IMViC on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The IMViC tests are a group of individual tests used in microbiology lab testing to identify an organism in the coliform group. A coliform is a 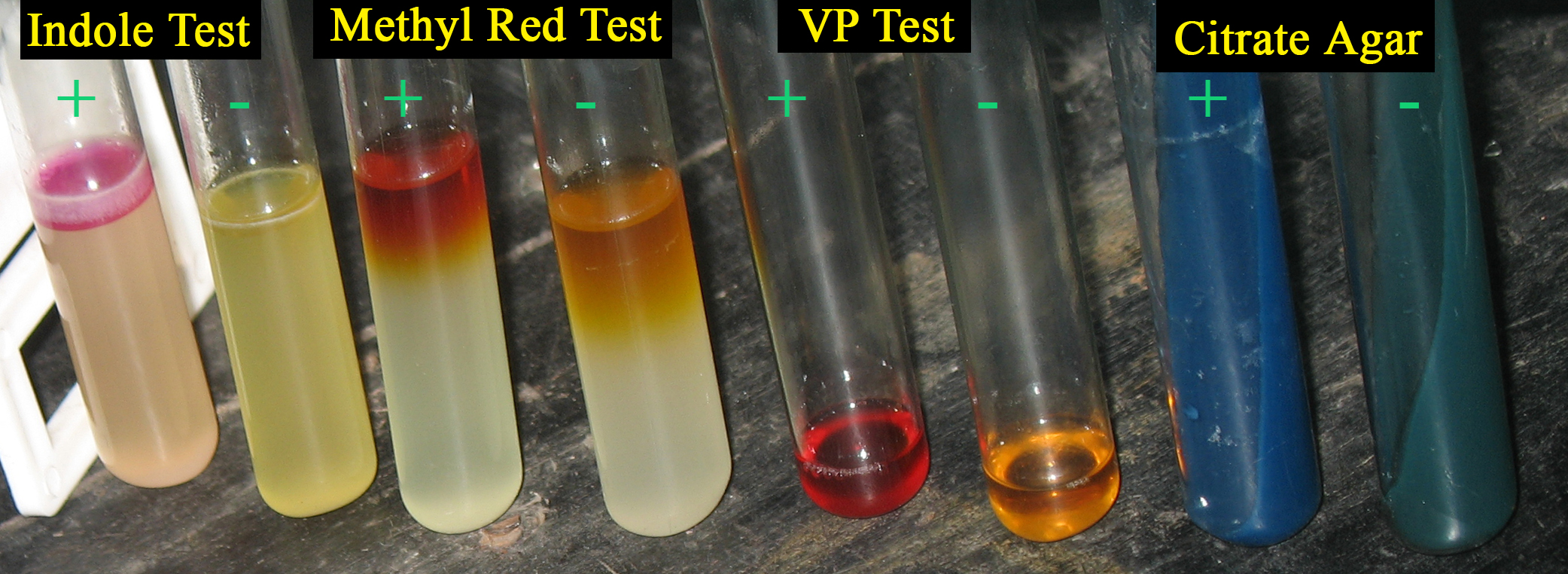
gram negative
The gram (originally gramme; SI unit symbol g) is a unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one one thousandth of a kilogram.
Originally defined as of 1795 as "the absolute weight of a volume of pure water equal to th ...
, aerobic, or facultative anaerobic rod, which produces gas from lactose within 48 hours. The presence of some coliforms indicate fecal contamination.
The term "IMViC" is an acronym for each of these tests. "I" is for indole test; "M" is for methyl red test; "V" is for Voges-Proskauer test, and "C" is for citrate test The citrate test detects the ability of an organism to use citrate as the sole source of carbon and energy.
Principle
Bacteria are inoculated on a medium containing sodium citrate and a pH indicator such as bromothymol blue. The medium also conta ...
. The lower case "i" is merely for "in" as the Citrate test requires coliform samples to be placed "in Citrate".
These tests are useful in distinguishing members of Enterobacteriaceae.

Indole test
In this test, the organism under consideration is grown in peptone water broth. It containstryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic ...
, which under the action of enzyme tryptophanase is converted to an Indole
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other c ...
molecule, pyruvate and ammonium. The indole is then extracted from the broth by means of xylene. The broth is sterilized for 15 minutes at around 121°c. To test the broth for indole production, Kovac's reagent . Kovac's reagent consist of amyl alcohol and para-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde and concentrated hydrochloric acid. Kovac's reagent is actually used to determine ability of an organism to separate indole from amino acid tryptophan and it is added after incubation. A positive result is indicated by a pink/red layer forming on top of the liquid.
Methyl red and Voges–Proskauer test
These tests both use the same broth for bacterial growth. The broth is called MRVP broth. After growth, the broth is separated into two different tubes, one for the methyl red (MR) test and one for the Voges-Proskauer (VP) test. The methyl red test detects production of acids formed during metabolism usingmixed acid fermentation
In biochemistry, mixed acid fermentation is the metabolic process by which a six-carbon sugar (e.g. glucose, ) is converted into a complex and variable mixture of acids. It is an anaerobic (non-oxygen-requiring) fermentation reaction that is ...
pathway using pyruvate as a substrate. The pH indicator Methyl Red is added to one tube and a red color appears at pH's lower than 4.2, indicating a positive test (mixed acid fermentation is used). The solution remaining yellow (pH = 6.2 or above) indicates a negative test, meaning the butanediol fermentation
2,3-Butanediol fermentation is anaerobic fermentation of glucose with 2,3-butanediol as one of the end products. The overall stoichiometry of the reaction is
:2 pyruvate + NADH --> 2 CO2 + 2,3-butanediol.
Butanediol fermentation is typical for th ...
is used.
The VP test uses alpha-naphthol and potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exp ...
to test for the presence of acetylmethylcarbinol (acetoin), an intermediate of the 2,3-butanediol fermentation pathway. After adding both reagents, the tube is shaken vigorously then allowed to sit for 5-10 minutes. A pinkish-red color indicates a positive test, meaning the 2,3-butanediol fermentation pathway is used.
Citrate test
This test uses Simmon's citrate agar to determine the ability of a microorganism to use citrate as its sole carbon source. The agar contains citrate and ammonium ions (nitrogen source) andbromothymol blue
Bromothymol blue (also known as bromothymol sulfone phthalein and BTB) is a pH indicator. It is mostly used in applications that require measuring substances that would have a relatively neutral pH (near 7). A common use is for measuring the pre ...
as an indicator. The citrate agar is green before inoculation, and turns blue as a positive test indicator, meaning citrate is utilized.
Usage
These IMViC tests are useful for differentiating the family Enterobacteriaceae, especially when used alongside the Urease test. The IMViC results of some important species are shown below.References