In-universe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A fictional universe, or fictional world, is a
A fictional universe, or fictional world, is a
by
 A fictional universe, or fictional world, is a
A fictional universe, or fictional world, is a self-consistent
In classical deductive logic, a consistent theory is one that does not lead to a logical contradiction. The lack of contradiction can be defined in either semantic or syntactic terms. The semantic definition states that a theory is consistent ...
setting
Setting may refer to:
* A location (geography) where something is set
* Set construction in theatrical scenery
* Setting (narrative), the place and time in a work of narrative, especially fiction
* Setting up to fail a manipulative technique to e ...
with events, and often other elements, that differ from the real world. It may also be called an imagined, constructed, or fictional realm (or world). Fictional universes may appear in novel
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itself ...
s, comics
a medium used to express ideas with images, often combined with text or other visual information. It typically the form of a sequence of panels of images. Textual devices such as speech balloons, captions, and onomatopoeia can indicate ...
, film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmospher ...
s, television show
A television show – or simply TV show – is any content produced for viewing on a television set which can be broadcast via over-the-air, satellite, or cable, excluding breaking news, advertisements, or trailers that are typically placed b ...
s, video game
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, controller, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This feedba ...
s, and other creative works.
The subject is most commonly addressed in reference to fictional universes that differ markedly from the real world, such as those that introduce entire fictional cities, countries, or even planets, or those that contradict commonly known facts about the world and its history, or those that feature fantasy or science fiction
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, parallel uni ...
concepts such as magic or faster than light travel—and especially those in which the deliberate development of the setting is a substantial focus of the work. When a large franchise
Franchise may refer to:
Business and law
* Franchising, a business method that involves licensing of trademarks and methods of doing business to franchisees
* Franchise, a privilege to operate a type of business such as a cable television p ...
of related works has two or more somewhat different fictional universes that are each internally consistent but not consistent with each other (such as a distinct plotline and set of characters in a comics version versus a television adaptation), each universe is often referred to as a continuity, though the term ''continuity'' as a mass noun
In linguistics, a mass noun, uncountable noun, non-count noun, uncount noun, or just uncountable, is a noun with the syntactic property that any quantity of it is treated as an undifferentiated unit, rather than as something with discrete elemen ...
usually has a broader meaning in fiction.
Definition
The term was first defined by comics historianDon Markstein
Don Markstein's Toonopedia (subtitled A Vast Repository of Toonological Knowledge) is an online encyclopedia of print cartoons, comic strips and animation, initiated February 13, 2001. Donald D. Markstein, the sole writer and editor of Toonopedi ...
, in a 1970 article in ''CAPA-alpha CAPA-alpha (sometimes abbreviated to K-a) was the first amateur press association (APA) devoted to comic books, started by Jerry Bails (the "father of comics fandom") in the United States in 1964.
History
In October 1964 Bails released the first i ...
''."THE MERCHANT OF VENICE meets THE SHIEK OF ARABI"by
Don Markstein
Don Markstein's Toonopedia (subtitled A Vast Repository of Toonological Knowledge) is an online encyclopedia of print cartoons, comic strips and animation, initiated February 13, 2001. Donald D. Markstein, the sole writer and editor of Toonopedi ...
(as "Om Markstein Sklom Stu"), in ''CAPA-alpha CAPA-alpha (sometimes abbreviated to K-a) was the first amateur press association (APA) devoted to comic books, started by Jerry Bails (the "father of comics fandom") in the United States in 1964.
History
In October 1964 Bails released the first i ...
'' #71 (September 1970); archived at Toonopedia
Markstein's criteria
# If characters A and B have met, then they are in the same universe; if characters B and C have met, then, transitively, A and C are in the same universe. # Characters cannot be connected by real people—otherwise, it could be argued thatSuperman
Superman is a superhero who appears in American comic books published by DC Comics. The character was created by writer Jerry Siegel and artist Joe Shuster, and debuted in the comic book '' Action Comics'' #1 ( cover-dated June 1938 and pu ...
and the Fantastic Four
The Fantastic Four is a superhero team appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. The team debuted in ''The Fantastic Four'' #1 (cover dated Nov. 1961), helping usher in a new level of realism in the medium. It was the first s ...
were in the same universe, as Superman met John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
, Kennedy met Neil Armstrong
Neil Alden Armstrong (August 5, 1930 – August 25, 2012) was an American astronaut and aeronautical engineer who became the first person to walk on the Moon in 1969. He was also a naval aviator, test pilot, and university professor.
