Image Registration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Image registration is the process of transforming different sets of data into one coordinate system. Data may be multiple photographs, data from different sensors, times, depths, or viewpoints. It is used in
2-D and 3-D Image Registration for Medical, Remote Sensing, and Industrial Applications
Wiley Press, 2005. One of the images is referred to as the ''moving'' or ''source'' and the others are referred to as the ''target'', ''fixed'' or ''sensed'' images. Image registration involves spatially transforming the source/moving image(s) to align with the target image. The reference frame in the target image is stationary, while the other datasets are transformed to match to the target. Intensity-based methods compare intensity patterns in images via correlation metrics, while feature-based methods find correspondence between image features such as points, lines, and contours. Intensity-based methods register entire images or sub-images. If sub-images are registered, centers of corresponding sub images are treated as corresponding feature points. Feature-based methods establish a correspondence between a number of especially distinct points in images. Knowing the correspondence between a number of points in images, a geometrical transformation is then determined to map the target image to the reference images, thereby establishing point-by-point correspondence between the reference and target images. Methods combining intensity-based and feature-based information have also been developed.
"Image Registration Using Log-Polar Mappings for Recovery of Large-Scale Similarity and Projective Transformations"
''IEEE Transactions on Image Processing'', vol. 14, No. 10, October, 2005. Due to properties of the
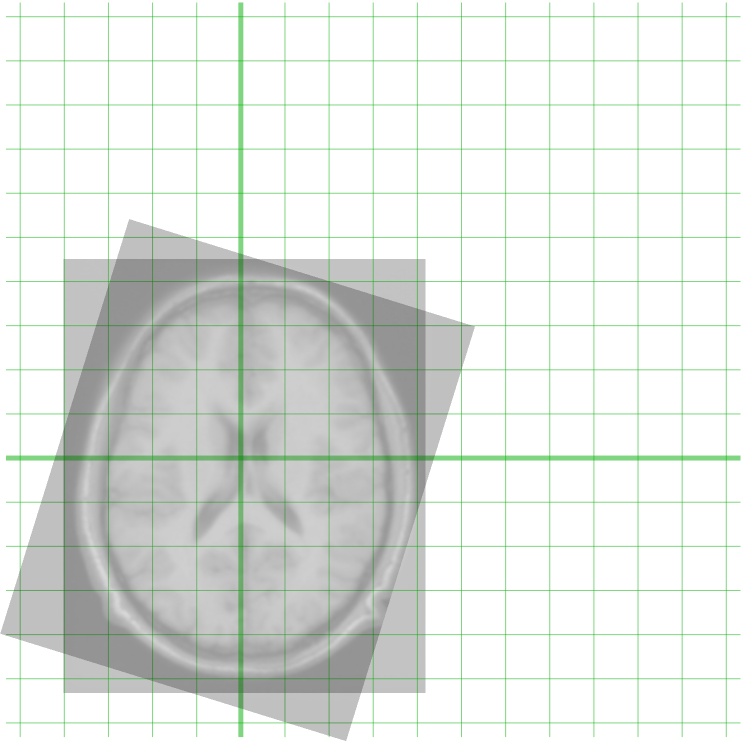 Image registration has applications in remote sensing (cartography updating), and computer vision. Due to the vast range of applications to which image registration can be applied, it is impossible to develop a general method that is optimized for all uses.
Image registration has applications in remote sensing (cartography updating), and computer vision. Due to the vast range of applications to which image registration can be applied, it is impossible to develop a general method that is optimized for all uses.
Image Alignment and Stitching: A Tutorial
Foundations and Trends in Computer Graphics and Computer Vision, 2:1-104, 2006. * B. Fischer, J. Modersitzki
Ill-posed medicine – an introduction to image registration
Inverse Problems, 24:1–19, 2008 * Barbara Zitová, Jan Flusser
Image registration methods: a survey
Image Vision Comput. 21(11): 977-1000 (2003). * C. Je and H.-M. Park
Optimized Hierarchical Block Matching for Fast and Accurate Image Registration
Signal Processing: Image Communication, Volume 28, Issue 7, pp. 779–791, August, 2013.
using
elastix
a toolbox for rigid and nonrigid registration of images.
niftyreg
a toolbox for doing near real-time robust rigid, affine (using block matching) and non-rigid image registration (using a refactored version of the free form deformation algorithm).
Image Compare
application automatically compares a pair of images and highlights their differences. This application runs in desktop and mobile phone browsers without requiring installation. {{DEFAULTSORT:Image Registration Computer vision Medical imaging
computer vision
Computer vision is an interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate tasks that the human ...
, medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to re ...
