Indigenous peoples in Mexico on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
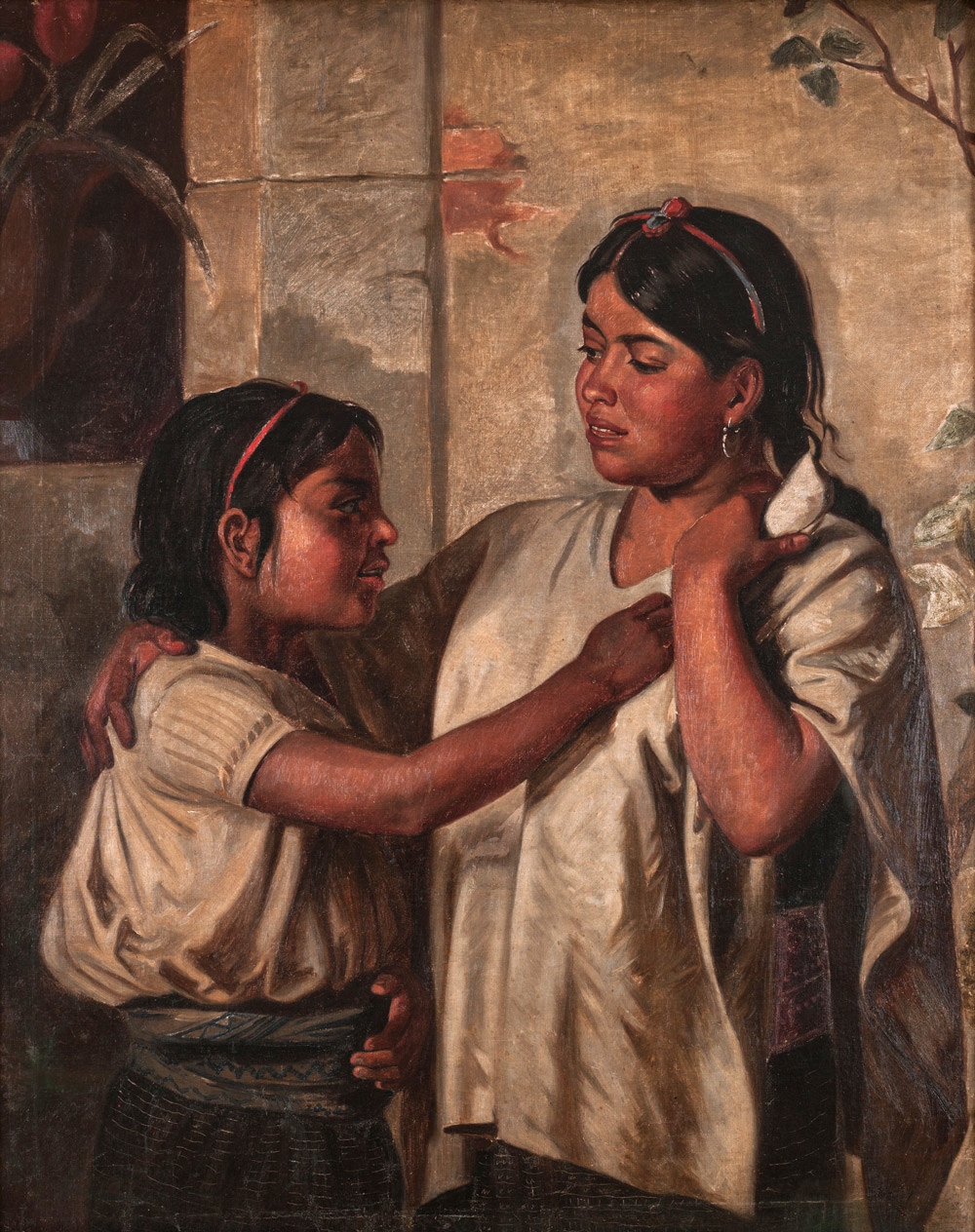 Indigenous peoples of Mexico ( es, gente indígena de México, pueblos indígenas de México), Native Mexicans ( es, nativos mexicanos) or Mexican Native Americans ( es, pueblos originarios de México, lit=Original peoples of Mexico), are those who are part of communities that trace their roots back to populations and communities that existed in what is now
Indigenous peoples of Mexico ( es, gente indígena de México, pueblos indígenas de México), Native Mexicans ( es, nativos mexicanos) or Mexican Native Americans ( es, pueblos originarios de México, lit=Original peoples of Mexico), are those who are part of communities that trace their roots back to populations and communities that existed in what is now
 In the second article of the
In the second article of the
Art. 2 The number of indigenous Mexicans is measured using constitutional criteria. The Mexican census does not classify individuals by
The category of ''indigena'' (indigenous) can be defined narrowly according to linguistic criteria including only persons that speak one of Languages of Mexico, Mexico's 89 indigenous languages, this is the categorization used by the National Mexican Institute of Statistics. It can also be defined broadly to include all persons who self-identify as having an indigenous cultural background, whether or not they speak the language of the indigenous group they identify with. This means that the percentage of the Mexican population defined as "indigenous" varies according to the definition applied; cultural activists have referred to the usage of the narrow definition of the term for census purposes as "statistical genocide". The indigenous peoples in Mexico have the right of free determination under the second article of the constitution. According to this article, indigenous peoples are granted: * the right to decide the internal forms of social, economic, political, and cultural organization; * the right to apply their own normative systems of regulation as long as human rights and gender equality are respected; * the right to preserve and enrich their languages and cultures; * the right to elect representatives before the municipal council where their territories are located; The Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Languages recognizes 89 indigenous languages as national languages, which have the same validity as Spanish in all territories where they are spoken. According to the National Institute of Statistics, Geography and Data Processing (INEGI), approximately 5.4% of the population speaks an indigenous language. The recognition of indigenous languages and the protection of indigenous cultures is granted not only to the ethnic groups indigenous to modern-day Mexican territory but also to other North American indigenous groups that migrated to Mexico from the United States in the nineteenth century and those who immigrated from
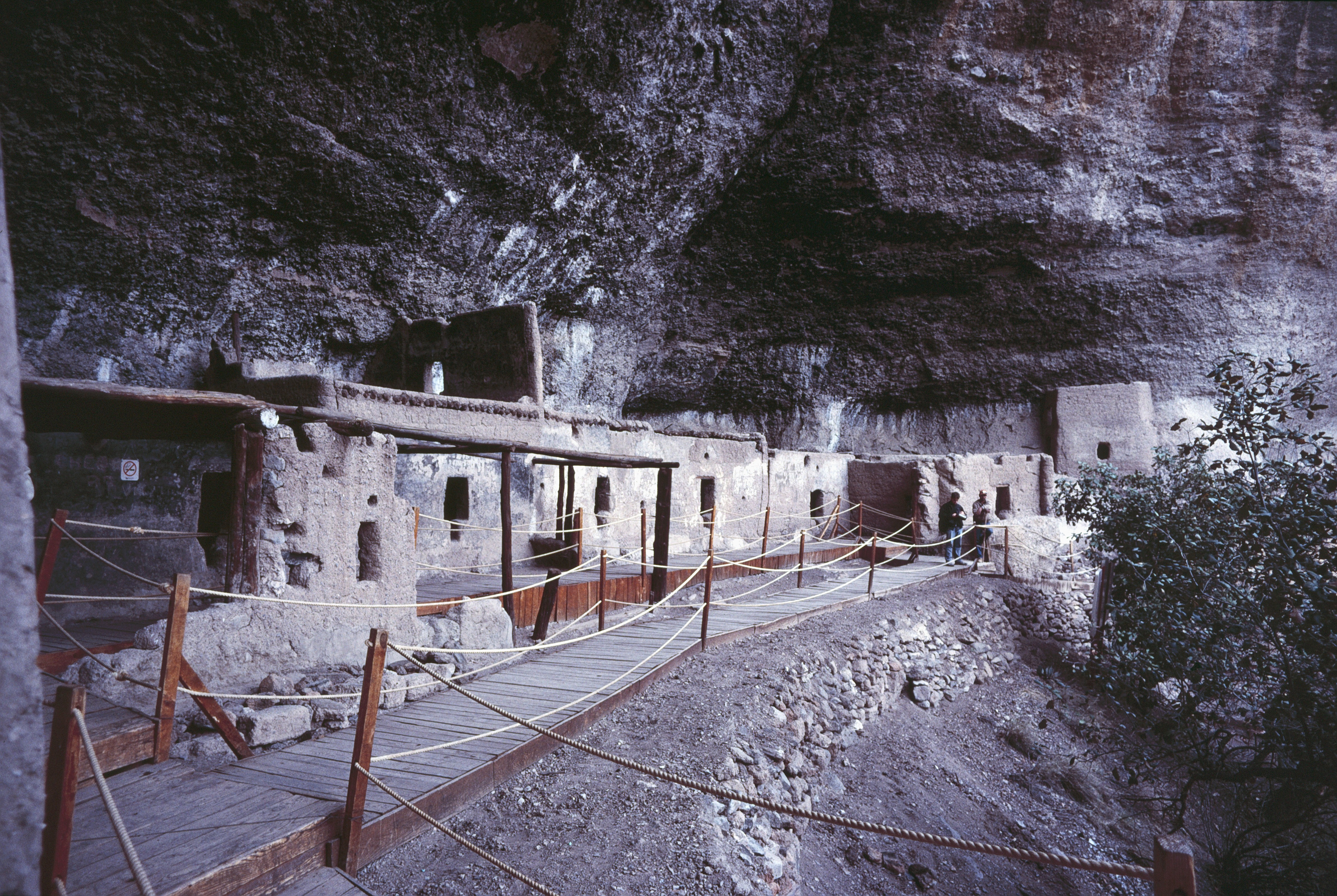

 During the early colonial era in central Mexico, Spaniards were more interested in access to indigenous labor than land ownership. The institution of the ''encomienda'', a crown grant of the labor of indigenous communities to conquerors was a key element of the imposition of Spanish rule. The Spanish crown initially maintained the indigenous sociopolitical system of local rulers and land tenure, with the
During the early colonial era in central Mexico, Spaniards were more interested in access to indigenous labor than land ownership. The institution of the ''encomienda'', a crown grant of the labor of indigenous communities to conquerors was a key element of the imposition of Spanish rule. The Spanish crown initially maintained the indigenous sociopolitical system of local rulers and land tenure, with the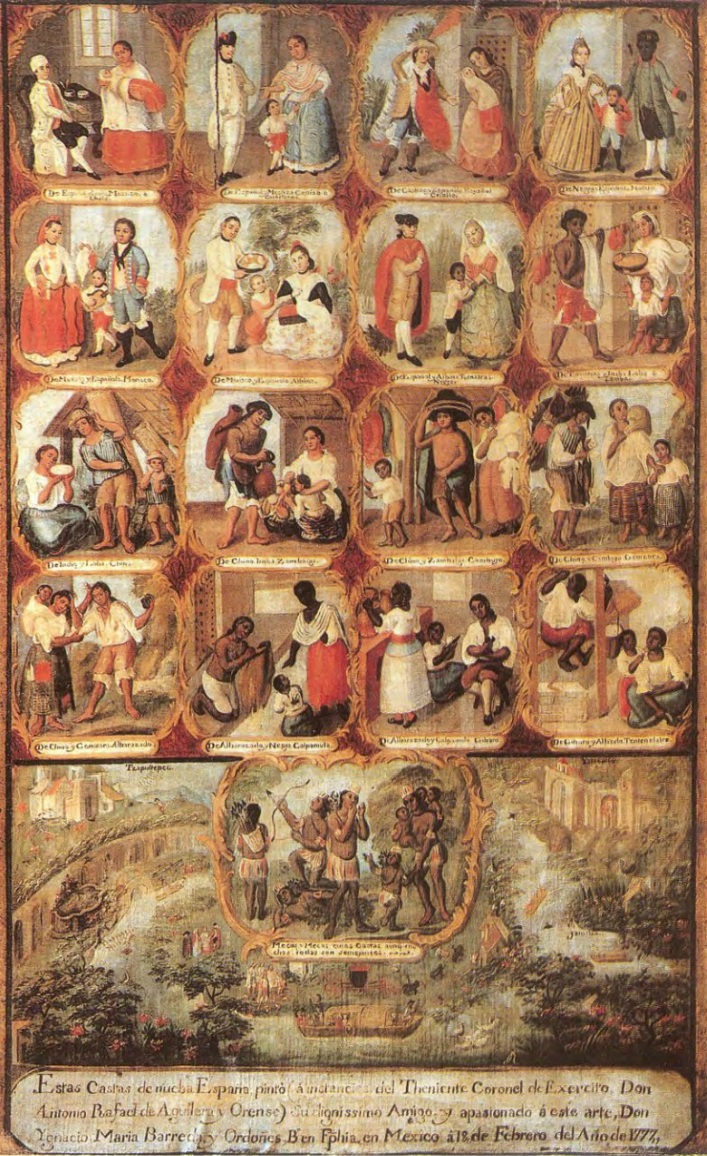 

 The
The
 The
The  In spite of the official recognition of indigenous peoples, the economic underdevelopment of their communities, accentuated by the crises of the 1980s and 1990s, has not allowed for the development of most indigenous communities. Thousands of indigenous Mexicans have emigrated to urban centers in Mexico and the United States. In Los Angeles, for example, the Mexican government has established electronic access to some of the consular services provided in Spanish as well as Zapotec and Mixe. Some of the Maya peoples of
In spite of the official recognition of indigenous peoples, the economic underdevelopment of their communities, accentuated by the crises of the 1980s and 1990s, has not allowed for the development of most indigenous communities. Thousands of indigenous Mexicans have emigrated to urban centers in Mexico and the United States. In Los Angeles, for example, the Mexican government has established electronic access to some of the consular services provided in Spanish as well as Zapotec and Mixe. Some of the Maya peoples of
 The Spanish crown had legal protections for indigenous individuals as well as their communities, including establishing a separate General Indian Court. The mid-nineteenth-century liberal reform removed them as part of its establishment of
The Spanish crown had legal protections for indigenous individuals as well as their communities, including establishing a separate General Indian Court. The mid-nineteenth-century liberal reform removed them as part of its establishment of
 The history of
The history of
 Some indigenous groups, particularly the Yucatec Maya in the
Some indigenous groups, particularly the Yucatec Maya in the
 The Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Languages recognizes 62 indigenous languages as "national languages" which have the same validity as Spanish in all territories where they are spoken. According to the National Institute of Statistics, Geography and Data Processing (INEGI), approximately 6.7% of the population speaks an indigenous language. That is, less than half of those identified as indigenous. 6,695,228 people 5 years or older were tallied as indigenous-language speakers in the 2010 census, an increase of about 650,000 from the 2000 census. In 2000, 6,044,547 people 5 years or older spoke an indigenous language.