...
, and Armstrong met the Fantastic Four.
#Characters cannot be connected by characters "that do not originate with the publisher"—otherwise it could be argued that Superman and the Fantastic Four were in the same universe, as both met Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the ...
.
# Specific fictionalized versions of real people—for instance, the version of Jerry Lewis
Jerry Lewis (born Joseph Levitch; March 16, 1926 – August 20, 2017) was an American comedian, actor, singer, filmmaker and humanitarian. As his contributions to comedy and charity made him a global figure in popular culture, pop culture ...
from DC Comics
DC Comics, Inc. ( doing business as DC) is an American comic book publisher and the flagship unit of DC Entertainment, a subsidiary of Warner Bros. Discovery.
DC Comics is one of the largest and oldest American comic book companies, with the ...
' ''The Adventures of Jerry Lewis
''The Adventures of Dean Martin and Jerry Lewis'' is the title of a celebrity comic book published by DC Comics and featuring the popular team of comedians Dean Martin and Jerry Lewis. The series ran for forty issues from 1952 through 1957, at w ...
'', who was distinct from the real Jerry Lewis in that he had a housekeeper with magical powers—''can'' be used as connections; this also applies to specific versions of public-domain fictional characters, such as Marvel Comics' version of Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the ...
or DC Comics' version of Robin Hood
Robin Hood is a legendary heroic outlaw originally depicted in English folklore and subsequently featured in literature and film. According to legend, he was a highly skilled archer and swordsman. In some versions of the legend, he is dep ...
.
#Characters are only considered to have met if they appeared together in a story; therefore, characters who simply appeared on the same front cover are not necessarily in the same universe.
Universe vs setting
What distinguishes a fictional universe from a simplesetting
Setting may refer to:
* A location (geography) where something is set
* Set construction in theatrical scenery
* Setting (narrative), the place and time in a work of narrative, especially fiction
* Setting up to fail a manipulative technique to e ...
is the level of detail and internal consistency. A fictional universe has an established continuity and internal logic that must be adhered to throughout the work and even across separate works. So, for instance, many books may be set in conflicting fictional versions of Victorian London
During the 19th century, London grew enormously to become a global city of immense importance. It was the largest city in the world from about 1825, the world's largest port, and the heart of international finance and trade. Railways connecting ...
, but all the stories of Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a " consulting detective" in the stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with observation, deduction, forensic science and ...
are set in ''the same'' Victorian London. However, the various film series based on Sherlock Holmes follow their own separate continuities, thus not taking place in the same fictional universe.
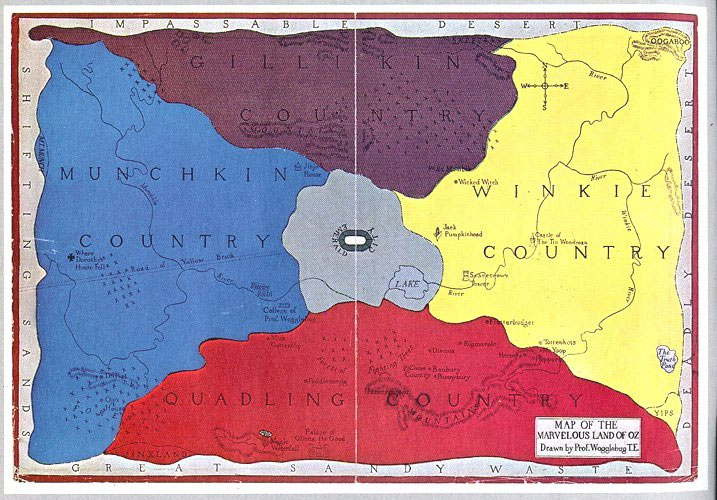
The history and geography of a fictional universe are well defined, and maps and timelines are often included in works set within them. Even new languages
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
may be constructed. When subsequent works are written within the same universe, care is usually taken to ensure that established facts of the canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the conceptual material accepted as official in a fictional universe by its fan base
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western ca ...
are not violated. Even if the fictional universe involves concepts such as elements of magic that don't exist in the real world, these must adhere to a set of rules established by the author.
A famous example of a detailed fictional universe is Arda
Arda or ARDA may refer to:
Places
*Arda (Maritsa), a river in Bulgaria and Greece
* Arda (Italy), a river in Italy
* Arda (Douro), a river in Portugal
*Arda, Bulgaria, a village in southern Bulgaria
* Arda, County Fermanagh, a townland in County ...
