...
, the field of anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
related to the various ethnic groups
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
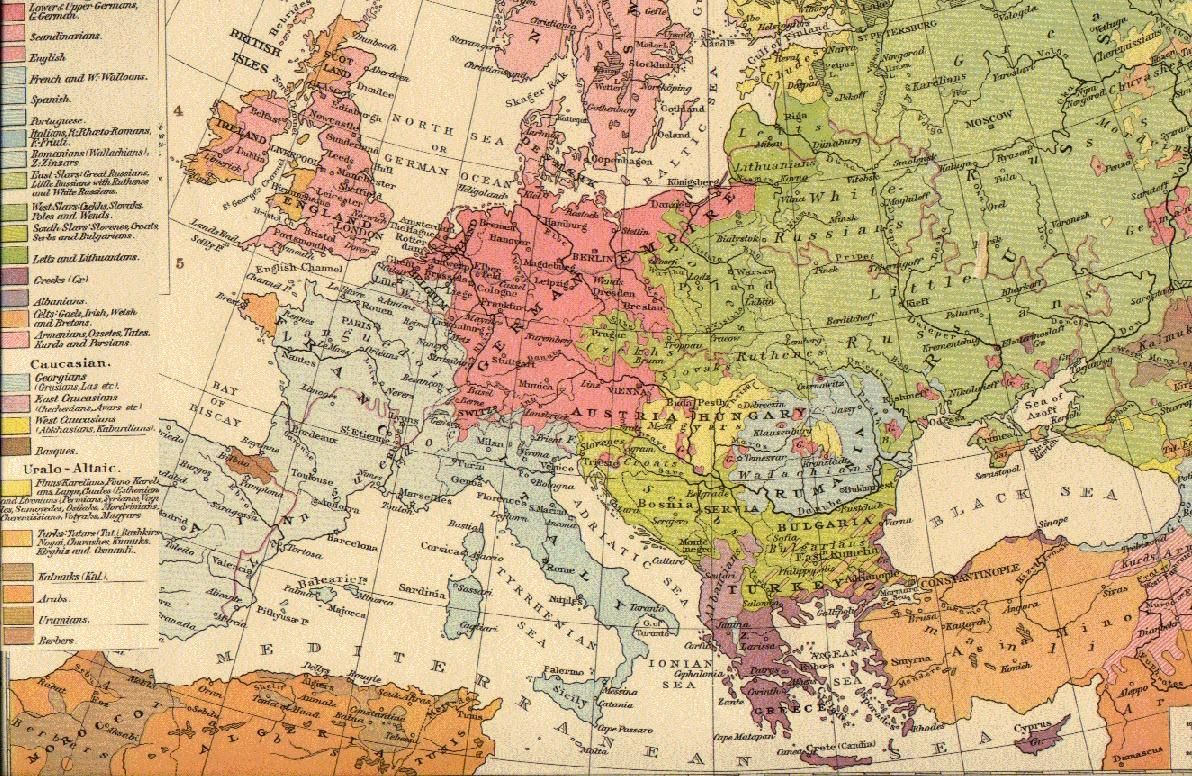
that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) count 87 distinct "''peoples of Europe''", of which 33 form the majority population in at least one sovereign state, while the remaining 54 constitute ethnic minorities
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number o ...
. The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of 770 million Europeans.Christoph Pan, Beate Sibylle Pfeil (2002), Minderheitenrechte in Europa. Handbuch der europäischen Volksgruppen
', Braumüller, (Google Books, snippet view). Als
2006 reprint by Springer
(Amazon, no preview) . The
Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
are the most populous among Europeans, with a population of roughly 120 million. There are no universally accepted and precise definitions of the terms " ethnic group" and "nationality
Nationality is a legal identification of a person in international law, establishing the person as a subject, a ''national'', of a sovereign state. It affords the state jurisdiction over the person and affords the person the protection of the ...
". In the context of European ethnography in particular, the terms ''ethnic group'', ''people'', ''nationality'' and ''ethno-linguistic group'', are used as mostly synonymous, although preference may vary in usage with respect to the situation specific to the individual countries of Europe.
Overview
About 20–25 million residents (3%) are members of diasporas of non-European origin. The population of the European Union, with some 450 million residents, accounts for two thirds of the current European population. BothSpain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
are special cases, in that the designation of nationality
Nationality is a legal identification of a person in international law, establishing the person as a subject, a ''national'', of a sovereign state. It affords the state jurisdiction over the person and affords the person the protection of the ...
, Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
and British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, may controversially take ethnic aspects, subsuming various regional ethnic groups (see nationalisms and regionalisms of Spain
Both the perceived nationhood of Spain, and the perceived distinctions between different parts of its territory derive from historical, geographical, linguistic, economic, political, ethnic and social factors.
Present-day Spain was formed in the ...
and native populations of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom is an ethnically diverse society. The largest ethnic group in the United Kingdom is White British, followed by Asian British. Ethnicity in the United Kingdom is formally recorded at the national level through a census. The 2 ...
).
Switzerland is a similar case, but the linguistic subgroups of the Swiss are discussed in terms of both ethnicity and language affiliations.
Linguistic classifications
Of the total population of Europe of some 740 million (as of 2010), close to 90% (or some 650 million) fall within three large branches ofIndo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
, these being;
* Romance
Romance (from Vulgar Latin , "in the Roman language", i.e., "Latin") may refer to:
Common meanings
* Romance (love), emotional attraction towards another person and the courtship behaviors undertaken to express the feelings
* Romance languages, ...
, including Aromanian, Arpitan, Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
, Corsican, French and other Langues d'oïl, Friulian, Galician, Istro-Romanian, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, Ligurian, Ladino, Megleno-Romanian, Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language, spoken in parts o ...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
*** Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
** Romanian cuisine, tradition ...
, Romansh, Sardinian and Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
.
* Germanic, including Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
, Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, Faroese, Frisian, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, Icelandic, Limburgish, Low Saxon, Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish ( ; also ''Luxemburgish'', ''Luxembourgian'', ''Letzebu(e)rgesch''; Luxembourgish: ) is a West Germanic language that is spoken mainly in Luxembourg. About 400,000 people speak Luxembourgish worldwide.