In previous censuses, information on the indigenous speaking population five years of age and older was obtained from the Mexican people. However, in the 2010 census, this approach was changed and the Government also began to collect data on people 3 years and older. With this new approach, it was determined that there were 6,913,362 people 3 years of age or more who spoke an indigenous language (218,000 children 3 and 4 four years of age fell into this category), accounting for 6.6% of the total population. The population of children aged 0 to 2 years in homes where the head of household or a spouse spoke an indigenous language was 678 954. The indigenous language speaking population has been increasing in absolute numbers for decades, but have nonetheless been falling in proportion to the national population.
The recognition of indigenous languages and the protection of indigenous cultures is granted not only to the ethnic groups indigenous to modern-day Mexican territory, but also to other North American indigenous groups that migrated to Mexico from the United States in the nineteenth century and those who immigrated from
The Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Languages recognizes 62 indigenous languages as "national languages" which have the same validity as Spanish in all territories where they are spoken. According to the National Institute of Statistics, Geography and Data Processing (INEGI), approximately 6.7% of the population speaks an indigenous language. That is, less than half of those identified as indigenous. 6,695,228 people 5 years or older were tallied as indigenous-language speakers in the 2010 census, an increase of about 650,000 from the 2000 census. In 2000, 6,044,547 people 5 years or older spoke an indigenous language.
In previous censuses, information on the indigenous speaking population five years of age and older was obtained from the Mexican people. However, in the 2010 census, this approach was changed and the Government also began to collect data on people 3 years and older. With this new approach, it was determined that there were 6,913,362 people 3 years of age or more who spoke an indigenous language (218,000 children 3 and 4 four years of age fell into this category), accounting for 6.6% of the total population. The population of children aged 0 to 2 years in homes where the head of household or a spouse spoke an indigenous language was 678 954. The indigenous language speaking population has been increasing in absolute numbers for decades, but have nonetheless been falling in proportion to the national population.
The recognition of indigenous languages and the protection of indigenous cultures is granted not only to the ethnic groups indigenous to modern-day Mexican territory, but also to other North American indigenous groups that migrated to Mexico from the United States in the nineteenth century and those who immigrated from
 According to the
According to the
 The majority of the indigenous population is concentrated in the central and southern states. According to the CDI, the states with the greatest percentage of indigenous population as of 2020 according to INEGI are:
The majority of the indigenous population is concentrated in the central and southern states. According to the CDI, the states with the greatest percentage of indigenous population as of 2020 according to INEGI are:
/ref> The indigenous groups within what is now Mexico are genetically distinct from each other. The genetic differences between geographically separated indigenous groups (e.g., between indigenous people living in the
 1Number of indigenous peoples that speak their Indigenous language
1Number of indigenous peoples that speak their Indigenous language

 Mexico is the nation of the Americas with the highest number of living languages in the early years of the 21st century, despite this cultural wealth, there is a technological disparity in education for indigenous peoples compared to other ethnic groups living in the country.
With the creation of the Secretaría de Educación Pública, SEP, the first indigenous education works for children and adults were carried out in order to eradicate illiteracy. However, the first educational policies for indigenous peoples did not work because they reduced the number of indigenous speakers with Spanish language literacy. In the year 2003 INALI was created, the first institution of the Mexican government that activated bilingualism by providing literacy in the mother language of indigenous speakers. But the poverty of the communities and the lack of teachers in indigenous languages limited progress in writing in the mother language.
Mexico is the nation of the Americas with the highest number of living languages in the early years of the 21st century, despite this cultural wealth, there is a technological disparity in education for indigenous peoples compared to other ethnic groups living in the country.
With the creation of the Secretaría de Educación Pública, SEP, the first indigenous education works for children and adults were carried out in order to eradicate illiteracy. However, the first educational policies for indigenous peoples did not work because they reduced the number of indigenous speakers with Spanish language literacy. In the year 2003 INALI was created, the first institution of the Mexican government that activated bilingualism by providing literacy in the mother language of indigenous speakers. But the poverty of the communities and the lack of teachers in indigenous languages limited progress in writing in the mother language.
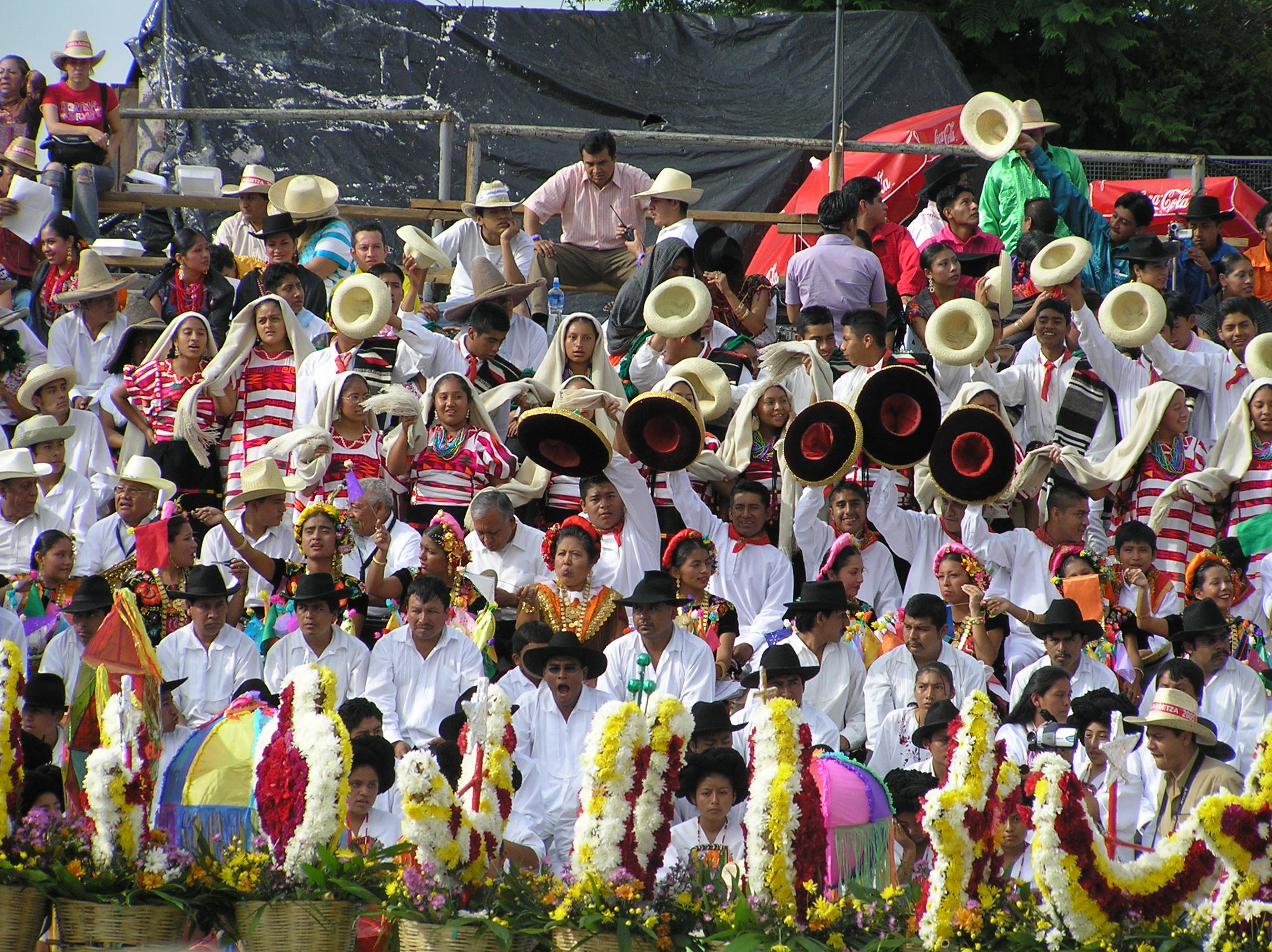 The Mexican Indigenous communities are enriched on celebrations, traditional costumes, oral heritage, medicine, literature, architecture and music by gender-separated groups. It includes parades of indigenous walking bands, native food, and statewide artisanal crafts, such as
The Mexican Indigenous communities are enriched on celebrations, traditional costumes, oral heritage, medicine, literature, architecture and music by gender-separated groups. It includes parades of indigenous walking bands, native food, and statewide artisanal crafts, such as
Experiencias de mujeres de la región cafetalera del Estado de Veracruz Radio Teocelo 2012
File:MOM D093 Donna Marina (La Malinche).jpg,
File:Tomas mejia c.1865.jpg,
Comisión Nacional para el Desarrollo de los Pueblos Indigenas
Consejo Nacional de Poblacion
Instituto Nacional de Estadistica y Geografia
Mexico and Southwest USA – Native Y-DNA Project
Archivo de Lenguas Indígenas de México
(El Colegio de México)
Information about the Native American tribes that historically lived on the US-Mexico Border
{{Authority control Demographics of Mexico Society of Mexico
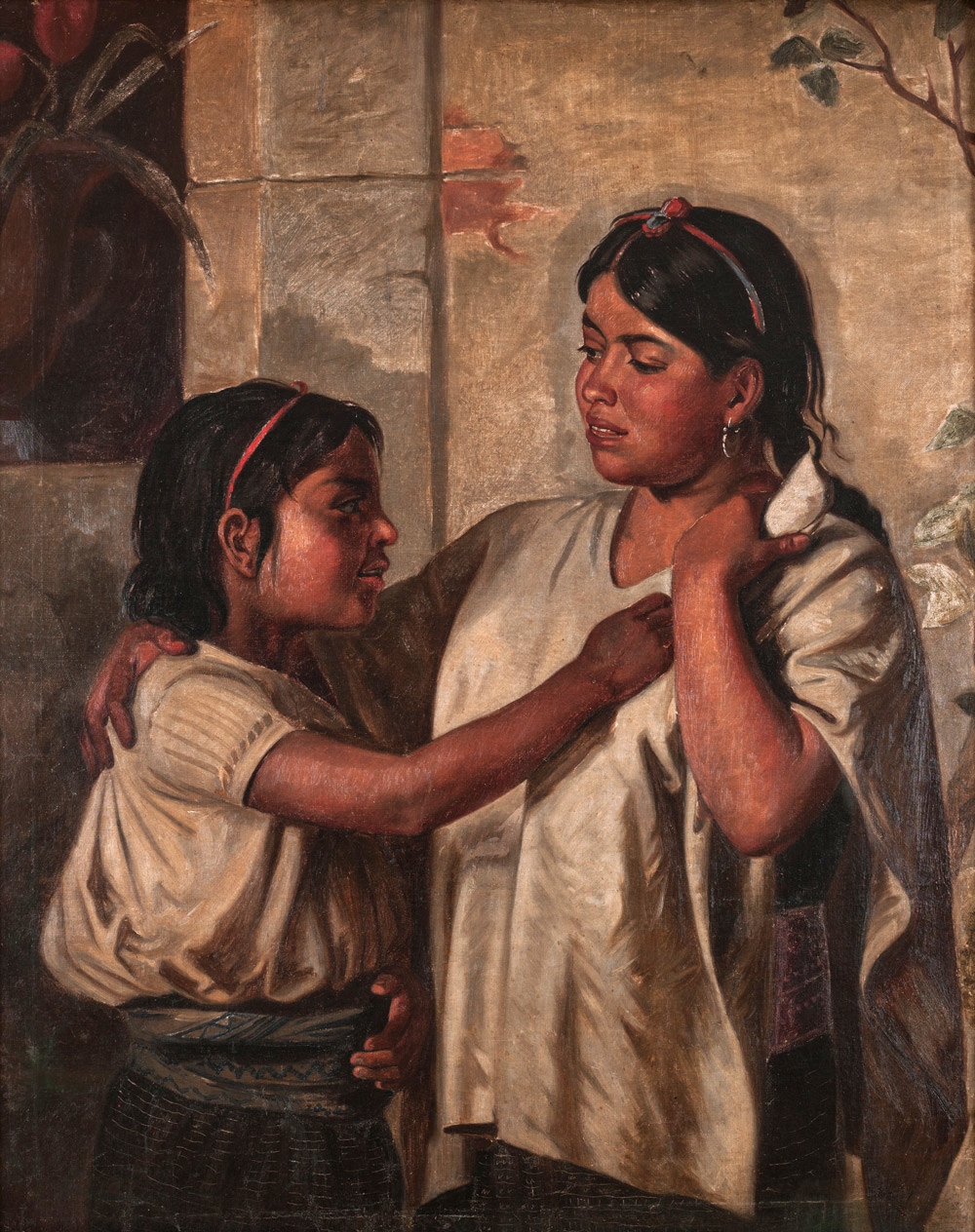 Indigenous peoples of Mexico ( es, gente indígena de México, pueblos indígenas de México), Native Mexicans ( es, nativos mexicanos) or Mexican Native Americans ( es, pueblos originarios de México, lit=Original peoples of Mexico), are those who are part of communities that trace their roots back to populations and communities that existed in what is now
Indigenous peoples of Mexico ( es, gente indígena de México, pueblos indígenas de México), Native Mexicans ( es, nativos mexicanos) or Mexican Native Americans ( es, pueblos originarios de México, lit=Original peoples of Mexico), are those who are part of communities that trace their roots back to populations and communities that existed in what is now Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
before the arrival of the Spanish.
The number of indigenous Mexicans is defined through the second article of the Mexican Constitution
The Constitution of Mexico, formally the Political Constitution of the United Mexican States ( es, Constitución Política de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos), is the current constitution of Mexico. It was drafted in Santiago de Querétaro, in ...
. The Mexican census does not classify individuals by race, using the cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.T ...
-ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
of indigenous communities that preserve their indigenous languages, traditions, beliefs, and cultures. According to the National Indigenous Institute (INI) and the National Institute of Indigenous Peoples
The National Institute of Indigenous Peoples ( es, Instituto Nacional de los Pueblos Indígenas, INPI) is a decentralized agency of the Mexican Federal Public Administration. It was established on December 4, 2018, though the earliest Mexican g ...