(more popularly known as Middle-earth
Middle-earth is the fictional setting of much of the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy. The term is equivalent to the '' Miðgarðr'' of Norse mythology and ''Middangeard'' in Old English works, including ''Beowulf''. Middle-earth is ...
), of J. R. R. Tolkien's books ''The Lord of the Rings
''The Lord of the Rings'' is an epic high-fantasy novel by English author and scholar J. R. R. Tolkien. Set in Middle-earth, intended to be Earth at some time in the distant past, the story began as a sequel to Tolkien's 1937 children's bo ...
'', ''The Hobbit
''The Hobbit, or There and Back Again'' is a children's fantasy novel by English author J. R. R. Tolkien. It was published in 1937 to wide critical acclaim, being nominated for the Carnegie Medal and awarded a prize from the ''N ...
'', and ''The Silmarillion
''The Silmarillion'' () is a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, assisted by the fantasy author Guy Gavri ...
''. He created first its languages
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
and then the world itself, which he states was "primarily linguistic in inspiration and was begun in order to provide the necessary 'history' for the Elvish tongues."
A modern example of a fictional universe
A fictional universe, or fictional world, is a self-consistent setting with events, and often other elements, that differ from the real world. It may also be called an imagined, constructed, or fictional realm (or world). Fictional universes ma ...
is that of the ''Avatar
Avatar (, ; ), is a concept within Hinduism that in Sanskrit literally means "descent". It signifies the material appearance or incarnation of a powerful deity, goddess or spirit on Earth. The relative verb to "alight, to make one's appear ...
'' film series, as James Cameron
James Francis Cameron (born August 16, 1954) is a Canadian filmmaker. A major figure in the post- New Hollywood era, he is considered one of the industry's most innovative filmmakers, regularly pushing the boundaries of cinematic capability ...
invented an entire ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
, with a team of scientists to test whether it was viable. Additionally, he commissioned a linguistics expert to invent the Na'vi language.
Virtually every successful fictional TV series
A television show – or simply TV show – is any content produced for viewing on a television set which can be broadcast via over-the-air, satellite, or cable, excluding breaking news, advertisements, or trailers that are typically placed b ...
or comic book
A comic book, also called comicbook, comic magazine or (in the United Kingdom and Ireland) simply comic, is a publication that consists of comics art in the form of sequential juxtaposed panels that represent individual scenes. Panels are of ...
develops its own "universe" to keep track of the various episodes or issues. Writers for that series must follow its story bible, This is a blog entry on the subject by a professional scriptwriter. which often becomes the series canon.
Frequently, when a series is perceived by its creators as too complicated or too self-inconsistent (because of, for example, too many writers), the producers or publishers may introduce retroactive continuity
Retroactive continuity, or retcon for short, is a literary device in which established diegetic facts in the plot of a fictional work (those established through the narrative itself) are adjusted, ignored, supplemented, or contradicted by a subs ...
(retcon) to make future editions easier to write and more consistent. This creates an alternate universe that future authors can write about. These stories about the universe or universes that existed before the retcon are usually not canonical, unless the franchise-holder gives permission. ''Crisis on Infinite Earths
"Crisis on Infinite Earths" is a 1985 American comic book crossover storyline published by DC Comics. The series, written by Marv Wolfman and pencilled by George Pérez, was first serialized as a 12-issue limited series from April 1985 to Mar ...
'' was an especially sweeping example.
Some writers choose to introduce elements or characters from one work into another, to present the idea that both works are set in the same universe. For example, the character of Ursula Buffay
Various characters appeared in the sitcom ''Friends'' and its spin-off series ''Joey'', which respectively aired for ten seasons and two seasons on NBC from 1994 to 2006. ''Friends'' featured six main cast members: Rachel Green-Geller (Jennifer A ...
from American sitcom
A sitcom, a portmanteau of situation comedy, or situational comedy, is a genre of comedy centered on a fixed set of characters who mostly carry over from episode to episode. Sitcoms can be contrasted with sketch comedy, where a troupe may use ...
''Mad About You
''Mad About You'' is an American television sitcom starring Paul Reiser and Helen Hunt as a married couple in New York City. It initially aired on NBC from September 23, 1992, to May 24, 1999, winning numerous awards including four Golden Glob ...
'' was also a recurring guest star in ''Friends
''Friends'' is an American television sitcom created by David Crane and Marta Kauffman, which aired on NBC from September 22, 1994, to May 6, 2004, lasting ten seasons. With an ensemble cast starring Jennifer Aniston, Courteney Cox, Li ...