, military automatic target recognition
Automatic target recognition (ATR) is the ability for an algorithm or device to recognize targets or other objects based on data obtained from sensors.
Target recognition was initially done by using an audible representation of the received signal ...
, and compiling and analyzing images and data from satellites. Registration is necessary in order to be able to compare or integrate the data obtained from these different measurements.
Algorithm classification
Intensity-based vs feature-based
Image registration or image alignment algorithms can be classified into intensity-based and feature-based.A. Ardeshir Goshtasby2-D and 3-D Image Registration for Medical, Remote Sensing, and Industrial Applications
Wiley Press, 2005. One of the images is referred to as the ''moving'' or ''source'' and the others are referred to as the ''target'', ''fixed'' or ''sensed'' images. Image registration involves spatially transforming the source/moving image(s) to align with the target image. The reference frame in the target image is stationary, while the other datasets are transformed to match to the target. Intensity-based methods compare intensity patterns in images via correlation metrics, while feature-based methods find correspondence between image features such as points, lines, and contours. Intensity-based methods register entire images or sub-images. If sub-images are registered, centers of corresponding sub images are treated as corresponding feature points. Feature-based methods establish a correspondence between a number of especially distinct points in images. Knowing the correspondence between a number of points in images, a geometrical transformation is then determined to map the target image to the reference images, thereby establishing point-by-point correspondence between the reference and target images. Methods combining intensity-based and feature-based information have also been developed.
Transformation models
Image registration algorithms can also be classified according to the transformation models they use to relate the target image space to the reference image space. The first broad category of transformation models includeslinear transformation
In mathematics, and more specifically in linear algebra, a linear map (also called a linear mapping, linear transformation, vector space homomorphism, or in some contexts linear function) is a mapping V \to W between two vector spaces that pre ...
s, which include rotation, scaling, translation, and other affine transforms. Linear transformation
In mathematics, and more specifically in linear algebra, a linear map (also called a linear mapping, linear transformation, vector space homomorphism, or in some contexts linear function) is a mapping V \to W between two vector spaces that pre ...
s are global in nature, thus, they cannot model local geometric differences between images.
The second category of transformations allow 'elastic' or 'nonrigid' transformations. These transformations are capable of locally warping the target image to align with the reference image. Nonrigid transformations include radial basis functions A radial basis function (RBF) is a real-valued function \varphi whose value depends only on the distance between the input and some fixed point, either the origin, so that \varphi(\mathbf) = \hat\varphi(\left\, \mathbf\right\, ), or some other fixe ...
( thin-plate or surface splines, multiquadrics, and compactly-supported transformations), physical continuum models (viscous fluids), and large deformation models (diffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse are differentiable.
Definition
Given two ...
s).
Transformations are commonly described by a parametrization, where the model dictates the number of parameters. For instance, the translation of a full image can be described by a single parameter, a translation vector. These models are called parametric models. Non-parametric models on the other hand, do not follow any parameterization, allowing each image element to be displaced arbitrarily.
There are a number of programs that implement both estimation and application of a warp-field. It is a part of the SPM and AIR
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
programs.
Transformations of coordinates via the law of function composition rather than addition
Alternatively, many advanced methods for spatial normalization are building on structure preserving transformationshomeomorphism
In the mathematical field of topology, a homeomorphism, topological isomorphism, or bicontinuous function is a bijective and continuous function between topological spaces that has a continuous inverse function. Homeomorphisms are the isom ...
s and diffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse are differentiable.
Definition
Given two ...
s since they carry smooth submanifolds smoothly during transformation. Diffeomorphisms are generated in the modern field of Computational Anatomy based on flows since diffeomorphisms are not additive although they form a group, but a group under the law of function composition. For this reason, flows which generalize the ideas of additive groups allow for generating large deformations that preserve topology, providing 1-1 and onto transformations. Computational methods for generating such transformation are often called LDDMM which provide flows of diffeomorphisms as the main computational tool for connecting coordinate systems corresponding to the geodesic flows of Computational Anatomy.
There are a number of programs which generate diffeomorphic transformations of coordinates via diffeomorphic mapping including MRI Studio and MRI Cloud.org
Spatial vs frequency domain methods
Spatial methods operate in the image domain, matching intensity patterns or features in images. Some of the feature matching algorithms are outgrowths of traditional techniques for performing manual image registration, in which an operator chooses corresponding control points (CP) in images. When the number of control points exceeds the minimum required to define the appropriate transformation model, iterative algorithms likeRANSAC Random sample consensus (RANSAC) is an iterative method to estimate parameters of a mathematical model from a set of observed data that contains outliers, when outliers are to be accorded no influence on the values of the estimates. Therefore, it a ...
can be used to robustly estimate the parameters of a particular transformation type (e.g. affine) for registration of the images.
