
was the founder and first ''
shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamak ...
'' of the
Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
of
Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the
Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ...
in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord
Oda Nobunaga and fellow
Oda subordinate
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Cour ...
. The son of a minor
daimyo, Ieyasu once lived as a hostage under daimyo
Imagawa Yoshimoto
was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) in the Sengoku period Japan. Based in Suruga Province, he was known as . he was one of the three ''daimyōs'' that dominated the Tōkaidō region.
He died in 1560 while marching to Kyoto to become S ...
on behalf of his father. He later succeeded as daimyo after his father's death, serving as a vassal and general of the
Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, severa ...
,
and building up his strength under
Oda Nobunaga.
After Oda Nobunaga's death, Ieyasu was briefly a rival of
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Cour ...
, before declaring his allegiance and fighting on his behalf. Under Toyotomi, Ieyasu was relocated to the
Kanto
Kantō (Japanese)
Kanto is a simplified spelling of , a Japanese word, only omitting the diacritics.
In Japan
Kantō may refer to:
*Kantō Plain
*Kantō region
*Kantō-kai, organized crime group
*Kanto (Pokémon), a geographical region in the ' ...
plains in eastern Japan, away from the Toyotomi power base in
Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of ...
. He built
his castle in the fishing village of
Edo (now
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
). He became the most powerful daimyo and the most senior officer under the
Toyotomi
The was a Japanese clan that ruled over the Japanese before the Edo period.
Unity and conflict
The most influential figure within the Toyotomi was Toyotomi Hideyoshi, one of the three "unifiers of Japan". Oda Nobunaga was another primary u ...
regime. Ieyasu preserved his strength in Toyotomi's failed attempt to
conquer Korea. After Toyotomi's death, Ieyasu seized power in 1600, after the
Battle of Sekigahara.
He received appointment as ''shōgun'' in 1603, and voluntarily abdicated from office in 1605, but remained in power until his death in 1616. He implemented a set of careful rules known as the ''
bakuhan'' system, designed to keep the daimyo and samurai in check under the Tokugawa Shogunate.
Background
During the
Muromachi period
The is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate (''Muromachi bakufu'' or ''Ashikaga bakufu''), which was officially established in 1338 by t ...
, the
Matsudaira clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan that descended from the Minamoto clan. It originated in and took its name from Matsudaira village, in Mikawa Province (modern-day Aichi Prefecture). During the Sengoku period, the chieftain of the main line of t ...
controlled a portion of
Mikawa Province
was an old province in the area that today forms the eastern half of Aichi Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Mikawa''" in . Its abbreviated form name was . Mikawa bordered on Owari, Mino, Shinano, and Tōtōmi Provinces.
Mi ...
(the eastern half of modern
Aichi Prefecture). Ieyasu's father,
Matsudaira Hirotada
was the lord of Okazaki Castle in Mikawa province, Japan during the Sengoku Period of the 16th century.
He is best known for being the father of Tokugawa Ieyasu, founder of the Tokugawa Shogunate.
Biography
Hirotada was the son of Matsudaira ...
, was a minor local warlord based at
Okazaki Castle
is a Japanese castle located in Okazaki, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. At the end of the Edo period, Okazaki Castle was home to the Honda clan, ''daimyō'' of Okazaki Domain, but the castle is better known for its association with Tokugawa Ieyasu an ...
who controlled a portion of the
Tōkaidō highway linking
Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin, Keihanshin metropolitan area along wi ...
with the eastern provinces. His territory was sandwiched between stronger and predatory neighbors, including the
Imagawa clan
was a Japanese samurai clan that claimed descent from the Seiwa Genji by way of the Kawachi Genji. It was a branch of the Minamoto clan by the Ashikaga clan.
Origins
Ashikaga Kuniuji, grandson of Ashikaga Yoshiuji, established himself in ...
based in
Suruga Province to the east and the
Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, severa ...
to the west. Hirotada's main enemy was
Oda Nobuhide
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and magistrate of the Sengoku period known as "Tiger of Owari" and also the father of Oda Nobunaga the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. Nobuhide was a deputy ''shugo'' (Shugodai) of lower Owari Province and head of the ...
, the father of
Oda Nobunaga.
Early life (1543–1556)

Tokugawa Ieyasu was born in
Okazaki Castle
is a Japanese castle located in Okazaki, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. At the end of the Edo period, Okazaki Castle was home to the Honda clan, ''daimyō'' of Okazaki Domain, but the castle is better known for its association with Tokugawa Ieyasu an ...
on the 26th day of the twelfth month of the eleventh year of
Tenbun
, also known as Tenmon, was a after ''Kyōroku'' and before '' Kōji''. This period spanned from July 1532 through October 1555. The reigning emperor was .
Change of era
* 1532 : At the request of Ashikaga Yoshiharu, the 12th ''shōgun'' of the ...