'', despite the two series having little else in common. Fellow NBC series ''Seinfeld
''Seinfeld'' ( ) is an American television sitcom created by Larry David and Jerry Seinfeld. It aired on NBC from July 5, 1989, to May 14, 1998, over nine seasons and 180 episodes. It stars Seinfeld as a fictionalized version of himself and ...
'' also contained crossover
Crossover may refer to:
Entertainment
Albums and songs
* ''Cross Over'' (Dan Peek album)
* ''Crossover'' (Dirty Rotten Imbeciles album), 1987
* ''Crossover'' (Intrigue album)
* ''Crossover'' (Hitomi Shimatani album)
* ''Crossover'' (Yoshino ...
references to ''Mad About You''. L. Frank Baum introduced the characters of Cap'n Bill
This is a list of characters in the original Oz books by American author L. Frank Baum. The majority of characters listed here unless noted otherwise have appeared in multiple books under various plotlines. ''Land of Oz, Oz'' is made up of four ...
and Trot
The trot is a ten-beat diagonal horse gait where the diagonal pairs of legs move forward at the same time with a moment of suspension between each beat. It has a wide variation in possible speeds, but averages about . A very slow trot is someti ...
(from ''The Sea Fairies
''The Sea Fairies'' is a children's fantasy novel written by L. Frank Baum, illustrated by John R. Neill, and published in 1911 by the Reilly & Britton Company, the publisher of Baum's series of Oz books.
Genre
As an underwater fantasy, Baum's ...
'') into the Oz series
The Oz books form a book series that begins with ''The Wonderful Wizard of Oz'' (1900) and relates the fictional history of the Land of Oz. Oz was created by author Lyman Frank Baum, L. Frank Baum, who went on to write fourteen full-length Oz books ...
in ''The Scarecrow of Oz
''The Scarecrow of Oz'' is the ninth book set in the Land of Oz written by L. Frank Baum. Published on July 16, 1915, it was Baum's personal favorite of the Oz books and tells of Cap'n Bill and Trot journeying to Oz and, with the help of the Scar ...
'', and they made a number of appearances in later Oz books. In science fiction, A. Bertram Chandler
Arthur Bertram Chandler (28 March 1912 in Aldershot, Hampshire, England – 6 June 1984 in Sydney, Australia) was an Anglo-Australian merchant marine officer, sailing the world in everything from tramp steamers to troop ships, but who later tu ...
introduced into his future Galactic civilization the character Dominic Flandry
Dominic Flandry is a fictional character and the protagonist of the second half of Poul Anderson's Technic History science fiction series. He first appeared in 1951.
The space opera series is set in the 31st century, during the waning days of ...
from Poul Anderson
Poul William Anderson (November 25, 1926 – July 31, 2001) was an American fantasy and science fiction author who was active from the 1940s until the 21st century. Anderson wrote also historical novels. His awards include seven Hugo Awards and ...
's quite different Galactic future (he had Anderson's consent)—on the assumption that these were two alternate history
Alternate history (also alternative history, althist, AH) is a genre of speculative fiction of stories in which one or more historical events occur and are resolved differently than in real life. As conjecture based upon historical fact, alte ...
timelines and that people could on some occasions cross from one to the other.
Scope
Sir Thomas More
Sir Thomas More (7 February 1478 – 6 July 1535), venerated in the Catholic Church as Saint Thomas More, was an English lawyer, judge, social philosopher, author, statesman, and noted Renaissance humanist. He also served Henry VIII as Lor ...
's ''Utopia
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imaginary community or society that possesses highly desirable or nearly perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book '' Utopia'', describing a fictional island soc ...
'' is one of the earliest examples of a cohesive fictional world with its own rules and functional concepts, but it comprises only one small island. Later fictional universes, like Robert E. Howard's '' Conan the Cimmerian'' stories or Lev Grossman
Lev Grossman (born June 26, 1969) is an American novelist and journalist who wrote ''The Magicians Trilogy'': '' The Magicians'' (2009), ''The Magician King'' (2011), and ''The Magician's Land'' (2014). He was the book critic and lead technology ...
's Fillory
''The Magicians'' is a new adult fantasy novel by the American author Lev Grossman, published in 2009 by Viking Press. It tells the story of Quentin Coldwater, a young man who discovers and attends a secret college of magic in New York. The nov ...
, are global in scope and some, like ''Star Wars
''Star Wars'' is an American epic space opera multimedia franchise created by George Lucas, which began with the eponymous 1977 film and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has been expanded into various film ...