(CDI), in 2012 the indigenous population was approximately 15 million people, divided into 68 ethnic groups. The 2020 Censo General de Población y Vivienda The Censo de Población y Vivienda (''Population and Housing Census'') is the main national population census for Mexico. It is compiled by the National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI), a decentralized agency of the Mexican Federal go ...
reported 11.8 million people living in households where someone speaks an indigenous language, and 23,232,391 people who self-identify as indigenous.
The indigenous population is distributed throughout the territory of Mexico but is especially concentrated in the Sierra Madre del Sur
The Sierra Madre del Sur is a mountain range in southern Mexico, extending from southern Michoacán east through Guerrero, to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca.
Geography
The Sierra Madre del Sur joins with the Eje Volcánico Tran ...
, the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
, the Sierra Madre Oriental
The Sierra Madre Oriental () is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that f ...
, the Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American ...
, and neighboring areas. The states with the largest indigenous population are Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, Huāxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the Federative Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 570 municipaliti ...
and Yucatán
Yucatán (, also , , ; yua, Yúukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán,; yua, link=no, Xóot' Noj Lu'umil Yúukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate mun ...
, with the latter having the highest percentage of indigenous population in its own territory. Since the Spanish colonization, the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and Bajio regions of Mexico have had lower percentages of indigenous peoples, but some notable groups include the Rarámuri
The Rarámuri or Tarahumara is a group of indigenous people of the Americas living in the state of Chihuahua in Mexico. They are renowned for their long-distance running ability.
Originally, inhabitants of much of Chihuahua, the Rarámuri re ...
, the Tepehuán
The Tepehuán are an indigenous people of Mexico. They live in Northwestern, Western, and some parts of North-Central Mexico. The indigenous Tepehuán language has three branches: Northern Tepehuan, Southeastern Tepehuan, Southwestern Tepehu ...
, the Yaqui
The Yaqui, Hiaki, or Yoeme, are a Native American people of the southwest, who speak a Uto-Aztecan language. Their homelands include the Río Yaqui valley in Sonora, Mexico, and the area below the Gila River in Arizona, Southwestern United Sta ...
s, and the Yoreme.
Definition
 In the second article of the
In the second article of the Mexican Constitution
The Constitution of Mexico, formally the Political Constitution of the United Mexican States ( es, Constitución Política de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos), is the current constitution of Mexico. It was drafted in Santiago de Querétaro, in ...
, Mexico defines itself as a pluricultural nation in recognition of the diverse ethnic groups that constitute it and where the indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
are the original foundation.Constitución Política de los Estados Unidos MexicanosArt. 2 The number of indigenous Mexicans is measured using constitutional criteria. The Mexican census does not classify individuals by
race
Race, RACE or "The Race" may refer to:
* Race (biology), an informal taxonomic classification within a species, generally within a sub-species
* Race (human categorization), classification of humans into groups based on physical traits, and/or s ...
, only the cultural-ethnicity of indigenous communities that preserve their indigenous languages, traditions, beliefs and cultures.The category of ''indigena'' (indigenous) can be defined narrowly according to linguistic criteria including only persons that speak one of Languages of Mexico, Mexico's 89 indigenous languages, this is the categorization used by the National Mexican Institute of Statistics. It can also be defined broadly to include all persons who self-identify as having an indigenous cultural background, whether or not they speak the language of the indigenous group they identify with. This means that the percentage of the Mexican population defined as "indigenous" varies according to the definition applied; cultural activists have referred to the usage of the narrow definition of the term for census purposes as "statistical genocide". The indigenous peoples in Mexico have the right of free determination under the second article of the constitution. According to this article, indigenous peoples are granted: * the right to decide the internal forms of social, economic, political, and cultural organization; * the right to apply their own normative systems of regulation as long as human rights and gender equality are respected; * the right to preserve and enrich their languages and cultures; * the right to elect representatives before the municipal council where their territories are located; The Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Languages recognizes 89 indigenous languages as national languages, which have the same validity as Spanish in all territories where they are spoken. According to the National Institute of Statistics, Geography and Data Processing (INEGI), approximately 5.4% of the population speaks an indigenous language. The recognition of indigenous languages and the protection of indigenous cultures is granted not only to the ethnic groups indigenous to modern-day Mexican territory but also to other North American indigenous groups that migrated to Mexico from the United States in the nineteenth century and those who immigrated from
Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Hon ...
in the 1980s.
History
Pre-Columbian civilizations
The prehispanic civilizations of what now is known as Mexico are often divided into two regions:Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
, the cultural area where several complex civilizations developed before the arrival of the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
in the sixteenth century, and Aridoamerica
Aridoamerica denotes an ecological region spanning Northern Mexico and the Southwestern United States, defined by the presence of the culturally significant staple foodstuff ''Phaseolus acutifolius'', a drought-resistant bean.Pratt and Nabhan ...
(or simply "The North"),Hamnett, Brian (1999), ''A Concise History of Mexico'', Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK the arid region north of the Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, which is also referred to as the Northern Tropic, is the most northerly circle of latitude on Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towa ...
which was less densely populated. Despite the conditions, the Mogollon culture
Mogollon culture () is an archaeological culture of Native American peoples from Southern New Mexico and Arizona, Northern Sonora and Chihuahua, and Western Texas. The northern part of this region is Oasisamerica, while the southern span of the M ...
and Peoples established urban population centers at Casas Grandes
Casas Grandes (Spanish for ''Great Houses''; also known as Paquimé) is a prehistoric archaeological site in the northern Mexican state of Chihuahua. Construction of the site is attributed to the Mogollon culture. Casas Grandes has been design ...
and Cuarenta Casas
Cuarenta Casas ''(literally "40 houses")'' is an archaeological site in the northern Mexican state of Chihuahua. Construction of the site is attributed to the Mogollon culture.
Located in Vallecito in the municipality of Casas Grandes, Chihuahu ...
in a vast territory that encompassed northern Chihuahua Chihuahua may refer to:
Places
* Chihuahua (state), a Mexican state
**Chihuahua (dog), a breed of dog named after the state
**Chihuahua cheese, a type of cheese originating in the state
**Chihuahua City, the capital city of the state
**Chihuahua Mu ...
state and parts of Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
and New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
in the United States.
Mesoamerica was densely populated by diverse indigenous ethnic groupsManuel Aguilar-Moreno (2004) ''A Handbook to Life in the Aztec World'' Facts of Life, Inc., USA which, although sharing common cultural characteristics, spoke different languages and developed unique civilizations.