, according to the
Japanese calendar
Japanese calendar types have included a range of official and unofficial systems. At present, Japan uses the Gregorian calendar together with year designations stating the year of the reign of the current Emperor. The written form starts with t ...
. Originally named , he was the son of , the
daimyo of
Mikawa of the
Matsudaira clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan that descended from the Minamoto clan. It originated in and took its name from Matsudaira village, in Mikawa Province (modern-day Aichi Prefecture). During the Sengoku period, the chieftain of the main line of t ...
, and , the daughter of a neighbouring
samurai lord, . His mother and father were step-siblings. They were 17 and 15 years old, respectively, when Takechiyo was born.
In the year of Takechiyo's birth, the Matsudaira clan was split. In 1543, Hirotada's uncle, Matsudaira Nobutaka defected to the
Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, severa ...
. This gave
Oda Nobuhide
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and magistrate of the Sengoku period known as "Tiger of Owari" and also the father of Oda Nobunaga the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. Nobuhide was a deputy ''shugo'' (Shugodai) of lower Owari Province and head of the ...
the confidence to attack Okazaki. Soon afterwards, Hirotada's father-in-law died, and his heir,
Mizuno Nobumoto
was a daimyō of Japan's Sengoku period. He was a son of Mizuno Tadamasa, and brother of Mizuno Tadashige. He is Tokugawa Ieyasu's uncle through Matsudaira Hirotada's marriage to his sister, Odai no Kata.
In 1542, Nobumoto sided with Oda Nobuhid ...
, revived the clan's traditional enmity against the Matsudaira and declared for Oda Nobuhide as well. As a result, Hirotada divorced
Odai-no-kata and sent her back to her family.
Hirotada later remarried to different wives, and Takechiyo eventually had 11 half-brothers and sisters.
Hostage life
As Oda Nobuhide continued to attack Okazaki, Hirotada turned to his powerful eastern neighbor,
Imagawa Yoshimoto
was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) in the Sengoku period Japan. Based in Suruga Province, he was known as . he was one of the three ''daimyōs'' that dominated the Tōkaidō region.
He died in 1560 while marching to Kyoto to become S ...
for assistance. Yoshimoto agreed to an alliance under the condition that Hirotada send his young heir to
Sunpu Domain
was a feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo period Japan. The domain centered at Sunpu Castle is what is now the Aoi-ku, Shizuoka. From 1869 it was briefly called .
History
During the Muromachi period, Sunpu was the capital of the ...
as a hostage.
Oda Nobuhide
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and magistrate of the Sengoku period known as "Tiger of Owari" and also the father of Oda Nobunaga the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. Nobuhide was a deputy ''shugo'' (Shugodai) of lower Owari Province and head of the ...
learned of this arrangement and had Takechiyo abducted.
Takechiyo was five years old at the time.
[ Screech, Timon (2006). ''Secret Memoirs of the Shoguns: Isaac Titsingh and Japan, 1779–1822''. London: RoutledgeCurzon. , pp. 85, 234; n.b., Screech explains
]Minamoto-no-Ieyasu was born in ''Tenbun'' 11, on the 26th day of the 12th month (1542) and he died in ''Genna'' 2, on the 17th day of the 4th month (1616); and thus, his contemporaries would have said that he lived 75 years. In this period, children were considered one year old at birth and became two the following New Year's Day; and all people advanced a year that day, not on their actual birthday.
Nobuhide threatened to execute Takechiyo unless his father severed all ties with the
Imagawa clan
was a Japanese samurai clan that claimed descent from the Seiwa Genji by way of the Kawachi Genji. It was a branch of the Minamoto clan by the Ashikaga clan.
Origins
Ashikaga Kuniuji, grandson of Ashikaga Yoshiuji, established himself in ...
. However, Hirotada refused, stating that sacrificing his own son would show his seriousness in his pact with the Imagawa. Despite this refusal, Nobuhide chose not to kill Takechiyo, but instead held him hostage for the next three years at the
Honshōji Temple in
Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a population of 2.3million in 2020. Located on the Pacific coast in central Honshu, it is the capital and the most po ...
. It is said that
Oda Nobunaga met Takechiyo at this place, when Takechiyo was 6 years old, and Nobunaga was 14 at that time.
In 1549, when Takechiyo was 6,
his father Hirotada was murdered by his own vassals, who had been bribed by the Oda clan. At about the same time, Oda Nobuhide died during an epidemic. Nobuhide's death dealt a heavy blow to the Oda clan.
In 1551, an army under the command of
Imagawa Sessai laid siege to the castle where
Oda Nobuhiro
was the eldest son of Oda Nobuhide. After Nobuhiro's father took Anjo Castle in Mikawa Province in 1540, the castle was given to Nobuhiro. During 1551, Nobuhiro was trapped by the Imagawa clan, but was saved when Oda Nobunaga handed over o ...