As a standard form of th ...
, Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
, Scots, Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
, and Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ve ...
. Afrikaans
Afrikaans (, ) is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper (i.e., the Hollandic dialect) used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their enslaved people. Afrikaans gra ...
, a daughter language of Dutch, is spoken by some South African and Namibian migrant populations.
* Slavic, including Belarusian, Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
, Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
, Kashubian, Macedonian, Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
, Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
, Rusyn, Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian () – also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia an ...
, Slovak, Slovenian
Slovene or Slovenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Slovenia, a country in Central Europe
* Slovene language, a South Slavic language mainly spoken in Slovenia
* Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Sloven ...
, Sorbian and Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
.
Three stand-alone Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
languages do not fall within larger sub-groups and are not closely related to those larger language families;
* Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(about 12 million)
* Albanian (about 9 million)
* Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
(about 3.5 million)
In addition, there are also smaller sub-groups within the Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
languages of Europe, including;
* Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
, including Latvian, Lithuanian, Samogitian and Latgalian.
* Celtic languages
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edwar ...
, including Breton, Cornish, Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
, Manx, Welsh, and Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well ...
.
* Iranic
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate ...
, mainly Ossetian in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
.
* Indo-Aryan is represented by the Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
language spoken by Roma people of eastern Europe, and is at root related to the Indo-Aryan languages of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
.
Besides the Indo-European languages, there are other language families
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in hi ...
on the European continent which are considered unrelated to Indo-European:
* Uralic languages
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian (w ...
, including Estonian, Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
, Hungarian, Komi, Livonian, Mari, Mordvin
The Mordvins (also Unified Mordvin people, Mordvinians, Mordovians; russian: мордва, Mordva, Mordvins (no equivalents in Moksha and Erzya)) is an obsolete but official term used in the Russian Federation to refer both to Erzyas and Moks ...
, Sámi
The Sámi ( ; also spelled Sami or Saami) are a Finno-Ugric-speaking people inhabiting the region of Sápmi (formerly known as Lapland), which today encompasses large northern parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and of the Murmansk Oblast, Ru ...
, Samoyedic, and Udmurt.
* Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia ( Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic l ...
, including Azeri
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic people living mainly in northwestern Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan. They are the second-most numer ...
, Bashkir, Chuvash, Gagauz, Kazakh, Nogai, Tatar
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
, and Turkish.
* in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigra ...
, including: Assyrian Neo-Aramaic
Suret ( syr, ܣܘܪܝܬ) ( �su:rɪtʰor �su:rɪθ, also known as Assyrian or Chaldean, refers to the varieties of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic (NENA) spoken by ethnic Assyrians, including those identifying as religious groups rather than eth ...
(spoken in parts of eastern Turkey and the Caucasus by Assyrian Christians), Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
(spoken by some Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
populations), and Maltese. Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
is spoken by some migrant communities from the Middle East and North Africa.
* Kartvelian languages
The Kartvelian languages (; ka, ქართველური ენები, tr; also known as South Caucasian, Kartvelic, and Iberian languagesBoeder (2002), p. 3) are a language family indigenous to the South Caucasus and spoken primari ...
(also known as South Caucasian languages
The Kartvelian languages (; ka, ქართველური ენები, tr; also known as South Caucasian, Kartvelic, and Iberian languagesBoeder (2002), p. 3) are a language family indigenous to the South Caucasus and spoken primari ...
), including Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
, Laz, Mingrelian Mingrelian may refer to:
*the Mingrelians
*the Mingrelian language
Mingrelian or Megrelian (, ) is a Kartvelian language spoken in Western Georgia (regions of Mingrelia and Abkhazia), primarily by the Mingrelians. The language was also called kol ...
, Svan, and Zan
Zan or ZAN, may refer to:
Geography
* Zhan, Kurdistan, Iran, also known as Zān
* Zhan, Lorestan, Iran, also known as Žān
* Zan, Tehran, a village in Tehran Province, Iran
Ethnicity and language
* Zans, the Zan People, people who speak the Za ...
.
* Northwest Caucasian languages, including Abkhaz, Abaza, Adyghe, Circassian, Kabardian, and Ubykh.
* Northeast Caucasian languages
The Northeast Caucasian languages, also called East Caucasian, Nakh-Daghestani or ''Vainakh-Daghestani'', is a family of languages spoken in the Russian republics of Dagestan, Chechnya and Ingushetia and in Northern Azerbaijan as well as in ...
, including Avar, Chechen, Dargin, Ingush, Lak, and Lezgian.
* Language isolates: Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
, spoken in the Basque regions of Spain and France, is an isolate language, the only one in Europe, and is believed to be unrelated to any other language, living or extinct.
* Mongolic languages exist in the form of Kalmyk, spoken in the South region of Russia.
History
Prehistoric populations
 The Basques have been found to descend from the population of the late
The Basques have been found to descend from the population of the late Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
or early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
directly.
By contrast, Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
groups of Europe (the Centum
Languages of the Indo-European family are classified as either centum languages or satem languages according to how the dorsal consonants (sounds of "K", "G" and "Y" type) of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) developed. An e ...
, Balto-Slavic
The Balto-Slavic languages form a branch of the Indo-European family of languages, traditionally comprising the Baltic and Slavic languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European bran ...
, and Albanian groups) migrated throughout most of Europe from the Pontic steppe
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from no ...
. They are assumed to have developed ''in situ'' through admixture of earlier Mesolithic and Neolithic populations with Bronze Age, proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo- ...
s.
The Finnic peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples, sometimes simply called Finns, are the nations who speak languages traditionally classified in the Finnic (now commonly '' Finno-Permic'') language family, and which are thought to have originated in the region of ...
are assumed to also be descended from Proto-Uralic
Proto-Uralic is the unattested reconstructed language ancestral to the modern Uralic language family. The hypothetical language is believed to have been originally spoken in a small area in about 7000–2000 BCE, and expanded to give different ...
populations further to the east, nearer to the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
, that had migrated to their historical homelands in Europe by about 3,000 years ago.