One of the most influential civilizations in Mesoamerica was the Olmec
The Olmecs () were the earliest known major Mesoamerican civilization. Following a progressive development in Soconusco, they occupied the tropical lowlands of the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated that ...
civilization, sometimes referred to as the "Mother Culture
A mother culture is a term for an earlier people's culture that has a great and widespread influence on some later cultures and people. Though the original culture may fade, the mother culture's influence grows for ages in the future. Later civiliz ...
of Mesoamerica". The later civilization in Teotihuacan
Teotihuacan ( Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'') (; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City. Teotihuacan is known today as ...
reached its peak around 600 AD when the city became the sixth largest city in the world, whose cultural and theological systems influenced the Toltec
The Toltec culture () was a pre-Columbian Mesoamerican culture that ruled a state centered in Tula, Hidalgo, Mexico, during the Epiclassic and the early Post-Classic period of Mesoamerican chronology, reaching prominence from 950 to 1150 CE. T ...
and Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
civilizations in later centuries. Evidence has been found on the existence of polyethnic
Polyethnicity, alternatively 'polyethnics'' and also pluriethnicity or multiethnicity, (from prefixes wikt:poly-, poly-, pluri-, wikt:multi-, multi- / all designating plurality), refers to specific cultural phenomena that are characterized by so ...
communities or neighborhoods in Teotihuacan (and other large urban areas like Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was ...
).
The Maya civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, ...
, influenced by other Mesoamerican civilizations, developed a vast cultural region in southeast Mexico and northern Central America, while the Zapotec and Mixtec
The Mixtecs (), or Mixtecos, are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as La Montaña Region and Costa Chica Regions of the state of Guerrero. The Mixtec Cult ...
cultures dominated the valley of Oaxaca
The Central Valleys ( es, Valles Centrales) of Oaxaca, also simply known as the Oaxaca Valley, is a geographic region located within the modern-day state of Oaxaca in southern Mexico. In an administrative context, it has been defined as comprising ...
and the Purépecha
The Purépecha (endonym pua, P'urhepecha ) are a group of indigenous people centered in the northwestern region of Michoacán, Mexico, mainly in the area of the cities of Cherán and Pátzcuaro.
They are also known by the pejorative " Tarascan ...
in western Mexico.
Trade
Scholars agree that significant systems of trading existed between the cultures ofMesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
, Aridoamerica
Aridoamerica denotes an ecological region spanning Northern Mexico and the Southwestern United States, defined by the presence of the culturally significant staple foodstuff ''Phaseolus acutifolius'', a drought-resistant bean.Pratt and Nabhan ...
and the American Southwest
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado ...
, and the architectural remains and artifacts share a commonality of knowledge attributed to this trade network. The routes stretched far into Mesoamerica and reached as far north as ancient communities that included such population centers in the United States such as Snaketown, Chaco Canyon
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in the American Southwest hosting a concentration of pueblos. The park is located in northwestern New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Farmington, in a remote c ...
, and Ridge Ruin near Flagstaff (considered some of the finest artifacts ever located).
Colonial era
By the time of the arrival of the Spanish in central Mexico, many peoples of Mesoamerica (with the notable exception of theTlaxcaltec
The Tlaxcalans, or Tlaxcaltecs, are a Nahua people who live in the Mexican state of Tlaxcala.
Pre-Columbian history
The Tlaxcaltecs were originally a conglomeration of three distinct ethnic groups who spoke Nahuatl, Otomi, and Pinome that compr ...
s and the Purépecha
The Purépecha (endonym pua, P'urhepecha ) are a group of indigenous people centered in the northwestern region of Michoacán, Mexico, mainly in the area of the cities of Cherán and Pátzcuaro.
They are also known by the pejorative " Tarascan ...
Kingdom of Michoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo (; Purépecha: ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Michoacán de Ocampo), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of ...
) were loosely joined under the Aztec Empire
The Aztec Empire or the Triple Alliance ( nci, Ēxcān Tlahtōlōyān, �jéːʃkaːn̥ t͡ɬaʔtoːˈlóːjaːn̥ was an alliance of three Nahua city-states: , , and . These three city-states ruled that area in and around the Valley of Mexi ...
, the last Nahua
The Nahuas () are a group of the indigenous people of Mexico, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua. They comprise the largest indigenous group in Mexico and second largest in El Salvador. The Mexica (Aztecs) were of Nahua ethnicity, a ...
civilization to flourish in Central Mexico. The capital of the empire, Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was ...
, became one of the largest urban centers in the world, with an estimated population of 350,000 inhabitants.
During the conquest of the Aztec Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, also known as the Conquest of Mexico or the Spanish-Aztec War (1519–21), was one of the primary events in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. There are multiple 16th-century narratives of the ev ...
, the Spanish conquistadors
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, ...
allied with other ethnic groups in the region, including the Tlaxcaltec
The Tlaxcalans, or Tlaxcaltecs, are a Nahua people who live in the Mexican state of Tlaxcala.
Pre-Columbian history
The Tlaxcaltecs were originally a conglomeration of three distinct ethnic groups who spoke Nahuatl, Otomi, and Pinome that compr ...
s. This strategy succeeded due to discontent with Aztec rule, which demanded tributes and used conquered peoples for ritual sacrifice. During the following decades, the Spanish consolidated their rule in what became the viceroyalty of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Amer ...
. Through the Valladolid Debate, the crown recognized the indigenous nobility in Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
as nobles, freed indigenous slaves, and kept the existing basic structure of indigenous city-states. Indigenous communities were incorporated as communities under Spanish rule.
As part of the Spanish incorporation of indigenous into the colonial system, the friars taught indigenous scribes to write their languages in Latin letters so that there is a large corpus of colonial-era documentation in the Nahuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have small ...
language, Mixtec
The Mixtecs (), or Mixtecos, are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as La Montaña Region and Costa Chica Regions of the state of Guerrero. The Mixtec Cult ...
, Zapotec, Yucatec Maya
Yucatec Maya (; referred to by its speakers simply as Maya or as , is one of the 32 Mayan languages of the Mayan language family. Yucatec Maya is spoken in the Yucatán Peninsula and northern Belize. There is also a significant diasporic commu ...
, and others. Such a written tradition likely took hold through existing practices of pictorial writing found in many indigenous codices
The codex (plural codices ) was the historical ancestor of the modern book. Instead of being composed of sheets of paper, it used sheets of vellum, papyrus, or other materials. The term ''codex'' is often used for ancient manuscript books, with ...
. New Philology New Philology generally refers to a branch of Mexican ethnohistory and philology that uses colonial-era native language texts written by Indians to construct history from the indigenous point of view. The name New Philology was coined by James Loc ...
scholars have utilized the colonial-era alphabetic documentation to illuminate the colonial experience of Mesoamerican peoples from their own viewpoints.
Conquerors awarded labor and tribute under the ''encomienda'' system benefitted financially. Since Mesoamerican peoples had existing requirements of labor duty and tribute in the pre-conquest era, indigenous officials were involved in maintaining this system in their communities. There was a precipitous decline in indigenous populations, mainly due to the spread of European diseases previously unknown in the America but also through war and forced labor. Pandemics wrought havoc, but indigenous communities recovered with fewer members.Gibson, ibid.Lockhart, ibid.
With contact between indigenous populations, Spaniards, African slaves
Slavery has historically been widespread in Africa. Systems of servitude and slavery were common in parts of Africa in ancient times, as they were in much of the rest of the ancient world. When the trans-Saharan slave trade, Indian Ocean ...
, and starting in the late sixteenth century, Asian slaves (''chinos'') brought as goods the trade via the Manila Galleon
fil, Galyon ng Maynila
, english_name = Manila Galleon
, duration = From 1565 to 1815 (250 years)
, venue = Between Manila and Acapulco
, location = New Spain ( Spanish Empir ...
there was an intermingling of groups, with mixed-race castas
() is a term which means "lineage" in Spanish and Portuguese and has historically been used as a racial and social identifier. In the context of the Spanish Empire in the Americas it also refers to a now-discredited 20th-century theoretical f ...
, particularly mestizos
(; ; fem. ) is a term used for racial classification to refer to a person of mixed European and Indigenous American ancestry. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturally European even though thei ...
, becoming a component of Spanish cities and to a lesser extent indigenous communities. The Spanish legal structure formally separated what they called the ''República de indios'' (the republic of Indians) from the ''República de españoles'' (republic of Spaniards), with the latter encompassing all those in the Hispanic sphere: Spaniards, Africans, and mixed-race castas. Although Indigenous peoples were marginalized in the colonial system, and often rebelled, the paternalistic structure of colonial rule supported the continued existence and structure of indigenous communities. The Spanish crown recognized the existing ruling group, gave protection to the land holdings of indigenous communities, and communities and individuals had access to the Spanish legal system. However, these codes were often ignored in practice, and racial discrimination was prevalent in New Spain.
In the religious sphere, indigenous men were banned from Christian priesthood, following an early Franciscan attempt that included fray Bernardino de Sahagún
Bernardino de Sahagún, OFM (; – 5 February 1590) was a Franciscan friar, missionary priest and pioneering ethnographer who participated in the Catholic evangelization of colonial New Spain (now Mexico). Born in Sahagún, Spain, in 1499, ...
to train an indigenous group. Mendicants of the Franciscan
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
, Dominican, and Augustinian orders initially evangelized indigenous in their own communities in what is often called the "spiritual conquest". On the northern frontiers, the Spanish created missions and settled indigenous populations in these complexes. The Jesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
were prominent in this enterprise until their expulsion from Spanish America in 1767. Catholicism, often with local characteristics, was the only permissible religion in the colonial era.
Indigenous land

 During the early colonial era in central Mexico, Spaniards were more interested in access to indigenous labor than land ownership. The institution of the ''encomienda'', a crown grant of the labor of indigenous communities to conquerors was a key element of the imposition of Spanish rule. The Spanish crown initially maintained the indigenous sociopolitical system of local rulers and land tenure, with the
During the early colonial era in central Mexico, Spaniards were more interested in access to indigenous labor than land ownership. The institution of the ''encomienda'', a crown grant of the labor of indigenous communities to conquerors was a key element of the imposition of Spanish rule. The Spanish crown initially maintained the indigenous sociopolitical system of local rulers and land tenure, with the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, also known as the Conquest of Mexico or the Spanish-Aztec War (1519–21), was one of the primary events in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. There are multiple 16th-century narratives of the eve ...
eliminating the superstructure of rule, and replacing it with Spanish.
The crown had several concerns about the encomienda. First was that the holders of encomiendas, called ''encomenderos,'' were becoming too powerful, essentially a seigneurial group that might challenge crown power (as shown in the conspiracy by conqueror Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca (; ; 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of w ...
's legitimate son and heir). The second was that the encomenderos were monopolizing indigenous labor, excluding newly arriving Spaniards. And third, the crown was concerned about the damage to the indigenous vassals and their communities by the institution. Through the New Laws of 1542
The New Laws (Spanish: ''Leyes Nuevas''), also known as the New Laws of the Indies for the Good Treatment and Preservation of the Indians (Spanish: ''Leyes y ordenanzas nuevamente hechas por su Majestad para la gobernación de las Indias y buen t ...
, the crown sought to phase out the ''encomienda'' and replace it with another crown mechanism of forced indigenous labor, the ''repartimiento
The ''Repartimiento'' () (Spanish, "distribution, partition, or division") was a colonial labor system imposed upon the indigenous population of Spanish America. In concept, it was similar to other tribute-labor systems, such as the ''mit'a'' of t ...
''. Indigenous labor was no longer monopolized by a small group of conquerors and their descendants but apportioned to a larger group of Spaniards. Through the ''repartimiento,'' indigenous peoples were obligated to perform low-paid labor for a certain number of weeks or months on Spanish enterprises, notably silver mining.
The land of indigenous peoples is used for material reasons as well as spiritual reasons. Religious, cultural, social, spiritual, and other events relating to their identity are also tied to the land. Indigenous people use collective property so that the aforementioned services that the land provides are available to the entire community and future generations. This was a stark contrast to the viewpoints of colonists that saw the land purely in an economic way where land could be transferred between individuals. Once the land of the indigenous people and therefore their livelihood was taken from them, they became dependent on those that had land and power. Additionally, the spiritual services that the land provided were no longer available and caused a deterioration of indigenous groups and cultures.