'', ''Honorverse
The Honorverse is a military science fiction book series, its two subseries, two prequel series, and anthologies created by David Weber and published by Baen Books. They are centered on the space navy career of the principal protagonist Honor ...
'', ''BattleTech
''BattleTech'' is a wargaming and military science fiction franchise launched by FASA Corporation in 1984, acquired by WizKids in 2001, which was in turn acquired by Topps in 2003; and published since 2007 by Catalyst Game Labs. The tradema ...
'', or the Lensman series
The ''Lensman'' series is a series of science fiction novels by American author E. E. "Doc" Smith. It was a runner-up for the 1966 Hugo award for Best All-Time Series, losing to the ''Foundation'' series by Isaac Asimov.
Plot
The series begin ...
, are galactic or even intergalactic.
A fictional universe may even concern itself with more than one interconnected universe through fictional devices such as dreams, "time travel
Time travel is the concept of movement between certain points in time, analogous to movement between different points in space by an object or a person, typically with the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine. Time travel is a ...
" or "parallel worlds". Such a series of interconnected universes is often called a multiverse
The multiverse is a hypothetical group of multiple universes. Together, these universes comprise everything that exists: the entirety of space, time, matter, energy, information, and the physical laws and constants that describe them. The dif ...
. Such multiverses have been featured prominently in science fiction since at least the mid-20th century.
The ''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the eponymous 1960s television series and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has expanded into vari ...
'' episode " Mirror, Mirror" introduced the Mirror Universe, in which the crew members of the Starship ''Enterprise'' were brutal rather than compassionate. The 2009 movie ''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the eponymous 1960s television series and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has expanded into vari ...
'' created an "alternate reality" and freed the ''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the eponymous 1960s television series and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has expanded into vari ...
'' franchise
Franchise may refer to:
Business and law
* Franchising, a business method that involves licensing of trademarks and methods of doing business to franchisees
* Franchise, a privilege to operate a type of business such as a cable television p ...
from continuity issues. In the mid-1980s, DC Comics
DC Comics, Inc. ( doing business as DC) is an American comic book publisher and the flagship unit of DC Entertainment, a subsidiary of Warner Bros. Discovery.
DC Comics is one of the largest and oldest American comic book companies, with the ...
''Crisis on Infinite Earths
"Crisis on Infinite Earths" is a 1985 American comic book crossover storyline published by DC Comics. The series, written by Marv Wolfman and pencilled by George Pérez, was first serialized as a 12-issue limited series from April 1985 to Mar ...
'' streamlined its fictional continuity by destroying most of its alternate universes.
Format
A fictional universe can be contained in a single work, as inGeorge Orwell
Eric Arthur Blair (25 June 1903 – 21 January 1950), better known by his pen name George Orwell, was an English novelist, essayist, journalist, and critic. His work is characterised by lucid prose, social criticism, opposition to totalit ...
's ''Nineteen Eighty-Four
''Nineteen Eighty-Four'' (also stylised as ''1984'') is a dystopian social science fiction novel and cautionary tale written by the English writer George Orwell. It was published on 8 June 1949 by Secker & Warburg as Orwell's ninth and fina ...
'' or Aldous Huxley
Aldous Leonard Huxley (26 July 1894 – 22 November 1963) was an English writer and philosopher. He wrote nearly 50 books, both novels and non-fiction works, as well as wide-ranging essays, narratives, and poems.
Born into the prominent Huxle ...
's ''Brave New World
''Brave New World'' is a dystopian novel by English author Aldous Huxley, written in 1931 and published in 1932. Largely set in a futuristic World State, whose citizens are environmentally engineered into an intelligence-based social hiera ...
'', or in serialized, series
Series may refer to:
People with the name
* Caroline Series (born 1951), English mathematician, daughter of George Series
* George Series (1920–1995), English physicist
Arts, entertainment, and media
Music
* Series, the ordered sets used in ...
-based, open-ended or round robin-style fiction.
In most small-scale fictional universes, general properties and timeline
A timeline is a display of a list of events in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale represen ...
events fit into a consistently organized continuity. However, in the case of universes that are rewritten or revised by different writer
A writer is a person who uses written words in different writing styles and techniques to communicate ideas. Writers produce different forms of literary art and creative writing such as novels, short stories, books, poetry, travelogues, ...
s, editors
Editing is the process of selecting and preparing written, photographic, visual, audible, or cinematic material used by a person or an entity to convey a message or information. The editing process can involve correction, condensation, or ...