, Nobuhide's illegitimate eldest son was living. Nobuhiro was trapped by the Imagawa clan but was saved by Oda Nobunaga, Nobuhide's second son and heir, through negotiations. Sessai made an agreement with Nobunaga to take Takechiyo back to Imagawa, and he agreed. So Takechiyo (now nine years old) was taken as a hostage to Sunpu. At Sunpu, he remained a hostage but was treated fairly well as a potentially useful future ally of the Imagawa clan until 1556 when he was 14 years old.
Service under Yoshimoto (1556–1560)
In 1556, Takechiyo officially came of age, with
Imagawa Yoshimoto
was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) in the Sengoku period Japan. Based in Suruga Province, he was known as . he was one of the three ''daimyōs'' that dominated the Tōkaidō region.
He died in 1560 while marching to Kyoto to become S ...
presiding over his ''
genpuku
is a Japanese coming-of-age ceremony which dates back to Japan's classical Nara Period (710–794 AD). /sup> This ceremony marked the transition from child to adult status and the assumption of adult responsibilities. The age of participat ...
'' ceremony. Following tradition, he changed his name from Matsudaira Takechiyo to . He was also briefly allowed to visit
Okazaki to pay his respects to the tomb of his father, and receive the homage of his nominal retainers, led by the ''
karō
were top-ranking samurai officials and advisors in service to the ''daimyōs'' of feudal Japan.
Overview
In the Edo period, the policy of ''sankin-kōtai'' (alternate attendance) required each ''daimyō'' to place a ''karō'' in Edo and anothe ...
''
Torii Tadayoshi.
One year later, at the age of 15 (according to
East Asian age reckoning
Countries in the East Asian cultural sphere (China, Korea, Japan, Vietnam, and their diasporas) have traditionally used specific methods of reckoning a person's numerical age based not on their birthday but the calendar year, and what age one is ...
), he married his first wife,
Lady Tsukiyama
Lady Tsukiyama or (d. 9 September 1579) was a Japanese noble lady and aristocrat from the Sengoku period. She was the chief consort of Tokugawa Ieyasu, the ''daimyō'' who would become the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunat ...
, a relative of Imagawa Yoshimoto, and changed his name again to . A year later, their son,
Matsudaira Nobuyasu
was the eldest son of Matsudaira Ieyasu. His ''tsūshō'' ("common name") was . He was called also , because he had become the lord of in 1570. Because he was a son of Tokugawa Ieyasu, he is often referred to, retroactively, as .
Biography
No ...
, was born. He was then allowed to return to
Mikawa Province
was an old province in the area that today forms the eastern half of Aichi Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Mikawa''" in . Its abbreviated form name was . Mikawa bordered on Owari, Mino, Shinano, and Tōtōmi Provinces.
Mi ...
. There, the Imagawa then ordered him to fight the
Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, severa ...
in a series of battles.
Motoyasu fought his first battle in 1558 at the
siege of Terabe
The siege of Terabe Castle took place in 1558 in feudal Japan. Terabe Castle was a possession of the Ogasawara clan of Mikawa province. The Siege of Terabe Castle was Matsudaira Motoyasu's first battle, who would later change his name to Tokug ...
. The lord of Terabe,
Suzuki Shigeteru, betrayed the Imagawa by defecting to
Oda Nobunaga. This was nominally within Matsudaira territory, so Imagawa Yoshimoto entrusted the campaign to Motoyasu and his retainers from Okazaki. Motoyasu led the attack in person, but after taking the outer defences, he burned the main castle and withdrew. As anticipated, the Oda forces attacked his rear lines, but Motoyasu was prepared and drove off the Oda army.
He then succeeded in delivering supplies in the siege of Odaka a year later. Odaka was the only one of five disputed frontier forts under attack by the Oda clan which remained in Imagawa hands. Motoyasu launched diversionary attacks against the two neighboring forts, and when the garrisons of the other forts went to their assistance, Motoyasu's supply column was able to reach Odaka.
Death of Yoshimoto
By 1559 the leadership of the
Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, severa ...
had passed to
Oda Nobunaga. In 1560,
Imagawa Yoshimoto
was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) in the Sengoku period Japan. Based in Suruga Province, he was known as . he was one of the three ''daimyōs'' that dominated the Tōkaidō region.
He died in 1560 while marching to Kyoto to become S ...
leading a large army of 25,000 men, invaded Oda clan territory. Motoyasu was assigned a separate mission to capture the stronghold of
Marune. As a result, he and his men were not present at the
Battle of Okehazama
The took place in June 1560 in Owari Province, located in today's Aichi Prefecture. In this battle, the heavily outnumbered Oda clan troops commanded by Oda Nobunaga defeated Imagawa Yoshimoto and established himself as one of the front-running ...
where Yoshimoto was killed in Nobunaga's surprise assault.