Reconstructed language
Linguistic reconstruction is the practice of establishing the features of an unattested ancestor language of one or more given languages. There are two kinds of reconstruction:
* Internal reconstruction uses irregularities in a single language to ...
s of Iron Age Europe
In Europe, the Iron Age is the last stage of the prehistoric period and the first of the protohistoric periods,The Junior Encyclopædia Britannica: A reference library of general knowledge. (1897). Chicago: E.G. Melvin. (seriously? 1897 "Junior ...
include Proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celti ...
, Proto-Italic
The Proto-Italic language is the ancestor of the Italic languages, most notably Latin and its descendants, the Romance languages. It is not directly attested in writing, but has been reconstructed to some degree through the comparative method. P ...
and Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic bran ...
, all of these Indo-European languages of the centum
Languages of the Indo-European family are classified as either centum languages or satem languages according to how the dorsal consonants (sounds of "K", "G" and "Y" type) of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) developed. An e ...
group, and Proto-Slavic
Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the unattested, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium B.C. through the 6th ...
and Proto-Baltic
Proto-Baltic (PB, PBl, Common Baltic) is the unattested, reconstructed ancestral proto-language of all Baltic languages. It is not attested in writing, but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method by gathering the collected dat ...
, of the satem
Languages of the Indo-European family are classified as either centum languages or satem languages according to how the dorsal consonants (sounds of "K", "G" and "Y" type) of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) developed. An ...
group. A group of Tyrrhenian languages appears to have included Etruscan __NOTOC__
Etruscan may refer to:
Ancient civilization
*The Etruscan language, an extinct language in ancient Italy
*Something derived from or related to the Etruscan civilization
**Etruscan architecture
**Etruscan art
**Etruscan cities
** Etrusca ...
, Rhaetian, Lemnian, and perhaps Camunic. A pre-Roman stage of Proto-Basque
Proto-Basque ( eu, aitzineuskara; es, protoeuskera, protovasco; french: proto-basque), or Pre-Basque, is the reconstructed predecessor of the Basque language before the Roman conquests in the Western Pyrenees.
Background
The first linguist wh ...
can only be reconstructed with great uncertainty.
Regarding the European Bronze Age, the only relatively likely reconstruction is that of Proto-Greek (ca. 2000 BC). A Proto-Italo-Celtic ancestor of both Italic and Celtic (assumed for the Bell beaker period), and a Proto-Balto-Slavic language (assumed for roughly the Corded Ware horizon) has been postulated with less confidence. Old European hydronymy has been taken as indicating an early (Bronze Age) Indo-European predecessor of the later centum languages.
According to geneticist David Reich (geneticist), David Reich, based on Ancient DNA, ancient human genomes that his laboratory sequenced in 2016, Europeans descend from a mixture of four distinct ancestral components.
Historical populations
Historical immigration

 Ethno-linguistic groups that arrived from outside Europe during historical times are:
*Phoenician colonies in the Mediterranean (including regions in
Ethno-linguistic groups that arrived from outside Europe during historical times are:
*Phoenician colonies in the Mediterranean (including regions in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, Malta, Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus and the Aegean Sea, Aegean), from about 1200 BC to the fall of Carthage after the Third Punic War in 146 BC.
*Assyrian conquest of Cyprus, Southern Caucasus (including parts of modern Armenia, Georgia (country), Georgia and Azerbaijan) and Cilicia during the Neo-Assyrian Empire (911–605 BC).
*Ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian influence: Achaemenid control of Thrace (512–343 BC) and the Bosporan Kingdom, Cimmerians (possible Iranians), Scythians, Sarmatians, Alans, Ossetes.
*The Jewish diaspora reached Europe in the Roman Empire period, the Italian Jews, Jewish community in Italy dating to around Siege of Jerusalem (70), AD 70 and records of Jews settling Central Europe (Gaul) from the 5th century (see History of the Jews in Europe).
*The Hunnic Empire (5th century AD), converged with the Barbarian invasions, contributing to the formation of the First Bulgarian Empire.
*The Slavic migrations (6th century AD), and the subsequent split into Eastern Slavs, Western Slavs and Southern Slavs.
*Avars (Carpathians), Avar Khaganate (c. 560s–800).
*The Bulgars (or Proto-Bulgarians), a semi-nomadic Turkic people, originally from Central Asia, eventually absorbed by the Slavs.
*The Magyars (Hungarians), an Uralic languages, Uralic-speaking people, and the Turkic Pechenegs and Khazars, arrived in Europe in about the 8th century (see Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin).
*The Caliphate, Arabs conquered Cyprus, Crete, Sicily (establishing the Emirate of Sicily in 831, from which they would be expelled in 1224), History of Islam in southern Italy, some places along the coast of southern Italy, Malta, Byzantine Empire, Greek Empire and most of Iberian Peninsula, Iberia (founding a polity known as Al-Andalus in 711, ruled also by Berber people, Berber dynasties of the Almoravides and the Almohads, from whose domain they would be expelled in 1492).
*Exodus of Maghreb Christians.
*The western Kipchaks known as Cumans entered the lands of present-day Ukraine in the 11th century.
*The Mongol invasion of Europe, Mongol/Tatar invasions (1223–1480), and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman control of the Balkans (1389–1878). These medieval incursions account for the presence of European Turkish people, Turks and Tatars.
*The Romani people arrived during the Late Middle Ages.
*The Mongol Kalmyks arrived in Kalmykia in the 17th century.
History of European ethnography

 The earliest accounts of European ethnography date from Classical Antiquity. Herodotus described the Scythians and Thraco-Illyrians. Dicaearchus gave a description of Greece itself, besides accounts of western and northern Europe. His work survives only fragmentarily, but was received by Polybius and others.
Roman Empire period authors include Diodorus Siculus, Strabo and Tacitus. Julius Caesar gives an account of the Celtic tribes of Gaul, while Tacitus describes the Germanic tribes of Magna Germania. A number of authors like Diodorus Siculus, Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias and Sallust depict the ancient Sardinians, Sardinian and Corsicans, Corsican peoples.
The 4th century Tabula Peutingeriana records the names of numerous peoples and tribes.