Colonial-era racial categories
The Spanish legal system divided racial groups into two basic categories, the ''República de Españoles'', consisting of all non-indigenous, but initially Spaniards and black Africans, and the ''República de Indios''. The degree to which racial category labels had legal and social consequences has been subject to academic debate since the idea of a "caste system" was developed byÁngel Rosenblat
Ángel Rosenblat (9 December 1902, Węgrów, Poland - 11 September 1984, Caracas) was a Poland-born Venezuelan philologist, essayist and hispanism, hispanist of Jewish descent.
Life
He and his family moved to Argentina when he was six and he sp ...
and Gonzalo Aguirre Beltrán
Gonzalo Aguirre Beltrán (January 20, 1908 in Tlacotalpan, Veracruz –1996 in Xalapa, Veracruz) was a Mexican anthropologist known for his studies of marginal populations. His work has focused on Afro-Mexican and indigenous populations. He was ...
in the 1940s. Both historians popularized the notion that racial status was a key organizing principle of Spanish colonial rule. However, recent academic studies have challenged this notion, considering it a flawed and ideologically-based reinterpretation of the colonial period.
When Mexico gained independence in 1821, the casta designations were eliminated as a legal structure, but racial divides remained. White Mexicans argued about what the solution was to the "Indian Problem", that is indigenous who continued to live in communities and were not integrated politically or socially as citizens of the new republic. The Mexican Constitution of 1824
The Federal Constitution of the United Mexican States of 1824 ( es, Constitución Federal de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos de 1824) was enacted on October 4 of 1824, after the overthrow of the Mexican Empire of Agustin de Iturbide. In the new Fr ...
has several articles pertaining to indigenous peoples.
Independence to the Mexican Revolution

Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence ( es, Guerra de Independencia de México, links=no, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from Spain. It was not a single, co ...
was a decade-long struggle ending in 1821, in which indigenous peoples participated for their own motivations. The new country was named after its capital city, Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley o ...
. The new flag had at its center a symbol of the Aztecs, an eagle perched on a nopal cactus. Mexico declared the abolition of slavery
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
in 1829 and the equality of all citizens before the law
Equality before the law, also known as equality under the law, equality in the eyes of the law, legal equality, or legal egalitarianism, is the principle that all people must be equally protected by the law. The principle requires a systematic r ...
in 1857. Indigenous communities continued to have rights as corporations to maintain land holdings until the liberal Reforma
REFORMA: The National Association to Promote Library & Information Services to Latinos and the Spanish Speaking, more commonly known as REFORMA, is an affiliate of the American Library Association formed in 1971 to promote library services to Lat ...
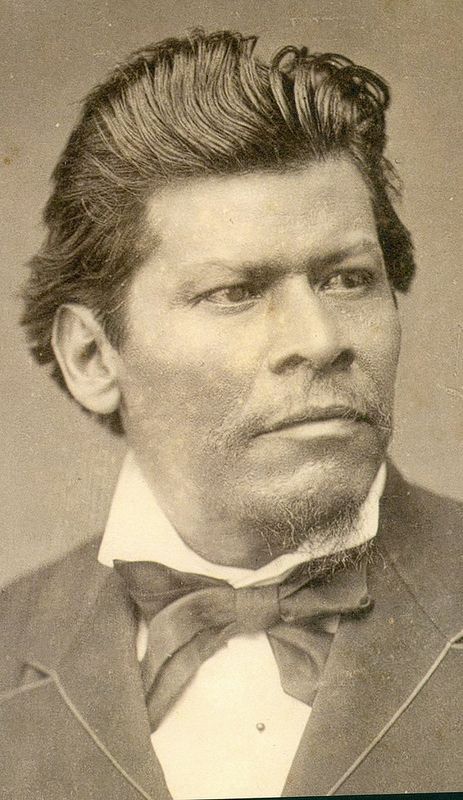
. Some indigenous individuals integrated into Mexican society, like Benito Juárez
Benito Pablo Juárez García (; 21 March 1806 – 18 July 1872) was a Mexican liberal politician and lawyer who served as the 26th president of Mexico from 1858 until his death in office in 1872. As a Zapotec, he was the first indigenous pre ...
of Zapotec ethnicity, the first indigenous president in the Americas. Juárez supported the removal of provisions protecting indigenous communal land holdings through the Lerdo law
The Lerdo Law ( Spanish: ''Ley Lerdo'') was the common name for the Reform law that was formally known as the Confiscation of Law and Urban Ruins of the Civil and Religious Corporations of Mexico. It targeted not only property owned by the Catho ...
.
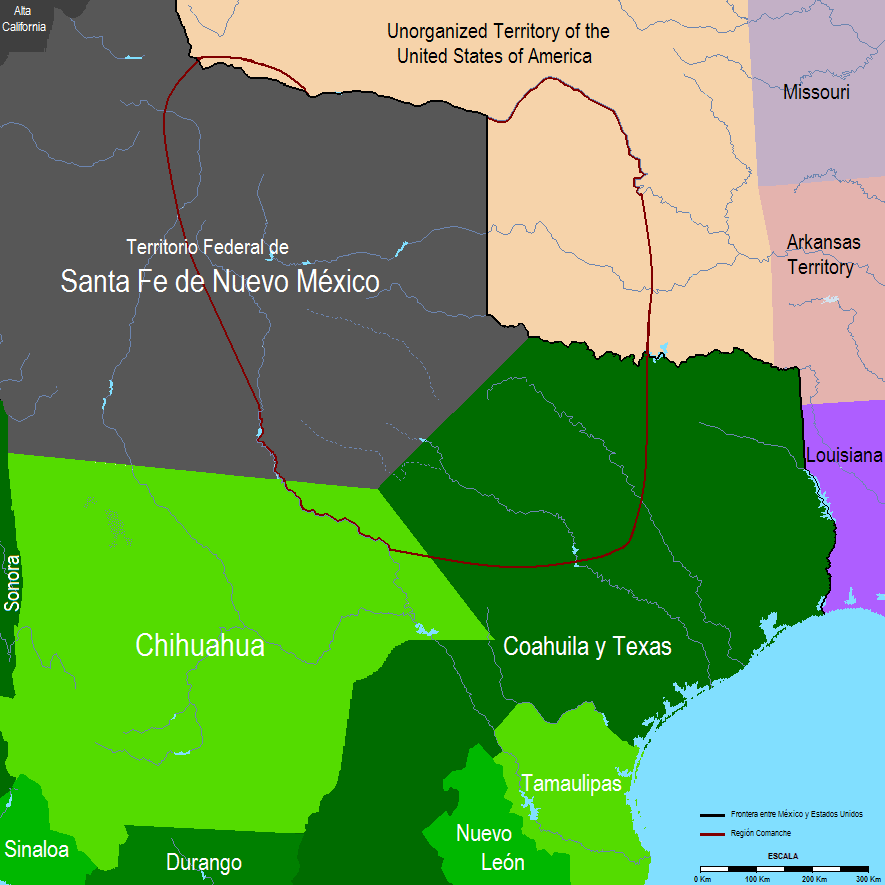
In the North of Mexico, indigenous peoples, such as the Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in ...
and Apache
The Apache () are a group of culturally related Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, which include the Chiricahua, Jicarilla, Lipan, Mescalero, Mimbreño, Ndendahe (Bedonkohe or Mogollon and Nednhi or Carrizaleño a ...
, who had acquired the horse, waged a successful warfare against the Mexican state. The Comanche controlled considerable territory, called the Comancheria
The Comancheria or Comanchería (Comanche: Nʉmʉnʉʉ Sookobitʉ, 'Comanche land') was a region of New Mexico, west Texas and nearby areas occupied by the Comanche before the 1860s. Historian Pekka Hämäläinen has argued that the Comancheria ...
. The Yaqui
The Yaqui, Hiaki, or Yoeme, are a Native American people of the southwest, who speak a Uto-Aztecan language. Their homelands include the Río Yaqui valley in Sonora, Mexico, and the area below the Gila River in Arizona, Southwestern United Sta ...
also had a long tradition of resistance, with the late nineteenth-century leader Cajemé
Cajemé / Kahe'eme ( Yoeme or Yaqui Language for "one who does not stop to drink ater'), born and baptized José María Bonifacio Leyba Pérez (also spelled Leyva and Leiva), was a prominent Yaqui military leader who lived in the Mexican state ...
being prominent during the Yaqui Wars
The Yaqui Wars, were a series of armed conflicts between New Spain, and its successor state, the Mexican Republic, against the Yaqui Natives. The period began in 1533 and lasted until 1929. The Yaqui Wars, along with the Caste War against the M ...
. The Mayo joined their Yaqui neighbors in rebellion after 1867. In Yucatán, Mayas
The Maya peoples () are an ethnolinguistic group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. The ancient Maya civilization was formed by members of this group, and today's Maya are generally descended from people ...
waged a protracted war against local Mexican control in the Caste War of Yucatán
The Caste War of Yucatán (1847–1915) began with the revolt of Native Maya people of the Yucatán Peninsula against Hispanic populations, called ''Yucatecos''. The latter had long held political and economic control of the region. A lengthy w ...
, which was most intensely fought in 1847 and lasted until 1915.
20th century
 The
The Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution ( es, Revolución Mexicana) was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from approximately 1910 to 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It resulted in the destruction ...
, a violent social and cultural movement that defined 20th-century Mexico, produced a nationalist sentiment that the indigenous peoples were the foundation of Mexican society in a movement known as ''indigenismo
''Indigenismo'' () is a political ideology in several Latin American countries which emphasizes the relationship between the nation state and indigenous nations and indigenous peoples. In some contemporary uses, it refers to the pursuit of great ...
''. Several prominent artists promoted the "Indigenous Sentiment" (''sentimiento indigenista'') of the country, including Frida Kahlo
Magdalena Carmen Frida Kahlo y Calderón (; 6 July 1907 – 13 July 1954) was a Mexican painter known for her many portraits, self-portraits, and works inspired by the nature and artifacts of Mexico. Inspired by the country's popular culture, ...
and Diego Rivera
Diego María de la Concepción Juan Nepomuceno Estanislao de la Rivera y Barrientos Acosta y Rodríguez, known as Diego Rivera (; December 8, 1886 – November 24, 1957), was a prominent Mexican painter. His large frescoes helped establish the ...
. Throughout the twentieth century, the government established bilingual education in some indigenous communities and published free bilingual textbooks. Some states of the federation appropriated an indigenous inheritance in order to reinforce their identity.
 In spite of the official recognition of indigenous peoples, the economic underdevelopment of their communities, accentuated by the crises of the 1980s and 1990s, has not allowed for the development of most indigenous communities. Thousands of indigenous Mexicans have emigrated to urban centers in Mexico and the United States. In Los Angeles, for example, the Mexican government has established electronic access to some of the consular services provided in Spanish as well as Zapotec and Mixe. Some of the Maya peoples of
In spite of the official recognition of indigenous peoples, the economic underdevelopment of their communities, accentuated by the crises of the 1980s and 1990s, has not allowed for the development of most indigenous communities. Thousands of indigenous Mexicans have emigrated to urban centers in Mexico and the United States. In Los Angeles, for example, the Mexican government has established electronic access to some of the consular services provided in Spanish as well as Zapotec and Mixe. Some of the Maya peoples of Chiapas
Chiapas (; Tzotzil and Tzeltal: ''Chyapas'' ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas), is one of the states that make up the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 124 municipalities ...
have revolted, demanding better social and economic opportunities, requests voiced by the EZLN
The Zapatista Army of National Liberation (, EZLN), often referred to as the Zapatistas (Mexican ), is a far-left political and militant group that controls a substantial amount of territory in Chiapas, the southernmost state of Mexico.
Sinc ...
.
