IC packaging on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
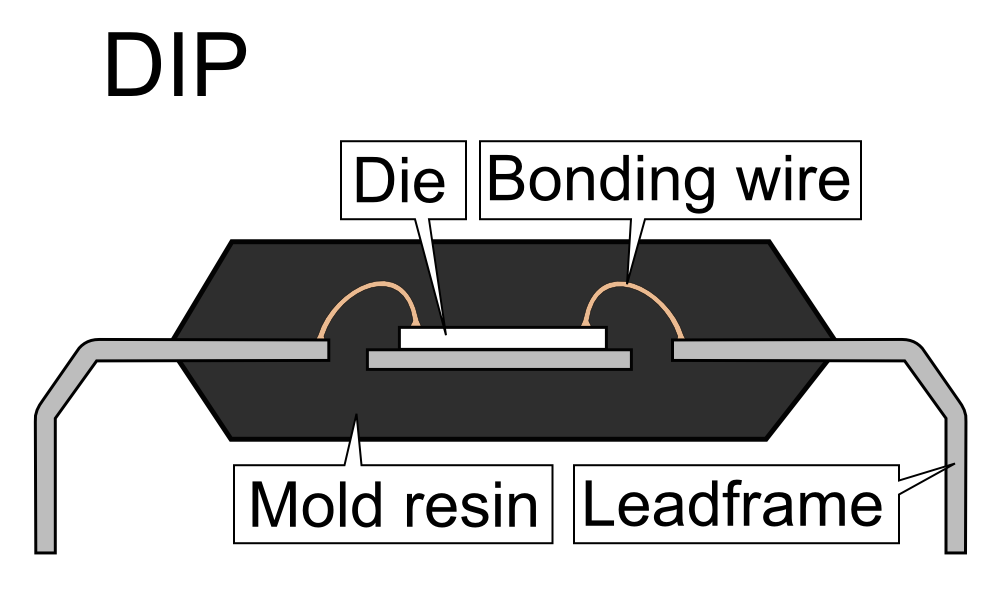 In electronics manufacturing, integrated circuit packaging is the final stage of
In electronics manufacturing, integrated circuit packaging is the final stage of
 The next big innovation was the ''area array package'', which places the interconnection terminals throughout the surface area of the package, providing a greater number of connections than previous package types where only the outer perimeter is used. The first area array package was a ceramic pin grid array package. Not long after, the plastic
The next big innovation was the ''area array package'', which places the interconnection terminals throughout the surface area of the package, providing a greater number of connections than previous package types where only the outer perimeter is used. The first area array package was a ceramic pin grid array package. Not long after, the plastic
3-D Packaging: A Technology Review.
June 23, 2005. Retrieved July 31, 2015
semiconductor device fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are p ...
, in which the block of semiconductor material is encapsulated in a supporting case that prevents physical damage and corrosion. The case, known as a " package", supports the electrical contacts which connect the device to a circuit board.
In the integrated circuit industry, the process is often referred to as packaging. Other names include semiconductor device assembly, assembly, encapsulation or sealing.
The packaging stage is followed by testing of the integrated circuit.
The term is sometimes confused with electronic packaging
Electronic packaging is the design and production of enclosures for electronic devices ranging from individual semiconductor devices up to complete systems such as a mainframe computer. Packaging of an electronic system must consider protection ...
, which is the mounting and interconnecting of integrated circuits (and other components) onto printed-circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich struc ...
s.
Design considerations
Electrical
The current-carrying traces that run out of the die, through the package, and into the printed circuit board (PCB) have very different electrical properties compared to on-chip signals. They require special design techniques and need much more electric power than signals confined to the chip itself. Therefore, it is important that the materials used as electrical contacts exhibit characteristics like low resistance, low capacitance and low inductance. Both the structure and materials must prioritize signal transmission properties, while minimizing any parasitic elements that could negatively affect the signal. Controlling these characteristics is becoming increasingly important as the rest of technology begins to speed up. Packaging delays have the potential to make up almost half of a high-performance computer's delay, and this bottleneck on speed is expected to increase.Mechanical and thermal
The integrated circuit package must resist physical breakage, keep out moisture, and also provide effective heat dissipation from the chip. Moreover, for RF applications, the package is commonly required to shield electromagnetic interference, that may either degrade the circuit performance or adversely affect neighboring circuits. Finally, the package must permit interconnecting the chip to a PCB. The materials of the package are either plastic (thermoset
In materials science, a thermosetting polymer, often called a thermoset, is a polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening (" curing") a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer ( resin). Curing is induced by heat or suitable radiation ...
or thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate ...
), metal (commonly Kovar
Kovar (trademark of CRS Holdings, inc., Delaware) is a nickel–cobalt ferrous alloy compositionally identical to Fernico 1, designed to have substantially the same thermal expansion characteristics as borosilicate glass (~5 × 10−6 /K betwe ...
) or ceramic. A common plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
used for this is epoxy-cresol
Cresols (also hydroxytoluene or cresylic acid) are a group of aromatic organic compounds. They are widely-occurring phenols (sometimes called ''phenolics'') which may be either natural or manufactured. They are also categorized as methylphenol ...