Ethnographers of Late Antiquity such as Agathias of Myrina Ammianus Marcellinus, Jordanes and Theophylact Simocatta give early accounts of the Slavs, the Franks, the Alamanni and the Goths.
Book IX of Isidore of Seville, Isidore's ''Etymologiae'' (7th century) treats ''de linguis, gentibus, regnis, militia, civibus'' (concerning languages, peoples, realms, war and cities).
Ahmad ibn Fadlan in the 10th century gives an account of the Bolghar and the Rus' peoples.
William Rubruck, while most notable for his account of the Mongols, in his account of his journey to Asia also gives accounts of the Tatars and the Alans.
Saxo Grammaticus and Adam of Bremen give an account of pre-Christian Scandinavia. The ''Chronicon Slavorum'' (12th century) gives an account of the northwestern Slavic tribes.
Gottfried Hensel in his 1741 ''Synopsis Universae Philologiae'' published one of the earliest ethno-linguistic map of Europe, showing the beginning of the ''pater noster'' in the various European languages and scripts.
In the 19th century, ethnicity was discussed in terms of scientific racism, and the ethnic groups of Europe were grouped into a number of "Race (classification of human beings), races", Mediterranean race, Mediterranean, Alpine race, Alpine and Nordic race, Nordic, all part of a larger "Caucasian race, Caucasian" group.
The beginnings of ethnic geography as an academic subdiscipline lie in the period following World War I, in the context of ethnic nationalism, nationalism, and in the 1930s exploitation for the purposes of fascist and Nazi propaganda, so that it was only in the 1960s that ethnic geography began to thrive as a ''bona fide'' academic subdiscipline.
The origins of modern ethnography are often traced to the work of Bronisław Malinowski, who emphasized the importance of fieldwork.
The emergence of population genetics further undermined the categorisation of Europeans into clearly defined racial groups. A 2007 study on the genetic history of Europe found that the most important genetic differentiation in Europe occurs on a line from the north to the south-east (northern Europe to the Balkans), with another east–west axis of differentiation across Europe, separating the indigenous Basques, Sardinians and Sami people, Sami from other European populations.
Despite these stratifications it noted the unusually high degree of European homogeneity: "there is low apparent diversity in Europe with the entire continent-wide samples only marginally more dispersed than single population samples elsewhere in the world."
The earliest accounts of European ethnography date from Classical Antiquity. Herodotus described the Scythians and Thraco-Illyrians. Dicaearchus gave a description of Greece itself, besides accounts of western and northern Europe. His work survives only fragmentarily, but was received by Polybius and others.
Roman Empire period authors include Diodorus Siculus, Strabo and Tacitus. Julius Caesar gives an account of the Celtic tribes of Gaul, while Tacitus describes the Germanic tribes of Magna Germania. A number of authors like Diodorus Siculus, Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias and Sallust depict the ancient Sardinians, Sardinian and Corsicans, Corsican peoples.
The 4th century Tabula Peutingeriana records the names of numerous peoples and tribes.
Ethnographers of Late Antiquity such as Agathias of Myrina Ammianus Marcellinus, Jordanes and Theophylact Simocatta give early accounts of the Slavs, the Franks, the Alamanni and the Goths.
Book IX of Isidore of Seville, Isidore's ''Etymologiae'' (7th century) treats ''de linguis, gentibus, regnis, militia, civibus'' (concerning languages, peoples, realms, war and cities).
Ahmad ibn Fadlan in the 10th century gives an account of the Bolghar and the Rus' peoples.
William Rubruck, while most notable for his account of the Mongols, in his account of his journey to Asia also gives accounts of the Tatars and the Alans.
Saxo Grammaticus and Adam of Bremen give an account of pre-Christian Scandinavia. The ''Chronicon Slavorum'' (12th century) gives an account of the northwestern Slavic tribes.
Gottfried Hensel in his 1741 ''Synopsis Universae Philologiae'' published one of the earliest ethno-linguistic map of Europe, showing the beginning of the ''pater noster'' in the various European languages and scripts.
In the 19th century, ethnicity was discussed in terms of scientific racism, and the ethnic groups of Europe were grouped into a number of "Race (classification of human beings), races", Mediterranean race, Mediterranean, Alpine race, Alpine and Nordic race, Nordic, all part of a larger "Caucasian race, Caucasian" group.
The beginnings of ethnic geography as an academic subdiscipline lie in the period following World War I, in the context of ethnic nationalism, nationalism, and in the 1930s exploitation for the purposes of fascist and Nazi propaganda, so that it was only in the 1960s that ethnic geography began to thrive as a ''bona fide'' academic subdiscipline.
The origins of modern ethnography are often traced to the work of Bronisław Malinowski, who emphasized the importance of fieldwork.
The emergence of population genetics further undermined the categorisation of Europeans into clearly defined racial groups. A 2007 study on the genetic history of Europe found that the most important genetic differentiation in Europe occurs on a line from the north to the south-east (northern Europe to the Balkans), with another east–west axis of differentiation across Europe, separating the indigenous Basques, Sardinians and Sami people, Sami from other European populations.
Despite these stratifications it noted the unusually high degree of European homogeneity: "there is low apparent diversity in Europe with the entire continent-wide samples only marginally more dispersed than single population samples elsewhere in the world."
Minorities

 The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of Europeans.
The member states of the Council of Europe in 1995 signed the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities. The broad aims of the convention are to ensure that the signatory states respect the rights of national minorities, undertaking to combat discrimination, promote equality, preserve and develop the culture and identity of national minorities, guarantee certain freedoms in relation to access to the media, minority languages and education and encourage the participation of national minorities in public life. The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities defines a national minority implicitly to include minorities possessing a territorial identity and a distinct cultural heritage. By 2008, 39 member states had signed and ratified the convention, with the notable exception of France.
The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of Europeans.
The member states of the Council of Europe in 1995 signed the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities. The broad aims of the convention are to ensure that the signatory states respect the rights of national minorities, undertaking to combat discrimination, promote equality, preserve and develop the culture and identity of national minorities, guarantee certain freedoms in relation to access to the media, minority languages and education and encourage the participation of national minorities in public life. The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities defines a national minority implicitly to include minorities possessing a territorial identity and a distinct cultural heritage. By 2008, 39 member states had signed and ratified the convention, with the notable exception of France.