, or producers, this continuity may be violated, by accident or by design.
The occasional publishing use of retroactive continuity (retcon
Retroactive continuity, or retcon for short, is a literary device in which established diegetic facts in the plot of a fictional work (those established through the narrative itself) are adjusted, ignored, supplemented, or contradicted by a subs ...
) often occurs due to this kind of revision or oversight. Members of fandom
A fandom is a subculture composed of fans characterized by a feeling of empathy and camaraderie with others who share a common interest. Fans typically are interested in even minor details of the objects of their fandom and spend a significant ...
often create a kind of fan-made
Fan labor, also called fan works, are the creative activities engaged in by fans, primarily those of various media properties or musical groups. These activities can include creation of written works (fiction, fan fiction and review literature), ...
canon ( fanon) to patch up such errors; "fanon" that becomes generally accepted sometimes becomes actual canon. Other fan-made additions to a universe (fan fiction
Fan fiction or fanfiction (also abbreviated to fan fic, fanfic, fic or FF) is fictional writing written in an amateur capacity by fans, unauthorized by, but based on an existing work of fiction. The author uses copyrighted characters, setti ...
, alternate universe, pastiche
A pastiche is a work of visual art, literature, theatre, music, or architecture that imitates the style or character of the work of one or more other artists. Unlike parody, pastiche pays homage to the work it imitates, rather than mocking i ...
, parody
A parody, also known as a spoof, a satire, a send-up, a take-off, a lampoon, a play on (something), or a caricature, is a creative work designed to imitate, comment on, and/or mock its subject by means of satiric or ironic imitation. Often its sub ...
) are usually not considered canonical unless they get authorized
Authorization or authorisation (see spelling differences) is the function of specifying access rights/privileges to resources, which is related to general information security and computer security, and to access control in particular. More for ...
.
Collaboration
Shared universes often come about when a fictional universe achieves great commercial success and attracts other media. For example, a successful movie may catch the attention of various book authors, who wish to write stories based on that movie. Under U.S. law, the copyright-holder retains control of all otherderivative work
In copyright law, a derivative work is an expressive creation that includes major copyrightable elements of an original, previously created first work (the underlying work). The derivative work becomes a second, separate work independent in ...
s, including those written by other authors, but they might not feel comfortable in those other mediums or may feel that other individuals will do a better job; therefore, they may open up the copyright on a shared-universe basis. The degree to which the copyright-holder or franchise
Franchise may refer to:
Business and law
* Franchising, a business method that involves licensing of trademarks and methods of doing business to franchisees
* Franchise, a privilege to operate a type of business such as a cable television p ...
retains control is often one of the points in the license agreement
A license (or licence) is an official permission or permit to do, use, or own something (as well as the document of that permission or permit).
A license is granted by a party (licensor) to another party (licensee) as an element of an agreeme ...
.
For example, the comic book ''Superman
Superman is a superhero who appears in American comic books published by DC Comics. The character was created by writer Jerry Siegel and artist Joe Shuster, and debuted in the comic book '' Action Comics'' #1 ( cover-dated June 1938 and pu ...
'' was so popular that it spawned over 30 different radio, television, and movie series and a similar number of video game
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, controller, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This feedba ...
s, as well as theme park rides, books, and songs. In the other direction, both ''Star Trek'' and ''Star Wars'' are responsible for hundreds of books and games of varying levels of canonicity.
Fictional universes are sometimes shared by multiple prose authors, with each author's works in that universe being granted approximately equal canonical status. For example, Larry Niven
Laurence van Cott Niven (; born April 30, 1938) is an American science fiction writer. His best-known works are '' Ringworld'' (1970), which received Hugo, Locus, Ditmar, and Nebula awards, and, with Jerry Pournelle, '' The Mote in God's E ...
's fictional universe Known Space
Known Space is the fictional setting of about a dozen science fiction novels and several collections of short stories written by Larry Niven. It has also become a shared universe in the spin-off ''Man-Kzin Wars'' anthologies. The Internet Spe ...
has an approximately 135-year period in which Niven allows other authors to write stories about the Man-Kzin Wars
''The Man-Kzin Wars'' is a series of military science fiction anthologies and is the name of the first. The short stories detail the eponymous conflicts between mankind and the Kzinti, set in Larry Niven's ''Known Space'' universe. However, Ni ...
. Other fictional universes, like the ''Ring of Fire'' series, actively court canonical stimulus from fans, but gate and control the changes through a formalized process and the final say of the editor and universe creator.