[
]
Early Rise (1560–1570)

Alliance with Nobunaga
With Imagawa Yoshimoto
was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) in the Sengoku period Japan. Based in Suruga Province, he was known as . he was one of the three ''daimyōs'' that dominated the Tōkaidō region.
He died in 1560 while marching to Kyoto to become S ...
dead, and the Imagawa clan
was a Japanese samurai clan that claimed descent from the Seiwa Genji by way of the Kawachi Genji. It was a branch of the Minamoto clan by the Ashikaga clan.
Origins
Ashikaga Kuniuji, grandson of Ashikaga Yoshiuji, established himself in ...
in a state of confusion, Motoyasu used the opportunity to assert his independence and marched his men back into the abandoned Okazaki Castle
is a Japanese castle located in Okazaki, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. At the end of the Edo period, Okazaki Castle was home to the Honda clan, ''daimyō'' of Okazaki Domain, but the castle is better known for its association with Tokugawa Ieyasu an ...
and reclaimed his ancestral seat.Lady Tsukiyama
Lady Tsukiyama or (d. 9 September 1579) was a Japanese noble lady and aristocrat from the Sengoku period. She was the chief consort of Tokugawa Ieyasu, the ''daimyō'' who would become the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunat ...
, and infant son, Nobuyasu, were held hostage in Sunpu by Imagawa Ujizane
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' who lived in the Sengoku through early Edo periods. He was the tenth head of the Imagawa clan, and was a son of Imagawa Yoshimoto and the father of Imagawa Norimochi and Shinagawa Takahisa.
Biography
Ujizane was ...
, Yoshimoto's heir.
In 1561, Motoyasu openly broke with the Imagawa and captured the fortress of Kaminogō. Kaminogō was held by Udono Nagamochi. Resorting to stealth, Motoyasu forces under Hattori Hanzō
or ''Second Hanzō'', nicknamed , was a famous Ninja of the Sengoku era, who served the Tokugawa clan as a ninja, credited with saving the life of Tokugawa Ieyasu and then helping him to become the ruler of united Japan. He is often a subje ...
attacked under cover of darkness, setting fire to the castle, and capturing two of Udono's sons, whom he used as hostages to exchange for his wife and son.[
In 1563, ]Matsudaira Nobuyasu
was the eldest son of Matsudaira Ieyasu. His ''tsūshō'' ("common name") was . He was called also , because he had become the lord of in 1570. Because he was a son of Tokugawa Ieyasu, he is often referred to, retroactively, as .
Biography
No ...
, the first son of Motoyasu, was married to Oda Nobunaga's daughter Tokuhime Tokuhime may refer to:
* Tokuhime (Oda) (徳姫) (1559–1636), daughter of Oda Nobunaga; also known as Gotokuhime
* Tokuhime (Tokugawa) (督姫) (1565–1615), daughter of Tokugawa Ieyasu
* (登久姫) (1576–1607), daughter of Matsudaira ...
.
Unification of Mikawa
In the February 1563, Matsudaira Motoyasu changed his name to Matsudaira Ieyasu. For the next few years Ieyasu was occupied with reforming the Matsudaira clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan that descended from the Minamoto clan. It originated in and took its name from Matsudaira village, in Mikawa Province (modern-day Aichi Prefecture). During the Sengoku period, the chieftain of the main line of t ...
and pacifying Mikawa. He also strengthened his key vassals by awarding them land and castles. These vassals included Ōkubo Tadayo
was a samurai general in the service of Tokugawa Ieyasu in the Azuchi–Momoyama period, subsequently becoming a ''Daimyō'' of Odawara Domain in early Edo period, Japan.
Biography
Ōkubo Tadayo was the eldest son of Ōkubo Tadakazu, a her ...
, Ishikawa Kazumasa
was a Japanese notable retainer under Tokugawa Ieyasu, who served him since childhood, when they were both hostages under the Imagawa in 1551.
Biography
Kazumasa, also accompanied Ieyasu in the Siege of Terabe 1558, and later at Siege of Mar ...
, Kōriki Kiyonaga
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' during the Azuchi–Momoyama and Edo periods. A native of Mikawa Province, Kiyonaga served the Tokugawa clan during its battles, until 1600. he was one of Ieyasu's "three magistrates" (san-bugyō).
Biography
Born i ...
, Sakai Tadatsugu
was one of the most favored and most successful military commanders serving Tokugawa Ieyasu in the late-Sengoku period. He is regarded as one of the Four Guardians of the Tokugawa (''Tokugawa-Shitennō''). along with Honda Tadakatsu, Ii Nao ...
, Honda Shigetsugu
(1529 – August 9, 1596), also known as , was a Japanese samurai of the Sengoku period through Azuchi-Momoyama Period, who served the Tokugawa clan. He served as one of Ieyasu's "three magistrates".
