Icelandic Army on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 * Military missions:
** within
* Military missions:
** within
Icelandic Coast Guard
Icelandic National Police
Iceland Air Defence System
Ministry of Justice and Ecclesiastical Affairs
Ministry for Foreign Affairs
{{Improve categories, date=December 2021

Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
's defence forces consist of the Icelandic Coast Guard
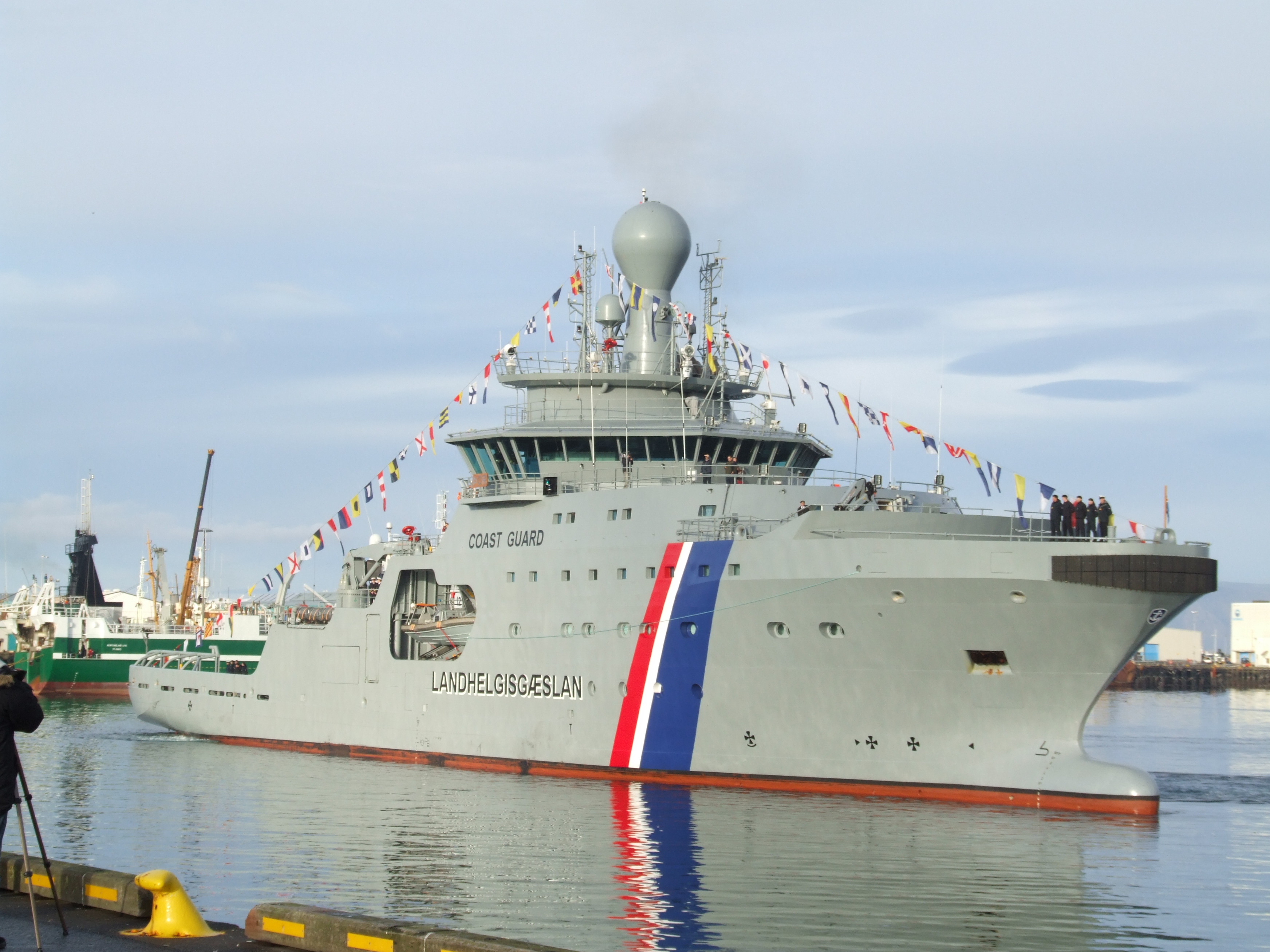
The Icelandic Coast Guard (, or simply ) is the Icelandic defence service responsible for search and rescue, maritime safety and security surveillance, and law enforcement in the seas surrounding Iceland. The Coast Guard maintains the Iceland ...