Other universes are created by one or several authors but are intended to be used non-canonically by others, such as the fictional settings for game
A game is a structured form of play, usually undertaken for entertainment or fun, and sometimes used as an educational tool. Many games are also considered to be work (such as professional players of spectator sports or games) or art (suc ...
s, particularly role-playing game
A role-playing game (sometimes spelled roleplaying game, RPG) is a game in which players assume the roles of characters in a fictional setting. Players take responsibility for acting out these roles within a narrative, either through literal ac ...
s and video games. Settings for the role-playing game ''Dungeons & Dragons
''Dungeons & Dragons'' (commonly abbreviated as ''D&D'' or ''DnD'') is a fantasy tabletop role-playing game (RPG) originally designed by Gary Gygax and Dave Arneson. The game was first published in 1974 by Tactical Studies Rules, Inc. (TS ...
'' are called campaign setting
A campaign setting is usually a fictional world which serves as a setting for a role-playing game or wargame campaign. A '' campaign'' is a series of individual adventures, and a ''campaign setting'' is the world in which such adventures and c ...
s; other games have also incorporated this term on occasion. Virtual world
A virtual world (also called a virtual space) is a computer-simulated environment which may be populated by many users who can create a personal avatar, and simultaneously and independently explore the virtual world, participate in its activities ...
s are fictional worlds in which online
In computer technology and telecommunications, online indicates a state of connectivity and offline indicates a disconnected state. In modern terminology, this usually refers to an Internet connection, but (especially when expressed "on line" ...
computer games, notably MMORPG
A massively multiplayer online role-playing game (MMORPG) is a video game that combines aspects of a role-playing video game and a massively multiplayer online game.
As in role-playing games (RPGs), the player assumes the role of a Player charac ...
s and MUDs, take place. A fictional crossover
A crossover is the placement of two or more otherwise discrete fictional characters, settings, or universes into the context of a single story. They can arise from legal agreements between the relevant copyright holders, unofficial efforts by ...
occurs when two or more fictional characters, series or universes cross over with one another, usually in the context of a character created by one author or owned by one company
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared ...
meeting a character created or owned by another. In the case where two fictional universes covering entire ''actual'' universes cross over, physical travel from one universe to another may actually occur in the course of the story. Such crossovers are usually, but not always, considered non-canonical by their creators or by those in charge of the properties
Property is the ownership of land, resources, improvements or other tangible objects, or intellectual property.
Property may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Property (mathematics)
Philosophy and science
* Property (philosophy), in philosophy an ...
involved.
Lists of fictional universes
For lists of fictional universes see: * List of fictional shared universes in film and television *List of fictional universes in animation and comics
This is a partial list of fictional universes created for comic books and animated film and television.
Animation
This is a partial list of fictional universes created for animated films or series.
Comics
This is a partial list of fictional univ ...
*List of fictional universes in literature
This is a list of fictional universes in literature.
See also
* List of science fiction universes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Fictional Universes in literature
Universes
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, incl ...
* List of science fiction universes
See also
*Alternate history
Alternate history (also alternative history, althist, AH) is a genre of speculative fiction of stories in which one or more historical events occur and are resolved differently than in real life. As conjecture based upon historical fact, alte ...
* Alternate universe
* Constructed world
* Continuity
* Diegesis
* Expanded universe
* Shared universe
A shared universe or shared world is a fictional universe from a set of creative works where more than one writer (or other artist) independently contributes a work that can stand alone but fits into the joint development of the storyline, chara ...
* Fantasy world
A fantasy world is a world created for/from fictional media, such as literature, film or games. Typical fantasy worlds involve magic or magical abilities, nonexistent technology and, sometimes, either a historical or futuristic theme. Some worl ...
* Fictional country
A fictional country is a country that is made up for fictional stories, and does not exist in real life, or one that people believe in without proof.
Sailors have always mistaken low clouds for land masses, and in later times this was given ...
* Fictional location
Fictional locations are places that exist only in fiction and not in reality, such as the Negaverse or Planet X. Writers may create and describe such places to serve as backdrop for their fictional works. Fictional locations are also created for ...
* Future history
A future history is a postulated history of the future and is used by authors of science fiction and other speculative fiction to construct a common background for fiction. Sometimes the author publishes a timeline of events in the history, whil ...
* Index of fictional places
* List of fantasy worlds
This is a list of fictional fantasy worlds and lands. The best-known lands or worlds, not necessarily the most encompassing, are listed. For example, Middle-earth is only a region of Arda in J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional universe, but it is far ...