Biography
He was known as Hachizo, Sakujur ...
, Amano Yasukage
was a Japanese samurai of the Sengoku period and early Edo period. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Amano Yasukage"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 26.
Who served the Tokugawa clan. He served as one of Ieyasu's "three magistrates".
Biography
Ya ...
and Hattori Hanzō
or ''Second Hanzō'', nicknamed , was a famous Ninja of the Sengoku era, who served the Tokugawa clan as a ninja, credited with saving the life of Tokugawa Ieyasu and then helping him to become the ruler of united Japan. He is often a subje ...
.
During this period, the Matsudaira clan also faced a threat from a different source. Mikawa was a major center for the Ikkō-ikki
were rebellious or autonomous groups of people that were formed in several regions of Japan in the 15th-16th centuries; backed up by the power of the Jōdo Shinshū sect of Buddhism, they opposed the rule of governors or ''daimyō''. Mainly co ...
movement, where peasants banded together with militant monks under the Jōdo Shinshū sect, and rejected the traditional feudal social order. Ieyasu undertook several battles to suppress this movement in his territories, including the Battle of Azukizaka (1564)
The or took place in 1564, when Matsudaira Motoyasu (later renamed Tokugawa Ieyasu), sought to destroy the growing threat of the Ikkō-ikki, a league of monks, samurai, and peasants who were strongly against samurai rule.
Background
Tensions bet ...
.[
]
Battle of Batogahara
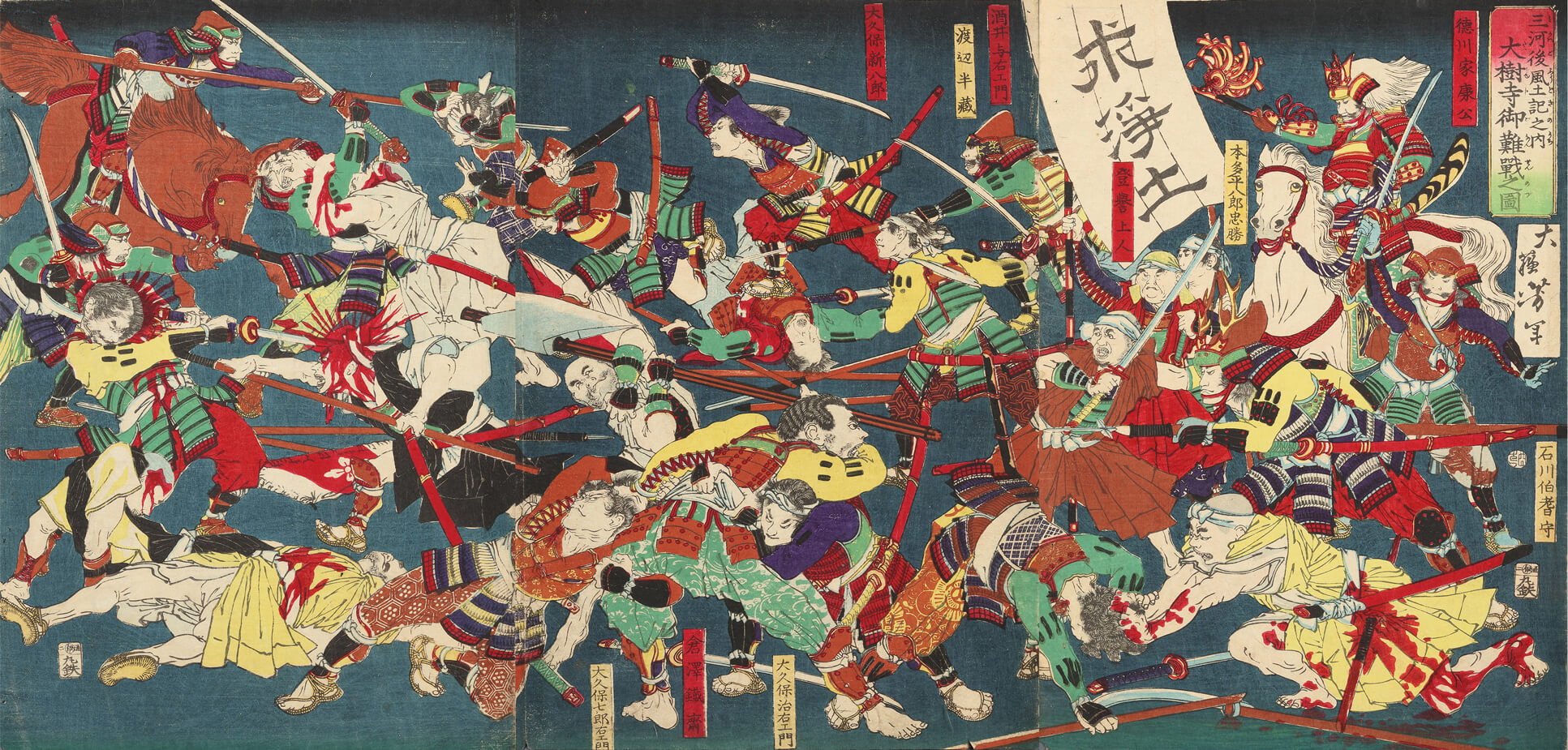 On January 15, 1564, Ieyasu had decided to concentrate his forces to attack and eliminate the
On January 15, 1564, Ieyasu had decided to concentrate his forces to attack and eliminate the Ikkō-ikki
were rebellious or autonomous groups of people that were formed in several regions of Japan in the 15th-16th centuries; backed up by the power of the Jōdo Shinshū sect of Buddhism, they opposed the rule of governors or ''daimyō''. Mainly co ...