- novolak (ECN). All three material types offer usable mechanical strength, moisture and heat resistance. Nevertheless, for higher-end devices, metallic and ceramic packages are commonly preferred due to their higher strength (which also supports higher pin-count designs), heat dissipation, hermetic performance, or other reasons. Generally speaking, ceramic packages are more expensive than a similar plastic package.
Some packages have metallic fins to enhance heat transfer, but these take up space. Larger packages also allow for more interconnecting pins.
Economic
Cost is a factor in selection of integrated circuit packaging. Typically, an inexpensive plastic package can dissipate heat up to 2W, which is sufficient for many simple applications, though a similar ceramic package can dissipate up to 50W in the same scenario. As the chips inside the package get smaller and faster, they also tend to get hotter. As the subsequent need for more effective heat dissipation increases, the cost of packaging rises along with it. Generally, the smaller and more complex the package needs to be, the more expensive it is to manufacture.History
Early integrated circuits were packaged in ceramic flat packs, which the military used for many years for their reliability and small size. The other type of packaging used in the 1970s, called the ICP (Integrated Circuit Package), was a ceramic package (sometime round as the transistor package), with the leads on one side, co-axially with the package axis. Commercial circuit packaging quickly moved to the dual in-line package (DIP), first in ceramic and later in plastic. In the 1980sVLSI
Very large-scale integration (VLSI) is the process of creating an integrated circuit (IC) by combining millions or billions of MOS transistors onto a single chip. VLSI began in the 1970s when MOS integrated circuit (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) ...
pin counts exceeded the practical limit for DIP packaging, leading to pin grid array (PGA) and leadless chip carrier
In electronics, a chip carrier is one of several kinds of surface-mount technology packages for integrated circuits (commonly called "chips"). Connections are made on all four edges of a square package; compared to the internal cavity for mount ...
(LCC) packages. Surface mount packaging appeared in the early 1980s and became popular in the late 1980s, using finer lead pitch with leads formed as either gull-wing or J-lead, as exemplified by small-outline integrated circuit
A small outline integrated circuit (SOIC) is a surface-mounted integrated circuit (IC) package which occupies an area about 30–50% less than an equivalent dual in-line package (DIP), with a typical thickness being 70% less. They are general ...
—a carrier which occupies an area about 30–50% less than an equivalent DIP, with a typical thickness that is 70% less.ball grid array
A ball grid array (BGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging (a chip carrier) used for integrated circuits. BGA packages are used to permanently mount devices such as microprocessors. A BGA can provide more interconnection pins than can be pu ...
(BGA), another type of area array package, became one of the most commonly used packaging techniques.
In the late 1990s, plastic quad flat pack (PQFP) and thin small-outline packages (TSOP) replaced PGA packages as the most common for high pin count devices, though PGA packages are still often used for microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circ ...
s. However, industry leaders Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
and AMD
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While it initially manufactur ...
transitioned in the 2000s from PGA packages to land grid array
The land grid array (LGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits (ICs) that is notable for having the pins on the socket (when a socket is used) rather than the integrated circuit. An LGA can be electrically connected to a ...
(LGA) packages.
Ball grid array
A ball grid array (BGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging (a chip carrier) used for integrated circuits. BGA packages are used to permanently mount devices such as microprocessors. A BGA can provide more interconnection pins than can be pu ...
(BGA) packages have existed since the 1970s, but evolved into flip-chip ball grid array (FCBGA) packages in the 1990s. FCBGA packages allow for much higher pin count than any existing package types. In an FCBGA package, the die is mounted upside-down (flipped) and connects to the package balls via a substrate that is similar to a printed-circuit board rather than by wires. FCBGA packages allow an array of input-output signals (called Area-I/O) to be distributed over the entire die rather than being confined to the die periphery.
Traces out of the die, through the package, and into the printed circuit board have very different electrical properties, compared to on-chip signals. They require special design techniques and need much more electric power than signals confined to the chip itself.
Recent developments consist of stacking multiple dies in single package called SiP, for '' System In Package'', or three-dimensional integrated circuit
A three-dimensional integrated circuit (3D IC) is a MOS (metal-oxide semiconductor) integrated circuit (IC) manufactured by stacking as many as 16 or more ICs and interconnecting them vertically using, for instance, through-silicon vias (TSVs) or ...
. Combining multiple dies on a small substrate, often ceramic, is called an MCM, or Multi-Chip Module
A multi-chip module (MCM) is generically an electronic assembly (such as a package with a number of conductor terminals or "pins") where multiple integrated circuits (ICs or "chips"), semiconductor dies and/or other discrete components are in ...
. The boundary between a big MCM and a small printed circuit board is sometimes blurry.R. Wayne Johnson, Mark Strickland and David Gerke, NASA Electronic Parts and Packaging Program.3-D Packaging: A Technology Review.
June 23, 2005. Retrieved July 31, 2015
Common package types
*Through-hole technology
In electronics, through-hole technology (also spelled "thru-hole") is a manufacturing scheme in which leads on the components are inserted through holes drilled in printed circuit boards (PCB) and soldered to pads on the opposite side, either ...