Frequency-domain methods find the transformation parameters for registration of the images while working in the transform domain. Such methods work for simple transformations, such as translation, rotation, and scaling. Applying the phase correlation Phase correlation is an approach to estimate the relative translative offset between two similar images (digital image correlation) or other data sets. It is commonly used in image registration and relies on a frequency-domain representation of t ...
method to a pair of images produces a third image which contains a single peak. The location of this peak corresponds to the relative translation between the images. Unlike many spatial-domain algorithms, the phase correlation method is resilient to noise, occlusions, and other defects typical of medical or satellite images. Additionally, the phase correlation uses the fast Fourier transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in ...
to compute the cross-correlation between the two images, generally resulting in large performance gains. The method can be extended to determine rotation and scaling differences between two images by first converting the images to log-polar coordinates.Zokai, S., Wolberg, G."Image Registration Using Log-Polar Mappings for Recovery of Large-Scale Similarity and Projective Transformations"
''IEEE Transactions on Image Processing'', vol. 14, No. 10, October, 2005. Due to properties of the
Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed ...
, the rotation and scaling parameters can be determined in a manner invariant to translation.
Single- vs multi-modality methods
Another classification can be made between single-modality and multi-modality methods. Single-modality methods tend to register images in the same modality acquired by the same scanner/sensor type, while multi-modality registration methods tended to register images acquired by different scanner/sensor types. Multi-modality registration methods are often used inmedical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to re ...
as images of a subject are frequently obtained from different scanners. Examples include registration of brain CT/ MRI images or whole body PET
A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive appearances, intelligence ...
/ CT images for tumor localization, registration of contrast-enhanced CT images against non-contrast-enhanced CT images for segmentation of specific parts of the anatomy, and registration of ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
and CT images for prostate
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and phys ...
localization in radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Rad ...
.
Automatic vs interactive methods
Registration methods may be classified based on the level of automation they provide. Manual, interactive, semi-automatic, and automatic methods have been developed. Manual methods provide tools to align the images manually. Interactive methods reduce user bias by performing certain key operations automatically while still relying on the user to guide the registration. Semi-automatic methods perform more of the registration steps automatically but depend on the user to verify the correctness of a registration. Automatic methods do not allow any user interaction and perform all registration steps automatically.Similarity measures for image registration
Image similarities are broadly used inmedical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to re ...
. An image similarity measure
In statistics and related fields, a similarity measure or similarity function or similarity metric is a real-valued function that quantifies the similarity between two objects. Although no single definition of a similarity exists, usually such meas ...
quantifies the degree of similarity between intensity patterns in two images. The choice of an image similarity measure depends on the modality of the images to be registered. Common examples of image similarity measures include cross-correlation
In signal processing, cross-correlation is a measure of similarity of two series as a function of the displacement of one relative to the other. This is also known as a ''sliding dot product'' or ''sliding inner-product''. It is commonly used f ...
, mutual information
In probability theory and information theory, the mutual information (MI) of two random variables is a measure of the mutual dependence between the two variables. More specifically, it quantifies the " amount of information" (in units such ...
, sum of squared intensity differences, and ratio image uniformity. Mutual information and normalized mutual information are the most popular image similarity measures for registration of multimodality images. Cross-correlation, sum of squared intensity differences and ratio image uniformity are commonly used for registration of images in the same modality.
Many new features have been derived for cost functions based on matching methods via large deformations have emerged in the field Computational Anatomy including
Measure matching which are pointsets or landmarks without correspondence, Curve matching and Surface matching via mathematical currents
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
and varifolds.
Uncertainty
There is a level ofuncertainty
Uncertainty refers to epistemic situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown. Uncertainty arises in partially observable ...
associated with registering images that have any spatio-temporal differences. A confident registration with a measure of uncertainty is critical for many change detection
In statistical analysis, change detection or change point detection tries to identify times when the probability distribution of a stochastic process or time series changes. In general the problem concerns both detecting whether or not a change ...
applications such as medical diagnostics.
In remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Ear ...
applications where a digital image pixel may represent several kilometers of spatial distance (such as NASA's LANDSAT
The Landsat program is the longest-running enterprise for acquisition of satellite imagery of Earth. It is a joint NASA / USGS program. On 23 July 1972, the Earth Resources Technology Satellite was launched. This was eventually renamed to La ...
imagery), an uncertain image registration can mean that a solution could be several kilometers from ground truth. Several notable papers have attempted to quantify uncertainty in image registration in order to compare results.Simonson, K., Drescher, S., Tanner, F., A Statistics Based Approach to Binary Image Registration with Uncertainty Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. 29, No. 1, January 2007Domokos, C., Kato, Z., Francos, J., Parametric estimation of affine deformations of binary images. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing ICASSP, the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, is an annual flagship conference organized of IEEE Signal Processing Society. All papers included in its proceedings have been indexed by Ei Compendex.