from Mikawa. In the Ikkō-ikki ranks were some of Ieyasu's vassals, like Honda Masanobu
was a commander and ''daimyō'' in the service of Tokugawa Ieyasu in Japan during the Azuchi-Momoyama and Edo periods.
In 1563, when an uprising against Ieyasu occurred in Mikawa Province, Masanobu took the side of the peasants against Ieyasu ...
and Natsume Yoshinobu, who had deserted him for the Ikkō-ikki rebellion out of religious sympathy.
Ieyasu was fighting in the front line and was nearly killed when struck by several bullets which did not penetrate his armour. Both sides were using the new gunpowder weapons which the Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
had introduced to Japan just 20 years earlier. At the end of battle, the Ikkō-ikki were defeated.
By 1565, Ieyasu became master of all of Mikawa Province
was an old province in the area that today forms the eastern half of Aichi Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Mikawa''" in . Its abbreviated form name was . Mikawa bordered on Owari, Mino, Shinano, and Tōtōmi Provinces.
Mi ...
.
Tokugawa clan
In 1567, Ieyasu started the family name "Tokugawa", finally making his name to Tokugawa Ieyasu. As he was a member of the Matsudaira clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan that descended from the Minamoto clan. It originated in and took its name from Matsudaira village, in Mikawa Province (modern-day Aichi Prefecture). During the Sengoku period, the chieftain of the main line of t ...
, he claimed descent from the Seiwa Genji
The is a line of the Japanese Minamoto clan that is descended from Emperor Seiwa, which is the most successful and powerful line of the clan. Many of the most famous Minamoto warriors, including Minamoto no Yoshiie, Minamoto no Yoritomo, the fo ...
branch of the Minamoto clan
was one of the surnames bestowed by the Emperors of Japan upon members of the imperial family who were excluded from the line of succession and demoted into the ranks of the nobility from 1192 to 1333. The practice was most prevalent during th ...
. However, there was no proof the Matsudaira clan are descendants of Emperor Seiwa
was the 56th emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 清和天皇 (56)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession.
Seiwa's reign spanned the years from 858 through 876.He was also the predecessor of Takeda ryu.
T ...
. Yet, his surname was changed with the permission of the Imperial Court, after writing a petition, and he was bestowed the courtesy title ''Mikawa-no-kami'' (Lord of Mikawa) and the court rank of '. Though the Tokugawa could claim some modicum of freedom, they were very much subject to the requests of Oda Nobunaga. Ieyasu remained an ally of Nobunaga and his Mikawa soldiers were part of Nobunaga's army which captured Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin, Keihanshin metropolitan area along wi ...
in 1568. At the same time, Ieyasu was eager to expand eastward to Tōtōmi Province
was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today western Shizuoka Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Tōtōmi''" in . Tōtōmi bordered on Mikawa, Suruga and Shinano Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was . The or ...
. Ieyasu and Takeda Shingen
, of Kai Province, was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' in feudal Japan. Known as the "Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful daimyō with exceptional military prestige in the late stage of the Sengoku period.
Shingen was a warlord of great ...
, the head of the Takeda clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan active from the late Heian period until the late 16th century. The clan was historically based in Kai Province in present-day Yamanashi Prefecture. The clan reached its greatest influence under the rule of Taked ...
in Kai Province, made an alliance for the purpose of conquering all the Imagawa
was a Japanese samurai clan that claimed descent from the Seiwa Genji by way of the Kawachi Genji. It was a branch of the Minamoto clan by the Ashikaga clan.
Origins
Ashikaga Kuniuji, grandson of Ashikaga Yoshiuji, established himself in t ...
territory.
Tōtōmi campaign
In 1569, Ieyasu's troops penetrated into Tōtōmi Province
was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today western Shizuoka Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Tōtōmi''" in . Tōtōmi bordered on Mikawa, Suruga and Shinano Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was . The or ...
. Meanwhile, Takeda Shingen
, of Kai Province, was a pre-eminent ''daimyō'' in feudal Japan. Known as the "Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful daimyō with exceptional military prestige in the late stage of the Sengoku period.