, which patrols Icelandic waters and monitors its airspace, and other services such as the National Commissioner's National Security and Special Forces Units. Iceland maintains no standing army, the only NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
member for which this is the case.
The Coast Guard consists of three ships and four aircraft and armed with small arms, naval artillery
Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for shore bombardment and anti-aircraft roles. The term generally refers to tube-launched projectile-firing weapons and exclude ...
, and air defence radar stations. The Coast Guard also maintains the Iceland Air Defence System, formerly part of the disestablished Defence Agency, which conducts surveillance from the ground of Iceland's air space.
Additionally, there is a Crisis Response Unit (ICRU), operated by the Ministry for Foreign Affairs In many countries, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs is the government department responsible for the state's diplomacy, bilateral, and multilateral relations affairs as well as for providing support for a country's citizens who are abroad. The entit ...
, which is a small peacekeeping force that has been deployed internationally, since 2008. This unit also has an unarmed component.
There is a treaty with the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, which until 2006 maintained the Naval Air Station Keflavik
Naval Air Station Keflavik (NASKEF) was a United States Navy station at Keflavík International Airport, Iceland, located on the Reykjanes peninsula on the south-west portion of the island. NASKEF was closed on 8 September 2006, and its facilitie ...
, regarding the defence of Iceland. The base, now operated by the Icelandic Coast Guard, has been regularly visited by the US military and other allied NATO members. In 2017 the United States announced its interest in renovating a hangar, in order to accommodate a Boeing P-8 Poseidon ASW aircraft at the air base.
There are also agreements concerning military and other security operations with Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
and other NATO countries.
Iceland holds the annual NATO exercises entitled Northern Viking Northern Viking is an annual NATO exercise held in Iceland. The exercises were held biennially until 2006 when the frequency was increased.
The purpose of the exercise is to test the capabilities of Iceland and its NATO allies, as well as increase t ...
. The most recent exercises were held in 2022, as well as the EOD exercise "Northern Challenge".
In 1997 Iceland hosted its first Partnership for Peace
The Partnership for Peace (PfP; french: Partenariat pour la paix) is a North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) program aimed at creating trust between the member states of NATO and other states mostly in Europe, including post-Soviet state ...
(PfP) exercise, "Cooperative Safeguard", which is the only multilateral PfP exercise so far in which Russia has participated. Another major PfP exercise was hosted in 2000. Iceland has also contributed ICRU peacekeepers to SFOR
The Stabilisation Force in Bosnia and Herzegovina (SFOR) was a NATO-led multinational peacekeeping force deployed to Bosnia and Herzegovina after the Bosnian war. Although SFOR was led by NATO, several non-NATO countries contributed troops. It ...
, KFOR and ISAF
' ps, کمک او همکاري '
, allies = Afghanistan
, opponents = Taliban Al-Qaeda
, commander1 =
, commander1_label = Commander
, commander2 =
, commander2_label =
, commander3 =
, command ...
.
Iceland has never participated in a full-scale war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
or invasion. Furthermore, the constitution of Iceland
The Constitution of Iceland ( Icelandic: ''Stjórnarskrá lýðveldisins Íslands'' "Constitution of the republic of Iceland") is the supreme law of Iceland. It is composed of 80 articles in seven sections, and within it the leadership arrangemen ...
has no mechanism to declare war.
History
In the period from the settlement of Iceland, in the 870s, until it became part of the realm of the Norwegian King, military defences of Iceland consisted of multiple chieftains (''Goðar'') and their free followers (''þingmenn'', ''bændur'' or ''liðsmenn'') organised according to the standard nordic military doctrine of the time in expeditionary armies such as the ''leiðangr''. These armies were divided into units according to the quality of the warriors and by birth. At the end of this period, the number of chieftains had diminished and their power had grown, to the detriment of their followers. This resulted in a long and bloody civil war known asAge of the Sturlungs
The Age of the Sturlungs or the Sturlung Era ( is, Sturlungaöld ) was a 42–44 year period of violent internal strife in mid-13th century Iceland. It is documented in the Sturlunga saga. This period is marked by the conflicts of local chieftai ...
. A typical battle involved fewer than 1000 men.