The first ICA ...
, 2008 However, many approaches to quantifying uncertainty or estimating deformations are computationally intensive or are only applicable to limited sets of spatial transformations.
Applications
 Image registration has applications in remote sensing (cartography updating), and computer vision. Due to the vast range of applications to which image registration can be applied, it is impossible to develop a general method that is optimized for all uses.
Image registration has applications in remote sensing (cartography updating), and computer vision. Due to the vast range of applications to which image registration can be applied, it is impossible to develop a general method that is optimized for all uses.
Medical image
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues ( physiology). Medical imaging seeks to r ...
registration (for data of the same patient taken at different points in time such as change detection or tumor monitoring) often additionally involves ''elastic'' (also known as ''nonrigid'') registration to cope with deformation of the subject (due to breathing, anatomical changes, and so forth). Nonrigid registration of medical images can also be used to register a patient's data to an anatomical atlas, such as the Talairach atlas for neuroimaging.
In astrophotography
Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object (the Moon) was taken in 1840, but it was no ...
image alignment and stacking are often used to increase the signal to noise ratio for faint objects. Without stacking it may be used to produce a timelapse of events such as a planet's rotation of a transit across the Sun. Using control points (automatically or manually entered), the computer performs transformations on one image to make major features align with a second or multiple images. This technique may also be used for images of different sizes, to allow images taken through different telescopes or lenses to be combined.
In cryo-TEM
Transmission electron cryomicroscopy (CryoTEM), commonly known as cryo-EM, is a form of cryogenic electron microscopy, more specifically a type of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) where the sample is studied at cryogenic temperatures (genera ...
instability causes specimen drift and many fast acquisitions with accurate image registration is required to preserve high resolution and obtain high signal to noise images. For low SNR data, the best image registration is achieved by cross-correlating all permutations of images in an image stack.
Image registration is an essential part of panoramic image creation. There are many different techniques that can be implemented in real time and run on embedded devices like cameras and camera-phones.
See also
* Computational Anatomy *Correspondence problem
The correspondence problem refers to the problem of ascertaining which parts of one image correspond to which parts of another image, where differences are due to movement of the camera, the elapse of time, and/or movement of objects in the photo ...
* Digital image correlation and tracking
* Georeferencing Georeferencing means that the internal coordinate system of a map or aerial photo image can be related to a geographic coordinate system. The relevant coordinate transforms are typically stored within the image file (GeoPDF and GeoTIFF are example ...
* Image correlation
* Image rectification Image rectification is a transformation process used to project images onto a common image plane. This process has several degrees of freedom and there are many strategies for transforming images to the common plane. Image rectification is used in ...
* Inverse consistency In image registration, inverse consistency measures the consistency of mappings between images produced by a image registration, registration algorithm. The inverse consistency error, introduced by Christiansen and Johnson in 2001, quantifies the di ...
* Point set registration
In computer vision, pattern recognition, and robotics, point-set registration, also known as point-cloud registration or scan matching, is the process of finding a spatial transformation (''e.g.,'' scaling, rotation and translation) that aligns ...
* Rubbersheeting
* Spatial normalization
In neuroimaging, spatial normalization is an image processing step, more specifically an image registration method. Human brains differ in size and shape, and one goal of spatial normalization is to deform human brain scans so one location in ...
* Spatial verification
References
External links
*Richard SzeliskiImage Alignment and Stitching: A Tutorial
Foundations and Trends in Computer Graphics and Computer Vision, 2:1-104, 2006. * B. Fischer, J. Modersitzki
Ill-posed medicine – an introduction to image registration
Inverse Problems, 24:1–19, 2008 * Barbara Zitová, Jan Flusser
Image registration methods: a survey
Image Vision Comput. 21(11): 977-1000 (2003). * C. Je and H.-M. Park
Optimized Hierarchical Block Matching for Fast and Accurate Image Registration
Signal Processing: Image Communication, Volume 28, Issue 7, pp. 779–791, August, 2013.
using
Matlab
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementat ...
.
elastix
a toolbox for rigid and nonrigid registration of images.
niftyreg
a toolbox for doing near real-time robust rigid, affine (using block matching) and non-rigid image registration (using a refactored version of the free form deformation algorithm).
Image Compare
application automatically compares a pair of images and highlights their differences. This application runs in desktop and mobile phone browsers without requiring installation. {{DEFAULTSORT:Image Registration Computer vision Medical imaging