Shingen was a warlord of great ...
's troops captured Suruga Province (including the Imagawa
was a Japanese samurai clan that claimed descent from the Seiwa Genji by way of the Kawachi Genji. It was a branch of the Minamoto clan by the Ashikaga clan.
Origins
Ashikaga Kuniuji, grandson of Ashikaga Yoshiuji, established himself in t ...
capital of Sunpu). Imagawa Ujizane
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' who lived in the Sengoku through early Edo periods. He was the tenth head of the Imagawa clan, and was a son of Imagawa Yoshimoto and the father of Imagawa Norimochi and Shinagawa Takahisa.
Biography
Ujizane was ...
fled to Kakegawa Castle
is a ''hirayama''-style Japanese castle. It was the seat of various ''fudai daimyō'' clans who ruled over Kakegawa Domain, Tōtōmi Province, in what is now central Kakegawa, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan.
Background
Kakegawa Castle is located ...
, which led to Ieyasu laying siege to Kakegawa. Ieyasu then negotiated with Ujizane, promising that if Ujizane should surrender himself and the remainder of Tōtōmi, Ieyasu would assist Ujizane in regaining Suruga. Ujizane had nothing left to lose, and Ieyasu immediately ended his alliance with , instead making a new alliance with Takeda's enemy to the north, Uesugi Kenshin
, later known as was a Japanese ''daimyō''. He was born in Nagao clan, and after adoption into the Uesugi clan, ruled Echigo Province in the Sengoku period of Japan. He was one of the most powerful ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku period. Known a ...
of the Uesugi clan
The is a Japanese samurai clan which was at its peak one of the most powerful during the Muromachi and Sengoku periods (14th to 17th centuries). Appert, Georges. (1888) ''Ancien Japon,'' p. 79./ref> At its height, the clan had three main branch ...
. Through these political manipulations, Ieyasu gained the support of the samurai of Tōtōmi Province.Hamamatsu
is a city located in western Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. the city had an estimated population of 791,707 in 340,591 households, making it the prefecture's largest city, and a population density of . The total area of the site was .
Overview
Ha ...
as the capital of his territory, placing his son Nobuyasu in charge of Okazaki.
Ieyasu and Nobunaga (1570-1582)
Battle of Anegawa
In 1570, Azai Nagamasa
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku period known as the brother-in-law and enemy of Oda Nobunaga. Nagamasa was head of the Azai clan seated at Odani Castle in northern Ōmi Province and married Nobunaga's sister Oichi in 1564, fathering ...
, the brother-in-law of Oda Nobunaga, broke his alliance with the Oda clan
The is a Japanese samurai family who were daimyo and an important political force in the unification of Japan in the mid-16th century. Though they had the climax of their fame under Oda Nobunaga and fell from the spotlight soon after, severa ...
during the siege of Kanegasaki. Soon Nobunaga was ready to punish Nagamasa for his treachery. Ieyasu led 5,000 of his men to support Nobunaga at the battle.[ The ]Battle of Anegawa
The Sengoku period (30 July 1570) occurred near Lake Biwa in Ōmi Province, Japan, between the allied forces of Oda Nobunaga and Tokugawa Ieyasu, against the combined forces of the Azai and Asakura clans._It_is_notable_as_the_first_battle ...
occurred near Lake Biwa
is the largest freshwater lake in Japan, located entirely within Shiga Prefecture (west-central Honshu), northeast of the former capital city of Kyoto. Lake Biwa is an ancient lake, over 4 million years old. It is estimated to be the 13th ol ...
in Ōmi Province
was a province of Japan, which today comprises Shiga Prefecture. It was one of the provinces that made up the Tōsandō circuit. Its nickname is . Under the '' Engishiki'' classification system, Ōmi was ranked as one of the 13 "great countr ...
. The allied forces of Oda Nobunaga and Tokugawa Ieyasu defeated the combined forces of the Azai clan
The , also rendered as Asai, was a Japanese clan during the Sengoku period.
History
The Azai was a line of ''daimyōs'' (feudal lords) seated at Odani Castle in northeastern Ōmi Province, located within present day Nagahama, Shiga Prefecture ...
and Asakura clan
The is a Japanese kin group. Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d'histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003).html" ;"title="DF 7 of 80">"Asakura", ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 3 DF_7_of_80">"Asa_...
,_and_saw_Nobunaga's_prodigious_use_of_ DF_7_of_80">"Asa_...
,_and_saw_Nobunaga's_prodigious_use_of_firearms">DF_7_of_80/nowiki>">DF_7_of_80">"Asa_...