Indigenous minorities
Notable indigenous minority populations in Europe that are recognized by the UN include the Uralic Nenets people, Nenets, Samoyedic peoples, Samoyed, and Komi peoples, Komi peoples of northern Russia; Circassians of southern Russia and the North Caucasus; Crimean Tatars, Krymchaks and Crimean Karaites of Crimea (Ukraine); Sámi people, Sámi peoples of northern Norway, Sweden, and Finland and northwestern Russia (in an area also referred to as Sápmi); Basques of Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country,Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and southern France; and the Sorbs, Sorbian people of Germany and Poland.
Non-indigenous minorities
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. In addition, over one million Turks were living in the Balkans in 2019 (especially in Bulgaria, Greece, Kosovo, North Macedonia and Romania), and approximately 400,000 Meskhetian Turks were living in the Eastern European regions of the Post-Soviet states (i.e. Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, Kazakhstan, Russia and Ukraine) in 2014.
**Jews: approx. 2.0 million, mostly in France, the UK, Russia and Germany. They are descended from the Israelites#Historical Israelites, Israelites of the Middle East (Southwest Asia), originating from the History of ancient Israel and Judah, historical kingdoms of Israel and Judah. Natural History 102:11 (November 1993): 12–19.
***Ashkenazi Jews: approx. 1.4 million, mostly in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, France, Russia, Germany and Ukraine. They are believed by scholars to have arrived from Israel via southern Europe in the Ancient Rome, Roman era and settled in France and Germany towards the end of the first millennium. The Nazi Holocaust wiped out the vast majority during World War II and forced most to flee, with many of them going to Israel.
***Sephardi Jews: approx. 0.3 million, mostly in France. They arrived via Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and Portugal in the pre-Ancient Rome, Roman and Roman eras, and were forcibly converted or expelled in the 15th and 16th centuries.
***Mizrahi Jews: approx. 0.3 million, mostly in France, via Islamic-majority countries of the Middle East.
***Italqim: approx. 50,000, mostly in Italy, since the 2nd century BC.
***Romaniotes: approx. 6,000, mostly in Greece, with communities dating at least from the 1st century AD.
***Crimean Karaites (Karaim): less than 4,000, mostly in Ukraine, Poland and Lithuania. They arrived in Crimea in the Middle Ages.
**Assyrian people, Assyrians: mostly in Sweden and Germany, as well as in Russia, Armenia, Denmark and Great Britain (see Assyrian diaspora). Assyrians have been present in Eastern Turkey since the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
(circa 2000 BCE).
**Kurds: approx. 2.5 million, mostly in the UK, Germany, Sweden and Turkey.
**Iraqi diaspora: mostly in the UK, Germany and Sweden, and can be of varying ethnic origin, including Arabs, Assyrian people, Assyrians, Kurds, Armenians, Shabak people, Shabaks, Mandeans, Iraqi Turkmen, Turks, Kawliya and Yezidis.
**Lebanese diaspora: especially in France, Netherlands, Germany, Cyprus and the UK.
**Syrian diaspora: Largest number of Syrians live in Germany, the Netherlands and Sweden and can be of varying ethnic origin, including; Arabs, Assyrian people, Assyrians, Kurds, Armenians, Arameans, Syrian Turkmen, Turks, Mhallami and Yezidis.
*List of ethnic groups of Africa, Africans
**List of ethnic groups of Africa#North Africa, North Africans (North African Arabs, Copts, Egyptian Copts, and Berber people, Berbers): approx. 5 million, mostly in France, Spain, Italy, the Netherlands and Sweden. The bulk of North African migrants are Moroccan diaspora, Moroccans, although France also has a large number of Algerians, and others may be from Egypt (including Copts), Libya and Tunisia.
**Horn of Africa, Horn Africans (Somalis, People of Ethiopia, Ethiopians, Demographics of Eritrea, Eritreans, Demographics of Djibouti, Djiboutians, and the Demographics of Sudan, Northern Sudanese): approx. 700,000, mostly in Scandinavia, the UK, the Netherlands, Germany, Switzerland, Austria, Finland, and Italy. Majority arrived to Europe as refugees. Proportionally few live in Italy despite former colonial ties, most live in the Nordic countries.
**Afro-European, Sub-Saharan Africans (many ethnicities including wikt:Afro-Caribbean, Afro-Caribbeans, African Americans, African-Americans, Afro-Latin Americans, Afro-Latinos and others by descent): approx. 5 million, mostly in the UK and France, with smaller numbers in the Netherlands, Germany, Italy, Spain, Portugal and elsewhere.
*Latin Americans: approx. 2.2 million, mainly in Spain and to a lesser extent Italy and the UK. See also Latin American Britons (80,000 Latin American born in 2001).
**Brazilian diaspora, Brazilians: around 280,000 in Portugal, and 50,000 in Italy and Germany each (mainly German-Brazilians).
** Chilean refugees escaping the Augusto Pinochet regime of the 1970s formed communities in France, Sweden, the UK, former East Germany and the Netherlands.
**Mexicans: about 21,000 in Spain and 14,000 in Germany
**Venezuelans: around 520,000 mostly in Spain (200,000), Portugal (100,000), France (30,000), Germany (20,000), UK (15,000), Ireland (5,000), Italy (5,000) and the Netherlands (1,000).
*South Asians: approx. 3–4 million, mostly in the UK but reside in smaller numbers in Germany and France. **Romani people, Romani (Gypsies): approx. 4 or 10 million (although estimates vary widely), dispersed throughout Europe but with large numbers concentrated in the Balkans area, they are of ancestral South Asian and European descent, originating from the North India, northern regions of the
**Romani people, Romani (Gypsies): approx. 4 or 10 million (although estimates vary widely), dispersed throughout Europe but with large numbers concentrated in the Balkans area, they are of ancestral South Asian and European descent, originating from the North India, northern regions of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
.