The Chiapas conflict
The Chiapas conflict ( Spanish: ''Conflicto de Chiapas'') comprises the 1994 Zapatista uprising, the 1995 Zapatista crisis and ensuing tension between the Mexican state and the indigenous peoples and subsistence farmers of Chiapas from the 1990 ...
of 1994 led to collaboration between the Mexican government and the Zapatista Army of National Liberation
The Zapatista Army of National Liberation (, EZLN), often referred to as the Zapatistas (Mexican ), is a far-left political and militant group that controls a substantial amount of territory in Chiapas, the southernmost state of Mexico.
Since ...
, a libertarian socialist
Libertarian socialism, also known by various other names, is a left-wing,Diemer, Ulli (1997)"What Is Libertarian Socialism?" The Anarchist Library. Retrieved 4 August 2019. anti-authoritarian, anti-statist and libertarianLong, Roderick T. (20 ...
indigenous political group. This movement generated international media attention and united many indigenous groups. In 1996 the San Andrés Larráinzar Accords were negotiated between the Zapatista Army of National Liberation and the Mexican government. The San Andrés accords were the first time that indigenous rights were acknowledged by the Mexican government.
The government has made certain legislative changes to promote the development of rural and indigenous communities and the promotion of indigenous languages. The second article of the Constitution was modified to include the right of self-determination and requires state governments to promote and ensure the economic development of indigenous communities as well as the preservation of their languages and traditions.
Rights
Constitutional
 The Spanish crown had legal protections for indigenous individuals as well as their communities, including establishing a separate General Indian Court. The mid-nineteenth-century liberal reform removed them as part of its establishment of
The Spanish crown had legal protections for indigenous individuals as well as their communities, including establishing a separate General Indian Court. The mid-nineteenth-century liberal reform removed them as part of its establishment of equality before the law
Equality before the law, also known as equality under the law, equality in the eyes of the law, legal equality, or legal egalitarianism, is the principle that all people must be equally protected by the law. The principle requires a systematic r ...
. The creation of a national identity not linked to racial or ethnic identity was an aim of Mexican liberalism.
In the late twentieth century, there has been a push for indigenous rights and a recognition of indigenous cultural identity. According to the constitutional reform of 2001, the following rights of indigenous peoples are recognized:
* acknowledgment as indigenous communities, right to self-ascription, and the application of their own regulatory systems
* preservation of their cultural identity, land, consultation, and participation
* access to the jurisdiction to the state and to development
* recognition of indigenous peoples and communities as a subject of public law
* self-determination and self-autonomy
* remunicipalization Remunicipalisation commonly refers to the return of previously privatised water supply and sanitation services to municipal authorities. It also encompasses regional or national initiatives.
Overview
The concept is broadly used to cover:
* Chang ...
for the advancement of indigenous communities
* administer own forms of communication and media
The second article of the Constitution of Mexico
The Constitution of Mexico, formally the Political Constitution of the United Mexican States ( es, Constitución Política de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos), is the current constitution of Mexico. It was drafted in Santiago de Querétaro, in th ...
recognizes and enforces the right of indigenous peoples and communities to self-determination and autonomy to:
V. Preserve and improve their habitat as well as preserve the integrity of their lands in accordance with this constitution. VI. Be entitled to the estate and land property modalities established by this constitution and its derived legislation, to all private property rights and communal property rights as well as to use and enjoy in a preferential way all the natural resources located at the places which the communities live in, except those defined as strategic areas according to the constitution. The communities shall be authorized to associate with each other in order to achieve such goals.
Through the land reforms
Land reform is a form of agrarian reform involving the changing of laws, regulations, or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform may consist of a government-initiated or government-backed property redistribution, generally of agricultural ...
of the early 20th century, some indigenous people had land rights under the ''ejido
An ''ejido'' (, from Latin ''exitum'') is an area of communal land used for agriculture in which community members have usufruct rights rather than ownership rights to land, which in Mexico is held by the Mexican state. People awarded ejidos in ...
'' system. Under ejidos, indigenous communities have usufruct rights of the land. Indigenous communities do this when they do not have the legal evidence to claim the land. In 1992, free market reforms allowed ejidos to be partitioned and sold. For this to happen, the PROCEDE program was established. The PROCEDE program surveyed, mapped, and verified the ejido lands. According to several analysts, the privatization of ejidos has undermined the economic base of indigenous communities.
Linguistic
 The history of
The history of linguistic rights
Linguistic rights are the human and civil rights concerning the individual and collective right to choose the language or languages for communication in a private or public atmosphere. Other parameters for analyzing linguistic rights include the ...
in Mexico began when the Spanish first made contact with Indigenous Languages during the colonial period. Beginning in the early sixteenth century, ''mestizaje'', the mixing of races and cultures, led to the mixing of languages as well. The Spanish Crown
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg
, coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain
, image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg
, incumbent = Felipe VI
, incumbentsince = 19 Ju ...
proclaimed Spanish to be the language of the empire; indigenous languages were used during the conversion of individuals to Catholicism. Because of this, indigenous languages were more widespread than Spanish from 1523 to 1581. During the late sixteenth century, the prevalence of the Spanish language increased.
Indigenous tongues are discriminated against and seen as not modern. By the seventeenth century, the elite minority were Spanish speakers. After independence in 1821, there was a shift to Spanish to legitimize the Mexican Spanish
Mexican Spanish ( es, español mexicano) is the variety of dialects and sociolects of the Spanish language spoken in Mexican territory. Mexico has the largest number of Spanish speakers, with more than twice as many as in any other country in ...
created by Mexican ''criollos
In Hispanic America, criollo () is a term used originally to describe people of Spanish descent born in the colonies. In different Latin American countries the word has come to have different meanings, sometimes referring to the local-born majo ...
''. The nineteenth century brought with it programs to provide bilingual education
In bilingual education, students are taught in two (or more) languages. It is distinct from learning a second language as a subject because both languages are used for instruction in different content areas like math, science, and history. The ...
at primary levels where they would eventually transition to Spanish-only education. Linguistic uniformity was sought out to strengthen national identity. This further excluded indigenous languages from power structures.
The Chiapas conflict
The Chiapas conflict ( Spanish: ''Conflicto de Chiapas'') comprises the 1994 Zapatista uprising, the 1995 Zapatista crisis and ensuing tension between the Mexican state and the indigenous peoples and subsistence farmers of Chiapas from the 1990 ...
of 1994 led to collaboration between the Mexican government and the Zapatista Army of National Liberation
The Zapatista Army of National Liberation (, EZLN), often referred to as the Zapatistas (Mexican ), is a far-left political and militant group that controls a substantial amount of territory in Chiapas, the southernmost state of Mexico.
Since ...
, an indigenous political group. In 1996 the San Andrés Larráinzar Accords were negotiated between the Zapatista Army of National Liberation and the Mexican government. The San Andrés accords were the first time that indigenous rights were acknowledged by the Mexican government. The San Andrés Accords did not explicitly state language but language was involved in matters involving culture and education.
In 2001, the second article of the constitution of Mexico was changed to recognize and enforce the right of indigenous peoples and communities to self-determination and therefore their autonomy to preserve and enrich their language, knowledge, and every part of their culture and identity.
In 2003, the General Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Peoples explicitly stated the protection of individual and collective linguistic rights of indigenous peoples. The final section also sanctioned the creation of a National Institute for Indigenous Languages (INALI) whose purpose is to promote the growth of indigenous languages in Mexico.
There has been a lack of enforcement of the law. For example, the General Law on Linguistic Rights of Indigenous People guarantees the right to a trial in the language of indigenous peoples with someone who understands their culture. According to the Mexican National Human Rights Commission
A human rights commission, also known as a human relations commission, is a body set up to investigate, promote or protect human rights.
The term may refer to international, national or subnational bodies set up for this purpose, such as nation ...
, Mexico has not abided by this law. Examples include Jacinta Francisca Marcial, an indigenous woman imprisoned for her alleged involvement in a 2006 kidnapping. After three years and the assistance of Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says it has more than ten million members and s ...
, she was released for lack of evidence.
Additionally, the General Law on Linguistics also guarantees bilingual and intercultural education. These efforts have been criticized on grounds that teachers do not know the indigenous language or do not prioritize its teaching. In fact, some studies argue that formal education has decreased the prevalence of indigenous languages. Some parents do not teach their children their indigenous language, and some children refuse to learn their indigenous language for fear of discrimination. Scholars argue that there needs to be a social change to elevate the status of indigenous languages in order for the law to be withheld so that indigenous languages are protected.
Women's
Indigenous women are often taken advantage of because they are women, indigenous, and often poor. Indigenous traditions have been used as a pretext by the Mexican government to deny rights to indigenous women, such as the right to own land. Additionally,violence against women
Violence against women (VAW), also known as gender-based violence and sexual and gender-based violence (SGBV), are violent acts primarily or exclusively committed against women or girls, usually by men or boys. Such violence is often c ...
has been regarded by the Mexican government as a cultural practice.
The EZLN
The Zapatista Army of National Liberation (, EZLN), often referred to as the Zapatistas (Mexican ), is a far-left political and militant group that controls a substantial amount of territory in Chiapas, the southernmost state of Mexico.
Sinc ...
accepted a Revolutionary Law for Women on March 8, 1993. The law is not fully enforced but shows solidarity between the indigenous movement and women. The Mexican government increased militarization of indigenous areas has made women more susceptible to harassment through military abuses. The government has remained largely inactive against denunciations of abuse of indigenous women by elements of the armed forces.
Indigenous women have formed many support organizations to improve their social position and gain financial independence. Indigenous women use national and international legislation to support their claims that go against cultural norms such as domestic violence. Reproductive justice
Reproductive justice is a critical feminist framework that was invented as a response to United States reproductive politics. The three core values of reproductive justice are the right to have a child, the right to not have a child, and the righ ...
is an important issue to indigenous communities because there is a lack of development in these areas and is less access to maternal care. Conditional cash transfer programs such as Oportunidades have been used to encourage indigenous women to seek formal health care.
Development and socio-economy
Generally, indigenous Mexicans are poorer than non-indigenous Mexicans, though social development varies between states, different indigenous ethnicities, and between rural and urban areas. In all states, indigenous people have higherinfant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
, and in some states, almost double that of the non-indigenous populations.
 Some indigenous groups, particularly the Yucatec Maya in the
Some indigenous groups, particularly the Yucatec Maya in the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
and some of the Nahua and Otomi peoples in central states have maintained higher levels of development while indigenous peoples in states such as the Guerrero
Guerrero is one of the 32 states that comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo and its largest city is Acapulcocopied from article, GuerreroAs of 2020, Guerrero the pop ...
or Michoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo (; Purépecha: ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Michoacán de Ocampo), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of ...
are ranked drastically lower than the average Mexican citizen in these fields. Despite certain indigenous groups such as the Maya or Nahua retaining high levels of development, the general indigenous population lives at a lower level of development than the general population.
Literacy rates are much lower for the indigenous, particularly in the southwestern states of Guerrero and Oaxaca due lack of access to education and a lack of educational literature available in indigenous languages. Literacy rates are also much lower, with 27% of indigenous children between 6 and 14 being illiterate compared to a national average of 12% in 2000. The Mexican government is required to provide education in indigenous languages but often fails to provide schooling in languages other than Spanish. As a result, many indigenous groups have resorted to creating their own small community educational institutions.
The indigenous population participates in the workforce longer than the national average, starting earlier and continuing longer. A major reason for this is that a significant number of the indigenous practice subsistence agriculture
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no ...
and receive no regular salaries. Indigenous people also have lower access to health care.
Demographics
Languages
 The Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Languages recognizes 62 indigenous languages as "national languages" which have the same validity as Spanish in all territories where they are spoken. According to the National Institute of Statistics, Geography and Data Processing (INEGI), approximately 6.7% of the population speaks an indigenous language. That is, less than half of those identified as indigenous. 6,695,228 people 5 years or older were tallied as indigenous-language speakers in the 2010 census, an increase of about 650,000 from the 2000 census. In 2000, 6,044,547 people 5 years or older spoke an indigenous language.