 Immediately after the victory at Sekigahara, Ieyasu redistributed land to the vassals who had served him. Ieyasu left some western daimyo unharmed, such as the
Immediately after the victory at Sekigahara, Ieyasu redistributed land to the vassals who had served him. Ieyasu left some western daimyo unharmed, such as the  On March 24, 1603, Tokugawa Ieyasu received the title of ''
On March 24, 1603, Tokugawa Ieyasu received the title of ''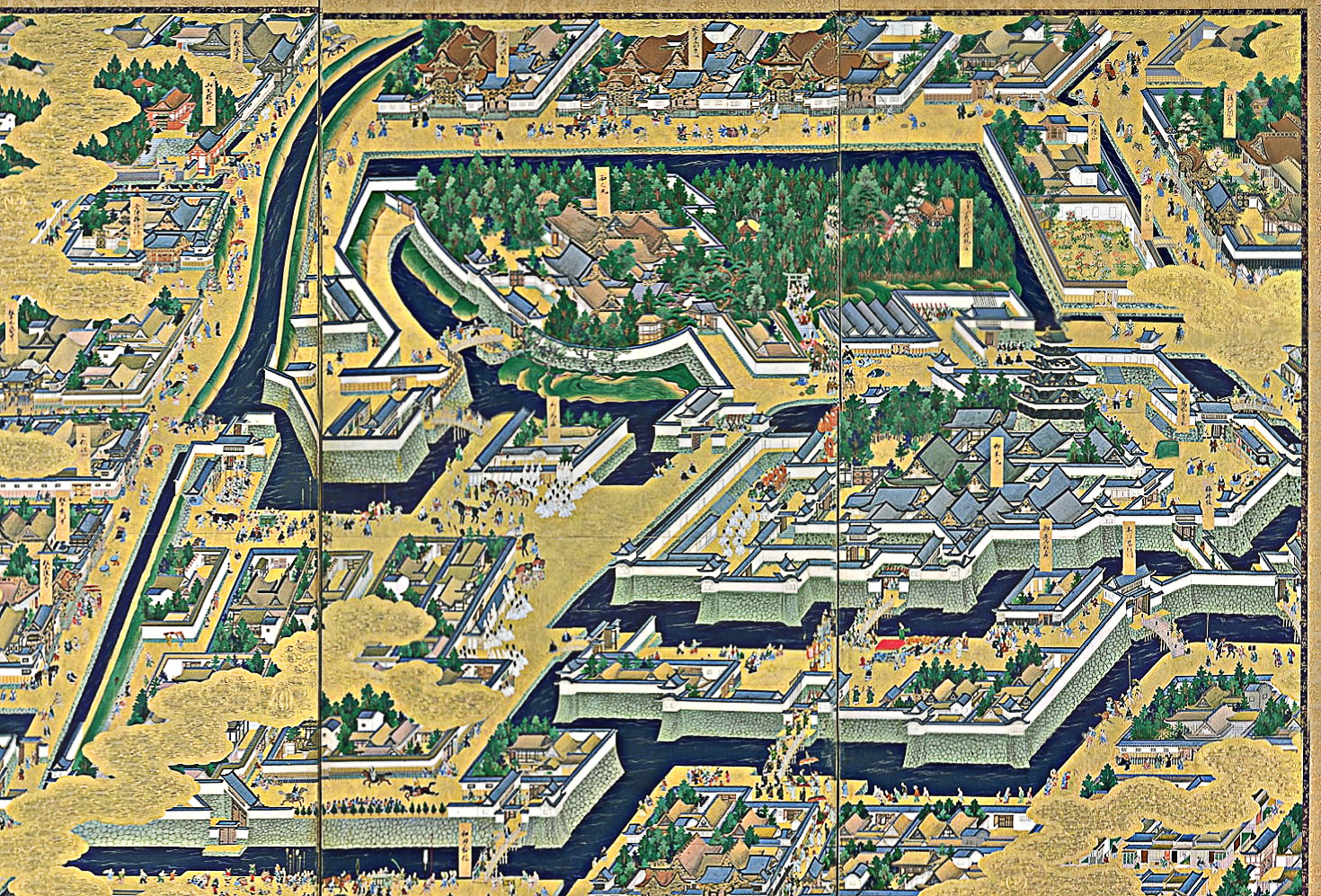

 As Ōgosho, Ieyasu also supervised diplomatic affairs with the
As Ōgosho, Ieyasu also supervised diplomatic affairs with the  The last remaining threat to Ieyasu's rule was
The last remaining threat to Ieyasu's rule was 
 Tokugawa Ieyasu had a number of qualities that enabled him to rise to power. He was both careful and bold—at the right times, and in the right places. Calculating and subtle, Ieyasu switched alliances when he thought he would benefit from the change. He allied with the
Tokugawa Ieyasu had a number of qualities that enabled him to rise to power. He was both careful and bold—at the right times, and in the right places. Calculating and subtle, Ieyasu switched alliances when he thought he would benefit from the change. He allied with the