* Surface-mount technology
* Chip carrier
* Pin grid array
* Flat package
* Small Outline Integrated Circuit
A small outline integrated circuit (SOIC) is a surface-mounted integrated circuit (IC) package which occupies an area about 30–50% less than an equivalent dual in-line package (DIP), with a typical thickness being 70% less. They are generall ...
* Chip-scale package
A chip scale package or chip-scale package (CSP) is a type of integrated circuit package.
Originally, CSP was the acronym for ''chip-size packaging.'' Since only a few packages are chip size, the meaning of the acronym was adapted to ''chip-scal ...
* Ball grid array
A ball grid array (BGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging (a chip carrier) used for integrated circuits. BGA packages are used to permanently mount devices such as microprocessors. A BGA can provide more interconnection pins than can be pu ...
* Transistor, diode, small pin count IC packages
* Multi-chip packages
Operations
''Die attachment'' is the step during which a die is mounted and fixed to the package or support structure (header).L. W. Turner (ed), ''Electronics Engineers Reference Book'', Newnes-Butterworth, 1976, , pages 11-34 through 11-37 For high-powered applications, the die is usually eutectic bonded onto the package, using e.g. gold-tin or gold-siliconsolder
Solder (; NA: ) is a fusible metal alloy used to create a permanent bond between metal workpieces. Solder is melted in order to wet the parts of the joint, where it adheres to and connects the pieces after cooling. Metals or alloys suitable ...
(for good heat conduction). For low-cost, low-powered applications, the die is often glued directly onto a substrate (such as a printed wiring board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich struc ...
) using an epoxy adhesive.
The following operations are performed at the packaging stage, as broken down into bonding, encapsulation, and wafer bonding steps. Note that this list is not all-inclusive and not all of these operations are performed for every package, as the process is highly dependent on the package type.
* IC bonding
**Wire bonding
Wire bonding is the method of making interconnections between an integrated circuit (IC) or other semiconductor device and its packaging during semiconductor device fabrication. Although less common, wire bonding can be used to connect an IC ...
**Thermosonic Bonding
Thermosonic bonding is widely used to wire bond silicon integrated circuits into computers. Alexander Coucoulas was named "Father of Thermosonic Bonding" by George Harman, the world's foremost authority on wire bonding, where he referenced Coucoul ...
** Down bonding
**Tape automated bonding
Tape-automated bonding (TAB) is a process that places bare semiconductor chips (dies) like integrated circuits onto a flexible circuit board (FPC) by attaching them to fine conductors in a polyamide or polyimide (like trade names Kapton or UPILE ...
**Flip chip
Flip chip, also known as controlled collapse chip connection or its abbreviation, C4, is a method for interconnecting dies such as semiconductor devices, IC chips, integrated passive devices and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), to exter ...
**Quilt packaging
Quilt Packaging (QP) is an integrated circuit packaging and chip-to-chip interconnect packaging technology that utilizes “ nodule” structures that extend out horizontally from the edges of microchips to make electrically and mechanically ro ...
** Film attaching
** Spacer attaching
*IC encapsulation
** Baking
**Plating
Plating is a surface covering in which a metal is deposited on a conductive surface. Plating has been done for hundreds of years; it is also critical for modern technology. Plating is used to decorate objects, for corrosion inhibition, to impro ...
** Lasermarking
** Trim and form
*Wafer bonding
Wafer bonding is a packaging technology on wafer-level for the fabrication of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), microelectronics and optoelectronics, ensuring a mechanically stable and hermetically sealed ...
See also
*List of integrated circuit packaging types
Integrated circuits are put into protective packages to allow easy handling and assembly onto printed circuit boards and to protect the devices from damage. A very large number of different types of package exist. Some package types have stand ...
* List of electronics package dimensions
Integrated circuits are put into protective packages to allow easy handling and assembly onto printed circuit boards and to protect the devices from damage. A very large number of different types of package exist. Some package types have standa ...
* B-staging
B-staging is a process that utilizes heat or UV light to remove the majority of solvent from an adhesive, thereby allowing a construction to be “staged”. In between adhesive application, assembly and curing, the product can be held for a period ...
* Potting (electronics)
In electronics, potting is a process of filling a complete electronic assembly with a solid or gelatinous compound for high voltage assemblies by excluding gaseous phenomena such as corona discharge, for resistance to shock and vibration, and for ...
* Quilt packaging
Quilt Packaging (QP) is an integrated circuit packaging and chip-to-chip interconnect packaging technology that utilizes “ nodule” structures that extend out horizontally from the edges of microchips to make electrically and mechanically ro ...
* Electronic packaging
Electronic packaging is the design and production of enclosures for electronic devices ranging from individual semiconductor devices up to complete systems such as a mainframe computer. Packaging of an electronic system must consider protection ...
* Decapping
Decapping (decapsulation) or delidding of an integrated circuit is the process of removing the protective cover or integrated heat spreader (IHS) of an integrated circuit so that the contained die is revealed for visual inspection of the micro cir ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Integrated Circuit Packaging Semiconductor device fabrication Chip carriers Packaging (microfabrication)