Amphibious operations were an important part of warfare in Iceland in this period, especially in the Westfjords
The Westfjords or West Fjords ( is, Vestfirðir , ISO 3166-2:IS: IS-4) is a large peninsula in northwestern Iceland and an administrative district, the least populous administrative district. It lies on the Denmark Strait, facing the east coas ...
, but large naval engagement
Naval warfare is combat in and on the sea, the ocean, or any other battlespace involving a major body of water such as a large lake or wide river. Mankind has fought battles on the sea for more than 3,000 years. Even in the interior of large la ...
s were rare. The largest such engagement, known as Flóabardagi
The Battle of the Gulf () was a naval battle on 25 June 1244 in Iceland's Húnaflói Bay, during the Age of the Sturlungs civil war. The conflicting parties were the followers of Þórður kakali Sighvatsson and those of Kolbeinn ungi Arnórsson. ...
, involved a few dozen ships in Húnaflói
Húnaflói (, "Huna Bay") is a large bay between Strandir and Skagaströnd in Iceland. It is about wide and long. The towns Blönduós and Skagaströnd are located on the bay's eastern side.
Fauna
The bay has been proposed as a protecte ...
(bay).
In the decades before the Napoleonic wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, the few hundred militiamen in the southwest of Iceland were mainly equipped with rusty and mostly obsolete medieval weaponry, including 16th-century halberd
A halberd (also called halbard, halbert or Swiss voulge) is a two-handed pole weapon that came to prominent use during the 13th, 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. The word ''halberd'' is cognate with the German word ''Hellebarde'', deriving from ...
s. When English raiders arrived in 1808, after sinking or capturing most of the Danish-Norwegian Navy in the Battle of Copenhagen, the amount of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
in Iceland was so small that the governor of Iceland, Count Trampe, could not offer any resistance.
In 1855, the Icelandic Army was re-established by Andreas August von Kohl, the sheriff in Vestmannaeyjar
Vestmannaeyjar (, sometimes anglicized as Westman Islands) is a municipality and archipelago off the south coast of Iceland.
The largest island, Heimaey, has a population of 4,414, most of whom live in the archipelago's main town, Vestmannaeyj ...
. In 1856, the king provided 180 rixdollars to buy guns, and a further 200 rixdollars the following year. The sheriff became the Captain of the new army, which become known as ''Herfylkingin'', "The Battalion". In 1860 von Kohl died, and Pétur Bjarnasen took over command. Nine years later Bjarnasen died without appointing a successor, and the army fell into disarray.
In 1918, Iceland regained sovereignty as a separate kingdom under the Danish king. Iceland established a Coast Guard shortly afterwards, but it was financially impossible to establish a standing army. The government hoped that a permanent neutrality would shield the country from invasion. But at the onset of Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, the government was concerned about a possible invasion, and decided to expand the Icelandic National Police (''Ríkislögreglan'') and its reserves into a military unit. Chief Commissioner of Police Agnar Kofoed Hansen had been trained in the Danish Army and he moved to train his officers. Weapons and uniforms were acquired, and they practised rifleshooting and military tactics near Laugarvatn
Laugarvatn () is the name of a lake and a small town in the south of Iceland. The lake is smaller than the neighbouring Apavatn.
Tourism
Laugarvatn lies within the Golden Circle, a popular tourist route, and acts as a staging post. The town has ...
. Hansen barely managed to train his 60 officers before the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
's invasion of Iceland
The invasion of Iceland (codenamed Operation Fork) by the Royal Navy and Royal Marines occurred on 10 May 1940, during World War II. The invasion took place because the British government feared that Iceland would be used by the Germans, who ...
on 10 May 1940. Agnar wanted to expand the forces, but the Icelandic Minister of Justice rejected his proposal.
In mid-1941 while still neutral the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
took over the occupation of Iceland
The Allied occupation of Iceland during World War II began with a British invasion intent on occupying and denying Iceland to Germany. The military operation, codenamed Operation Fork, was conducted by the Royal Navy and Royal Marines. In t ...
from the British but not with Iceland's approval. The stationing of US forces in Iceland continued well after the war, eventually codified in the Agreed Minute. In 1949 Iceland was a founding member of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
and was the sole member that did not have a standing army, joining NATO on the condition that it would not be expected to establish one. However, its strategic geographic position in the Atlantic made it an invaluable member. Expansion of forces by Iceland was therefore concentrated primarily in the Icelandic Coast Guard, which saw action in a series of confrontations with British fishing vessels and Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
warships known as the Cod Wars
The Cod Wars ( is, Þorskastríðin; also known as , ; german: Kabeljaukriege) were a series of 20th-century confrontations between the United Kingdom (with aid from West Germany) and Iceland about fishing rights in the North Atlantic. Each of ...