* Mythical place
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrati ...
* Paracosm
A paracosm is a detailed imaginary world thought generally to originate in childhood. The creator of a paracosm has a complex and deeply felt relationship with this subjective universe, which may incorporate real-world or imaginary characters ...
* Parallel universe
* Planets in science fiction
Planets in science fiction are fictional planets that appear in various media of the science fiction genre as story-settings or depicted locations.
Planet lists
For planets from specific fictional milieux, use the following lists:
Literature ...
* Setting
Setting may refer to:
* A location (geography) where something is set
* Set construction in theatrical scenery
* Setting (narrative), the place and time in a work of narrative, especially fiction
* Setting up to fail a manipulative technique to e ...
* Simulated reality
The simulation theory is the hypothesis that reality could be simulated—for example by quantum computer simulation—to a degree indistinguishable from "true" reality. It could contain conscious minds that may or may not know that they live i ...
* Virtual reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a simulated experience that employs pose tracking and 3D near-eye displays to give the user an immersive feel of a virtual world. Applications of virtual reality include entertainment (particularly video games), edu ...
*Multiverse
The multiverse is a hypothetical group of multiple universes. Together, these universes comprise everything that exists: the entirety of space, time, matter, energy, information, and the physical laws and constants that describe them. The dif ...
References
*Alberto Manguel
Alberto Manguel (born March 13, 1948, in Buenos Aires) is an Argentine-Canadian anthologist, translator, essayist, novelist, editor, and a former Director of the National Library of Argentina. He is the author of numerous non-fiction books such ...
and Gianni Guadalupi
Gianni is an Italian name (occasionally a surname), a short form of the Italian Giovanni and a cognate of John meaning God is gracious. Gianni is the most common diminutive of Giovanni in Italian.
People with this given name
* Gianni Agnelli ( ...
: ''The Dictionary of Imaginary Places
''The Dictionary of Imaginary Places'' (1980, 1987, 1999) is a book written by Alberto Manguel and Gianni Guadalupi. It takes the form of a catalogue of fantasy lands, islands, cities, and other locations from world literature—"a Baedecker ...
'', New York : Harcourt Brace, c2000.
* Brian Stableford
Brian Michael Stableford (born 25 July 1948) is a British academic, critic and science fiction writer who has published more than 70 novels. His earlier books were published under the name Brian M. Stableford, but more recent ones have dropped ...
: ''The Dictionary of Science Fiction Places'', New York : Wonderland Press, c1999.
* Diana Wynne Jones
Diana Wynne Jones (16 August 1934 – 26 March 2011) was a British novelist, poet, academic, literary critic, and short story writer. She principally wrote fantasy and speculative fiction novels for children and young adults. Although usually d ...
: ''The Tough Guide to Fantasyland'', New York : Firebird, 2006. , Explains and parodies the common features of a standard fantasy world
* George Ochoa
George Ochoa (born April 29, 1962) is an American guitarist that started being active in 1987.
History
George Ochoa began his musical career with the band Prophet. Ochoa was a part of the band alongside Dion Sanchez and Roger Martinez who would ...
and Jeffery Osier Jeffery may refer to:
* Jeffery (name), including a list of people with the name
* Jeffery (automobile), an early American automobile manufacturer
* Thomas B. Jeffery Company
* Jeffery Boulevard, a major north–south street on the South Side of Ch ...
: ''Writer's Guide to Creating A Science Fiction Universe'', Cincinnati, Ohio : Writer's Digest Books
''Writer's Digest'' is an American magazine aimed at beginning and established writers. It contains interviews, market listings, calls for manuscripts, and how-to articles.
History
''Writer's Digest'' was first published in December 1920 under ...
, 1993.
* Michael Page and Robert Ingpen
Robert Roger Ingpen AM, FRSA (born 13 October 1936) is an Australian graphic designer, illustrator, and writer. For his "lasting contribution" as a children's illustrator he received the biennial, international Hans Christian Andersen Medal i ...
: ''Encyclopedia of Things That Never Were ''Encyclopedia of Things That Never Were'' is a book by Robert Ingpen and Michael Page published in 1985.
Plot summary
''Encyclopedia of Things That Never Were'' is a book detailing myth and magic written by Page and painted by Ingpen.
Reception
...
: Creatures, Places, and People'', 1987.
{{Authority control
Continuity (fiction)
Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the univers ...
Imagination
Setting
Worldbuilding