**Non-resident Indian and person of Indian origin, Indians: approx. 2 million, mostly in the UK, also in Netherlands, Italy, in Germany and France.
**Pakistani diaspora, Pakistanis: approx. 1,000,000, mostly in the UK, but also in France, Spain, Germany and Italy.
**Bangladeshi residing in Europe estimated at over 500,000, mostly in the UK.
**British Sri Lankans, Sri Lankans: approx. 200,000, mainly in the UK.
**Nepalese in the United Kingdom, Nepalese: approx. 50,000 in the UK.
**Afghanistan, Afghans, about 100,000 to 200,000, most happen to live in the UK, but Germany and Sweden are destinations for Afghan immigrants since the 1960s.
*Southeast Asians
**Overseas Filipino, Filipinos: above 1 million, mostly in Italy, the UK, France, Germany, and Spain.
**Others of multiple nationalities, ca. total 1 million, such as Culture of Indonesia, Indonesians in the Netherlands, Thai people, Thais in the UK and Sweden, Vietnamese people, Vietnamese in France and former East Germany, and Khmer people, Cambodians in France, together with Myanmar, Burmese, Malaysian people, Malaysian, Singaporean, Timorese and Lao people, Laotian migrants. See also Vietnamese people in the Czech Republic.
*Ethnic groups in Asia#East Asia, East Asians
**Overseas Chinese, Chinese: approx. 1.7 million, mostly in France, Russia, the UK, Spain, Italy and the Netherlands.
**Japanese diaspora#Europe, Japanese: mostly in the UK and a sizable community in Düsseldorf, Germany.
**Koreans: 100,000 estimated (excludes a possible 100,000 more in Russia), mainly in the UK, France and Germany. See also Koryo-saram.
**Mongols, Mongolians in Germany.
*North Americans
**U.S. and Canadian expatriates: American British and Canadian British, Canadiens and Acadians in France, as well as Americans/Canadians of European ancestry residing elsewhere in Europe.
***African Americans (i.e. African American British) who are Americans of black/African ancestry reside in other countries. In the 1920s, African-American entertainers established a colony in Paris (African Americans in France, African American French) and descendants of World War II/Cold War-era black American soldiers stationed in France, Germany and Italy are well known.
*Others
**European diaspora – Australians, New Zealanders, South Africans (mostly White South Africans of Afrikaner and British descent), and white Namibians, Demographics of Zimbabwe, Zimbabweans, Kenyans, Malawians and Zambians mainly in the UK, together with white Angolans and Mozambique, Mozambicans, mainly of Portuguese people, Portuguese descent.
**Pacific Islanders: A small population of Tahitians of Polynesians, Polynesian origin in mainland France, Fijians in the United Kingdom from Fiji and Māori in the United Kingdom of the Māori people of New Zealand, a small number of Tongans and Samoans, also in the United Kingdom.
**Indigenous peoples of the Americas, a scant few in the European continent of American Indian ancestry (often Latin Americans in Spain, France and the UK; Inuit in Greenlandic people in Denmark, Denmark), but most may be children or grandchildren of U.S. soldiers from American Indian tribes by intermarriage with local European women.
European identity
Historical
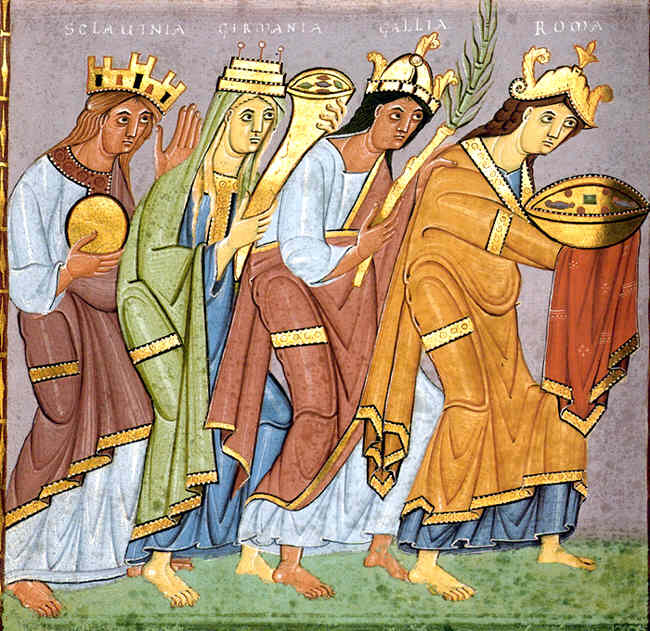
 Medieval notions of a relation of the peoples of Europe are expressed in terms of genealogy of mythical founders of the individual groups.
The Europeans were considered the descendants of Japheth from early times, corresponding to the division of the known world into T and O map, three continents, the descendants of Shem peopling Asia and those of Ham, son of Noah, Ham peopling Roman North Africa, Africa. Identification of Europeans as "Japhetites" is also reflected in early suggestions for terming the
Medieval notions of a relation of the peoples of Europe are expressed in terms of genealogy of mythical founders of the individual groups.
The Europeans were considered the descendants of Japheth from early times, corresponding to the division of the known world into T and O map, three continents, the descendants of Shem peopling Asia and those of Ham, son of Noah, Ham peopling Roman North Africa, Africa. Identification of Europeans as "Japhetites" is also reflected in early suggestions for terming the Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
"Japhetic".
In this tradition, the ''Historia Brittonum'' (9th century) introduces a genealogy of the peoples of the Migration Period based on the sixth-century Frankish Table of Nations as follows,
:''The first man that dwelt in Europe was Alanus, with his three sons, Hisicion, Armenon, and Neugio. Hisicion had four sons, Francus, Romanus, Alamanus, and Bruttus. Armenon had five sons, Gothus, Valagothus, Cibidus, Burgundus, and Longobardus. Neugio had three sons, Vandalus, Saxo, and Boganus.''
:''From Hisicion arose four nations—the Franks, the Italic peoples, Latins, the Alamanni, Germans, and Britons (historical), Britons; from Armenon, the Visigoths, Gothi, Ostrogoths, Valagothi, Gepids, Cibidi, Burgundi, and Longobardi people, Longobardi; from Neugio, the Bogari, Vandali, Saxones, and Turingi, Tarincgi. The whole of Europe was subdivided into these tribes.''