. None of the Cod Wars
The Cod Wars ( is, Þorskastríðin; also known as , ; german: Kabeljaukriege) were a series of 20th-century confrontations between the United Kingdom (with aid from West Germany) and Iceland about fishing rights in the North Atlantic. Each of ...
meet any of the common thresholds for a conventional war and they may more accurately be described as militarised interstate disputes.
The Iceland Defense Force (IDF) was a military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
command
Command may refer to:
Computing
* Command (computing), a statement in a computer language
* COMMAND.COM, the default operating system shell and command-line interpreter for DOS
* Command key, a modifier key on Apple Macintosh computer keyboards
* ...
of the United States Armed Forces
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is ...
from 1951 to 2006. The IDF, created at the request of NATO, came into existence when the United States signed an agreement to provide for the defense of Iceland. The IDF also consisted of civilian Icelanders and military members of other NATO nations. The IDF was downsized after the end of the Cold War and the U.S. Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Sign ...
maintained four to six interceptor aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are c ...
at the Naval Air Station Keflavik
Naval Air Station Keflavik (NASKEF) was a United States Navy station at Keflavík International Airport, Iceland, located on the Reykjanes peninsula on the south-west portion of the island. NASKEF was closed on 8 September 2006, and its facilitie ...
, until they were withdrawn on 30 September 2006. Since May 2008, NATO nations have periodically deployed fighters to patrol Icelandic airspace under the Icelandic Air Policing
Icelandic Air Policing is a NATO operation conducted to patrol Iceland's airspace. As Iceland does not have an air force, in 2006 it requested that its NATO allies periodically deploy fighter aircraft to Keflavik Air Base to provide protection o ...
mission.
During the Icesave dispute
The Icesave dispute was a diplomatic dispute between Iceland, and the Netherlands and the United Kingdom that began after the privately owned Icelandic bank Landsbanki was placed in receivership on 7 October 2008. As ''Landsbanki'' was one of ...
with the British and Dutch governments, Iceland made it clear that UK patrols in its airspace were not appropriate given the state of affairs and subsequently on 14 November 2008 the UK had to cancel its patrols and defense of the Icelandic airspace, which before the dispute had been scheduled to start in December 2008.
After withdrawal of US forces in 2006, Iceland reorganized some military infrastructure in the form of the Icelandic Defence Agency (''Varnarmálastofnun Íslands'') founded in 2008. under the Minister for Foreign Affairs. The Agency took over operations at Naval Air Station Keflavik
Naval Air Station Keflavik (NASKEF) was a United States Navy station at Keflavík International Airport, Iceland, located on the Reykjanes peninsula on the south-west portion of the island. NASKEF was closed on 8 September 2006, and its facilitie ...
, but was closed in 2011 in the wake of the economic crisis, with functions distributed to the existing organizations.
The Icelandic Coast Guard now handles the military infrastructure in the country.
Coast Guard
Shortly after Iceland reclaimed its sovereignty in 1918, the Icelandic Coast Guard was founded. Its first vessel, a former Danish research vessel, was armed with a 57 mm cannon. The Coast Guard is responsible for protecting Iceland's sovereignty and vital interests including the most valuable natural resource—its fishing areas—as well as providing security, search, and rescue services to Iceland's fishing fleet. In 1952, 1958, 1972, and 1975, the government progressively expanded Iceland's exclusive economic zone to . This led to a conflict with the United Kingdom, among other states, known as the "Cod War
The Cod Wars ( is, Þorskastríðin; also known as , ; german: Kabeljaukriege) were a series of 20th-century confrontations between the United Kingdom (with aid from West Germany) and Iceland about fishing rights in the North Atlantic. Each o ...
s". The Icelandic Coast Guard and the Royal Navy confronted each other on several occasions during these years. Although few rounds were fired, there were many intense moments. Today the Coast Guard remains Iceland's premier fighting force equipped with armed patrol vessels and aircraft and partaking in peacekeeping operations in foreign lands.
The Coast Guard has four vessels and four aircraft (one fixed wing and three helicopters) at their disposal.
Iceland Air Defence System
The Iceland Air Defence System or ''Íslenska Loftvarnarkerfið'' was founded in 1987, and operates fourradar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
complexes, a software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated software documentation, documentation and data (computing), data. This is in contrast to Computer hardware, hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
...
and support facility and a command and report centre. It is a part of the Coast Guard.