In previous censuses, information on the indigenous speaking population five years of age and older was obtained from the Mexican people. However, in the 2010 census, this approach was changed and the Government also began to collect data on people 3 years and older. With this new approach, it was determined that there were 6,913,362 people 3 years of age or more who spoke an indigenous language (218,000 children 3 and 4 four years of age fell into this category), accounting for 6.6% of the total population. The population of children aged 0 to 2 years in homes where the head of household or a spouse spoke an indigenous language was 678 954. The indigenous language speaking population has been increasing in absolute numbers for decades, but have nonetheless been falling in proportion to the national population.
The recognition of indigenous languages and the protection of indigenous cultures is granted not only to the ethnic groups indigenous to modern-day Mexican territory, but also to other North American indigenous groups that migrated to Mexico from the United States in the nineteenth century and those who immigrated from
The Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Languages recognizes 62 indigenous languages as "national languages" which have the same validity as Spanish in all territories where they are spoken. According to the National Institute of Statistics, Geography and Data Processing (INEGI), approximately 6.7% of the population speaks an indigenous language. That is, less than half of those identified as indigenous. 6,695,228 people 5 years or older were tallied as indigenous-language speakers in the 2010 census, an increase of about 650,000 from the 2000 census. In 2000, 6,044,547 people 5 years or older spoke an indigenous language.
In previous censuses, information on the indigenous speaking population five years of age and older was obtained from the Mexican people. However, in the 2010 census, this approach was changed and the Government also began to collect data on people 3 years and older. With this new approach, it was determined that there were 6,913,362 people 3 years of age or more who spoke an indigenous language (218,000 children 3 and 4 four years of age fell into this category), accounting for 6.6% of the total population. The population of children aged 0 to 2 years in homes where the head of household or a spouse spoke an indigenous language was 678 954. The indigenous language speaking population has been increasing in absolute numbers for decades, but have nonetheless been falling in proportion to the national population.
The recognition of indigenous languages and the protection of indigenous cultures is granted not only to the ethnic groups indigenous to modern-day Mexican territory, but also to other North American indigenous groups that migrated to Mexico from the United States in the nineteenth century and those who immigrated from Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Hon ...
in the 1980s.States
The five states with the largest indigenous-language-speaking populations are: *Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, Huāxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the Federative Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 570 municipaliti ...
, with 1,165,186 indigenous language speakers, accounting for 34.2% of the state's population.
* Chiapas
Chiapas (; Tzotzil and Tzeltal: ''Chyapas'' ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas), is one of the states that make up the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 124 municipalities ...
, with 1,141,499 indigenous language speakers, accounting for 27.2% of the state's population.
* Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
, with 644,559 indigenous language speakers, accounting for 9.4% the state's population.
* Puebla
Puebla ( en, colony, settlement), officially Free and Sovereign State of Puebla ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its cap ...
, with 601,680 indigenous language speakers, accounting for 11.7% of the state's population.
* Yucatán
Yucatán (, also , , ; yua, Yúukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán,; yua, link=no, Xóot' Noj Lu'umil Yúukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate mun ...
, with 537,516 indigenous language speakers, accounting for 30.3% of the state's population.
These five states accounted for 61.1% of all indigenous language speakers in Mexico. Most indigenous Mexicans do not speak their own languages and speak only Spanish. This is reflected in these five states' populations. Although Oaxaca, Chiapas, Veracruz, Puebla, and Yucatán have 34.2%, 27.2%, 9.4%, 11.7%, and 30.3% of their populations speaking an indigenous language, these states' indigenous populations are 65.73%, 36.15%, 29.25%, 35.28%, 65.4% respectively.
Population statistics
National Commission for the Development of the Indigenous Peoples
The National Institute of Indigenous Peoples ( es, Instituto Nacional de los Pueblos Indígenas, INPI) is a decentralized agency of the Mexican Federal Public Administration. It was established on December 4, 2018, though the earliest Mexican g ...
(CDI), there were 25,694,928 indigenous people reported in Mexico in 2015, which constitutes 21.5% of the population of Mexico. This is a significant increase from the 2010 census, in which indigenous Mexicans accounted for 14.9% of the population, and numbered 15,700,000 Most indigenous communities have a degree of financial, political autonomy under the legislation of "usos y costumbres ("customs and traditions"; literally, "uses and customs") is indigenous customary law in Latin America. Since the era of Spanish colonialism, authorities have recognized local forms of rulership, self governance, and juridical practice, with varyin ...
", which allows them to regulate internal issues under customary law
A legal custom is the established pattern of behavior that can be objectively verified within a particular social setting. A claim can be carried out in defense of "what has always been done and accepted by law".
Customary law (also, consuetudina ...
.
The indigenous population of Mexico has in recent decades increased both in absolute numbers as-well as a percentage of the population. This is largely due to increased self-identification as indigenous, as well as indigenous women having higher birth rates than the country average. Indigenous peoples are also more likely to live in rural areas, but many reside in urban or suburban areas, particularly in the central states of Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
, Puebla
Puebla ( en, colony, settlement), officially Free and Sovereign State of Puebla ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its cap ...
, Tlaxcala
Tlaxcala (; , ; from nah, Tlaxcallān ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tlaxcala ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tlaxcala), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is ...
, Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley o ...
and the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
.
According to the CDI, the states with the greatest percentage of indigenous population are: Yucatán
Yucatán (, also , , ; yua, Yúukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán,; yua, link=no, Xóot' Noj Lu'umil Yúukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate mun ...
, with 65.40%, Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo ( , ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Quintana Roo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Quintana Roo), is one of the 31 states which, with Mexico City, constitute the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into 11 mu ...
with 44.44% and Campeche
Campeche (; yua, Kaampech ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Campeche ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Campeche), is one of the 31 states which make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Located in southeast Mexico, it is bordered by ...
with 44.54% of the population being indigenous, most of them Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a popul ...
; Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, Huāxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the Federative Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 570 municipaliti ...
with 65.73% of the population, the most numerous groups being the Mixtec
The Mixtecs (), or Mixtecos, are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as La Montaña Region and Costa Chica Regions of the state of Guerrero. The Mixtec Cult ...
and Zapotec peoples
The Zapotecs ( Valley Zapotec: ''Bën za'') are an indigenous people of Mexico. The population is concentrated in the southern state of Oaxaca, but Zapotec communities also exist in neighboring states. The present-day population is estimated at a ...
; Chiapas
Chiapas (; Tzotzil and Tzeltal: ''Chyapas'' ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas), is one of the states that make up the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 124 municipalities ...
has 36.15%, the majority being Tzeltal and Tzotzil Maya; Hidalgo
Hidalgo may refer to:
People
* Hidalgo (nobility), members of the Spanish nobility
* Hidalgo (surname)
Places
Mexico
* Hidalgo (state), in central Mexico
* Hidalgo, Coahuila, a town in the north Mexican state of Coahuila
* Hidalgo, Nuevo Le� ...
with 36.21%, the majority being Otomi
The Otomi (; es, Otomí ) are an indigenous people of Mexico inhabiting the central Mexican Plateau (Altiplano) region.
The Otomi are an indigenous people of Mexico who inhabit a discontinuous territory in central Mexico. They are linguisticall ...
; Puebla
Puebla ( en, colony, settlement), officially Free and Sovereign State of Puebla ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its cap ...
with 35.28%, and Guerrero
Guerrero is one of the 32 states that comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo and its largest city is Acapulcocopied from article, GuerreroAs of 2020, Guerrero the pop ...
with 33.92%, mostly Nahua people
The Nahuas () are a group of the indigenous people of Mexico, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua. They comprise the largest indigenous group in Mexico and second largest in El Salvador. The Mexica (Aztecs) were of Nahua ethnicity, a ...
and the states of San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of San Luis Potosí ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de San Luis Potosí), is one of the 32 states which compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and i ...
and Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
both home to a population of 19% indigenous people, mostly from the Totonac
The Totonac are an indigenous people of Mexico who reside in the states of Veracruz, Puebla, and Hidalgo. They are one of the possible builders of the pre-Columbian city of El Tajín, and further maintained quarters in Teotihuacán (a city ...
, Nahua and Teenek (Huastec) groups.
States
Population genetics
In 2011 a large scale mitochondrial sequencing in Mexican Americans revealed 85 to 90% of maternal mtDNA lineages are of Native American origin, with the remainder having European (5–7%) or African ancestry (3–5%). Thus the observed frequency of Native American mtDNA in Mexican/Mexican Americans is higher than was expected on the basis of autosomal estimates of Native American admixture for these populations i.e. ~ 30–46%http://www.biomedcentral.com/content/pdf/1471-2148-11-293.pdf “For mtDNA variation, some studies have measured Native American, European and African contributions to Mexican and Mexican American populations, revealing 85 to 90% of mtDNA lineages are of Native American origin, with the remainder having European (5–7%) or African ancestry (3–5%). Thus the observed frequency of Native American mtDNA in Mexican/Mexican Americans is higher than was expected on the basis of autosomal estimates of Native American admixture for these populations i.e. ~ 30–46%. The difference is indicative of directional mating involving preferentially immigrant men and Native American women. This type of genetic asymmetry has been observed in other populations, including Brazilian individuals of African ancestry, as the analysis of sex specific and autosomal markers has revealed evidence for substantial European admixture that was mediated mostly through men. In our 384 completely sequenced Mexican American mitochondrial genomes, 12 (3.1%) are of African ancestry belonging to haplogroups L0a1a’3’, L2a1, L3b, L3d and U6a7; 52 (13.6%) belong to European haplogroups HV, JT, U1, U4, U5; and K and the majority (320, 83.3%) are of Native American ancestry.�/ref> The indigenous groups within what is now Mexico are genetically distinct from each other. The genetic differences between geographically separated indigenous groups (e.g., between indigenous people living in the
Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
compared to indigenous people living in western Mexico) can be as large as the genetic differences seen between a European and an East Asian person.
Populations of more than 100,000
Populations of less than 20,000
 1Number of indigenous peoples that speak their Indigenous language
1Number of indigenous peoples that speak their Indigenous language

Education
 Mexico is the nation of the Americas with the highest number of living languages in the early years of the 21st century, despite this cultural wealth, there is a technological disparity in education for indigenous peoples compared to other ethnic groups living in the country.
With the creation of the Secretaría de Educación Pública, SEP, the first indigenous education works for children and adults were carried out in order to eradicate illiteracy. However, the first educational policies for indigenous peoples did not work because they reduced the number of indigenous speakers with Spanish language literacy. In the year 2003 INALI was created, the first institution of the Mexican government that activated bilingualism by providing literacy in the mother language of indigenous speakers. But the poverty of the communities and the lack of teachers in indigenous languages limited progress in writing in the mother language.
Mexico is the nation of the Americas with the highest number of living languages in the early years of the 21st century, despite this cultural wealth, there is a technological disparity in education for indigenous peoples compared to other ethnic groups living in the country.
With the creation of the Secretaría de Educación Pública, SEP, the first indigenous education works for children and adults were carried out in order to eradicate illiteracy. However, the first educational policies for indigenous peoples did not work because they reduced the number of indigenous speakers with Spanish language literacy. In the year 2003 INALI was created, the first institution of the Mexican government that activated bilingualism by providing literacy in the mother language of indigenous speakers. But the poverty of the communities and the lack of teachers in indigenous languages limited progress in writing in the mother language.
Culture
Pre-Hispanic
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, ...
-style textiles. Each costume and dance usually has a local indigenous historical and cultural meaning.
The Guelaguetza
The Guelaguetza , or Los lunes del cerro (Mondays on the Hill), is an annual indigenous cultural event in Mexico that takes place in the city of Oaxaca, capital of the state of Oaxaca, and nearby villages. The celebration features traditional co ...
is an indigenous cultural event in Mexico that takes place in the city of Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, Huāxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the Federative Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 570 municipaliti ...