The text goes then on to list the genealogy of Alanus, connecting him to Japheth via eighteen generations.
European culture
European culture is largely rooted in what is often referred to as its "common cultural heritage". Due to the great number of perspectives which can be taken on the subject, it is impossible to form a single, all-embracing conception of European culture. Nonetheless, there are core elements which are generally agreed upon as forming the cultural foundation of modern Europe. One list of these elements given by K. Bochmann includes: *A common cultural and spiritual heritage derived from Greco-Roman antiquity, Christianity, the Renaissance and its Humanism, the political thinking of the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment, and the French Revolution, and the developments of Modernity, including all types of socialism; *A rich and dynamic material culture that has been extended to the other continents as the result of industrialization and colonialism during the "Great Divergence"; *A specific conception of the individual expressed by the existence of, and respect for, a legality that guarantees human rights and the Political freedom, liberty of the individual; *A plurality of states with different political orders, which are condemned to live together in one way or another; *Respect for peoples, states and nations outside Europe. Berting says that these points fit with "Europe's most positive realisations". The concept of European culture is generally linked to the classical definition of the Western world. In this definition, Western culture is the set of Western literature, literary, Science, scientific, Political modernity, political, European art, artistic and European philosophy, philosophical principles which set it apart from other civilizations. Much of this set of traditions and knowledge is collected in the Western canon. The term has come to apply to countries whose history has been strongly marked by European immigration or settlement during the 18th and 19th centuries, such as the Americas, and Australasia, and is not restricted to Europe.Religion
 Since the High Middle Ages, most of Europe has been dominated by Christianity. There are three major denominations: Roman Catholic, Protestant and Eastern Orthodox, with Protestantism restricted mostly to Northern Europe, and Orthodoxy to Eastern Europe, East and South Slavs, South Slavic regions, Romania, Moldova, Greece, and Georgia (country), Georgia. The Armenian Apostolic Church, part of the Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Church, is also in Europe – another branch of Christianity (world's oldest National Church). Catholicism, while typically centered in Western Europe, also has a very significant following in Central Europe (especially among the Germanic peoples, Germanic, West Slavs, Western Slavic and Hungarians, Hungarian peoples/regions) as well as in Ireland (with some in Great Britain).
Christianity has been the dominant religion shaping European culture for at least the last 1700 years.Cambridge University Historical Series, ''An Essay on Western Civilization in Its Economic Aspects'', p.40: Hebraism, like Hellenism, has been an all-important factor in the development of Western Civilization; Judaism, as the precursor of Christianity, has indirectly had had much to do with shaping the ideals and morality of western nations since the christian era.Caltron J.H Hayas, ''Christianity and Western Civilization'' (1953), Stanford University Press, p.2: That certain distinctive features of our Western civilization — the civilization of western Europe and of America— have been shaped chiefly by Judaeo – Graeco – Christianity, Catholic and Protestant.Horst Hutter, University of New York, ''Shaping the Future: Nietzsche's New Regime of the Soul And Its Ascetic Practices'' (2004), p.111:three mighty founders of Western culture, namely Socrates, Jesus, and Plato.Fred Reinhard Dallmayr, ''Dialogue Among Civilizations: Some Exemplary Voices'' (2004), p.22: Western civilization is also sometimes described as "Christian" or "Judaeo- Christian" civilization. Modern philosophical thought has very much been influenced by Christian philosophers such as St Thomas Aquinas and Erasmus, and throughout most of its history, Europe has been nearly equivalent to Christian culture. The Christian culture was the predominant force in Western culture, western civilization, guiding the course of philosophy, art, and science. The notion of "Europe" and the "Western World" has been intimately connected with the concept of "Christendom, Christianity and Christendom" many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity.
Christianity is still the largest religion in Europe; according to a 2011 survey, 76.2% of Europeans considered themselves Christians. Also according to a study on Religiosity in the European Union in 2012, by Eurobarometer, Christianity is the largest religion in the European Union, accounting for 72% of the European Union, EU's population. As of 2010 Catholics were the largest Christians, Christian group in Europe, accounting for more than 48% of European Christians. The second-largest Christian group in Europe were the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox, who made up 32% of European Christians. About 19% of European Christians were part of the Protestant tradition. Russia is the largest Christian country in Europe by population, followed by Germany and Italy.
Islam has some tradition in the Balkans and the
Since the High Middle Ages, most of Europe has been dominated by Christianity. There are three major denominations: Roman Catholic, Protestant and Eastern Orthodox, with Protestantism restricted mostly to Northern Europe, and Orthodoxy to Eastern Europe, East and South Slavs, South Slavic regions, Romania, Moldova, Greece, and Georgia (country), Georgia. The Armenian Apostolic Church, part of the Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Church, is also in Europe – another branch of Christianity (world's oldest National Church). Catholicism, while typically centered in Western Europe, also has a very significant following in Central Europe (especially among the Germanic peoples, Germanic, West Slavs, Western Slavic and Hungarians, Hungarian peoples/regions) as well as in Ireland (with some in Great Britain).
Christianity has been the dominant religion shaping European culture for at least the last 1700 years.Cambridge University Historical Series, ''An Essay on Western Civilization in Its Economic Aspects'', p.40: Hebraism, like Hellenism, has been an all-important factor in the development of Western Civilization; Judaism, as the precursor of Christianity, has indirectly had had much to do with shaping the ideals and morality of western nations since the christian era.Caltron J.H Hayas, ''Christianity and Western Civilization'' (1953), Stanford University Press, p.2: That certain distinctive features of our Western civilization — the civilization of western Europe and of America— have been shaped chiefly by Judaeo – Graeco – Christianity, Catholic and Protestant.Horst Hutter, University of New York, ''Shaping the Future: Nietzsche's New Regime of the Soul And Its Ascetic Practices'' (2004), p.111:three mighty founders of Western culture, namely Socrates, Jesus, and Plato.Fred Reinhard Dallmayr, ''Dialogue Among Civilizations: Some Exemplary Voices'' (2004), p.22: Western civilization is also sometimes described as "Christian" or "Judaeo- Christian" civilization. Modern philosophical thought has very much been influenced by Christian philosophers such as St Thomas Aquinas and Erasmus, and throughout most of its history, Europe has been nearly equivalent to Christian culture. The Christian culture was the predominant force in Western culture, western civilization, guiding the course of philosophy, art, and science. The notion of "Europe" and the "Western World" has been intimately connected with the concept of "Christendom, Christianity and Christendom" many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity.