Iceland's NATO allies also regularly deploy fighter aircraft to patrol the country's airspace as part of the Icelandic Air Policing
Icelandic Air Policing is a NATO operation conducted to patrol Iceland's airspace. As Iceland does not have an air force, in 2006 it requested that its NATO allies periodically deploy fighter aircraft to Keflavik Air Base to provide protection o ...
mission.
Icelandic Crisis Response Unit
The Icelandic Crisis Response Unit (ICRU) (or ''Íslenska friðargæslan'' or "The Icelandic Peacekeeping Guard") is an expeditionary peacekeeping force maintained by the Ministry for Foreign Affairs. It is manned by personnel from Iceland's other services, armed or not, including theNational Police National Police may refer to the national police forces of several countries:
*Afghanistan: Afghan National Police
*Haiti: Haitian National Police
*Colombia: National Police of Colombia
*Cuba: Cuban National Police
*East Timor: National Police of ...
, Coast Guard, emergency services and healthcare system. Because of the military nature of most of the ICRU's assignments, all of its members receive basic infantry combat training. This training has often been conducted by the Norwegian Army
The Norwegian Army ( no, Hæren) is the land warfare service branch of the Norwegian Armed Forces. The Army is the oldest of the Norwegian service branches, established as a modern military organization under the command of the King of Norway ...
, but the Coast Guard and the Special Forces are also assigned to train the ICRU.
Most of the ICRU's camouflage and weaponry is procured from abroad, with some indigenous development. Some arms and uniforms are also borrowed from the Norwegian Defence Forces.
The formation and employment of the unit have met controversy in Iceland, especially by people on the left of the political scale. In October 2004, three ICRU personnel were wounded in a suicide bombing on Chicken Street
Chicken Street ( prs, کوچه مرغ ''Koch-e Murgha'') is a narrow street located in the Shahr-e Naw district of Kabul east of the Asamayi. It has been an iconic shopping street in the city and popular with foreigners, famous for its carpets, ...
in Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
that killed a 13-year old Afghan girl and a 23-year old American woman. The incident resulted in severe critisism of the group's commander, Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge o ...
Hallgrímur Sigurðsson, as despite orders not to leave Kabul Airport unless absolutely necessary, he took the group to Chicken Street to shop carpets. Few weeks later, his command was passed to Lt. Colonel Garðar Forberg, followed by Colonel Lárus Atlason.
In 2008, the uniformed ICRU deployed personnel still armed for self-defense returned their weapons and changed to civilian clothing. The policy since 2008 is that, unless under special circumstances, ICRU personnel do not wear uniforms or carry weapons.
ICRU missions
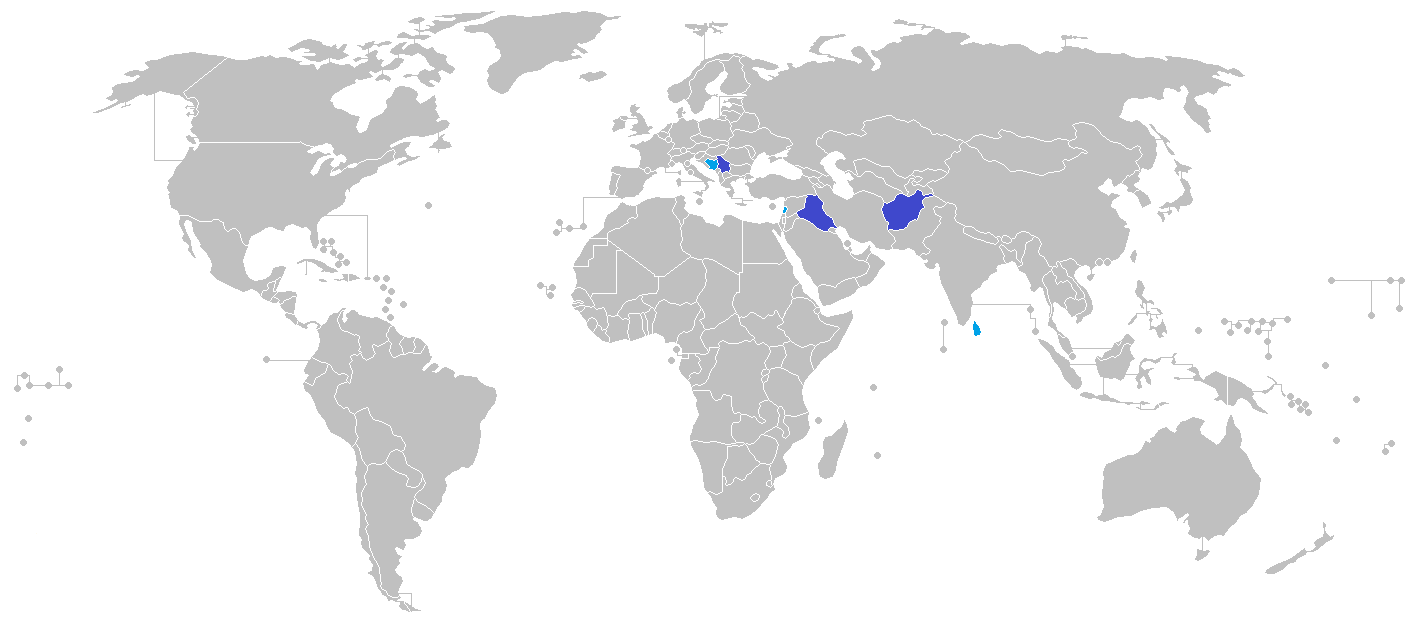