. A similar celebration is the Atlixcayotl in Atlixco, Puebla. While this celebrations have attracted an increasing number of tourists, are primarily of deep cultural importance for the indigenous peoples of the country and is important for the survival of these cultures. Xantolo is another indigenous cultural event in the Huasteca
La Huasteca is a geographical and cultural region located partially along the Gulf of Mexico and including parts of the states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Puebla, Hidalgo (state), Hidalgo, San Luis Potosí, Querétaro and Guanajuato. It is roughly de ...
(Hidalgo, Veracruz and San Luis Potosí) celebrated with Day of the Deaths.
The anthropologist and chef Raquel Torres Cerdán
Raquel Torres Cerdán, also Raquel Torres (born 19 November 1948) is a Mexican anthropologist and restauranteur, who has worked to record, preserve and showcase the cuisines of the indigenous peoples of Veracruz, through her restaurants and food ...
has recorded and ensured the preservation of many of the indigenous cuisines of Veracruz.SABORES A TRADICIÓN.Experiencias de mujeres de la región cafetalera del Estado de Veracruz Radio Teocelo 2012
Notable people
Pre-Independence figures
La Malinche
Marina or Malintzin ( 1500 – 1529), more popularly known as La Malinche , a Nahua woman from the Mexican Gulf Coast, became known for contributing to the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire (1519–1521), by acting as an interpreter, ad ...
, historic figure. (Popoluca)
File:Cuauhtémoc.png, Cuauhtémoc
Cuauhtémoc (, ), also known as Cuauhtemotzín, Guatimozín, or Guatémoc, was the Aztec ruler ('' tlatoani'') of Tenochtitlan from 1520 to 1521, making him the last Aztec Emperor. The name Cuauhtemōc means "one who has descended like an eagle ...
, king and military leader. (Nahua)
File:Tzilacatzin.jpg, Tzilacatzin, military soldier. (Otomi)
File:Monumento a Francisco Tenamaxtle.JPG, Francisco Tenamaztle
Francisco is the Spanish and Portuguese form of the masculine given name ''Franciscus''.
Nicknames
In Spanish, people with the name Francisco are sometimes nicknamed "Paco". San Francisco de Asís was known as ''Pater Comunitatis'' (father of ...
, military leader. (Caxcan)
File:Jacinto Canek.jpg, Jacinto Canek
Jacinto Canek or Jacinto Uc de los Santos (c. 1731 in barrio de San Román, Campeche City, City of Campeche, New Spain – December 14, 1761 in Mérida, Yucatán, Mérida, New Spain), was an 18th-century Maya peoples, Maya revolutionary who fo ...
, activist. (Yucatec Maya)
File:Conin perfil.jpg, Conín, military leader. (Otomi)
File:Juan-Diego.jpg, Juan Diego
Juan Diego Cuauhtlatoatzin, also known as Juan Diego (; 1474–1548), was a Chichimec peasant and Marian visionary. He is said to have been granted apparitions of the Virgin Mary on four occasions in December 1531: three at the hill of Tepeyac an ...
, religious figure. (Nahua)
Indigenous Mexicans
Tomás Mejía Camacho
José Tomás de la Luz Mejía Camacho, better known as Tomás Mejía (September 17, 1820 – June 19, 1867), was a Mexican soldier of Otomi background, who consistently sided with the Conservative Party throughout its nineteenth century confli ...
, military soldier. (Otomi)
File:Geronimo agn 1913.jpg, Geronimo
Geronimo ( apm, Goyaałé, , ; June 16, 1829 – February 17, 1909) was a prominent leader and medicine man from the Bedonkohe band of the Ndendahe Apache people. From 1850 to 1886, Geronimo joined with members of three other Central Apache b ...
, military soldier. (Apache)
File:Cajeme2.jpg, Cajemé
Cajemé / Kahe'eme ( Yoeme or Yaqui Language for "one who does not stop to drink ater'), born and baptized José María Bonifacio Leyba Pérez (also spelled Leyva and Leiva), was a prominent Yaqui military leader who lived in the Mexican state ...
, military leader. (Yaqui)
File:Benito juarez circa 1868 cropped.jpg, Benito Juárez
Benito Pablo Juárez García (; 21 March 1806 – 18 July 1872) was a Mexican liberal politician and lawyer who served as the 26th president of Mexico from 1858 until his death in office in 1872. As a Zapotec, he was the first indigenous pre ...
, ex-president. (Zapotec)
File:Ignacio Manuel Altamirano Basilio.jpg, Ignacio Manuel Altamirano
Ignacio Manuel Altamirano Basilio (; 13 November 1834 – 13 February 1893) was a Mexican radical liberal writer, journalist, teacher and politician. He wrote ''Clemencia'' (1869), which is often considered to be the first modern Mexican novel.
...
, writer and politician. (Nahua)
File:Sabina002.jpg, María Sabina
María Sabina Magdalena García (22 July 1894 – 22 November 1985) was a Mazatec ''curandera'', shaman and poet who lived in Huautla de Jiménez, a town in the Sierra Mazateca area of the Mexican state of Oaxaca in southern Mexico."Sabina Rothe ...
, curandera and farmer. (Mazatec)
File:Toledo-portrait.jpg, Francisco Toledo
Francisco Benjamín López Toledo (17 July 1940 – 5 September 2019) was a Mexican Zapotec painter, sculptor, and graphic artist. In a career that spanned seven decades, Toledo produced thousands of works of art and became widely regarded as ...
, activist, and painter. (Zapotec)
File:Comandanta Ramona by bastian.jpg, Comandanta Ramona
Comandanta Ramona (1959 – January 6, 2006) was an officer of the Zapatista Army of National Liberation (EZLN), a revolutionary Indigenous autonomist organization based in the southern Mexican state of Chiapas.
Biography
Ramona was born in ...
, activist, and military leader. (Tzotzil)
File:Adela Calva Reyes (cropped).jpg, Adela Calva Reyes
Adela Calva Reyes (1967 – 2 March 2018) was an indigenous Mexican writer, author and playwright of the Otomi people.
Biography
Adela was born in 1967 in San Ildefonso, Tepejí del Río, State of Hidalgo. She remembered poverty in her childhood ...
, activist, and writer. (Otomi)
File:Manzanero cine (cropped).jpg, Armando Manzanero
Armando Manzanero Canché (7 December 1935 – 28 December 2020) was a Mexican Mayan musician, singer, composer, actor and music producer, widely considered the premier Mexican romantic composer of the postwar era and one of the most successfu ...
, musician, singer and composer. (Yucatec Maya)
File:Natalio Hernández.jpg, Natalio Hernández
Natalio Hernández Hernández (born 27 July 1947), also known as Natalio Hernández Xocoyotzin and by the pseudonym José Antonio Xokoyotsij, is a Mexican Nahua intellectual and poet, from Lomas del Dorado, Ixhuatlan de Madero the state of Veracru ...
, activist, and writer. (Nahua)
File:Macedonia Blas Flores.jpg, Macedonia Blas Flores
Macedonia Blas Flores (born 1958) is a Mexican human rights activist of hñañú origin. She was a candidate for the Nobel Peace Prize in 2005, because of the activism she wages against the violence suffered by the women of her tribe, the Otomi. ...
, activist. (Otomi)
File:Marichuy.jpg, María de Jesús Patricio Martínez
María de Jesús Patricio Martínez (born 23 December 1963), also known as Marichuy, is a Nahua traditional medicine healer and human rights activist in Mexico. She was chosen as "representative indigenous spokeswoman" by National Indigenous Congr ...
, activist and politician. (Nahua)
File:MX MC RECITAL DE POESIA INDIGENA VI (37155536425).jpg, Briceida Cuevas
Briceida Cuevas, also known as Briceida Cuevas Cob (born Tepakán, Calkiní, Campeche, Mexico, July 12, 1969) is a Mayan poet. She writes poems about everyday life in Yucatec Maya, many of which have been translated into Spanish, French and Engli ...
, writer. (Yucatec Maya)
File:Marisol Ceh Moo on Notimex TV.jpg, Marisol Ceh Moo
Marisol Ceh Moo (also Sol Ceh born May 12, 1968) is a Mexican Maya writer and professor, born in Calotmul, Yucatán, Mexico. She writes in Yucatec and in Spanish, and is known for her efforts to revitalize and protect the Yucatec Maya language. He ...
, activist, and writer. (Yucatec Maya)
File:Amaranta Gómez Regalado.jpg, Amaranta Gómez Regalado
Amaranta Gómez Regalado (born 1977) is a Mexican Muxe social anthropologist, political candidate, HIV prevention activist, social researcher, columnist and promoter of pre-Columbian indigenous cultural identity.
Biography
Gómez was born in 19 ...
, activist and politician. (Zapotec)
File:Carlos Salcido1.jpg, Carlos Salcido
Carlos Arnoldo Salcido Flores (; born 2 April 1980) is a Mexican former professional footballer. He started his career as a centre-back and played most of it as left-back, then converted to defensive midfielder and ended it as centre-back. He ...
, soccer player. (Nahua)
File:Ricardo Osorio.jpg, Ricardo Osorio
Ricardo Osorio Mendoza (born 30 March 1980) is a Mexican former professional footballer who played as a defender.
Club career Early career
Born in Huajuapan de León, Oaxaca, Osorio made his debut in the Primera División de México in 2001� ...
, soccer player. (Mixtec)
File:Yalitza Aparicio Oscars 2019.jpg, Yalitza Aparicio
Yalitza Aparicio Martínez (; born 11 December 1993) is a Mexican actress and preschool teacher. She made her film debut as Cleo in Alfonso Cuarón's 2018 drama ''Roma'', which earned her a nomination for the Academy Award for Best Actress. In 2 ...
, actress and model. (Mixtec and Triqui)
File:Jose Everardo (MEX) 2009.jpg, Everardo Cristóbal
José Everardo Cristóbal Quirino (born August 11, 1986 in Urandén, Michoacán) is a Mexican sprint canoeist who has been competing since 2005.
His first successful international performance was in 2006, when he won the silver medal in C ...
, sprint canoeist. (Purépecha)
See also
*Colonial Mexico
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 ...
*Indigenismo in Mexico
Indigenismo is a Latin American nationalist political ideology that began in the late nineteenth century and persisted throughout the twentieth that attempted to construct the role of indigenous populations in the nation-state. The ideology was par ...
*Indigenous peoples of California
The indigenous peoples of California (known as Native Californians) are the indigenous inhabitants who have lived or currently live in the geographic area within the current boundaries of California before and after the arrival of Europeans. ...
* Indigenous peoples of the North American Southwest
*Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
*Mesoamerican chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of prehispanic Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian (first human habitation until 3500 BCE); the Archaic (before 2600 BCE), the Preclassic or Formative (2500 BCE –&nb ...
*Mexican Indian Wars
Indigenous rebellions in Mexico and Central America were conflicts of resistance initiated by indigenous peoples against European colonial empires and settler states that occurred in the territory of the continental Viceroyalty of New Spain and Br ...
References
Sources
* * * * * *Further reading
General
* * *Prehispanic era
* * * * Duverger, Christian (1999): ''Mesoamérica, arte y antropología.'' CONACULTA-Landucci Editores. Paris. * * * * * * * * * * * * Miller, Mary Ellen. (2001). ''El arte de mesoamérica''. "Colecciones El mundo del arte". Ediciones Destino.Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
, España. .
*
*
*
*
*
*
Postconquest era
* * * * * * * * * * *Postcolonial era
*External links
Comisión Nacional para el Desarrollo de los Pueblos Indigenas
Consejo Nacional de Poblacion
Instituto Nacional de Estadistica y Geografia
Mexico and Southwest USA – Native Y-DNA Project
Archivo de Lenguas Indígenas de México
(El Colegio de México)
Information about the Native American tribes that historically lived on the US-Mexico Border
{{Authority control Demographics of Mexico Society of Mexico