Christianity is still the largest religion in Europe; according to a 2011 survey, 76.2% of Europeans considered themselves Christians. Also according to a study on Religiosity in the European Union in 2012, by Eurobarometer, Christianity is the largest religion in the European Union, accounting for 72% of the European Union, EU's population. As of 2010 Catholics were the largest Christians, Christian group in Europe, accounting for more than 48% of European Christians. The second-largest Christian group in Europe were the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox, who made up 32% of European Christians. About 19% of European Christians were part of the Protestant tradition. Russia is the largest Christian country in Europe by population, followed by Germany and Italy.
Islam has some tradition in the Balkans and the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
due to conquest and colonization from the Ottoman Empire in the 16th to 19th centuries, as well as earlier though discontinued long-term presence in Al-Andalus, much of Iberia as well as Islam in Sicily, Sicily. Muslims account for the majority of the populations in Albania, Azerbaijan, Kosovo, Northern Cyprus (controlled by Turkish people, Turks), and Bosnia and Herzegovina. Significant minorities are present in the rest of Europe. Russia also has one of the largest Islam in Russia, Muslim communities in Europe, including the Tatars of the Idel-Ural, Middle Volga and multiple groups in the Caucasus, including Chechens, Caucasian Avars, Avars, Ingush people, Ingush and others. With 20th-century migrations, Muslims in Western Europe have become a noticeable minority. According to the Pew Forum, the total number of Muslims in Europe in 2010 was about 44 million (6%), while the total number of Muslims in the European Union in 2007 was about 16 million (3.2%).
Judaism has a long History of the Jews in Europe, history in Europe, but is a small minority religion, with History of the Jews in France, France (1%) the only European country with a Jewish population in excess of 0.5%. The Jewish population of Europe is composed primarily of two Jewish ethnic divisions, groups, the Ashkenazi Jews, Ashkenazi and the Sephardi Jews, Sephardi. Ancestors of Ashkenazi Jews likely migrated to Central Europe Ashkenazi Jews#Origins, at least as early as the 8th century, while Sephardi Jews established themselves Spanish and Portuguese Jews, in Spain and Portugal at least one thousand years before that. Jews originated in the Levant where they resided for thousands of years until the 2nd century AD, when they spread around the Mediterranean and into Europe, although small communities were known to exist in Greece as well as the Balkans since at least the 1st century BC. Jewish history was notably affected by the Holocaust and emigration (including Aliyah, as well as emigration to American Jews, America) in the 20th century. The Jewish population of Europe in 2010 was estimated to be approximately 1.4 million (0.2% of European population) or 10% of the world's Jewish population. In the 21st century, France has the largest Jewish population by country, Jewish population in Europe, followed by the United Kingdom, Germany, Russia and Ukraine.
In modern times, significant secularization since the 20th century, notably in Secularism in France, secularist France, Estonia and the Czech Republic. Currently, distribution of theism in Europe is very heterogeneous, with more than 95% in Poland, and less than 20% in the Czech Republic and Estonia. The 2005 Eurobarometer poll found that 52% of EU citizens believe in God. According to a Pew Research Center Survey in 2012 the Irreligion, Religiously Unaffiliated (Atheists and Agnostics) make up about 18.2% of the European population in 2010. According to the same Survey the Religiously Unaffiliated make up the majority of the population in only two European countries: Czech Republic (76%) and Estonia (60%).
Pan-European identity
"Pan-European identity" or "Europatriotism" is an emerging sense of personal identification with Europe, or the European Union as a result of the gradual process of European integration taking place over the last quarter of the 20th century, and especially in the period after the end of the Cold War, since the 1990s. The foundation of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, OSCE following the 1990s Paris Charter has facilitated this process on a political level during the 1990s and 2000s. From the later 20th century, 'Europe' has come to be widely used as a synonym for the European Union even though there are millions of people living on the European continent in non-EU member states. The prefix ''pan'' implies that the identity applies throughout Europe, and especially in an EU context, and 'pan-European' is often contrasted with nation-state, national identity.This is particularly the case among proponents of the so-called confederation, confederalist or neofunctionalism, neo-functionalist position on European integration. Eder and Spohn (2005:3) note: "The evolutionary thesis of the making of a European identity often goes with the assumption of a simultaneous decline of national identities. This substitution thesis reiterates the well-known confederalist/neo-functionalist position in the debate on European integration, arguing for an increasing replacement of the nation-state by European institutions, against the intergovernmentalist/realist position, insisting on the continuing primacy of the nation-state."European ethnic groups by sovereign state
See also
*European diaspora *Central Asians *Demography of Europe *Emigration from Europe **European American **White Latin American *Ethnic groups in the Middle East *Eurolinguistics *Federal Union of European Nationalities *Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities *Genetic history of Europe **Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of Europe *Immigration to Europe **Afro-Europeans **Turks in Europe *Languages of Europe *List of ethnic groups *Nomadic peoples of Europe *Peoples of the Caucasus *White peopleNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * *Online article
* *
Full text on google books
*
Online version
* part I: Europe, pp. 1–100. * * *Panikos Panayi, ''Outsiders: A History of European Minorities'' (London: Hambledon Press, 1999) * * * * * * * * *
Further reading
* GROWup - Geographical Research On War, Unified Platform, ETH Zurich,Ethnic Power Relations (EPR) Atlas
' *Ron Balsdon,
The Cultural Mosaic of the European Union: Why National Boundaries and the Cultures Inside Still Matter
'
Migration Policy Institute – Country and Comparative Data
* * {{Western world Ethnic groups in Europe,