The ICRU has been or is operating in: * Military missions:
** within
* Military missions:
** within ISAF
' ps, کمک او همکاري '
, allies = Afghanistan
, opponents = Taliban Al-Qaeda
, commander1 =
, commander1_label = Commander
, commander2 =
, commander2_label =
, commander3 =
, command ...
** within NTM-1 (and the Coast Guard within Dancon/Irak)
** , within KFOR
* Civilian missions:
** within EUPM
** within MACC-SL
** within SLMM
The Sri Lanka Monitoring Mission (SLMM) was a multinational body that existed from 2002 to 2008 to monitor the ceasefire between the Government of Sri Lanka and the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE, also known as the ''Tamil Tigers'') during ...
List of small-arms used by Icelandic forces
*Glock 17
Glock is a brand of polymer- framed, short recoil-operated, locked-breech semi-automatic pistols designed and produced by Austrian manufacturer Glock Ges.m.b.H. The firearm entered Austrian military and police service by 1982 after it was th ...
— Sidearm (Pistol)
* AG-3
The Heckler & Koch G3 (''Gewehr'' 3) is a 7.62×51mm NATO, select-fire battle rifle developed in the 1950s by the German armament manufacturer Heckler & Koch (H&K) in collaboration with the Spanish state-owned design and development agency CETM ...
— Battle Rifle
* Heckler & Koch MP5
The Heckler & Koch MP5 (german: Maschinenpistole 5) is a 9x19mm Parabellum submachine gun, developed in the 1960s by a team of engineers from the German small arms manufacturer Heckler & Koch. There are over 100 variants and clones of the MP5, ...
— Sub-Machine Gun
* Blaser R93 — Sniper Rifle
* Rheinmetall MG3
The MG 3 is a German general-purpose machine gun chambered for the 7.62×51mm NATO cartridge. The weapon's design is derived from the World War II era MG 42 ''Einheitsmaschinengewehr'' (Universal machine gun) that fired the 7.92×57mm Mauser ro ...
– General-Purpose Machine Gun
See also
*List of countries without armed forces
This is a list of countries without armed forces. The term ''country'' here means sovereign states and not dependencies (e.g., Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Bermuda) whose defense is the responsibility of another country or an army alternative ...
* List of wars involving Iceland
* GIUK gap
The GIUK gap (sometimes written G-I-UK) is an area in the northern Atlantic Ocean that forms a naval choke point. Its name is an acronym for ''Greenland, Iceland'', and the ''United Kingdom'', the gap being the two stretches of open ocean betwe ...
References
Further reading
* Birgir Loftsson, ''Hernaðarsaga Íslands : 1170–1581'', Pjaxi. Reykjavík. 2006. * Þór Whitehead, ''The Ally who came in from the cold : a survey of Icelandic Foreign Policy 1946–1956'', Centre for International Studies. University of Iceland Press. Reykjavík. 1998.External links
Icelandic Coast Guard
Icelandic National Police
Iceland Air Defence System
Ministry of Justice and Ecclesiastical Affairs
Ministry for Foreign Affairs
{{Improve categories, date=December 2021